Typhoon Effects on Surface Phytoplankton Biomass Based on Satellite-Derived Chlorophyll-a in the East Sea During Summer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Typhoon Selection
2.2. Data Collection: Satellite and Argo Float
2.3. Estimating the Typhoons’ Impact on the Environment in the East Sea
3. Results
3.1. The Features of Typhoons in the East Sea during Summer
3.2. Chl-a Variability before and after the Typhoons
3.3. Differences in Satellite- and ARGO-Derived SST before and after the Typhoons in the East Sea
4. Discussion
4.1. The Typhoon Effects on Surface Phytoplankton Biomass in the East Sea
4.2. Comparison of the Typhoon Effects Between This Study and Previous Studies
| Location | Typhoon | Chl-a (mg m−3) | Source | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Date | Intensity | Before | After | Change (%) | ||
| Bay of Bengal | Hudhud | Oct 2014 | TC * | 0.15 | 3.6 | 2300 | Giridhkumar et al. [76] |
| North Atlantic Ocean | Michael | Sep 2000 | Normal | 0.08 | 0.14 | 79.9 | Babin et al. [32] |
| South Taiwan, Sea | Kai-Tak | Jul 2000 | Strong | ≤0.1 | 3.2 ± 4.4 | 3100 | Lin et al. [11] |
| South Taiwan, Sea | Damrey | Sep 2005 | Strong | 0.16 | 1.05 | 577 | Zheng and Tang. [77] |
| 0.07 | 0.61 | 771 | Pan et al. [78] | ||||
| Gulf of Mexico | Ivan | Sep 2004 | Very Strong | 0.24 | 0.99 | 312 | Walker et al. [79] |
| South Taiwan, Sea | Parma | Oct 2009 | Very Strong | 0.08 | 0.73 | 812 | Zhao et al. [80] |
| East Sea | Megi | Aug 2004 | Normal | 0.29 | 0.64 | 118 | Son et al. [33] |
| East Sea | Navi | Oct 2013 | Strong | 0.27 | 0.31 | 12 | Jeong [30] |
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, T.; Kim, E.; Lee, M.; Cha, D.H.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.; Boo, K.O. Characteristics of tropical cyclones over the western North Pacific related to extreme ENSO and a climate regime shift in sub-seasonal forecasting with GloSea5. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 61, 2637–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Meteorological Administration. Korea Climate Change Assessment Report. 2020; Korea Meteorological Administration: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2020; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.B.; Jeong, O.J.; Moon, Y.S. The Moving Speed of Typhoons of Recent Years (2018–2020) and Changes in Total Precipitable Water Vapor Around the Korean Peninsula. J. Korean Earth Sci. Soc. 2021, 42, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Meteorological Administration. Typhoon History and Statistics. Available online: https://www.weather.go.kr/w/typhoon/typ-history.do (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Wang, Z.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Wu, H.; Bai, R.; Li, T.; Zhu, B.; Gong, F. Assessing the effect of strong wind events on the transport of particulate organic carbon in the Changjiang River estuary over the last 40 years. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 288, 113477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.L. On the influence of tropical cyclones on the sea surface temperature. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Tropical Meteorology; Hutchings, J.W., Ed.; New Zealand Meteorological Service: Wellington, New Zealand, 1964; pp. 614–622. [Google Scholar]
- Pudov, V.D.; Varfolomeyev, A.A.; Fedorov, K.N. Vertical structure of the wake of a typhoon in the upper ocean. Oceanol. Acad. Sci. USSR 1978, 18, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Taira, K.; Kitagawa, S.; Otobe, H.; Asai, T. Observation of temperature and velocity from a surface buoy moored in the Shikoku Basin (OMLET-88)—An oceanic response to a Typhoon. J. Oceanogr. 1993, 49, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.H. A numerical study of sea surface cooling with the passage of typhoon Abby in the Northwestern Pacific. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. 2008, 41, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.H.; Masuda, A. Temperature Variations in the Mixed Layer with the Passage of Typhoons Using One-Dimensional Numerical Model. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 51, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.; Liu, W.T.; Wu, C.C.; Wong, G.T.F.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, Z.Q.; Liang, W.D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.K. New evidence for enhanced ocean primary production triggered by tropical cyclone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1718–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Liu, C.-T.; Chuang, W.; Yang, Y.; Shiah, F.-K.; Tang, T.; Chung, S. Enhanced buoyancy and hence upwelling of subsurface Kuroshio waters after a typhoon in the southern East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2003, 42, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; He, P.; Xia, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Typical Marine Ecological Disasters in China Attributed to Marine Organisms and Their Significant Insights. Biology 2024, 13, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.W.; Kim, B.S.; Jung, H.K.; Lee, C.I. Distributional Changes in Fishery Resource Diversity Caused by Typhoon Pathways in the East/Japan Sea. Fishes 2023, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.A.; Bonham, P.I.; Swadling, K.M. Phytoplankton blooms in the Huon Estuary, Tasmania: Top-down or bottom-up control? J. Plankton Res. 2008, 7, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinder, V.A.; Popovich, C.A.; Molinero, J.C.; Marcovecchio, J. Phytoplankton summer bloom dynamics in the Bahía Blanca Estuary in relation to changing environmental conditions. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 52, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, Y.-B.; Kang, J.H.; Park, C.H.; Baek, S.H. Seasonal distribution of phytoplankton and environmental factors in the offshore waters of Dokdo: Comparison between 2018 and 2019. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2020, 38, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.G.; Park, J.H. Long-term changes in zooplankton and its relationship with squid, Todarodes pacificus, catch in Japan/East Sea. Fish. Oceanogr. 2002, 11, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yang, E.J.; Kim, K.H.; Shin, C.-W.; Park, J.; Yoo, S.; Hyun, J.-H. Impact of an anticyclonic eddy on the summer nutrient and Chl-a distributions in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Japan Sea). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 69, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-H.; Son, S.; Park, J.-W.; Kwak, J.H.; Kang, C.-K.; Son, Y.B.; Kwon, J.-N.; Lee, S.H. Enhanced biological activity by an anticyclonic warm eddy during early spring in the East Sea (Japan Sea) detected by the geostationary ocean color satellite. Ocean. Sci. J. 2012, 47, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, S.; Aita, M.N.; Tadokoro, K.; Saino, T.; Sugisaki, H.; Nakata, K. From climate regime shifts to lower-trophic level phenology: Synthesis of recent progress in retrospective studies of the western North Pacific. Prog. Oceanogr. 2008, 77, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-R.; Kim, K.; Kang, D.-J.; Park, S.Y.; Park, M.-K.; Kim, Y.-G.; Min, H.S.; Min, D. The East Sea (Japan Sea) in change: A story of dissolved oxygen. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 1999, 33, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, K.-R.; Min, D.-H.; Volkov, Y.; Yoon, J.-H.; Takematsu, M. Warming and structural changes in the East (Japan) Sea: A clue to future changes in global oceans? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3293–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.J.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.-G.; Kim, K.; Kim, K.-R. A moving-boundary box model (MBBM) for oceans in change: An application to the East/Japan Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.T.; Son, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Kang, J.J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Lee, C.I.; Kang, C.K.; Lee, S.H. Long-term pattern of primary productivity in the East/Japan sea based on ocean color data derived from MODIS-Aqua. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Choy, E.J.; Jeong, H.D.; Kim, K.R.; Kang, C.K. Monthly measured primary and new productivities in the Ulleung Basin as a biological “hot spot” in the East/Japan Sea. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4405–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, Y.O.; Sohn, M.H.; Moon, C.H.; Baek, S.H. Seasonal phytoplankton growth and distribution pattern by environmental factor changes in inner and outer bay of Ulsan, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2016, 21, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Li, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, J.; Hu, C.; Chen, D.; Ning, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, C. Changes of temperature and bio-optical properties in the South China Sea in response to Typhoon Lingling, 2001. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, G.; Tan, D.; Huang, P.; Yan, H.; Gao, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; et al. Basin-wide responses of the South China Sea environment to Super Typhoon Mangkhut (2018). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.C. Analysis of ocean color data for observation on the ocean environment change caused by typhoon path. J. Korean Assoc. Geogr. Inf. Stud. 2013, 16, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-K.; Niiler, P. Ocean response to typhoon Rusa in the south sea of Korea and in the East China sea. J. Soc. Oceanogr. Korea 2003, 38, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Babin, S.M.; Carton, J.A.; Dickey, T.D.; Wiggert, J.D. Satellite evidence of hurricane-induced phytoplankton blooms in an oceanic desert. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Platt, T.; Bouman, H.; Lee, D.; Sathyendranath, S. Satellite observation of chlorophyll and nutrients increase induced by typhoon Megi in the Japan/East Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L05607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Mao, Z.; Han, G.; Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Tao, B. Optimal PAR intensity for spring bloom in the northwest Pacific marginal seas. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapiano, M.R.P.; Brown, C.W.; Schollaert, S.; Vargas, M. Establishing a global climatology of marine phytoplankton phenological characteristics. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C08026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Son, S.; Jo, C.O.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Joo, H. Revised chlorophyll-a algorithms for satellite ocean color sensors in the East/Japan Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 60, 102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boss, E.; Siegel, D.A.; Shea, D.M. Carbon-based ocean productivity and phytoplankton physiology from space. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellacicco, M.; Volpe, G.; Colella, S.; Pitarch, J.; Santoleri, R. Influence of photoacclimation on the phytoplankton seasonal cycle in the Mediterranean Sea as seen by satellite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashjian, C.; Arone, R.; Davis, C.; Jones, B.; Kahru, M.; Lee, C.; Mitchell, B.G. Biological structure and seasonality in the Japan/East Sea. Oceanography 2006, 19, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, C.O.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, K.A.; Park, J.J.; Park, M.K.; Li, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.E.; Kim, J.Y.; et al. Spatial distribution of seasonality of SeaWiFS chlorophyll-a concentrations in the East/Japan Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 139, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Saitoh, S.I.; Ishizaka, J.; Isoda, Y.; Kishino, M. Temporal and spatial variability of phytoplankton pigment concentrations in the Japan Sea derived from CZCS images. J. Oceanogr. 2000, 56, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Son, S.; Dahms, H.; Park, J.; Lim, J.; Noh, J.; Kwon, J.; Kang, C. Decadal changes of phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in the East Sea/Sea of Japan. Oceanology 2014, 54, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Ishizaka, J.; Yoo, S.; Kim, H.C.; Chiba, S. Seasonal and interannual variability of sea surface chlorophyll a concentration in the Japan/East (JES). Prog. Oceanogr. 2004, 61, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robusto, C.C. The Cosine-Haversine Formula. Am. Math. Mon. 1957, 64, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ortenzio, F.; Iudicone, D.; de Boyer Montegut, C.; Testor, P.; Antoine, D.; Marullo, S.; Santoleri, R.; Madec, G. Seasonal Variability of the Mixed Layer Depth in the Mediterranean Sea as Derived from In Situ Profiles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L12605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Sprintall, J.; Gille, S.T.; Talley, L. Southern Ocean mixed-layer depth from Argo float profiles. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C06013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, E.; Talley, L.D.; Suga, T. Temporal variability of winter mixed layer in the mid- to high-latitude North Pacific. J. Oceanogr. 2007, 63, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, G.; Qi, Y.; Li, W. Impact of barrier layer on typhoon-induced sea surface cooling. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2011, 52, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.C.; Liu, Q.Y.; Jia, Y.L.; Fan, C.W. Evidence of barrier layer in the Sulu and Celebes Seas. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 3299–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprintall, J.; Tomczak, M. Evidence of the barrier layer in the surface layer of the tropics. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1992, 97, 7305–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pailler, K.; Bourlès, B.; Gouriou, Y. The barrier layer in the western tropical Atlantic Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2069–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Suga, T.; Hanawa, K. Barrier Layers in the Subtropical Gyres of the World’s Oceans. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.H. Introduction to Physical Oceanography; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 135–210. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/160216 (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Mei, W.; Xie, S.-P.; Primeau, F.; McWilliams, J.C.; Pasquero, C. Northwestern Pacific typhoon intensity controlled by changes in ocean temperatures. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltz, G.R.; McPhaden, M.J. The role of oceanic heat advection in the evolutions of tropical north and south Atlantic SST anomalies. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 6122–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, J.; Suh, Y.S.; Park, H.; Chang, K.I.; Kim, K.-R.; Kang, C.-K. Summer primary productivity and phytoplankton community composition driven by different hydrographic structures in the East/Japan Sea and the Western Subarctic Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 4505–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Park, K.-A.; Kang, C.-K.; Kim, G. Satellite-Observed Chlorophyll-a Concentration Variability and Its Relation to Physical Environmental Changes in the East Sea (Japan Sea) from 2003 to 2015. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Jang, C.J.; Oh, I.S.; Park, J.J. Climatology of the mixed layer depth in the East/Japan Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 96–97, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Choy, E.J.; Park, H.J.; Kang, D.J.; Lee, T.; Chang, K., II; Kim, K.R.; Kang, C.K. High primary productivity and f-ratio in summer in the Ulleung basin of the East/Japan Sea. Deep. Sea Res. Part. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2013, 79, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Effects of multiple dynamic processes on chlorophyll variation in the Luzon Strait in summer 2019 based on glider observation. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 41, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, D.J.; Robinson, A.R.; Siegel, D.A.; Jannasch, H.W.; Johnson, R.; Dickeys, T.; McNeil, J.; Michaels, A.F.; Knap, A.H. Influence of mesoscale eddies on new production in the Sargasso Sea. Nature 1998, 394, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, I.-I.; Lee, M.-A.; Chang, J. Effects of cold eddy on phytoplankton production and assemblages in Luzon Strait bordering the South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2007, 63, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.Y.; Zhan, H.G.; Cai, S.Q.; Li, Z.M. Eddy effects on surface chlorophyll in the northern South China Sea: Mechanism investigation and temporal variability analysis. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2016, 112, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Wang, Y.; Xing, X.; Yan, Y.; Xue, H.; Wells, M.; Boss, E. A limited effect of sub-tropical typhoons on phytoplankton dynamics. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Xing, X.; Chai, F.; Yan, X.H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H. Far-field impacts of a super typhoon on upper ocean phytoplankton dynamics. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 643608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F. Upper ocean response to a hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, T.; Morimoto, H.; Igeta, Y.; Ichikawa, T. Macroscale-wide nutrient inversions in the subsurface layer of the Japan Sea during summer. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 7476–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, R.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, D.; Guan, C. An Investigation of Impacts of Surface Waves-Induced Mixing on the Upper Ocean under Typhoon Megi (2010). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Choi, M.S.; Oh, H.Y.; Song, Y.-H.; Noh, J.-H.; Kim, K.H. Seasonal export fluxes of particulate organic carbon from 234Th/238U disequilibrium measurements in the Ulleung basin (Tsushima basin) of the East Sea (Sea of Japan). J. Oceanogr. 2011, 67, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, T.; Lee, T.; Kim, G.; Chang, K.I.; Na, T.; Kim, K.R. Prevailing subsurface chlorophyll maximum (SCM) layer in the East Sea and its relation to the physico-chemical properties of water masses. Ocean. Polar Res. 2012, 34, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevelde, T.; Legendre, L.; Therriault, J.-C.; Demers, S.; Bah, A. Subsurface chlorophyll maximum and hydrodynamics of the water column. J. Mar. Res. 1987, 45, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, J.J. The deep chlorophyll maximum: Comparing vertical profiles of chlorophyll. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 39, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L. The influence of water stability on the vertical structure of a phytoplankton community. Mar. Biol. 1979, 52, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K.; DesAutels, C.; Holloway, C.; Korty, R. Environmental control of tropical cyclone intensity. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 843–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Composite of Typhoon-Induced Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll-a Responses in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2020JC016243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girishkumar, M.S.; Thangaprakash, V.P.; Udaya Bhaskar, T.V.S.; Suprit, K.; Sureshkumar, N.; Baliarsingh, S.K.; Shivaprasad, S. Quantifying tropical cyclone’s effect on the biogeochemical processes using profiling float observations in the Bay of Bengal. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 1945–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Tang, D. Offshore and nearshore chlorophyll increases induced by typhoon winds and subsequent terrestrial rainwater runoff. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 333, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Shi, J.; Gao, H.; Guo, X.; Yao, X.; Gong, X. Contributions of physical and biogeochemical processes to phytoplankton biomass enhancement in the surface and subsurface layers during the passage of Typhoon Damrey. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2017, 122, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.D.; Leben, R.; Balasubramanian, S. Hurricane-forced upwelling and chlorophyllaenhancement within cold-core cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L18610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Han, G.Q.; Zhang, S.W.; Wang, D.X. Two phytoplankton blooms near Luzon Strait generated by lingering Typhoon Parma. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, D. Typhoon-Induced Variability of the Oceanic Surface Mixed Layer Observed by Argo Floats in the Western North Pacific Ocean. Atmos. Ocean. 2012, 50, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Kim, H.J.; Moon, I.J. Seasonal differences in tropical cyclone—Induced sea surface cooling in the western North Pacific. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2024, 150, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.I.; Park, M.O. Time series changes in sea-surface temperature, chlorophyll a, nutrients, and sea-wind in the East/Japan Sea on the left-and right-hand sides of Typhoon Shanshan’s track. Ocean. Sci. J. 2010, 45, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature 2005, 436, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. A case study of the response of northwest Pacific upper ocean to typhoon. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2019, 38, 562–568. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, S.; Ohta, S. Patterns of bottom environments and macrobenthos communities along the depth gradient in the bathyal zone off Sanriku, Northwestern Pacific. J. Oceanogr. 1989, 45, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith Jr, K.L.; Kaufmann, R.S.; Baldwin, R.J.; Carlucci, A.F. Pelagic-benthic coupling in the abyssal eastern North Pacific: An 8-year time-series study of food supply and demand. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooday, A.J.; Pfannkuche, O.; Lambshead, P.J.D. An apparent lack of response by metazoan meiofauna to phytodetritus deposition in bathyal north-eastern Atlantic. J. Mar. Biol. Soc. UK 1996, 76, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L.S. Effects of hurricane Allen on reef fish assemblages near Discovery Bay, Jamaica. Coral Reefs 1983, 2, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kang, S. The status and research direction for fishery resources in the East Sea/Sea of Japan. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Res. 1998, 1, 44–58. [Google Scholar]

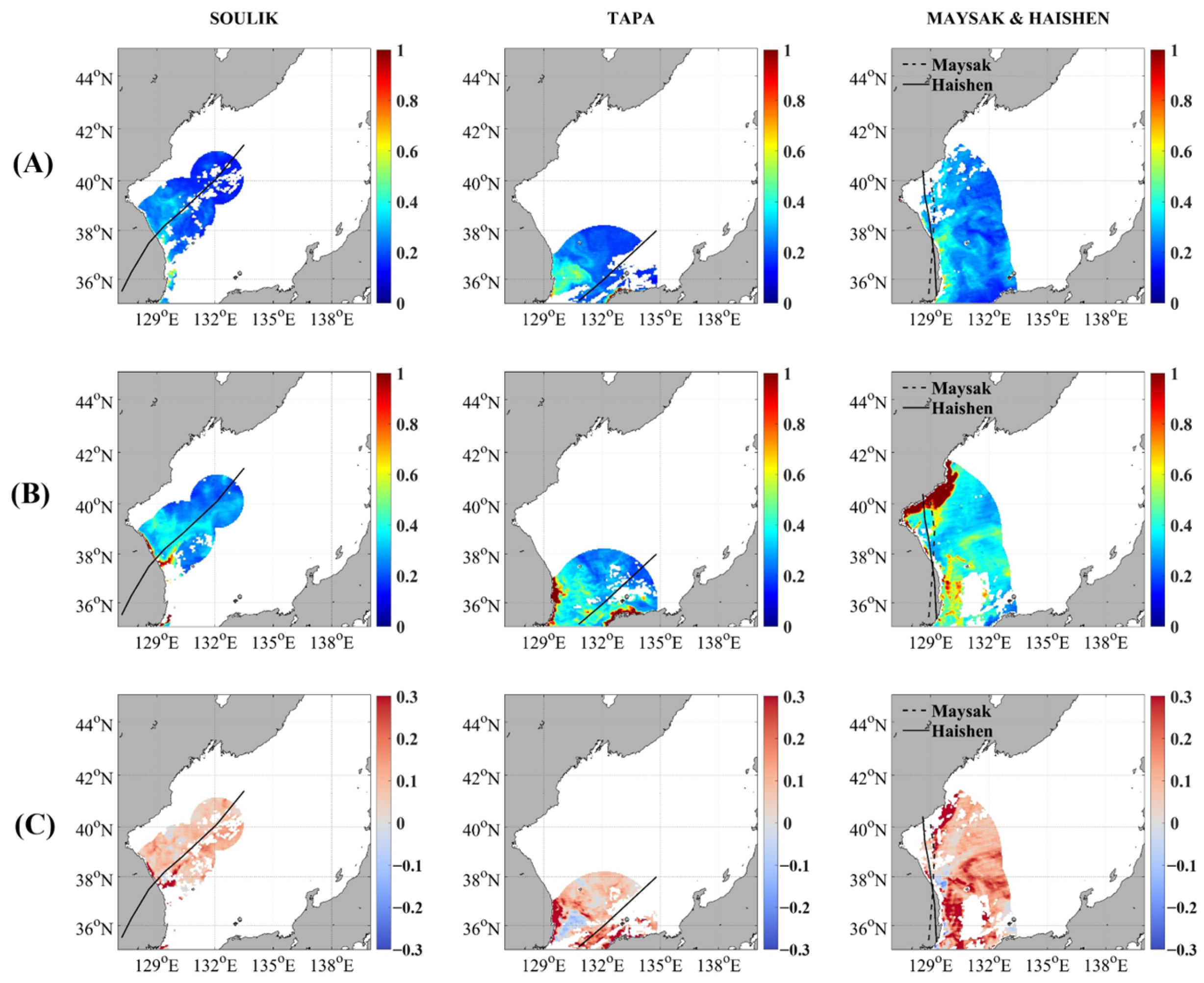
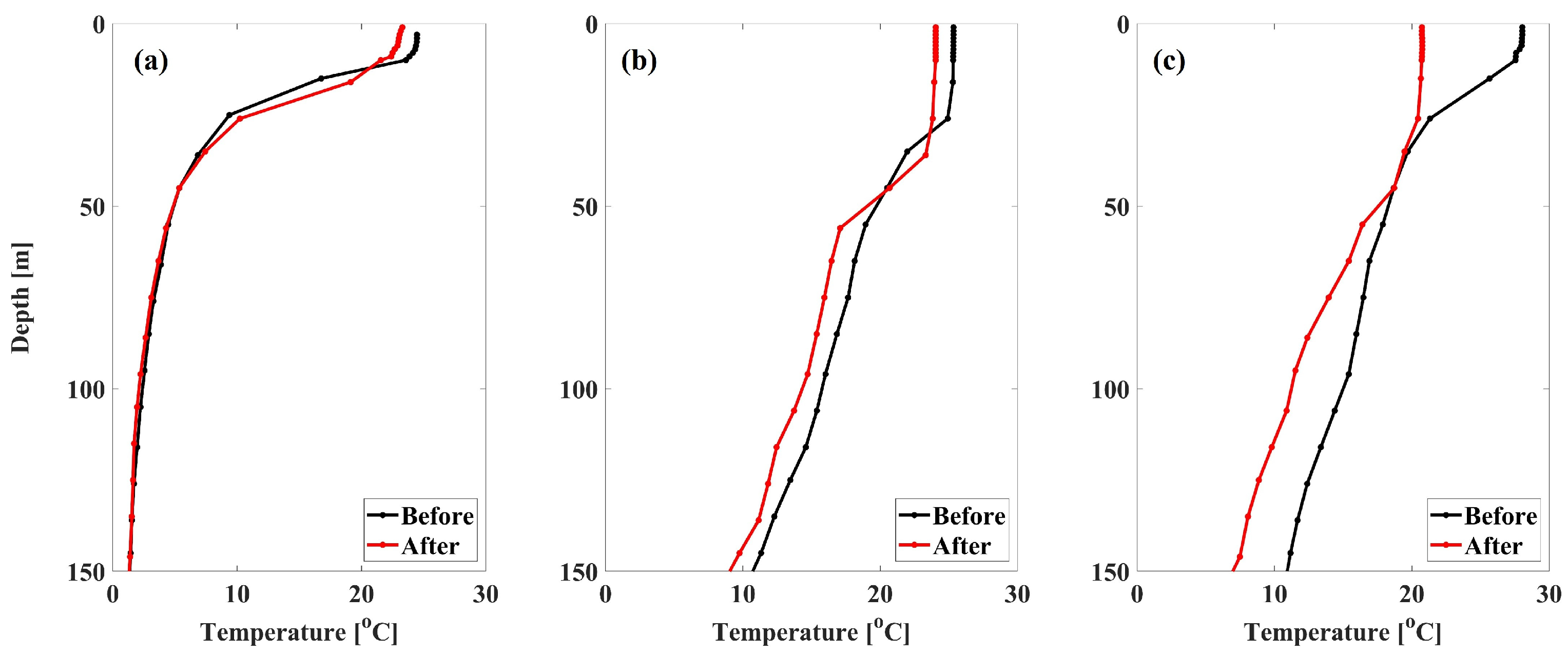
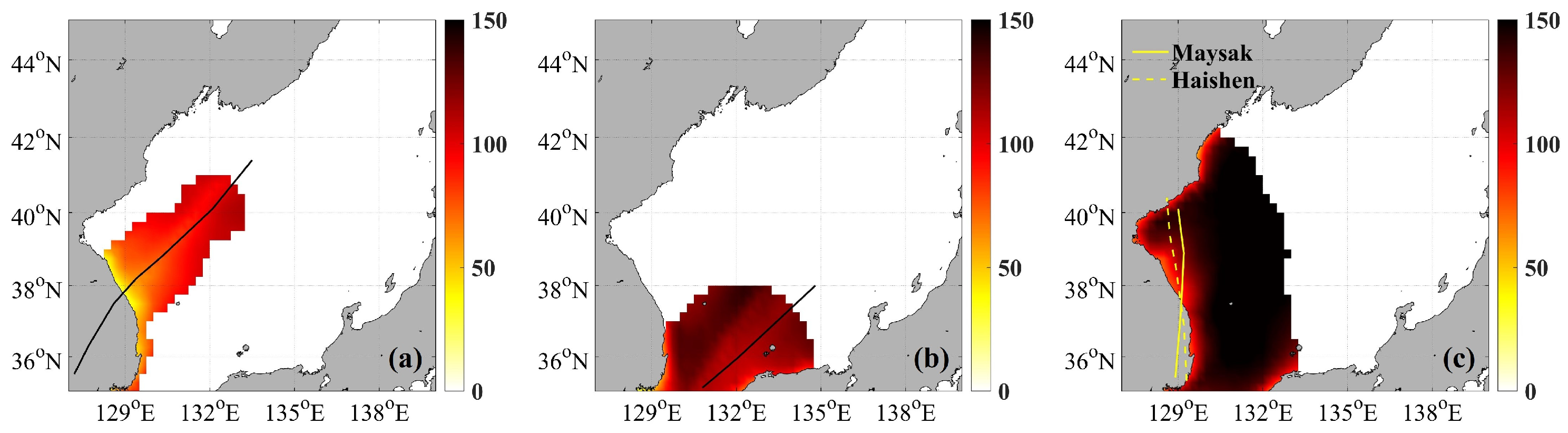
| No. | SOULIK | TAPA | MAYSAK HAISHEN (MH) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float No. | 2901784 | 2901783 | 2901792 | ||
| Date | Typhoon | Entry | 24-August-2018 | 23-September-2019 | 03-September-2020 |
| Exit | 25-August-2018 | 23-September-2019 | 07-September-2020 | ||
| Argo | Before | 23-August-2018 | 19-September-2019 | 29-August-2020 | |
| After | 30-August-2018 | 26-September-2019 | 12-September-2020 | ||
| Location | Before | Latitude (°N) | 38.726 | 36.878 | 36.769 |
| Longitude (°E) | 131.139 | 134.125 | 130.92 | ||
| After | Latitude (°N) | 38.612 | 36.911 | 36.875 | |
| Longitude (°E) | 131.671 | 134.361 | 131.559 | ||
| Name of Typhoon | Typhoon Lifetime | Duration [h] | Track Length [km] | Minimum Center Pressure [hPa] | Maximum Wind Speed [m/s] | Intensity | Missing Ratio of SST (%) | Missing Ratio of Chl-a (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Ocean | ||||||||
| SOULIK | 16 August 2018. 09:00~25 August 2018 03:00 | 24 | 12 | 566 | 985 | 24 | Weak | 4.9 | 15.0 |
| TAPA | 19 September 2019 15:00~23 September 2019 09:00 | 9 | 6 | 481 | 985 | 27 | Normal | 8.8 | 22.0 |
| MH | 28 August 2020 15:00~7 September 2020 21:00 | 21 | 15 | 630 | 955 | 39 | Strong | 11.0 | 17.8 |
| SOULIK | TAPA | MH | Mean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl-a (mg m−3) | Before | 0.22 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.26 |
| After | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.53 | 0.43 | |
| Difference | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.17 | |
| /% | /50.0% | /53.6% | /89.3% | /65.4% | |
| Area | SOULIK | TAPA | MH | Mean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite | Before | Strong wind radius | 25.6 | 25.0 | 25.4 | 25.3 |
| After | 23.7 | 23.4 | 21.2 | 22.8 | ||
| Difference | −1.9 | −1.6 | −4.1 | −2.5 | ||
| Argo float /∆T(DE) | Before | 24.5/17.2 | 25.3/21.2 | 28/17.6 | 26.3/18.7 | |
| After | 23.3/17.3 | 24/20.3 | 20.7/14.8 | 23.7/17.5 | ||
| Difference | −1.2/0.1 | −1.3/−0.9 | −7.3/−2.8 | −2.7/−1.2 | ||
| Category | SOULIK | TAPA | MH | Means |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Ekman Depth (DE) (m): strong wind radius | 67 | 104 | 105 | 92 |
| Variables | Time | SOULIK | TAPA | MH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLD (m) * | Before | 9.9 | 18.4 | 9.9 |
| After | 9.9 | 23.8 | 17.9 | |
| Difference | - | 5.4 | 8.0 | |
| ILD (m) * | Before | 8.6 | 26.2 | 10.0 |
| After | 6.5 | 31.6 | 28.0 | |
| Difference | −1.9 | 5.4 | 18.0 | |
| Barrier layer thickness (m) | Before | - | 7.8 | 0.1 |
| After | - | 7.8 | 10.1 | |
| Difference | - | - | 10.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, H.; Ahn, J.; Kang, J.J.; Hwang, J.D.; Youn, S.; Oh, H.; Joo, H.; Kim, C. Typhoon Effects on Surface Phytoplankton Biomass Based on Satellite-Derived Chlorophyll-a in the East Sea During Summer. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122369
Jung H, Ahn J, Kang JJ, Hwang JD, Youn S, Oh H, Joo H, Kim C. Typhoon Effects on Surface Phytoplankton Biomass Based on Satellite-Derived Chlorophyll-a in the East Sea During Summer. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122369
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, HwaEun, JiSuk Ahn, Jae Joong Kang, Jae Dong Hwang, SeokHyun Youn, HyunJu Oh, HuiTae Joo, and Changsin Kim. 2024. "Typhoon Effects on Surface Phytoplankton Biomass Based on Satellite-Derived Chlorophyll-a in the East Sea During Summer" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122369
APA StyleJung, H., Ahn, J., Kang, J. J., Hwang, J. D., Youn, S., Oh, H., Joo, H., & Kim, C. (2024). Typhoon Effects on Surface Phytoplankton Biomass Based on Satellite-Derived Chlorophyll-a in the East Sea During Summer. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122369







