A Comparison of Methods to Quantify Nano- and/or Microplastic (NMPs) Deposition in Wild-Caught Eastern Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) Growing in a Heavily Urbanized, Subtropical Estuary (Galveston Bay, USA)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling Design
2.3. Field Collections—Surface Waters
2.4. Field Collections—Oysters
2.5. Condition Index Analysis: Oyster Health Proxy
2.6. Microplastic Analysis—Categorization and Counting
2.7. Microplastic Analysis—Chemical Analysis
2.8. QAQC, Controls and Blanks
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality
3.2. Microplastics—Field, Sampling and Procedural Blanks
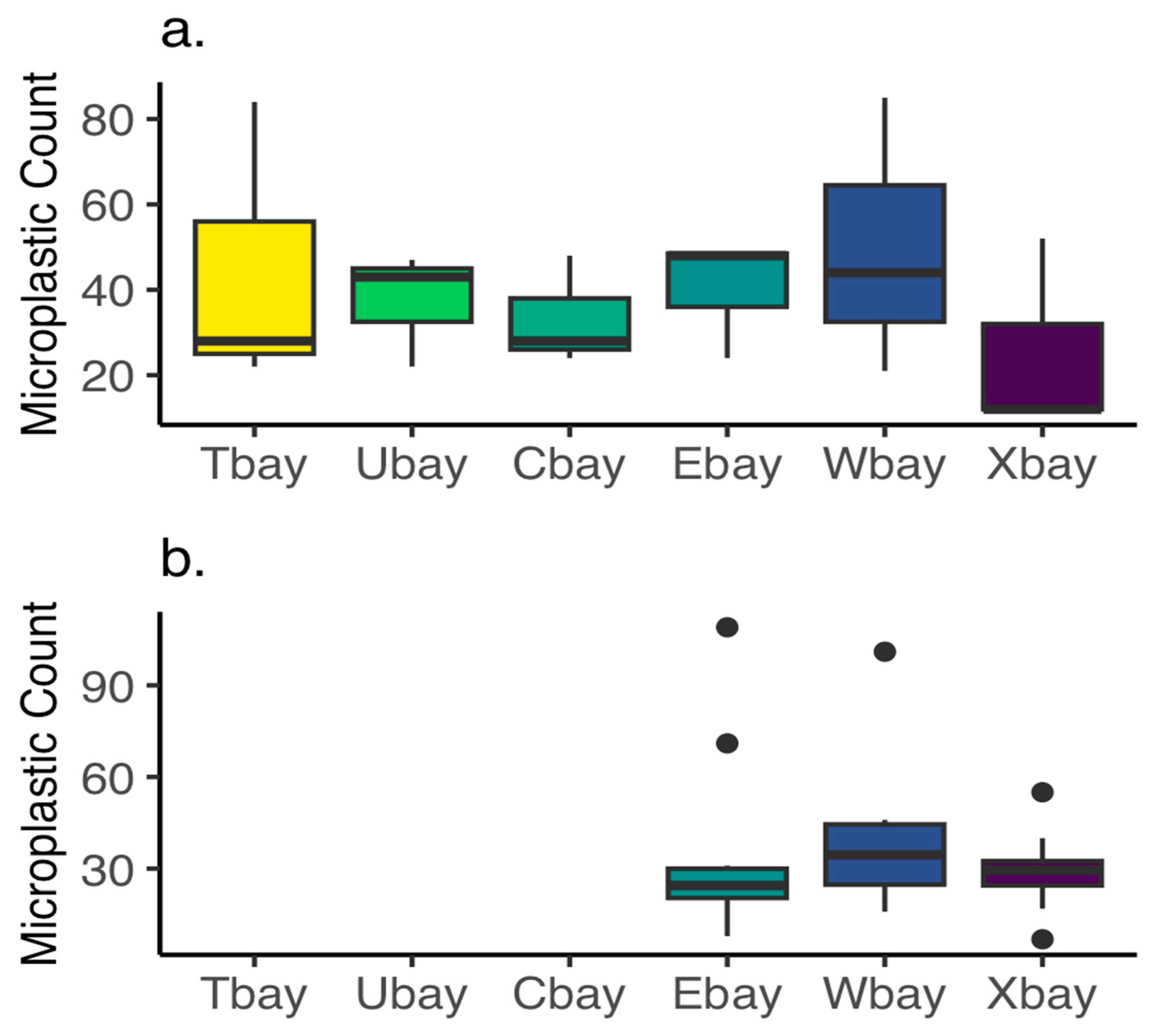
3.3. Microplastics—Surface Waters
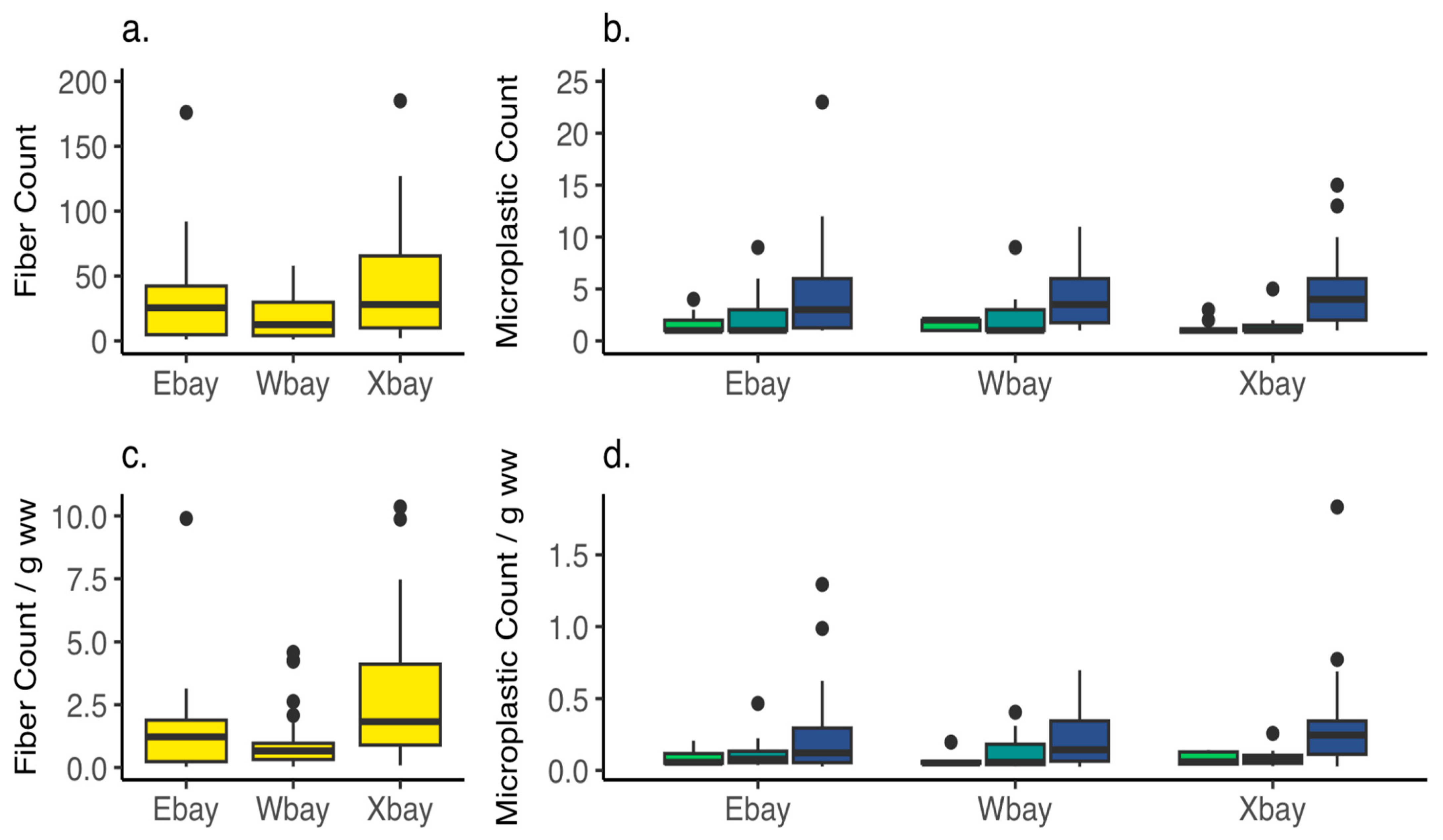
3.4. Microplastics—Oysters
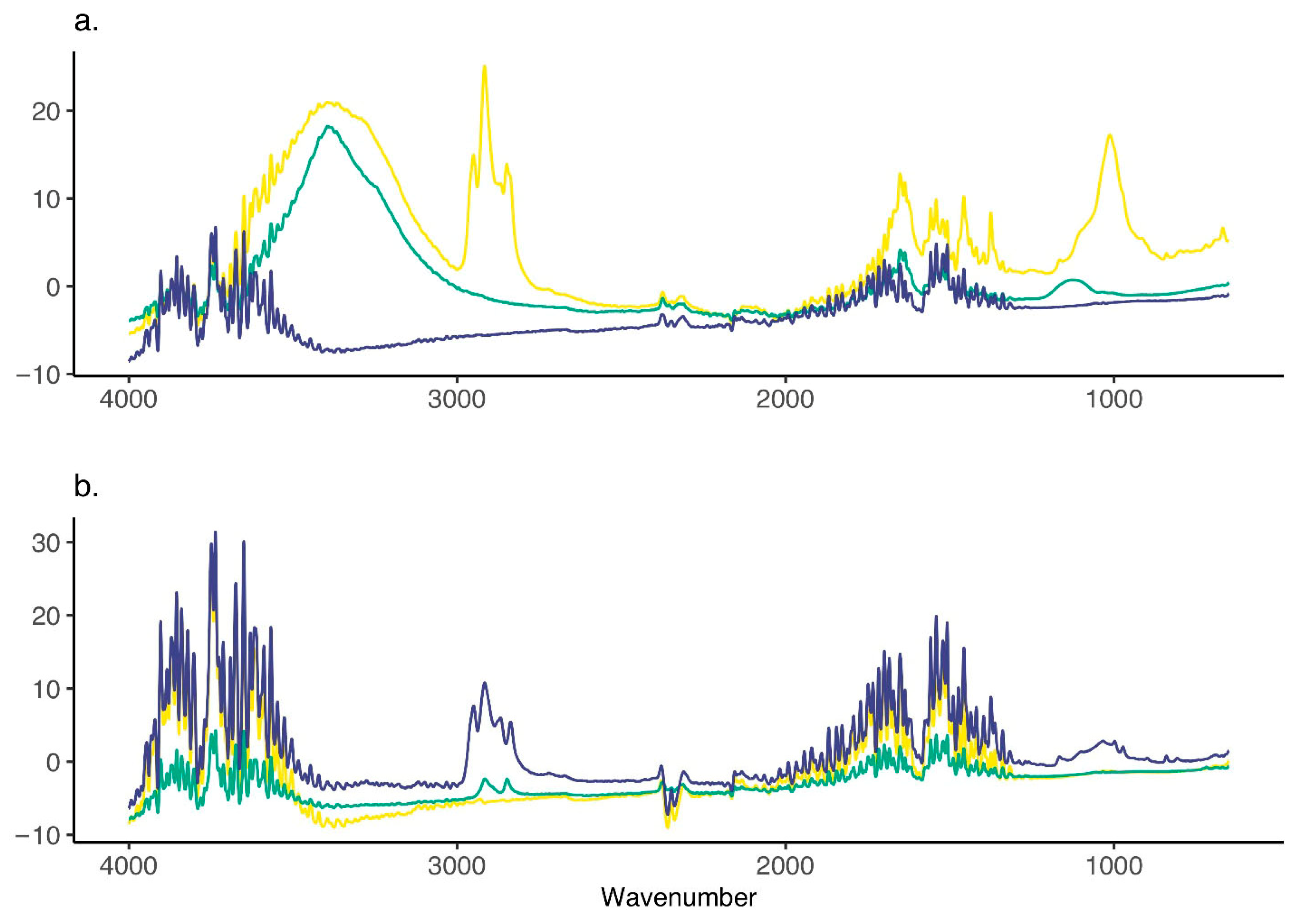
3.5. Chemical Analysis of Microplastics—ATR-FTIR
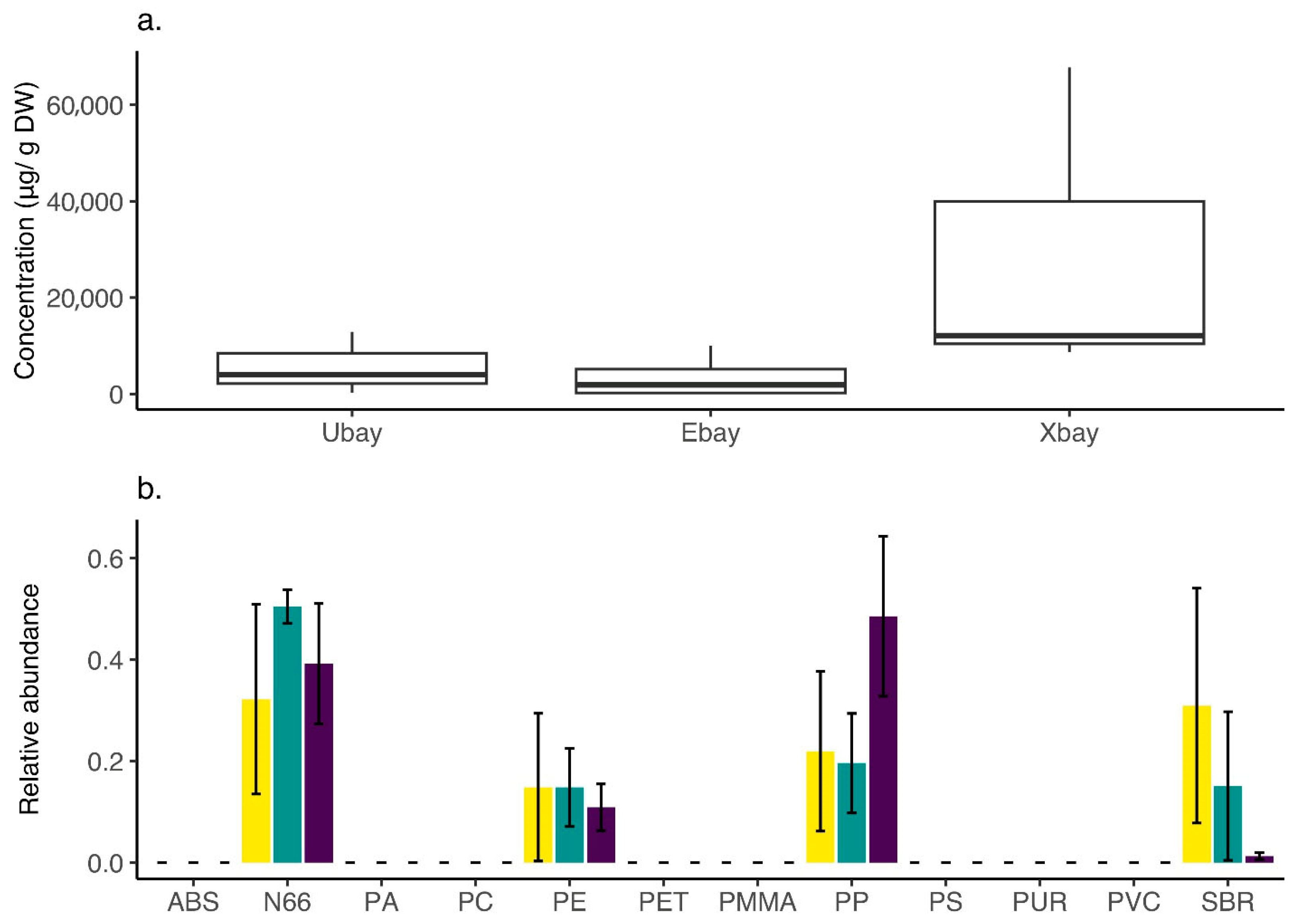
3.6. Chemical Analysis of Microplastics—Py-GCMS/MS
4. Discussion
4.1. Dominant MPs in the Bay and Oysters
4.2. Sources and Sinks of MPs
4.3. Impact on Oyster Health—Condition Index
4.4. Impact on Human Health
4.5. Methods Comparison
4.6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith, K.L., Jr. Plastics on the Sargasso Sea surface. Science 1972, 175, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Hu, Y.B.; Zeng, E.Y.; Guo, Y. Microplastics: A review of analytical methods, occurrence and characteristics in food, and potential toxicities to biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Tahir, A.; Williams, S.L.; Baxa, D.V.; Lam, R.; Miller, J.T.; Teh, F.C.; Werorilangi, S.; Teh, S.J. Anthropogenic debris in seafood: Plastic debris and fibers from textiles in fish and bivalves sold for human consumption. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M. The story of plastic pollution: From the distant ocean gyres to the global policy stage. Oceanography 2020, 33, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.F.; Sun, C.; He, C.; Li, J.; Ju, P.; Li, F. Microplastics in four bivalve species and basis for using bivalves as bioindicators of microplastic pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway, S.E.; Mladinich, K.; Blaschik, N.; Holohan, B.A.; Ward, J.E. A Critical Assessment of Microplastics in Molluscan Shellfish with Recommendations for Experimental Protocols, Animal Husbandry, Publication, and Future Research. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2023, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, U.; Kumari, P.; Ghosh, A.; Sinha, A.; Jena, S.; Kirti, A.; Gupta, A.; Choudhury, A.; Simnani, F.Z.; Nandi, A.; et al. Detrimental consequences of micropolymers associated plasticizers on endocrinal disruption. Mater Today Biol. 2024, 27, 101139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortuza, A.; Meese, E.; Wharton, M.; Ghann, B.; Petersen, L.H.; Quigg, A.; Wells, R.J.; Kaiser, K.; Hala, D. Comparing Persistent (PAHs and PCBs) and Emerging (Nano(Micro)Plastics) Pollutant Body-Burdens in Oysters and Fish from Matagorda Bay (Texas, USA). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 221, 118495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Björn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzle, R.E.; Greene, J.K.; Coen, L.D. Seston removal by natural and constructed intertidal eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) reefs: A comparison with previous laboratory studies, and the value of in situ methods. Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, B.L. Biology of Oysters. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 41, p. 260. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Microplastics in commercial bivalves from China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.N.; Poirier, L.; Pham, Q.T.; Lagarde, F.; Zalouk-Vergnoux, A. Factors influencing the microplastic contamination of bivalves from the French Atlantic coast: Location, season and/or mode of life? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootton, N.; Sarakinis, K.; Varea, R.; Reis-Santos, P.; Gillanders, B.M. Microplastic in oysters: A review of global trends and comparison to southern Australia. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, I.G.; Rouse, D.B. Evaluating Sediment Accretion on a Relic Oyster Reef in Mobile Bay, Alabama. J. Appl. Aquac. 2000, 10, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.L.; Townsend, E.C. Faunal utilization of created intertidal eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) reefs in the southeastern United States. Estuaries 2000, 23, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scyphers, S.B.; Powers, S.P.; Heck, K.L. Ecological Value of Submerged Breakwaters for Habitat Enhancement on a Residential Scale. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, J.H.; Baillie, C.J.; Baukus, A.; Carlyle, R.; Fodrie, F.J.; Gittman, R.K.; Hughes, A.R.; Kimbro, D.L.; Lee, J.; Lenihan, H.S.; et al. Fish and invertebrate use of restored vs. natural oyster reefs in a shallow temperate latitude estuary. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.W.; Brumbaugh, R.D.; Airoldi, L.; Carranza, A.; Coen, L.D.; Crawford, C.; Defeo, O.; Edgar, G.J.; Hancock, B.; Kay, M.C.; et al. Oyster Reefs at Risk and Recommendations for Conservation, Restoration, and Management. BioScience 2011, 61, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, E.V.; Pine III, W.E.; Havens, K.; Kane, A.S.; Walters, C.J.; Irani, T.; Lindsey, A.B.; Morris, J.G. Collapse of a historic oyster fishery: Diagnosing causes and identifying paths toward increased resilience. Ecol. Soc. 2015, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, L.J.; Sacks, P.E.; Bobo, M.Y.; Richardson, D.L.; Coen, L.D. Impact of Hurricanes and Boat Wakes on Intertidal Oyster Reefs in the Indian River Lagoon: Reef Profiles and disease Prevalence. Environ. Restor. 2007, 700, 506–522. [Google Scholar]
- Marenghi, F.; Ashton-Alcox, K.; Wong, R.; Reynolds, B.; Ozbay, G. Dredge efficiency on natural oyster grounds in Delaware Bay and its application in monitoring the Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) stock in Delaware, USA. Fish. Res. 2017, 186, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Park, K.; Jensen, C.; Dellapenna, T.M.; Zhang, W.G.; Shi, Y. Massive oyster kill in Galveston Bay caused by prolonged low-salinity exposure after Hurricane Harvey. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, M.H.; Hackney, A.; Heath, S.A. Intertidal oyster reef mapping and population analysis in west Galveston Bay, Texas. Ecologies 2025, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenihan, H.; Peterson, C. How habitat degradation through fishery disturbance enhances impacts of hypoxia on oyster reefs. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, L.D.; Luckenbach, M.W. Developing success criteria and goals for evaluating oyster reef restoration: Ecological function or resource exploitation? Ecol. Eng. 2000, 15, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona-Hernández, A.; Jurgens, L.J.; Pollack, J.B.; Du, J.; Jensen, C.C.; Quigg, A. Impact of Perkinsus marinus on oyster health: A survey after a regional data gap. J. Shellfish Res. 2025, 44, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigg, A.; Gaona-Hernández, A.; Hochman, M.; Ray, S.M.; Schwarz, J. Applied Time Series Analyses (2000–2017) of Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus (Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic Strains) in the Eastern Oyster. Crassostrea virginica. Bact. 2025, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, C.; Swanson, K.; Weatherall, T.; Cebrian, J. Accumulation and distribution of marine debris on barrier islands across the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Mauro, R.; Kupchik, M.J.; Benfield, M.C. Abundant Plankton-Sized Microplastic Particles in Shelf Waters of the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribic, C.A.; Sheavly, S.B.; Rugg, D.J. Trends in marine debris in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean (1996–2009). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, E.; Du, J.; Park, K.; Kaiser, K. Quantifying the Connectivity of Microplastic Pollution in the Texas–Louisiana Coastal Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. Water 2024, 4, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, J.W.; Guillen, G.; Steinhaus, J.; Cox, E.; Sager, M.; Huette, M. Microplastics in the Galveston Bay Watershed: The Big Impacts of Tiny Pollution, Final Report. (Report No. EIH24-002); Prepared for the Galveston Bay Estuary Program (Contract Number 582-21-10096); Environmental Institute of Houston, University of Houston Clear Lake: Houston, TX, USA, 2024; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie, C.G.; Matsumoto, J.; Solis, R.S. Analysis of the Influence of Water Plan Strategies on Inflows and Salinity in Galveston Bay. In Final Report to the United States Army Corps of Engineers, Contract #R0100010015; Texas Water Development Board: Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Texas Parks and Wildlife Department (TPWD). Bag and Length Limits by Species. 2024. Available online: https://tpwd.texas.gov/regulations/outdoor-annual/fishing/saltwater-fishing/bag-length-limits (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Lawrence, D.R.; Scott, G.I. The Determination and Use of Condition Index of Oysters. Estuaries 1982, 5, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbe, G.R.; Albright, B.W. An improvement to the determination of meat condition index for the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin 1791). J. Shellfish. Res. 2003, 22, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Mercado-Silva, N. Condition index of the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin, 1791) in Sapelo Island Georgia—Effects of site, position on bed and pea crab parasitism. J. Shellfish. Res. 2005, 24, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Hanke, M.H.; Posey, M.H.; Alphin, T.D. The influence of habitat characteristics on intertidal oyster Crassostrea virginica populations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 571, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaut, A.; Hermabessiere, L.; Duflos, G. Current frontiers and recommendations for the study of microplastics in seafood. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaut, A.; Cassone, A.L.; Frere, L.; Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Rinnert, E.; Riviere, G.; Lambert, C.; Soudant, P.; Hubet, A.; et al. Microplastics in seafood: Benchmark protocol for their extraction and characterization. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.F.; Li, J.X.; Sun, C.J.; He, C.F.; Jiang, F.H.; Gao, F.I.; Zheng, L. Separation and identification of microplastics in digestive system of bivalves. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 46, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, C.J.; Hudson, M.D.; Russell, A.E. Evaluation of existing methods to extract microplastics from bivalve tissue: Adapted KOH digestion protocol improves filtration at single digit pore size. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Shim, W.J.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Hong, S.H. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in market bivalves from South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covernton, G.A.; Collicutt, B.; Gurney-Smith, H.J.; Pearce, C.M.; Dower, J.F.; Ross, P.S.; Dudas, S.E. Microplastics in bivalves and their habitat in relation to shellfish aquaculture proximity in coastal British Columbia, Canada. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2019, 11, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.L.; Motti, C.A.; Kroon, F.J. Solving a Sticky Situation: Microplastic Analysis of Lipid-Rich Tissue. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 563565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SigmaAldrich. Polyamide Nylon-6,6. 2025. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/substance/polyamidenylon661234598765 (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- EůP. Nylon 66: A Deep Dive into Properties, Benefits and Uses. 2025. Available online: https://eupegypt.com/blog/plastic-knowledge/nylon-66-properties-benefits-and-applications/ (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Kaeppler, A.; Windrich, F.; Laeder, M.G.; Malanin, M.; Fischer, D.; Labrenz, M.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Voit, B. Identification of microplastics by FTIR and Raman microscopy: A novel silicon filter substrate opens the important spectral range below 1300 cm-1 for FTIR transmission measurements. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6791–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalanathan, M.; Schwehr, K.A.; Bretherton, L.; Genzer, J.; Hillhouse, J.; Xu, C.; Williams, A.; Santschi, P.; Quigg, A. Diagnostic tool to ascertain marine phytoplankton exposure to chemically enhanced water accommodated fraction of oil using Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Friesen, L.W.; Granberg, M.E.; Hassellöv, M.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Magnusson, K. An efficient and gentle enzymatic digestion protocol for the extraction of microplastics from bivalve tissue. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Department of State Health Services (TDSHS). Characterization of Potential Adverse Health Effects Associated with Consuming Fish from Sabine Lake, Texas. 2019. Available online: https://www.dshs.texas.gov/sites/default/files/seafood/PDF2/Risk-Characterization/Sabine-Lake-RC-2010.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2011).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primpke, S.; Wirth, M.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G. Reference database design for the automated analysis of microplastic samples based on Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5131–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baechler, B.R.; Granek, E.F.; Hunter, M.V.; Conn, K.E. Microplastic concentrations in two Oregon bivalve species: Spatial, temporal, and species variability. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2019, 5, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Perez-Guevara, F.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. The current state of microplastic pollution in the world’s largest gulf and its future directions. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, H.R.; Donnelly, M.J.; Walters, L.J. Quantity and types of microplastics in the organic tissues of the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica and Atlantic mud crab Panopeus herbstii from a Florida estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keisling, C.; Harris, R.D.; Blaze, J.; Coffin, J.; Byers, J.E. Low concentrations and low spatial variability of marine microplastics in oysters (Crassostrea virginica) in a rural Georgia estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, T.; Batish, I.; Ovissipour, R. Prevalence of Microplastics in the Eastern Oyster Crassostrea virginica in the Chesapeake Bay: The Impact of Different Digestion Methods on Microplastic Properties. Toxics 2022, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, L.J.; Craig, C.A.; Dark, E.; Wayles, J.; Encomio, V.; Coldren, G.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Fox, D.W.; Zhai, L. Quantifying Spatial and Temporal Trends of Microplastic Pollution in Surface Water and in the Eastern Oyster Crassostrea virginica for a dynamic Florida Estuary. Environments 2022, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Levinton, J.S.; Shumway, S.E.; Cucci, T. Particle sorting in bivalves: In vivo determination of the pallial organs of selection. Mar. Biol. 1998, 131, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Shumway, S.E. Separating the grain from the chaff: Particle selection in suspension- and deposit-feeding bivalves. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 300, 83–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladinich, K.; Holohan, B.A.; Shumway, S.E.; Ward, J.E. The relationship between microplastics in eastern oysters (Crassostrea virginica) and surrounding environmental compartments in Long Island Sound. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 189, 106040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Zhao, S.; Holohan, B.; Mladinich, K.; Griffin, T.; Wozniak, J.; Shumway, S. Selective ingestion and egestion of plastic particles by the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) and eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica): Implications for using bivalves as bioindicators of microplastic pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8776–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.; Williams, L.; Watts, J.E.M.; Hale, M.S.; Couceiro, F.; Preston, J. The plastic Trojan horse: Biofilms increase microplastic uptake in marine filter feeders impacting microbial transfer and organism health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines worldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.A.; Garneau, D.; Sutton, R.; Chu, Y.; Ehmann, K.; Barnes, J.; Fink, P.; Papazissimos, D.; Rogers, D.L. Microplastic pollution is widely detected in US municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibers from domestic washing machines: Effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; O’Brien, S.; Harris, J.M.; Samanipour, S.; Kaserzon, S.; Mueller, J.F.; Galloway, T.; Thomas, K.V. Out of sight but not out of mind: Size fractionation of plastics bioaccumulated by field deployed oysters. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2021, 2, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisco, J.; Jiang, X.; Urias-Quiroz, J.A.; Lu, K.; Xue, J.; Liu, Z. Occurrence, Distribution and Composition of Microplastics in Bays and Estuaries of the Texas Coastal Bend; Report for the Coastal Bend Bays and Estuaries Program; 2025; p. 31. Report prepared by University of Texas Marine Science Institute, TX, USA. Available online: https://www.cbbep.org/manager/wp-content/uploads/2431_FinalReport-1.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Mo, C.; Neilson, B. Standardization of oyster soft tissue dry weight measurements. Water Res. 1994, 28, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; Fraissinet-Tachet, S.; O’Brien, S.; Gallen, M.; Samanipour, S.; Kaserzon, S.; Mueller, J.F.; Galloway, T.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Selected Plastics in High-Commercial-Value Australian Seafood by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 715, 136924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, G.T.; Fernando, H.; Elfrink, C.; Ansari, G.A.S.; Sullivan, J.; Heathman, T.; Quigg, A.; Petronella Croisant, S.; Wade, T.L.; Santschi, P.H. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) cycling and fates in Galveston Bay, Texas, USA. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Emmerik, T.; Mellink, Y.; Hauk, R.; Waldschlager, K.; Schreyers, L. Rivers as plastic reservoirs. Front. Water 2022, 3, 786936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Al Nahian, S.; Madadi, R.; Haider, S.M.B.; De-la-Torre, G.E.; Walker, T.R.; Jonathan, M.P.; Cowger, W.; Khandaker, M.U.; Idris, A.M. Spatiotemporal trends and characteristics of microplastic contamination in a large river-dominated estuary. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2023, 25, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, M.H.; Hargrove, J.M.; Alphin, T.D.; Posey, M.H. Oyster utilization and host variation of the oyster pea crab (Zaops ostreum). J. Shellfish Res. 2015, 34, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, J.S.; Mann, R. A Comparison of Methods for Calculating Condition Index in Eastern Oysters, Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin, 1791). J. Shellfish. Res. 1992, 11, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, S.V.L.; Liddle, C.R.; Atherall, C.A.; Chapman, E.; Watkins, M.; Calaminus, S.D.J.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastics in human blood: Polymer types, concentrations and characterisation using μFTIR. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Song, M. Potential Health Impact of Microplastics: A Review of Environmental Distribution, Human Exposure, and Toxic Effects. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Katsouli, J.; Marczylo, E.L.; Gant, T.W.; Wright, S.; Bernardino de la Serna, J. The potential impacts of micro-and-nano plastics on various organ systems in humans. EBioMedicine 2024, 99, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihart, A.J.; Garcia, M.A.; El Hayek, E.; Liu, R.; Olewine, M.; Kingston, J.D.; Castillo, E.F.; Gullapalli, R.R.; Howard, T.; Bleske, B.; et al. Bioaccumulation of microplastics in decedent human brains. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Cowger, W.; Erdle, L.M.; Coffin, S.; Villarrubia-Gómez, P.; Moore, C.J.; Carpenter, E.J.; Day, R.H.; Thiel, M.; Wilcox, C. A growing plastic smog, now estimated to be over 170 trillion plastic particles afloat in the world’s oceans—Urgent solutions required. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Scholz-Bottcher, B.M. Microplastics analysis in environmental samples—Recent pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method improvements to increase the reliability of mass-related data. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 2489–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Courtene-Jones, W.; Boucher, J.; Pahl, S.; Raubenheimer, K.; Koelmans, A.A. Twenty years of microplastic pollution research—What have we learned? Science 2024, 386, l2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafy, A.; Akter Liza, A.; Nazrul Islam, M.; Morsaline Billah, M.; Tareq Arafat, S.; Moshiur Rahman, M.; Mustafizur Rahman, S. Microplastics Pollution: A Brief Review of Its Source and Abundance in Different Aquatic Ecosystems. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 9, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.G.; Nguyen, N.S.H.; Zhang, T.; Tran, H.-T.; Mukherjee, S.; Naidu, R. A review of microplastic pollution and human health risk assessment: Current knowledge and future outlook. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1606332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdogan, Z.; Guven, B. Microplastics in the environment: A critical review of current understanding and identification of future research needs. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziani, K.; Ioniță-Mîndrican, C.B.; Mititelu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Negrei, C.; Moroșan, E.; Drăgănescu, D.; Preda, O.T. Microplastics: A Real Global Threat for Environment and Food Safety: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients 2023, 25, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadat, A.M.; Emami, S.K.; Hamidifar, H.; Shilsar, M.J.F. Microplastic pollution in water Systems of the Global South: A review. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2026, 276, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Oyster MP Counting | Oyster (Condition Index) | Oyster (Py-GCMS/MS) | Water MP Counting | Water (ATR-FTIR) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trinity Bay (Tbay) | N = 9 | ||||
| Kemah/Seabrook (Ubay) | N = 9 | N = 4 | |||
| Dickinson/Central Bay (Cbay) | N = 10 | N = 9 | N = 2 | ||
| East Bay (Ebay) | N = 36 | N = 20 | N = 10 | N = 9 | |
| West Bay (Wbay) | N = 36 | N = 45 | N = 9 | ||
| Christmas Bay (Xbay) | N = 34 | N = 45 | N = 10 | N = 9 |
| Salinity | Water Temperature (°C) | Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Depth (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trinity Bay (Tbay) | 13.57 ± 0.93 | 22.40 ± 0.20 | 7.25 ± 0.006 | 3.97 ± 0.32 | 2.90 ± 0.15 |
| Kemah/Seabrook (Ubay) | 16.30 ± 1.0 | 19.90 ± 0.10 | 8.32 ± 0.08 | 2.97 ± 0.23 | 3.60 ± 0.06 |
| Dickinson/Central Bay (Cbay) | 16.73 ± 0.47 | 18.17 ± 0.24 | 8.81 ± 0.267 | 2.43 ± 0.57 | 2.76 ± 0.63 |
| East Bay (Ebay) | 20.97 ± 1.13 | 19.87 ± 0.07 | 7.96 ± 0.05 | 4.13 ± 0.33 | 1.78 ± 0.22 |
| West Bay (Wbay) | 21.77 ± 0.17 | 17.50 ± 0.20 | 8.58 ± 0.02 | 4.87 ± 0.12 | 1.50 ± 0.24 |
| Christmas Bay (Xbay) | 24.43 ± 0.07 | 24.00 ± 0.17 | 6.48 ± 0.13 | 4.90 ± 0.67 | 0 ± 0 |
| Water | Oyster Tissues | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Fiber | Film | Fragment | Other | Fiber | Film | Fragment | Other |
| Black | 254 | 2 | 12 | 347 | 8 | 22 | 1 | |
| Blue | 149 | 5 | 75 | 1 | 219 | 8 | 45 | |
| Brown | 2 | 5 | 1 | |||||
| Clear | 609 | 11 | 23 | 3 | 2415 | 57 | 148 | 31 |
| Green | 4 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Gray | 38 | 5 | 64 | 2 | 2 | |||
| Multi | 5 | |||||||
| Orange | 5 | 1 | 10 | |||||
| Pink | 12 | 197 | 28 | 4 | 9 | |||
| Purple | 7 | 8 | ||||||
| Red | 6 | 86 | 11 | 118 | ||||
| Silver | 1 | |||||||
| White | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | |
| Yellow | 7 | 10 | 1 | |||||
| Sampling Site | Location | Material Identified | Pearson’s r |
|---|---|---|---|
| Station 1 | Upper Houston Ship Channel (Ubay) | Polyamide | 0.55 |
| Station 1 | Upper Houston Ship Channel (Ubay) | Polypropylene | 0.71 |
| Station 2 | Morgan’s Point (Ubay) | Polyamide | 0.54 |
| Station 3 | El Jardin (Ubay) | Silicone | 0.61 |
| Station 4 | Seabrook (Ubay) | Polyethylene | 0.55 |
| Station 4 | Seabrook (Ubay) | Ethylene propylene | 0.86 |
| Station 5 | San Leon (Cbay) | Polyethylene terephthalate | 0.53 |
| Station 6 | Texas City (Cbay) | Silica gel | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciesielski, M.; Hanke, M.; Jurgens, L.J.; Kamalanathan, M.; Mortuza, A.; Gahn, M.B.; Hala, D.; Kaiser, K.; Quigg, A. A Comparison of Methods to Quantify Nano- and/or Microplastic (NMPs) Deposition in Wild-Caught Eastern Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) Growing in a Heavily Urbanized, Subtropical Estuary (Galveston Bay, USA). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112065
Ciesielski M, Hanke M, Jurgens LJ, Kamalanathan M, Mortuza A, Gahn MB, Hala D, Kaiser K, Quigg A. A Comparison of Methods to Quantify Nano- and/or Microplastic (NMPs) Deposition in Wild-Caught Eastern Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) Growing in a Heavily Urbanized, Subtropical Estuary (Galveston Bay, USA). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112065
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiesielski, Melissa, Marc Hanke, Laura J. Jurgens, Manoj Kamalanathan, Asif Mortuza, Michael B. Gahn, David Hala, Karl Kaiser, and Antonietta Quigg. 2025. "A Comparison of Methods to Quantify Nano- and/or Microplastic (NMPs) Deposition in Wild-Caught Eastern Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) Growing in a Heavily Urbanized, Subtropical Estuary (Galveston Bay, USA)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112065
APA StyleCiesielski, M., Hanke, M., Jurgens, L. J., Kamalanathan, M., Mortuza, A., Gahn, M. B., Hala, D., Kaiser, K., & Quigg, A. (2025). A Comparison of Methods to Quantify Nano- and/or Microplastic (NMPs) Deposition in Wild-Caught Eastern Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) Growing in a Heavily Urbanized, Subtropical Estuary (Galveston Bay, USA). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112065







