Vulnerability of Black Sea Mesozooplankton to Anthropogenic and Climate Forcing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Design
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hydrographic and Nutrient Conditions
3.2. Mesozooplankton Community and Spatial–Seasonal Patterns
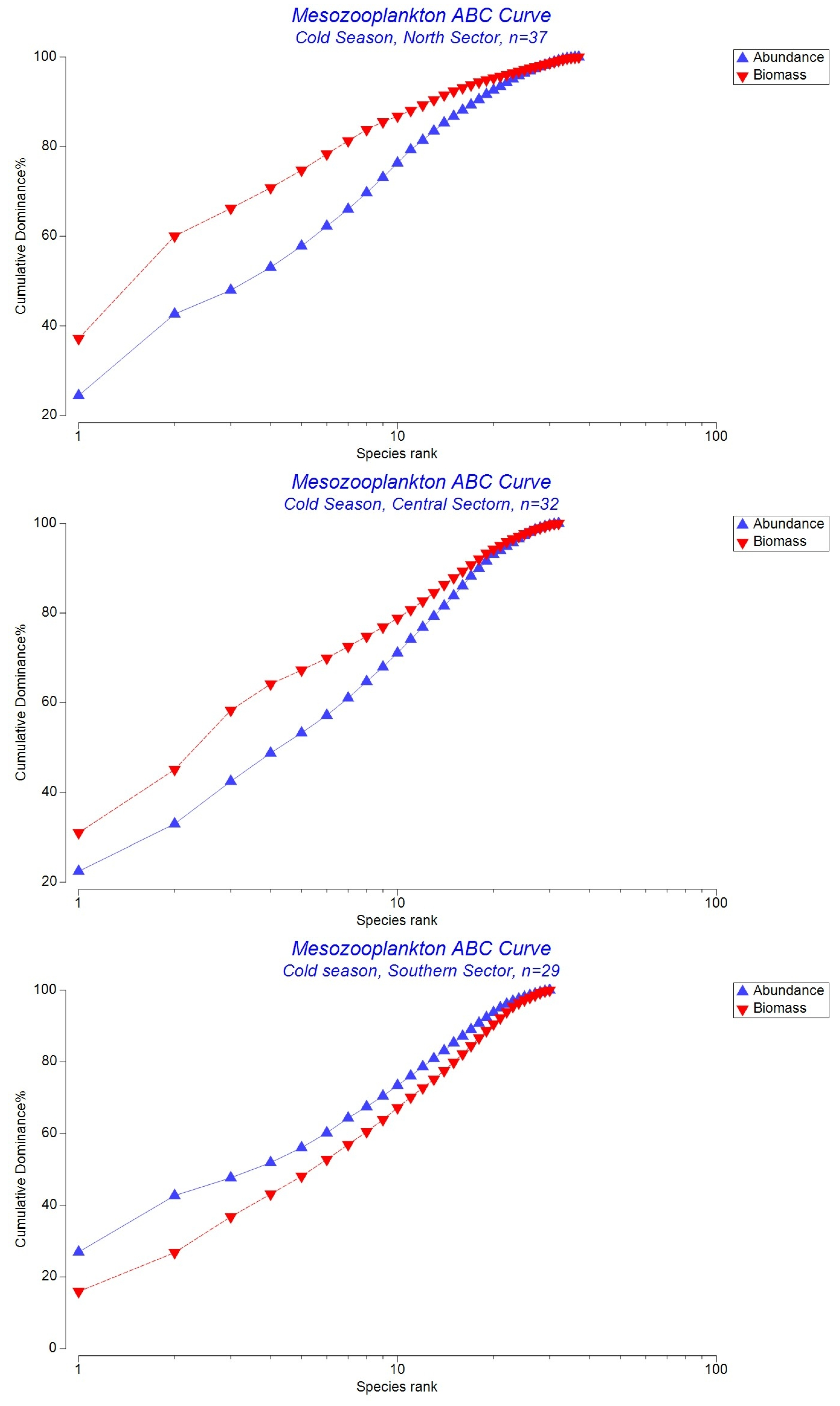
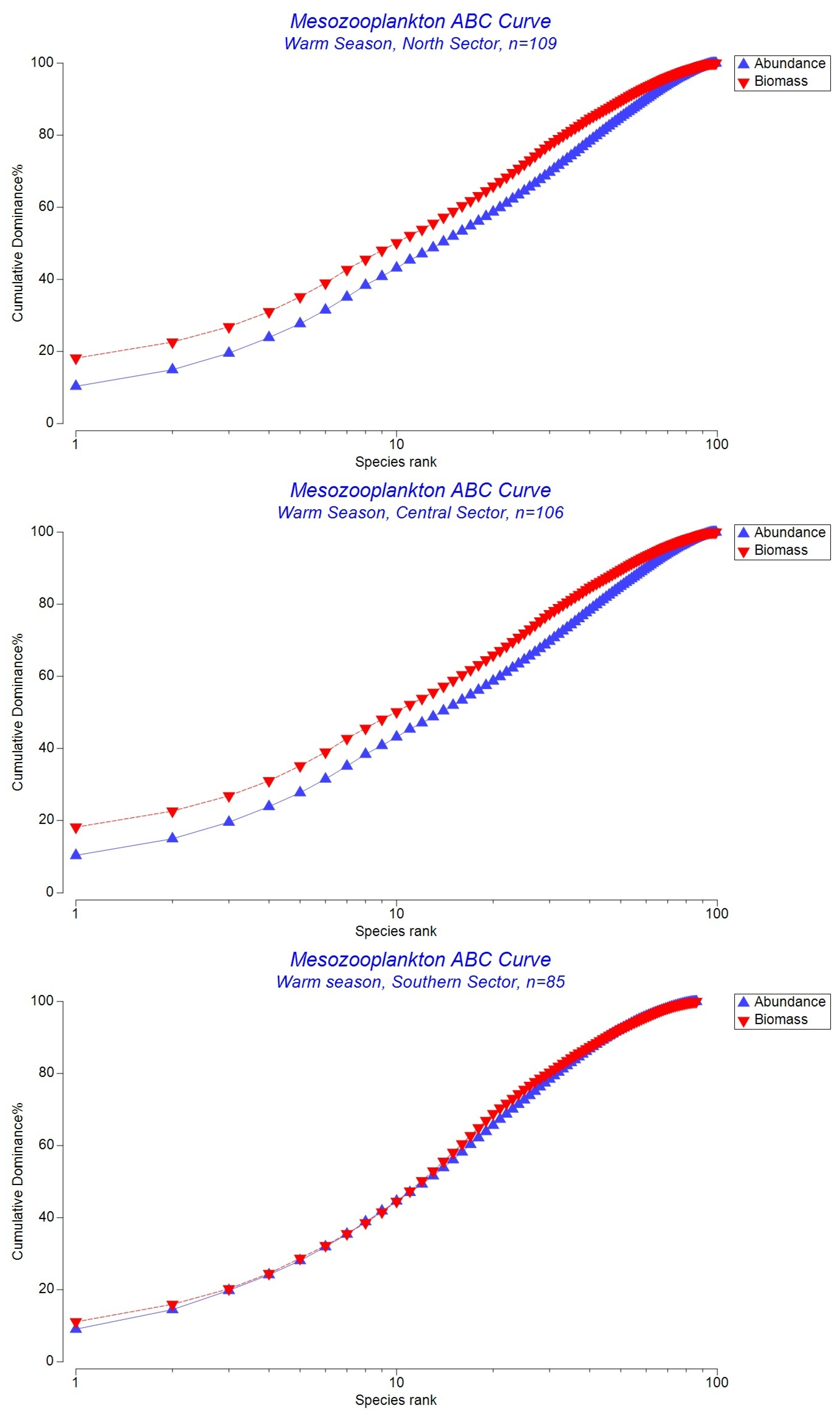
3.3. Abundance-Biomass Comparison (ABC) Curves
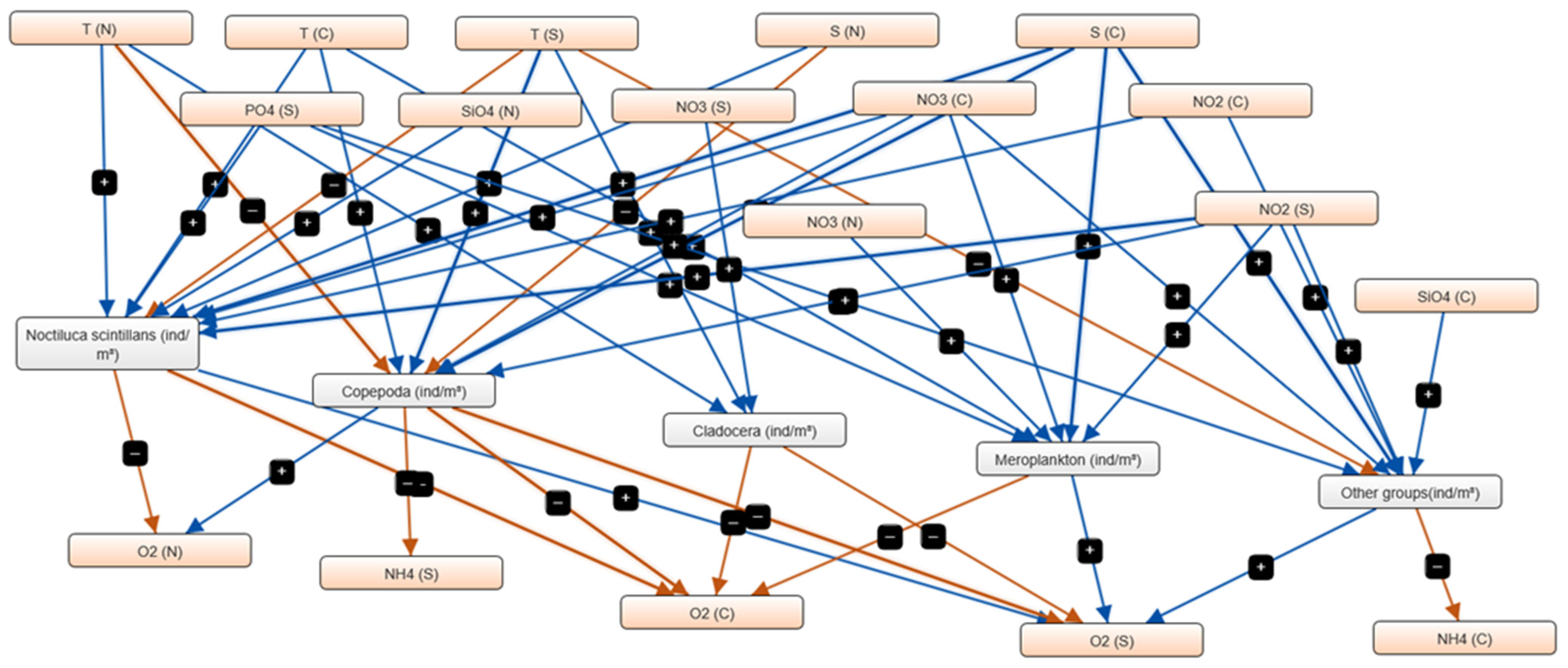
3.4. Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping (FCM) of Mesozooplankton–Environment Interactions
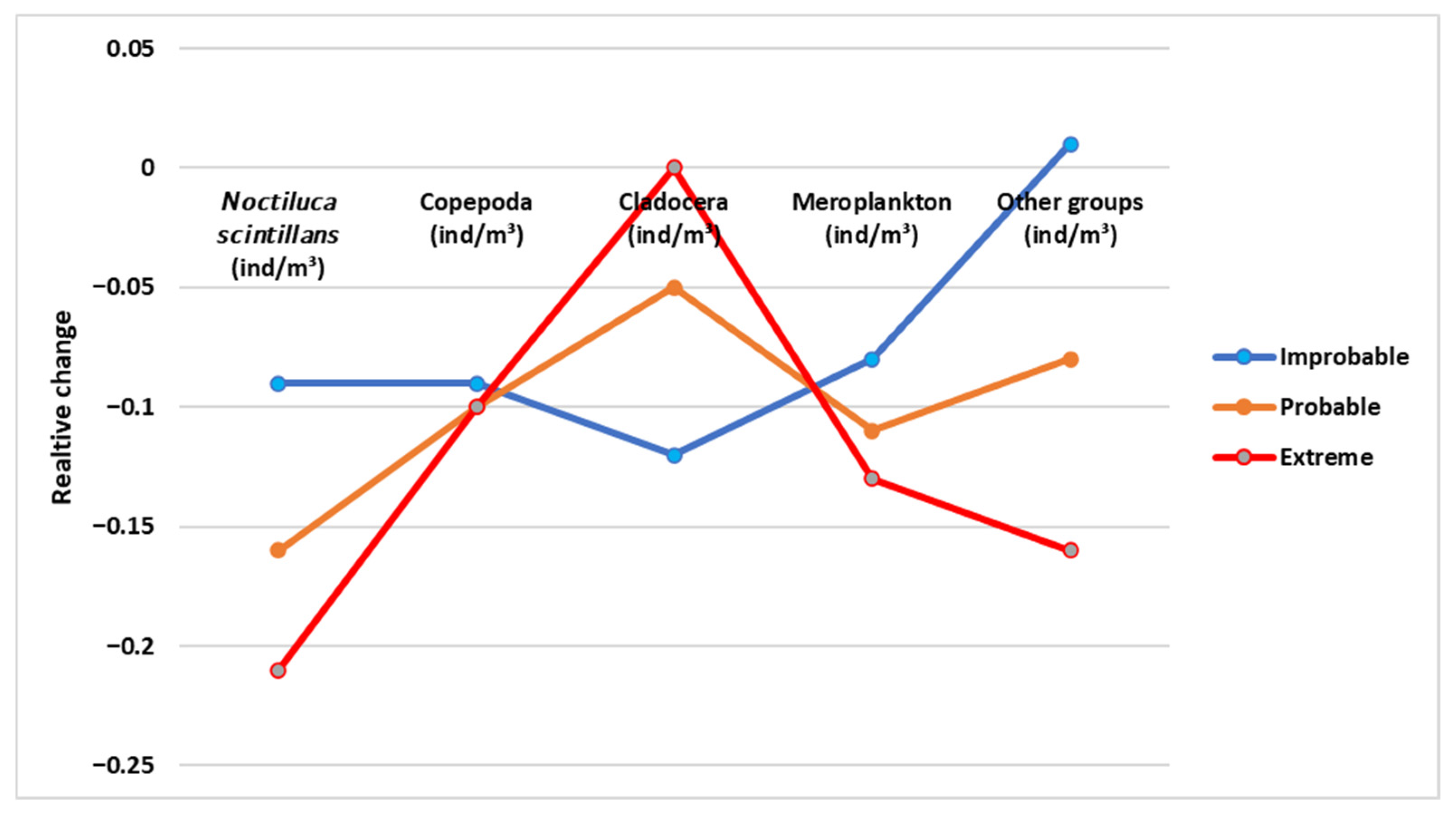
3.5. Climate Change Scenario Simulations
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial–Seasonal Differentiation of Mesozooplankton Communities
4.2. Community Disturbance and Abundance–Biomass (ABC) Patterns
4.3. Environmental Drivers and Network Connectivity
4.4. Climate Change Scenarios and System Sensitivity
4.5. Body Size as an Indicator of Environmental and Ecosystem Change
4.6. Implications for Ecosystem-Based Management and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Abundance–Biomass Comparison |
| ANOSIM | Analysis of similarity |
| FCM | Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping |
| RDA | Redundancy Analysis |
| MSFD | Marine Strategy Framework Directive |
| N | North |
| C | Central |
| S | South |
| PRIMER | Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| GES | Good Environmental Status |
| K- | K-selected species |
References
- Harris, R.; Wiebe, P.; Lenz, J.; Skjoldal, H.R.; Huntley, M. ICES Zooplankton Methodology Manual; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lomartire, S.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. The Key Role of Zooplankton in Ecosystem Services: A Perspective of Interaction between Zooplankton and Fish Recruitment. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J. In Hot Water: Zooplankton and Climate Change. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchman, E.; Ohman, M.D.; Kiørboe, T. Trait-Based Approaches to Zooplankton Communities. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, G.; Richardson, A.; Robinson, C. Climate Change and Marine Plankton. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisinicu, E.; Lazǎr, L. Assessing the Black Sea Mesozooplankton Community Following the Nova Kakhovka Dam Breach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisinicu, E.; Harcota, G.E. Baseline Assessment of Black Sea Food Web Integrity Using a Zooplankton-Based Approach Under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bișinicu, E.; Lazăr, L.; Timofte, F. Dynamics of Zooplankton along the Romanian Black Sea Coastline: Temporal Variation, Community Structure, and Environmental Drivers. Diversity 2023, 15, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisinicu, E.; Lazar, L. Exploring Mesozooplankton Insights by Assessing the Ecological Status of Black Sea Waters Under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Oceans 2024, 5, 923–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, Y. An Introduction to the Black Sea Ecology; Smil Edition and Publishing Agency: Odessa, Ukraine, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitsev, Y.P.; Alexandrov, B.G.; Berlinsky, N.A.; Zenetos, A. Seas around Europe: The Black Sea: An Oxygen-Poor Sea. In Europe’s Biodiversity: Biogeographical Regions and Seas; European Environment Agency (EEA): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, L.; Boicenco, L.; Moncheva, S. Impact of the Rivers on the Black Sea Ecosystem; Lazăr, L., Boicenco, L., Moncheva, S., Eds.; CD Press: Constanța, Romania, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Coatu, V.; Ţigănuş, D.; Oros, A.; Lazăr, L. Analysis of Hazardous Substance Contamination of the Marine Ecosystem in the Romanian Black Sea Coast, Part of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (2008/56/EEC) Implementation. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2013, 43, 174–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ristea, E.; Pârvulescu, O.C.; Lavric, V.; Oros, A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Seawater and Sediments Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast: Spatial Distribution and Environmental Implications. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, A.; Coatu, V.; Damir, N.; Danilov, D.; Ristea, E. Recent Findings on the Pollution Levels in the Romanian Black Sea Ecosystem: Implications for Achieving Good Environmental Status (GES) Under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (Directive 2008/56/EC). Sustainability 2024, 16, 9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cociasu, A.; Varga, L.; Lazar, L.; Vasiliu, D. Recent Data Concerning the Evolution of the Eutrophication Level Indicators in Romanian Seawater. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2009, 10, 701–730. [Google Scholar]
- Ristea, E.; Bisinicu, E.; Lavric, V.; Parvulescu, O.C.; Lazar, L. A Long-Term Perspective of Seasonal Shifts in Nutrient Dynamics and Eutrophication in the Romanian Black Sea Coast. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cîndescu, A.-C.; Petrișoaia, S.; Marin, D.; Buga, L.; Sirbu, G.; Spinu, A. The Variability of the Beach Morphology and the Evolution of the Shoreline in the Strongly Anthropized Sector of Eforie North, the Romanian Coast of the Black Sea. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2024, 53, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cîndescu, A.-C.; Petrișoaia, S.; Buga, L.; Spînu, A. Morphological Dynamics Of An Engineered Coastline: A Case Study From Constanța, Black Sea Coast Of Romania. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2025, 55, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespremeanu, E.; Golumbeanu, M. The Black Sea; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vereshchaka, A. Navigating the Zooplankton Realm: Oceans of Diversity Beneath the Sea Surface. Diversity 2024, 16, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bișinicu, E.; Boicenco, L.; Pantea, E.; Timofte, F.; Lazăr, L.; Vlas, O. Qualitative Model of the Causal Interactions between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, and Environmental Factors in the Romanian Black Sea. Phycology 2024, 4, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L.; Boicenco, L.; Pantea, E.; Timofte, F.; Vlas, O.; Bișinicu, E. Modeling Dynamic Processes in the Black Sea Pelagic Habitat—Causal Connections between Abiotic and Biotic Factors in Two Climate Change Scenarios. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özesmi, U.; Özesmi, S.L. Ecological Models Based on People’s Knowledge: A Multi-Step Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping Approach. Ecol. Model. 2004, 176, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anninsky, B.E.; Finenko, G.A.; Kideys, A.E.; Datsyk, N.A. Environmental Control on Macro- and Mesozooplankton Biomass off Sevastopol Bay: A 20-Year Analysis. Mar. Env. Res. 2025, 211, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazăr, L. (Ed.) ANEMONE Deliverable 2.1. Anthropogenic Pressures and Impacts on the Black Sea Coastal Ecosystem; CD Press: Constanța, Romania, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, L.; Spanu, A.; Boicenco, L.; Oros, A.; Damir, N.; Bisinicu, E.; Abaza, V.; Filimon, A.; Harcota, G.; Marin, O.; et al. Methodology for Prioritizing Marine Environmental Pressures under Various Management Scenarios in the Black Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1388877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshenko, E.; Panasenkova, I.; Osadchiev, A.; Belyakova, P.; Fomin, V. Synoptic and Seasonal Variability of Small River Plumes in the Northeastern Part of the Black Sea. Water 2023, 15, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, M.; Alvera-Azcaráte, A.; Buga, L.; Capet, A.; Constantin, S.; D’ortenzio, F.; Doxaran, D.; Faugeras, Y.; Garcia-Espriu, A.; Golumbeanu, M.; et al. Monitoring Black Sea Environmental Changes from Space: New Products for Altimetry, Ocean Colour and Salinity. Potentialities and Requirements for a Dedicated in-Situ Observing System. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 998970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Ibáñez, C.; Lazar, L.; Raimbault, P.; Giani, M. Flow Regime and Nutrient-Loading Trends from the Largest South European Watersheds: Implications for the Productivity of Mediterranean and Black Sea’s Coastal Areas. Water 2019, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisinicu, E.; Harcota, G.E.; Lazar, L. Interactions between Environmental Factors and the Mesozooplankton Community from the Romanian Black Sea Waters. Turk. J. Zool. 2023, 47, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, B.; Arashkevich, E.; Gubanova, A.; Korshenko, A. Manual for Mesozooplankton Sampling and Analysis in the Black Sea Monitoring; Black Sea Commission: Istanbul, Turkey, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Petipa, T.S. On the Mean Weight of the Principle Forms of Zooplankton in the Black Sea. Sevast. Biol. Stn. 1957, 9, 39–57. [Google Scholar]
- Shiganova, T.A.; Kazmin, A.S. Variability of Mesozooplankton, Abiotic Factors and Ecological Status of Marine Environment in the North-Eastern Part of the Black Sea. Mar. Env. Res. 2024, 202, 106805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. Methods of Seawater Analysis, 3rd ed.; Grasshoff, K., Kremling, K., Ehrhardt, M., Eds.; Willey-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mullin, J.B.; Riley, J.P. The Spectrophotometric Determination of Nitrate in Natural Waters, with Particular Reference to Sea-Water. Anal. Chim. Acta 1955, 12, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIBCO Software, Inc. TIBCO Statistica, Version 14.0.1.25; TIBCO Software, Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2023.
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis, 3rd ed.; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Warwick, R.M.; Clarke, K.R. Relearning the ABC: Taxonomic changes and abundance/biomass relationships in disturbed benthic communities. Mar. Biol. 1994, 118, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Meng, W.; Liu, L.; Lin, K. Evaluation of the Ecological Status with Benthic Indices in the Coastal System: The Case of Bohai Bay (China). Front. Env. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, T.; Fiasca, B.; Di Cicco, M.; Vaccarelli, I.; Tabilio Di Camillo, A.; Crisante, S.; Galassi, D.M.P. Effectiveness of Biomass/Abundance Comparison (ABC) Models in Assessing the Response of Hyporheic Assemblages to Ammonium Contamination. Water 2022, 14, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.A.; Zanre, E.; Gray, S.R.J. Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for Applied Sciences and Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 54, pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, G. iModeler Manual: A Quick Guide for Fuzzy Cognitive Modelling. EcoAdapt Working Paper Series N2. 2014. Available online: https://agritrop.cirad.fr/583310/1/ID583310.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Gray, S.A.; Gray, S.; Cox, L.J.; Henly-Shepard, S. Mental Modeler: A Fuzzy-Logic Cognitive Mapping Modeling Tool for Adaptive Environmental Management. In Proceedings of the 2013 46th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 7–10 January 2013; pp. 965–973. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, İ. Cladoceran Species and Their Population Abundance across the Black Sea from West to East during Summer 2020. J. Nat. Hist. 2025, 59, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, J.B.; Vargas, L.; Collin, R. Zooplankton Abundance Reflects Oxygen Concentration and Dissolved Organic Matter in a Seasonally Hypoxic Estuary. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Carter, T.R.; Ebi, K.; Harrison, P.A.; Kemp-Benedict, E.; Kok, K.; Kriegler, E.; Preston, B.L.; Riahi, K.; Sillmann, J.; et al. Achievements and Needs for the Climate Change Scenario Framework. Nat. Clim. Change 2020, 10, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, J.; Middelburg, J.J.; Fennel, K.; Jickells, T.D. What Proportion of Riverine Nutrients Reaches the Open Ocean? Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, D.J.; Ding, P.X. Variation of Nutrients in Response to the Highly Dynamic Suspended Particulate Matter in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Plume. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Jorgensen, N.O.G.; Balode, M.; Purina, I. Variability in Inorganic and Organic Nitrogen Uptake Associated with Riverine Nutrient Input in the Gulf of Riga, Baltic Sea. Estuaries 2007, 24, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzinger, S.P.; Mayorga, E.; Bouwman, A.F.; Kroeze, C.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Billen, G.; Van Drecht, G.; Dumont, E.; Fekete, B.M.; Garnier, J.; et al. Global River Nutrient Export: A Scenario Analysis of Past and Future Trends. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, GB0A08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y. Contrasting effects of river inflow and seawater intrusion on zooplankton community structure in Jiaozhou bay, the Yellow Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 192, 106194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Xing, X.; Hu, B.; Gan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of River Damming on Nutrient Transport and Transformation and Its Countermeasures. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1078216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arashkevich, E.G.; Stefanova, K.; Bandelj, V.; Siokou, I.; Terbiyik Kurt, T.; Ak Orek, Y.; Timofte, F.; Timonin, A.; Solidoro, C. Mesozooplankton in the Open Black Sea: Regional and Seasonal Characteristics. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 135, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkoǧlu, M.; Koray, T. Phytoplankton Species’ Succession and Nutrients in the Southern Black Sea (Bay of Sinop). Turk. J. Bot. 2002, 26, 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- Turkoglu, M. Red Tides of the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca Scintillans Associated with Eutrophication in the Sea of Marmara (the Dardanelles, Turkey). Oceanologia 2013, 55, 709–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopuz, U.; Feyzioglu, A.M.; Valente, A. An Unusual Red-Tide Event of Noctiluca Scintillans (Macartney) in the Southeastern Black Sea. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 14, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytan, U.; Senturk, Y. Dynamics of Noctiluca Scintillans (Macartney) Kofoid & Swezy and Its Contribution to Mesozooplankton in the Southeastern Black Sea. Aquat. Sci. Eng. 2018, 33, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kideys, A.E. Ecology: Fall and Rise of the Black Sea Ecosystem. Science 2002, 297, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalov, G.M.; Grishin, A.N.; Rodionov, S.; Mihneva, V. Trophic Cascades Triggered by Overfishing Reveal Possible Mechanisms of Ecosystem Regime Shifts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10518–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskalov, G.M.; Boicenco, L.; Grishin, A.N.; Lazar, L.; Mihneva, V.; Shlyakhov, V.A.; Zengin, M. Architecture of Collapse: Regime Shift and Recovery in an Hierarchically Structured Marine Ecosystem. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbrächter, M.; Qi, Z. Aspects of Noctiluca (Dinophyceae) Population Dynamics, Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Piontkovski, S.A.; Serikova, I.M.; Evstigneev, V.P.; Prusova, I.Y.; Zagorodnaya, Y.A.; Al-Hashmi, K.A.; Al-Abri, N.M. Seasonal Blooms of the Dinoflagellate Algae Noctiluca Scintillans: Regional and Global Scale Aspects. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikishina, A.B.; Drits, A.V.; Vasilyeva, Y.V.; Timonin, A.G.; Solovyev, K.A.; Ratkova, T.N.; Sergeeva, V.M. Role of the Noctiluca Scintillans Population in the Trophic Dynamics of the Black Sea Plankton over the Spring Period. Oceanology 2011, 51, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollevier, A.; Mortelmans, J.; Aubert, A.; Deneudt, K.; Vandegehuchte, M.B. Noctiluca Scintillans: Dynamics, Size Measurements and Relationships With Small Soft-Bodied Plankton in the Belgian Part of the North Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 777999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mee, L.; Friedrich, J.; Gomoiu, M. Restoring the Black Sea in Times of Uncertainty. Oceanography 2012, 18, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuatters-Gollop, A.; Mee, L.D.; Raitsos, D.E.; Shapiro, G.I. Non-Linearities, Regime Shifts and Recovery: The Recent Influence of Climate on Black Sea Chlorophyll. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunev, O.A.; Moncheva, S.; Carstensen, J. Long-Term Variability of Vertical Chlorophyll a and Nitrate Profiles in the Open Black Sea: Eutrophication and Climate Change. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 294, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncheva, S.; Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Pagou, K.; Krastev, A. Phytoplankton Blooms in Black Sea and Mediterranean Coastal Ecosystems Subjected to Anthropogenic Eutrophication: Similarities and Differences. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 53, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncheva, S.; Dontcheva, V.; Shtereva, G.; Kamburska, L.; Malej, A.; Gorinstein, S. Application of Eutrophication Indices for Assessment of the Bulgarian Black Sea Coastal Ecosystem Ecological Quality. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerakaris, V.; Varkitzi, I.; Orlando-Bonaca, M.; Kikaki, K.; Mozetič, P.; Lardi, P.I.; Francé, J. Benthic-pelagic coupling of marine primary producers under different natural and human-induced pressures’ regimes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 909927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Velikova, V. Abrupt Transition of the Northwestern Black Sea Shelf Ecosystem from a Eutrophic to an Alternative Pristine State. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 405, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuatters-Gollop, A.; Gilbert, A.J.; Mee, L.D.; Vermaat, J.E.; Artioli, Y.; Humborg, C.; Wulff, F. How Well Do Ecosystem Indicators Communicate the Effects of Anthropogenic Eutrophication? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, Y. Recent Changes in the Trophic Structure of the Black Sea. Fish. Ocean. 1992, 1, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, G.; Jespersen, P. Variations saisonnières chez quelques Copépodes planctoniques marins. In Meddelelser fra Kommissionen for Havundersøgelser; Serie: Plankton; C.A. Reitzel: Copenhague, Denmark, 1920; Volume 2, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, F. An Investigation into the Relationship of Sea Temperature and Food Supply to the Size of the Planktonic Copepod Temora Longicornis Müller in the North Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1981, 13, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uye, S.I. Resting Egg Production as a Life History Strategy of Marine Planktonic Copepods. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 37, 440–449. [Google Scholar]
- Belmonte, G.; Vaglio, I.; Rubino, F.; Alabiso, G. Zooplankton Composition along the Confinement Gradient of the Taranto Sea System (Ionian Sea, South-Eastern Italy). J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 128, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, C.R.; Hirst, A.G.; Atkinson, D. A Synthesis of Major Environmental-Body Size Clines of the Sexes within Arthropod Species. Oecologia 2019, 190, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Payne, M.R.; Kiørboe, T. Trait Biogeography of Marine Copepods—An Analysis across Scales. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Vogt, M.; Elizondo, U.H.; Righetti, D.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Gruber, N. Major Restructuring of Marine Plankton Assemblages under Global Warming. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, A.; Lilley, M.K.S.; Hirst, A.G.; McEvoy, A.J.; Tarran, G.A.; Widdicombe, C.; Fileman, E.S.; Woodward, E.M.S.; Schmidt, K.; Smyth, T.J.; et al. Increasing Nutrient Stress Reduces the Efficiency of Energy Transfer through Planktonic Size Spectra. Limnol. Ocean. 2021, 66, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L.; Rodino, S.; Pop, R.; Tiller, R.; D’Haese, N.; Viaene, P.; De Kok, J.-L. Sustainable Development Scenarios in the Danube Delta—A Pilot Methodology for Decision Makers. Water 2022, 14, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisinicu, E.; Harcota, G.E.; Lazǎr, L.; Niţǎ, V.; Țotoiu, A.; Ţiganov, G. Fish Abundance and Mesozooplankton Resource: A Study on Sprattus Sprattus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Actinopterygii: Clupeidae) in the Romanian Black Sea Waters. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2024, 76, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alelio, D.; Montresor, M.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Margiotta, F.; Sarno, D.; Ribeira d’Alcalà, M. Plankton Food-Webs: To What Extent Can They Be Simplified? Adv. Ocean. Limnol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Steinberg, D.; Bronk, D.; Tang, K. Marine Plankton Food Webs and Climate Change; William & Mary VIMS: Gloucester Point, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Maciej Gliwicz, Z. On the Different Nature of Top-down and Bottom-up Effects in Pelagic Food Webs. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 2296–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crise, A.; Kaberi, H.; Ruiz, J.; Zatsepin, A.; Arashkevich, E.; Giani, M.; Karageorgis, A.P.; Prieto, L.; Pantazi, M.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, D.; et al. A MSFD Complementary Approach for the Assessment of Pressures, Knowledge and Data Gaps in Southern European Seas: The PERSEUS Experience. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
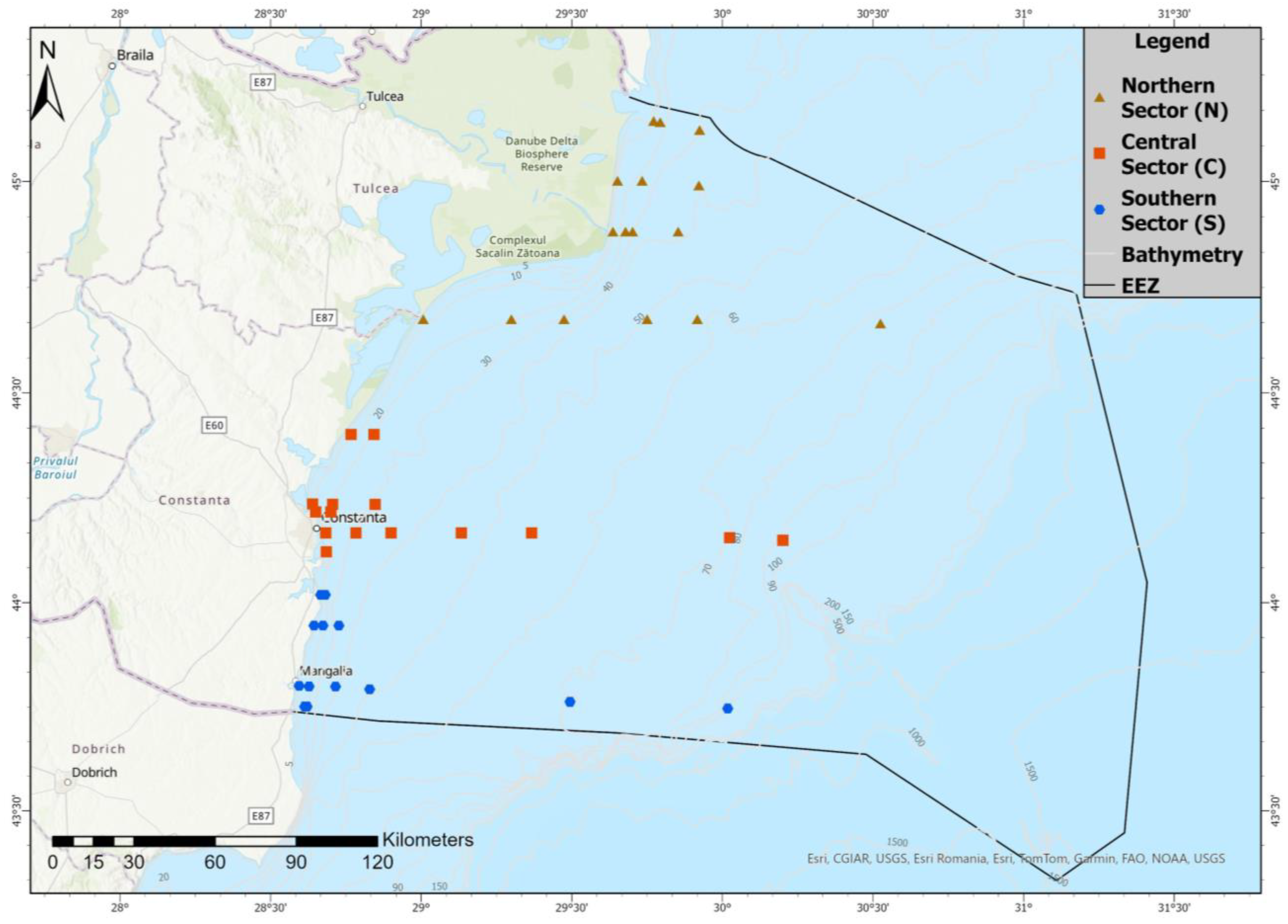

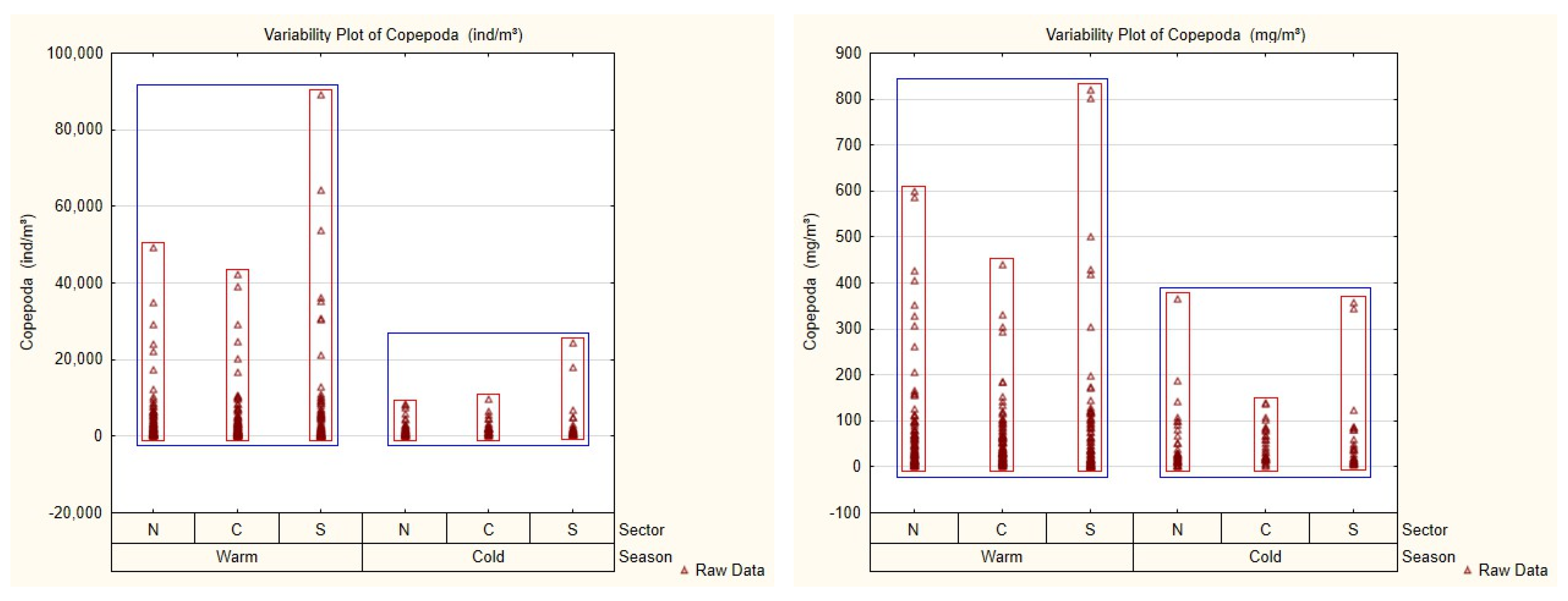
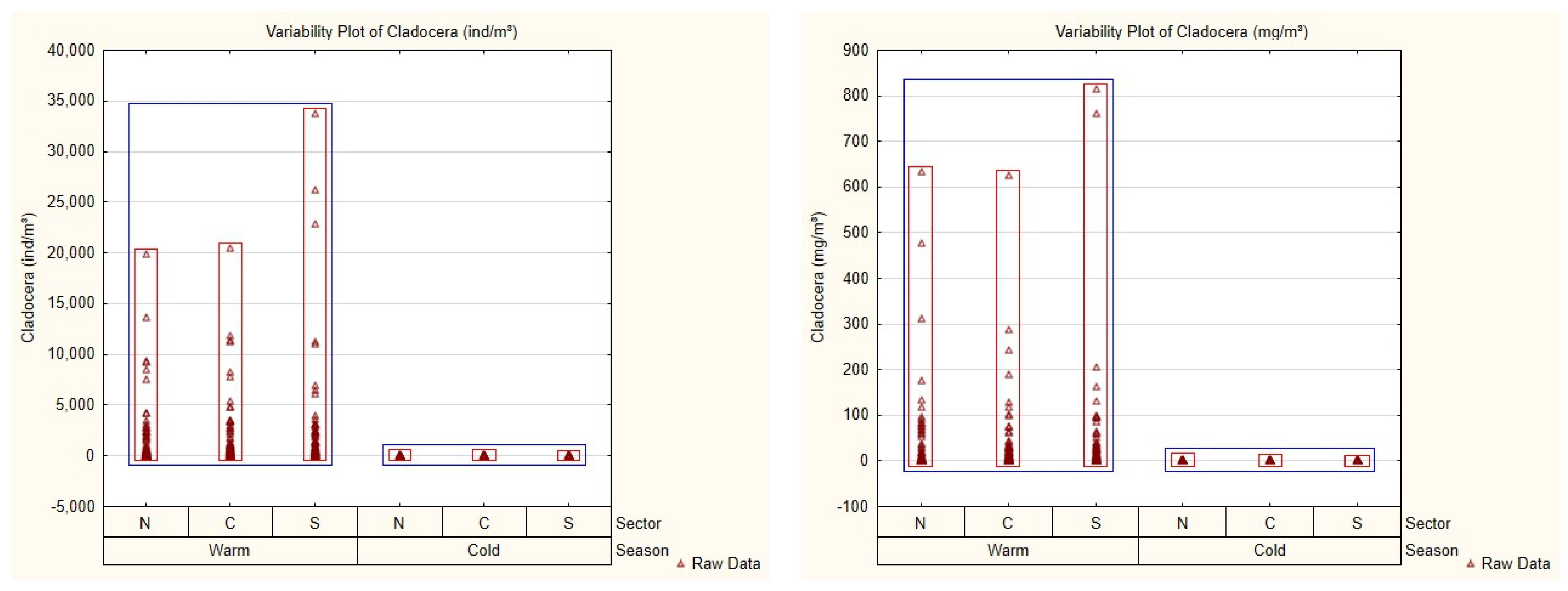
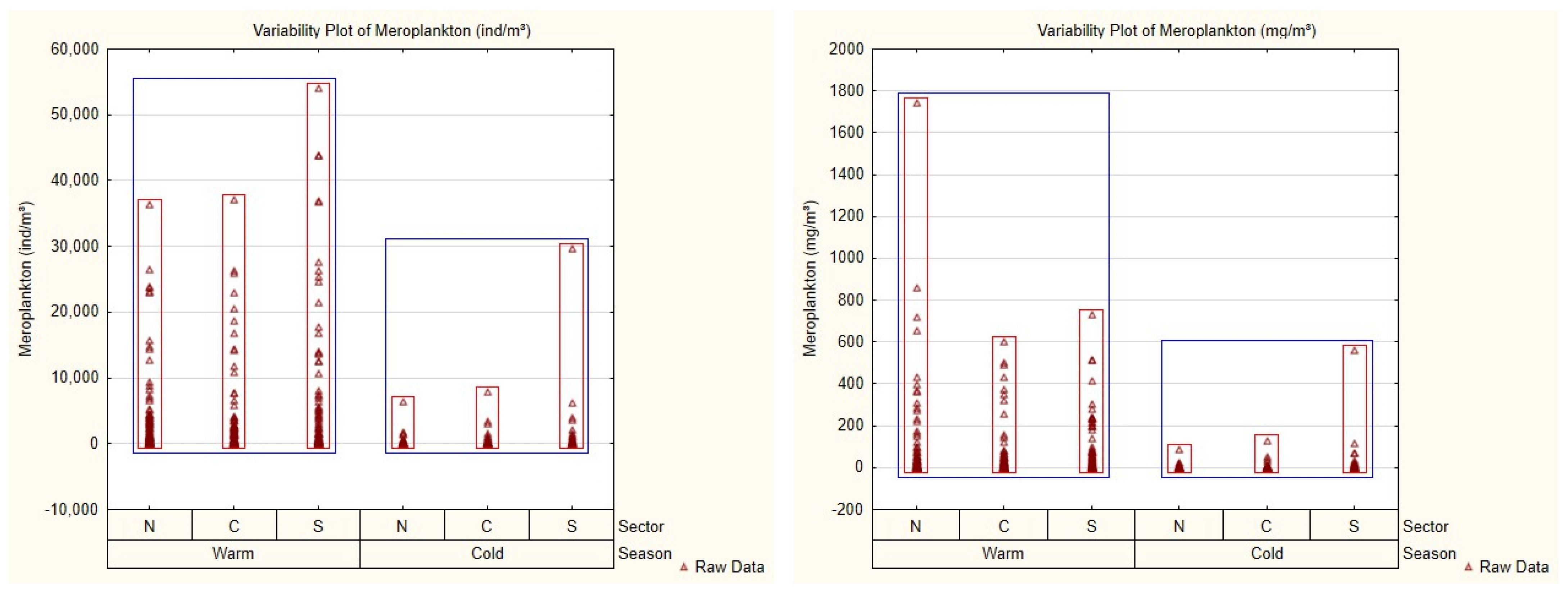
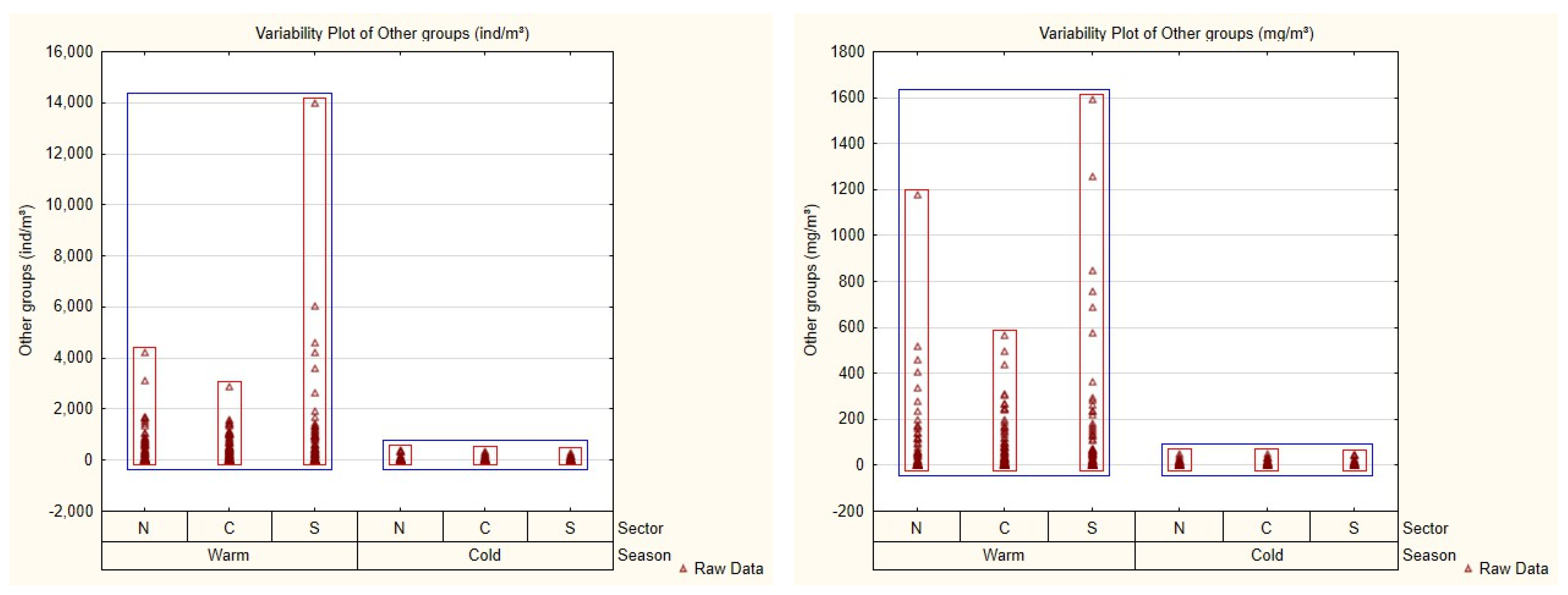



| Season | Sector | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold | N | - | 14 | - | 11 | 12 | - | - | - | 37 |
| C | - | 13 | - | 5 | 14 | - | - | - | 32 | |
| S | - | 11 | - | 13 | 5 | - | - | - | 29 | |
| Warm | N | 12 | 14 | 16 | 6 | 6 | 16 | 14 | 15 | 99 |
| C | 17 | 16 | 14 | 6 | 7 | 21 | 10 | 15 | 106 | |
| S | 18 | 11 | 12 | 6 | - | 13 | 12 | 13 | 85 |
| Scenario | Temperature | Salinity | Ecological Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improbable | ↓ (cooling) | ↑ (increase) | Unlikely regional cooling; stronger marine influence. |
| Probable | ↑ (warming) | ↓ (decrease) | Most likely outcome: warming with reduced freshwater retention. |
| Extreme | ↑↑ (strong warming) | ↓↓ (strong decrease) | High-emissions trajectory; intensified freshwater inflow, stratification, and eutrophication risk. |
| Sector | Season | T (°C) | S (‰) | O2 (µM) | PO4 (µM) | SiO4 (µM) | NO2 (µM) | NO3 (µM) | NH4 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Cold | 8.07 ± 2.17 | 14.59 ± 3.74 | 345.72 ± 26.75 | 0.56 ± 0.53 | 32.49 ± 27.70 | 0.90 ± 1.31 | 5.22 ± 4.46 | 4.99 ± 4.67 |
| C | Cold | 9.37 ± 1.98 | 17.05 ± 1.66 | 316.74 ± 26.81 | 0.27 ± 0.23 | 34.23 ± 39.15 | 0.30 ± 0.18 | 3.85 ± 4.31 | 5.91 ± 11.03 |
| S | Cold | 8.99 ± 1.33 | 16.57 ± 1.17 | 327.52 ± 35.60 | 0.18 ± 0.17 | 20.17 ± 17.20 | 0.45 ± 0.23 | 2.59 ± 2.06 | 6.54 ± 5.05 |
| N | Warm | 21.35 ± 2.98 | 12.33 ± 5.04 | 335.94 ± 54.68 | 0.47 ± 0.46 | 17.15 ± 19.71 | 2.62 ± 6.74 | 7.20 ± 8.09 | 8.65 ± 8.61 |
| C | Warm | 22.53 ± 2.89 | 15.30 ± 2.78 | 310.98 ± 52.50 | 0.25 ± 0.31 | 5.08 ± 3.90 | 1.90 ± 4.58 | 4.68 ± 7.19 | 8.36 ± 7.47 |
| S | Warm | 21.85 ± 2.98 | 15.09 ± 3.04 | 295.79 ± 44.45 | 0.31 ± 0.32 | 4.92 ± 4.52 | 2.64 ± 6.21 | 4.89 ± 9.66 | 7.98 ± 8.06 |
| Sector | Season | W Value | Ecological Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | Cold | 0.119 | Relatively stable community. Biomass dominance indicates good structural integrity, though small taxa remain numerous. |
| C | Cold | 0.102 | Moderately stable community. Biomass above abundance, but smaller W suggests slightly higher stress than in the northern sector. |
| S | Cold | –0.102 | Disturbed community. Abundance exceeds biomass, indicating dominance of small, opportunistic taxa and loss of structural complexity. |
| N | Warm | 0.088 | Weak stability. Biomass slightly exceeds abundance; the community retains some structure, but stress begins to increase under summer conditions. |
| C | Warm | 0.088 | Weak stability. Narrow biomass–abundance gap; balanced contributions of small opportunists and larger species. |
| S | Warm | 0.016 | Transitional toward disturbance. The convergence of abundance and biomass curves suggests declining structural stability and a shift toward opportunistic, stress-tolerant taxa. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bisinicu, E.; Lazar, L. Vulnerability of Black Sea Mesozooplankton to Anthropogenic and Climate Forcing. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112151
Bisinicu E, Lazar L. Vulnerability of Black Sea Mesozooplankton to Anthropogenic and Climate Forcing. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112151
Chicago/Turabian StyleBisinicu, Elena, and Luminita Lazar. 2025. "Vulnerability of Black Sea Mesozooplankton to Anthropogenic and Climate Forcing" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112151
APA StyleBisinicu, E., & Lazar, L. (2025). Vulnerability of Black Sea Mesozooplankton to Anthropogenic and Climate Forcing. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112151







