Ship Detection under Low-Visibility Weather Interference via an Ensemble Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The paper has proposed a novel integrated framework for detecting and recognizing ships navigating in low-visibility maritime environments.
- The paper has proposed the use of a weighted BiFPN in the YOLOv5 detector, achieving top-down and bottom-up multi-scale feature fusion to improve the accuracy of ship detection in low-energy image restoration.
- The paper’s proposed framework achieves an average accuracy of 96.3%, a recall of 95.35%, and a harmonic mean of 95.85% in detecting maritime traffic ships under rain streak and foggy weather conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rain-Streak and Fog Imaging Modeling
2.2. Generative Adversarial Network
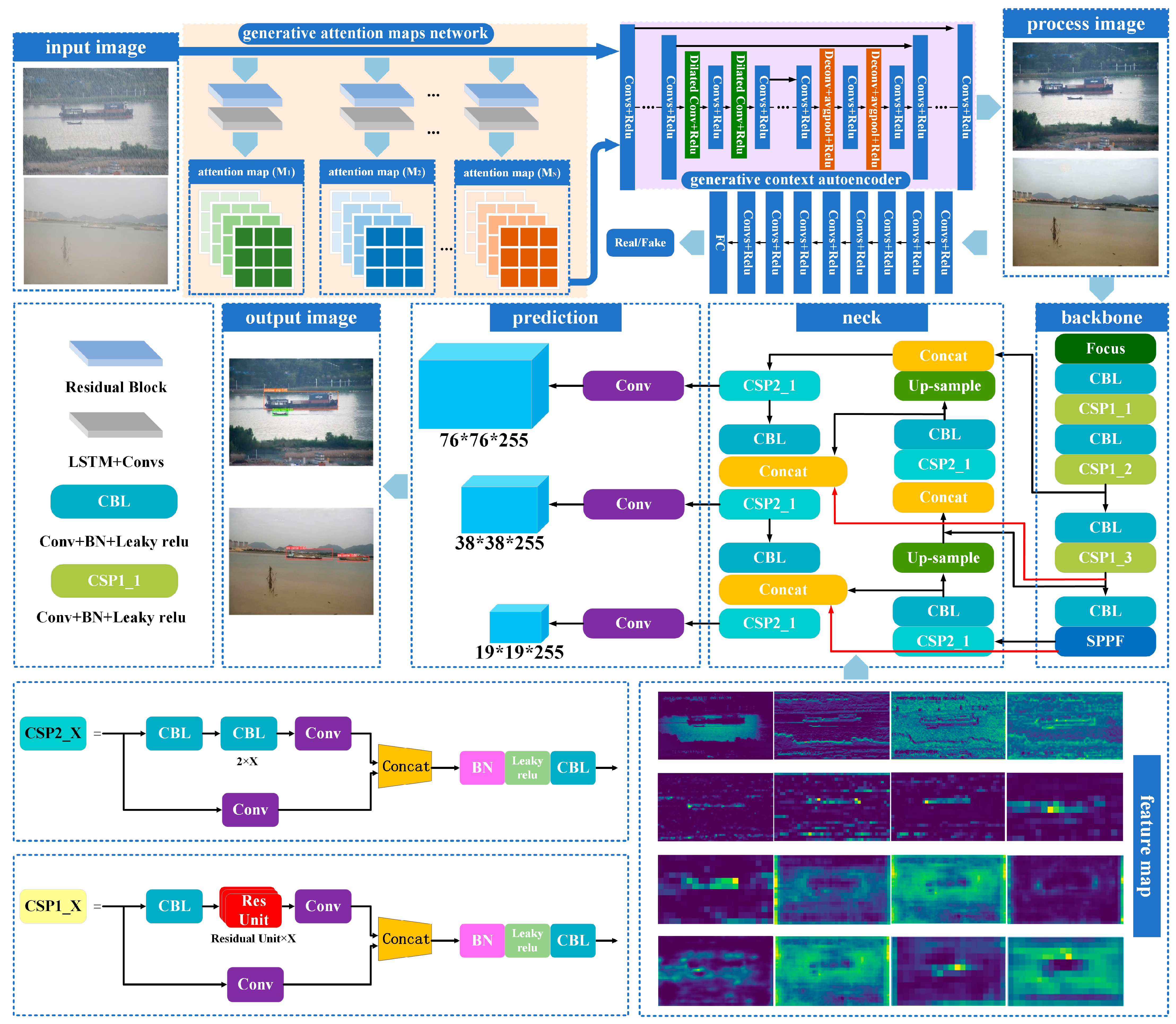
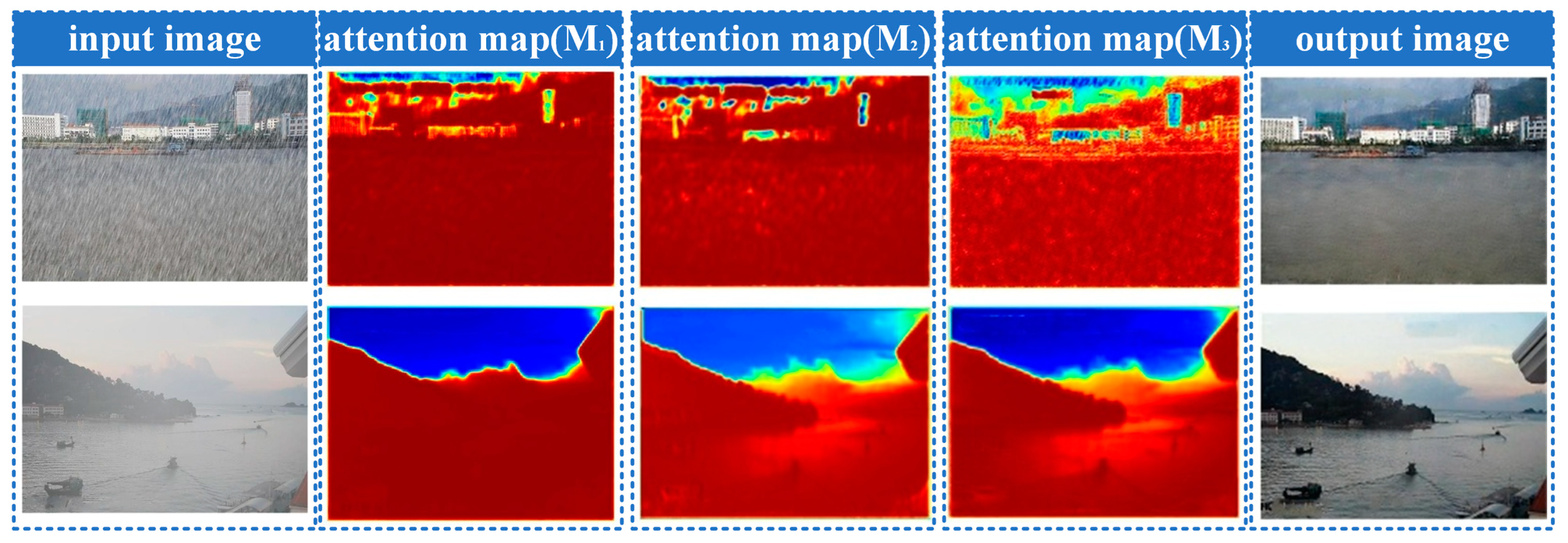
2.3. Generative Attention Map Network
2.4. Generative Context Autoencoder
2.5. Detection Method
2.6. Introduce the BiFPN Structure
3. Experimental Design
3.1. Data Description
3.2. Evaluation Indicators
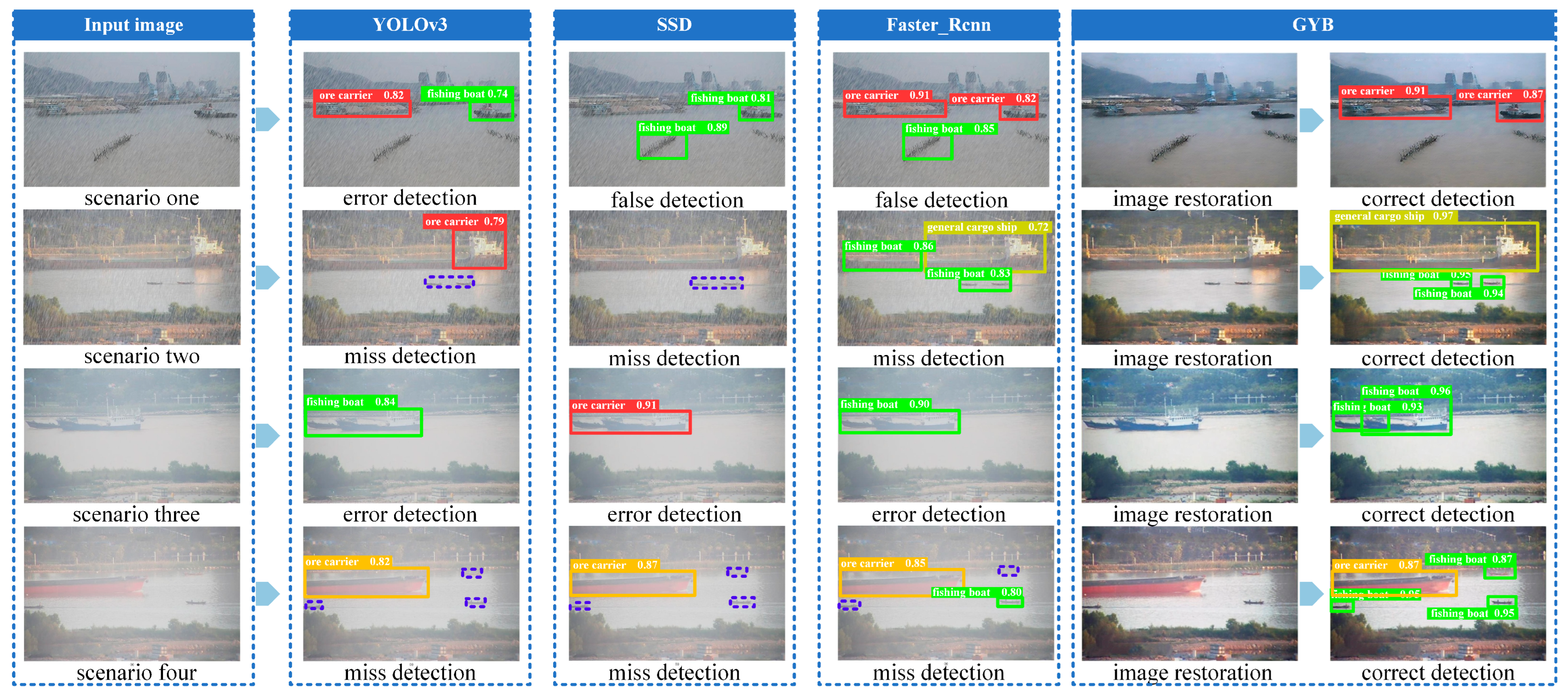
4. Discussion and Result
4.1. Discussion
4.2. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.W.; Nie, J.; Garg, S.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hossain, M.S. Data-Driven Trajectory Quality Improvement for Promoting Intelligent Vessel Traffic Services in 6G-Enabled Maritime IoT Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 5374–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, S. Deep learning based efficient ship detection from drone-captured images for maritime surveillance. Ocean Eng. 2023, 285, 115440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volden, Ø.; Cabecinhas, D.; Pascoal, A.; Fossen, T.I. Development and experimental evaluation of visual-acoustic navigation for safe maneuvering of unmanned surface vehicles in harbor and waterway areas. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, N.; d’Afflisio, E.; Braca, P.; Millefiori, L.M.; Carniel, S.; Willett, P. Next-Gen Intelligent Situational Awareness Systems for Maritime Surveillance and Autonomous Navigation [Point of View]. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnsen, C.H.; Moeslund, T.B. Rain Removal in Traffic Surveillance: Does it Matter? IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 2802–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cao, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Meng, D. Online Rain/Snow Removal from Surveillance Videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, K.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, G.; Li, Y.; Sun, X. A Ship Rotation Detection Model in Remote Sensing Images Based on Feature Fusion Pyramid Network and Deep Reinforcement Learning. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Lang, L.; Wu, L.; Xu, L.; Yan, S.; Fan, Q.; Zheng, W.; Jin, R.; Lv, R.; et al. An Improved Ship Detection Algorithm for an Airborne Passive Interferometric Microwave Sensor (PIMS) Based on Ship Wakes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5302012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Cai, J.; Chen, Q. Multi-resolution visual fiducial and assistant navigation system for unmanned aerial vehicle landing. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Sui, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Vision-based environment perception and autonomous obstacle avoidance for unmanned underwater vehicle. Appl. Ocean Res. 2023, 134, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, B.; Yang, L. Accurate Real-time Ship Target detection Using Yolov4. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Wuhan, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Tian, J.; Gao, P.; Li, L. Ship Detection and Fine-Grained Recognition in Large-Format Remote Sensing Images Based on Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020–2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 2859–2862. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Dong, C. Rapid Ship Detection Method on Movable Platform Based on Discriminative Multi-Size Gradient Features and Multi-Branch Support Vector Machine. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Du, W.; Wu, W. Saliency-Aware Convolution Neural Network for Ship Detection in Surveillance Video. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Li, M.; He, Y. An Effective Instance-Level Contrastive Training Strategy for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 4007505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Q.; Shang, W.L.; Luo, Q.; Yu, K. AI-Empowered Speed Extraction via Port-Like Videos for Vehicular Trajectory Analysis. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 4541–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guan, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G. Marine Targets Detection for Scanning Radar Images Based on Radar- YOLONet. In Proceedings of the 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 15–19 December 2021; pp. 1256–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Hwang, J.N.; Xing, G.; Liu, H. RODNet: A Real-Time Radar Object Detection Network Cross-Supervised by Camera-Radar Fused Object 3D Localization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2021, 15, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. LMO-YOLO: A Ship Detection Model for Low-Resolution Optical Satellite Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4117–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, R.W.; Qu, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Lv, Y. Asynchronous Trajectory Matching-Based Multimodal Maritime Data Fusion for Vessel Traffic Surveillance in Inland Waterways. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, H. Robust Detection and Tracking Method for Moving Object Based on Radar and Camera Data Fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 10761–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.L.; Gao, Z.; Daina, N.; Zhang, H.; Long, Y.; Guo, Z.; Ochieng, W.Y. Benchmark Analysis for Robustness of Multi-Scale Urban Road Networks Under Global Disruptions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.W.; Srivastava, G.; Zhang, Y.; Djenouri, Y.; Aloqaily, M. Privacy-Preserving Multiobjective Sanitization Model in 6G IoT Environments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 5340–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; He, Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Sotelo, M.A.; Li, Z. YOLOv5-Fog: A Multiobjective Visual Detection Algorithm for Fog Driving Scenes Based on Improved YOLOv5. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 2515612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaballah, M.; Kenk, M.A.; Muhammad, K.; Minaee, S. Vehicle Detection and Tracking in Adverse Weather Using a Deep Learning Framework. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 4230–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. EfficientDet: Scalable and Efficient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10778–10787. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, R.; Yu, X.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Y. Removing Raindrops and Rain Streaks in One Go. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9143–9152. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ji, H. Removing Rain from a Single Image via Discriminative Sparse Coding. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3397–3405. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Tan, R.T.; Guo, X.; Lu, J.; Brown, M.S. Rain Streak Removal Using Layer Priors. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2736–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Nayar, S.K.; Narasimhan, S.G. Vision in bad weather. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 822, pp. 820–827. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Contrast restoration of weather degraded images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, R.; Tan, R.T.; Yang, W.; Su, J.; Liu, J. Attentive Generative Adversarial Network for Raindrop Removal from A Single Image. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2482–2491. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Du, W.; Li, C. SeaShips: A Large-Scale Precisely Annotated Dataset for Ship Detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 20, 2593–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ship Category | Resolution | Image Distortion | Small Target Detection | Ship Obstruction | Hull Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ore carrier | 1920 × 1080 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Bulk cargo carries | 1920 × 1080 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Container ship | 1920 × 1080 | √ | / | √ | √ |
| General cargo ship | 1920 × 1080 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Fishing boat | 1920 × 1080 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Passenger ship | 1920 × 1080 | √ | / | √ | √ |
| Datasets | Evaluation Indicators | |
|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | |
| Rain streaks | 30.32 | 0.9289 |
| Fog | 32.68 | 0.9360 |
| Data | Model | Evaluation Indicators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | F1 | fps | ||||
| rain streaks | GYB | 95.2% | 94.3% | 94.8% | 0.970 | 0.701 | 28.67 |
| YOLOv3 | 71.7% | 48.4% | 57.8% | 0.578 | 0.256 | 11.98 | |
| SSD | 83.5% | 79.4% | 81.4% | 0.822 | 0.434 | 6.47 | |
| Faster_Rcnn | 60.6% | 59.7% | 61.0% | 0.614 | 0.294 | 3.26 | |
| fog | GYB | 97.4% | 96.4% | 96.9% | 0.984 | 0.742 | 29.06 |
| YOLOv3 | 69.9% | 58.9% | 60.6% | 0.867 | 0.268 | 12.68 | |
| SSD | 89.8% | 84.9% | 87.3% | 0.867 | 0.408 | 7.03 | |
| Faster_Rcnn | 61.2% | 63.5% | 62.3% | 0.655 | 0.317 | 3.78 | |
| Rain Streaks | Evaluation Indicators | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | F1 | |||
| ore carrier | 94.8% | 92.6% | 93.7% | 0.971 | 0.660 |
| passenger ship | 94.4% | 92.9% | 93.6% | 0.971 | 0.656 |
| container ship | 99.9% | 100% | 99.9% | 0.995 | 0.783 |
| bulk cargo carrier | 92.8% | 92.1% | 92.4% | 0.949 | 0.696 |
| general cargo ship | 95.9% | 95.1% | 95.5% | 0.971 | 0.737 |
| fishing boat | 93.5% | 93.0% | 93.2% | 0.963 | 0.662 |
| Fog | Evaluation Indicators | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | F1 | |||
| ore carrier | 98.4% | 90.7% | 94.4% | 0.985 | 0.714 |
| passenger ship | 98.3% | 96.5% | 97.4% | 0.966 | 0.715 |
| container ship | 96.7% | 99.0% | 97.8% | 0.995 | 0.786 |
| bulk cargo carrier | 97.2% | 97.7% | 97.4% | 0.99 | 0.766 |
| general cargo ship | 99.2% | 97.7% | 98.4% | 0.992 | 0.771 |
| fishing boat | 94.7% | 96.7% | 95.7% | 0.974 | 0.703 |
| Data | Model | Evaluation Indicators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | F1 | fps | ||||
| Rain streaks | YOLOv5 | 65.0% | 34.1% | 44.7% | 0.405 | 0.216 | 33.37 |
| YOLOv5 + BiFPN | 74.1% | 41.6% | 53.3% | 0.503 | 0.288 | 31.75 | |
| GY | 80.3% | 85.3% | 82.7% | 0.887 | 0.516 | 30.45 | |
| GYB | 95.2% | 94.3% | 94.8% | 0.970 | 0.701 | 28.67 | |
| Fog | YOLOv5 | 70.8% | 55.5% | 62.2% | 0.622 | 0.368 | 35.37 |
| YOLOv5 + BiFPN | 75.9% | 49.1% | 48.1% | 0.580 | 0.351 | 30.85 | |
| GY | 83.6% | 70.0% | 76.2% | 0.786 | 0.509 | 29.78 | |
| GYB | 97.4% | 96.4% | 96.9% | 0.984 | 0.742 | 29.06 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wei, C.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xian, J. Ship Detection under Low-Visibility Weather Interference via an Ensemble Generative Adversarial Network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112065
Chen X, Wei C, Xin Z, Zhao J, Xian J. Ship Detection under Low-Visibility Weather Interference via an Ensemble Generative Adversarial Network. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112065
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xinqiang, Chenxin Wei, Zhengang Xin, Jiansen Zhao, and Jiangfeng Xian. 2023. "Ship Detection under Low-Visibility Weather Interference via an Ensemble Generative Adversarial Network" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112065
APA StyleChen, X., Wei, C., Xin, Z., Zhao, J., & Xian, J. (2023). Ship Detection under Low-Visibility Weather Interference via an Ensemble Generative Adversarial Network. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112065







