Self-Organizing of Waves and Sandy Bottom Relief—Laboratory Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
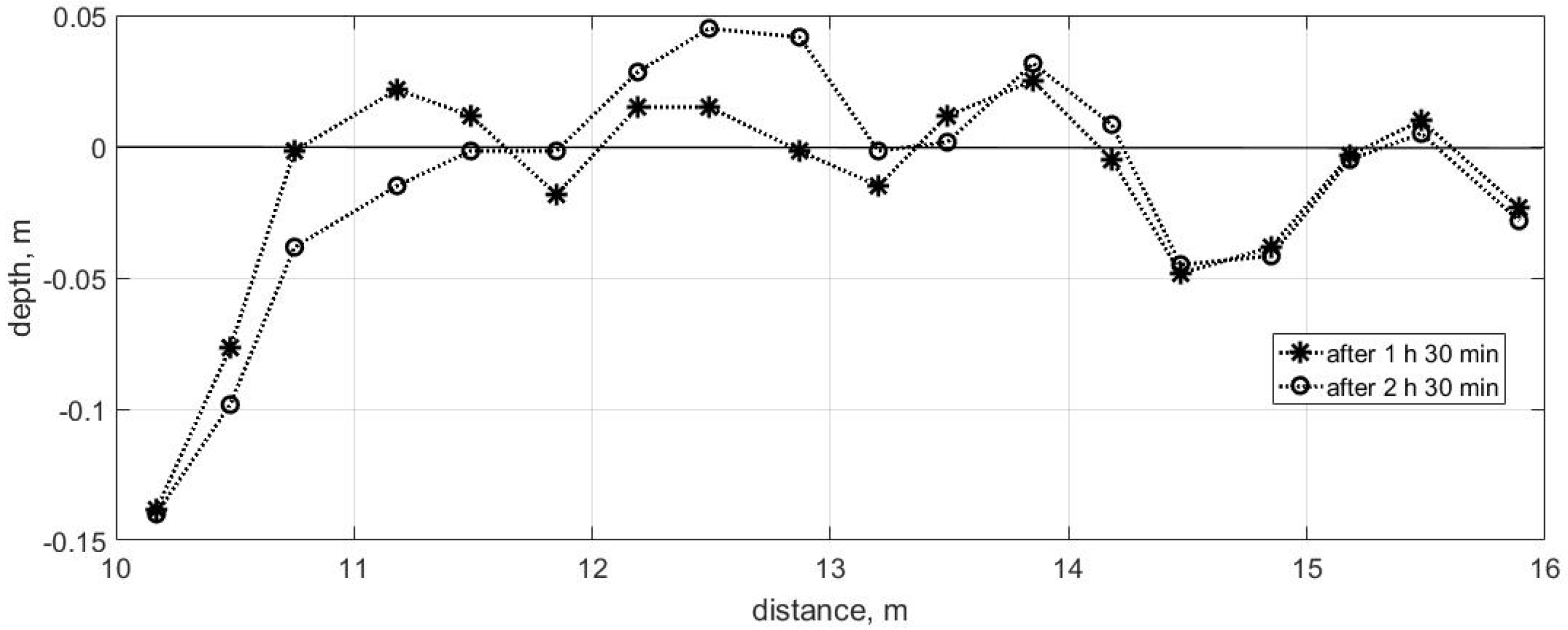
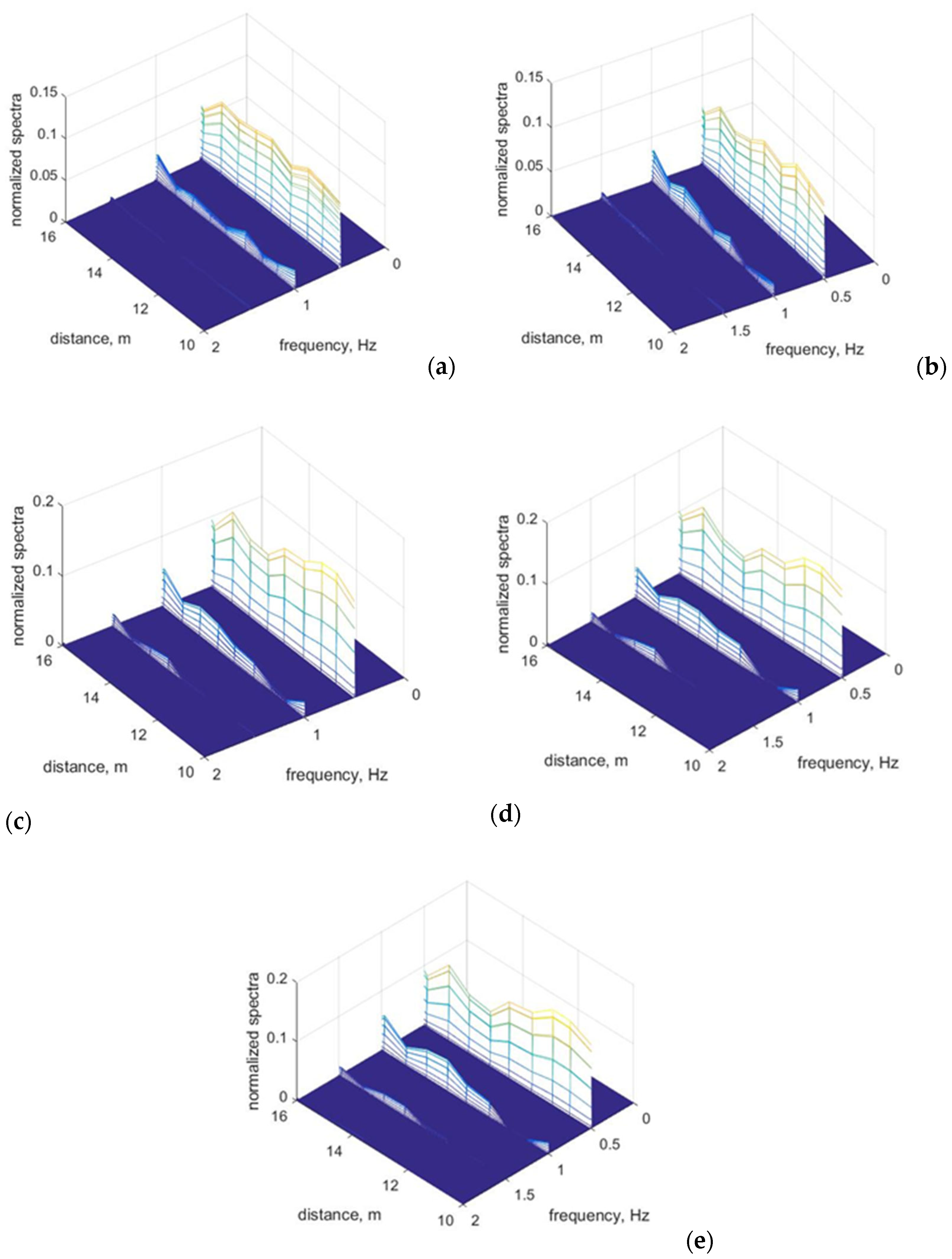
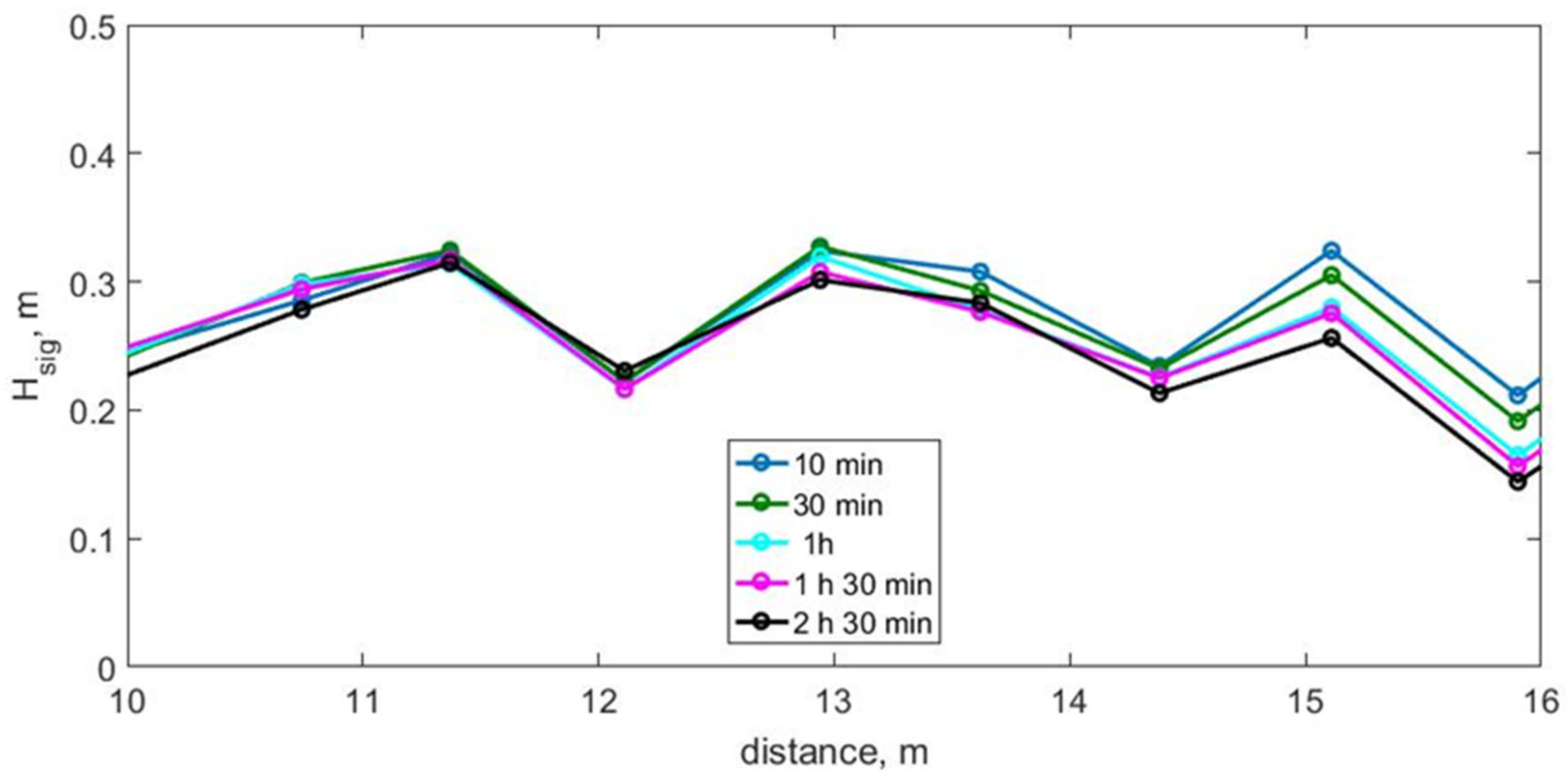
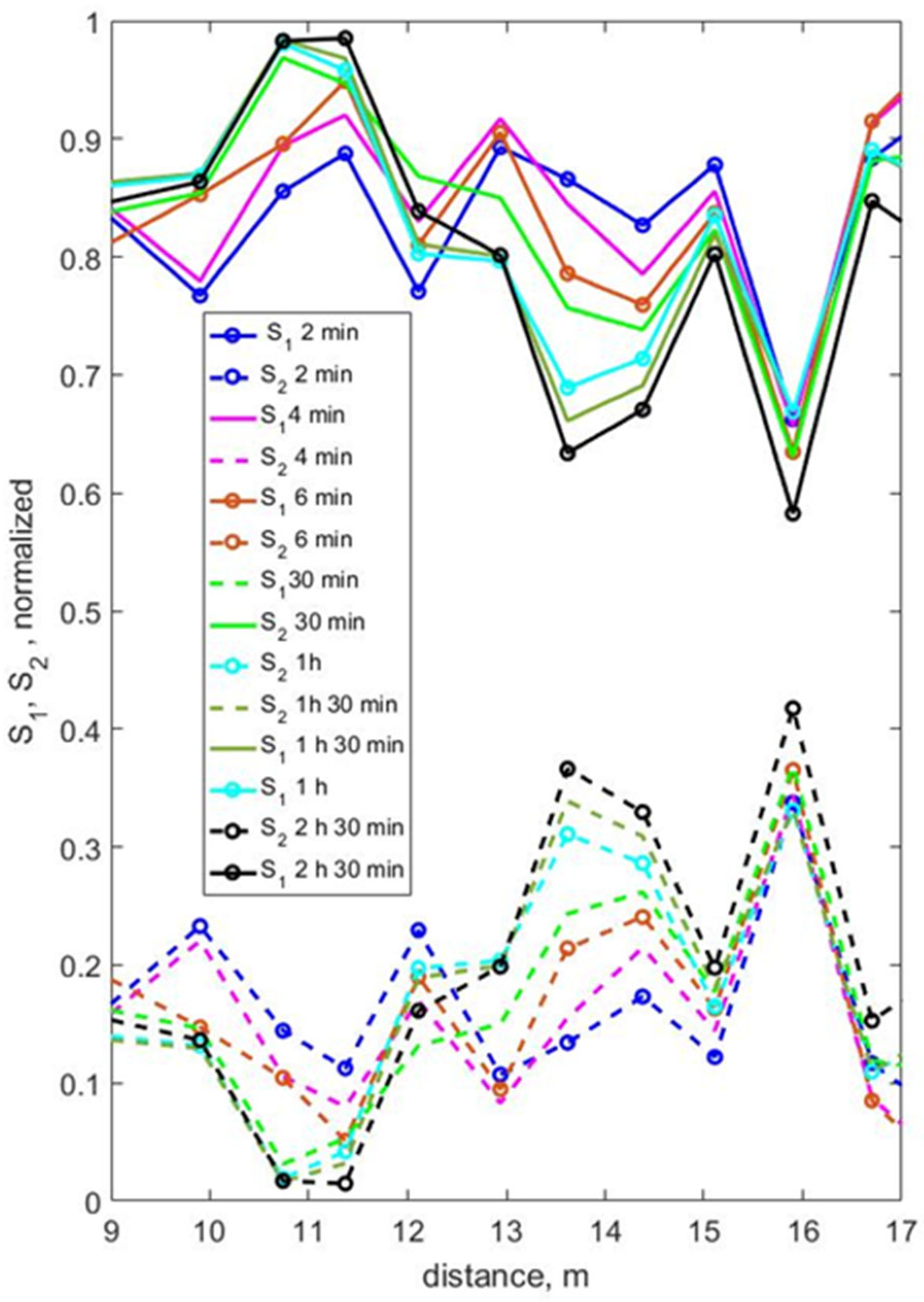
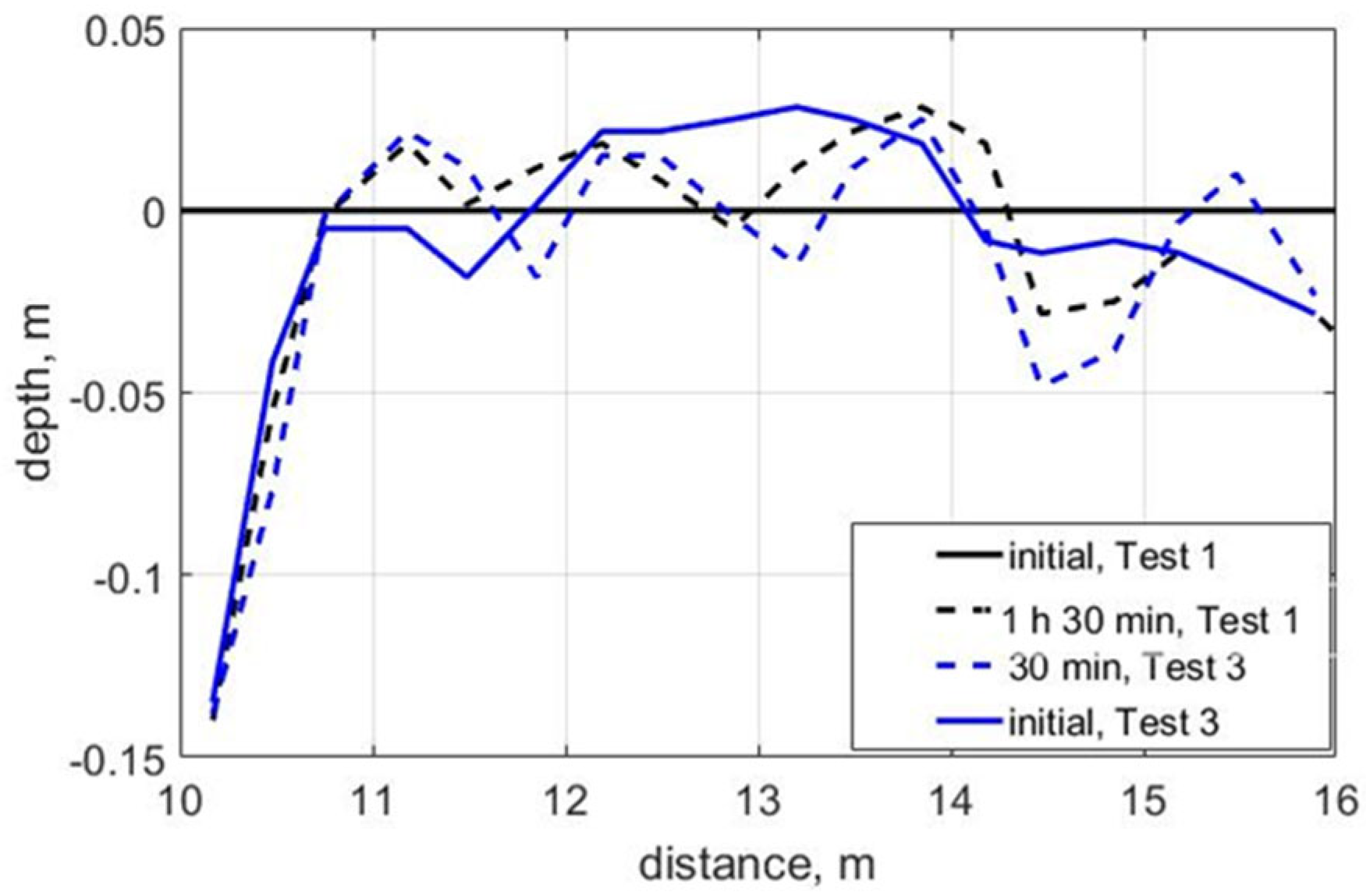
3.1. Wave Transformation and Bottom Deformation, Test 1
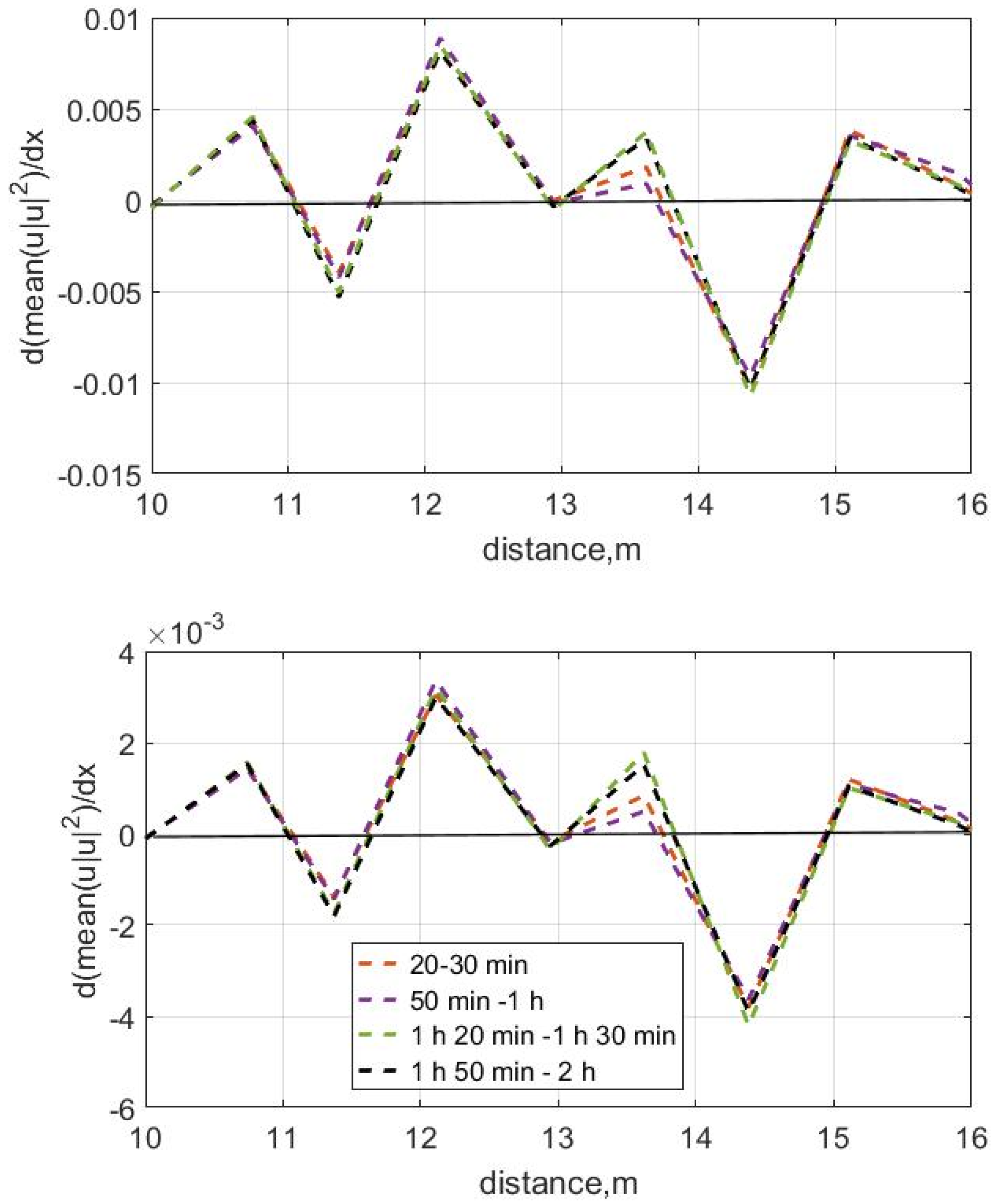
3.2. Wave Transformation and Bottom Deformations, Test 2
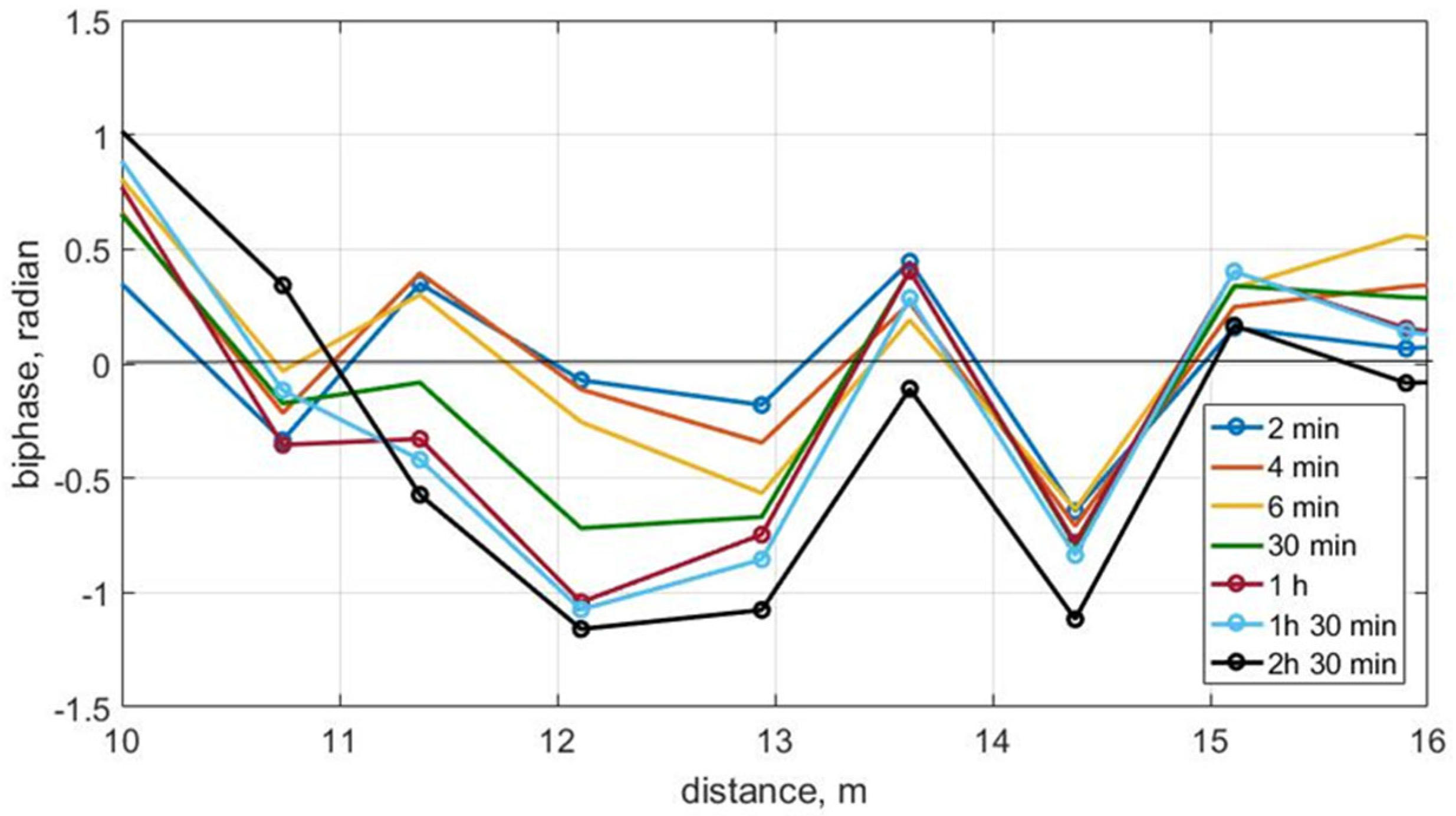
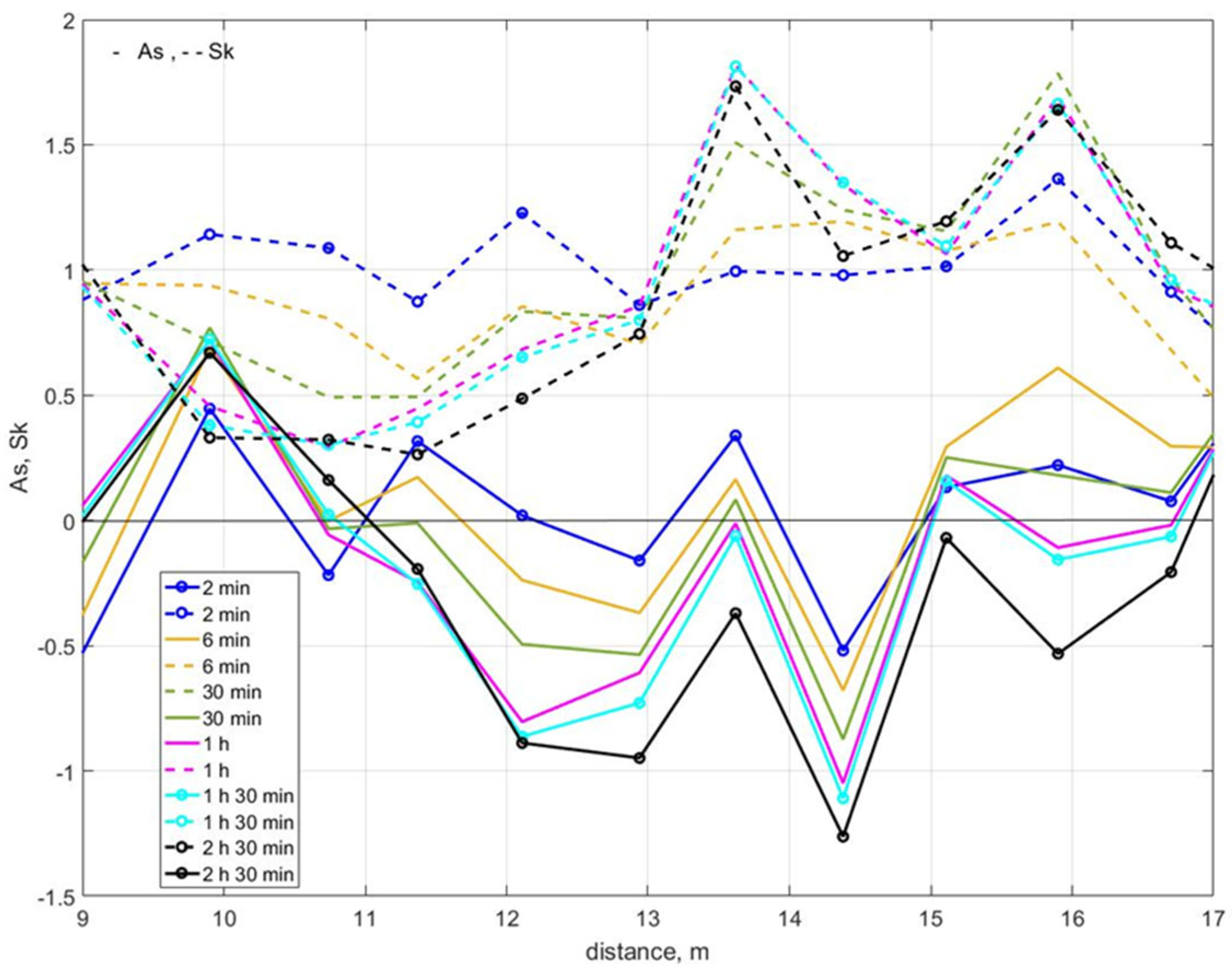
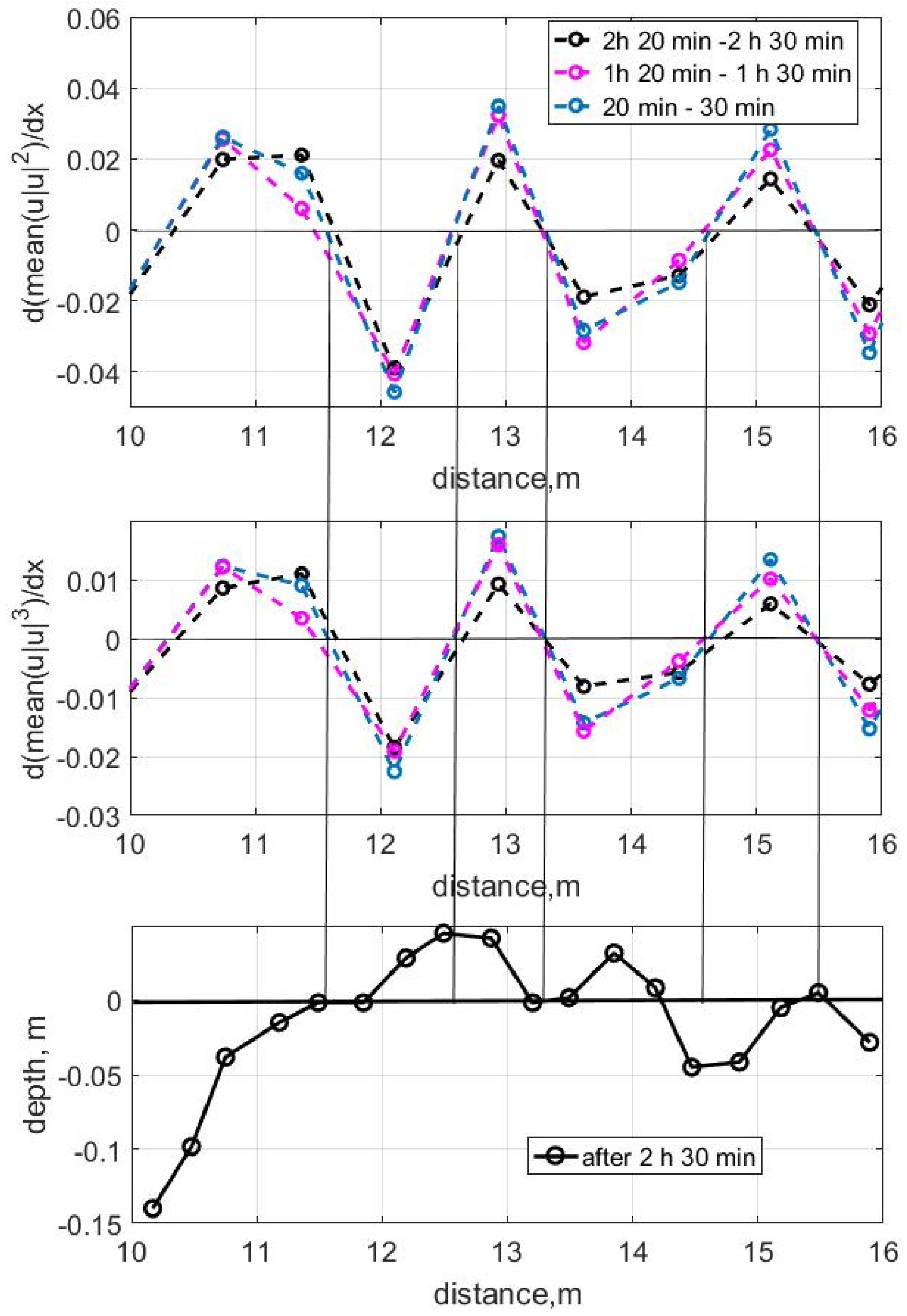
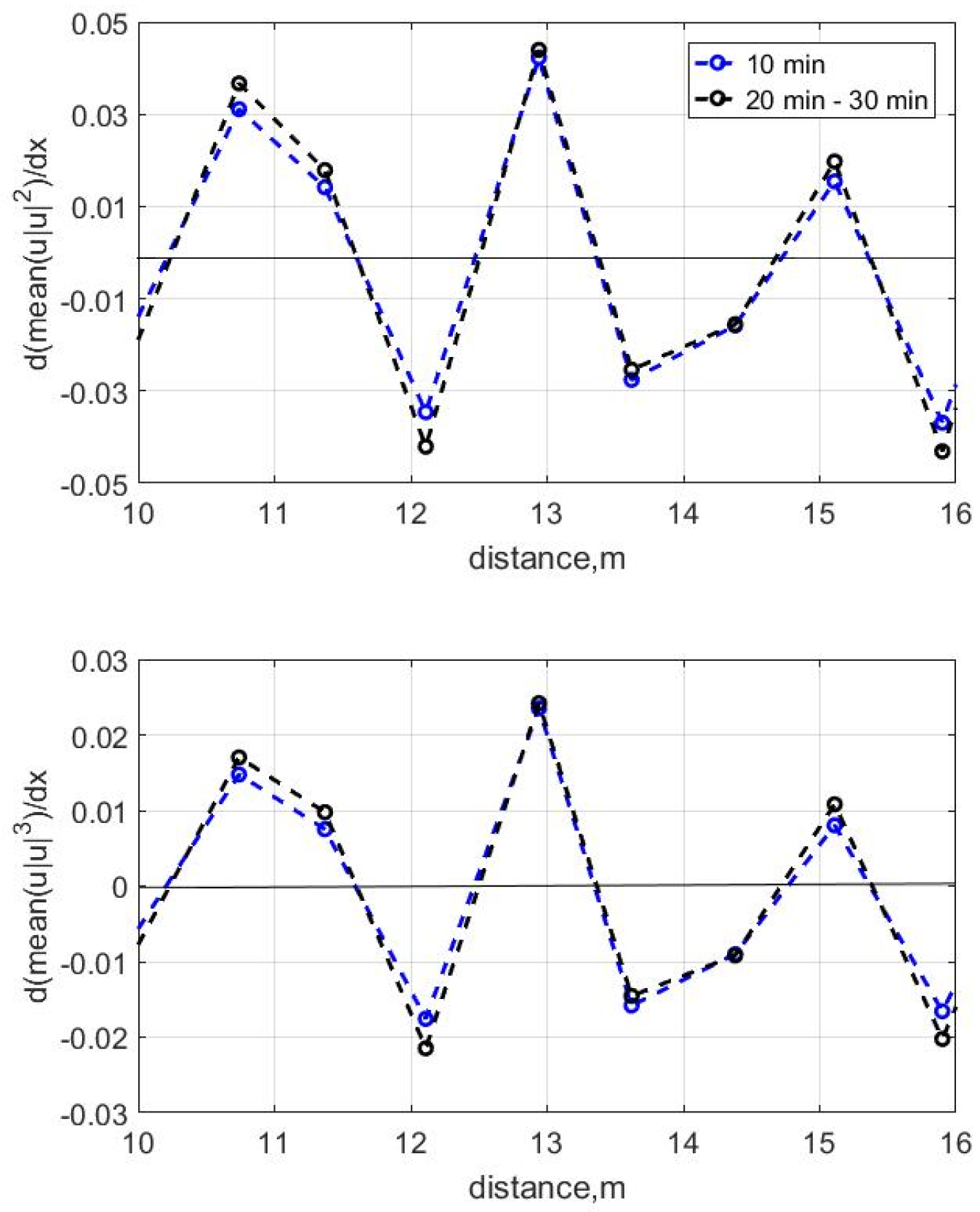
3.3. Wave Transformation and Bottom Deformations, Test 3
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masselink, G.; Puleo, J.A. Swash-zone morphodynamics. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, J.M.; Van Der Zanden, J.; Cáceres, I.; Ribberink, J.S. The influence of wave groups and wave-swash interactions on sediment transport and bed evolution in the swash zone. Coast. Eng. 2018, 140, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, D.; Pinto, J.P.; Pires-Silva, A.A.; Fortunato, A.B. Infragravity wave energy changes on a dissipative barred beach: A numerical study. Coast. Eng. 2018, 140, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.; Conley, D.; Masselink, G.; Leonardi, N.; McCarroll, R.J.; Scott, T. The impact of waves and tides on residual sand transport on a sediment-poor, energetic, and macrotidal continental shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 4974–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, T.; Silva, P.A.; Sancho, F.; Temperville, A. Analytical approximate wave form for asymmetric waves. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, T.; Michallet, H.; Silva, P.A.; Sancho, F.; van der A, D.A.; Ruessink, B.G. Bed shear stress under skewed and asymmetric oscillatory flows. Coast. Eng. 2013, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarkey, J.; Davies, A.G. Free-stream velocity descriptions under waves with skewness and asymmetry. Coast. Eng. 2012, 68, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Maribona, J.; Lara, J.L.; Maza, M.; Losada, I.J. Analysis of the mechanics of breaker bar generation in cross-shore beach profiles based on numerical modelling. Coast. Eng. 2022, 177, 104172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellón, E.; Aniel-Quiroga, I.; González, M.; Medina, R.; Vidal, C. Working with nature to enhance beach accretion: Laboratory experiments of beach ploughing. Coast. Eng. 2023, 180, 104267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derek, W.T.J.; Short, A.D. Sandy Beach Morphodynamics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C.; Ribberink, J.C.; van der Werf, J.; Walstra, D.J.R. Coastal sediment dynamics: Recent advances and future research needs. J. Hydraul. Res. 2013, 51, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergillos, R.J.; Masselink, G.; Ortega-Sánchez, M. Coupling cross-shore and longshore sediment transport to model storm response along a mixed sand-gravel coast under varying wave directions. Coast. Eng. 2017, 129, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, R. Influence of Wave Shape on Sediment Transport in Coastal Regions. Arch. Hydro-Eng. Environ. Mech. 2018, 65, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailard, J.A. An energetics total load sediment transport model for a plane sloping beach. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 10938–10954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribberink, J.S. Bed-load transport for steady flows and unsteady oscillatory flows. Coast. Eng. 1998, 34, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, R.L.; Damgaard, J.S. Bedload sediment transport in coastal water. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Unified view of sediment transport by currents and waves, I: Initiation of motion, bed roughness, and bed-load transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Unified view of sediment transport by currents and waves, II: Suspended transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 668–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruessink, B.G.; van der Berg, T.J.J.; van Rijn, L.C. Modeling sediment transport beneath skewed asymmetric waves above a plane bed. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, C11021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruessink, B.G.; Ramaekers, G.; van Rijn, L.C. On the parameterization of the free-stream non-linear wave orbital motion in nearshore morphodynamic models. Coast. Eng. 2012, 65, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.V.L.; Michallet, H.; Silva, P.A. Improving the parameterization of wave non-linearities—The importance of wave steepness, spectral bandwidth and beach slope. Coast. Eng. 2017, 121, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.V.L.; Silva, P.A.; Michallet, H.; Abreu, T.; Moura, D.; Fortes, C.J. Parameterizations of wave non-linearity from local wave parameters: A comparison with field data. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saprykina, Y.V.; Shtremel, M.N.; Kuznetsov, S.Y. On the possibility of biphase parametrization for wave transformation in the coastal zone. Oceanology 2017, 57, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczar-Karakiewicz, B.; Davidson-Arnott, R. Nearshore bar formation by non-linear process—A comparison of model results and field data. Mar. Geol. 1987, 77, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczar-Karakiewicz, B.; Jackson, L.A. The Analysis and Role of Bars on the Protection of a Beach System Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia. Coast. Eng. Proc. 1990, 22, 2265–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Capalain, C.; Boczar-Karakiewicz, B. Modeling of hydrodynamics and sedimentary processes related to unbroken progressive shallow water waves. J. Coast. Res. 1992, 8, 419–441. [Google Scholar]
- Chapalain, G.; Boczar-Karakiewicz, B. Modelling of multicomponent sandy beds evolution under shallow water waves. Coast. Eng. Proc. 1990, 22, 2213–2226. [Google Scholar]
- Saprykina, Y. The Influence of Wave Nonlinearity on Cross-Shore Sediment Transport in Coastal Zone: Experimental Investigations. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, S.; Saprykina, Y. Nonlinear Wave Transformation in Coastal Zone: Free and Bound Waves. Fluids 2021, 6, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saprykina, Y.V.; Kuznetsov, S.Y.; Andreeva, N.; Shtremel, M.N. Scenarios of nonlinear wave transformation in coastal zone. Oceanology 2013, 53, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtremel, M.; Saprykina, Y.; Ayat, B. The Method for Evaluating Cross-Shore Migration of Sand Bar under the Influence of Nonlinear Waves Transformation. Water 2022, 14, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenkinsopp, C.E.; Hunter, A.J.; Baldock, T.E.; Bayle, P.M.; Bosboom, J.; Conley, D.; Masselink, G. Repeatability of beach morphology change under identical wave forcing. Coast. Eng. 2024, 189, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, F.; Hurther, D.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Alsina, J.M. Influence of the initial on the sediment transport processes during post-storm on shorebar migration. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2023, 128, e2022JC019299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, T.E.; Birrien, F.; Atkinson, A.; Shimamoto, T.; Wu, S.; Callaghan, D.P.; Nielsen, P. Morphological hysteresis in the evolution of beach profiles under sequences of wave climates—Part 1; observations. Coast. Eng. 2017, 128, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, F.; Michallet, H.; Certain, R.; Barthélemy, E. Experimental Flume Simulation of Sandbar Dynamics. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 56, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Marple, S.L., Jr. Digital Spectral Analysis with Applications; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1987; 492p. [Google Scholar]
- Herbers, T.; Lowe, R.; Guza, R. Field observations of orbital velocities and pressure in weakly nonlinear surface gravity waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1992, 245, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stive, M.J.F. A model for cross-shore sediment transport. Coast. Eng. Proc. 1986, 20, 1550–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelvink, J.A.; Stive, M.J.F. Bar-generating cross-shore flow mechanism on a beach. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 4785–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Powers, E. Digital bispectral analysis and its application to non-linear wave interaction. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1979, 1, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgar, S.; Guza, R.T. Observation of bispectra of shoaling surface gravity waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1985, 161, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saprykina, Y.V.; Kuznetsov, S.Y.; Kuznetsova, O.A.; Shugan, I.V.; Chen, Y.-Y. Wave Breaking Type as a Typical Sign of Nonlinear Wave Transformation Stage in Coastal Zone. Phys. Wave Phen. 2020, 28, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saprykina, Y.V.; Kuznetsov, S.Y.; Divinskii, B.V. Influence of processes of nonlinear transformations of waves in the coastal zone on the height of breaking waves. Oceanology 2017, 57, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| d10, mm | d25, mm | Md, mm | d75, mm | d90, mm | S (Sorting Coefficient) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 1.32 |
| Test | Wave Height, m | Wave Period, s | Duration | Wave Breaking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.36 | 2 | 2 h 30 min | Spilling 15–16.7 m (first 30 min) Plunging 13–13.5 m, bore up to 16.7 m (50–60 min of wave action) Spilling 10–11 m, plunging 14–15 m, bore up to the wave absorber (1 h 30 min of wave action) Plunging 13–15 m, bore up to 16.7 m (2 h of wave action) |
| 2 | 0.1 | 3 | 2 h | No breaking |
| 3 | 0.4 | 2 | 30 min | Spilling 10.74 m, plunging 13.62 m (first 4 min of wave action) Spilling 10.74–12.11 m, plunging 14.38–15.11 m, bore up to 16.7 (5–30 min of wave action) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saprykina, Y.; Kuznetsov, S. Self-Organizing of Waves and Sandy Bottom Relief—Laboratory Experiments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112066
Saprykina Y, Kuznetsov S. Self-Organizing of Waves and Sandy Bottom Relief—Laboratory Experiments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112066
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaprykina, Yana, and Sergey Kuznetsov. 2025. "Self-Organizing of Waves and Sandy Bottom Relief—Laboratory Experiments" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112066
APA StyleSaprykina, Y., & Kuznetsov, S. (2025). Self-Organizing of Waves and Sandy Bottom Relief—Laboratory Experiments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112066







