Abstract
Oil spills pose a significant threat to marine ecosystems, with potentially adverse impacts on fish in early-life stages. Despite numerous studies reporting the developmental toxicity of oil exposure, knowledge about the recovery capacity of fish after oil exposure remains limited. Therefore, this study investigated the effects of water-accommodated fractions (WAFs) of Oman crude oil on the development and oxidative stress of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) embryos during a 7-day acute exposure period followed by a 14-day recovery period in clean seawater. Results revealed that WAF exposure caused concentration-dependent developmental toxicity gradually becoming apparent during the recovery period, including reduced survival and hatching rates, and increased morphological abnormalities. During the exposure period, low WAF concentrations triggered antioxidant responses (elevated SOD and CAT activities, and GSH content), while higher concentrations caused a concentration-dependent increase in lipid peroxidation (elevated MDA content). Differently, during the recovery period, all groups showed impaired antioxidant capacity (decreased SOD, CAT, GSH) and immune function (reduced AKP activity). Principal component analysis revealed strong correlations between survival, oxidative stress markers, and developmental toxicity. These findings could provide valuable insights into the recovery capacity of fish exposed to crude oil and give references for assessing the recovery potential of marine ecosystems after oil spills.
1. Introduction
Petroleum serves as a critical driving force for global economic development, with world economic expansion significantly accelerating both oil trade and maritime transportation industries. However, this growth has been accompanied by a concerning increase in marine oil spill incidents [1,2]. Oil spills represent one of the most severe global anthropogenic threats to marine ecosystems, introducing complex mixtures of petroleum hydrocarbons into marine environments and causing significant ecological damage that can persist for decades [3]. The frequency of major oil spill incidents has risen alarmingly with the expansion of global oil trade and maritime transport activities [2]. Recent catastrophic events, such as the 2011 Penglai 19-3 oil field spill in Bohai Bay of China that contaminated approximately 5500 km² of marine area, and the 2018 Sanchi oil tanker explosion that released over 111,300 tons of natural gas condensate into East China Sea, highlight the continuing threat posed by oil pollution to marine ecosystems [1,4]. These incidents result in widespread marine contamination, severely disrupting ecological balance and threatening numerous marine species.
Crude oil is a complex chemical mixture containing thousands of compounds with diverse physicochemical properties, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which have been identified as the primary toxic components affecting marine organisms [5,6,7]. PAHs can bioaccumulate in marine organisms through multiple exposure pathways, including direct absorption from water, contact with contaminated sediments, and dietary intake [8]. Among marine organisms, fish are particularly vulnerable to oil pollution, with their early-life stages (ELSs) exhibiting heightened sensitivity due to their small size, developmental plasticity, and incomplete development of detoxification systems [9,10]. Since the 1989 Exxon Valdez oil tanker spill in Alaska, researchers have comprehensively investigated crude oil toxicity in fish, with special emphasis on ELS, finding that even trace levels of crude oil exposure can cause lasting cardiac defects in developing fish [11,12,13]. Fish embryos and larvae are exceptionally susceptible to environmental contaminants due to their high surface-to-volume ratio, enhanced ability to absorb and accumulate PAHs, immature immune systems, and underdeveloped organs such as the liver and kidneys that would normally aid in detoxification processes [14,15]. These studies have uncovered consistent patterns of developmental abnormalities across different fish species exposed to oil, including pericardial and yolk sac edema, cardiac arrhythmias, and axial malformations. This constellation of symptoms, collectively known as blue sac disease (BSD), has become a recognized marker of oil toxicity in fish embryos characterized by edemas, congestion of peripheral blood circulation, hemorrhage, and craniofacial malformations [16,17,18], which could subsequently lead to decreased hatching success and increased mortality rates [5,6,19,20].
These morphological abnormalities may result from direct embryotoxicity, disruption of key developmental pathways, or secondary effects of physiological dysfunction [5,21,22]. Numerous studies have indicated that petroleum hydrocarbons and their associated organic compounds significantly reduce fish survival rates, cause hatching abnormalities, and induce oxidative stress through increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals, which can lead to cellular damage and developmental disorders [7,17,23,24,25]. Oxidative stress has been identified as a key mechanism of petroleum hydrocarbon toxicity, arising from an imbalance between ROS generation and antioxidant defense systems, which can lead to cellular damage in fish exposed to oil pollutants, manifested through changes in biomarker levels [26,27,28]. ROS include highly reactive molecules such as superoxide anion (O2•−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radical (OH•), which can damage cellular components including lipids, proteins, and DNA, leading to functional impairment and cell apoptosis [29,30]. Fish possesses antioxidant defense systems comprising enzymatic components such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), as well as non-enzymatic components including glutathione (GSH), vitamin E, and vitamin C that work together to neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative damage [24,31,32]. Disruption of these systems can lead to lipid peroxidation, indicated by elevated malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, protein oxidation, and DNA damage, ultimately resulting in cellular dysfunction and developmental abnormalities [33,34]. Beyond oxidative stress, petroleum hydrocarbons may also modulate immune responses in aquatic organisms, affecting their resistance to pathogens and overall health status [35]. Alkaline phosphatase (AKP) is a lysosomal enzyme involved in multiple physiological processes, including immune function, and has been utilized as a biomarker for assessing the immunotoxicity of environmental pollutants, with alterations in AKP activity potentially reflecting changes in immune status, metabolic function, or tissue damage following toxicant exposure [36,37].
While numerous studies have documented the immediate developmental toxicity of crude oil exposure in fish ELS as previously mentioned, a knowledge limitation still exists regarding the recovery capacity of affected fishes following acute exposure. This knowledge limitation is particularly significant because in natural environments, fish embryos and larvae may experience transient oil exposure followed by migration or dispersal to uncontaminated waters [14,17,38]. Furthermore, the embryonic-larval stages exhibit high sensitivity to environmental pollutants, making them particularly susceptible to toxic damage, especially in the ELS immediately after fertilization [10,39]. Current research predominantly focuses on acute or subacute exposure patterns to evaluate toxicological impacts, with a relatively few studies assessing recovery capacity after exposure to oil pollution. Most existing research has employed continuous exposure designs without examining post-exposure recovery dynamics, which might limit our ability to predict the long-term ecological consequences of oil spills and develop effective remediation strategies [40]. In addition, given that newly hatched fish may migrate to uncontaminated waters, investigating the relationship between oil pollution exposure, resilience, and early development also has important ecological and practical implications.
Marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) serves as an ideal fish model for marine ecotoxicological research, due to its small size, short generation cycle, transparent embryos, and well-characterized developmental processes—with the key period for reproductive system formation occurring at 7 days post-fertilization (dpf), sexual maturity at 90 dpf, stable spawning at 100–130 dpf [41,42,43]—and high sensitivity to pollutants, making rapid detection of environmental contamination possible [18,43,44]. Unlike its freshwater relative (Oryzias latipes), marine medaka can tolerate a wide range of salinity levels, making it particularly suitable for studying toxicity in marine and estuarine environments [43,45]. These characteristics make it especially appropriate for investigating developmental toxicity and recovery dynamics following exposure to environmental contaminants such as petroleum hydrocarbons, as demonstrated by previous studies examining various toxicants in this species [3,10,16,46]. Therefore, the present study employed marine medaka as the test model species to investigate the developmental toxicity of water-accommodated fractions (WAFs) of Oman crude oil (OCO) on fish ELS during acute exposure to OCO WAF with different environmentally relevant concentrations (7 d exposure period) and subsequent recovery in clean seawater (14 d recovery period). The study observed and detected the survival rate, hatching success, morphological abnormalities (BSD scoring system), oxidative stress indicators (SOD, CAT, GSH), lipid peroxidation (MDA), and immune response (AKP), aiming to elucidate the mechanisms of early fish developmental toxicity induced by oil pollution and self-recovery capacity. The results of this study could provide valuable insights into the ecotoxicological impact assessments of oil spills on marine organisms and give an important reference for assessing the recovery potential of marine ecosystems following environmental disturbances.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Chemical Analysis of Exposure Solutions
Oman crude oil (OCO) with a density of 0.8669 g·cm−3 (31.44° API gravity) was sourced from Dalian Petroleum Company Limited (Liaoning, China) and used to prepare the WAF stock solution following Singer’s guidelines [5,6,47,48]. The WAF stock solution was prepared at an oil-loading ratio of 25 g/L. The bottle was sealed with a Teflon-lined cap to prevent volatile hydrocarbon loss. The mixture was stirred at low energy (non-vortex, approximately 100 rpm) for 23 h, followed by a 1 h settling period in the dark at room temperature to allow for phase separation. The WAF stock solution was then collected from the bottom of the bottle to avoid oil droplets. WAF exposure solutions were prepared by diluting the WAF stock solution with artificial seawater to achieve three nominal test concentrations: low (L-WAF, 5% v/v), medium (M-WAF, 10% v/v), and high (H-WAF, 25% v/v). Artificial seawater (30 psu (practical salinity unit)) was prepared by dissolving Instant Ocean® Sea Salt (Aquarium Systems, Sarrebourg, France) in reverse osmosis-purified water. All test solutions were prepared fresh daily throughout the exposure period.
Total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) concentrations in the WAF exposure solutions were determined using the ultraviolet spectrophotometry method according to the Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC) GB 17378.4-2007 guidelines for marine monitoring [49]. Briefly, 100 mL of each WAF solution was extracted twice with 10 mL of n-hexane (C6H14). The extracts were analyzed using an Epoch 2 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (BioTek, Shoreline, WA, USA) at wavelengths of 225 nm. All samples were analyzed in triplicate. PAH analysis was conducted according to the gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) method of EPA and ISO guidelines [50,51] using a 7890B GC/5977A MSD (Agilent, Santa Clara, CO, USA). The detailed information for analysis procedures, method detection limits, and quality control was described in our previous studies [5,6,48].
2.2. Marine Medaka Maintenance and Embryo Collection
Marine medakas (Oryzias melastigma) were sourced from the State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science, Xiamen University (Fujian, China). The maintenance environmental conditions were controlled with temperature maintained at 27.5 ± 0.5 °C, pH levels at 7.9 ± 0.2, salinity at 30 ± 1 PSU, and a light–dark cycle of 14:10 h. Continuous aeration was provided throughout the maintenance period to ensure adequate dissolved oxygen levels. The nutritional regimen for adult marine medaka consisted of live Artemia nauplii administered twice daily, supplemented with commercial dry feed (TetraMin, Melle, Germany) once daily. For obtaining embryos, sexually mature marine medakas (approximately 90 d after hatching) were transferred to breeding containers with a male-to-female ratio of 1:1. Spawning was triggered around 3 h after the onset of light, according to the OECD Test No. 236 guidelines [52] and previous studies [5,6,53,54]. Fertilized eggs were harvested within 3 hpf (hour post-fertilization), and only those at the early blastula stage showing normal developmental patterns were selected for subsequent tests.
2.3. Experimental Design
The experiment consisted of two periods: a 7 d acute exposure period (0–7 dpf) followed by a 14 d recovery period (8–21 dpf). During the exposure period, marine medaka embryos were randomly assigned to four treatment groups, control (clean artificial seawater), L-WAF (5% v/v), M-WAF (10% v/v), and H-WAF (25% v/v), of which the nominal concentrations were within the range reported in actual oil spill scenarios [55]. For each treatment, 150 embryos were used, with 3 replicates of 50 embryos each. The embryos were placed in 100 mL glass beakers containing 100 mL of the test solutions following the OECD Test No. 236 guidelines [52]. The beakers were covered with lid films to minimize evaporation and incubated in a temperature-controlled chamber at 27.5 ± 0.5 °C with a 14 h light/10 h dark photoperiod. The test solutions were renewed daily (80% renewal) to maintain consistent exposure concentrations. During solution renewal, dead embryos were removed, counted, and preserved in 10% neutral buffered formalin for morphological assessment using an IX73 research inverted microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). At 7 dpf (end of exposure period), a subset of embryos from each treatment group (15 individuals per replicate) was sampled for biochemical analyses, among which 6 embryos per replicate were randomly preserved for morphological assessments before biochemical analysis. The surviving embryos from each treatment group were transferred to clean artificial seawater for the 14 d recovery period. During the recovery period, the embryos and larvae were maintained under the same conditions as during the exposure period, except that they were exposed to clean artificial seawater instead of WAF exposure solutions. At 21 dpf (end of recovery period), 15 larvae per replicate were sampled for biochemical analyses, among which 6 larvae per replicate were randomly assessed for morphological abnormalities. Throughout both periods, water was renewed daily, and embryos were monitored daily for mortality, hatching, and morphological abnormalities. Samples for biochemical analyses were collected at 7 dpf (end of exposure period) and 21 dpf (end of recovery period) from each treatment group, flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C for subsequent analyses.
2.4. Lethal and Sublethal Morphological Assessment
Survival rates were calculated daily as the percentage of live embryos relative to the initial number in each treatment group. Embryos were considered dead if they exhibited coagulation, lack of heartbeat, lack of somite formation, or non-detachment of the tail [52]. Hatching rates were determined as the percentage of embryos that successfully hatched at the end of the observation period. The time to hatch was also recorded by monitoring the embryos twice daily during the hatching period. Morphological abnormalities were assessed using the BSD scoring system, which has been widely used to evaluate developmental toxicity in fish embryos exposed to petroleum hydrocarbons [16,39]. Each embryo or larva was examined under the IX73 research inverted microscope and scored based on the following criteria: yolk sac edema (YE, 0–3 points), pericardial edema (PE, 0–3 points), heart malformation (HM, 1 point), hemorrhage (HE, 1 point), craniofacial malformation (CM, 1 point), spinal deformity (SD, 1 point), decreased circulation (DC, 1 point), fin rot (FR, 1 point), and loss of mobility (LA, 1 point). For yolk sac and pericardial edema, the severity was scored as follows: 0 = no edema, 1 = mild edema (slight separation of the membrane from the yolk or heart), 2 = moderate edema (pronounced separation of the membrane), and 3 = severe edema (extreme separation of the membrane, potentially impeding movement or circulation). For the other abnormalities, a score of 1 was assigned if the abnormality was present, regardless of severity. Dead (DE) individuals received the maximum BSD score of 13 points. The mean BSD score was calculated for each treatment group at 7 dpf and 21 dpf (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Detailed criteria for the blue sac disease (BSD) scoring system used to assess morphological abnormalities in marine medaka embryos and larvae.
2.5. Antioxidant Defense Capacity Assessment
For biochemical analyses, the samples were homogenized in ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution (10 mM, pH 7.4) using a D-130 handheld homogenizer (Wiggens, Wuppertal, Germany) at 1000 rpm for 2 min while keeping the samples on ice to prevent enzyme degradation. The homogenates were centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 15 min at 4 °C using a Sorvall Legend Micro 17 microcentrifuge (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA), and the supernatants were collected for subsequent analyses.
Total protein (TP) content was determined using the Bradford Coomassie-binding method with bovine serum albumin (BSA) as the standard [56]. Briefly, 10 μL of the supernatant was mixed with 200 μL of Bradford reagent (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China) in a 96-well microplate and incubated for 5 min at room temperature, and the absorbance was measured at 595 nm using the Epoch2 microplate reader (BioTek, USA). TP content was calculated using a standard curve prepared with BSA (0–1 mg/mL) and expressed as mgprot/mL.
SOD activity was measured using the water-soluble tetrazolium salt (WST-1) method, which is based on the inhibition of the reduction of WST-1 by the superoxide radical generated by the xanthine/xanthine oxidase system [57]. Briefly, 20 μL of the supernatant was mixed with 200 μL of the reaction mixture containing WST-1, xanthine, and xanthine oxidase in a 96-well microplate. The plate was incubated at 37 °C for 20 min, and the absorbance was measured at 450 nm. SOD activity was calculated using a standard curve and expressed as U/mgprot, where one unit (U) of SOD activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to inhibit the reduction of WST-1 by 50%.
CAT activity was determined using the ammonium molybdate-chromogenic method, which measures the rate of hydrogen peroxide decomposition [48,58]. Briefly, 10 μL of the supernatant was mixed with 100 μL of hydrogen peroxide solution (65 mM) and incubated at 37 °C for 1 min. The reaction was stopped by adding 100 μL of ammonium molybdate solution (32.4 mM), and the absorbance was measured at 405 nm. CAT activity was calculated using a standard curve and expressed as U/mgprot.
Reduced GSH content was assessed using the 5,5′-dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) method, also known as Ellman’s reagent method [59,60]. Briefly, 20 μL of the supernatant was mixed with 180 μL of the reaction mixture containing DTNB in a 96-well microplate. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 5 min, and the absorbance was measured at 412 nm. Reduced GSH content was calculated using a standard curve and expressed as μmol/mgprot.
2.6. Lipid Peroxidation Assessment
Lipid peroxidation was evaluated by measuring MDA content using the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) method, which is based on the reaction between MDA and TBA that forms a red-colored complex [20,61]. Briefly, 100 μL of the supernatant obtained from sample homogenization was mixed with 200 μL of TBA reagent containing trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and TBA in a test tube. The mixture was heated in a boiling water bath for 15 min, cooled to room temperature, and centrifuged at 3500 g for 10 min. The supernatant (200 μL) was transferred to a 96-well microplate, and the absorbance was measured at 532 nm. The MDA content was calculated using a standard curve prepared with 1,1,3,3-tetraethoxypropane (a precursor of MDA) and expressed as nmol/mgprot.
2.7. Non-Specific Immune Response Assessment
AKP activity was determined using the 4-aminoantipyrine method, which measures the rate of p-nitrophenol formation from p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) under alkaline conditions [48,62]. Briefly, 20 μL of the supernatant obtained from sample homogenization was mixed with 100 μL of the reaction mixture containing pNPP in a 96-well microplate. The plate was incubated at 37 °C for 15 min, and the reaction was stopped by adding 80 μL of sodium hydroxide solution (1.5 M). The absorbance was measured at 520 nm. AKP activity was calculated using a standard curve prepared with p-nitrophenol and expressed as U/mgprot.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism Ver 10.2 (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA). The normality and homogeneity of variance were assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test and Levene’s test, respectively. When necessary, data were log-transformed or arcsine-transformed to meet the assumptions of parametric tests. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to evaluate the effects of treatment (control, L-WAF, M-WAF, and H-WAF) and periods (exposure and recovery) on the measured parameters, with treatment as the between-subject factor and time as the within-subject factor, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. When the assumption of sphericity was violated (as determined by Mauchly’s test), the Greenhouse–Geisser correction was applied. Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to explore the relationships among the various observed parameters measured during the experiment. The data were standardized (z-score transformation) before PCA to account for differences in measurement scales. The Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy and Bartlett’s test of sphericity were conducted to assess the suitability of the data for PCA. Principal components with eigenvalues greater than 1 were retained, and varimax rotation was applied to facilitate interpretation of the loadings. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to assess the relationships between pairs of variables. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) correlation matrix was visualized using a heatmap with hierarchical clustering to identify patterns of relationships. For all statistical tests, differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05. Graphical representations were created using GraphPad Prism.
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Analysis in the Water-Accommodated Fractions (WAFs) of Oman Crude Oil (OCO) Stock Solution and Exposure Solution
TPH concentrations in the OCO WAF exposure solutions were 0.37 ± 0.03 mg/L, 0.58 ± 0.02 mg/L, and 0.99 ± 0.05 mg/L for the L-WAF, M-WAF, and H-WAF groups, respectively, manifesting a non-linear relationship between TPH concentrations (mg/L) and the nominal concentrations (%, v/v) of OCO WAF exposure solutions with a goodness of fit r2 = 0.998. For the 16 priority PAHs in the OCO WAF stock solution, as we reported previously [5], the total concentrations of PAHs (ΣPAHs) were 6.35 ± 0.11 μg/L. Component analysis revealed that in the OCO WAF stock solution, 2-ring PAHs (accounting for 58.6% of ΣPAHs) were the most abundant, followed by 3-ring (20.2%), 4-ring (13.2%), and ≥5-ring (8.0%) PAHs. The predominant PAHs were naphthalene (43.9%), followed by phenanthrene (15.5%) and fluorene (7.80%). ΣPAH concentrations in the OCO WAF exposure solutions were 0.28 ± 0.06 μg/L, 0.61 ± 0.09 μg/L, and 1.63 ± 0.04 μg/L for the L-WAF, M-WAF, and H-WAF groups, respectively.
3.2. Lethal and Sublethal Morphological Effects of OCO WAF on Marine Medaka Early-Life Stages (ELS) During Exposure and Recovery Periods
Survival rates of marine medaka embryos exhibited a concentration-dependent decrease in response to OCO WAF exposure (Figure 1A). At the end of the exposure period (7 dpf), survival rates in all groups remained relatively high, with no statistically significant differences observed (p > 0.05) between the control (98.5 ± 2.4%) and L-WAF (96.2 ± 2.1%, p = 0.998), M-WAF (90.9 ± 3.7%, p = 0.455), or H-WAF (90.9 ± 1.8%, p = 0.436) groups. However, the adverse effects of OCO WAF exposure on survival became more pronounced during the recovery period (8–21 dpf), particularly in the M-WAF and H-WAF groups (Figure 1B). At the end of the recovery period (21 dpf), survival rates in the M-WAF (72.0 ± 3.8%) and H-WAF (63.6 ± 5.6%) groups were significantly lower than in the control (91.7 ± 2.8%, p = 0.007 < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively). The L-WAF group also exhibited reduced survival (79.6 ± 4.9%) compared to the control, though this difference did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.061 > 0.05). Notably, when comparing survival rates within each group at the end of exposure period (7 dpf) and at the end of recovery period (21 dpf), significant decreases were observed in all OCO WAF exposure groups (L-WAF: p = 0.005 < 0.01; M-WAF: p = 0.002 < 0.01; H-WAF: p < 0.001), while no significant change was detected in the control (p = 0.577). These results indicated that the toxic effects of acute OCO WAF exposure on the survival of marine medaka persisted and progressively manifested even after the embryos were transferred to clean water, suggesting potential persistent developmental impairment.
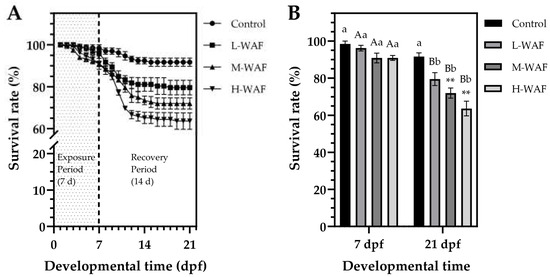
Figure 1.
Survival rates of marine medaka embryos/larvae exposed to water-accommodated fractions (WAFs) of Oman crude oil (OCO) during the exposure and recovery periods (n = 50). (A) Time-course dynamics of survival rates throughout the 21 d developmental time, showing the 7 d acute exposure period (0–7 dpf, shaded area) followed by a 14 d recovery period (8–21 dpf) in clean artificial seawater. (B) Comparison of survival rates at 7 dpf (end of exposure period) and 21 dpf (end of recovery period) across treatment groups. Control: artificial seawater; L-WAF: 5% (v/v) WAF; M-WAF: 10% (v/v) WAF; H-WAF: 20% (v/v). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA. Asterisks (**) indicate significant differences between WAF treatments and control at the same developmental time (p < 0.01). Lowercase (p < 0.05) and uppercase (p < 0.01) letters indicate significant differences between exposure and recovery periods within the same treatment group.
For hatching, OCO WAF exposure significantly altered hatching patterns in marine medaka embryos (Figure 2A). The timing of hatching initiation varied among the groups, with embryos in the control exhibiting normal hatching initiation (8–9 dpf), embryos in the L-WAF group showing premature hatching (7–8 dpf), and both embryos in the M-WAF and H-WAF groups exhibiting delayed hatching (9–10 dpf). All groups reached hatching plateaus after 12–14 dpf. In addition, hatching rates showed an obvious concentration-dependent response, with significant reductions observed in all groups compared to the control (99.2 ± 1.1%). The L-WAF group showed a moderately reduced hatching rate (88.1 ± 3.9%, p = 0.041 < 0.05), while more substantial decreases were observed in the M-WAF (84.9 ± 4.2%, p = 0.005 < 0.01) and H-WAF (75.4 ± 5.9%, p < 0.001) groups. Hatching rate results indicated that OCO WAF exposure disrupted the normal hatching time and significantly compromised overall hatching success, with higher concentrations producing more severe effects. Regarding the morphological malformations, BSD score results revealed significant morphological abnormalities in marine medaka exposed to OCO WAF in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 2B). At the end of the exposure period (7 dpf), the L-WAF group showed a subtle but non-significant increase in the BSD score (0.94 ± 0.39, p = 0.457) compared to the control (0.23 ± 0.27). In contrast, M-WAF (2.68 ± 0.59, p < 0.05) and H-WAF (2.78 ± 0.50, p < 0.05) groups showed significantly elevated BSD scores compared to the control. The main observed abnormalities included yolk sac edema, pericardial edema, and craniofacial malformations, which increased in frequency and severity with higher WAF nominal concentrations. Following the 14 d recovery period in clean seawater, all the WAF exposure groups still maintained significantly elevated BSD scores (3.57 ± 1.07, p = 0.028 < 0.05 for L-WAF; 5.55 ± 0.89, p = 0.003 < 0.01 for H-WAF; and 8.61 ± 1.76, p < 0.001 for H-WAF) compared to the control even after the recovery period, indicating persistent morphological developmental impairments following OCO WAF exposure that could not be fully remediated during the recovery period. The increasing BSD scores during the recovery period, concurrent with the reduced survival rates, suggested that the developmental abnormalities may have contributed to the delayed mortality. Embryos that initially survived during the exposure period but sustained sublethal developmental damage may have ultimately succumbed during subsequent development due to the severity or progression of these abnormalities.
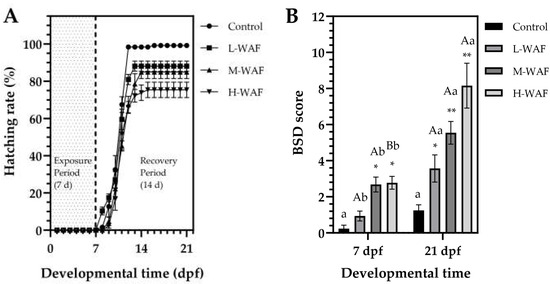
Figure 2.
Hatching rates and blue sac disease (BSD) score of marine medaka embryos/larvae exposed to water-accommodated fractions (WAFs) of Oman crude oil (OCO) during the exposure and recovery periods. (A) Time-course dynamics of hatching rates throughout the 21 d developmental time, showing the 7 d acute exposure period (0–7 dpf, shaded area) followed by a 14 d recovery period (8–21 dpf) in clean artificial seawater (n = 50). (B) Comparison of BSD scores at 7 dpf (end of exposure period) and 21 dpf (end of recovery period) across treatment groups (n = 6). Control: artificial seawater; L-WAF: 5% (v/v) WAF; M-WAF: 10% (v/v) WAF; H-WAF: 20% (v/v). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA. Asterisks (* and **) indicate significant differences between WAF treatments and control at the same developmental time (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively). Lowercase (p < 0.05) and uppercase (p < 0.01) letters indicate significant differences between exposure and recovery periods within the same treatment group.
3.3. Effects of OCO WAF on the Antioxidant Defense Capacity of Marine Medaka on ELS During Exposure and Recovery Periods
For TP content, as depicted in Figure 3A, at the end of exposure period (7 dpf), a non-monotonic response pattern was observed, with significant decreases in TP content in both L-WAF (2.77 ± 0.07 mgprot/mL, p < 0.001) and H-WAF (2.87 ± 0.09 mg/mL, p < 0.001) groups compared to the control (3.53 ± 0.05 mgprot/mL), while the M-WAF group (3.47 ± 0.13 mgprot/mL, p = 0.985 > 0.05) showed no significant difference. At the end of recovery period (21 dpf), all treatment groups exhibited relatively similar TP content (L-WAF: 1.59 ± 0.03 mgprot/mL, p = 0.073; M-WAF: 1.56 ± 0.02 mg/mL, p = 0.147; H-WAF: 1.60 ± 0.01 mg/mL, p = 0.055) with no significant differences (p > 0.05) from the control (1.37 ± 0.04 mgprot/mL). However, a marked reduction in TP content was observed in all groups between 7 dpf and 21 dpf (p < 0.001 for all groups), which likely reflected normal physiological changes associated with embryonic development and hatching.
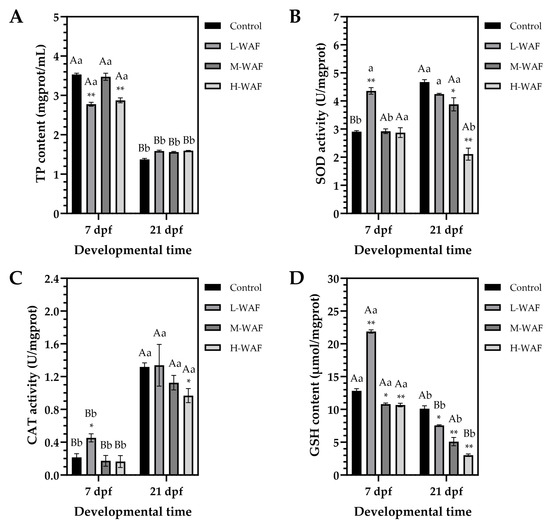
Figure 3.
Changes in total protein (TP) content (A), superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (B), catalase (CAT) activity (C), and reduced glutathione (GSH) content (D) of marine medaka embryos/larvae exposed to water-accommodated fractions (WAF) of Oman crude oil (OCO) at 7 dpf (end of exposure period) and 21 dpf (end of recovery period) across treatment groups (n = 9). Control: artificial seawater; L-WAF: 5% (v/v) WAF; M-WAF: 10% (v/v) WAF; H-WAF: 20% (v/v). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA. Asterisks (* and **) indicate significant differences between WAF treatments and control at the same developmental time (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively). Lowercase (p < 0.05) and uppercase (p < 0.01) letters indicate significant differences between exposure and recovery periods within the same treatment group.
As depicted in Figure 3B, at the end of exposure period (7 dpf), only the L-WAF group exhibited a significant elevation in SOD activity (4.36 ± 0.16 U/mgprot, p < 0.001) compared to the control (2.91 ± 0.05 U/mgprot), while M-WAF (2.92 ± 0.12 U/mgprot, p = 0.995) and H-WAF (2.87 ± 0.25 U/mgprot, p = 0.873) groups maintained activity levels similar to the control (p > 0.05). At the end of recovery period (21 dpf), an obvious concentration-dependent reduction in SOD activity was observed, with the control showing a significant increase (4.67 ± 0.12 U/mgprot, p < 0.001 compared to that at 7 dpf), while M-WAF (3.88 ± 0.33 U/mgprot, p = 0.037 < 0.05) and H-WAF (2.11 ± 0.30 U/mgprot, p < 0.001) groups exhibited significantly lower levels compared to the control. The L-WAF group maintained relatively stable SOD activity from 7 dpf to 21 dpf (4.25 ± 0.04 U/mgprot at 21 dpf, p = 0.971 > 0.05 compared to 7 dpf). The pattern of SOD activity changes, particularly the significant reduction in the H-WAF group during the recovery period (p = 0.027 compared to that at 7 dpf), indicated a potential impairment of antioxidant defense mechanisms following high-concentration OCO WAF exposure.
Regarding the CAT activity (Figure 3C), at the end of exposure period (7 dpf), only the L-WAF group showed significantly elevated CAT activity (0.45 ± 0.07 U/mgprot, p = 0.047 < 0.05) compared to the control (0.22 ± 0.06 U/mgprot), while M-WAF (0.17 ± 0.09 U/mgprot, p = 0.984) and H-WAF (0.16 ± 0.10 U/mgprot, p = 0.947) groups exhibited activity levels comparable to the control (p > 0.05). At the end of recovery period (21 dpf), CAT activity had increased significantly in all groups (p < 0.001 for all groups compared to those at 7 dpf), consistent with normal developmental progression. However, the H-WAF group exhibited significantly lower CAT activity (0.97 ± 0.12 U/mgprot, p = 0.038 < 0.05) compared to the control (1.32 ± 0.07 U/mgprot), while L-WAF (1.34 ± 0.36 U/mgprot, p = 0.993) and M-WAF (1.13 ± 0.13 U/mgprot, p = 0.158) groups showed no significant differences from the control (p < 0.05). Changes in the CAT activity suggested that while all treatment groups caused the increase in CAT activity, high-concentration OCO WAF exposure resulted in a less robust increase, potentially indicating a compromised capacity to detoxify hydrogen peroxide during later developmental stages.
As depicted in Figure 3D, at the end of exposure period (7 dpf), the L-WAF group showed a marked elevation in GSH content (21.88 ± 0.36 μmol/mgprot, p < 0.001) compared to the control (12.83 ± 0.47 μmol/mgprot), while both M-WAF (10.80 ± 0.25 μmol/mgprot, p = 0.012) and H-WAF (10.67 ± 0.38 μmol/mgprot, p = 0.007) groups caused a significant reduction in the GSH content (p < 0.05). At the end of recovery period (21 dpf), all groups, including the control, showed significant reductions in GSH content compared to those at 7 dpf (control: p = 0.026 < 0.05; L-WAF: p < 0.001; M-WAF: p = 0.015 < 0.05; H-WAF: p = 0.007 < 0.01). However, the magnitude of this reduction was concentration-dependent in the treatment groups, resulting in significantly lower GSH content in all OCO WAF exposure groups (L-WAF: 7.56 ± 0.14 μmol/mgprot, p = 0.015 < 0.05; M-WAF: 5.09 ± 0.88 μmol/mgprot, p = 0.007 < 0.01; H-WAF: 3.02 ± 0.28 μmol/mgprot, p < 0.001) compared to the control (10.10 ± 0.64 μmol/mgprot). The observed concentration-dependent depletion of GSH content during the recovery period, particularly severe in the H-WAF group (70.1% reduction from control), suggested a progressive impairment of the glutathione-dependent detoxification system following acute OCO WAF exposure.
3.4. Effects of OCO WAF on the Lipid Peroxidation of Marine Medaka on ELS During Exposure and Recovery Periods
MDA, a key biomarker of lipid peroxidation and oxidative damage, exhibited an obvious concentration- and time-dependent pattern in response to OCO WAF exposure at the end of the exposure and recovery periods (Figure 4). At the end of the exposure period (7 dpf), a pronounced concentration-dependent elevation in MDA content was observed across all treatment groups compared to the control (2.69 ± 0.05 nmol/mgprot), with incremental increases in the L-WAF (4.40 ± 0.05 nmol/mgprot, p < 0.001), M-WAF (6.96 ± 0.10 nmol/mgprot, p < 0.001), and H-WAF (9.26 ± 0.14 nmol/mgprot, p < 0.001) groups. Intriguingly, the pattern of MDA accumulation was substantially altered at the end of the recovery period (21 dpf). The control exhibited a significant increase in MDA content (5.34 ± 0.02 nmol/mgprot, p = 0.033 < 0.05, compared to that at 7 dpf), reflecting normal physiological processes associated with embryonic development and metabolic changes post-hatching. The L-WAF group maintained elevated MDA contents (6.46 ± 0.04 nmol/mgprot), which remained significantly higher than the control (p = 0.007 < 0.01) and also showed a significant increase compared to that at 7 dpf (p = 0.018 < 0.05). In contrast, both M-WAF and H-WAF groups showed substantial reductions in MDA content at 21 dpf (M-WAF: 4.21 ± 0.13 nmol/mgprot, p = 0.007 < 0.01; H-WAF: 4.55 ± 0.20 nmol/mgprot, p < 0.001, compared to those at 7 dpf), resulting in levels significantly lower than the control (p = 0.0026 < 0.01 and p = 0.085 < 0.05, respectively). This reversal pattern in MDA contents during the recovery period, particularly in the higher concentration treatment groups, suggested a complex compensatory response.
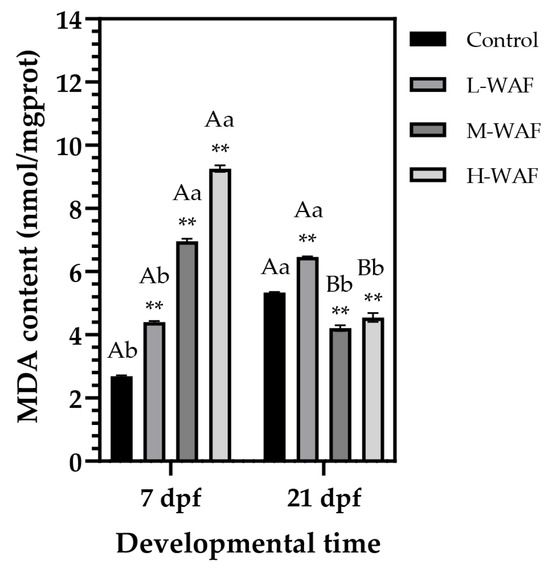
Figure 4.
Changes in malondialdehyde (MDA) content of marine medaka embryos/larvae exposed to water-accommodated fractions (WAFs) of Oman crude oil (OCO) at 7 dpf (end of exposure period) and 21 dpf (end of recovery period) across treatment groups (n = 9). Control: artificial seawater; L-WAF: 5% (v/v) WAF; M-WAF: 10% (v/v) WAF; H-WAF: 20% (v/v). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA. Asterisks (**) indicate significant differences between WAF treatments and control at the same developmental time (p < 0.01). Lowercase (p < 0.05) and uppercase (p < 0.01) letters indicate significant differences between exposure and recovery periods within the same treatment group.
3.5. Effects of OCO WAF on the Immune Function of Marine Medaka on ELS During Exposure and Recovery Periods
AKP, an important enzyme involved in immune processes in fish, exhibited marked temporal changes in marine medaka response to OCO WAF exposure (Figure 5). At the end of exposure period (7 dpf), no significant differences in the AKP activity were observed (p > 0.05) between any of the treatment groups (L-WAF: 24.95 ± 0.72 King U/mgprot, p = 0.973; M-WAF: 22.57 ± 0.20 King U/mgprot, p = 0.229; H-WAF: 30.46 ± 0.40 King U/mgprot, p = 0.168) and the control group (26.37 ± 0.58 King U/mgprot), suggesting that the direct impact of acute OCO WAF exposure on AKP-mediated immune function was subtle during the early embryonic development period. However, at the end of recovery period (21 dpf), a significant increase in the AKP activity was observed in all groups, with the control group showing nearly a 7-fold increase (183.81 ± 2.17 King U/mgprot, p < 0.001 compared to that at 7 dpf), reflecting the normal developmental progression and increased immunocompetence associated with hatching and early larval growth. All OCO WAF exposure groups exhibited significantly lower AKP activity compared to the control at 21 dpf, with obvious concentration-dependent suppression effects (L-WAF: 148.90 ± 1.53 King U/mgprot, p = 0.004; M-WAF: 123.26 ± 1.22 King U/mgprot, p < 0.001; H-WAF: 148.74 ± 2.78 King U/mgprot, p = 0.008). In addition, the M-WAF group caused the most pronounced reduction in the AKP activity (approximately 33% lower than control), while both the L-WAF and H-WAF groups exhibited similar levels of suppression (approximately 19% lower than control), suggesting complex mechanisms underlying the delayed effects of OCO WAF exposure on immune function development. Despite the significant suppression relative to the control, all treatment groups still showed apparent increases in AKP activity from 7 dpf to 21 dpf (p < 0.001 for all groups).
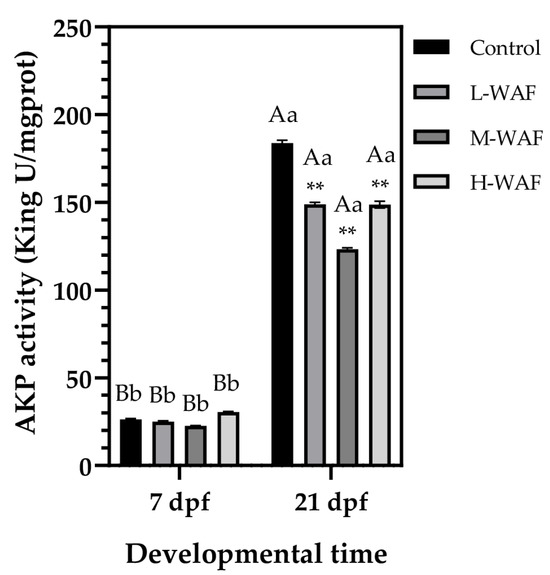
Figure 5.
Changes in alkaline phosphatase (AKP) activity of marine medaka embryos/larvae exposed to water-accommodated fractions (WAFs) of Oman crude oil (OCO) at 7 dpf (end of exposure period) and 21 dpf (end of recovery period) across treatment groups (n = 9). Control: artificial seawater; L-WAF: 5% (v/v) WAF; M-WAF: 10% (v/v) WAF; H-WAF: 20% (v/v) WAF. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA. Asterisks (**) indicate significant differences between WAF treatments and control at the same developmental time (p < 0.01). Lowercase (p < 0.05) and uppercase (p < 0.01) letters indicate significant differences between exposure and recovery periods within the same treatment group.
3.6. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Pearson Correlation Analysis
The PCA biplot (Figure 6A) revealed distinct patterns in the biomarker responses of marine medaka embryos exposed to OCO WAF. The first two principal components (PC1 and PC2) accounted for 82.3% of the total variance in the dataset (58.2% and 24.1%, respectively), indicating that the PCA effectively captures the majority of variation in the observed biomarkers. The distribution of biomarkers on the PCA biplot revealed obvious clustering patterns with biological significance. Hatching rate, CAT activity, and AKP activity formed a closely associated group in the positive region of PC1, indicating strong positive inter-relationships among these parameters. Conversely, the BSD score appeared in the positive region of PC1 and the negative region of PC2, suggesting its association with developmental toxicity markers. Survival rate and TP content were positioned in the negative region of PC1, exhibiting negative relationships with the biomarkers in the positive PC1 region. SOD activity showed a strong positive loading on PC2, indicating its unique contribution to the dataset variance that is distinct from the primary toxicity responses captured by PC1. GSH content was positioned between survival and SOD activity, reflecting its role in both antioxidant defense and survival capacity. Interestingly, MDA content showed moderate loadings on both PC1 and PC2, suggesting its association with multiple biological processes affected by OCO WAF exposure.
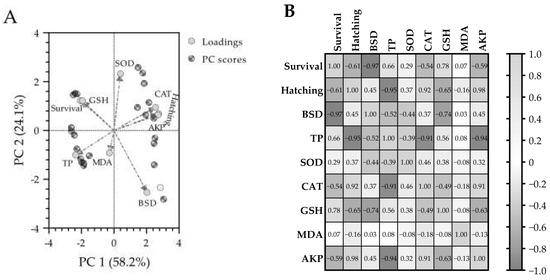
Figure 6.
Principal component analysis (PCA) biplot (A) and Pearson correlation coefficient matrix heatmap (B) of the observed biomarkers in marine medaka exposed to water-accommodated fractions (WAFs) of Oman crude oil (OCO) with different nominal concentration during the 7 d acute exposure period and following a 14 d recovery period in clean artificial seawater. The PCA biplot (A) illustrates the separation of the observed biomarker profiles. Loading vectors (light gray dashed lines) indicate the contribution of each biomarker to the principal component (PC) axes. In the Pearson correlation matrix (B), values represent Pearson correlation coefficients (r). Color intensity represents correlation coefficient values ranging from −1.00 (dark gray) to 1.00 (light gray). BSD: blue sac disease score; TP: total protein content; SOD: superoxide dismutase activity; CAT: catalase activity; GSH: reduced glutathione content; MDA: malondialdehyde content; AKP: alkaline phosphatase activity.
The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) matrix heatmap (Figure 6B) revealed significant relationships among the observed biomarkers. Survival rate exhibited a very strong negative correlation with BSD score (r = −0.97) and a strong positive correlation with GSH content (r = 0.78), highlighting the crucial role of GSH in maintaining survival capacity and mitigating developmental toxicity. Hatching rate showed exceptionally strong positive correlations with both AKP activity (r = 0.98) and CAT activity (r = 0.92), while showing a strong negative correlation with TP content (r = −0.95). Beyond its strong negative correlation with survival rate, the BSD score also showed a significant negative correlation with GSH content (r = −0.74), further substantiating the link between oxidative stress and developmental toxicity. TP content exhibited strong negative correlations with multiple parameters, including hatching rate (r = −0.95), CAT activity (r = −0.91), and AKP activity (r = −0.94), indicating the complex relationship between protein metabolism and developmental toxicity.
4. Discussion
In the present study, results showed that acute exposure of marine medaka embryos to OCO WAF induced obvious concentration-dependent developmental toxicity. During the 7 d exposure period, we observed that embryo survival and hatching success decreased significantly with increasing WAF concentration, while the incidence of malformations (notably edema and hemorrhaging characteristic of BSD) rose correspondingly. These BSD signs we documented, including yolk sac and pericardial edema, impaired circulation, and cardiac deformities, were apparent at higher WAF concentrations. Our observations were consistent with typical oil-induced embryo-larval syndrome in various fish species as observed in other studies [7,16,17,18,38]. These adverse effects aligned with previous reports in fish ELS exposed to crude oil or its derived hydrocarbons, including elevated embryonic mortality, delayed or failed hatching, and teratogenic outcomes like edema, hemorrhage, and cardiac defects in aquatic species, such as pink salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha), Pacific herring (Clupea pallasi), mahi mahi (Coryphaena hippurus), and zebrafish (Danio rerio) [5,6,11,63,64]. For instance, Mu et al. [65] observed significantly increased mortality rates and BSD scores in marine medaka embryos exposed to WAFs, chemically enhanced WAFs (CEWAFs), and biologically enhanced WAFs (BEWAFs) of crude oil. Similarly, Pannetier et al. [66] reported elevated mortality rates in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) embryos, larvae, and juveniles following benzo[a]pyrene exposure, with mortality predominantly occurring during the hatching period. Notably, after transferring larvae to clean seawater for 14 d (recovery period), partial recovery was observed in L- and M-WAF groups. Hatching rates elevated and edema partially subsided in these groups, suggesting that mild damage was reversible upon the removal of oil exposure. However, larvae from the H-WAF exposure still exhibited significantly lower survival and growth than the control, and the BSD symptoms (e.g., pericardial edema) persisted or even progressed, indicating that severe embryonic damage could not be fully ameliorated during the recovery. It is well documented in previous studies that embryonic exposure to crude oil, even at sublethal concentrations, could cause latent or delayed developmental disruptions in fish ELS that persist and potentially exacerbate during subsequent ontogenetic development [7,38,67,68]. For example, polar cod (Boreogadus saida) embryos exposed to low ∑PAHs levels showed sublethal heart abnormalities and reduced larval fitness that did not immediately resolve post-hatch [69]. Our study corroborated these findings, as mortality of marine medaka exposed to OCO WAF occurred mainly between 8 and 11 dpf during the recovery period, coinciding with the hatching period. The stage-specific sensitivity observed in this study corresponded with research by Mager et al. [70], who reported that mahi mahi exhibited developmental time-dependent toxicity to crude oil WAFs, with the post-hatching period showing the higher vulnerable developmental stage, which might be explained by several physiological and toxicological mechanisms. Though larger fish (larvae or adults) could rapidly detoxify and eliminate PAHs, early embryos have limited metabolic capacity, leading to significant bioaccumulation of dissolved PAHs [71]. Our results also revealed both partial recovery capacity at lower TPH concentrations and severe developmental toxicity caused by crude oil at higher TPH concentrations, as evidenced by the insufficient 14 d recovery period for full compensation of early developmental damage in high-concentration exposure groups, indicating that even acute embryotoxic exposure to oil pollution could lead to lasting ontogenetic consequences.
Petroleum hydrocarbons can stimulate excessive ROS production during biotransformation, elevating ROS levels in marine organisms and inducing oxidative damage to biological macromolecules, including proteins, lipids, and DNA [26,27,28]. The antioxidant defense systems of marine organisms could mitigate oxidative damage by maintaining stable cellular redox states and keeping ROS at relatively homeostatic levels [17,48,72]. Antioxidant enzymes and factors such as SOD, CAT, GSH, and glutathione S-transferase (GST) play crucial roles in this process [23,73,74]. As important endogenous antioxidant enzymes, SOD could catalyze O2•− to H2O2, and CAT decomposes H2O2 into harmless byproducts H2O and O2, which are the first defense lines of the antioxidant system for cellular protection [73,74,75]. GSH, a non-enzymatic antioxidant, also possesses the ability to eliminate ROS and free radicals to protect against oxidative stress, primarily functioning as a substrate of GST and GPx enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of H2O2 into H2O and O2 [76,77]. During the 7 d exposure period, marine medaka embryos exhibited significant oxidative stress, as evidenced by alterations in antioxidant parameters (SOD, CAT and GSH). We observed that SOD and CAT activities changed in a concentration-dependent manner: being upregulated at lower TPH concentrations (as an adaptive response to rising ROS level) with observed statistical differences indicating a substantial upregulation of antioxidant defense for cellular protection, and being downregulated at the higher TPH concentration indicating a suppression or severe impairment of antioxidant capacity with potentially profound consequences for cellular health and development. The observed biphasic response was also a common pattern in fish exposed to environmental contaminants, manifesting that low concentrations of oil-derived hydrocarbon exposure could induce antioxidant defenses, but excessive ROS at high-concentration exposure would overwhelm and inhibit enzyme function [17,48,78]. A similar trend was reported in mudskipper (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris) tissues exposed to crude oil, where SOD and GPx activities were induced at low concentrations of oil-derived hydrocarbons but significantly inhibited at the highest concentrations [78]. Furthermore, the depletion of GSH content observed in marine medaka exposed to the H-WAF group further supported an overwhelming oxidative burden; GSH was consumed in neutralizing peroxides and oxidized under severe stress, compromising the cellular redox balance and detoxification capacity [32,48,79]. Similarly, Milinkovitch et al. [80] also found significantly elevated antioxidant enzyme activity and significantly reduced GSH content in golden grey mullet (Liza aurata) juveniles after acute crude oil exposure. During the 14 d recovery period in clean water, the pattern of antioxidant response altered, particularly in L- and M-WAF groups, where SOD and CAT activities tended to normalize toward control levels and MDA content reduced, suggesting that marine medaka larvae could recuperate their antioxidant capacity once the exogenous pollutants were removed. Recovery of antioxidant enzyme function has also been reported in other fish species during the recovery periods, as evidenced by juvenile African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) who showed SOD activity returning to baseline after a week of recovery from pro-oxidant exposure [81]. However, in the H-WAF group, despite initial compensatory increases in enzyme activities, the antioxidant system became overwhelmed by excessive ROS production, resulting in a significant reduction in SOD and CAT activities and GSH content. Our results were consistent with previous studies documenting that under prolonged exposure to high concentrations of pollutants, the antioxidant defense systems would often be overwhelmed, leading to the depletion of key antioxidants and the eventual failure of the defense mechanisms [17,32]. High concentrations of oil-derived hydrocarbons caused a significant increase in ROS production, leading to cellular damage, and excessive ROS levels eventually impaired the capacity of the organism’s antioxidant enzymes to neutralize the damage [82]. These findings are also consistent with the research by Kerambrun et al. [79] that reported significantly elevated GST and CAT activities in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles following 48 h and 96 h acute crude oil exposure. After recovery in clean water, enzyme activities in the 48 h exposure group decreased to control levels, while GST activity in the 96 h exposure group remained significantly elevated.
Damage to the antioxidant defense system could lead to insufficient capacity for scavenging ROS, resulting in a significant net increase in ROS levels [74,83]. The excessive ROS could subsequently attack biological membrane components such as phospholipids, membrane receptors, and polyunsaturated fatty acids associated with enzymes, leading to membrane dysfunction. MDA, a degradation product of lipid peroxidation, serves as an indicator of ROS-induced lipid peroxidation levels [20,31]. The increase in MDA levels in the L-WAF and M-WAF groups after 7 d exposure revealed lipid membrane damage due to the persistent ROS activity, even though the antioxidant systems were still active. This pattern was more pronounced at high concentrations of oil-derived hydrocarbons (H-WAF), where MDA levels increased significantly, suggesting that the oxidative damage exceeded the repair capacity of the cells [48]. The literature on oxidative stress in marine organisms also supports our results, with many studies showing that exposure to high concentrations of pollutants could cause an imbalance between ROS production and the organism’s ability to detoxify and repair damage, leading to significant lipid peroxidation [20,84,85]. Li et al. [72] reported similar results, with significantly increased MDA content in sea cucumbers (Apostichopus japonicus) exposed to crude oil WAFs. However, after recovery in clean water, MDA content in marine medaka larvae decreased to levels similar to the control, with only slight inhibition in the H-WAF group, suggesting effective recovery from lipid peroxidation damage through the action of the antioxidant defense system. These findings aligned with research by Sureda et al. [86] that investigated changes in antioxidant and detoxification systems in Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) exposed to oil from the Don Pedro oil spill incident. One month after the incident, antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, GST, GPx) were significantly elevated, and lipid peroxidation (MDA content) was significantly induced. However, two months post-incident, all parameters returned to levels similar to the control, demonstrating recovery capabilities.
Our results also revealed that crude oil exposure appeared to affect the immune function of medaka embryos, as reflected by changes in AKP activity. Phosphatases constitute essential components of non-specific immune defense in fish, and AKP, a lysosomal marker enzyme widely distributed in cell membranes, catalyzes phosphate compound hydrolysis and participates in phosphate group transfer and metabolism, closely related to growth, digestion, absorption, and immune defense functions [87]. In our study, marine medaka embryos exposed to high concentrations of oil-derived hydrocarbon exposure (H-WAF) showed slightly induced AKP activity, suggesting increased metabolic rates of nutrients in marine medaka as an adaptive response to oil exposure. However, during 14 d recovery in clean water, AKP activity in exposed marine medaka larvae was significantly inhibited compared to the control group, possibly due to AKP consumption during detoxification or enzyme activity reduction caused by cellular damage, indicating a lasting immune disturbance. It is possible that surviving larvae exposed to crude oil were in a pro-inflammatory state despite the observed reduction in AKP, potentially indicating an inflammatory response that exceeded the regulatory capacity of AKP to regulate. The decrease in AKP activity would likely also impair nutrient metabolism efficiency in marine medaka, thereby resulting in the observed persistent sublethal growth impairment and developmental abnormalities. Similar patterns have been observed in other aquatic organisms. Weng et al. [88] reported that Manila clams (Ruditapes philippinarum) exposed to diesel WAF showed a strongly induced acid phosphatase (ACP) activity in heart and gill tissues during initial exposure, but activity was inhibited with increasing exposure time and concentration, indicating enhanced cytotoxic effects and toxic damage. Cao et al. [89] observed significantly decreased ACP and AKP activities in zebrafish liver tissue under fluoride stress, indicating substantial immunotoxicity.
In conclusion, this study revealed that acute exposure of marine medaka in ELSs to OCO WAF exhibited concentration-dependent developmental toxicity, characterized by reduced survival, delayed hatching/hatching failure, and BSD symptoms including pericardial edema and cardiac deformities. At lower concentrations of oil-derived hydrocarbons, partial recovery was observed when larvae were transferred to clean seawater, while severe embryonic damage from high concentrations of oil-derived hydrocarbons could not be fully mitigated, indicating lasting ontogenetic consequences even after acute exposure. Petroleum hydrocarbons triggered oxidative stress with a biphasic antioxidant response pattern, manifested that enzyme (SOD, CAT) activities were upregulated at lower concentrations but exhausted at higher concentrations, alongside GSH depletion indicating overwhelming oxidative burden. Although antioxidant parameters and lipid peroxidation markers mostly normalized during the recovery period in lower-concentration groups, persistent inhibition of AKP activity across all treatment groups suggests lasting immune dysfunction and impaired nutrient metabolism, consistent with observed growth impairments. The delayed onset of mortality and persistent or worsening BSD scores during the recovery phase represent particularly intriguing findings with significant ecological implications. Sublethal cardiac dysfunction induced during the exposure period, though initially compensated for, may progress to systemic failure during the energetically demanding hatching process, when metabolic requirements increase substantially. Moreover, the continuous allocation of energy resources toward detoxification and antioxidant defense may deplete energy reserves needed for normal development, creating a metabolic deficit that becomes critical during key developmental windows. From an ecological perspective, these findings suggest that even transient oil exposure could significantly impact fish population recruitment success by causing delayed mortality that coincides with critical life-stage transitions. Traditional acute toxicity assessments that fail to include recovery periods may substantially underestimate the true ecological impact of oil spills. Furthermore, the concentration-dependent recovery patterns observed in this study indicate that while fish populations may recover from low-level exposures, higher concentration exposures, even if brief, could lead to persistent population-level effects that extend well beyond the period of direct exposure, particularly if multiple environmental stressors are present simultaneously. Despite the inability to measure tissue TPH concentrations in marine medaka embryos due to their small size and technical limitations, future studies would implement more sensitive analytical techniques to quantify bioaccumulation and elimination kinetics, thereby providing comprehensive insights into the toxicological mechanisms of petroleum hydrocarbons in fish ELS. Our findings could enhance our understanding of crude oil toxicity mechanisms in fish ELS and highlight that even short-term embryonic exposure to oil pollutants can result in persistent developmental and physiological consequences that may not be fully resolved during recovery periods, contributing to better risk assessments and management strategies for marine ecosystems following oil spills.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. (Xishan Li) and D.X.; methodology, X.L. (Xishan Li); software, X.L. (Xishan Li), Y.D. and H.G.; validation, Y.D., X.L. (Xishan Li), H.G. and X.L. (Xin Li); formal analysis, Y.D., H.G. and X.L. (Xin Li); investigation, Y.D., X.L. (Xishan Li), H.G. and H.W.; resources, X.L. (Xishan Li) and D.X.; data curation, Y.D., H.G., X.L. (Xin Li), J.D. and H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.D., X.L. (Xishan Li), and H.G.; writing—review and editing, Y.D., X.L. (Xishan Li), and H.G.; visualization, Y.D., and H.G.; supervision, X.L. (Xishan Li), G.L. and D.X.; project administration, X.L. (Xishan Li), G.L. and D.X.; funding acquisition, X.L. (Xishan Li) and D.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2023YFC3108303; the Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 2024-BS-016; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42206158; and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, grant number 3132023156. The APC was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2023YFC3108303.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their availability to review this work. Their valuable comments and suggestions have improved the quality of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, D.; Zhu, L. Assessing China’s legislation on compensation for marine ecological damage: A case study of the Bohai oil spill. Mar. Pol. 2014, 50, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Wan, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, T.; Fei, Y. Oil spills from global tankers: Status review and future governance. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lou, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, R.; Peng, M.; Gao, D.; Lei, W. Embryonic exposure to water accommodated fraction of crude oil inhibits reproductive capability in adult female marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, F. The long-term prediction of the oil-contaminated water from the Sanchi collision in the East China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, D.; Ding, G.; Fan, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, X. Exposure to water-accommodated fractions of two different crude oils alters morphology, cardiac function and swim bladder development in early-life stages of zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, D.; Ju, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Ding, G.; Liao, G. Phenotypic and transcriptomic consequences in zebrafish early-life stages following exposure to crude oil and chemical dispersant at sublethal concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Chen, S.; Xiong, D. Water-accommodated fractions of crude oil and its mixture with chemical dispersant impairs oxidase stress and energy metabolism disorders in Oryzias melastigma embryos. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, J.P.; Sommers, F.C.; Ylitalo, G.M.; Sloan, C.A. Altered growth and related physiological responses in juvenile Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) from dietary exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 2364–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incardona, J.P.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L. Defects in cardiac function precede morphological abnormalities in fish embryos exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 196, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Yao, Z.; Cong, Y.; Wang, J. Acute and chronic effects of crude oil water-accommodated fractions on the early life stages of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma, McClelland, 1839). Toxics 2023, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incardona, J.P.; Carls, M.G.; Holland, L.; Linbo, T.L.; Baldwin, D.H.; Myers, M.S.; Peck, K.A.; Tagal, M.; Rice, S.D.; Scholz, N.L. Very low embryonic crude oil exposures cause lasting cardiac defects in salmon and herring. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incardona, J.P.; Carls, M.G.; Teraoka, H.; Sloan, C.A.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor–independent toxicity of weathered crude oil during fish development. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carls, M.G.; Holland, L.; Larsen, M.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L.; Incardona, J.P. Fish embryos are damaged by dissolved PAHs, not oil particles. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 88, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherr, G.N.; Fairbairn, E.; Whitehead, A. Impacts of petroleum-derived pollutants on fish development. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 5, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodson, P.V. The toxicity to fish embryos of PAH in crude and refined oils. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Ding, G.; Li, X.; Xiong, D. Comparison of toxicity effects of fuel oil treated by different dispersants on marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) embryo. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Liang, C.; Xu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xiong, D. Stranded heavy fuel oil exposure causes deformities, cardiac dysfunction, and oxidative stress in marine medaka Oryzias melastigma using an oiled-gravel-column system. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 51, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Wang, J.; Jin, F.; Wang, X.; Hong, H. Comparative embryotoxicity of phenanthrene and alkyl-phenanthrene to marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, R.A.; Short, J.W.; Rice, S.D. Sensitivity of fish embryos to weathered crude oil: Part II. Increased mortality of pink salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) embryos incubating downstream from weathered Exxon Valdez crude oil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Liao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Zou, Y.; Yang, W.; Xiong, D. Oxidative stress responses in the respiratory tree and the body wall of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) to high temperature. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 21288–21298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billiard, S.M.; Querbach, K.; Hodson, P.V. Toxicity of retene to early life stages of two freshwater fish species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incardona, J.P.; Carls, M.G.; Day, H.L.; Sloan, C.A.; Bolton, J.L.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L. Cardiac arrhythmia is the primary response of embryonic Pacific herring (Clupea pallasi) exposed to crude oil during weathering. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regoli, F.; Giuliani, M.E. Oxidative pathways of chemical toxicity and oxidative stress biomarkers in marine organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 93, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Shen, G.; Shen, X. Oxidative stress in shellfish Sinonovacula constricta exposed to the water accommodated fraction of zero sulfur diesel oil and Pinghu crude oil. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, J.; Fang, X.; Thornton, C.; Mei, W.; Barbazuk, W.B.; Duke, M.; Scheffler, B.E.; Willett, K.L. Effects on specific promoter DNA methylation in zebrafish embryos and larvae following benzo[a]pyrene exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 163, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, J.S.; Pereira, T.S.B.; Boscolo, C.N.P.; Garcia, M.N.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, C.A.; de Almeida, E.A. Oxidative stress, biotransformation enzymes and histopathological alterations in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to new and used automotive lubricant oil. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 234, 108770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlahogianni, T.; Dassenakis, M.; Scoullos, M. Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 64, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadauskas-Henrique, H.; Braz-Mota, S.; Campos, D.F.; dos Santos Barroso, H.; Kochhann, D.; Luis Val, A.; Maria Fonseca de Almeida-Val, V. Oil spill in an amazon blackwater environment: Biochemical and physiological responses of local fish species. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liao, G.; Ju, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, N.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, Y. Antioxidant response and oxidative stress in the respiratory tree of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) following exposure to crude oil and chemical dispersant. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, D.; Li, N.; Zou, Y.; Yang, W.; Ju, Z.; Liao, G. Effects of crude oil and chemically dispersed crude oil on the antioxidant response and apoptosis in the respiratory tree of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus). In Proceedings of the 2021 6th Asia Conference on Environment and Sustainable Development, Phuket, Thailand, 6–8 November 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone, D.R. Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, D.B.; Mello, A.d.A.; Allodi, S.; de Barros, C.M. Acute exposure to water-soluble fractions of marine diesel oil: Evaluation of apoptosis and oxidative stress in an ascidian. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturve, J.; Hasselberg, L.; Fälth, H.; Celander, M.; Förlin, L. Effects of North Sea oil and alkylphenols on biomarker responses in juvenile Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, S73–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, S.; Deschaux, P. The effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the immune system of fish: A review. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 77, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bado-Nilles, A.; Quentel, C.; Thomas-Guyon, H.; Le Floch, S. Effects of two oils and 16 pure polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on plasmatic immune parameters in the European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (Linné). Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasparakis, C.; Esbaugh, A.J.; Burggren, W.; Grosell, M. Physiological impacts of Deepwater Horizon oil on fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 224, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Wang, X.; Jin, F.; Wang, J.; Hong, H. The role of cytochrome P4501A activity inhibition in three- to five-ringed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons embryotoxicity of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurel, B.J.; Copeman, L.A.; Iseri, P.; Spencer, M.L.; Hutchinson, G.; Nordtug, T.; Donald, C.E.; Meier, S.; Allan, S.E.; Boyd, D.T.; et al. Embryonic crude oil exposure impairs growth and lipid allocation in a keystone Arctic forage fish. iScience 2019, 19, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, Y.; Takahashi, C. Development of an in vivo acute bioassay using the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Lee, B.-Y.; Han, J.; Jeong, C.-B.; Hwang, D.-S.; Lee, M.-C.; Kang, H.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, D.; Kim, J.; et al. The genome of the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, J.; Cai, L.; Xu, J.-H.; Wang, K.-J.; Au, D.W.T. The marine medaka Oryzias melastigma—A potential marine fish model for innate immune study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Li, D.; Shen, R.; Wang, X.; Shi, D. Mechanisms of hexabromocyclododecanes induced developmental toxicity in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 152, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.M.; Kim, J.; Choi, I.Y.; Raisuddin, S.; Au, D.W.; Leung, K.M.; Wu, R.S.; Rhee, J.S.; Lee, J.S. Omics of the marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) and its relevance to marine environmental research. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 113, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Ruan, J.; Lu, M.; Chen, M.; Dai, Z.; Zuo, Z. Combined effects of ocean acidification and crude oil pollution on tissue damage and lipid metabolism in embryo–larval development of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1847–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.M.; Aurand, D.; Bragin, G.E.; Clark, J.R.; Coelho, G.M.; Sowby, M.L.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Standardization of the preparation and quantitation of water-accommodated fractions of petroleum for toxicity testing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zou, Y.; Xuan, H.; Yang, W.; Liao, G.; Wang, C.; Xiong, D. Impact of physically and chemically dispersed crude oil on the antioxidant defense capacities and non-specific immune responses in sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 17378.4-2007; The Specification for Marine Monitoring-Part 4: Seawater Analysis. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 44–45.
- EPA. Method 8270D: Semivolatile Organic Compounds by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, Part of Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 28540:2011; Water Quality-Determination of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in Water-Method Using Gas Chromatography with Mass Spectrometric Detection (GC-MS). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; p. 24.
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems Test No. 236: Fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test. In Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Grisle, S.; Schlenk, D. Effects of salinity on aldicarb toxicity in Juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and striped bass (Morone saxatilis × chrysops). Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 64, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado, R.; Shi, D.; Schlenk, D. Effects of salinity on the toxicity and biotransformation of l-selenomethionine in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) embryos: Mechanisms of oxidative stress. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 108, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Xiong, D.; Yang, M.; Xiong, Y.; Ding, G. Parental exposure to heavy fuel oil induces developmental toxicity in offspring of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peskin, A.V.; Winterbourn, C.C. Assay of superoxide dismutase activity in a plate assay using WST-1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 103, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Góth, L. A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin. Chim. Acta 1991, 196, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, I.K.; Vierheller, T.L.; Thorne, C.A. Assay of glutathione reductase in crude tissue homogenates using 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal. Biochem. 1988, 175, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.E.; Smith, M.J. The determination of serum acid and alkaline phosphatase activity with 4-aminoantipyrine (A.A.P.). J. Clin. Pathol. 1954, 7, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incardona, J.P.; Vines, C.A.; Anulacion, B.F.; Baldwin, D.H.; Day, H.L.; French, B.L.; Labenia, J.S.; Linbo, T.L.; Myers, M.S.; Olson, O.P.; et al. Unexpectedly high mortality in Pacific herring embryos exposed to the 2007 Cosco Busan oil spill in San Francisco Bay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E51–E58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.G.; Mager, E.M.; Grosell, M.; Pasparakis, C.; Schlenker, L.S.; Stieglitz, J.D.; Benetti, D.; Hazard, E.S.; Courtney, S.M.; Diamante, G.; et al. Time- and oil-dependent transcriptomic and physiological responses to Deepwater Horizon oil in mahi-mahi (Coryphaena hippurus) embryos and larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7842–7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Jin, F.; Ma, X.; Lin, Z.; Wang, J. Comparative effects of biological and chemical dispersants on the bioavailability and toxicity of crude oil to early life stages of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannetier, P.; Morin, B.; Clérandeau, C.; Lacroix, C.; Cabon, J.; Cachot, J.; Danion, M. Comparative biomarker responses in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) exposed to benzo[a]pyrene and challenged with betanodavirus at three different life stages. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, M.L.; Giebichenstein, J.; Teisrud, R.N.; Laurent, J.; Frantzen, M.; Meador, J.P.; Sorensen, L.; Hansen, B.H.; Reinardy, H.C.; Laurel, B.; et al. Combined effects of crude oil exposure and warming on eggs and larvae of an arctic forage fish. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philibert, D.A.; Lyons, D.D.; Tierney, K.B. Comparing the effects of unconventional and conventional crude oil exposures on zebrafish and their progeny using behavioral and genetic markers. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahrgang, J.; Dubourg, P.; Frantzen, M.; Storch, D.; Dahlke, F.; Meador, J.P. Early life stages of an arctic keystone species (Boreogadus saida) show high sensitivity to a water-soluble fraction of crude oil. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, E.M.; Pasparakis, C.; Schlenker, L.S.; Yao, Z.; Bodinier, C.; Stieglitz, J.D.; Hoenig, R.; Morris, J.M.; Benetti, D.D.; Grosell, M. Assessment of early life stage mahi-mahi windows of sensitivity during acute exposures to Deepwater Horizon crude oil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Kim, M.; Yim, U.H.; Ha, S.Y.; Shim, W.J.; Chae, Y.S.; Kim, H.; Incardona, J.P.; Linbo, T.L.; Kwon, J.H. Differential toxicokinetics determines the sensitivity of two marine embryonic fish exposed to Iranian heavy crude oil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13639–13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Li, N.; Gao, Y.; Ju, Z.; Liao, G.; Xiong, D. Combined effects of elevated temperature and crude oil pollution on oxidative stress and apoptosis in sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus, Selenka). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: Concept and some practical aspects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Li, X.; Huo, C.; Chu, S.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.; Wan, J.; Liu, R. Evaluation of fluorene-caused ecotoxicological responses and the mechanism underlying its toxicity in Eisenia fetida: Multi-level analysis of biological organization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Glutathione and modulation of cell apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, L.; Zhao, Q.; Tao, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, R.; Zhang, G.; Wu, W. Evaluation of the acute toxic effects of crude oil on intertidal mudskipper (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris) based on antioxidant enzyme activity and the integrated biomarker response. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerambrun, E.; Le Floch, S.; Sanchez, W.; Thomas Guyon, H.; Meziane, T.; Henry, F.; Amara, R. Responses of juvenile sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax, exposed to acute concentrations of crude oil, as assessed by molecular and physiological biomarkers. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinkovitch, T.; Imbert, N.; Sanchez, W.; Le Floch, S.; Thomas-Guyon, H. Toxicological effects of crude oil and oil dispersant: Biomarkers in the heart of the juvenile golden grey mullet (Liza aurata). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 88, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, N.E.; Nathan, A.A.; Mathias, N.U.; Nwani, C.D. Genotoxicity and oxidative stress evaluations in juvenile African catfish Clarias gariepinus exposed to NPK fertilizer. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2020, 32, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.-H.; Ko, J.; Lee, E.-H.; Choi, K.-M.; Kim, M.; Yim, U.H.; Lee, J.-S.; Shim, W.J. RNA seq- and DEG-based comparison of developmental toxicity in fish embryos of two species exposed to Iranian heavy crude oil. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 196, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozhan, K.; Zahraeifard, S.; Smith, A.P.; Bargu, S. Induction of reactive oxygen species in marine phytoplankton under crude oil exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18874–18884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xiong, D.; Ren, H.; Chen, H.; Ju, Z. Exposure of adult sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius to stranded heavy fuel oil causes developmental toxicity on larval offspring. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, H.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Ju, Z.; Xiong, D. Sex-specific differences in the toxic effects of heavy fuel oil on sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus intermedius). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureda, A.; Box, A.; Tejada, S.; Blanco, A.; Caixach, J.; Deudero, S. Biochemical responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis as biomarkers of acute environmental pollution caused by the Don Pedro oil spill (Eivissa Island, Spain). Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallès, J.-P. Biology, environmental and nutritional modulation of skin mucus alkaline phosphatase in fish: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.; Bo, J.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, F.; Xie, Q.; Fang, C.; Jiang, Y. Responses of lysosomal biomarkers from the clam Ruditapes philippinarum to water soluble fraction of diesel oil. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2020, 39, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Feng, C.; Xie, L.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Yun, S.; Guo, W.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Meng, R.; et al. Sesamin attenuates histological alterations, oxidative stress and expressions of immune-related genes in liver of zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to fluoride. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).