Static and Discrete Berth Allocation for Large-Scale Marine-Loading Problem by Using Iterative Variable Grouping Genetic Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Berth Allocation Problem
2.2. Cooperative Coevolutionary Method
3. Modeling Large-Scale Berth Allocation Problem
3.1. Problem Analysis
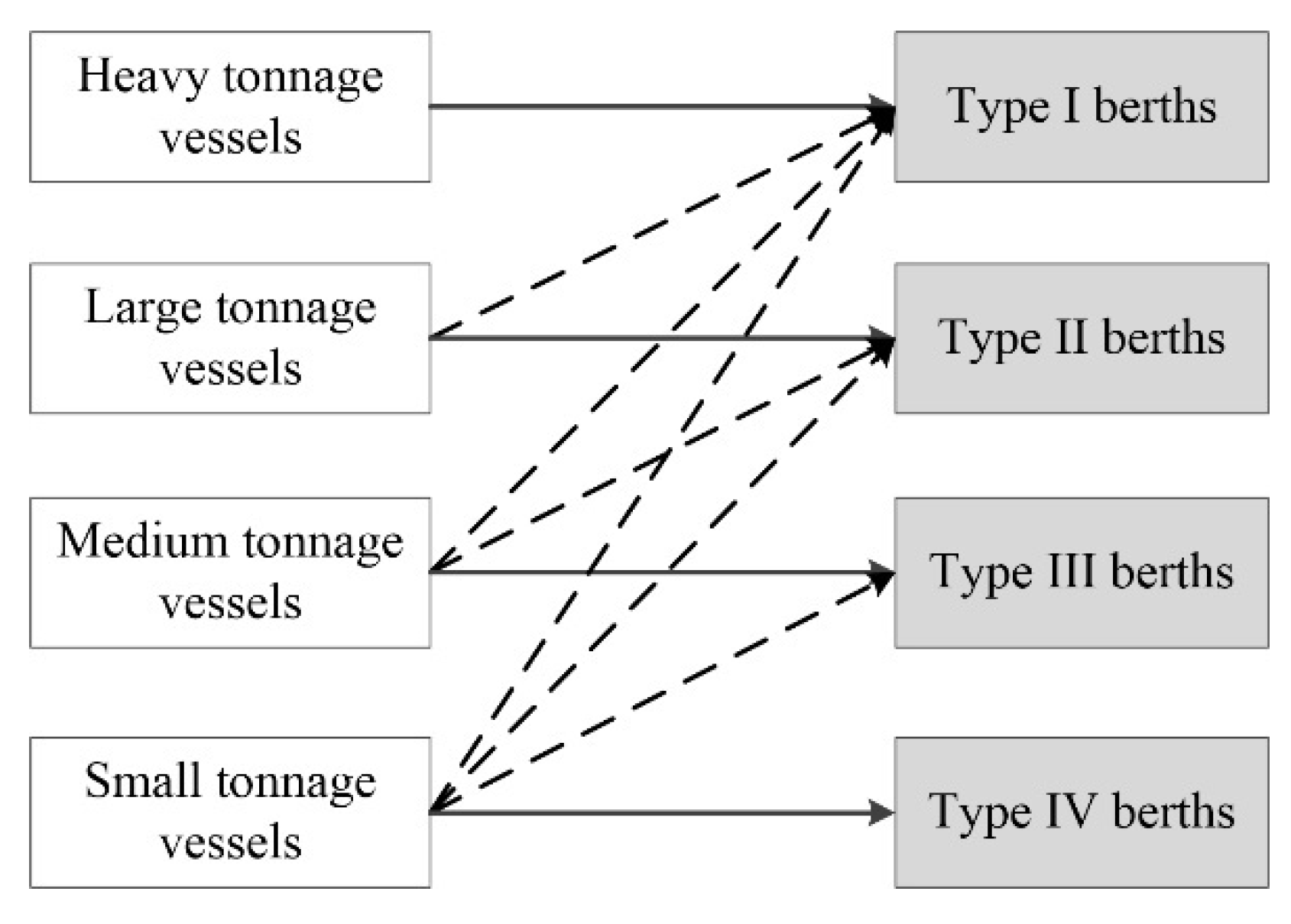
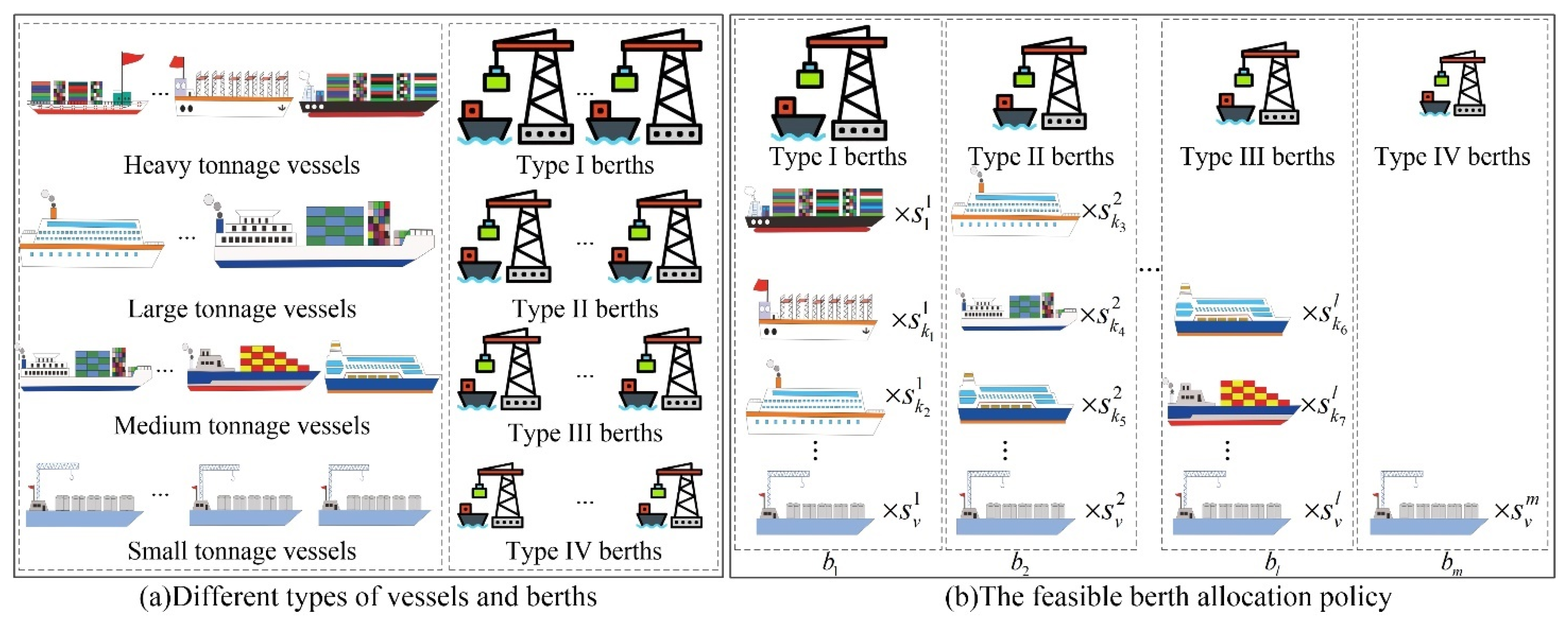
3.1.1. Loading Capability
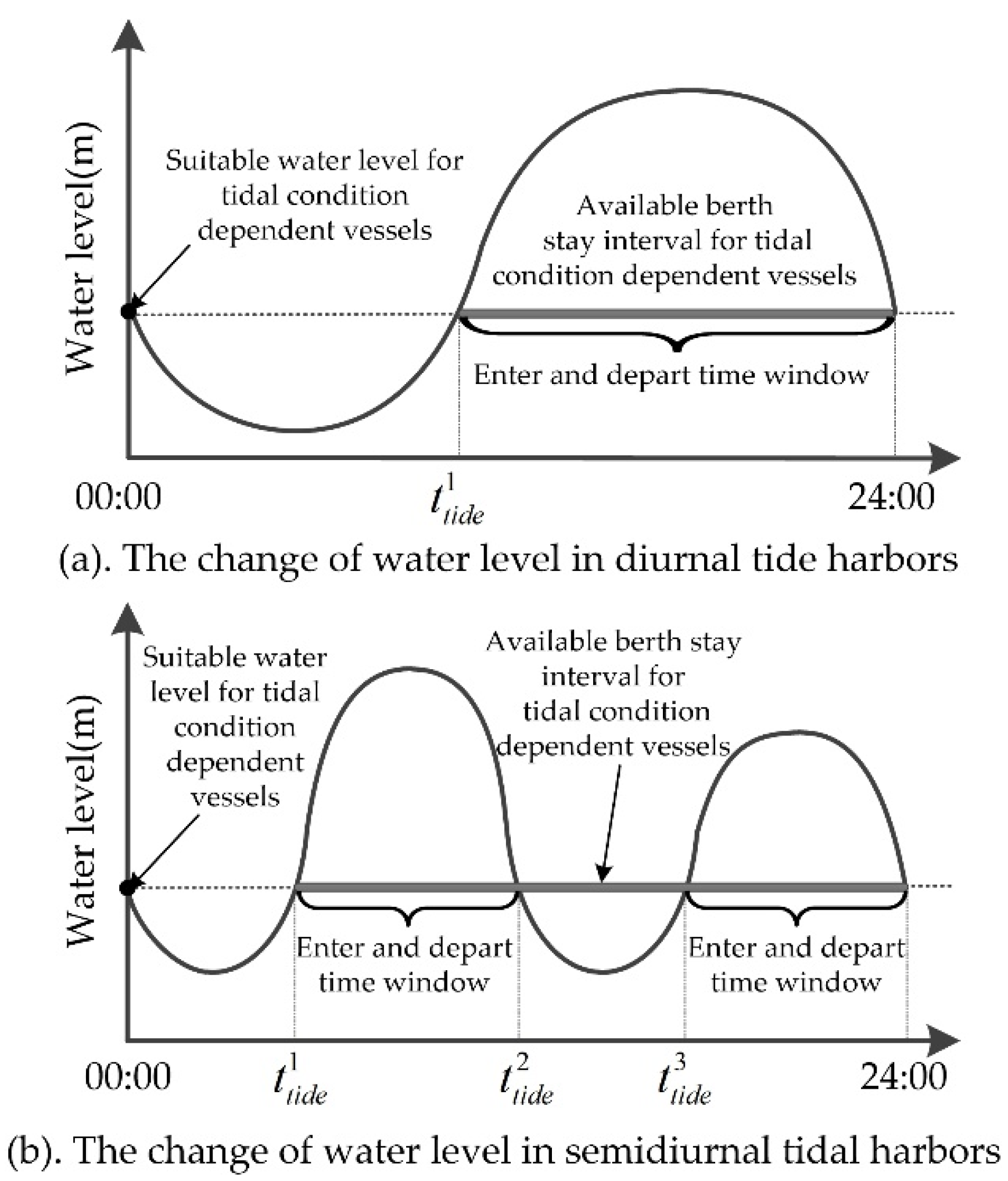
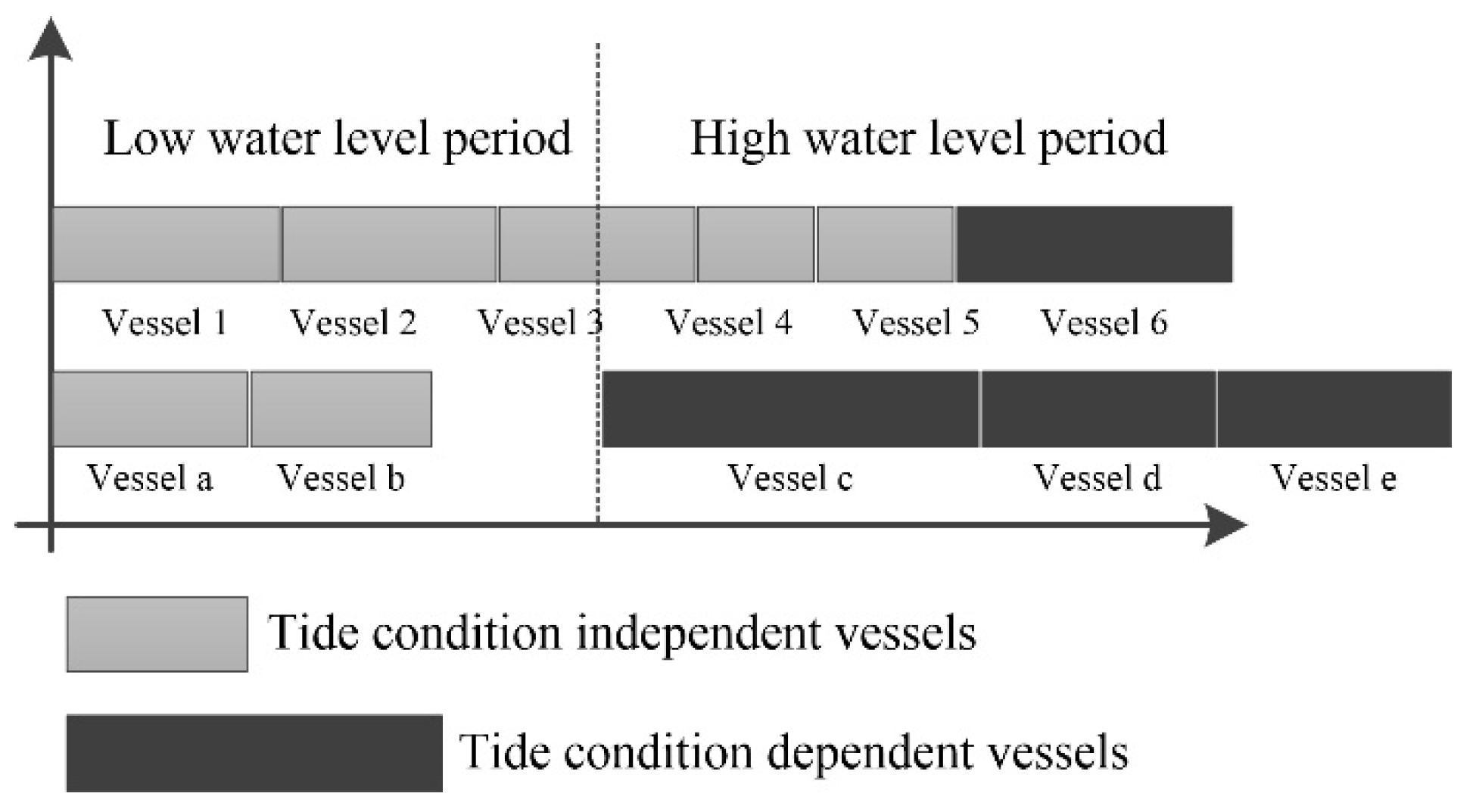
3.1.2. The Tidal Condition
3.1.3. The Allocation Efficiency Requirement
3.2. Problem Analysis
4. Iterative-Variable-Grouping-Genetic-Algorithm-Based Method
4.1. The Characteristics of the Large-Scale Berth Allocation Problem
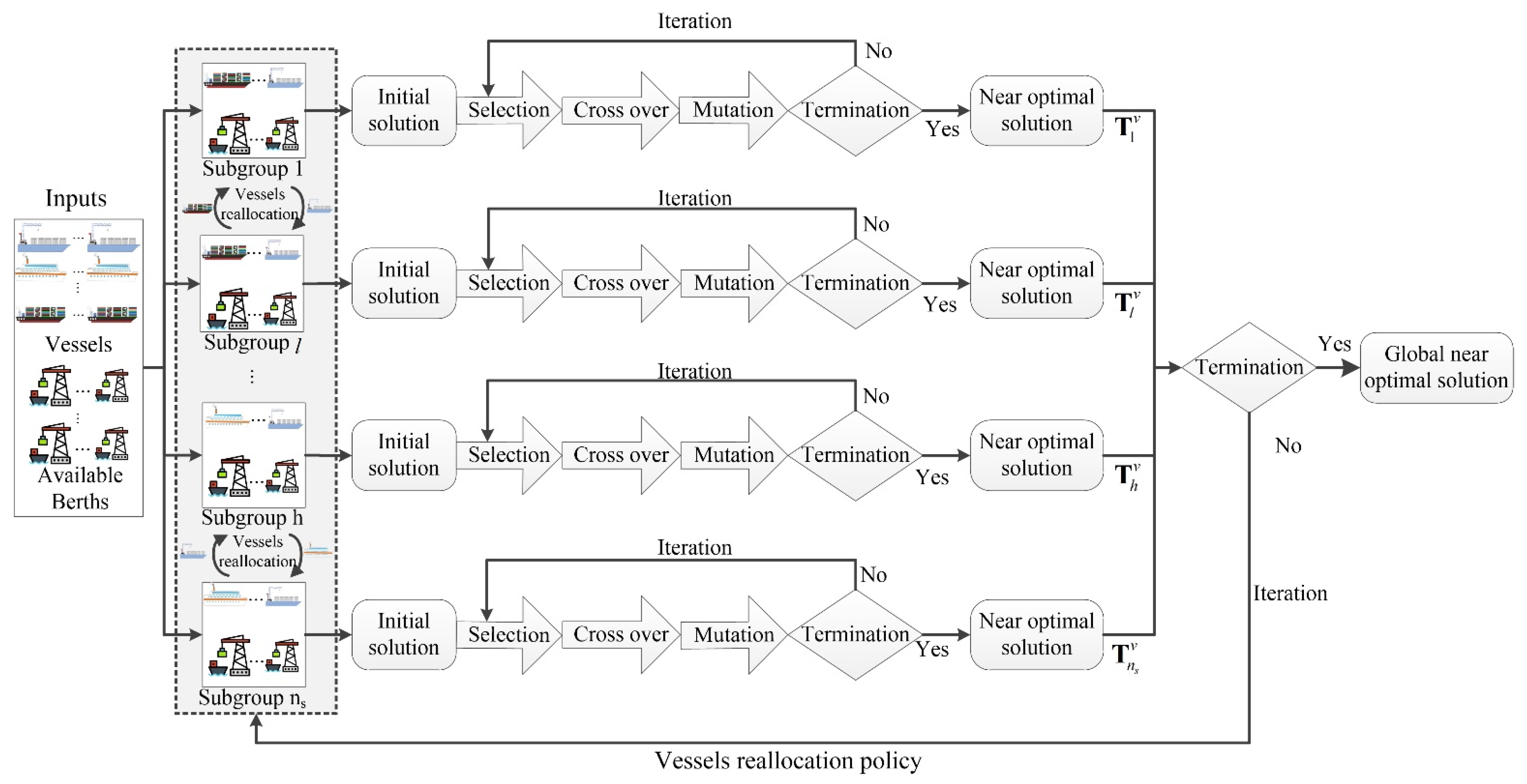
4.2. Iterative Variable Grouping Genetic Algorithm
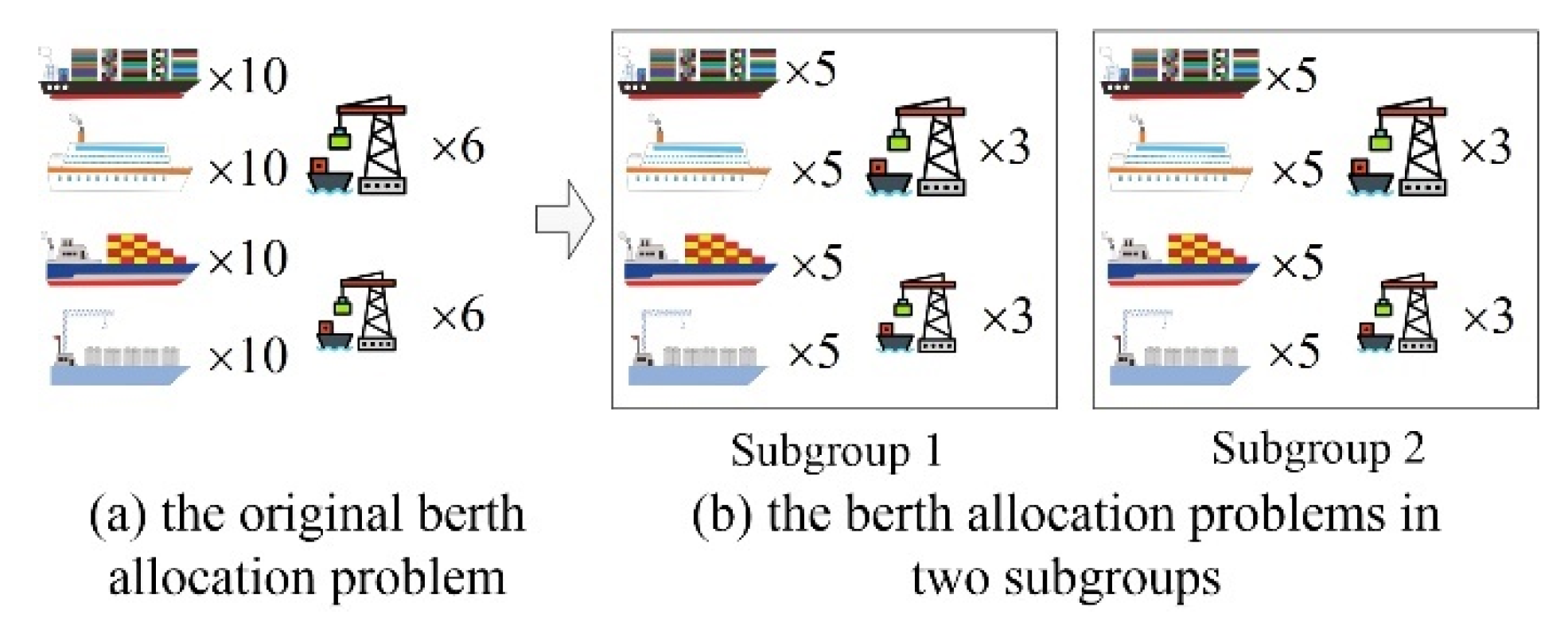
4.2.1. Initial Grouping Strategy
- (1)
- The number of vessels and berths should be kept in medium scale in each group;
- (2)
- To improve the computational efficiency, the number of each type of vessels and berths should be divided as evenly as possible;
- (3)
- Each type of vessel should be distributed to the subgroups according to the number of correspondence berths.
4.2.2. Searching the Near-Optimal Plans by Using the Genetic Algorithm
- Chromosome
- Population
- Crossover
- Mutation
- Fitness function
- Selection method
4.2.3. Iterative Vessel Reallocation Policy
5. Computational Experiments
5.1. Large-Scale Berth Allocation Scenario
5.1.1. Scenario Introduction
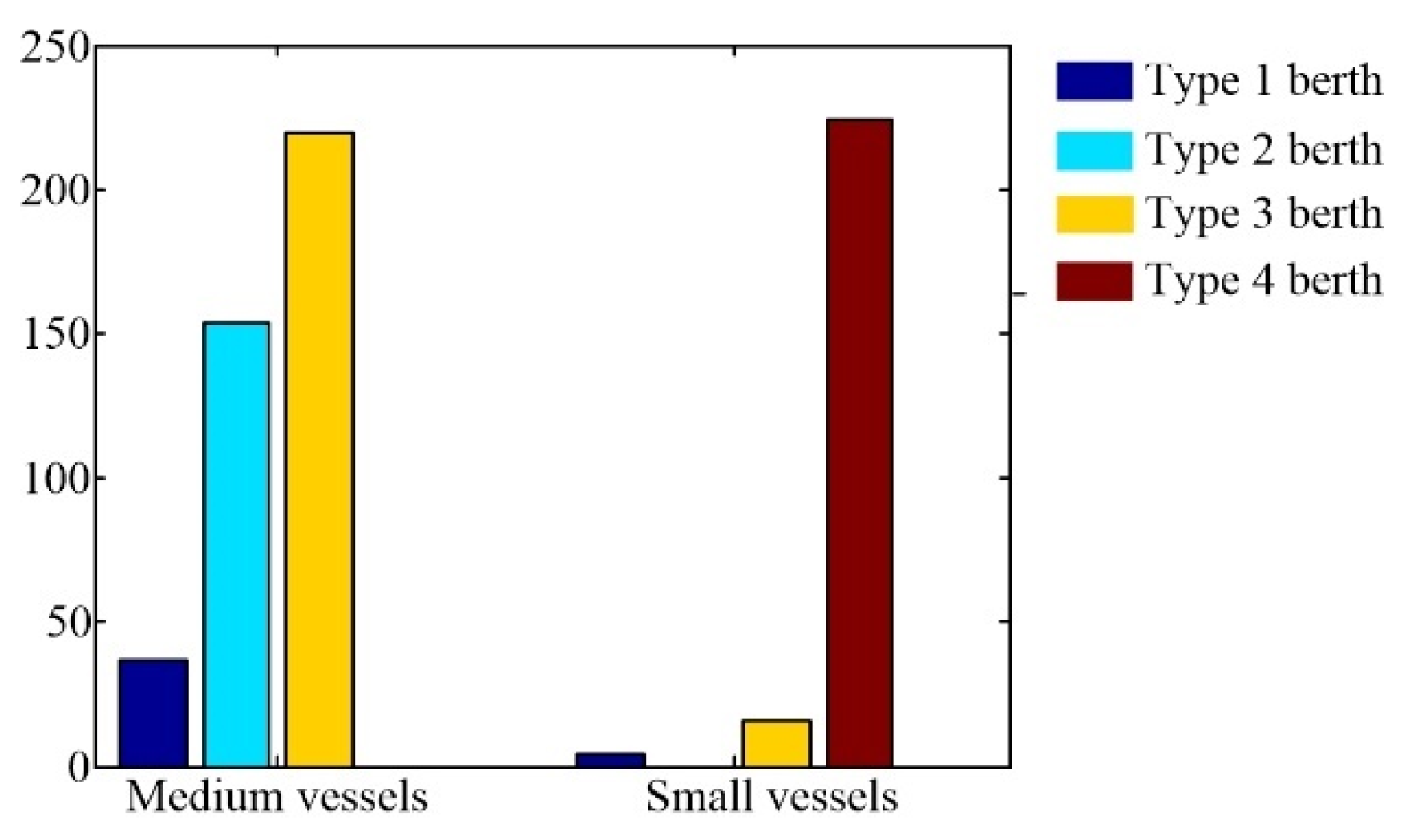
5.1.2. Parameters’ Validation
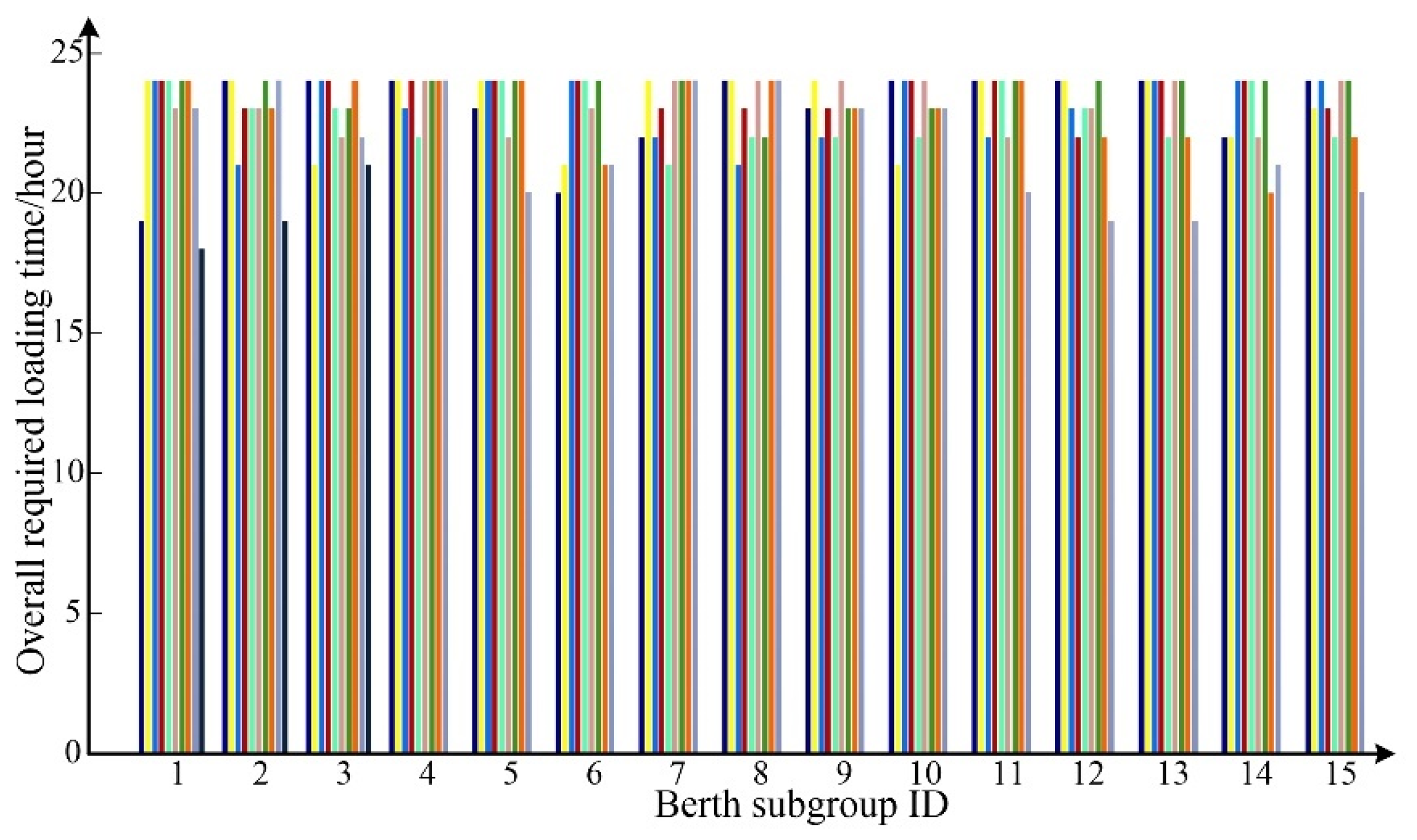
5.1.3. Performance Evaluation
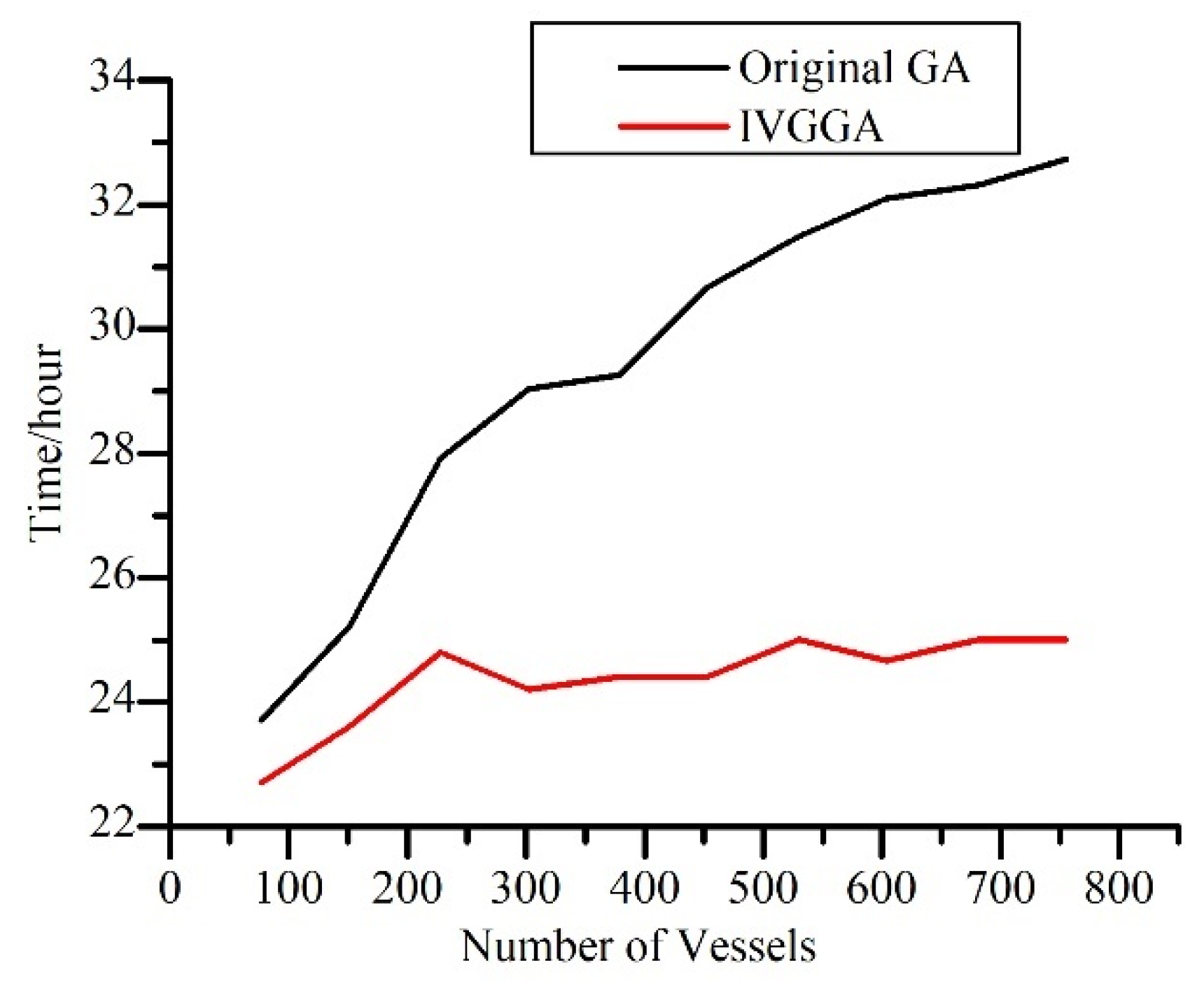
5.2. Comparison with Original Genetic Algorithm
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNCTAD. Review of Maritime Transport. 2021. Available online: https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/rmt2021ch1_en.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Nica-Rus, L.; Kaiter, E.-H. Outdated Ships and Their Future During (Non) Pandemic Times. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 635, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyaka, J.-C.B.; Yadavalli, V.S.S. Decision support framework for facility location and demand planning for humanitarian logistics. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2021, 12, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, D.; Singh, A.; Das, A.; Bera, U.K. A Post-Disaster Humanitarian Relief Logistic Model: Evacuation and Transportation. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Pune, India, 6–8 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkapici, D.B.; Ertem, M.A.; Aygüneş, H. Intermodal humanitarian logistics model based on maritime transportation in Istanbul. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hillebrandt-Andrade, C.; Vanacore, E. Citizen science for studying earthquakes. Science 2022, 376, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, L. Modeling multiple humanitarian objectives in emergency response to large-scale disasters. Transp. Res. Part E 2015, 75, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhuge, D.; Lee, L.H.; Chew, E.P. Daily berth planning in a tidal port with channel flow control. Transp. Res. Part B 2017, 106, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrkal, K.; Zuglian, S.; Røpke, S.; Larsen, J.; Lusby, R.M. Models for the discrete berth allocation problem: A computational comparison. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2011, 47, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.-B. An emergency logistics distribution approach for quick response to urgent relief demand in disasters. Transp. Res. Part E 2007, 43, 687–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, Ç.; Lalla-Ruiz, E.; Lam, J.S.L.; Voß, S. Mathematical programming formulations for the strategic berth template problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 124, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeau, J.-F.; Laporte, G.; Legato, P.; Moccia, L. Models and tabu search heuristics for the berth-allocation problem. Transp. Sci. 2005, 39, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cahyono, R.T.; Flonk, E.J.; Jayawardhana, B. Discrete-Event Systems Modeling and the Model Predictive Allocation Algorithm for Integrated Berth and Quay Crane Allocation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-W.; Hong, W.-C.; Geng, J.; Wang, J. Berth and quay crane coordinated scheduling using multiobjective chaos cloud particle swarm optimization algorithm. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 3163–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheimanoff, N.; Fontane, F.; Kitri, M.N.; Tchernev, N. A reduced VNS based approach for the dynamic continuous berth allocation problem in bulk terminals with tidal constraints. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 168, 114215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacalhau, E.T.; Casacio, L.; de Azevedo, A.T. New hybrid genetic algorithms to solve dynamic berth allocation problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. Container Ship Three-Dimensional Loading Problem Based on Hybrid Genetic Algorithm. Master’s thesis, Huazhong University of Science & Technology, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, M.A.; De Jong, K.A. A cooperative coevolutionary approach to function optimization. In Proceedings of the Parallel Problem Solving from Nature—PPSN III International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, The Third Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature, Jerusalem, Israel, 9–14 October 1994; Davidor, Y., Schwefel, H.P., Männer, R., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; Volume 866, pp. 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yu, B.; Qi, M. PGGA: A predictable and grouped genetic algorithm for job scheduling Future Generation Computer. Systems 2006, 22, 588–599. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, A.; Nagaiwa, K.; Chan, W.T. Efficient planning of berth allocation for container terminals in Asia. J. Adv. Transp. 1997, 31, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Tian, Y.; Sawaragi, T. A tree search method for the container loading problem with shipment priority. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 214, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, A.; Nishimura, E.; Papadimitriou, S. Berth allocation with service priority. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2003, 37, 437–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ji, D.; Ge, Y. Research on Project Optimization of Ship Loading Berth Allocation Based on Genetic Algorithm. Fire Control. Command. Control 2017, 4, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Iris, Ç.; Pacino, D.; Ropke, S.; Larsen, A. Integrated Berth Allocation and Quay Crane Assignment Problem: Set partitioning models and computational results. Transp. Res. Part E 2015, 81, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, C.-L.; Leung, J.Y.-T. Berth allocation with time-dependent physical limitations on vessels. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 216, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalla-Ruiz, E.; Expósito-Izquierdo, C.; Melián-Batista, B.; Moreno-Vega, J.M. A Set-Partitioning-based model for the Berth Allocation Problem under Time-Dependent Limitations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 250, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepler, X.; Absi, N.; Feillet, D.; Sanlaville, E. The stochastic discrete berth allocation problem. EURO J. Transp. Logist. 2019, 8, 363–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, Ç.; Pacino, D.; Ropke, S. Improved formulations and an Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search heuristic for the integrated berth allocation and quay crane assignment problem. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2017, 105, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, Ç.; Lam, J.S.L. Recoverable robustness in weekly berth and quay crane planning. Transp. Res. Part B 2019, 122, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasm, O.A.; Diabat, A.; Cheng, T.C.E. The integrated berth allocation, quay crane assignment and scheduling problem: Mathematical formulations and a case study. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 291, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, F.; Zong, T.; Li, X. Cooperative Co-evolution with Formula-based Variable Grouping for Large-Scale Global Optimization. Evol. Comput. 2018, 26, 569–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunfio, G.A. Adaptation in Cooperative Coevolutionary Optimization. In Adaptation and Hybridization in Computational Intelligence; Fister, I., Fister, I., Jr., Eds.; Adaptation, Learning, and Optimization; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 18, pp. 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, E.S.; Esmaeelzadeh, V.; Eslami, M. A Hierarchical Sub-Chromosome Genetic Algorithm (HSC-GA) to Optimize Power Consumption and Data Communications Reliability in Wireless Sensor Networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2015, 80, 1579–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Introducing Subchromosome Representations. In: Extending the Scalability of Linkage Learning Genetic Algorithms. Stud. Fuzziness Soft Comput. 2006, 190, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, S.; Gu, G. Tidal types and characteristics of the harbors along the Guangxi coast. J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 28, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Z.; Huang, F. A variable-grouping based genetic algorithm for large-scale integer programming. Inf. Sci. 2006, 176, 2869–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Peng, K.; Chen, K.; Li, J. Evolutionary crew scheduling with adaptive chromosomes. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2013, 56, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, A.; Hansen, N.; Mauny, N.; Ros, R.; Schoenauer, M. Bio-Inspired Continuous Optimization: The Coming of Age; Invited Talk at CEC: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsekas, D.P. Nonlinear Programming, 3rd ed.; Athena Scientific: Belmont, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kallioras, N.A.; Lagaros, N.D.; Avtzis, D.N. Pity beetle algorithm-A new metaheuristic inspired by the behavior of bark beetles. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 121, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, G.; Hao, X. A general approach to solving hardware and software partitioning problem based on evolutionary algorithms. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2021, 159, 102998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-P.; Chiang, T.-L.; Wang, C.-N.; Fu, H.-P.; Chou, C.-C. A Hybrid GA with Variable Quay Crane Assignment for Solving Berth Allocation Problem and Quay Crane Assignment Problem Simultaneously. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Types of Berths | Number | ID Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 29 | B1~B29 |
| 2 | 40 | B30~B69 |
| 3 | 41 | B70~B110 |
| 4 | 28 | B111~B138 |
| Vessel Type | v1 | v2 | v3 | v4 | v5 | v6 | v7 | v8 | v9 | v10 | v11 | v12 | v13 | v14 | v15 | v16 | v17 | v18 | v19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 76 | 23 | 17 | 63 | 13 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 31 | 12 | 10 | 200 | 36 | 8 | 8 | 13 | 2 | 17 | 213 |
| Loading time | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 15 | 18 | 5 | 4 |
| Tonnage type | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Subgroup ID | Number of Vessels after Adjustment | Added Vessels | Removed Vessels |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 52 | v13:1,v15:1 | v12:2 |
| 2 | 52 | v2:1,v14:1,v19:1 | v1:1,v13:2, |
| 3 | 52 | v1:1,v2:1,v15:1 | v13:2,v16:1 |
| 4 | 52 | v1:1 | v16:1 |
| 5 | 46 | v3:1,v10:1,v13:1,v16:1,v18:1 | v4:1,v5:1,v12:7,v15:1 |
| 6 | 46 | v1:1,v12:1 | v4:1,v9:1,v13:2,v18:1,v19:2 |
| 7 | 53 | v12:2,v13:1,v19:1 | v16:1 |
| 8 | 52 | v4:1,v5:1,v9:1,v12:2,v19:1 | v1:3,v15:1 |
| 9 | 52 | v1:1,v9:1,v12:2,v13:1 | v3:1,v15:1,v19:1 |
| 10 | 51 | v4:1,v12:1,v13:1,v15:1 | v2:1,v9:1 |
| 11 | 49 | v12:1,v13:1,v16:1 | v2:1,v10:1,v14:1 |
| 12 | 50 | v1:1 | |
| 13 | 49 | v16:1 | v1:1 |
| 14 | 49 | ||
| 15 | 49 |
| Scenario Type | Number of Vessels | The Range of Number of Available Berths |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 77 | (15, 16) |
| 2 | 151 | (29, 31) |
| 3 | 228 | (43, 45) |
| 4 | 302 | (56, 58) |
| 5 | 379 | (70, 72) |
| 6 | 453 | (84, 86) |
| 7 | 530 | (97, 99) |
| 8 | 604 | (111, 113) |
| 9 | 681 | (125, 127) |
| 10 | 755 | (140, 141) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, D.; Niu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, S. Static and Discrete Berth Allocation for Large-Scale Marine-Loading Problem by Using Iterative Variable Grouping Genetic Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091294
Yin D, Niu Y, Yang J, Yu S. Static and Discrete Berth Allocation for Large-Scale Marine-Loading Problem by Using Iterative Variable Grouping Genetic Algorithm. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(9):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091294
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Dong, Yifeng Niu, Jian Yang, and Shaobo Yu. 2022. "Static and Discrete Berth Allocation for Large-Scale Marine-Loading Problem by Using Iterative Variable Grouping Genetic Algorithm" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 9: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091294
APA StyleYin, D., Niu, Y., Yang, J., & Yu, S. (2022). Static and Discrete Berth Allocation for Large-Scale Marine-Loading Problem by Using Iterative Variable Grouping Genetic Algorithm. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(9), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091294








