Abstract
Two new species of free-living marine nematodes from mangrove wetlands of Beihai, Guangxi province in China, are described and illustrated. Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. is characterized by a head continuous with the body, an amphidial fovea pouch-shaped, pharynx expanding gradually but not forming a posterior bulb, spicules sclerotized, blade-shaped, slightly curved ventrally, proximal part enlarged with a prominent central septum, posterior part slender and handle-like; gubernaculum small, composed of two distally connected sheet-like structures with tooth-like ends, and lacking apophysis. Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. is characterized by a cuticle that is finely annulated, labial sensilla papilliform, cephalic setae four in number, amphideal fovea loop-shaped, exhibiting a double-contoured appearance, pharyngeal bulb well-developed, internal cuticular lumen tripartite, lateral epidermal ridges present, spicules slender with an enlarged capitulum, gubernaculum boat-shaped, precloacal supplements absent, tail conical with two setose protuberances, three pairs of subventral preanal setae, and a pair of papillae situated anterior to the anus. Nearly full-length SSU sequences and D2-D3 of LSU sequences are provided for the new species. Phylogenetic analysis of SSU provided support for the current classification status of the two new species. In the SSU phylogenetic tree, the family Ironidae was recovered as a separate monophyletic clade. However, the phylogenetic relationships within the family Desmodoridae were complicated, and the subfamilies Desmodorinae and Spiriniinae were polyphyletic. A comprehensive taxonomic approach combining morphological observations and molecular phylogeny construction would be particularly valuable in a more robust nematode taxonomy.
1. Introduction
Free-living marine nematodes represent a ubiquitous and often dominant constituent of meiofaunal communities in marine sediments and occupy various trophic levels in the marine benthic food web. They can serve as food for macrobenthos and consume benthic microorganisms and organic debris from the upper sediment layers. Thereby, they facilitate processes of the recycling and regeneration of nutrients. Furthermore, nematodes are highly responsive to the geochemical properties of sediments, establishing them as reliable bioindicators for assessing biodiversity and monitoring environmental perturbations [1]. Despite their ecological significance, the taxonomic composition of free-living marine nematodes remains largely unresolved. Current records from Chinese marine waters document fewer than 600 described species, a figure estimated to represent less than half of the true total diversity [2,3]. Given these substantial taxonomic gaps, concerted efforts to investigate the nematode fauna in China are imperative.
The genus Trissonchulus Cobb, 1920, belongs to the family Ironidae de Man, 1876, a group established by de Man (1876) with Ironus Bastian, 1865, as its type genus [4]. Species of Trissonchulus inhabit a broad range of habitats, from marine and continental waters to occasionally terrestrial environments [5]. The genus itself was established by Cobb (1920), with Trissonchulus oceanus designated as its type species. The generic diagnosis has been changed several times [6,7,8,9], and the taxonomy of this genus is still questionable. At present, 17 valid species, including a terrestrial species, have been described within the genus [10]. The genus Trissonchulus is diagnosed by a combination of characters, including a truncate to dome-shaped lip region with three prominent labial flaps, very short setiform cephalic sensilla, the absence of a posterior pharyngeal bulb, a frequent reduction in the anterior genital branch, and a relatively short tail. The most recent taxonomic contributions to this genus were made by Chen & Guo [11] and Nguyen Vu Thanh & Gagarin [12]. To date, only a single species of Trissonchulus has been recorded from Chinese waters.
The genus Metachromadora Filipjev, 1918 is classified under the subfamily Spiriniinae (Gerlach & Murphy, 1965) within the family Desmodoridae (Filipjev, 1922) of the order Desmodorida. It is a taxon with a long and complex taxonomic history. Since its establishment, it has undergone multiple significant revisions and reorganizations [13]. The phylogenetic relationships within the genus remain somewhat uncertain to this day, and it is considered to be highly heterogeneous [14]. Gerlach (1951) erected five subgenera within Metachromadora: Bradylaimus Stekhoven, 1931; Chromadoropsis Filipjev, 1918; Metonyx Chitwood, 1936; Metachromadora Filipjev, 1918; and Neonyx Cobb, 1933, primarily based on longitudinal striations on the head, shape of amphidial fovea, distribution patterns of somatic setae, presence of precloacal supplements, and presence of lateral alae. The subgenus Metachromadoroides was later proposed by Timm (1961), constituting the sixth addition to the genus, defined by the presence of a lateral ridge, amphidial fovea on a plaque, and presence or absence of tubular supplements [15]. Furstenberg & Vincx (1988) described three Chromadoropsis Filipjev, 1918 species (C. granulosus, C. longispiculosa, and C. namibiensi) from Southern Africa and the North Sea, and reinstated the subgenus Chromadoropsis to the independent genus level [16]. Later, Verschelde et al. (1995) subsequently proposed the genus Papillonema with P. danieli, based on the presence of prominent papilliform labial sensillae and three strangely shaped precloacal supplements; Chromadoropsis clavatum Verschelde, Muthumbi & Vincx, 1995 was transferred to this genus at the same time [17]. Despite these revisions, Metachromadora remains a species-rich genus, containing 33 valid species.
The development of molecular biology techniques [18] allows an objective, empirical analysis of the evolutionary history of the nematodes [1,19], and it is also a favorable complement to morphological identification of nematodes. Both the 18S rDNA and 28S rDNA were applied to investigate phylogenetic relationships of the nematodes at different taxonomic levels, such as phylum [20], order [21], superfamily [22], family [23], genus [24], and species [25].
Until now, about 500 species of nematodes have been identified in the South China Sea. There have been continuous reports of new nematode species from this region [26]. However, many species in this region are still unknown. An investigation of the biodiversity of free-living marine nematodes in the South China Sea was carried out in October 2023. Trissonchulus, Metachromadora, Daptonema, and Ptycholaimellus were the main dominant genera in this survey. Two unrecorded species belonging to the families Ironidae and Desmodoridae were discovered, and they are described here as Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. and Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. Their 18S rRNA gene and the D2/D3 region of the 28S rRNA gene were both amplified. The purpose of this work is to offer morphological and molecular analysis of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. and Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. with a discussion of the systematic position of these new species.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Morphological Analysis
Sediment samples for this study were collected in October 2023 from a mangrove wetland in Tieshan Harbor (109°36′ E, 21°36′ N), Beihai, Guangxi Province. Sampling was conducted using a syringe with an internal diameter of 2.6 cm, penetrating the top layer to a depth of 8 cm. Samples designated for molecular analysis were immediately preserved in 95% ethanol and stored at −20 °C. Those intended for morphological examination were fixed in 5% formalin seawater solution. In the laboratory, formalin-fixed samples were processed through sieves with mesh apertures of 500 µm and 42 µm to separate macrofauna from meiofauna. The retained material was gently washed with tap water to remove fine silt and clay particles. Meiofaunal organisms were extracted from the sediment matrix using Ludox TM-50 colloidal silica (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Nematodes were manually isolated under a stereoscopic microscope and transferred to a glycerol-ethanol solution (5:5:90 ratio) for approximately two weeks to ensure dehydration and preservation. Following the evaporation of ethanol, the specimens were permanently mounted on glass slides for morphological examination. Morphological observation and morphometric analyses were performed using a differential interference contrast microscope (Leica DM2500, CMS Gmbh, Wetzlar, Germany) equipped with a DMC5400 digital camera (CMS Gmbh, Wetzlar, Germany). All measurements, including curved structures quantified along the arc or median axis, were obtained using Leica software of LAS X version 3.3.3. Type specimens were deposited in the Marine Biological Museum of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Qingdao).
Morphometric abbreviations follow standard de Man indices: a (body length/width), b (body length/pharynx length), c (body length/tail length), c′ (tail length/anal width), c.b.d. (corresponding body diameter), and V% (relative vulva position).
2.2. Molecular Analysis
Prior to DNA extraction, specimens were washed three times in phosphate buffer to remove residual ethanol. Individual nematodes were then dissected into fragments using a sterile scalpel to facilitate lysis. Genomic DNA was extracted from the tissue fragments using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), following the manufacturer’s protocol. Nearly full-length 18S rRNA gene fragments were amplified via PCR with the Ex Taq polymerase kit (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan) and the primer pair 18S-G18S4 (5′-GCTTGTCTCAAAGATTAAGCC-3′) and 18S-18P (5′-TGATCCWKCYGCAGGTTCAC-3′) [27]. The D2/D3 expansion segments of the 28S rRNA gene were amplified using primers D2A (5′-ACAAGTACCGTGAGGGAAAGTTG-3′) and D3B (5′-TCGGAAGGAACCAGCTACTA-3′). The composition of the PCR reaction mixture and the thermal cycling program were performed as described by Sun and Huang [25] and De Ley et al. [28]. PCR amplicons were purified from agarose gels, cloned into a plasmid vector, and commercially sequenced in both directions by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) using an ABI 3730XL DNA Analyzer (Applied Biosystems Inc., Foster City, CA, USA). The resulting nucleotide sequences have been deposited in the GenBank database. For phylogenetic analysis, publicly available 18S rDNA sequences representing the families Ironidae, Leptosomatidae, Oxystominidae, Rhabdolaimidae, and Desmodoridae were retrieved from GenBank. All sequences were curated and initially aligned using Geneious v. 9.0.2 (Biomatters Ltd., Auckland, New Zealand). Construction of phylogenetic trees based on maximum likelihood analyses was performed following the previously published approaches of Sun and Huang [25]. The optimal model for Bayesian inference (BI) analysis was selected using PartitionFinder 2 v2.1.1 [29]. BI analysis was performed with PhyloSuite v1.2.3 [30,31,32]. The resulting phylogenetic tree was visualized in FigTree v1.4.4.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Taxonomy of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov.
Class Enoplea De Ley & Blaxter, 2004
Subclass Enoplia Pearse, 1942
Order Enoplida Filipjev, 1929
Suborder Ironina Siddiqi, 1983
Superfamily Ironoidea de Man, 1876
Family Ironidae de Man, 1876
Subfamily Thalassironinae Andrássy, 1976
Genus Trissonchulus Cobb, 1920
Diagnosis (according to Schmidt-Rhaesa, 2014) [33]. Cuticle smooth. Stoma with well-developed lips, buccal cavity sclerotized tubular, with three or four teeth and denticles in some species. Inner labial sensilla are papilliform; outer labial and cephalic sensilla are papilliform or very short setae. The amphidial fovea is pouch-shaped. The pharynx is posteriorly enlarged or with a basal bulb. Spicules are short, thick, and blunt. Tail is very short, wide, and blunt with caudal glands.
3.1.1. Type Material
A total of seven adult specimens (three males and four females) were subjected to detailed morphological examination and morphometric analysis. Holotype: ♂1 on slide B3-1-3. Paratypes: ♂2 on slide B3-1-11, ♂3,♀1,♀2, ♀3, and ♀4 on slide B3-1-2.
3.1.2. Type Locality and Habitat
Muddy surface sediment (0–5 cm) in a mangrove wetland in Tieshan Harbor, Beihai, Guangxi Province, China (109°36′ E, 21°36′ N).
3.1.3. Etymology
The species epithet refers to the country of origin, China.
3.1.4. Measurements
Comprehensive morphometric data for all examined specimens are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Individual measurements of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. (in µm except a, b, c, c′, and V%).
3.1.5. Description of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3)
Males. Body cylindrical (Figure 1A). Cuticle smooth and unornamented. Head conical, continuous with body. An inner circle of six small labial papillae and an outer circle of six labial papillae. Four larger papilliform cephalic sensilla. Amphids are pouch-shaped (Figure 2B) and located adjacent to the cephalic sensilla (Figure 1C). The buccal cavity consists of a cup-shaped anterior section and a strong cuticularized posterior rod (Figure 2A). The anterior of the cuticularized rod bears three solid, curved, claw-like teeth, two subventral and one dorsal. In juveniles, two or three smaller replacement teeth are located a short distance behind the functional ones. The anterior end of the cuticularized rod bears a small dorsal tooth and two larger subventral teeth. Pharynx about 412–435 µm long, expanding gradually along its length but not forming a definite posterior swelling or bulb, corresponding body diameter 70–74 µm at posterior extremity. The extreme anterior end of the pharynx is fused to the body wall dorsally and ventrolaterally. Cardia semicircular, well developed. Nerve ring encircling the pharynx slightly in front of the middle of the pharynx. The excretory pore is difficult to identify. Ventral gland not observed. Tail short, stout, and blunt, with small conical papillae, appearing to be tube-like under the cuticle (Figure 1D). Spinneret opening ventrally near the end of the tail.
The reproductive system is diagnostically diorchic, featuring two opposed testes. The anterior testis is longer than the posterior one and is reflexed contralaterally; the anterior testis lies to the left of the intestine, while the posterior testis lies to the right. Spicules sclerotized, blade-shaped, slightly curved ventrally, proximal part enlarged with a prominent central septum (about half the length of the spicules), posterior part slender and handle-like (Figure 2C). Gubernaculum small, composed of two distally connected sheet-like structures, with a tooth-like end, and lacking apophysis (Figure 1E and Figure 2D). No pre-cloacal supplements. The somatic musculature comprises oblique bands that originate in the dorso-lateral region and insert ventro-posteriorly. Caudal glands present.
Females. Similarly to males in most aspects (Figure 1B,F). Tail rounded with conoid papillae on distinct cuticular elevations (Figure 1G and Figure 3C). The reproductive system is didelphic-amphidelphic, reflexed, and located to the right of the intestine. The vulva is situated at 45.9–51.9% of body length (Figure 3D).
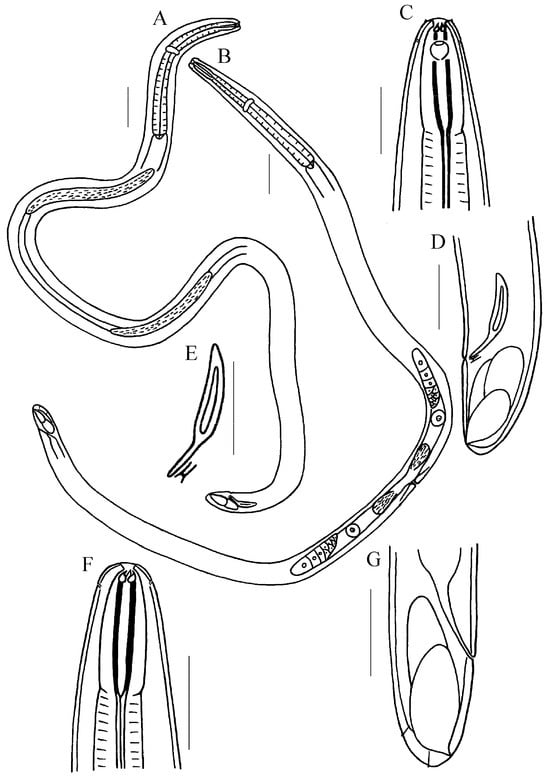
Figure 1.
Line drawing of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. (A) entire view of holotype; (B) entire view of female; (C) lateral view of male anterior part, showing buccal cavity, teeth, cephalic sensilla, and amphidial fovea; (D) lateral view of holotype posterior region, showing spicule, gubernaculum, and caudal glands; (E) lateral view of spicule and gubernaculum; (F) lateral view of female anterior part, showing buccal cavity and teeth; (G) lateral view of female posterior region. Scale bars: (A,B) = 100 µm; (C–G) = 50 µm.
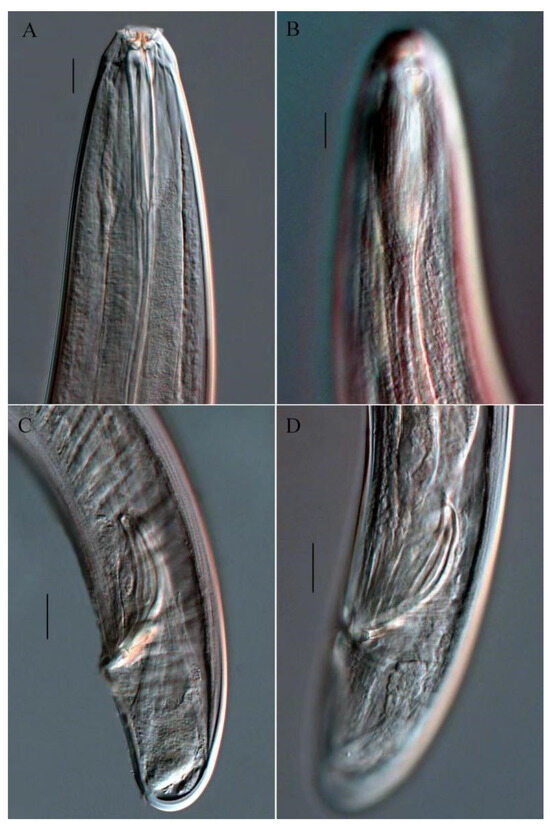
Figure 2.
Microphotograph of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. (A) anterior end of holotype, showing buccal cavity and teeth; (B) anterior end of male, showing amphidial fovea; (C) posterior end of holotype, showing spicule and tail; (D) posterior end of male, showing spicule and gubernaculum. Scale bars: 20 µm.
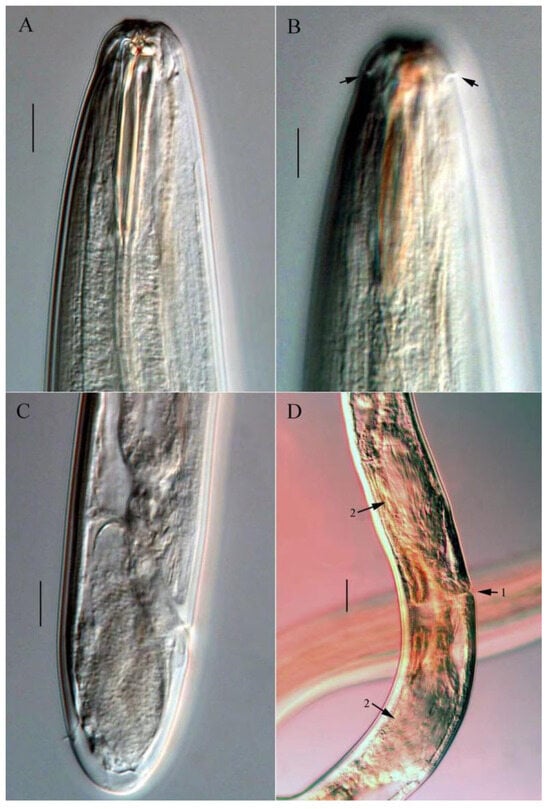
Figure 3.
Microphotograph of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. (A) anterior end of female, showing buccal cavity and teeth; (B) anterior end of female, showing cephalic papillae (arrows); (C) posterior end of female, showing tail and caudal papilla; (D) vulva region of female, showing vulva (arrow 1) and spermatheca (arrow 2). Scale bars: 20 µm.
3.1.6. Differential Diagnosis and Discussion
Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. is characterized by its head not set off from the rest of the body; spicules sclerotized, blade-shaped, slightly curved ventrally, proximal part enlarged with a prominent central septum, posterior part slender and handle-like; gubernaculum small, composed of two distally connected sheet-like structures, with a tooth-like end, and lacking apophysis; and a short, blunt tail. All the morphological features of the new species are consistent with the description of the genus. There are 17 valid species in this genus, and only two species with a continuous head (not set off from the rest of the body), including T. janetae and T. latispiculum. It differs from T. janetae in number of teeth (3 vs. 4), shorter body length (2730–3252 µm vs. 3550–4980 µm), higher de Man’s ratio b (6.4–7.2 vs. 4.9–6.1), shorter tail (58–66 µm vs. 110–170 µm in length, c = 43.3–56.3 vs. 28.7–34.2), shorter spicules (62–65 µm vs. 93–104 µm), and shorter gubernaculum (14–19 µm vs. 47–62 µm) [34]. The new species most closely resembles T. latispiculum (the only species of the genus that has been described in China) but differs from it by body length (2730–3051 µm vs. 3560–4123 µm), lower de Man’s ratio c (43.3–48.5 vs. 53.1–59.7), and differently shaped spicules and gubernaculum [11]. It is also morphologically close to T. latus, and it can be easily distinguished by its shorter and slender body (body length 2730–3051 µm vs. 4920 µm, a = 37.9–44.5 vs. 22.2), shorter spicules (62–65 µm vs. 137 µm), shorter gubernaculum (14–19 µm vs. 68 µm), varying spinneret opening (opening ventrally vs. terminally), and spicule shape [35].
3.2. Taxonomy of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov.
Class Chromadorea Inglis, 1983
Subclass Chromadoria Pearse, 1942
Order Desmodorida De Coninck, 1965
Superfamily Desmodoroidea Filipjev, 1922
Family Desmodoridae Filipjev, 1922
Subfamily Spiriniinae Gerlach & Murpy, 1965
Genus Metachromadora Filipjev, 1918
Diagnosis (according to Filipjev, 1918) [36]: Annulated cuticle with or without lateral ridges; the presence of somatic setae, in one subgenus (Metonyx), they are dense and positioned in 10 ordered longitudinal rows. Inner labial sensilla are papilliform; outer labial and cephalic sensilla are papilliform or setiform. Amphid with a double-contoured or loop-shaped to circular fovea. Stoma cylindrical with dorsal tooth; subventral teeth present or absent. The pharynx terminates in a large, heavily cuticularized bulb, the internal lining of which often partitions the lumen into two or three distinct sections. Precloacal supplements of various forms or absent.
3.2.1. Type Material
A total of five adult specimens (three males and two females) were subjected to detailed morphological examination and morphometric analysis. Holotype: ♂1 on slide C3-1-20. Paratypes: ♂2 on slide C3-1-20, ♂3 and ♀1 on slides C3-1-8, and ♀2 on slide C3-1-18.
3.2.2. Type Locality and Habitat
The surface layer (0–5 cm) of muddy sediment in a mangrove wetland at Tieshan Harbor, Beihai, Guangxi Province, China (109°36′ E, 21°36′ N).
3.2.3. Etymology
The species epithet sinica refers to its typical country, China.
3.2.4. Measurements
Comprehensive morphometric data for all examined specimens are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Measurements of individuals of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. (in µm except ratios).
3.2.5. Description of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. (Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6)
Males. Body cylindrical, 973–998 µm in length (Figure 5A). Cuticle finely annulated. The head region is bluntly conical. Labial sensilla comprise six internal and six external papilliform, well-developed structures (Figure 4A). Cephalic setae are four in number, 2–3 µm in length (Figure 6B). Cervical setae absent. Somatic setae not detected. Amphideal fovea loop-shaped, exhibiting a double-contoured appearance; width 11–12 µm, corresponding to 61.1–70.6% of the body diameter at that level (Figure 4A and Figure 6A). Buccal cavity 26–30 µm deep, armed with three teeth: a prominent dorsal tooth and two diminutive subventral teeth (Figure 4B). Pharyngeal bulb well-developed, its length accounting for 36.6–41.0% of total pharyngeal length; internal cuticular lumen tripartite (Figure 4A and Figure 6A). Cardia is small and muscular. The nerve ring is situated anterior to the pharyngeal bulb. Secretory-excretory pore not observed. Lateral epidermal ridges approximately 2 µm wide (ca. 1/20 of mid-body diameter), originating near the anterior margin of the pharyngeal bulb and extending posteriorly to the mid-tail region (Figure 4D and Figure 6C).
Male reproductive system monorchic, testis outstretched. The vas deferens is displaced to the right side of the intestine. Spicules paired, slender, arcuate ventrally, 47–50 µm long, exceeding body diameter at cloacal level, with an enlarged capitulum. Gubernaculum boat-shaped, 27–28 µm in length, parallel to spicules, apophyses absent (Figure 4D and Figure 6D). Precloacal supplements are absent. Tail conical, 1.9–2.2 times cloacal body diameter, terminating in a spinneret (5–6 µm) and adorned with sparse spiniform setae. Two setose protuberances are located ventrally on the tail, positioned 30–36 µm and 33–39 µm posterior to the cloaca, respectively. Three pairs of subventral preanal setae, approximately 5–6 µm long, are present. A single pair of papillae is situated immediately anterior to the anus (Figure 4D and Figure 6D). Caudal glands present but indistinct.
Females. Generally resemble males but are larger in size, with greater body width, shorter tail, and more developed pharyngeal bulb (Figure 4C,E). The reproductive system is amphidelphic, comprising two opposed, reflexed ovaries. The anterior ovary is disposed to the left of the intestine, and the posterior ovary lies on the right (Figure 5B). The vagina is strongly sclerotized. Two well-developed genital glands are present. The vulva has a transverse slit, positioned posterior to the mid-body (53.8–54.3% of total body length). Sperm cells are consistently observed within the uterus. Tail lacking protuberances and setae.
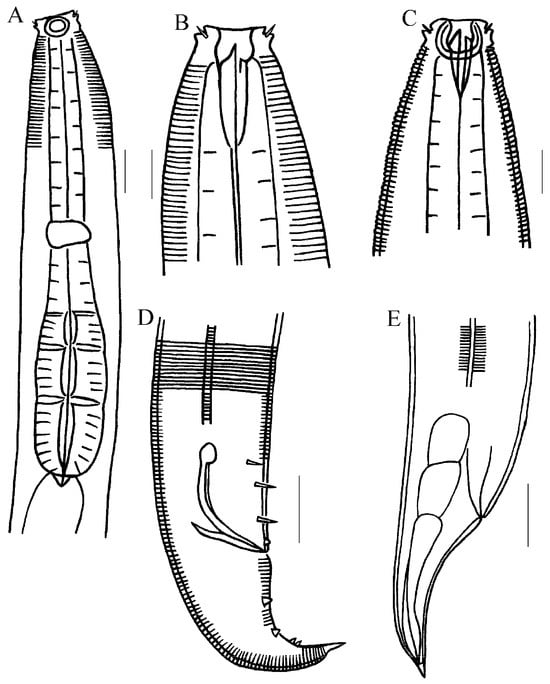
Figure 4.
Line drawing of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. (A) anterior end of male, showing outer labial setae, cephalic setae, amphid, nerve ring, and pharyngeal bulb; (B) anterior end of male, showing outer labial setae, cephalic setae, and teeth; (C) anterior end of female, showing outer labial setae, cephalic setae, amphid, and teeth; (D) posterior end of male, showing lateral ridge, spicules, gubernaculum, precloacal setae, and tail papillae; (E) posterior end of female, showing lateral ridge, caudal glands, and tail. Scale bar: (A,D,E) = 20 μm; (B,C) = 10 μm.
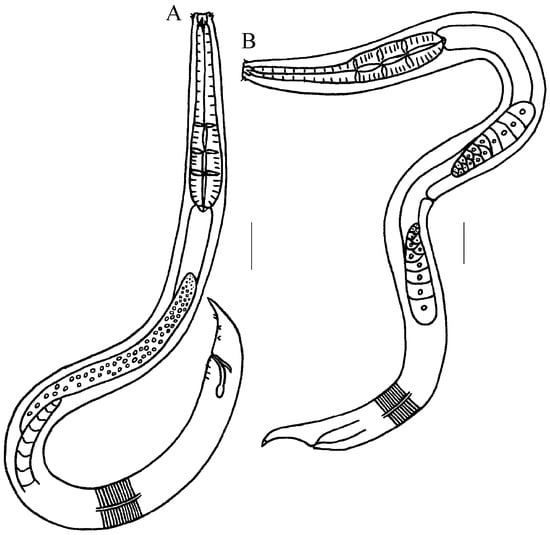
Figure 5.
Line drawing of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. (A) entire view of male; (B) entire view of female. Scale bar: (A,B) = 50 μm.
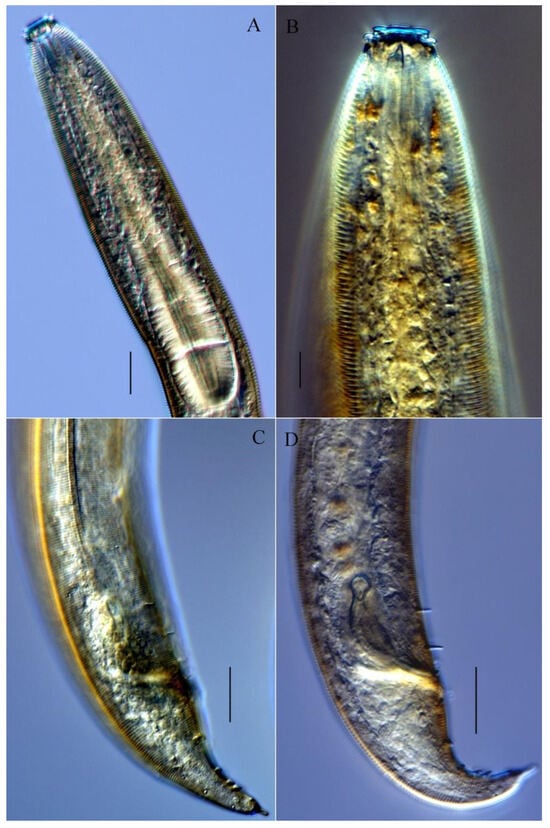
Figure 6.
Microphotograph of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. (A) Pharyngeal region of male, showing amphid and pharyngeal bulb; (B) lateral view of male anterior end, showing anterior sensilla, cephalic setae, and dorsal tooth; (C) posterior end of male, showing lateral ridge, precloacal setae, and tail papillae; (D) lateral view of male cloacal region, showing spicules, gubennaculum, precloacal setae, and tail papillae. Scale bar: (A,C,D) = 20 µm; (B) = 10 µm.
3.2.6. Differential Diagnosis and Discussion
The newly described species Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. is diagnosed by the following morphological features: a finely striated cuticle with lateral ridges; an obtusely conical cephalic region; four cephalic setae; a loop-shaped amphidial fovea displaying double contours; a pharynx featuring a tripartite cuticularized lumen; spicules with a well-developed capitulum; a canoe-shaped gubernaculum lacking an apophysis; absence of precloacal supplements; three pairs of subventral preanal setae; a single pair of papillae positioned anterior to the anus; and a short, conical tail bearing two ventral setose protuberances.
All morphological characteristics of the new species align completely with the diagnostic features of the subgenus Metachromadoroides [15]. There are ten valid species within Metachromadoroides Timm, 1961 [25], and supplements are absent in three species, including M. zaixsi, M. orientalis, and M. vulgaris. The new species differs from M. zaixsi by relatively thinner body (a = 22.6–23.7 vs. a = 10.5–19.3), shorter tail (c = 15.0–16.1 vs. c = 6.8–10.1), amphids shape (loop-shaped and have double contours vs. loop-shaped with one and a quarter closed turns), gubernaculum length (27–28 vs. 36 µm), number of precloacal setae (3 vs. 7–10), and protuberances on tail (2 vs. absent). The new species could be distinguished from M. vulgaris by body length (973–998 µm vs. 1100–1200 µm), spicule length (47–50 µm vs. 72 µm), and protuberances on the tail (2 vs. absent). The new species differs from M. orientalis in more slender body (a = 22.6–23.7 vs. a = 13–15), thinner tail (c’ = 1.9–2.2 vs. c’ = 1.0–1.3), amphids shape (loop-shaped and have double contours vs. loop-shaped, open top, and have double contour), cuticularized internal cavity of pharynx bulb (tripartite vs. bipartite), spicules length (47–50 µm vs. 59–63 µm), and protuberances on tail (2 vs. 1 small protuberance with three or four short spike setae).
Two species of the genus, M. xiamenensis and M. parobscura, have been previously described in China. The new species could be distinguished from them by precloacal supplements (absent vs. present), amphid shape (loop-shaped and have double contours vs. loop-shaped, doubly contoured with an open top), and cuticularized internal cavity of pharynx bulb (tripartite vs. bipartite).
3.3. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
Nearly full-length SSU sequences and D2-D3 of LSU sequences were obtained for Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. and Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. in this study. All sequences were subsequently deposited in GenBank, and the accession numbers were PQ452397 (for SSU sequence of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov., 1701 bp), PQ452407 and PQ452530 (for D2-D3 of LSU sequences of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov., 754–756 bp), PX367981 (for SSU sequence of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov., 1543 bp), and PX367982 (for D2-D3 of LSU sequences of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov., 786 bp). Due to the high congruence between the maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) trees based on SSU sequences, only the ML trees were presented.
3.3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov
Most of the Trissonchulus SSU sequences in the databases are short (700–800 bp) and not assigned to species levels. The SSU sequences of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. were blasted with sequences in the NCBI genebank. Trissonchulus sp. (Accession number JQ071931), which was not identified to species level, had the highest similarity to the new species (percentage of identity was 91.37%). Because Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. most closely resembles T. latispiculum; both SSU sequences of these two species were aligned with MegAlign (DNAStar). The percentage of the base divergence between these two species was 7% (63/897). In the phylogenetic tree (ML) based on SSU sequences, Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. was placed within the family Ironidae and formed a high-support clade clustering with other Trissonchulus species (100% posterior probability and bootstrap support) (Figure 7). This branch showed that Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. and T. latispiculum clustered together (86% posterior probability and 83% bootstrap support), then it grouped with Trissonchulus sp. (Accession number JQ071931). The new species differed markedly from T. latispiculum in the morphology of its copulatory spicules and gubernaculum, and the characteristics of these two structures are key diagnostic features for species identification. Therefore, despite similarities in other morphological traits, Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. is a new species different from T. latispiculum. SSU phylogenetic analyses also provided support for the current classification of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov.
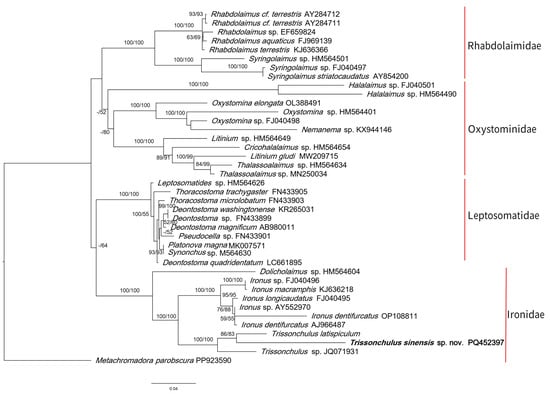
Figure 7.
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of SSU sequences, showing the evolutionary placement of Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. (highlighted in bold). Statistical support, shown as posterior probabilities (left) and bootstrap values (right), is displayed on the relevant branches, with dashes (–) indicating values below 50%.
The sequences used to construct the phylogenetic trees belong to four families, including Ironidae, Leptosomatidae, Oxystominidae (three families of superfamily Ironoidea), and Rhabdolaimidae. In the SSU phylogenetic tree, each family was recovered as a separate monophyletic clade. The Ironidae was monophyletic, consistent with previous phylogenetic analysis results based on 18S rDNA [21,37]. Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. appeared to be more closely related to the Ironus (with 100% support) than to the Dolicholaimus, as the latter formed a separate clade (Figure 7). Ironus is a heterogeneous taxon, with remarkable diversity in the structure of the dorsal tooth and the tail size and shape [1]. The genus could be considered as a typical freshwater genus, with very few species occurring in brackish water [33], and occupies the separate subfamily Ironinae, whereas Trissonchulus is mostly represented by marine species. Dolicholaimus and Trissonchulus are extremely similar in morphology, and six Trissonchulus species were transferred from Dolicholaimus, including T. acutus, T. benepapillosus, T. latus, T. oceanus, T. obtusus, and T. raskii [10]. There has been controversy over the identification of these two genera. Our systematic analysis indicated that they were separate genera, consistent with the views of Platonova and Mokievsky [38] and Lorenzen [39]. Trissonchulus could be distinguished from Dolicholaimus based on several significant features, such as the nature of the lips and lip sensilla, the reduction in the anterior genital branch, and the tail type [5].
Syringolaimus is another closely related genus of Trissonchulus, and T. benepapillosus was transferred from Syringolaimus [10]. It was included in the phylogenetic analysis because of its uncertain taxonomic status. It is characterized by a densely striated cuticle, not developed lips, labial and cephalic sensilla absent or papilliform, a pharynx with an oval or rounded basal bulb, a tail long, narrow with a long, cylindrical part [33]. Most classifications placed Syringolaimus within the family Ironidae, but some placed this genus within the Rhabdolaimidae [7]. The Ironidae appeared to be polyphyletic when Syringolaimus was included in the phylogenetic analysis [1,21]. This was contrary to the morphologically monophyletic nature of the Ironidae established by Lorenzen. Our analyses supported that the Ironidae were monophyletic, and the SSU tree showed the sister relationship between Syringolaimus and Rhabdolaimus (100% posterior probability and bootstrap support) (Figure 7). The similarity between Rhabdolaimus and Syringolaimus is also closely confirmed by the morphology of three minute, outwardly directed teeth, their digestive systems, and tails.
3.3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov.
SSU phylogenetic analyses mainly focused on the family Desmodoridae. Desmodoridae comprises six subfamilies: Desmodorinae Filipjev, 1922; Spiriniinae Gerlach & Murphy, 1965; Pseudonchinae Gerlach & Riemann, 1973; Stilbonematinae Cobb, 1936; Molgolaiminae Jensen, 1978; and Prodesmodorinae Lorenzen, 1981. The subfamilies Pseudonchinae, Molgolaiminae, and Prodesmodorinae each contain only a single genus. The genus Pseudonchus (Pseudonchinae) was excluded from the present phylogenetic tree due to short sequence length (its SSU sequence being only 866 bp), but it possesses distinctive buccal cavity characteristics (bilateral symmetric, large tubular, with rows of odontia at the anterior margin). In the phylogenetic tree, the subfamilies Molgolaiminae (Molgolaimus) and Prodesmodorinae (Prodesmodora) formed a distinct clade (<50% posterior probability and bootstrap support of 80%) (Figure 8). The former is primarily distributed in marine environments, while the latter inhabits terrestrial and freshwater habitats. Compared to other subfamilies, they share a finely and weakly striated cuticle, a round amphideal fovea, and a cuticularized pharyngeal bulb. The two subfamilies differ markedly in buccal cavity structure and the arrangement of cephalic setae.
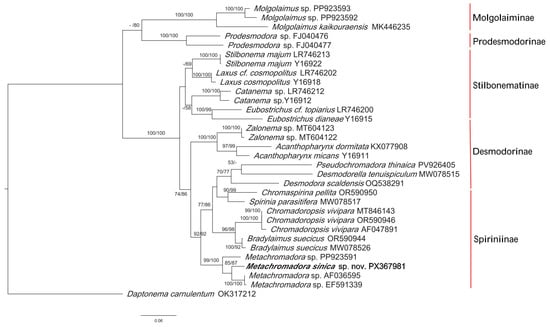
Figure 8.
The phylogenetic tree (ML) based on SSU sequences. The tree illustrates the phylogenetic position of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. (shown in bold). Statistical support, shown as posterior probabilities (left) and bootstrap values (right), is displayed on the relevant branches, with dashes (–) indicating values below 50%.
Subfamilies Stilbonematina, Desmodorinae, and Spiriniinae formed a well-supported monophyletic clade (100% posterior probability and bootstrap support) (Figure 8). The genera of Stilbonematina formed a poorly supported monophyletic clade (<50% posterior probability and bootstrap support), which is in agreement with the phylogenetic tree constructed by Megen et al. [40]. Armenteros also suggested that the monophyly of Stilbonematinae was not fully supported [41]. Within the Stilbonematina clade, Laxus and Stilbonema grouped together; both genera possess peculiar lateral ornamentation: the former exhibits an irregularly annulated, reticulated, or fingerprint-patterned surface, whereas the latter is distinctly annulated with broad annules. Catanema and Eubostrichus are extremely similar morphologically, and Catanema exile was transferred from Eubostrichus. They differ in the shape of the amphideal fovea and the presence/absence of a gubernacular apophysis.
Desmodorinae and Spiriniinae together formed another clade (74% posterior probability and bootstrap support of 86%). Within this clade, these two subfamilies appeared polyphyletic, which is consistent with Megen’s conclusions [40]. The genera Acanthopharynx and Zalonema formed a subclade. These genera possess unique diagnostic characteristics: Acanthopharynx has an elongate, tripartite pharyngeal bulb (half the length of the pharynx), while Zalonema is characterized by a rounded, triangular cephalic capsule and the presence of eight subcephalic setae. Another subclade includes the other genera of Desmodorinae and Spiriniinae. Metchromadora was distinguished from other genera within its subfamily by its papilliform labial sensilla. Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. formed a high-support clade clustering with other Metachromadora species. SSU phylogenetic analyses confirmed the current classification of Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. (Figure 8). Desmodora, Desmodorella, and Pseudochromadora, three genera of subfamily Desmodorinae, clustered with Spirinia and Chromaspirina (two genera of subfamily Spiriniinae), albeit with low support (<50% posterior probability and bootstrap support). Molecular evidence, based upon the small subunit of ribosomal DNA (SSU rDNA), indicated that the family Desmodoridae was highly polyphyletic [40]. While Armenteros demonstrated that Desmodoridae was a monophyletic group, the subfamilies Desmodorinae and Spiriniinae were not monophyletic [41]. Furthermore, the systematics of this family remained poorly understood due to conflicting morphological characters that hinder the resolution of relationships among taxa, and their taxonomic status requires further support from additional sequence data.
4. Conclusions
Based on a combination of molecular phylogenies with morphological systems, two new species, Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. and Metachromadora sinica sp. nov., from the South China Sea, were identified. Trissonchulus sinensis sp. nov. differs from other species in this genus by the lengths and shapes of spicules and gubernaculum. Metachromadora sinica sp. nov. can be diagnostically separated from its congeners by the following combination of features: amphid shape, cuticularized internal cavity of pharynx bulb, protuberances on tail, number of precloacal setae, and absence of precloacal supplements. ML and BI topology based on SSU sequences confirmed the taxonomic position of the two new species. The SSU phylogenetic tree showed that the family Ironidae was monophyletic, and the phylogenetic relationships within the family Desmodoridae were highly complex: the subfamilies Molgolaiminae and Prodesmodorinae were monophyletic, Desmodorinae and Spiriniinae were polyphyletic groups, whereas the monophyly of Stilbonematinae received only weak support. The current phylogenetic understanding of the family Desmodoridae represents the most updated understanding of these groups. It is also challenged by insufficient taxonomic representation, which hinders robust systematic resolution. In summary, with the augmentation of the nematode genomic data resource, the convergence of morphological techniques with advanced molecular analyses would facilitate the discovery of cryptic species and unveil complex evolutionary relationships.
Author Contributions
Preparation of specimens, R.B.; data measurement and writing—original draft preparation, J.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.H.; funding acquisition, J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China. (ZR2021MD108).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Chunyan Ji for sample collection and are grateful to Xin Zhao for valuable suggestions for the phylogenetic analysis. We are also sincerely thankful to YiChien Lee for providing the 18S rRNA gene sequences of Trissonchulus latispiculum.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Meldal, B.H.M.; Debenham, N.J.; De Ley, P.; De Ley, I.T.; Vanfleteren, J.R.; Vierstraete, A.R.; Bert, W.; Borgonie, G.; Moens, T.; Tyler, P.A.; et al. An improved molecular phylogeny of the Nematoda with special emphasis on marine taxa. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 42, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Zhai, H.X.; Huang, Y. Three new species of the order Enoplida (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 43, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Bai, R.B.; Zhai, H.X.; Huang, Y. Species list of free-living marine nematodes in the Yellow Sea, China. J. Liaocheng Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 37, 34–52. [Google Scholar]
- De Man, J.G. Onderzoekingen over vrij in de aarde levende Nematoden. Tijdschr. Ned. Dierkd. Ver. 1876, 2, 78–196. [Google Scholar]
- Tahseen, Q.; Mehdi, S.J. Taxonomy and relationships of a new and the first continental species of Trissonchulus Cobb, 1920 along with two species of Ironus (Nematoda: Ironidae) collected from Coal mines. Nematol. Mediterr. 2009, 37, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. Freilebende marine Nematoden des Mittelmeeres. IV. Freilebende marine Nematoden der Fischereigrunde bei Alexandrien. Zool. Jahrb. (Syst.) 1943, 76, 323–380. [Google Scholar]
- Chitwood, B.G. North American marine nematodes. Tex. J. Sci. 1951, 3, 617–672. [Google Scholar]
- Yeates, G.W. Studies on nematodes from dune sands: 3. Oncholaimidae, Ironidae, Alaimidae and Mononchidae. N. Z. J. Sci. 1967, 10, 299–321. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, H.M.; Warwick, R.M. Free-living marine nematodes. Part I. British Enoplids. In Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series); Kermack, D.M., Barnes, R.S.K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1983; Volume 28, pp. 169–171. [Google Scholar]
- Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available online: https://www.nemys.ugent.be (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Chen, Y.Z.; Guo, Y.Q. Three new and two known free-living marine nematode species of the family Ironidae from the East China Sea. Zootaxa 2015, 4018, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Gagarin, V.G. Two new species of free-living marine nematodes (Nematoda: Enoplida) from the near-mouth area of the Yen River in Vietnam. Biol. Morya 2015, 41, 340–348. [Google Scholar]
- De Ward, C.T.P. New species of Hopperia (Nematoda, Comesomatidae) and Metachromadora (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from Patagonia, Chubut, Argentina. Zootaxa 2004, 542, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincx, M. Free-Living Marine Nematodes from the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, State University of Ghent, Gent, Belgium, 1989; p. 678. [Google Scholar]
- Timm, R.W. The marine nematodes of the Bay of Bengal. Proc. Pak. Acad. Sci. 1961, 1, 25–88. [Google Scholar]
- Furstenberg, J.P.; Vincx, M. Three new species of Chromadoropsis (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from Southern Africa and the North Sea. S. Afr. J. Zool. 1988, 23, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Verschelde, D.; Muthumbi, A.; Vincx, M. Papillonema danieli gen. et sp.n. and Papillonema clavatum (Gerlach, 1957) comb.n. (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from the Ceriops mangrove sediments of Gazi Bay, Kenya. Hydrobiologia 1995, 316, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Yan, Y.L.; Su, F.; Huang, X.R.; Xia, D.D.; Jiang, X.X.; Dong, Y.H.; Lv, P.; Chen, F.Y.; Lv, Y.W. Research progress in gene editing technology. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2021, 26, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Ke, H.M.; Liu, Y.C.; Song, Y.S.; Chiu, Y.W.; Tang, P.; Chen, Y.R.; Chen, P.J.; Lu, H.H.S.; Lo, C.F.; et al. Single-worm long-read sequencing reveals genome diversity in free-living nematodes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 8035–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, P.; Blaxter, M.L. A new system for Nematoda: Combining morphological characters with molecular trees, and translating clades into ranks and taxa. In Nematology Monographs and Perspectives; Cook, R., Hunt, D.J., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 633–653. [Google Scholar]
- Bik, H.M.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Thomas, W.K.; Lunt, D.H. Moving towards a complete molecular framework on the Nematoda: A focus on the Enoplida and early-branching clades. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Guo, W.; Wang, C. Description of two new species, Sphaerolaimus obesus sp. nov. and Pseudosteineria articulata sp. nov. (Nematoda, Sphaerolaimoidea) from the Yellow Sea, China and phylogenetic analysis within superfamily Sphaerolaimoidea with combined ribosome DNA sequences. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2025, 43, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venekey, V.; Gheller, P.F.; Kandratavicius, N.; Cunha, B.P.; Souza, G.F.; Fonseca, G.; Maria, T.F. The state of the art of Chromadoridae (Nematoda, Chromadorida): A historical review, diagnoses and comments about valid and dubious genera and a list of valid species. Zootaxa 2019, 4578, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, D.; Fu, S.; Zhao, Z.Q. New nematode species from the continental slope of New Zealand (Chromadorea, Microlaimida, and Chromadorida), and unexpected placement of the genus Molgolaimus Ditlevsen, 1921. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 2267–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Y. Metachromadora parobscura sp. nov. and Molgolaimus longicaudatus sp. nov. (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from Mangrove Wetlands of China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xu, K. Two new species of Promonhystera Wieser, 1956 (Nematoda: Monhysterida: Xyalidae) from the South China Sea. Zootaxa 2024, 5399, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, I.T.; De Ley, P.; Vierstraete, A.; Waerebeek, K.V.; Vanfleteren, J.; Vierstraete, A.R.; Bert, W.; Borgonie, G. Phylogenetic analysis of Meloidogyne small subunit rDNA. J. Nematol. 2002, 34, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- De Ley, P.; De Ley, I.T.; Morris, K.; Abebe, E.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Yoder, M.; Heras, J.; Waumann, D.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; Jay Burr, A.H.; et al. An integrated approach to fast and informative morphological vouchering of nematodes for applications in molecular barcoding. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Lei, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, H.; Wang, G. Using PhyloSuite for molecular phylogeny and tree-based analyses. iMeta 2023, 2, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Ed.) Handbook of Zoology: Gastrotricha, Cycloneuralia and Gnathifera (Vol. Nematoda); De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014; p. 759. [Google Scholar]
- Inglis, W.G. Free-living nematodes from South Africa. Bull. Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) 1961, 7, 291–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, W. Free-living marine nematodes. I. Enoplida. Acta Univ. Lund. 1953, 49, 1–155. [Google Scholar]
- Filipjev, I.N. Free-living marine nematodes of the vicinities of Sevastopol. Tr. Osoboi Zool. Labor. Sevastopol. Biol. St. RAN. 1918, Ser. 1, 218–219. [Google Scholar]
- Mordukhovich, V.V.; Semenchenko, A.A.; Fadeeva, N.P.; Zograf, J.K. One new genus and two new free-living deep-sea nematode species with discussion of phylogeny of the family Leptosomatodae Filipjev, 1916. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 178, 102160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platonova, T.A.; Mokievsky, V.O. Revision of the marine nematodes of the family Ironidae (Nematoda: Enoplida). Zoosystematica Ross. 1994, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzen, S. The Phylogenetic Systematics of Freeliving Nematodes; The Ray Society: London, UK, 1994; p. 383. [Google Scholar]
- van Megen, H.; van den Elsen, S.; Holterman, M.; Karssen, G.; Mooyman, P.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. A phylogenetic tree of nematodes based on about 1200 full-length small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Nematology 2009, 11, 927–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteros, M.; Rojas-Corzo, A.; Ruiz-Abierno, A.; Derycke, S.; Backeljau, T.; Decraemer, W. Systematics and DNA barcoding of free-living marine nematodes with emphasis on tropical desmodorids using nuclear SSU rDNA and mitochondrial COI sequences. Nematology 2014, 16, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).