Monitoring Non-Indigenous Species with Passive Sampling Methods in an Oceanic Island
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
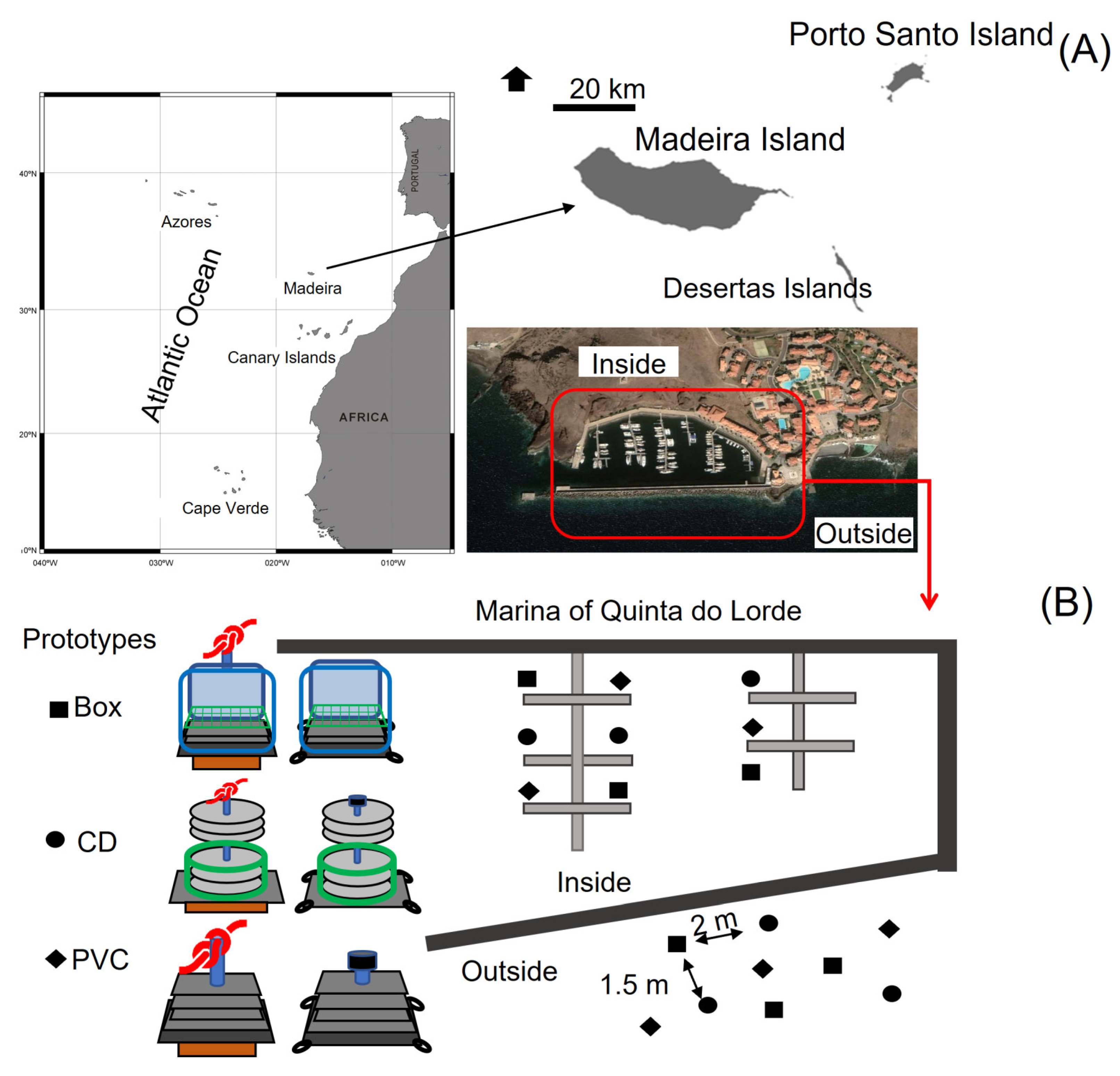
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Prototype Construction
2.3. Anchor and Deployment System
2.4. Retrieval of the Prototype Units and Laboratory Work
2.5. Data Analysis
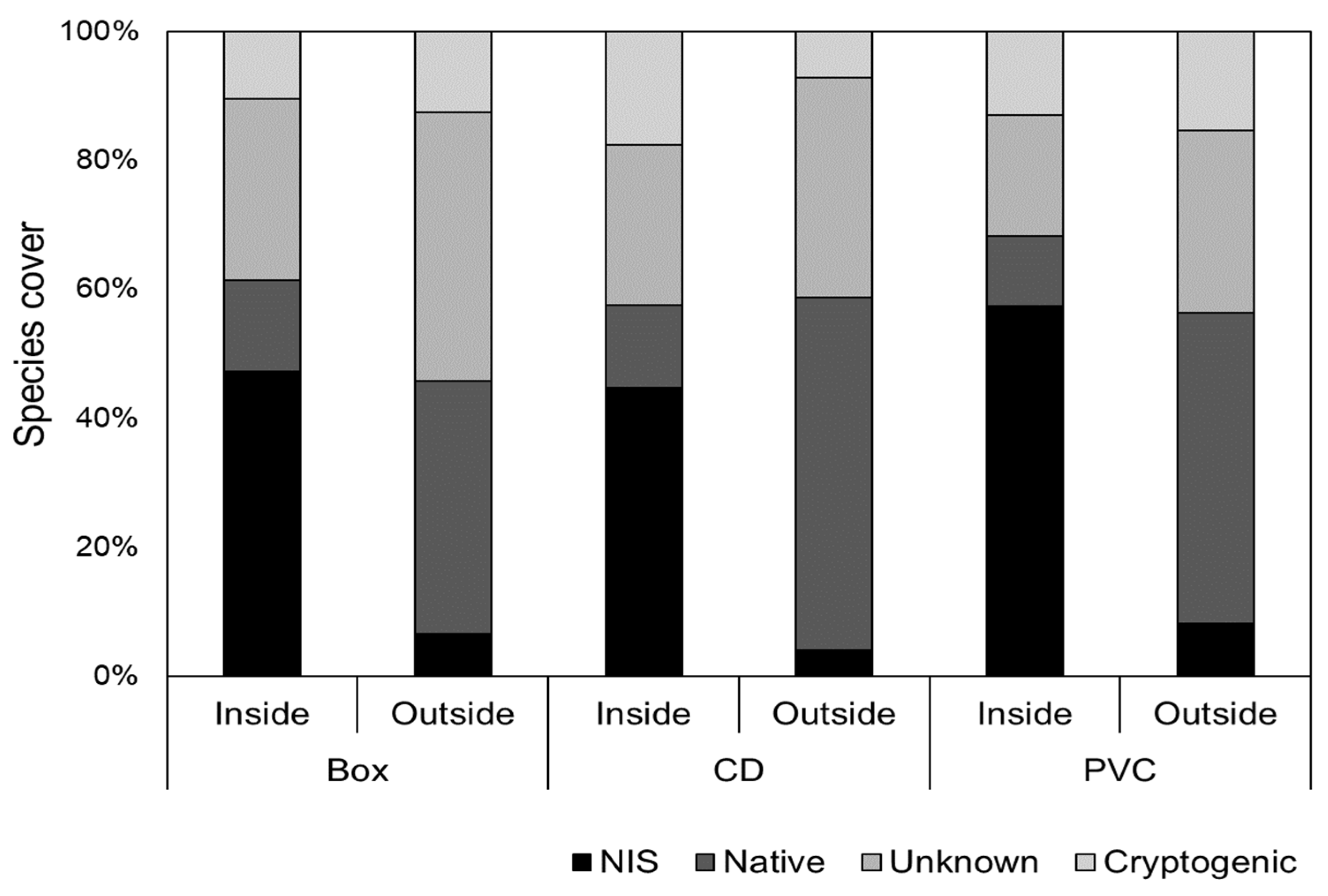
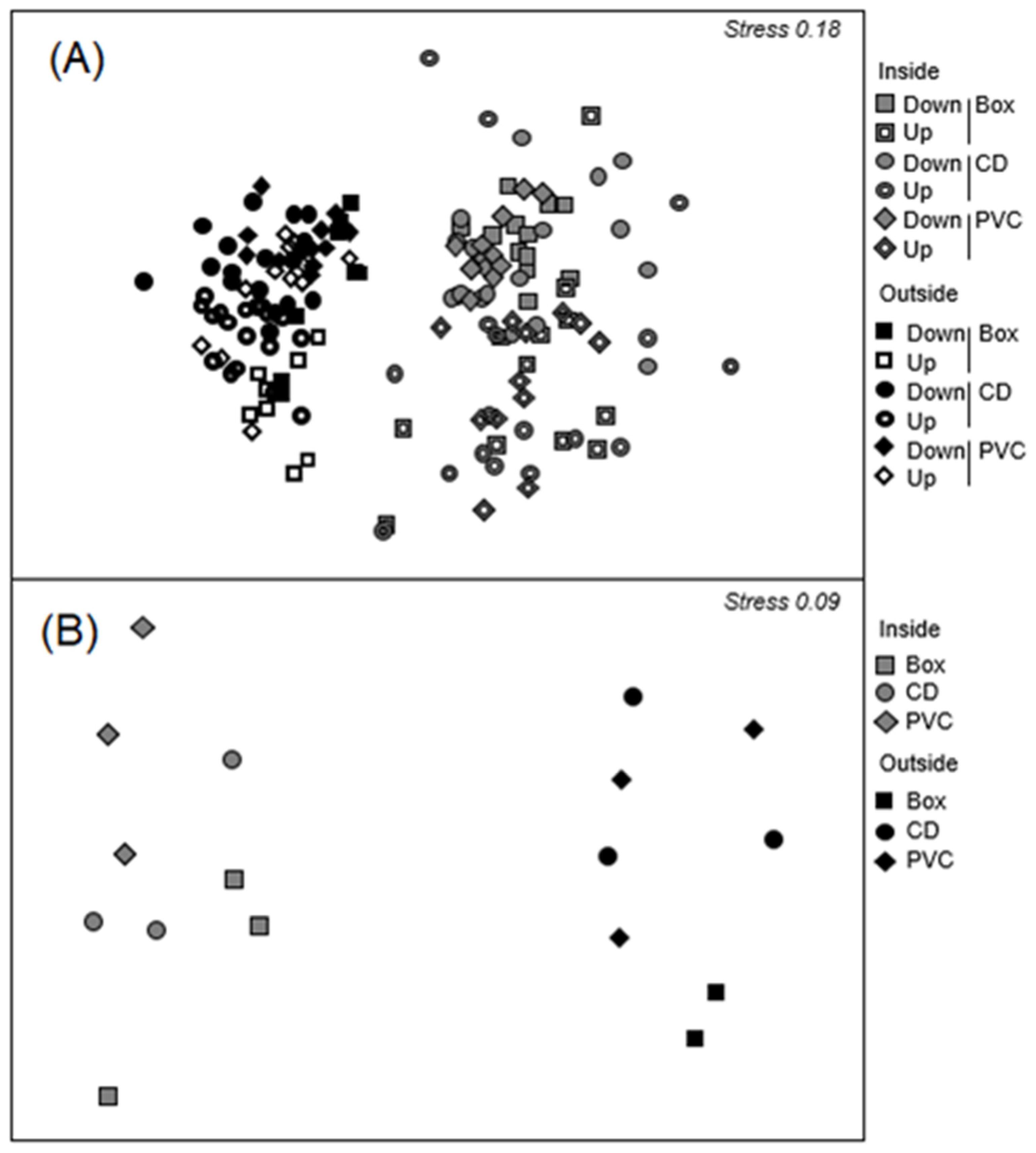
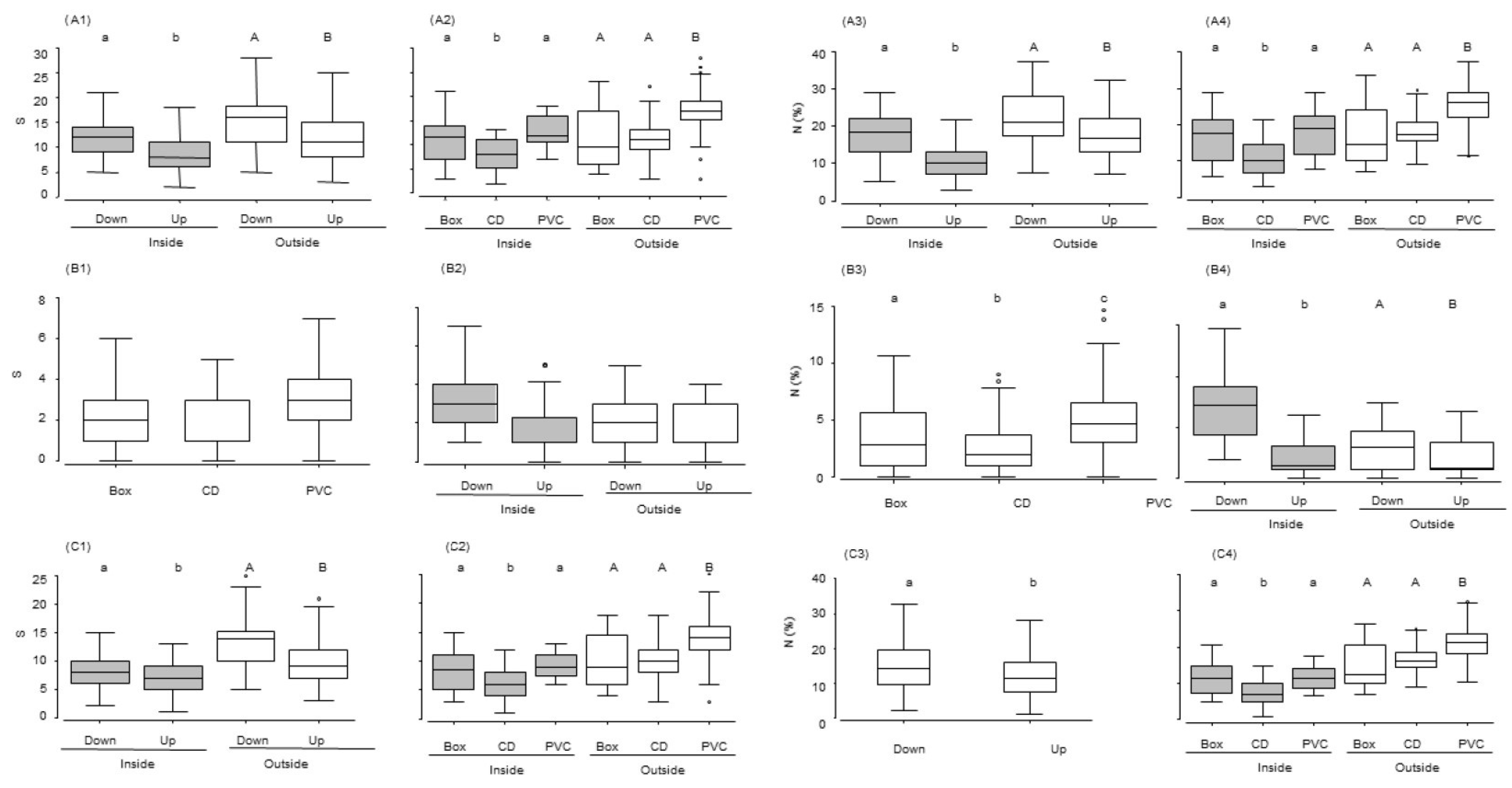
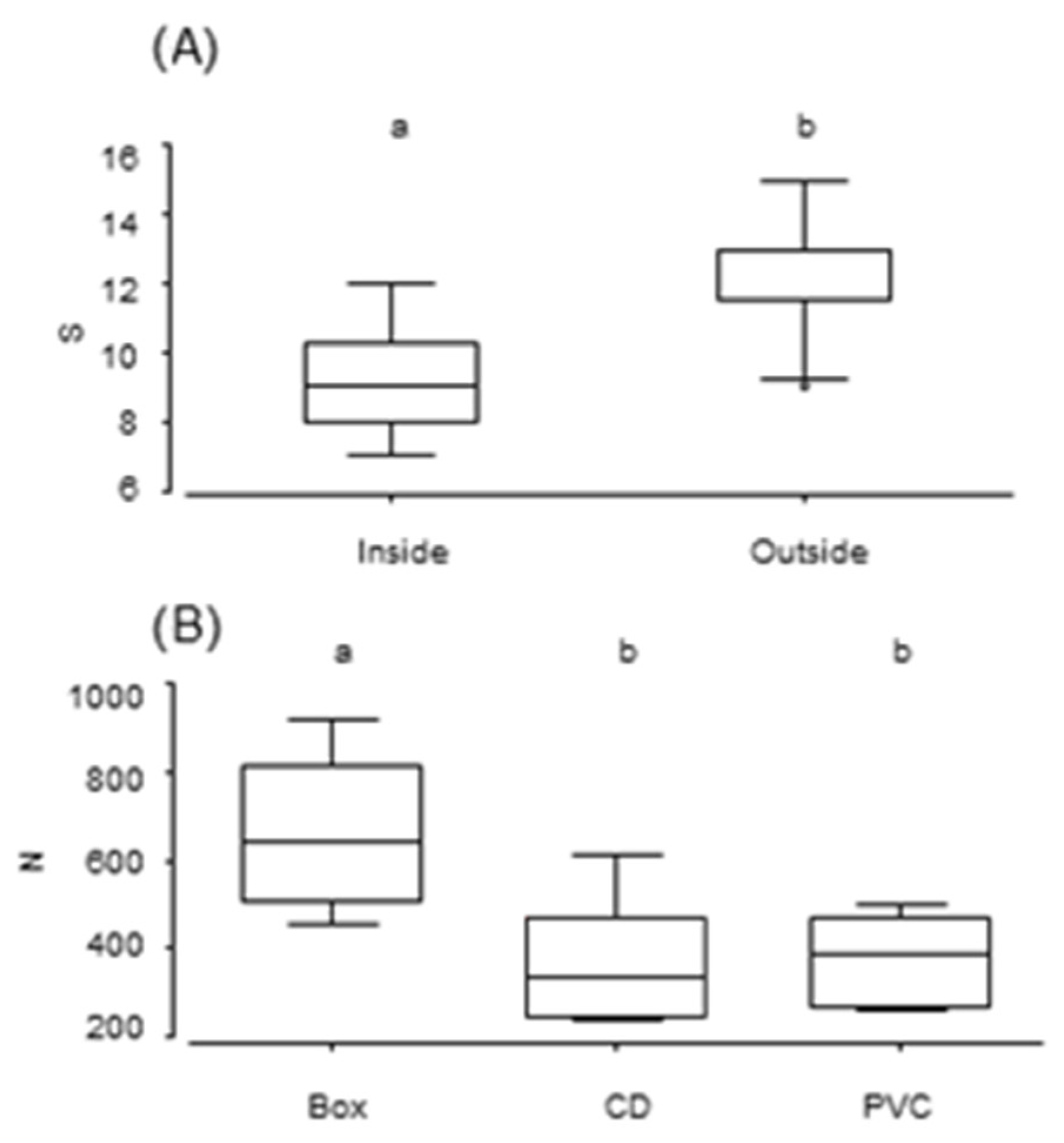
3. Results
3.1. Sessile Fauna
3.2. Mobile Fauna
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pecl, G.T.; Araújo, M.B.; Bell, J.D.; Blanchard, J.; Bonebrake, T.C.; Chen, I.C.; Clark, T.D.; Colwell, R.K.; Danielsen, F.; Evengård, B.; et al. Biodiversity Redistribution under Climate Change: Impacts on Ecosystems and Human Well-Being. Science 2017, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essl, F.; Dullinger, S.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kühn, I.; Lenzner, B.; Pauchard, A.; Pyšek, P.; et al. A Conceptual Framework for Range-Expanding Species That Track Human-Induced Environmental Change. Bioscience 2019, 69, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.; Hulme, P.E. Impact of Biological Invasions on Ecosystem Services; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.R.; Bouchet, P.J.; Miller, D.L.; Evans, P.G.H.; Waggitt, J.; Ford, A.T.; Marley, S.A. Shipping in the North-East Atlantic: Identifying Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Change. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carić, H.; Mackelworth, P. Cruise Tourism Environmental Impacts - The Perspective from the Adriatic Sea. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 102, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägerbrand, A.K.; Brutemark, A.; Barthel Svedén, J.; Gren, I.M. A Review on the Environmental Impacts of Shipping on Aquatic and Nearshore Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleri, F.; Chapman, M.G. The Introduction of Coastal Infrastructure as a Driver of Change in Marine Environments. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, N.; Williamson, A.; Aguero, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Geeves, W. Marine Invasive Alien Species: A Threat to Global Biodiversity. Mar. Policy 2003, 27, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, I.; Berecibar, E.; Castro, N.; Costa, J.L.; Frias, P.; Henriques, F.; Moreira, P.; Oliveira, P.M.; Silva, G.; Chainho, P. Assessment of the Colonization and Dispersal Success of Non-Indigenous Species Introduced in Recreational Marinas along the Estuarine Gradient. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, J.L.; Gamboa, R.L.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M.D. Assessing the Global Threat of Invasive Species to Marine Biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Wiuf, C.; Rasmussen, M.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Orlando, L.; Willerslev, E. Monitoring Endangered Freshwater Biodiversity Using Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, K.C.; Schaefer, N.; Bishop, M.J.; Nakagawa, S.; Brooks, P.R.; Knights, A.M.; Strain, E.M.A. Material Type Influences the Abundance but Not Richness of Colonising Organisms on Marine Structures. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 307, 114549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.M.; Fofonoff, P.W.; Steves, B.P.; Carlton, J.T. Invasion History and Vector Dynamics in Coastal Marine Ecosystems: A North American Perspective. Aquat. Ecosyst. Heal. Manag. 2015, 18, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, M.J.; Obenat, S.M. Fouling Assemblages of Native, Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species on Artificial Structures, Depths and Temporal Variation Fouling Assemblages of Native, Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species on Artificial Structures, Depths and Temporal Variation. J. Sea Res. 2019, 144, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilizzi, L.; Copp, G.H.; Hill, J.E.; Adamovich, B.; Aislabie, L.; Akin, D.; Al-Faisal, A.J.; Almeida, D.; Azmai, M.N.A.; Bakiu, R.; et al. A Global-Scale Screening of Non-Native Aquatic Organisms to Identify Potentially Invasive Species under Current and Future Climate Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thresher, R.E.; Kuris, A.M. Options for Managing Invasive Marine Species. Biol. Invasions 2004, 6, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.M.; Carlton, J.T.; Grosholz, E.D.; Hines, A.H. Global Invasions of Marine and Estuarine Habitats by Non-Indigenous Species: Mechanisms, Extent, and Consequences. Am. Zool. 1997, 37, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Png-gonzalez, L.; Gestoso, I.; Soledad, Á.; Nogueira, N. Non-Indigenous Species on Artificial Coastal Environments: Experimental Comparison between Aquaculture Farms and Recreational Marinas. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, J.; Caronni, S.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; Marchini, A. Role of Commercial Harbours and Recreational Marinas in the Spread of Non-Indigenous Fouling Species. Biofouling 2017, 33, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacabelos, E.; Martins, G.M.; Thompson, R.; Prestes, A.C.L.; Azevedo, J.M.N.; Neto, A.I. Material Type and Roughness Influence Structure of Inter-Tidal Communities on Coastal Defenses. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parretti, P.; Canning-Clode, J.; Ferrario, J.; Marchini, A.; Botelho, A.Z.; Ramalhosa, P.; Costa, A.C. Free Rides to Diving Sites: The Risk of Marine Non-Indigenous Species Dispersal. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, J.; Occhipinti, A.; Bandi, A. High Occurrence of Non-Indigenous Species on Recreational Boat Hulls in the Mediterranean Sea. Biol. Mar. Mediterr 2019, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Canning-Clode, J.; Fofonoff, P.; McCann, L.; Carlton, J.T.; Ruiz, G. Marine Invasions on a Subtropical Island: Fouling Studies and New Records in a Recent Marina on Madeira Island (Eastern Atlantic Ocean). Aquat. Invasions 2013, 8, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinos, T.; Andreas, P.; David, C.; Stavros, A.; Cátia, B.; Angela, B.G.; Ulrik, B.; Simona, B.; Christian, B.; João, C.; et al. Marine Strategy Framework Directive Descriptor 2, Non-Indigenous Species; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021; ISBN 9789276322573. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiamis, K.; Gervasini, E.; Deriu, I.; D’Amico, F.; Nunes, A.L.; Addamo, A.M.; Cardoso, A.C.; D’Amico, F.; Nunes, A.L.; Addamo, A.M.; et al. Baseline Distribution of Invasive Alien Species of Union Concern; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; ISBN 9789279688188. [Google Scholar]
- Pagad, S.; Genovesi, P.; Carnevali, L.; Scalera, R.; Clout, M. IUCN SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group: Invasive Alien Species Information Management Supporting Practitioners, Policy Makers and Decision Takers. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2015, 6, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Albano, P.G.; Garcia, E.L.; Stern, N.; Tsiamis, K.; Galanidi, M. Established Non-Indigenous Species Increased by 40% in 11 Years in the Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, I.C.; Zabin, C.J.; Chang, A.L.; Brown, C.W.; Sytsma, M.D.; Ruiz, G.M. Recreational Boats as Potential Vectors of Marine Organisms at an Invasion Hotspot. Aquat. Biol. 2010, 11, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; González-Sánchez, M.; Ostalé-Valriberas, E.; Cervera-Currado, L.; Guerra-García, J.M. Starting the Stowaway Pathway: The Role of Dispersal Behavior in the Invasion Success of Low-Mobile Marine Species. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2797–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, R.B.; Bradley, D.; Mayorga, J.; Goodell, W.; Friedlander, A.M.; Sala, E.; Costello, C.; Gaines, S.D. A Global Network of Marine Protected Areas for Food. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28134–28139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.M.; Fofonoff, P.W.; Carlton, J.T.; Wonham, M.J.; Hines, A.H. Invasion of Coastal Marine Communities in North America: Apparent Patterns, Processes, and Biases. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 481–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outinen, O.; Forsström, T.; Yli-Rosti, J.; Vesakoski, O.; Lehtiniemi, M. Monitoring of Sessile and Mobile Epifauna – Considerations for Non-Indigenous Species. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribano, G.; Marchini, A.; Ros, M. Population Dynamics and Life History Traits of the Non-Indigenous Paranthura Japonica Richardson (1909) in a Recently Invaded Mediterranean Site. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 46, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangussu, L.C.; Altvater, L.; Haddad, M.A.; Cabral, A.C.; Heyse, H.L.; Rocha, R.M. Substrate Type as a Selective Tool against Colonization by Non-Native Sessile Invertebrates. Brazilian J. Oceanogr. 2010, 58, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rivera, C.; Ruiz, G.; Crooks, J.; Wasson, K.; Lonhart, S.; Fofonoff, P.; Steves, B.; Rumrill, S.; Brancato, M.; Pegau, S.; et al. Broad-Scale Non-Indigenous Species Monitoring Along the West Coast in National Marine Sanctuaries and National Estuarine Research Reserves: Report to National Fish & Wildlife Foundation. Otro 2005, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tamburini, M.; Keppel, E.; Marchini, A.; Repetto, M.F.; Ruiz, G.M.; Ferrario, J.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. Monitoring Non-Indigenous Species in Port Habitats: First Application of a Standardized North American Protocol in the Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 700730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marraffini, M.L.; Ashton, G.V.; Brown, C.W.; Chang, A.L.; Ruiz, G.M. Settlement Plates as Monitoring Devices for Non-Indigenous Species in Marine Fouling Communities. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2017, 8, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obst, M.; Exter, K.; Allcock, A.L.; Arvanitidis, C.; Axberg, A.; Bustamante, M.; Cancio, I.; Carreira-Flores, D.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Chatzigeorgiou, G.; et al. A Marine Biodiversity Observation Network for Genetic Monitoring of Hard-Bottom Communities (ARMS-MBON). Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 572680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danovaro, R.; Carugati, L.; Berzano, M.; Cahill, A.E.; Carvalho, S.; Chenuil, A.; Corinaldesi, C.; Cristina, S.; David, R.; Dell’Anno, A.; et al. Implementing and Innovating Marine Monitoring Approaches for Assessing Marine Environmental Status. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino-Alvarez, L.A.; Vital, X.G.; Castillo-Cupul, R.E.; Suárez-Mozo, N.Y.; Ugalde, D.; Cervantes-Campero, G.; Muciño-Reyes, M.R.; Homá-Canché, P.; Hernández-Díaz, Y.Q.; Sotelo-Casas, R.; et al. Evaluation of the Use of Autonomous Reef Monitoring Structures (Arms) for Describing the Species Diversity of Two Coral Reefs in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Diversity 2021, 13, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, R.M.A.; Sangrà, P. Complex Geophysical Wake Flows Madeira Archipelago Case Study. Ocean Dyn. 2012, 62, 683–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, N.; Ramalhosa, P.; Jiménez, J.; Costa, J.L.; Gestoso, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Exploring Marine Invasions Connectivity in a NE Atlantic Island through the Lens of Historical Maritime Traffic Patterns. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 37, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, N.; Gestoso, I.; Marques, C.S.; Ramalhosa, P.; Costa, L. Anthropogenic Pressure Leads to More Introductions: Marine Traffic and Artificial Structures in Offshore Islands Increases Non-Indigenous Species. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhosa, P.; Camacho-Cruz, K.; Bastida-Zavala, R.; Canning-Clode, J. First Record of Branchiomma Bairdi McIntosh, 1885 (Annelida: Sabellidae) from Madeira Island, Portugal (Northeastern Atlantic Ocean). BioInvasions Rec. 2014, 3, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhosa, P.; Souto, J.; Canning-Clode, J. Diversity of Bugulidae (Bryozoa, Cheilostomata) Colonizing Artificial Substrates in the Madeira Archipelago (NE Atlantic Ocean). Helgol. Mar. Res. 2017, 71, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestoso, I.; Ramalhosa, P.; Oliveira, P.; Canning-Clode, J. Marine Protected Communities against Biological Invasions: A Case Study from an Offshore Island. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, J.; Ramalhosa, P.; Canning-Clode, J. Three Non-Indigenous Species from Madeira Harbors, Including a New Species of Parasmittina (Bryozoa). Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestoso, I.; Ramalhosa, P.; Canning-Clode, J. Biotic Effects during the Settlement Process of Non-Indigenous Species in Marine Benthic Communities. Aquat. Invasions 2018, 13, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.; Monteiro, J.; Castro, N.; Rilov, G.; Canning-Clode, J. Cronius Ruber (Lamarck, 1818) Arrives to Madeira Island: A New Indication of the Ongoing Tropicalization of the Northeastern Atlantic. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 2699–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhosa, P.; Nebra, A.; Gestoso, I.; Canning-Clode, J. First Record of the Non-Indigenous Isopods Paracerceis Sculpta (Holmes, 1904) and Sphaeroma Walkeri Stebbing, 1905 (Isopoda, Sphaeromatidae) for Madeira Island. Crustaceana 2017, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.T. Biological Invasions and Cryptogenic Species. Ecology 1996, 77, 1653–1655. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2265767 (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Chainho, P.; Fernandes, A.; Amorim, A.; Ávila, S.P.; Canning-Clode, J.; Castro, J.J.; Costa, A.C.; Costa, J.L.; Cruz, T.; Gollasch, S.; et al. Non-Indigenous Species in Portuguese Coastal Areas, Coastal Lagoons, Estuaries and Islands. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhosa, P.; Gestoso, I.; Rocha, R.M.; Lambert, G.; Canning-Clode, J. Ascidian Biodiversity in the Shallow Waters of the Madeira Archipelago: Fouling Studies on Artificial Substrates and New Records. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 43, 101672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, K.E.; Gill, S.M. Coral Point Count with Excel Extensions (CPCe): A Visual Basic Program for the Determination of Coral and Substrate Coverage Using Random Point Count Methodology. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, M.M.; Grech, M.G.; Stenert, C.; Maltchik, L.; Epele, L.B.; McLean, K.I.; Kneitel, J.M.; Bell, D.A.; Greig, H.S.; Gagne, C.R.; et al. Does Taxonomic and Numerical Resolution Affect the Assessment of Invertebrate Community Structure in New World Freshwater Wetlands? Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, L.; Turon, X.; Perkol-Finkel, S.; Rius, M. Corridors for Aliens but Not for Natives: Effects of Marine Urban Sprawl at a Regional Scale. Divers. Distrib. 2015, 21, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A New Method for Non-Parametric Multivariate Analysis of Variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). Wiley StatsRef Stat. Ref. Online 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N.; Sommerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Devon, UK, 2014; p. 221. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario, J.; Gestoso, I.; Ramalhosa, P.; Cacabelos, E.; Duarte, B.; Caçador, I. Marine Fouling Communities from Artificial and Natural Habitats: Comparison of Resistance to Chemical and Physical Disturbances. Aquat. Invasions 2020, 15, 196–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, L.; Ramalhosa, P.; Canning-Clode, J.; Gestoso, I. Variability in the Settlement of Non-Indigenous Species in Benthic Communities from an Oceanic Island. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2018, 72, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revanales, T.; Guerra-García, J.M.; Ros, M. Colonization Dynamics of Potential Stowaways Inhabiting Marinas: Lessons from Caprellid Crustaceans. Water 2022, 14, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, R.F.; Johnston, E.L. Pollution Reduces Native Diversity and Increases Invader Dominance in Marine Hard-Substrate Communities. Divers. Distrib. 2008, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, N.; Ramalhosa, P.; Cacabelos, E.; Costa, J.; Canning-Clode, J.; Gestoso, I. Winners and Losers: Prevalence of Non-Indigenous Species under Simulated Marine Heatwaves and High Propagule Pressure. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 668, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauff, R.P.M.; Davoult, D.; Greff, S.; Bohner, O.; Coudret, J.; Jacquet, S.; Loisel, S.; Rondeau, S.; Sevin, L.; Wafo, E.; et al. Pollution Gradient Leads to Local Adaptation and Small-Scale Spatial Variability of Communities and Functions in an Urban Marine Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.L.; Dafforn, K.A.; Clark, G.F.; Rius, M.; Floerl, O. How Anthropogenic Activities Affect the Establishment and Spread of Non-Indigenous Species Post-Arrival; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Volume 55, ISBN 9781351987592. [Google Scholar]
- David, R.; Uyarra, M.C.; Carvalho, S.; Anlauf, H.; Borja, A.; Cahill, A.E.; Carugati, L.; Danovaro, R.; De Jode, A.; Feral, J.P.; et al. Lessons from Photo Analyses of Autonomous Reef Monitoring Structures as Tools to Detect (Bio-)Geographical, Spatial, and Environmental Effects. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait, L.; Inglis, G. Optimising Settlement Arrays for Surveillance of Non-Indigenous Biofouling Species; Publications Logistics Officer, Ministry for Primary Industries: Wellington, New Zealand, 2016; Volume 0, ISBN 9781776654260.
- Lindegren, M.; Gabellini, A.P.; Munk, P.; Edelvang, K.; Hansen, F.T. Identifying Key Processes and Drivers Affecting the Presence of Non-Indigenous Marine Species in Coastal Waters. Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 2835–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.C.K.; McKindsey, C.W.; Johnson, L.E. Detecting Rare Species With Passive Sampling Tools: Optimizing the Duration and Frequency of Sampling for Benthic Taxa. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, S.; Davoult, D.; Lejeusne, C.; Kenworthy, J.M.; Bohner, O.; Loisel, S.; Gauff, R.P.M. Persistent Dominance of Non-Indigenous Species in the Inner Part of a Marina Highlighted by Multi-Year Photographic Monitoring. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 690, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryley, M.; Carve, M.; Piola, R.; Scardino, A.J.; Shimeta, J. Comparison of Biofouling on 3D-Printing Materials in the Marine Environment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 164, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, A.; Cowling, M.J. The Effects of Surface Topography on the Accumulation of Biofouling. Philos. Mag. 2003, 83, 2779–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhosa, P.; Gestoso, I.; Duarte, B.; Caçador, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Metal Pollution Affects Both Native and Non-Indigenous Biofouling Recruitment in a Subtropical Island System. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (A) sessile fraction | |||||||||
| Source | df | Full community | NIS/Native ratio | ||||||
| Composition | Cover (%) | S | Cover (%) | ||||||
| MS | Pseudo- F | MS | Pseudo- F | MS | Pseudo- F | MS | Pseudo- F | ||
| L | 1 | 106330.0 | 65.66 ** | 1010.3 | 38.53 *** | 352.0 | 20.96 ** | 39.9 | 28.54 ** |
| P | 2 | 9459.5 | 5.84 ** | 712.4 | 27.17 *** | 419.6 | 24.98 ** | 0.0 | 0.01 |
| O | 1 | 19398.0 | 11.98 ** | 1572.9 | 59.98 *** | 571.1 | 34.00 ** | 19.6 | 14.05 ** |
| LxP | 1 | 6235.0 | 3.85 ** | 163.0 | 6.217 ** | 60.0 | 3.57 * | 0.1 | 0.08 |
| LxO | 1 | 9320.3 | 5.76 ** | 18.7 | 0.71 | 16.2 | 0.97 | 17.2 | 12.28 ** |
| PxO | 2 | 1632.7 | 1.01 | 35.3 | 1.35 | 19.4 | 1.15 | 0.2 | 0.17 |
| LxPxO | 2 | 1451.6 | 0.90 | 25.5 | 0.97 | 1.7 | 0.10 | 0.1 | 0.09 |
| Res | 146 | 1619.4 | 26.2 | 16.8 | 1.4 | ||||
| Total | 157 | ||||||||
| Source | df | Native species | NIS | ||||||
| Cover (%) | S | Cover (%) | S | ||||||
| MS | Pseudo- F | MS | Pseudo- F | MS | Pseudo- F | MS | Pseudo- F | ||
| L | 1 | 2046.3 | 123.28 *** | 471.1 | 44.32 *** | 180.9 | 46.07 *** | 11.3 | 6.59* |
| P | 2 | 304.7 | 18.36 *** | 196.5 | 18.48 *** | 85.5 | 21.78 *** | 37.3 | 21.81 *** |
| O | 1 | 427.2 | 25.74 *** | 281.4 | 26.47 *** | 360.7 | 91.85 *** | 44.9 | 26.22 *** |
| LxP | 1 | 127.0 | 7.65 *** | 34.1 | 3.21 * | 5.2 | 1.32 | 3.2 | 1.90 |
| LxO | 1 | 57.6 | 3.47 | 53.10 | 4.99 * | 142.0 | 36.16 *** | 8.3 | 4.85 * |
| PxO | 2 | 12.2 | 0.74 | 15.9 | 1.50 | 7.4 | 1.88 | 0.7 | 0.41 |
| LxPxO | 2 | 10.4 | 0.63 | 0.8 | 0.08 | 4.5 | 1.15 | 1.7 | 1.01 |
| Res | 146 | 16.6 | 10.6 | 3.9 | 1.7 | ||||
| Total | 157 | ||||||||
| (B) mobile fraction | |||||||||
| Source | df | ||||||||
| Composition | Cover (%) | S | |||||||
| MS | Pseudo - F | MS | Pseudo - F | MS | Pseudo - F | ||||
| L | 1 | 5197.8 | 23.56 *** | 840.5 | 0.04 | 46.2 | 15.87 ** | ||
| P | 629.7 | 2.86 ** | 150630.0 | 6.34 * | 2.5 | 0.85 | |||
| LxP | 196.0 | 0.89 | 16944.0 | 0.71 | 2.7 | 0.94 | |||
| Res | 20 | 220.6 | 23761.0 | 2.9 | |||||
| Total | 23 | ||||||||
| (A) | L × P | |||||
| Inside | ||||||
| Status | Box prototype (Av. Sim = 22.61) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% |
| NIS | Parasmittina alba | 13.93 | 6.7 | 0.58 | 29.65 | 29.65 |
| U | Spirorbis sp. | 3.24 | 4.23 | 1.42 | 18.71 | 48.36 |
| N | Salmacina dysteri | 2.53 | 2.63 | 0.44 | 11.65 | 60 |
| NIS | Exaiptasia diaphana | 0.84 | 1.39 | 0.73 | 6.14 | 66.14 |
| C | Nolella gigantea | 1.64 | 1.22 | 0.37 | 5.39 | 71.53 |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 1.39 | 1.17 | 0.63 | 5.18 | 76.71 |
| C | Diplosoma listerianum | 1.43 | 0.72 | 0.36 | 3.17 | 79.88 |
| U | Mycale sp.2 | 1.09 | 0.66 | 0.36 | 2.9 | 82.78 |
| CD prototype (Av. Sim = 20.62) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% | |
| NIS | Parasmittina alba | 7.91 | 6.09 | 0.59 | 29.54 | 29.54 |
| U | Spirorbis sp. | 2.8 | 4.38 | 0.93 | 21.23 | 50.78 |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 1.86 | 2.65 | 0.67 | 12.85 | 63.62 |
| N | Polysiphonia sertularioides | 1.09 | 1.71 | 0.51 | 8.31 | 71.93 |
| C | Diplosoma listerianum | 3.29 | 1.52 | 0.3 | 7.38 | 79.31 |
| N | Salmacina dysteri | 0.54 | 0.94 | 0.34 | 4.56 | 83.87 |
| PVC prototype (Av. Sim = 32.90) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% | |
| NIS | Parasmittina alba | 15.79 | 9.71 | 0.63 | 29.52 | 29.52 |
| U | Spirorbis sp. | 4.8 | 5.55 | 1.32 | 16.86 | 46.38 |
| NIS | Exaiptasia diaphana | 1.28 | 3.05 | 1.06 | 9.28 | 55.66 |
| N | Polysiphonia sertularioides | 2.81 | 2.82 | 0.78 | 8.57 | 64.23 |
| N | Salmacina dysteri | 1.14 | 1.88 | 0.81 | 5.71 | 69.95 |
| NIS | Celleporaria inaudita | 1.53 | 1.72 | 0.69 | 5.24 | 75.19 |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 0.97 | 1.51 | 0.88 | 4.59 | 79.78 |
| U | Nemoderma | 0.68 | 1.29 | 0.64 | 3.91 | 83.68 |
| Outside | ||||||
| Box prototype (Av. Sim = 38.34) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% | |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 18.01 | 25.09 | 1.87 | 65.44 | 65.44 |
| N | Spirobranchus triqueter | 2.79 | 4.09 | 0.8 | 10.68 | 76.12 |
| U | Nemoderma | 3.04 | 2.66 | 0.56 | 6.94 | 83.05 |
| Outside CD-prototype (Av. Sim = 42.49) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% | |
| N | Spirobranchus triqueter | 22.94 | 18.63 | 1.23 | 43.86 | 43.86 |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 17.39 | 15.35 | 1.05 | 36.12 | 79.98 |
| C | Kirchenpaueria halecioides | 2.68 | 2.67 | 1.08 | 6.28 | 86.26 |
| Outside PVC-prototype (Av. Sim = 45.92) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% | |
| N | Spirobranchus triqueter | 19.35 | 15.88 | 1.15 | 34.57 | 34.57 |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 16.13 | 13.24 | 1.27 | 28.84 | 63.42 |
| C | Cribrilaria radiata | 4.78 | 3.46 | 0.89 | 7.54 | 70.96 |
| C | Kirchenpaueria halecioides | 2.82 | 1.96 | 1.26 | 4.27 | 75.23 |
| NIS | Parasmittina alba | 2.65 | 1.56 | 0.67 | 3.4 | 78.63 |
| C | Favosipora purpurea | 1.41 | 1.32 | 1.12 | 2.87 | 81.5 |
| (B) | L × O | |||||
| Inside | ||||||
| Status | Down (Av. Sim = 38.67) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% |
| NIS | Parasmittina alba | 22.53 | 20.9 | 1.37 | 54.06 | 54.06 |
| U | Spirorbis sp. | 5.45 | 6.15 | 1.49 | 15.91 | 69.97 |
| C | Diplosoma listerianum | 5.13 | 3.03 | 0.5 | 7.85 | 77.82 |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 1.27 | 1.1 | 0.67 | 2.85 | 80.67 |
| Up (Av. Sim = 21.15) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% | |
| U | Spirorbis sp. | 1.54 | 4.26 | 0.88 | 20.15 | 20.15 |
| N | Polysiphonia sertularioides | 2.46 | 3.28 | 0.64 | 15.49 | 35.64 |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 1.67 | 2.71 | 0.71 | 12.8 | 48.45 |
| N | Salmacina dysteri | 1.7 | 2.55 | 0.52 | 12.07 | 60.52 |
| NIS | Exaiptasia diaphana | 0.91 | 2.47 | 0.7 | 11.67 | 72.19 |
| NIS | Parasmittina alba | 1.23 | 1.33 | 0.34 | 6.31 | 78.5 |
| U | Nemoderma | 1.78 | 0.88 | 0.41 | 4.14 | 82.64 |
| Outside | ||||||
| Down (Av. Sim = 42.44) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% | |
| N | Spirobranchus triqueter | 26.04 | 22.24 | 1.3 | 52.39 | 52.39 |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 8.61 | 8.19 | 1.29 | 19.3 | 71.69 |
| C | Cribrilaria radiata | 3.06 | 1.64 | 0.61 | 3.86 | 75.55 |
| C | Kirchenpaueria halecioides | 2.05 | 1.47 | 0.86 | 3.47 | 79.02 |
| U | Nemoderma | 1.81 | 1.22 | 0.59 | 2.88 | 81.9 |
| Up (Av. Sim = 44.34) | Av. Abund | Av. Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% | Cum.% | |
| N | Lithophyllum incrustans | 25.44 | 30 | 1.98 | 67.67 | 67.67 |
| N | Spirobranchus triqueter | 9.26 | 7.03 | 0.94 | 15.84 | 83.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diem, A.; Ramalhosa, P.; Cacabelos, E.; Ferrario, J.; Castro, N.; Henriques, F.; Monteiro, J.G.; Chainho, P.; Pham, C.K.; Canning-Clode, J.; et al. Monitoring Non-Indigenous Species with Passive Sampling Methods in an Oceanic Island. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020264
Diem A, Ramalhosa P, Cacabelos E, Ferrario J, Castro N, Henriques F, Monteiro JG, Chainho P, Pham CK, Canning-Clode J, et al. Monitoring Non-Indigenous Species with Passive Sampling Methods in an Oceanic Island. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(2):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020264
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiem, Anna, Patrício Ramalhosa, Eva Cacabelos, Jasmine Ferrario, Nuno Castro, Filipe Henriques, João Gama Monteiro, Paula Chainho, Christopher Kim Pham, João Canning-Clode, and et al. 2023. "Monitoring Non-Indigenous Species with Passive Sampling Methods in an Oceanic Island" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 2: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020264
APA StyleDiem, A., Ramalhosa, P., Cacabelos, E., Ferrario, J., Castro, N., Henriques, F., Monteiro, J. G., Chainho, P., Pham, C. K., Canning-Clode, J., Paula, J., & Gestoso, I. (2023). Monitoring Non-Indigenous Species with Passive Sampling Methods in an Oceanic Island. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(2), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020264






