Integrated Sediment and Mussel Chemical Analysis for Environmental Quality Assessment in Rovinj’s Coastal Waters (Northern Adriatic, Croatia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area, Sediment Collection, and Mussel Watch
2.2. Sediment and Mussel Characterization
2.3. Contaminant Analyses
2.4. Good Environmental Status Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Sediment Properties
3.2. Heavy Metals and Metalloids
| Pb | Zn | As | Cd | Cu | Ni | Cr | Hg | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | M | S | M | S | M | S | M | S | M | S | M | S | M | S | M | |
| S1 | 26 | 0.4 | 47 | 134 | 7.9 | 16 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 25 | 3.3 | 16 | 1.2 | 26 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| S2 | 15 | - | 37 | - | 6.5 | - | 0.1 | - | 17 | - | 18 | - | 16 | - | 0.2 | - |
| S3 | 21 | - | 62 | - | 5.9 | - | 0.1 | - | 15 | - | 30 | - | 39 | - | 0.1 | - |
| S4 | 24 | 0.4 | 68 | 259 | 8.2 | 14 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 16 | 3.5 | 35 | 1.2 | 47 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| S5 | 11 | - | 43 | - | 4.4 | - | 0.1 | - | 13 | - | 12 | - | 19 | - | 0.1 | - |
| Contaminant presence in sediments across the Adriatic Sea 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| R1 | 21–721 | 68–1050 | 7.7–34 | 0.1–3.4 | 25–372 | 71–154 | 63–124 | 0.05–6.9 | ||||||||
| AS | 10–164 | 23–353 | - | 0.08–2.36 | 8–85 | - | - | 0.1–6.2 | ||||||||
| MS | 119 | 387 | - | 0.07 | 79 | 25 | 32 | - | ||||||||
| Sediment quality guidelines 2−5 | ||||||||||||||||
| N1 | 100 | - | 276 | - | 25 | - | 1.2 | - | 45 | - | 37 | - | 90 | - | 0.4 | - |
| C (I) | 30 | - | 150 | - | 20 | - | 0.25 | - | 35 | - | 30 | - | 70 | - | 0.15 | - |
| C (II) | 83 | - | 360 | - | 52 | - | 2.6 | - | 51 | - | 46 | - | 560 | - | 0.63 | - |
| ERL | 46.7 | - | 150 | - | 8.2 | - | 1.2 | - | 34 | - | 20.9 | - | 81 | - | 0.15 | - |
| ERM | 218 | - | 410 | - | 70 | - | 9.6 | - | 270 | - | 51.6 | - | 370 | - | 0.71 | - |
| TEL | 30.24 | - | 124 | - | 7.24 | - | 0.68 | - | 18.7 | - | 15.9 | - | 52.3 | - | 0.13 | - |
| PEL | 112.18 | - | 271 | - | 41.6 | - | 4.21 | - | 108.2 | - | 42.8 | - | 160.4 | - | 0.7 | - |
3.3. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Polychlorinated Biphenyls
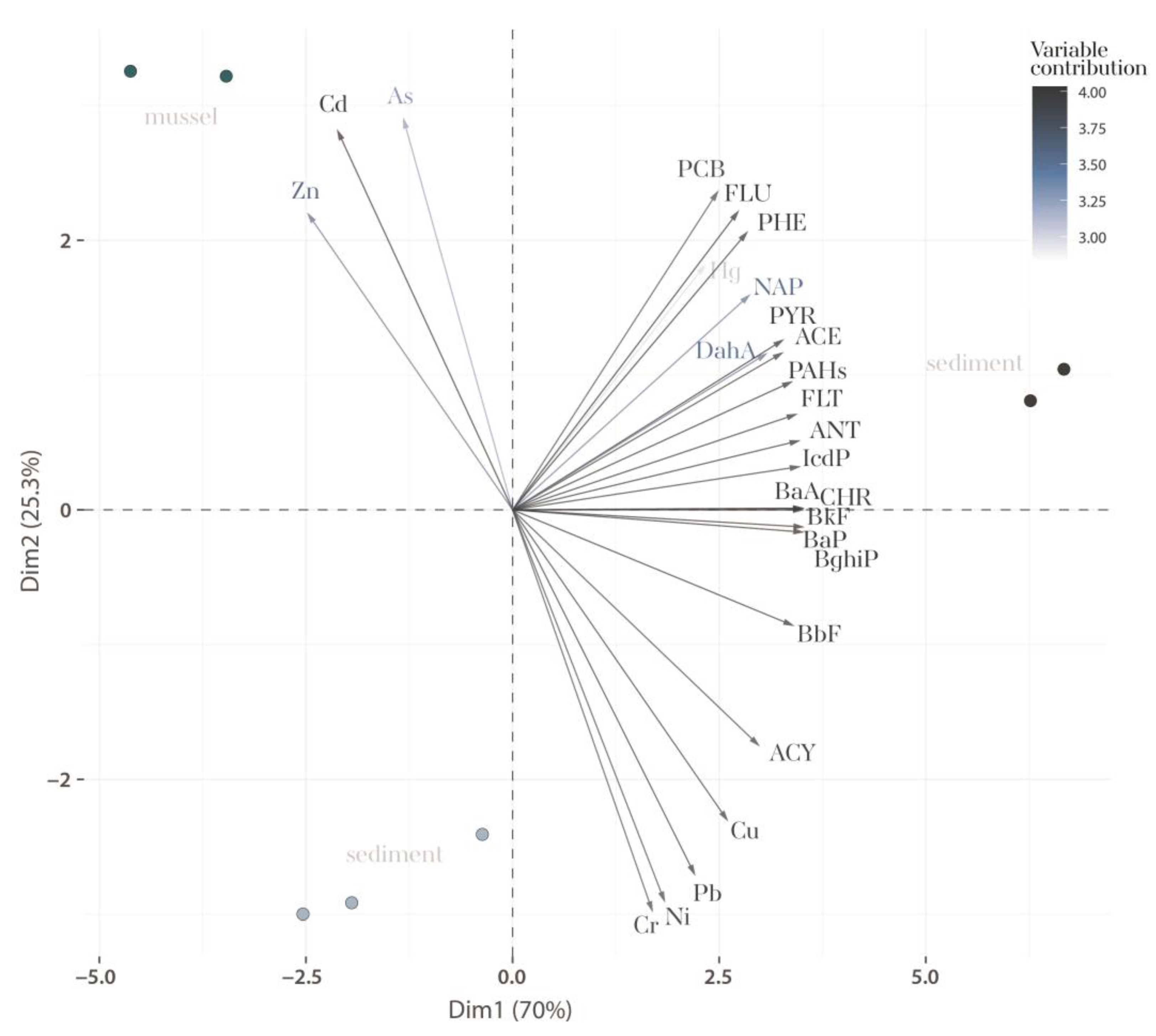
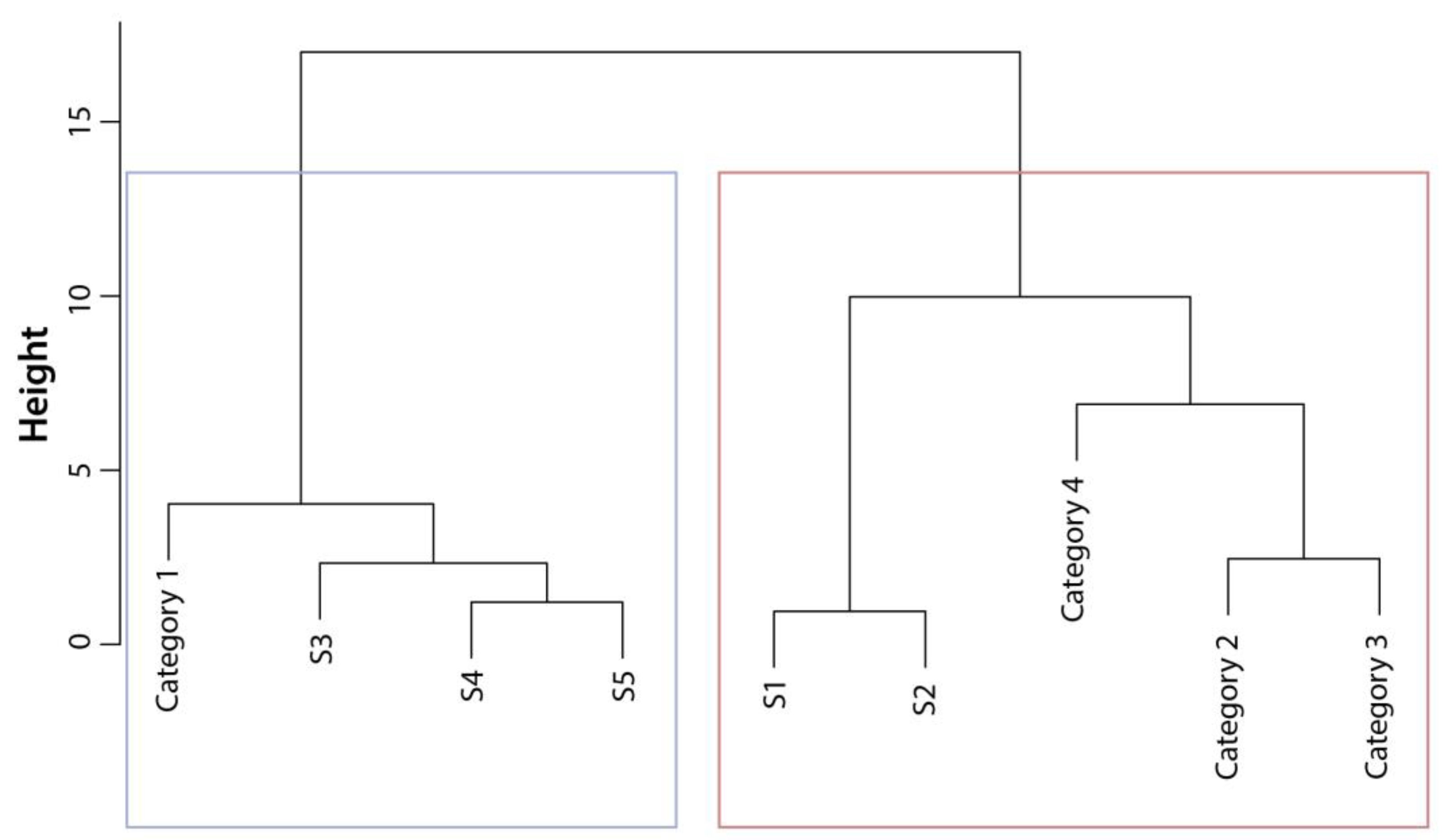
3.4. Contaminant Profiles Across Marine Environments
3.5. Toxic Effect Quotients
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feldstein, T.; Kashman, Y.; Abelson, A.; Fishelson, L.; Mokady, O.; Bresler, V.; Erel, Y. Marine molluscs in environmental monitoring: III. Trace metals and organic pollutants in animal tissue and sediments. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2003, 57, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero, V.; Hanke, G. Chemical Contaminants Entering the Marine Environment from Sea-Based Sources: A Review with a Focus on European Seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenton, T.M.; Held, H.; Kriegler, E.; Hall, J.W.; Lucht, W.; Rahmstorf, S.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Tipping Elements in the Earth’s Climate System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elskus, A.A.; LeBlanc, L.A.; Latimer, J.S.; Page, D.S.; Harding, G.C.H.; Wells, P.G. Monitoring Chemical Contaminants in the Gulf of Maine, Using Sediments and Mussels (Mytilus edulis): An Evaluation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihelčić, G.; Lojen, S.; Dolenec, T.; Kniewald, G. Trace Metals Conservation in Morinje Bay Sediment: Historical Record of Anthropogenic Imissions into a Shallow Adriatic Bay. Croat. Chem. Acta 2006, 79, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Avellan, A.; Duarte, A.; Rocha-Santos, T. Organic Contaminants in Marine Sediments and Seawater: A Review for Drawing Environmental Diagnostics and Searching for Informative Predictors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traven, L. Sources, Trends and Ecotoxicological Risks of PAH Pollution in Surface Sediments from the Northern Adriatic Sea (Croatia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduč, T.; Šlejkovec, Z.; Falnoga, I.; Mori, N.; Budič, B.; Kovačić, I.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Hamer, B. Environmental Status of the NE Adriatic Sea, Istria, Croatia: Insights from Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Condition Indices, Stable Isotopes and Metal(Loid)s. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, E. Marine Mussels: Ecology, Physiology, Genetics and Culture; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricchia, A.M.; Chiavarini, S.; Cremisini, C.; Martini, F.; Morabito, R. PAHs, PCBs, and DDE in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1993, 26, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, N.; Fafanđel, M.; Piškur, V. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Ecotoxicological Characterization of Seawater, Sediment, and Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Gulf of Rijeka, the Adriatic Sea, Croatia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 52, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penezić, A.; Gašparović, B.; Cuculić, V.; Strmečki, S.; Djakovac, T.; Mlakar, M. Dissolved Trace Metals and Organic Matter Distribution in the Northern Adriatic, an Increasingly Oligotrophic Shallow Sea. Water 2022, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchaca, I.; Rodríguez, J.G.; Borja, Á.; Belzunce-Segarra, M.J.; Franco, J.; Garmendia, J.M.; Larreta, J. Determination of Polychlorinated Biphenyl and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Marine Regional Sediment Quality Guidelines within the European Water Framework Directive. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 30, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decision on Adopting the Action Programme of the Marine Environment and Coastal Area Management Strategy, Concerning the Monitoring and Observation System for the Continuous Assessment of the State of the Adriatic Sea. Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/dodatni/434153.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Directive-2008/56-EN—EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/56/oj/eng (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Decision-2017/848-EN—EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dec/2017/848/oj/eng (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Strategija Upravljanja Morskim Okolišem i Obalnim Područjem. Available online: https://mingo.gov.hr/o-ministarstvu-1065/djelokrug/uprava-vodnoga-gospodarstva-i-zastite-mora-2033/strategija-upravljanja-morskim-okolisem-i-obalnim-podrucjem-1441/1441 (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Bakke, T.; Källqvist, T.; Ruus, A.; Breedveld, G.D.; Hylland, K. Development of Sediment Quality Criteria in Norway. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Action Program of the Strategy for the Management of the Marine Environment and Coastal Area: Monitoring and Observation System for the Ongoing Assessment of the State of the Adriatic Sea (2021–2026). Available online: https://mingo.gov.hr/UserDocsImages/Uprava_vodnoga_gospodarstva_i_zast_mora/Strategija_upravljanja_morem/Akcijski%20program%20Sustav%20pra%C4%87enja%202021_2026.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Vilibić, I.; Terzić, E.; Vrdoljak, I.; Dominović Novković, I.; Vodopivec, M.; Ciglenečki, I.; Djakovac, T.; Hamer, B. Extraordinary Mucilage Event in the Northern Adriatic in 2024—A Glimpse into the Future Climate? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2025, 317, 109222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikelj, K.; Juračić, M. Eastern Adriatic Coast (EAC): Geomorphology and Coastal Vulnerability of a Karstic Coast. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikelj, K.; Žigić, V.; Juračić, M. Origin and Distribution of Surface Sediments in the Grgur Channel, Adriatic Sea, Croatia. Geol. Croat. 2009, 69, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikelj, K.; Jakšić, L.; Aščić, Š.; Juračić, M. Characterization of the Fine-Grained Fraction in the Surface Sediment of the Eastern Adriatic Channel Areas. Acta Adriat. 2016, 57, 195–208. [Google Scholar]
- Molina Jack, M.E.; Bakiu, R.; Castelli, A.; Čermelj, B.; Fafanđel, M.; Georgopoulou, C.; Giorgi, G.; Iona, A.; Ivankovic, D.; Kralj, M.; et al. Heavy Metals in the Adriatic-Ionian Seas: A Case Study to Illustrate the Challenges in Data Management When Dealing With Regional Datasets. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 571365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obhođaš, J.; Valković, V. Contamination of the Coastal Sea Sediments by Heavy Metals. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2010, 68, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelikan, J.; Majnarić, N.; Maurić Maljković, M.; Pikelj, K.; Hamer, B. Physico-Chemical and Ecotoxicological Evaluation of Marine Sediments Contamination: A Case Study of Rovinj Coastal Area, NE Adriatic Sea, Croatia. Toxics 2022, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipizer, M.; Berto, D.; Cermelj, B.; Fafandjel, M.; Formalewicz, M.; Hatzianestis, I.; Ilijanić, N.; Kaberi, H.; Kralj, M.; Matijevic, S.; et al. Trace Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Eastern Mediterranean Sediments: Concentration Ranges as a Tool for Quality Control of Large Data Collections. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perić, L.; Fafanđel, M.; Glad, M.; Bihari, N. Heavy Metals Concentration and Metallothionein Content in Resident and Caged Mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis from Rijeka Bay, Croatia. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar]
- Glad, M.; Bihari, N.; Jakšić, Ž.; Fafanđel, M. Comparison between Resident and Caged Mussels: Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Accumulation and Biological Response. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 129, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.E.; Batel, R.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, I.M. Traditional and modern biomedical prospecting: Part I—The history. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2004, 1, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiozzi, D.; Smojver, Ž. Application of multi-criteria analysis of determining sea port development models in the spatial concept of a town, based on the example of the town of Rovinj. Teh. Vjesn. 2020, 27, 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriele, B. Rovigno D’istria. Guida Storica Artistica e Culturale, Italy. 2012. Available online: https://www.istra.hr/pbdownloadf/rovinj_culture_it.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2025).
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. GRADISTAT: A Grain Size Distribution and Statistics Package for the Analysis of Unconsolidated Sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L. The Distinction between Grain Size and Mineral Composition in Sedimentary-Rock Nomenclature. J. Geol. 1954, 62, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privileggio, L.; Balković, I.; Grozić, K.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Jaklin, A.; Suman, D.; Brumnić, L.; Maurić Maljković, M.; Labura, H.; Oštir, S.; et al. Field and Laboratory Observation of Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Predation by Flatworm Stylochus mediterraneus. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 36, 102164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedes, F. Determination of Total Lipid Using Non-Chlorinated Solvents. Analyst 1999, 124, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 14084:2003; Foodstuffs—Determination of Trace Elements—Determination of Lead, Cadmium, Zinc, Copper and Iron by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS) After Microwave Digestion. iTeh, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2003. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/446d0bd2-4c65-4d15-a586-852f4a653f70/en-14084-2003 (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- EN 13804:2013; Foodstuffs—Determination of Elements and Their Chemical Species—General Considerations and Specific Requirements. iTeh, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/d7f910be-61a0-437a-a9b8-739221257c31/en-13804-2013 (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- ISO 8288:1986; Water Quality—Determination of Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, Zinc, Cadmium and Lead—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Methods. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1986.
- ISO 15586:2003; Water Quality—Determination of Trace Elements Using Atomic Absorption Spectrometry with Graphite Furnace. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- EPA Method 3541; Automated Soxhlet Extraction. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-06/documents/epa-3541.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- EPA Method 3603C; Cleanup. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/3600c.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- Alebić-Juretić, A. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediments from the Rijeka Bay area, Northern Adriatic, Croatia, 1998–2006. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA Method 1668C; Chlorinated Biphenyl Congeners in Water, Soil, Sediment, Biosolids, and Tissue by HRGC/HRMS. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/method_1668c_2010.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- Borja, A.; Elliott, M.; Andersen, J.H.; Cardoso, A.C.; Carstensen, J.; Ferreira, J.G.; Heiskanen, A.-S.; Marques, J.C.; Neto, J.M.; Teixeira, H.; et al. Good Environmental Status of Marine Ecosystems: What Is It and How Do We Know When We Have Attained It? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; MacDonald, D.D. Recommended Uses of Empirically Derived, Sediment Quality Guidelines for Marine and Estuarine Ecosystems. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 1998, 4, 1019–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorleon, G.; Rigaud, S.; Techer, I. Sediment Quality and Ecological Risk Assessment in Mediterranean Harbors of Occitanie, France: Implications for Sustainable Dredged Material Management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 217, 118097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive-2000/60-EN—Water Framework Directive-EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2000/60/oj/eng (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Directive-2014/101-EN—EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2014/101/oj/eng (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Burton, G., Jr. Allen Sediment Quality Criteria in Use around the World. Limnology 2002, 3, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of Adverse Biological Effects within Ranges of Chemical Concentrations in Marine and Estuarine Sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.D.; Carr, R.S.; Calder, F.D.; Long, E.R.; Ingersoll, C.G. Development and Evaluation of Sediment Quality Guidelines for Florida Coastal Waters. Ecotoxicology 1996, 5, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and Evaluation of Consensus-Based Sediment Quality Guidelines for Freshwater Ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCready, S.; Birch, G.F.; Long, E.R.; Spyrakis, G.; Greely, C.R. An evaluation of Australian sediment quality guidelines. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 50, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A. Practical Guide to Principal Component Methods in R: PCA, M (CA), FAMD, MFA, HCPC, Factoextra. Available online: https://www.datanovia.com/en/wp-content/uploads/dn-tutorials/book-preview/principal-component-methods-in-r-preview.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2025).
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vdović, N.; Juračić, M. Sedimentological and Surface Characteristics of the Northern and Central Adriatic Sediments. Geol. Croat. 1993, 46, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Najdek, M.; Travizzi, A.; Bogner, D.; Blazina, M. Low Impact of Marine Fish Farming on Sediment and Meiofauna in Limski Channel (Northern Adriatic, Croatia). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2007, 16, 784–791. [Google Scholar]
- Amorosi, A.; Sammartino, I.; Dinelli, E.; Campo, B.; Guercia, T.; Trincardi, F.; Pellegrini, C. Provenance and Sediment Dispersal in the Po-Adriatic Source-to-Sink System Unraveled by Bulk-Sediment Geochemistry and Its Linkage to Catchment Geology. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 234, 104202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, E.D. The Mussel Watch—A First Step in Global Marine Monitoring. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1975, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, I.; Boutiba, Z.; Merabet, A.; Chèvre, N. Integrated Use of Biomarkers and Condition Indices in Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) for Monitoring Pollution and Development of Biomarker Index to Assess the Potential Toxic of Coastal Sites. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakšić, Ž.; Batel, R.; Bihari, N.; Mičić, M.; Zahn, R.K. Adriatic Coast as a Microcosm for Global Genotoxic Marine Contamination––A Long-Term Field Study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrov, N.; Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Hlača, B.; Barišić, D. A Recent History of Metal Accumulation in the Sediments of Rijeka Harbor, Adriatic Sea, Croatia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combi, T.; Pintado-Herrera, M.G.; Lara-Martin, P.A.; Miserocchi, S.; Langone, L.; Guerra, R. Distribution and Fate of Legacy and Emerging Contaminants along the Adriatic Sea: A Comparative Study. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harasim, P.; Filipek, T. Nickel in the environment. J. Elem. 2015, 20, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Siepak, M. Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of Reservoirs in the Lowland Area of Western Poland: Concentrations, Distribution, Sources and Ecological Risk. Water 2019, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmore, G.; Wang, W. Comparison of Metal Accumulation in Mussels at Different Local and Global Scales. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudammoussi, M.E.; Hammoudani, Y.E.; Haboubi, K.; Bourjila, A.; Achoukhi, I.; Bouhaj, S.; El Kasmi, A.; Farissi, H.E.; Dimane, F. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Sediments and Mussels along the Moroccan Mediterranean Coast: A Spatial Assessment. Environ. Chall. 2025, 20, 101195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attig, H.; Dagnino, A.; Negri, A.; Jebali, J.; Boussetta, H.; Viarengo, A.; Dondero, F.; Banni, M. Uptake and Biochemical Responses of Mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis Exposed to Sublethal Nickel Concentrations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Cukrov, N. A Critical Evaluation of Using Bulk Sediment Instead of Fine Fraction in Environmental Marine Studies, Investigated on Example of Rijeka Harbor, Croatia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apitz, S.E.; Barbanti, A.; Bocci, M.; Carlin, A.; Montobbio, L.; Bernstein, A.G. The Sediments of the Venice Lagoon (Italy) Evaluated in a Screening Risk Assessment Approach: Part I—Application of International Sediment Quality Guidelines. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2007, 3, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besada, V.; Fumega, J.; Vaamonde, A. Temporal trends of Cd, Cu, Hg, Pb and Zn in mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from the Spanish North-atlantic coast 1991–1999. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 288, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adami, G.; Barbieri, P.; Fabiani, M.; Piselli, S.; Predonzani, S.; Reisenhofer, E. Levels of cadmium and zinc in hepatopancreas of reared Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Gulf of Trieste (Italy). Chemosphere 2002, 48, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Barbosa, A.; Gutiérrez-Galindo, E.A.; Flores-Muñoz, G. Mytilus californianus as an indicator of heavy metals on the northwest coast of Baja California, Mexico. Mar. Environ. Res. 2000, 49, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popowich, A.; Zhang, Q.; Le, X.C. Arsenobetaine: The ongoing mystery. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notar, M.; Leskovšek, H.; Faganeli, J. Composition, Distribution and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments of the Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajt, O. Sedimentary Record of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea)–Distribution, Origin and Temporal Trends. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 946618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavodnik, D.; Vidakovic, J.; Amoureux, L. Contribution to sediment macrofauna in the area of Rovinj (North Adriatic Sea). Cah. De Biol. Mar. 1985, 26, 431–444. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, D.; Shiu, W.Y.; Lee, S.C. Handbook of Physical-Chemical Properties and Environmental Fate for Organic Chemicals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Solé, M.; Freitas, R.; Viñas, L.; Rivera-Ingraham, G.A. Biomarker considerations in monitoring petrogenic pollution using the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31854–31862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Filho, B.M.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A. Environmental monitoring approaches for the detection of organic contaminants in marine environments: A critical review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 33, e00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, E.M.A.; Lai, R.W.S.; White, C.A.; Piarulli, S.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Airoldi, L.; O’Brien, A. Marine pollution-emerging issues and challenges. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 918984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, M.; Ragone, R.; Dell’Anna, M.M.; Romanazzi, G.; Damiani, L.; Mastrorilli, P. Improved identification of pollution source attribution by using PAH ratios combined with multivariate statistics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Parliament and Council. Directive 2013/39/EU of 12 August 2013 Amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, L226, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- De Lazzari, A.; Rampazzo, G.; Pavoni, B. Geochemistry of Sediments in the Northern and Central Adriatic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 59, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picer, M.; Picer, N. Long-Term Trends of DDTs and PCBs in Sediment Samples Collected from the Eastern Adriatic Coastal Waters. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991, 47, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, R.; Dachs, J. Polychlorinated biphenyls in the global ocean. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Mamindy-Pajany, Y.; Hamer, B.; Roméo, M.; Géret, F.; Galgani, F.; Durmiši, E.; Hurel, C.; Marmier, N. The Toxicity of Composted Sediments from Mediterranean Ports Evaluated by Several Bioassays. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

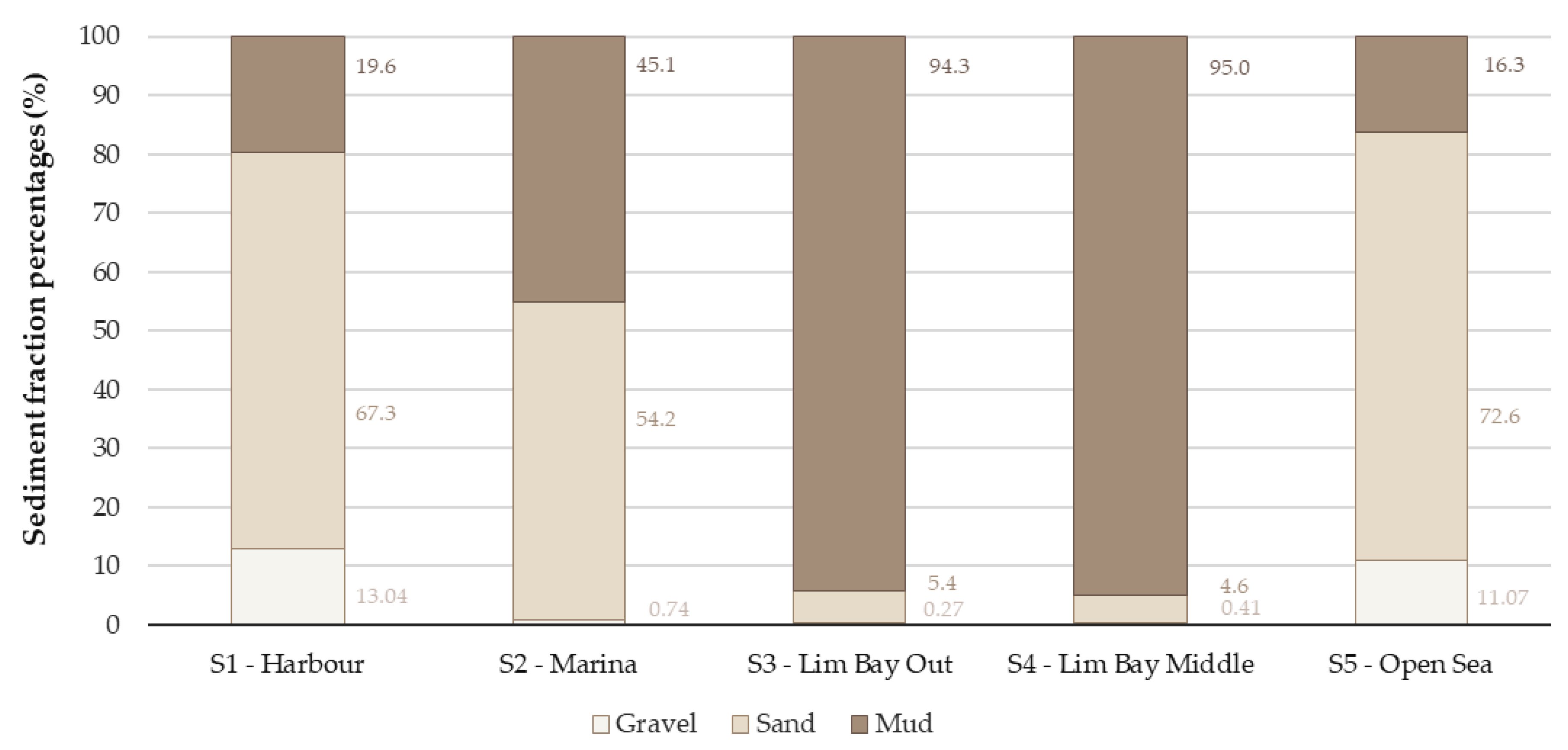
| Harbor (S1) | Marina (S2) | Lim Bay Out (S3) | Lim Bay Middle (S4) | Open Sea (S5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment class 1 | Slightly gravelly muddy sand | Slightly gravelly muddy sand | Slightly sandy mud | Slightly sandy mud | Gravelly muddy sand |
| Water content (%) | 28.03 | 22.38 | 44.24 | 47.90 | 16.91 |
| TOM (%) | 1.88 | 1.20 | 2.77 | 3.11 | 0.98 |
| Location | Mortality (%) | Meat Yield (%) | Lipid Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lim Bay | <2.00 | 18.94 ± 2.60 | 3.69 |
| Harbor | 26.67 | 13.08 ± 1.74 | 5.50 |
| PAHs (µg/kg DW) | Sampling Sites | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | ||||||
| N° Rings | Harbor | Marina | Lim Bay Out | Lim Bay Middle | Open Sea | |||||
| S | M | S | M | |||||||
| Naphtalene | 2 | 2.19 b,e,g,i | <1 | 1.36 a,e,g,i | <1 a,e,g,i | <1 a,e,g,i | <1 | <1 a,e,g,i | ||
| Acenaphtylene | 3 | <5 b,e,g,i | <1 | <5 b,e,g,i | <5 b,e,g,i | <5 b,e,g,i | <1 | <5 b,e,g,i | ||
| Acenaphtene | 3 | 22.30 b,f,h,j | 0.78 | 24.40 b,f,h,j | <1 a,e,g,i | <1 a,e,g,i | 0.76 | <1 a,e,g,i | ||
| Fluorene | 3 | 26.20 b,f,h,j | 3.78 | 28.30 b,f,h,j | 1.20 a,e,g,i | <1 a,e,g,i | 2.97 | <1 a,e,g,i | ||
| Phenanthrene (Phe) | 3 | 346.00 b,f,h,j | 31.00 | 424.00 b,f,h,j | 12.90 b,e,g,i | 4.64 a,e,g,i | 28.30 | 3.55 a,e,g,i | ||
| Anthracene (Ant) | 3 | 71.90 c,e,g,j | 0.57 | 87.80 c,f,h,j | 1.99 b,e,gi | <1 a,e,gi | 0.41 | <1 a,e,gi | ||
| Fluoranthene (Flt) | 4 | 609.00 c,f,h,j | 8.83 | 759.00 c,f,h,j | 18.60 b,e,g,i | 7.77 a,e,g,i | 5.36 | 3.79 a,e,g,i | ||
| Pyrene (Pyr) | 4 | 570.00 c,f,g,j | 18.40 | 731.00 c,f,h,j | 16.80 b,e,g,i | 5.15 a,e,g,i | 8.93 | 3.73 a,e,g,i | ||
| Chrysene | 4 | 201.00 b,e,g,j | <1 | 259.00 b,e,g,j | 6.52 b,e,g,i | 2.37 a,e,g,i | <1 | 1.24 a,e,g,i | ||
| Benzo(a)anthracene | 4 | 275.00 d,f,h,j | <1 | 304.00 d,f,h,j | 7.00 b,e,g,i | 1.98 a,e,g,i | <1 | 1.59 a,e,g,i | ||
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 5 | 156.00 c,e | <1 | 278.00 c,e | 18.30 a,e | 6.03 a,e | <1 | 5.22 a,e | ||
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene | 5 | 167.00 b,e | <1 | 167.00 b,e | 5.63 b,e | 2.40 b,e | <1 | 1.19 b,e | ||
| Benzo(a)pyrene | 5 | 343.00 b,e,g,j | <1 | 324.00 b,e,g,j | 7.55 b,e,g,i | 2.72 a,e,g,i | <1 | 2.17 a,e,g,i | ||
| Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | 5 | 16.50 b,e,g,j | <1 | 3.24 a,e,g,i | <1 a,e,g,i | <1 a,e,g,i | <1 | <1 a,e,g,i | ||
| Benzo(g,h,i)perylene | 6 | 240.00 d,e | <1 | 169.00 d,e | 6.60 a,e | 2.66 a,e | <1 | 2.03 a,e | ||
| Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | 6 | 133.00 d,e | <1 | 89.90 d,e | 3.93 a,e | 1.80 a,e | <1 | <1 a,e | ||
| ∑PAHs (µg/kg DW) | 3179.00 c,g,j | 63.40 | 3641.00 c,g,j | 107.00 a,g,i | 37.50 a,g,i | 46.70 | 24.50 a,g,i | |||
| Ant/(Ant + Phe) | 3 | 0.17 | - | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.10 | - | 0.12 | ||
| Phe/Ant | 3 | 4.81 | - | 4.83 | 6.48 | 9.28 | - | 7.10 | ||
| Flt/(Flt + Pyr) | 4 | 0.52 | - | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.60 | - | 0.50 | ||
| Flt/Pyr | 4 | 1.07 | - | 1.04 | 1.11 | 1.51 | - | 1.02 | ||
| Sediment Quality Guidelines | National SQG | French SQG | NOAA/EPA | Consensus SQG | ||||||
| C I a | C II b | C III c | C IV d | N1 e | N2 f | ERL g | ERM h | TEL i | PEL j | |
| Naphtalene | <2 | 2–290 | 290–1000 | 1000–2000 | 160 | 1130 | 160 | 2100 | 34.57 | 390.64 |
| Acenaphtylene | <1.6 | 1.6–33 | 33–85 | 85–850 | 40 | 340 | 44 | 640 | 5.87 | 127.87 |
| Acenaphtene | <4.8 | 2.4–160 | 160–360 | 360–3600 | 15 | 260 | 16 | 500 | 6.71 | 88.9 |
| Fluorene | <6.8 | 6.8–260 | 260–510 | 510–5100 | 20 | 280 | 19 | 540 | 21.17 | 144.35 |
| Phenanthrene (Phe) | <6.8 | 6.8–500 | 500–1200 | 1200–2300 | 240 | 870 | 240 | 1500 | 86.68 | 543.53 |
| Anthracene (Ant) | <1.2 | 1.2–31 | 31–100 | 100–1000 | 85 | 590 | 85.3 | 1100 | 46.85 | 245 |
| Fluoranthene (Flt) | <8 | 8–170 | 170–1300 | 1300–2600 | 600 | 2850 | 600 | 5100 | 112.82 | 1493.54 |
| Pyrene (Pyr) | <5.2 | 5.2–280 | 280–2800 | 2800–5600 | 500 | 1500 | 665 | 2600 | 152.66 | 1397.6 |
| Chrysene | <4.4 | 4.4–280 | 280–280 | 280–560 | 380 | 1590 | 384 | 2800 | 107.77 | 845.98 |
| Benzo(a)anthracene | <3.6 | 3.6–60 | 60–90 | 90–900 | 260 | 930 | 251 | 1600 | 74.83 | 692.53 |
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 46 | 46–240 | 240–490 | 490–4900 | 400 | 900 | - | - | - | - |
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene | - | <210 | 210–480 | 480–4800 | 200 | 400 | - | - | - | - |
| Benzo(a)pyrene | <6 | 6–420 | 420–830 | 830–4200 | 430 | 1015 | 430 | 1600 | 88.81 | 763.22 |
| Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | <12 | 12–590 | 590–1200 | 1200–12,000 | 60 | 160 | 63.4 | 260 | 6.22 | 134.61 |
| Benzo(g,h,i)perylene | <18 | 18–21 | 21–31 | 31–310 | 1700 | 5650 | - | - | - | - |
| Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | <20 | 20–47 | 47–70 | 70–700 | 1700 | 5650 | - | - | - | - |
| ∑PAHs (µg/kg DW) | <300 | 300–2000 | 2000–6000 | 6000–20,000 | 300,000 | 2,000,000 | 4022 | 44,792 | 1684.1 | 16,770.4 |
| Total PCBs (mg/kg DW) in Sediment Samples 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Harbor (S1) | 0.3283 | |
| Marina (S2) | 0.8903 | |
| Lim Bay Out (S3) | 0.0257 | |
| Lim Bay Middle (S4) | <0.01 | |
| Open Sea (S5) | <0.01 | |
| SQGs (mg/kg DW) 2 | ||
| Category (I) | 0.005 | |
| Category (II) | 1.0 | |
| ERM | 0.400 | |
| PEC | 0.676 | |
| ERL | 0.050 | |
| Individual congeners (mg/kg DW) in mussel samples 3 | ||
| Harbor (S1) | Lim Bay (S4) | |
| PCB 53 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 52 | 0.059 | 0.038 |
| PCB 101 | 0.007 | 0.003 |
| PCB 81 | 0.013 | 0.007 |
| PCB 77 | 0.004 | <0.001 |
| PCB 123 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 118 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 114 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 153 | 0.007 | 0.004 |
| PCB 105 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 138 | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| PCB 126 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 167 | <0.002 | <0.002 |
| PCB 156 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 157 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 180 | <0.002 | <0.002 |
| PCB 169 | <0.002 | <0.002 |
| PCB 170 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 189 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| PCB 194 | <0.002 | <0.002 |
| Total PCBs | 0.099 | 0.054 |
| QPECm 1 | normQPECm 2 | P 1 | P 2 | Interpretation of Both QPECm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harbor (S1) | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.34 | 0.25 | Moderate probability of toxic effects |
| Marina (S2) | 0.56 | 0.44 | 0.84 | 0.82 | High probability of toxic effects |
| Lim Bay Out (S3) | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.11 | Low probability |
| Lim Bay Middle (S4) | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.10 | Low probability |
| Open Sea (S5) | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.12 | Low probability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelikan, J.; Grozić, K.; Privileggio, L.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Smodlaka Tanković, M.; Pikelj, K.; Glad, M.; Hamer, B. Integrated Sediment and Mussel Chemical Analysis for Environmental Quality Assessment in Rovinj’s Coastal Waters (Northern Adriatic, Croatia). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112212
Pelikan J, Grozić K, Privileggio L, Pavičić-Hamer D, Smodlaka Tanković M, Pikelj K, Glad M, Hamer B. Integrated Sediment and Mussel Chemical Analysis for Environmental Quality Assessment in Rovinj’s Coastal Waters (Northern Adriatic, Croatia). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112212
Chicago/Turabian StylePelikan, Jadranka, Kristina Grozić, Luca Privileggio, Dijana Pavičić-Hamer, Mirta Smodlaka Tanković, Kristina Pikelj, Marin Glad, and Bojan Hamer. 2025. "Integrated Sediment and Mussel Chemical Analysis for Environmental Quality Assessment in Rovinj’s Coastal Waters (Northern Adriatic, Croatia)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112212
APA StylePelikan, J., Grozić, K., Privileggio, L., Pavičić-Hamer, D., Smodlaka Tanković, M., Pikelj, K., Glad, M., & Hamer, B. (2025). Integrated Sediment and Mussel Chemical Analysis for Environmental Quality Assessment in Rovinj’s Coastal Waters (Northern Adriatic, Croatia). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112212






