Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in “Figure 1. (a) Schematic representation of sea surface height data in the study area. (b) Schematic of sea surface height data after center differencing.” as published. The latitude and longitude labels in the image are incorrect. The corrected “Figure 1. (a) Schematic representation of sea surface height data in the study area. (b) Schematic of sea surface height data after center differencing.” appears below.
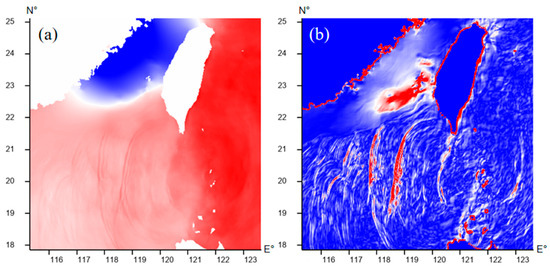
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic representation of sea surface height data in the study area. (b) Schematic of sea surface height data after center differencing.
Text Correction
There was an error in the original publication [1]. The study area should be located between 17.86° N and 25.11° N, but we mistakenly wrote it as 9.89° N and 17.14° N.
A correction has been made to 2. Materials and Methods, 2.1. Study Area and Dataset Creation, first paragraph:
The study area is located in the SCS, specifically between 115.31° E and 123.64° E longitude, and 17.86° N and 25.11° N latitude, focusing on the identification of ISWs within the Luzon Strait. The Luzon Strait region is characterized by unique topography and complex oceanic background, which make it conducive to the generation and propagation of ISWs [30,31]. This region provides a wealth of samples suitable for training the ISW identification network.
New Affiliation
The authors added a new affiliation, Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China, after affiliation 2.
The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Wan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, S.; Xie, J.; Li, S.; Song, T. A TransUNet-Based Intelligent Method for Identifying Internal Solitary Waves in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Submitted for possible open access publication under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).