Assessing the Influence of Typhoons on Salt Intrusion in the Modaomen Estuary within the Pearl River Delta, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. The Model and the Simulations
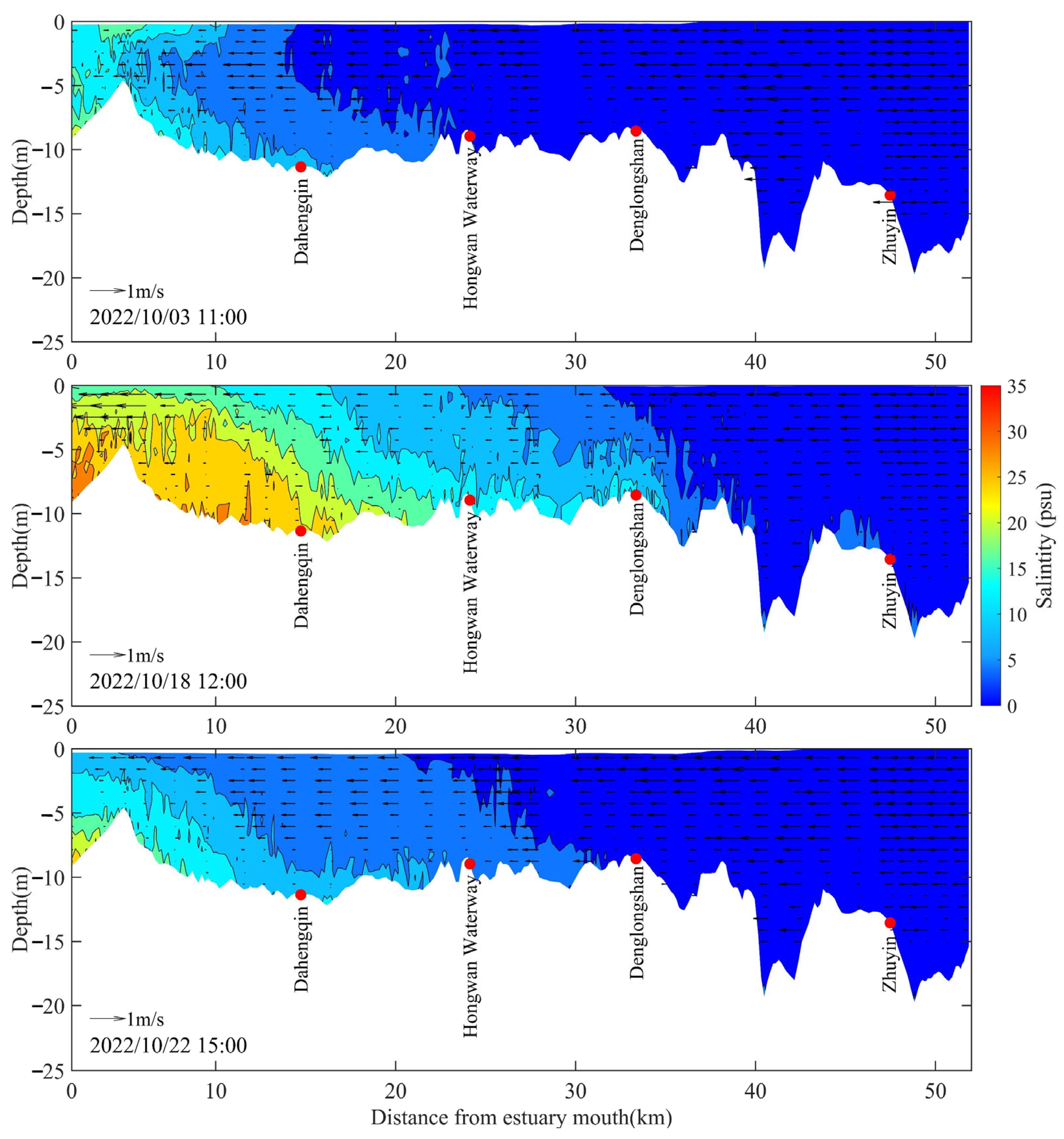
3. Results
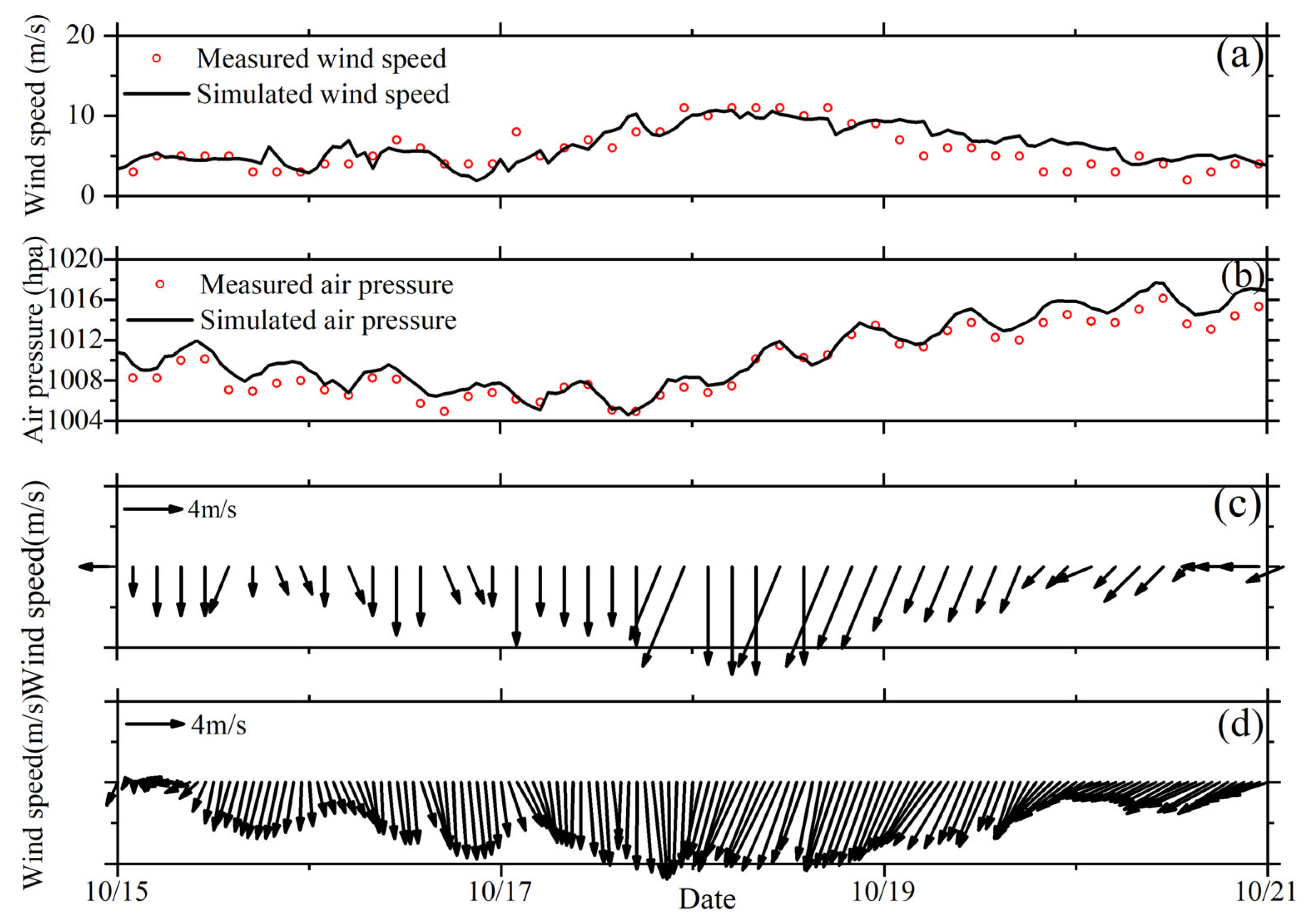
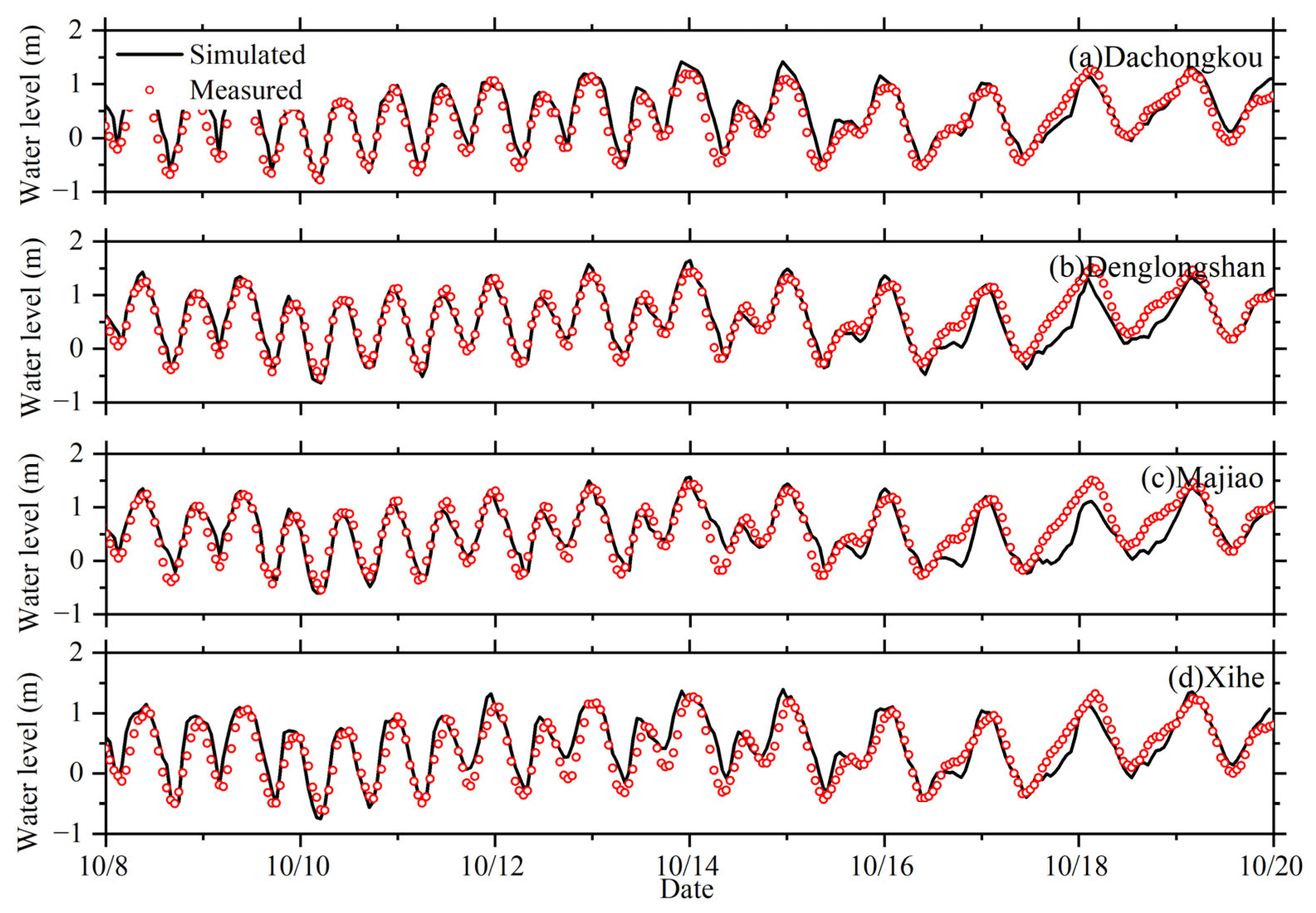
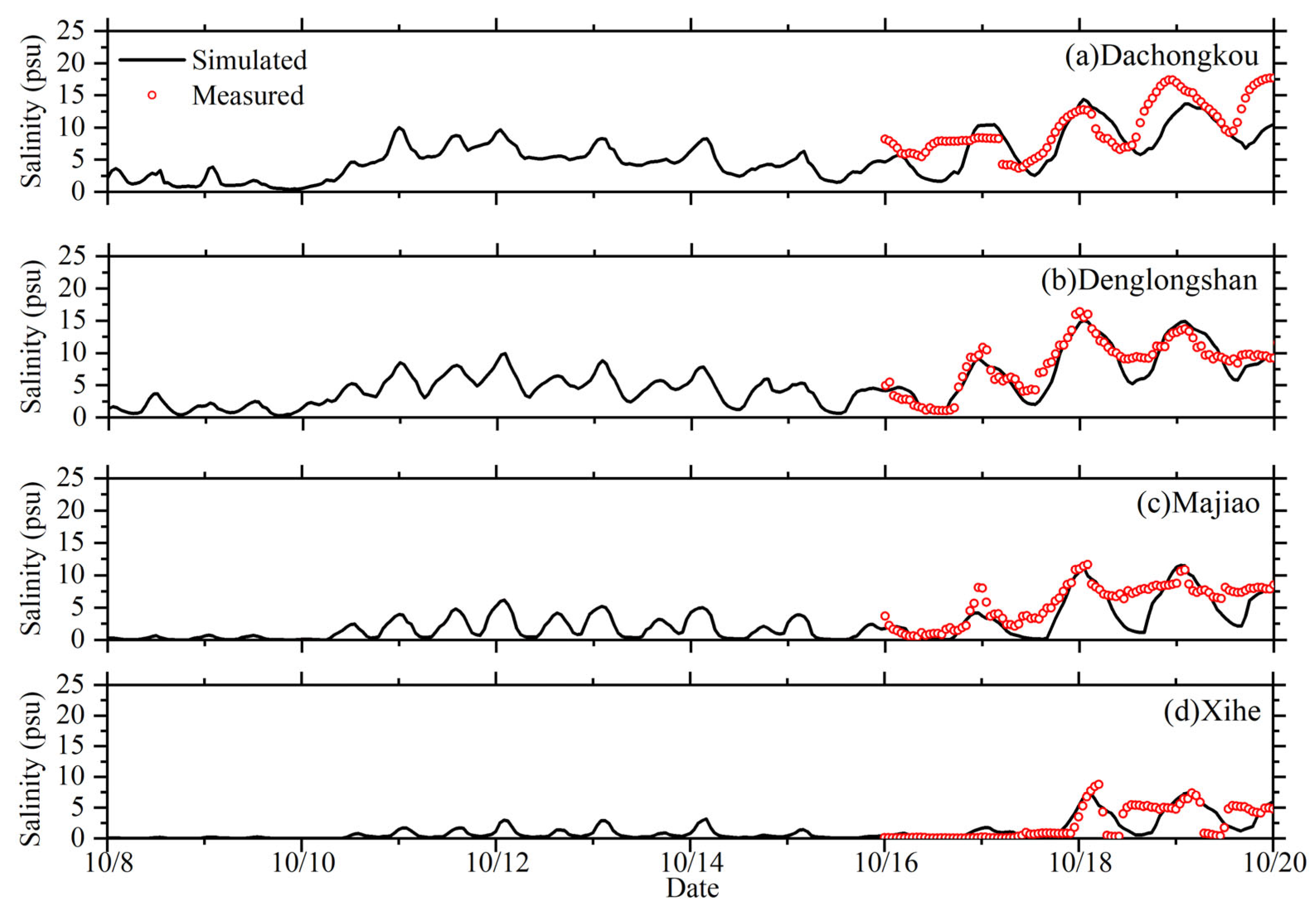
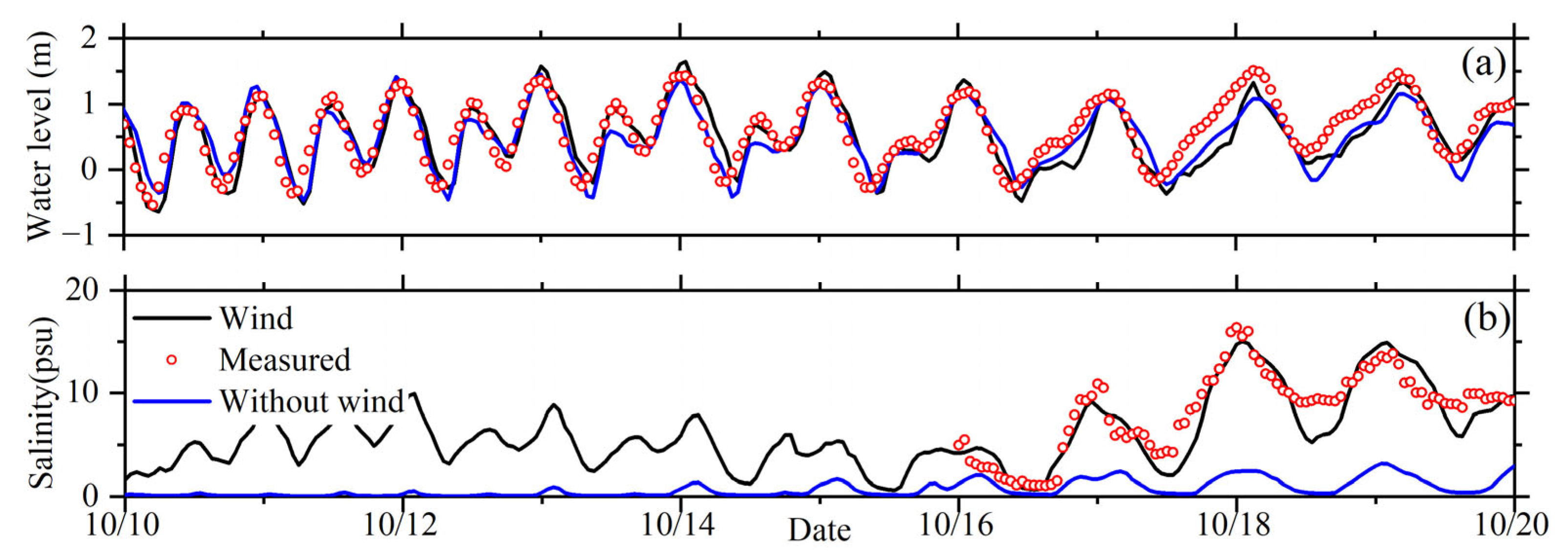
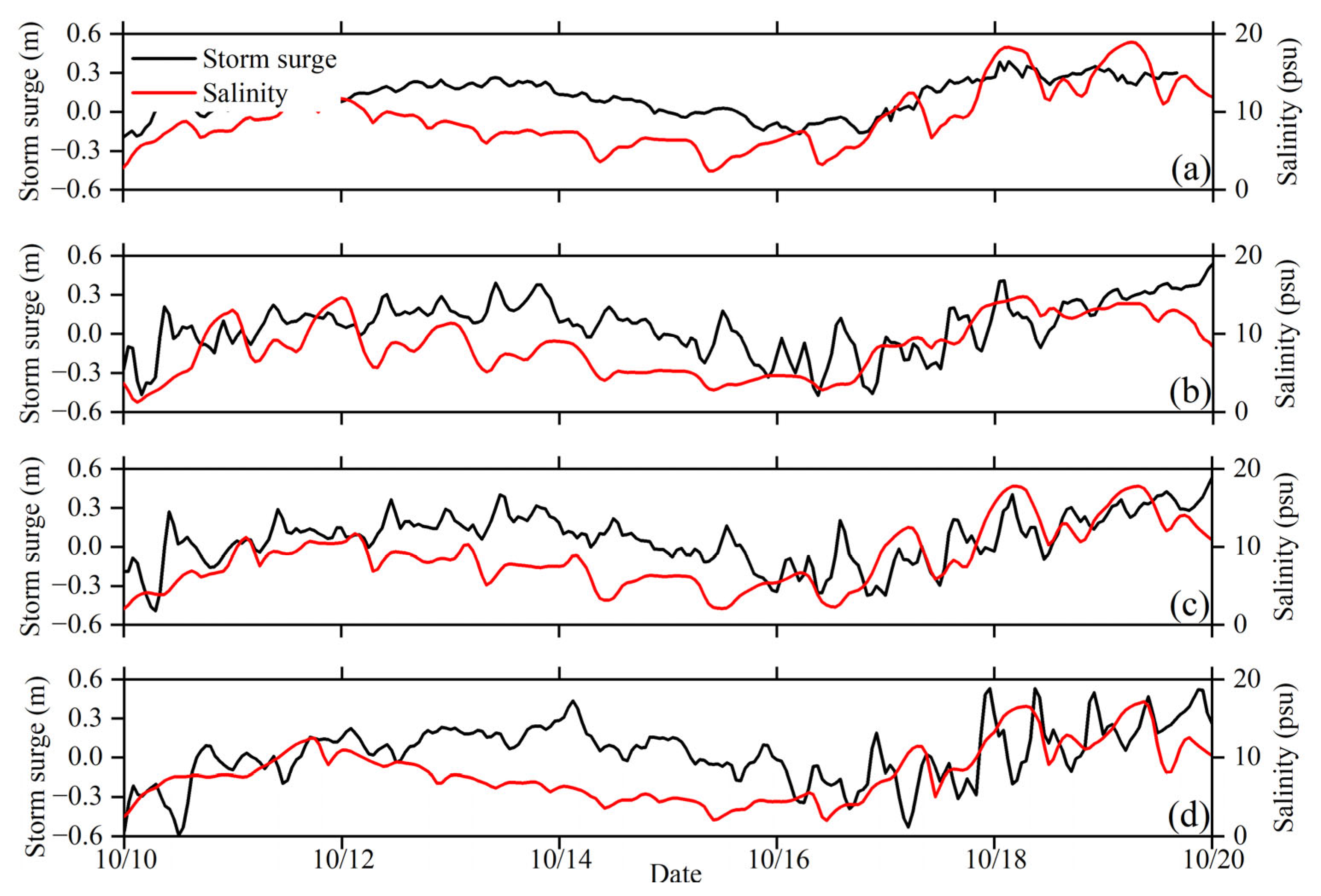
3.1. Model Validation
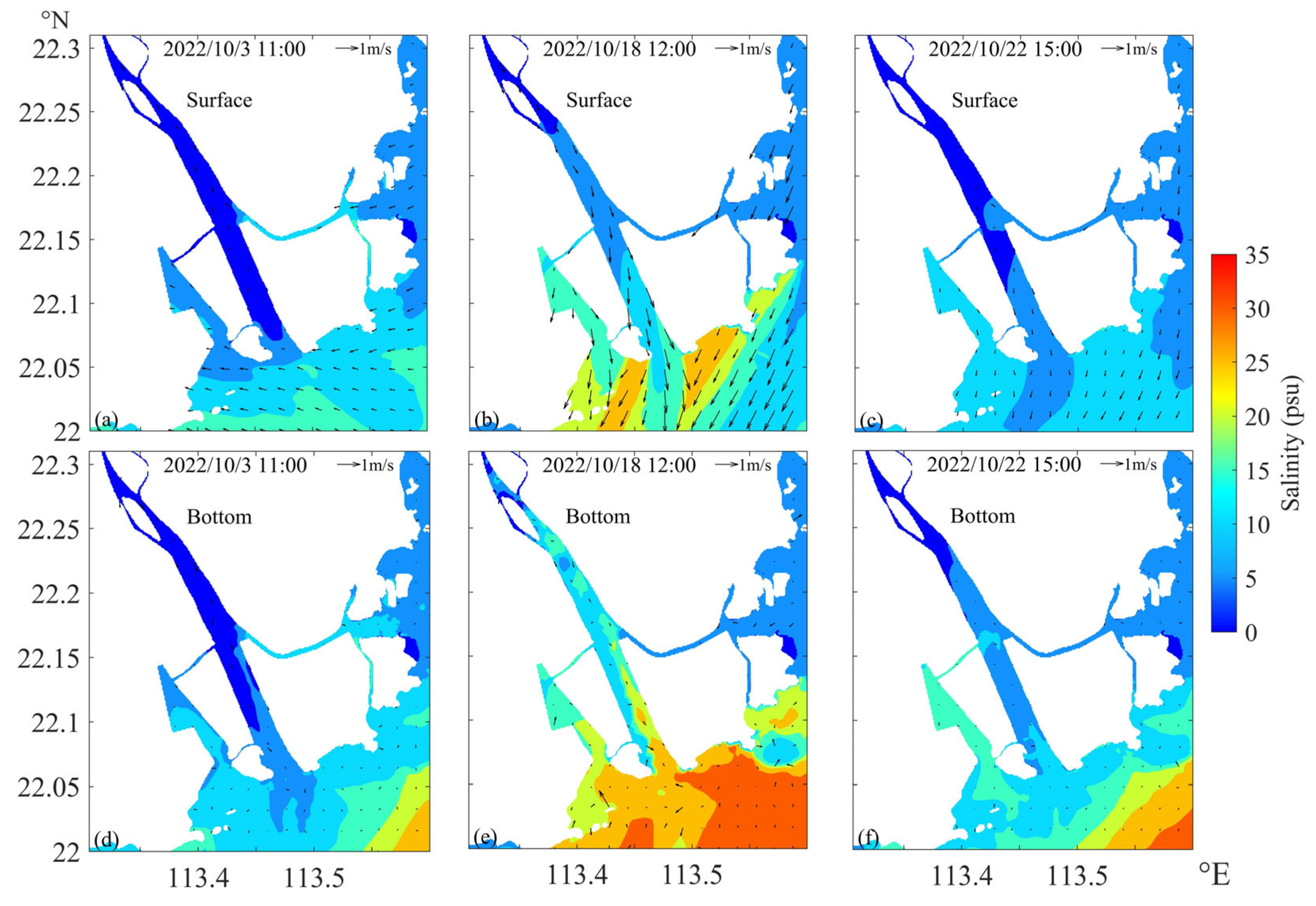
3.2. Modeled Salinity under Typhoon Nesat
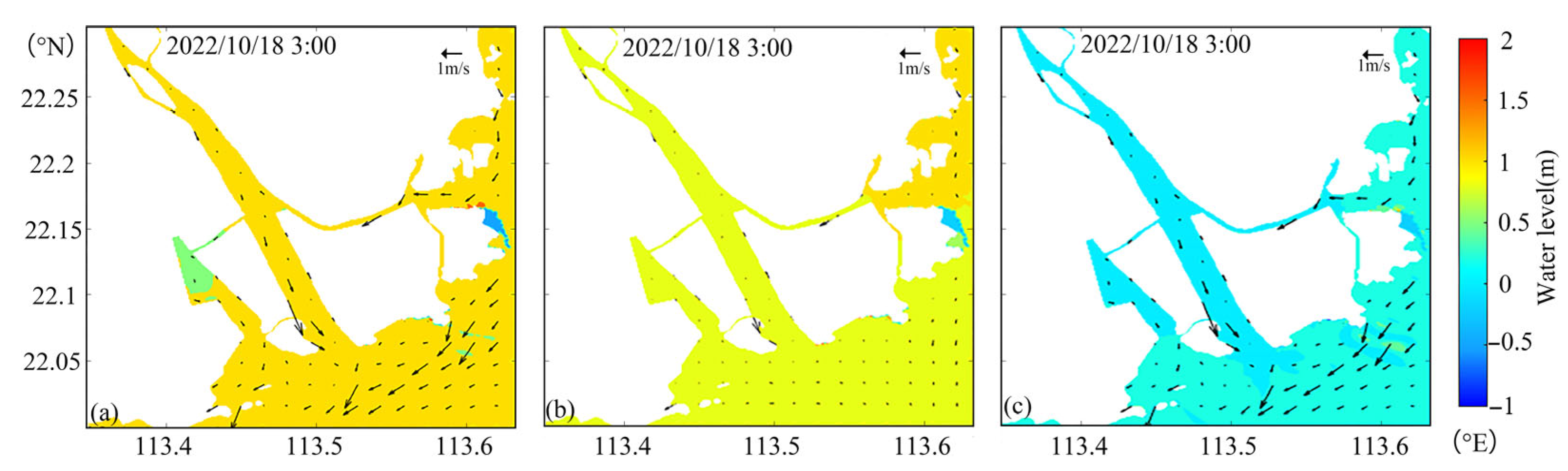
3.3. Impacts of Typhoon Winds on Salt Intrusion
4. Discussion
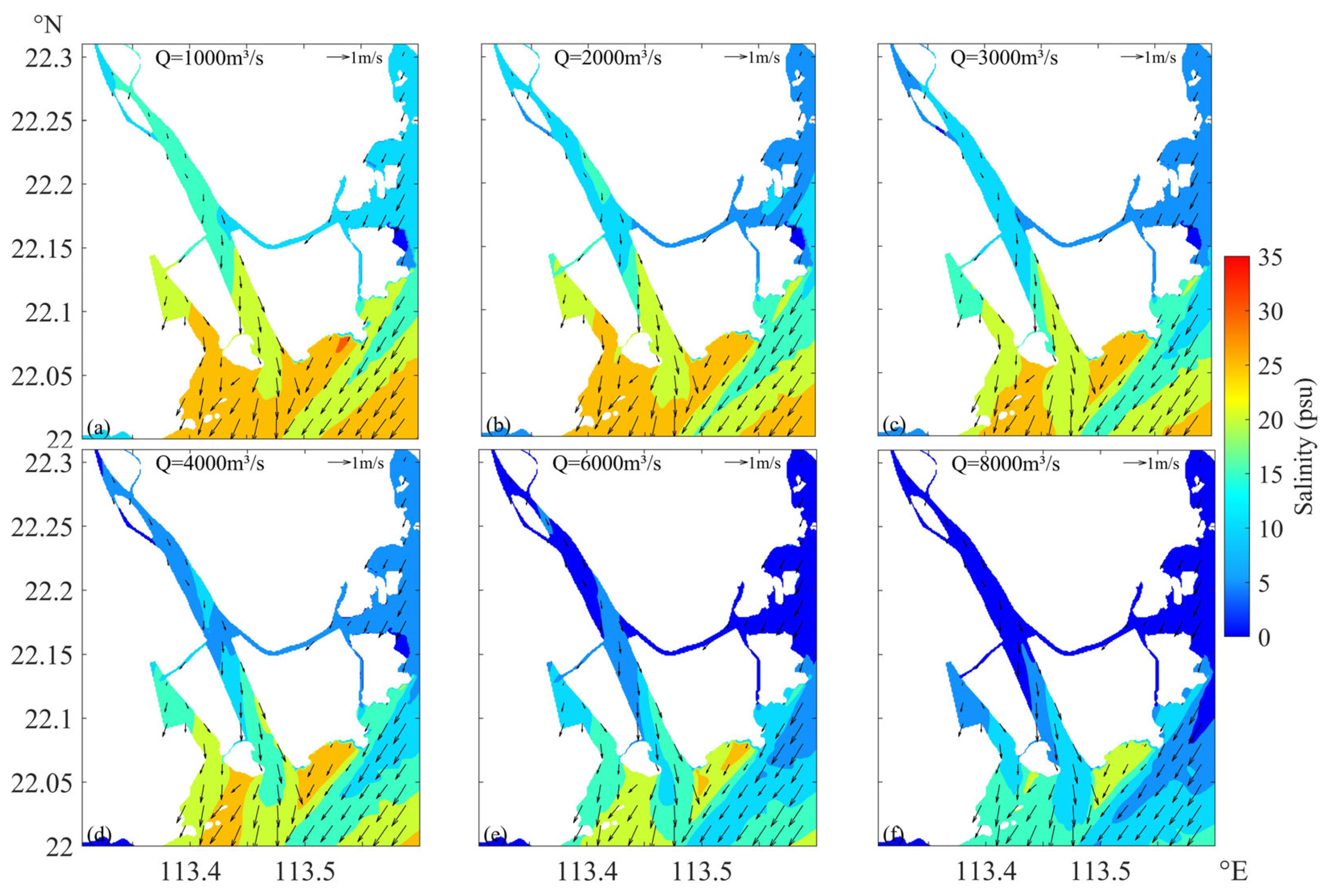
4.1. Effects of River Discharge
4.2. Effects of Tide
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quang, N.; Sasaki, J.; Higa, H.; Huan, N.H. Spatiotemporal variation of turbidity based on Landsat 8 OLI in Cam Ranh Bay and Thuy Trieu Lagoon, Vietnam. Water 2017, 9, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, N.; Ngoc, P.K.; Sasaki, J. Study on the variation of bed shear stress by using swan model in Cam Ranh Bay and Thuy Trieu Lagoon. Vietnam. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2017, 17, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, L.; Wu, H.; Gu, J.; Lyu, H. Dynamic mechanism of an extremely severe saltwater intrusion in the Changjiang estuary in February 2014. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 5043–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoitink, A.J.F.; Jay, D.A. Tidal river dynamics: Implications for deltas. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 240–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellafiore, D.; Ferrarin, C.; Maicu, F.; Manfè, G.; Lorenzetti, G.; Umgiesser, G.; Zaggia, L.; Levinson, A.V. Saltwater intrusion in a mediterranean delta under a changing climate. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean 2021, 126, e2020JC016437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Geyer, W.R. Response to channel deepening of the salinity intrusion, estuarine circulation, and stratification in an Urbanized estuary. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2019, 124, 4784–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R. Factors controlling saltwater intrusion across multi-time scales in estuaries, Chester River, Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 223, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.Y.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Yang, Q.S.; Ou, S.Y.; Lei, Y.P. Influence of river discharge and dredging on tidal wave propagation: Modaomen estuary case. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 138, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCready, P.; Geyer, R.W. Advances in estuarine physics. Ann. Rev. Mar Sci. 2010, 2, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.W.; Hoitink, A.J.F.; Zheng, J.; Kstner, K.; Zhang, W. Analytical model captures intratidal variation in salinity in a convergent, well-mixed estuary. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4309–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monismith, S.G.; Kimmerer, W.; Burau, J.R.; Stacey, M.T. Structure and flow-induced variability of the subtidal salinity field in northern San Francisco Bay. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 3003–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Park, K. A modeling study of water and salt exchange for a micro-tidal, stratified northern Gulf of Mexico estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 96–97, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M. Wind-driven lateral circulation in a stratified estuary and its effects on the along-channel flow. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C09005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E.; Friedrichs, C.; Brubaker, J. Control of estuarine stratification and mixing by wind-induced straining of the estuarine density field. Estuaries 2005, 28, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Sanford, L.P. Axial wind effects on stratification and longitudinal salt transport in an idealized, partially mixed estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 1905–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savenije, H.H.G. Salinity and Tides in Alluvial Estuaries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Valentine, J.R.; Sklenar, S.; Weis, K.R.; Dardeau, M.R. The effects of Hurricane Ivan in the inner part of Mobile Bay, Alabama. J. Coast. Res. 2007, 23, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhong, L.J.; Boicourt, W.C.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, D.L. Hurricane-induced storm surges, currents and destratification in a semi-enclosed bay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, D.A.; Uncles, R.J.; Largier, J.; Geyer, W.R.; Vallino, J.; Boynton, W.R. A review of recent developments in estuarine scalar flux estimation. Estuaries 1997, 20, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncles, R.J. Estuarine physical processes research: Some recent studies and progress. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 829–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, D.W. Observation of circulation in coastal plain estuaries. In Estuaries; Lauff, G.H., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Twigt, D.J.; Goede, E.D.; Zijl, F.; Schwanenberg, D.; Chiu, A.Y.W. Coupled 1D–3D hydrodynamic modelling, with application to the Pearl River Delta. Ocean. Dyn. 2009, 59, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, Y.X.; Zheng, J.H.; Li, L.; Dong, X.; Cai, H.J. Temporal and spatial variability of annual extreme water level in the Pearl River Delta region, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 69, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.J.; Yan, S.L.; Chen, X.; Lian, Y.; Xin, Y. Wavelet analysis of the dynamic characteristic of saltwater intrusion- A case study in the Pearl River Estuary of China. Ocean Coast Manag. 2014, 95, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.P.; Lin, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.Z.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, H. Effect of winds and waves on salt intrusion in the Pearl River estuary. Ocean Sci. 2018, 14, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Wang, C.N.; Pareja‐Roman, L.F.; Zhu, J.R.; Chant, R.J.; Wang, G.H. Effects of typhoon on saltwater intrusion in a high discharge estuary. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2022, 127, e2021JC018206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.P.; Shen, J. The response of salt intrusion to changes in river discharge and tidal mixing during the dry season in the Modaomen Estuary, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 769–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Dee, D. ERA5 reanalysis is in production. In ECMWF Newsletter No. 147; Lentze, G., Ed.; European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): Reading, UK, 2016; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.P.; Lin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, H.Y. The response of salt intrusion to changes in river discharge, tidal range, and winds, based on wavelet analysis in the Modaomen China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 219, 106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.J.; Ye, F.; Stanev, E.V.; Grahorn, S. Seamless cross-scale modelling with SCHISM. Ocean Model. 2016, 102, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Erofeeva, S.Y. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.I.; Somerfield, P.J.; Gilbert, F.J. Quantifying uncertainty in high-resolution coupled hydrodynamic-ecosystem models. J. Mar. Syst. 2006, 64, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

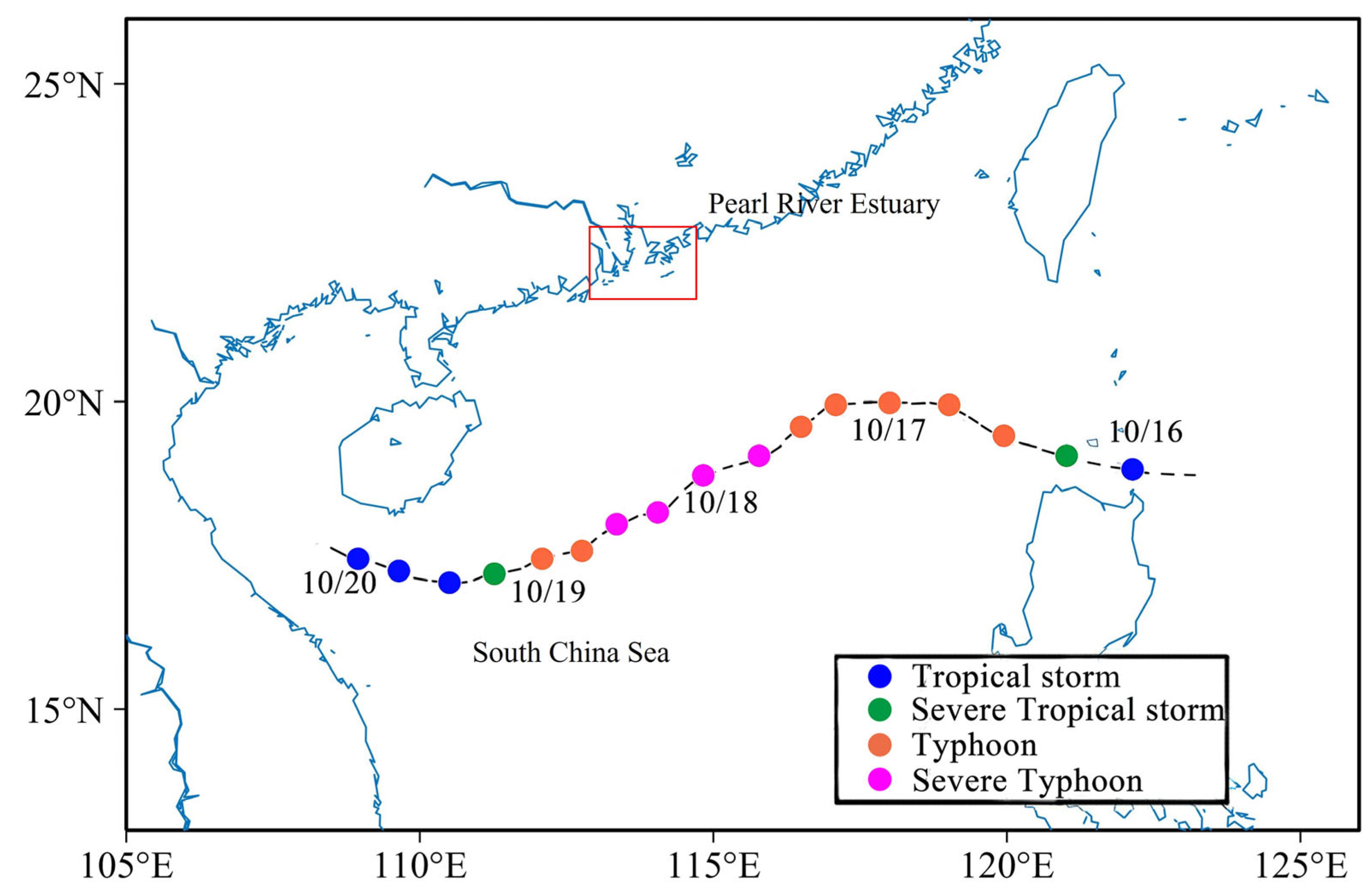
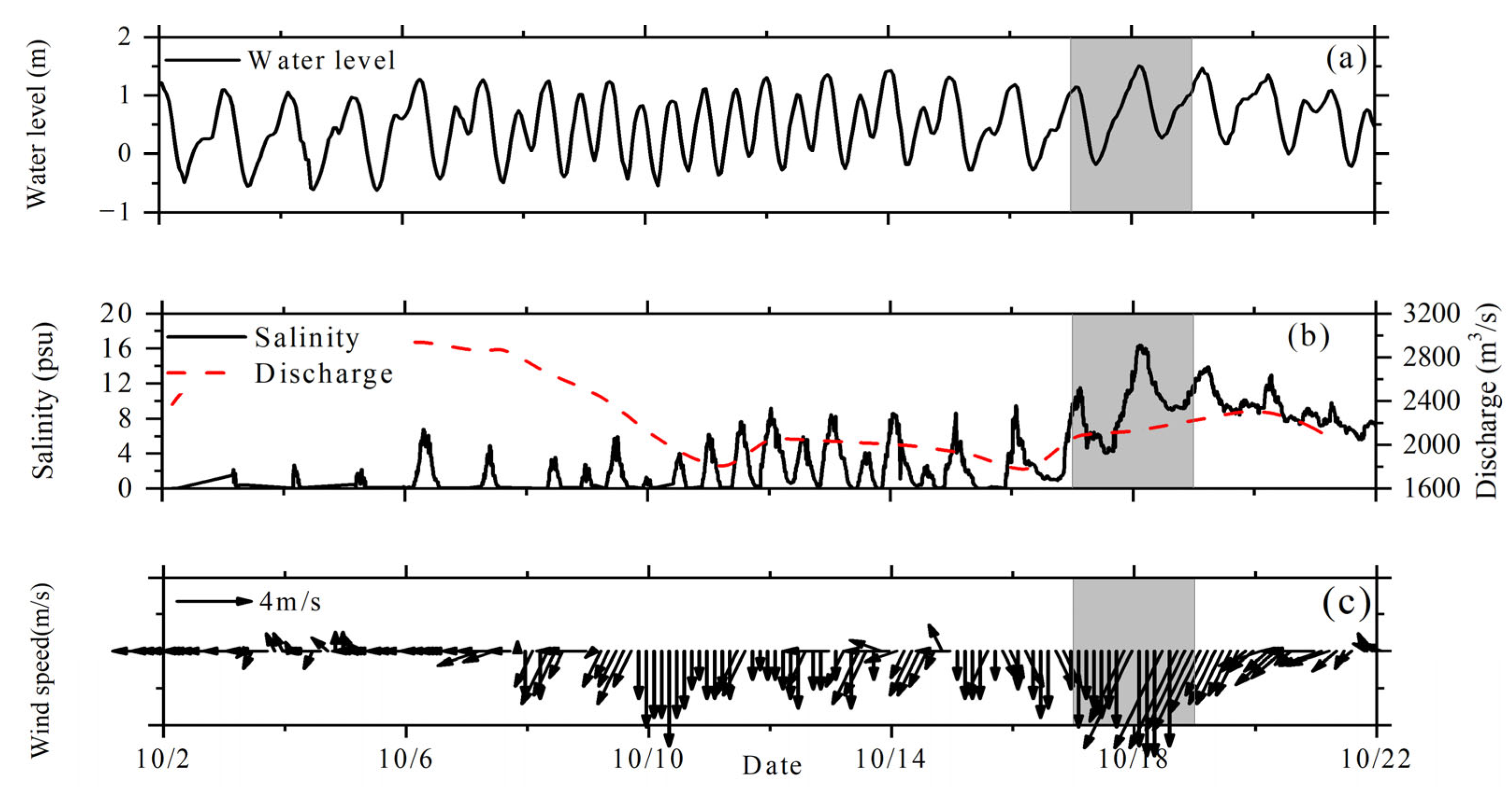
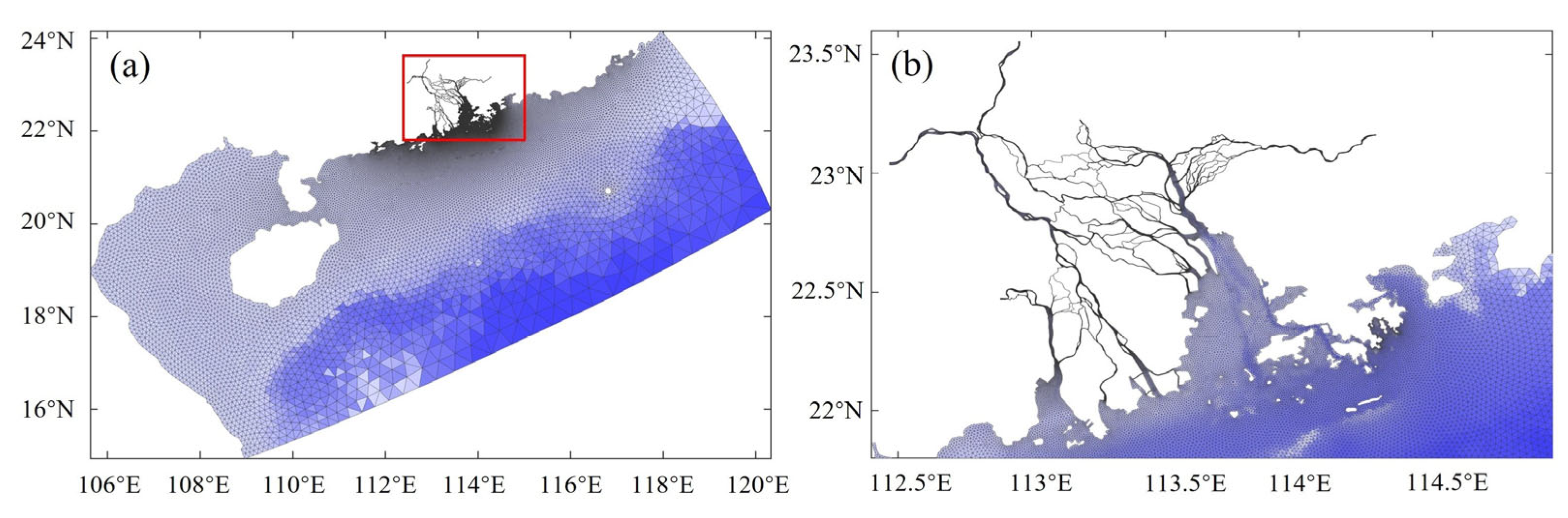
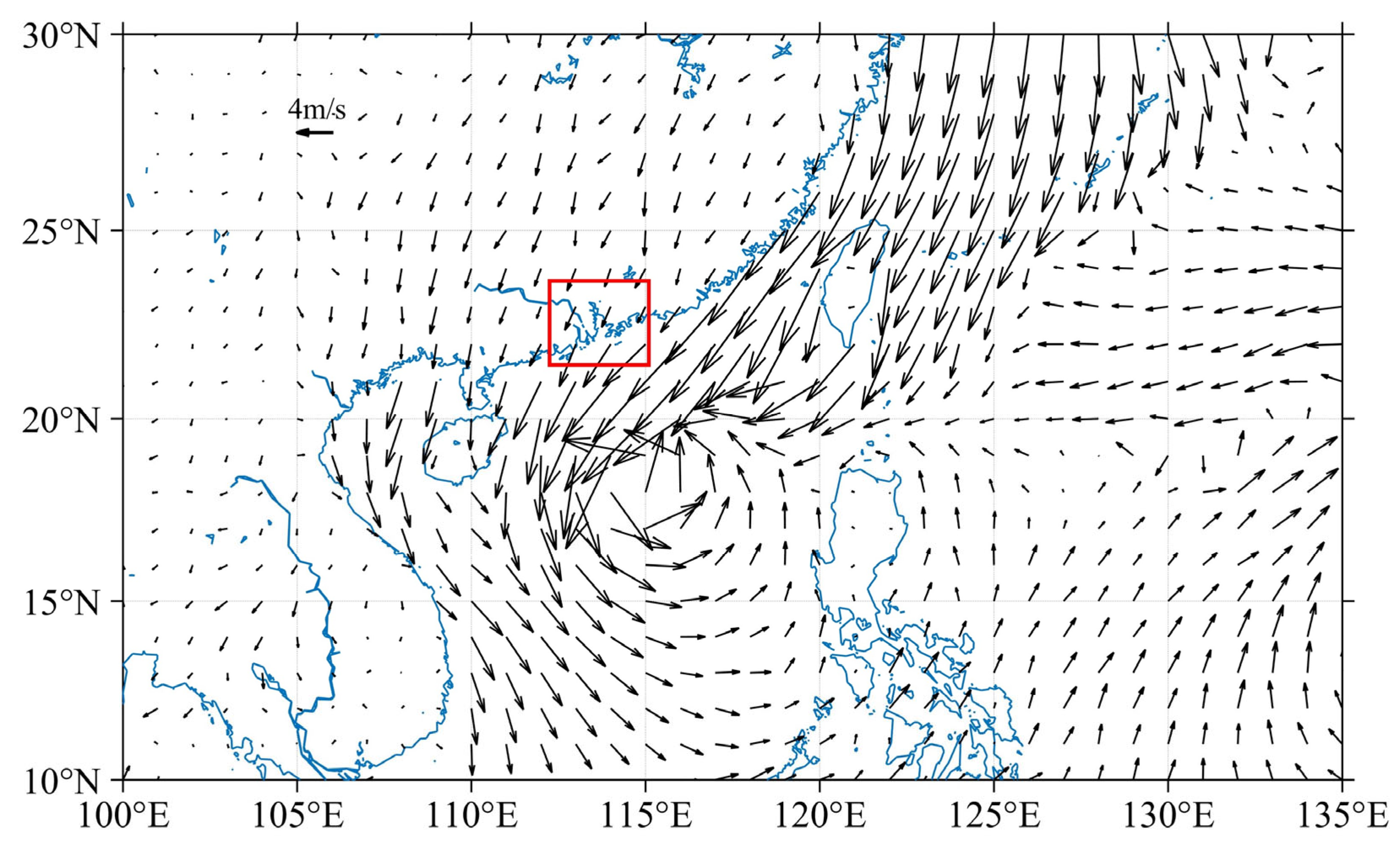


| Run Case | River Discharge (m3/s) | Tides | Wind | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaoyao Station | Shijiao Station | Total | |||
| Case 1 | Real-time Monitoring Data | Neap tide (TR * 1.26 m) | Typhoon Nesat | ||
| Case 2 | Real-time Monitoring Data | Neap tide | No wind | ||
| Case 3 | 875 | 125 | 1000 | Neap tide | Typhoon Nesat |
| Case 4 | 1750 | 250 | 2000 | Neap tide | Typhoon Nesat |
| Case 5 | 2625 | 375 | 3000 | Neap tide | Typhoon Nesat |
| Case 6 | 3500 | 500 | 4000 | Neap tide | Typhoon Nesat |
| Case 7 | 5250 | 750 | 6000 | Neap tide | Typhoon Nesat |
| Case 8 | 7000 | 1000 | 8000 | Neap tide | Typhoon Nesat |
| Case 9 | Real-time Monitoring Data | Intermediate tide after spring tide (TR 1.47 m) | Typhoon Nesat | ||
| Case 10 | Real-time Monitoring Data | Intermediate tide after neap tide (TR 1.30 m) | Typhoon Nesat | ||
| Case 11 | Real-time Monitoring Data | Spring tide (TR 1.97 m) | Typhoon Nesat | ||
| Station | RMSE | SS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Level (m) | Salinity (psu) | Water Level | Salinity | |
| Xihe | 0.17 | 2.18 | 0.90 | 0.72 |
| Majiao | 0.21 | 2.57 | 0.77 | 0.65 |
| Denglongshan | 0.18 | 1.87 | 0.86 | 0.82 |
| Dachongkou | 0.22 | 3.04 | 0.73 | 0.57 |
| Station | Discharge in October (m3/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Mean | |
| Gaoyao (in West River) | 10,659 | 1847 | 4841 |
| Shijiao (in North River) | 1119 | 242 | 640 |
| Total | 11,662 | 2155 | 5482 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, H.; Yang, J.; Liang, J.; Ji, X. Assessing the Influence of Typhoons on Salt Intrusion in the Modaomen Estuary within the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010022
Yang F, Xu Y, Zhang W, Zou H, Yang J, Liang J, Ji X. Assessing the Influence of Typhoons on Salt Intrusion in the Modaomen Estuary within the Pearl River Delta, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fang, Yanwen Xu, Wei Zhang, Huazhi Zou, Jie Yang, Jingxi Liang, and Xiaomei Ji. 2024. "Assessing the Influence of Typhoons on Salt Intrusion in the Modaomen Estuary within the Pearl River Delta, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010022
APA StyleYang, F., Xu, Y., Zhang, W., Zou, H., Yang, J., Liang, J., & Ji, X. (2024). Assessing the Influence of Typhoons on Salt Intrusion in the Modaomen Estuary within the Pearl River Delta, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010022






