Abstract
In this paper, a robust composite dynamic event-triggered formation control scheme is proposed for multiple underactuated surface vehicles (USVs) from two aspects, i.e., guidance and control. In the guidance module, a novel dual-layer line-of-sight (DLLOS) guidance principle is incorporated into the leader–follower framework to generate the reference path. To overcome the problem of unavailable leader velocity information, an adaptive speed controller is designed to adjust the navigational speed of followers. As for the control part, by utilizing the dynamic event-triggered method, the operational frequency of actuators can be reduced in a flexible manner. That can effectively avoid the excessive wear and chattering phenomenon of actuators. Furthermore, by the fusing of the radial basis function neural networks (RBF NNs) and the robust neural damping technique, the model uncertainty, environmental disturbances and some unknown parameters can be remodeled, and only two gain-related adaptive laws need to be updated online. The serial–parallel estimation model (SPEM) is established to predict the velocity variables, and the approximation performance of NNs can be enhanced by virtue of the derived prediction error. Through the Lyapunov stable theorem, all control signals in the closed-loop system are guaranteed semi-globally uniformly ultimately bounded (SGUUB) stability. Finally, digital simulations are illustrated to verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed algorithm.
1. Introduction
Over the past several decades, the underactuated surface vehicle (USV) has been widely investigated as a hot topic in the marine control and engineering field. Due to its characteristics of flexible deriving, strong autonomy and high safety, the USV has been applied to various offshore practices, e.g., maritime search and rescue, suspicious target enclosing, territorial water guarding and so on. Within the control problem of USV, there mainly exist three types, i.e., trajectory tracking, dynamic positioning and formation control. It is worth noting that the formation control problem of multiple USVs has become the central issue in marine cybernetics, among which the leader–follower method is the most popular on account of its flexibility and simplicity. However, some new challenges have emerged in ocean engineering—for example, the unavailability of velocity constraints and the excessive chattering of actuators. Therefore, how to develop a novel control scheme to deal with the current challenges is of great significance to the marine industry.
Generally speaking, the autonomous navigation system of USVs can be divided into two critical subsystems: the guidance subsystem and the control subsystem. To be specific, the guidance subsystem is used to provide reference signals (i.e., the reference position, desired heading angle and velocity information) for the formation. Currently, the line-of-sight (LOS) guidance principle has been intensively explored in the path-following control strategy, and some fruitful results can be found in [1,2,3]. The LOS guidance principle implements a look-ahead distance, mimicking an experienced sailor, and produces a desired route and the desired heading angle which are required to be fed into the inner dynamic loop. In [4], an integrated LOS guidance principle was developed for the USV to remove the effect of drifting interference. To render a good tracking performance in a straight line, gain-variable LOS guidance was designed by adding an integrated gain function into the former algorithm [5]. To further deal with the area-constraint tracking problem, the error-constrained line-of-sight (ECLOS) guidance law was developed to guarantee that tracking errors cannot exceed a specific range [6]. From the above discussion, it is obvious that LOS guidance has been widely studied. Meanwhile, the corresponding guidance principle has been applied to some special areas. For example, in [7], integrated LOS guidance was implemented in an unmanned wind sailboat, and three navigation modes, i.e., cross-wind, upwind and downwind, were proposed. In [8], to address the path-following problem for USVs with unknown sideslip angle, a novel predictor-based line-of-sight (PLOS) guidance principle was developed, and the fast and smooth identification of the sideslip angle could be guaranteed. For the path-following mission of unmanned underwater vehicles, an improved three-dimensional (3-D) LOS guidance was designed by using the kinematics transformation theory [9]. However, it should be noted that the above LOS guidance results cannot be directly applied to the formation control problem of multiple USVs, and some practical sailing issues have not been taken into consideration. That is, in marine practice, the position and heading angle information can be measured by the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and gyrocompass equipment [10]. The velocity information of the leader, however, cannot be directly obtained by all the follower ships. Thus, how to develop a new guidance principle for the leader–follower formation to address the above problem deserves further investigation.
For the control subsystem, it is well known that the corresponding function is to generate control orders/signals and transmit them to the actuators. However, with regard to the traditional controller, the control orders are required to be continuously transmitted to the actuators, which may lead to some unnecessary consumption of the communication channel and the frequent chattering phenomenon [11]. For this purpose, the event-triggered control, as an effective tool to handle this problem, has received increasing interest from the control community, and plenty of works have been published focusing on the nonlinear strict-feedback system [12,13,14]. In [15], an event-triggered input strategy with a fixed threshold parameter was proposed, and the measurement errors between the actuator model and the event-triggered mechanism could be compensated by introducing an intermediate control law. To further decrease the communication rate in the sensor-to-controller channel, the model-based event-triggered method was presented by employing a state-based triggering condition [16]. In this way, the system state and the derived neural weight estimator can be updated at each triggered point. In [17], a novel event-triggered communication mechanism was designed for the multi-agent nonlinear system which could effectively reduce the communication burden between agents and their neighbors. Furthermore, the event-triggered method has been intensively studied in the ship motion control field [18,19,20]. For example, in [21], a guidance-based event-triggered control law was designed for a fully actuated surface vessel to reduce the communication burden. To address the compound effect of actuator fault and input saturation, a novel fault-tolerant event-triggered tracking controller was proposed to guarantee the globally ultimately bounded convergence [22]. Currently, a dynamic event-triggered strategy with an adjustable threshold has been developed and has attracted ever-increasing attention [23]. Compared with the static event-triggered method, the dynamic event-triggered control strategy can achieve a more flexible manner of economizing communication. However, up to today, there are no dynamic event-triggered approaches suitable for USVs to execute their corresponding missions.
Moreover, regarding system uncertainty and unknown external disturbance, a class of approximation-based control algorithm is presented via neural networks (NNs) and the fuzzy logic system (FLS) [24]. The approximation effect of model uncertain terms can enhance the control performance of the closed-loop control system. By virtue of the minimal learning parameter (MLP) technique, the enormous weight matrix can be compressed into an unknown parameter, and the derived controller has a concise form and need not calculate the plentiful weight information [25]. To deal with a more practical case, an MLP-based concise robust controller was developed for marine vessels in [26]. For the possibility of enhancing the approximation performance of NNs/FLS, an adaptive composite learning approach has been reported in [27]. The serial–parallel estimation model (SPEM) was constructed to estimate the system dynamics variables, where the predicted error can further improve the approximation ability of NNs [28]. Meanwhile, a large number of interesting results have been reported for USVs—for example, sliding mode control [29], observer-based control [30], model predictive control [31], etc.
Invoked by the above literature review, a novel robust composite dynamic event-triggered formation control scheme has been proposed for USVs under the marine practice constraint. The main merits of the proposed algorithm can be summarized as:
(1) A novel dual-layer line-of-sight (DLLOS) guidance principle is proposed for the leader–follower formation configuration. In the leader layer, an adaptive LOS guidance law is designed to generate the reference path for the leader according to the waypoint information. That can effectively eliminate the buffeting frequency and improve the tracking accuracy during the steering process. As for the follower layer, an adaptive speed controller is developed to address the constraint of the leader’s unobtainable velocity information. In this way, the smooth reference route of the formation can be programmed in accordance with the guidance requirement.
(2) By resorting to the dynamic event-triggered mechanism, the control order can be intermittently and flexibly sent to the actuating devices (i.e., the propeller and the rudder); thus, the communication occupancy from the controller to the actuator can be largely reduced without any additional impact on the system output performance. Besides, by fusing the radial basis function neural networks (RBF NNs) and the robust neural damping technique, the perturbation caused by the system uncertainty and ocean environment can be effectively stabilized, and only two gain-related adaptive parameters are required to be updated instead of the burdensome weight matrix. Meanwhile, the SPEM is constructed to predict the velocity variables and enhance the estimating performance of the composite adaptive parameters.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, the nonlinear mathematical model and the problem formulation are provided. Section 3 is devoted to developing the corresponding guidance principle, including the leader layer and the follower layer. Section 4 gives a systematic procedure for the proposed controller, and analyses of the system stability and performance of the controller are formulated using the Lyapunov theory. In Section 5, a numerical simulation is given to verify the effectiveness of the proposed controller. Section 6 gives some concluding remarks.
2. Problem for Formulation and Preliminaries
2.1. Nonlinear Mathematical Model of USV
Based on the Newtonian and Lagrangian mechanics [32], the nonlinear mathematical model for the USV can be established as Equations (1) and (2).
Most marine ships are underactuated, meaning that they are equipped with propellers and rudders for surge and yaw motions only, while being without any actuators for the direct control of sway motion. In Figure 1, denotes the earth-fixed frame, and indicates the body-fixed frame. In Equations (1) and (2), describes the surge, sway and yaw angles for the USV. denotes the surge, the sway and the yaw velocity in the body-fixed framework. are the unknown parameters used to express the additional mass. are used to express the unknown hydrodynamic damping parameters. and denote the external disturbances caused by the sea wind, current and waves. denote the system input variables, i.e., the main engine speed and the rudder angle. To facilitate the following control design, one defines . are the nonlinear functions, which can be expressed as Equation (3).
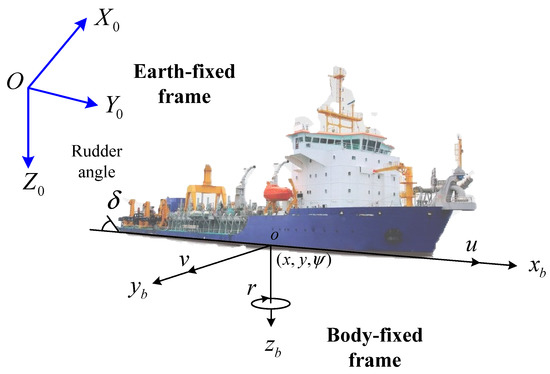
Figure 1.
The body-fixed frame and earth-fixed frame.
are utilized to express the unknown gain function due to the consideration of actuating devices, which can be calculated as Equation (4). Due to the limited power generated by the propeller and rudder, there must exist the upper and lower bounded values such that .
where and denote the interference extents around the propeller and the rudder. indicates the water density. and denote the diameter and progress coefficients of the propeller, respectively. indicates the thrust coefficient, which is a nonlinear function of . and are used to express the dimensions of x-coordinates which are related to the rudder blade and the gravity center of the ship hull. and are the rudder area and the aspect ratio, respectively. denotes the length between the bow perpendicular and the aft perpendicular. and are the relative surge and sway speeds of the rudder, respectively.
Assumption 1.
The environmental disturbancesandsatisfy thatand, in whichandare unknown positive bounded constants of the disturbances and only used for stability analysis.
Assumption 2.
The sway velocityof the USV is always passive-bounded stable. The detailed proof process can be found in the literature [33].
Remark 1.
Since the ocean’s environments keeps changing with finite energies, the disturbances acting on the ship’s hull are unknown, time-varying and bounded. Thus, Assumption 1 is reasonable in marine practice. Furthermore, as reported in [33], it is easy to systematically analyze the passive-boundedness of the sway velocityof the USV. Due to the hydrodynamic damping forces in the nonlinear mathematical model being dominant in the sway direction and because, as a result, the sway velocity is damped out by such forces, Assumption 2 is realistic. This assumption can also be easily satisfied in marine practice on account of its sway velocity being attenuated by the hydrodynamic damping force in the sway direction. The interested reader is referred to [33] for a detailed discussion about this assumption.
2.2. RBF NN Approximation
For the nonlinear control system, the RBF NNs and the FLS are two effective tools to deal with the unknown model terms. On that note, the RBF NN approximation technique is introduced here to remodel the unknown system terms of the USV. Lemma 1 is useful in the following controller design.
Lemma 1.
For any given nonlinear continuous functionwithdefined by a compact set, one can approximate the nonlinear function as Equation (5) by using the RBF NN approximation technique [24].
In Equation (5), indicates the approximation error with the unknown upper bound . is the basic function with the Gaussian form, and is the number of NN nodes. can be described by Equation (6).
where denotes the standard deviation and the indicates central abscissa. is the ideal weight matrix with the form of Equation (7), is the dimension number of the vector .
The control objective of this note includes two points: (1) the formation can track the predefined waypoints-based planned path accurately, and in particular, the followers can track the leader with a desired configuration without the leader’s unavailable velocity information; (2) all the control signals in the closed-loop system are guaranteed to be stable and semi-globally uniformly ultimately bounded.
3. DLLOS Guidance Principle
The proposed leader–follower framework with the DLLOS guidance principle can be seen in Figure 2. In marine practice, the ship formation always navigates along the waypoint-based planned path. For the follower ship, the leader’s information and the bearing angle and distance are required to define the desired formation configuration. However, in most existing leader–follower methods, the position and velocity information of the leader are assumed to be known to all followers, which is very unreasonable. For this purpose, a novel DLLOS guidance principle is proposed to address these practical problems at two layers, i.e., the leader layer and the follower layer.
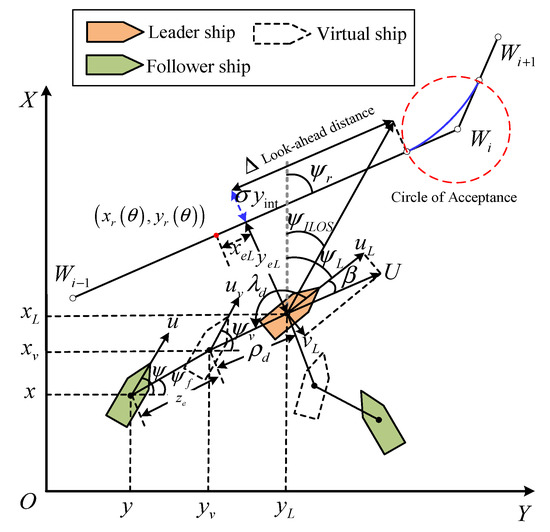
Figure 2.
The leader–follower framework with the DLLOS guidance principle.
Leader layer. In the leader layer, an adaptive LOS guidance law is designed for the leader to track the waypoint-based path. That can avoid the buffeting frequency of the heading angle and enhance the tracking performance. In the proposed guidance, the parameterized reference path is generated by the waypoints with . Considering the straight line as the reference path, the slope of the path is defined as . denotes the reference position, and is the path’s parametrized variables. Define the cross-tracking error and the along-tracking error of the leader as Equation (8).
Then, the kinematic error dynamics can be derived as Equation (9).
In Equation (9), is the resultant velocity of the leader, which can be calculated as and satisfies . The desired angle of the virtual point can be calculated as with and . denotes the sideslip angle of the leader ship. indicates the linear velocity of the virtual point, which is calculated as Equation (10).
In Equation (10), denotes the look-ahead distance, and indicate the designed minimum and maximum values of the look-ahead distance. is the curvature of the current position, and denote the positive designed control parameters. indicates the integrated item of the cross-tracking error with .
Define . To compensate the along-tracking error and the cross-tracking error , the corresponding LOS guidance law can be proposed as Equation (11).
Besides, the updating law of the path variable can be designed as Equation (12).
To control the leader’s tracking of the parameterized path, one can design the kinematic virtual control law as Equation (13). The kinetics control law for the leader is the same to the follower, which will be designed in Section 4.
In Equation (13), indicates the control parameters designed by the user, and denotes the heading angle error. To guarantee that the leader could track the reference path, one introduces the Theorem 1 as follows.
Theorem 1.
For the leader ship dynamics (9) with linear velocity (10), the LOS guidance law (11) and the kinematic control law (13), for any bounded initial state, the leader can track the reference path with small bounded errors, and all the related control signals can converge to the origin asymptotically.
Proof.
Choose the Lyapunov candidate function as Equation (14).
Considering Equations (9)–(13) and taking the derivative of Equation (14), one can obtain Equation (15).
Thus, for any given , we have , and then the following inequality can be obtained.
In Equation (16), . Therefore, the proposed guidance law can guarantee that all the tracking errors of the leader converge to the zero asymptotically. The proof is finished. □
Follower layer. In the follower layer, a virtual ship strategy with an adaptive speed controller is developed to program the smooth reference path for the followers. In marine practice, the velocity of the leader cannot be directly obtained by the followers, which is always neglected in the existing leader–follower formation control strategies. Thus, an adaptive speed controller will be developed, and the virtual ship will be introduced into the leader–follower framework. In this way, the followers are allowed to track the smooth path generated by the virtual ship mediately, rather than tracking the reference position directly.
In the earth-fixed frame, the reference position can be calculated from the position vector of the leader with the desired bearing angle and distance , which can be expressed as Equation (17).
To facilitate the following expression, Equation (17) can be rewritten as the vector form, i.e., Equation (18).
Then, the derivation of the reference position can be calculated as Equation (19).
where the speed vector is . It is worth noting that the vector includes the velocity information of the leader, which may be unknowable in marine practice. Referring to Assumption 2, one can obtain an unknown positive value such that . Thus, to overcome the constraint of the leader’s unknown speed information, we introduce the virtual ship dynamics as Equation (20).
In Equation (19), denotes the speed controller, which can be designed as Equation (20).
In Equation (20), denotes the control parameter diagonal matrix, and denotes the tracking error between the reference position and the virtual ship. indicates a positive constant, and denotes the estimating variable of , which can be updated by the adaptive law in Equation (21).
In Equation (20), and denote the control parameters. indicates the initial variable of the . To ensure that the virtual ship tracks the reference position, one introduces the Theorem 2 as follows.
Theorem 2.
Under Assumption 2, consider the virtual ship system (19) with the adaptive speed controller (20) and the adaptive updating law (21). For any bounded initial state, the virtual ship can track the reference trajectory of the followers. Besides, all the signals are proven to have semi-globally ultimately uniformly bounded (SGUUB) stability.
Proof.
Choose the Lyapunov candidate function as Equation (22).
Differentiating Equation (22), the time derivation of can be expressed as Equation (23).
By submitting the , and into Equation (23), one can further obtain Equation (24).
Substituting the speed controller (20) and the adaptive law (21) into Equation (24), the following inequality can be obtained.
Thus, Equation (26) can finally be derived.
In Equation (26), and . Integrating both sides of Equation (26), we have . It is worth noting that , which denotes that all the corresponding tracking errors are bounded by suitably adjusting the control parameters. Thus, the proof is finished. □
4. Robust Composite Dynamic Event-Triggered Controller
In this section, by using the backstepping method, the robust composite dynamic event-triggered formation control algorithm is proposed for USVs. To reduce the communication occupancy in the channel from the controller to the actuators, the dynamic event-triggered mechanism is designed by introducing an immediate signal as the system control input. The following Section 4.1 introduces the corresponding design of the dynamic event-triggered mechanism. Section 4.2 is used to present the formation controller derivation details.
4.1. Design of the Dynamic Event-Triggered Meachnisam
Motivated by the event-triggered method for the strict feedback system in [15], we design a dynamic event-triggered mechanism with an adjustable threshold parameter. This can guarantee that when the size of the control input is large, a long updating interval can be allowed; when the size of the input variable is small or approaches to zero, the threshold is shrunk to improve the control performance. The corresponding mechanism is designed as
In Equation (28), the event-triggered measurement error can be defined as , and denotes the event-triggered parameter used to avoid the Zeno behavior. When the event-triggered mechanism is triggering, the intermittent control input . To affect the inter-executive interval, the dynamic adjustable threshold can be designed as Equation (29), which has an adaptive form.
In Equation (29), denotes the control parameter set by the user. As seen from Equation (28), it is apparent that holds for the entire duration. Then, there should exist two unknown parameters and to express the event-triggered measurement error, i.e., Equation (30). For the cases and , the detailed expression of the parameters and can be derived as Equation (31).
In Equation (31), indicates any number such that . Thus, referring to Equations (30) and (31), the control input can be rewritten as Equation (32).
Remark 2.
Compared to the event-triggered method in [15], there are several characteristics. First, the proposed event-triggered method takes the steerable actuating input as the event-triggered input signal, which can facilitate its practical implementation in the marine industry. Second, the threshold parameteris not fixed all the time, and it can be adjusted according to the adaptive law (29). Thus, the developed dynamic event-triggered mechanism has greater flexible superiority than the traditional event-triggered method. Besides, to avoid the problem of the Zeno behavior, i.e., the infinite triggering times in a limited interval period, a skillful analysis will be developed in Section 4.3.
4.2. The Control Design for USVs
In this subsection, the detailed control design process will be presented, which includes the kinematic and kinetic parts.
Step 1: In this step, the kinematic tracking errors can be defined as Equation (33).
To facilitate the control law design, one defines . The azimuth angle in Equation (33) can be derived as Equation (34).
According to the mathematical model (1) and the tracking error (33), the kinematic virtual control laws can be derived as Equation (35).
In Equation (35), denote the designed control parameters. Then, the dynamic surface control (DSC) technique is utilized to avoid the constraint of the repeat differentiation of virtual control laws, namely the “explosion of complexity” problem. Thus, two first-order low-pass filters, , have been introduced, i.e., Equation (36) and allow the virtual control laws to pass through them over the time constants , respectively.
Define the dynamic surface errors as . Then, the derivative of the dynamic surface errors can be calculated as Equation (37).
In Equation (37), are bounded variables, and there exist two positive constants satisfying .
Step 2: In this step, the kinetic errors can be defined to facilitate the following controller design.
Then, considering Equations (2) and (38), the error dynamics can be obtained as Equation (39).
According to the Lemma 1, the system unknown function can be approximated as Equation (40).
In Equation (40), , . One defines and , and then and can be obtained. By substituting the control input signal Equation (32) and the unknown function Equation (40) into Equation (39), the kinetic tracking error dynamics can be rewritten as Equation (41).
with
In Equation (41), the robust neural damping terms can be constructed as Equation (42). Note that the variables , , and are all bounded. Besides, the terms and are also bounded and satisfy that and where are two positive constants. Then, the corresponding damping terms can be compressed as Equation (43).
In Equation (43), , and . To ensure the control orders generated by the controller transmit to the actuators smoothly, the executive serve system is also introduced to acquire the steerable control input variables, i.e., the main engine speed and the rudder angle . However, that will cause a non-negligible challenge, that is, the unknown actuating gains problem. For this purpose, the gain-related adaptive parameters are used to compensate for the gain uncertainty. Specifically, are the estimation of ; and . By incorporating the adaptive parameters, the immediate control laws and the actual control input can be derived as Equation (44).
In Equation (44), denote the control parameters. , and . Furthermore, to improve the control accuracy and predict the navigational velocity, the SPEM is established, and the corresponding SPEM-based prediction error can be defined as Equation (45).
The velocity prediction model can be constructed as Equation (46).
Combining Equation (41) with Equations (44)–(46), the derivative of the prediction variables can be calculated as Equation (47).
In Equations (46) and (47), are the positive control parameters, which determine the estimative performance of the velocity predictors. Recalling the above discussions, the corresponding gain-related composite adaptive learning parameters can be derived as Equation (48).
In Equation (48), indicate the adaptive control parameters set by the user. Finally, the Table 1 is given to summarize the key variables and their interpretations.

Table 1.
Interpretation of the key parameters.
4.3. Stability Analysis
In this section, the stability of the closed-loop control system will be proven by employing the Lyapunov stability criterion. The main results can be seen in Theorem 1.
Theorem 3.
Under Assumptions 1 and 2, for the considered USV mathematical model (1–2), all the state errors can stay close to the neighborhood of zero with the dynamic event-triggered mechanism (27, 28, 29), the actual control input (44), the velocity prediction model (47) and the composite adaptive laws (48), and the SGUUB stability can be guaranteed by selecting the proper parameters.
Proof.
One can choose the Lyapunov candidate function as Equation (49).
By using Equations (33), (35), (41) and (47), the derivative of the can be represented as Equation (50).
with the Young’s inequalities as
To facilitate the stability analysis, the following inequality can be derived.
Submitting Equations (44), (48), (53) and (54) into Equation (50), the derivative of the can be derived as Equation (55).
where and are positive constants satisfying Equation (56).
One can obtain Equation (57) by integrating Equation (55).
will converge to while by adjusting the designed control parameters and the adaptive parameters. The proof has been completed. □
To avoid the so-called “Zeno” behavior, we will provide an effective way to prove that there exists a positive time value satisfying . For the consideration of , we can obtain Equation (58).
Due to the fact that is differentiable and all the variables involved are bounded, there exists a positive constant such that holds. Besides, it is obvious that and . Thus, one can derive that . According to above analysis, the Zeno behavior is successfully ruled out.
5. Numerical Simulation
In this section, two simulation examples, i.e., the simulation experiment with the DLLOS guidance and the comparative experiment, have been carried out to verify the effectiveness and the superiority of the proposed control algorithm. For this purpose, we chose the USV plant named “Austal Patrol” with length and width as the control objective. In accordance with marine practical engineering, we introduce the executive serve system to generate steerable control orders rather than the unmeasurable control effort. The model parameter can be found in Table 2, and the more detailed information can be referred to in [34].

Table 2.
Parameter illustration of the considered model plant.
5.1. The Simulation with the DLLOS Guidance
In marine practice, the ship formation should navigate along the waypoints-based path. However, in most existing literature about formation control, this core problem has not been widely taken into consideration. Thus, in this subsection, five waypoints, , , , and , are set to verify the effectiveness of the proposed DLLOS guidance-based control scheme. Besides, to simulate a more practical navigation environment, the physical-based mathematical model is employed to generate the sea wind and wind-generated irregular waves. Specifically, the wind disturbance is always generated by the NORSOK wind spectrum, which consists of the mean wind and disturbing wind. The wave disturbance is generated by the JONSWAP wave spectrum, including the energy spectrum and the direction spectrum. The detailed construction process of these spectra can be found in [32]. Figure 3 gives the 2-D sketch field of surface wind and the 3-D irregular wave disturbances.
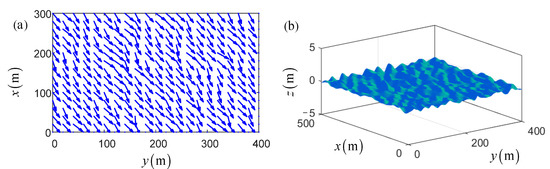
Figure 3.
The simulated marine environment: (a) the 2-D sketch field of surface wind; (b) the 3-D irregular waves.
To carry out the formation auto-navigation task, the initial states of the formation including three USVs (i.e., the leader, follower 1 and the follower 2) can be selected as for the leader and and for the followers. Furthermore, the designed control parameters and the adaptive parameters can be seen in Equation (59).
Under the marine environmental disturbances, the formation autonomous navigation can be seen in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. The formation trajectories of USVs with the proposed DLLOS guidance principle are displayed in Figure 4, and it is obvious that the leader can sail along with the waypoints and the followers can track the virtual ship’s generated smooth path with a favorable performance. Therefore, the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm can be verified.
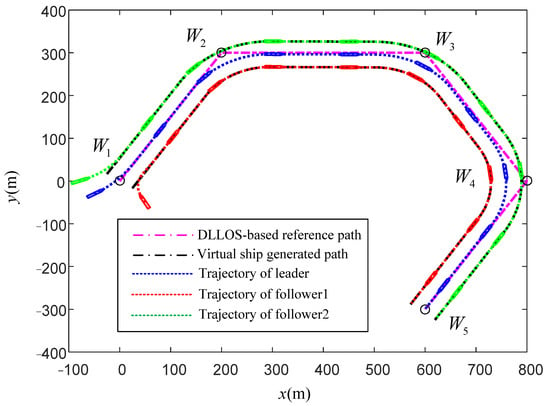
Figure 4.
The formation trajectories for USVs with the DLLOS guidance.
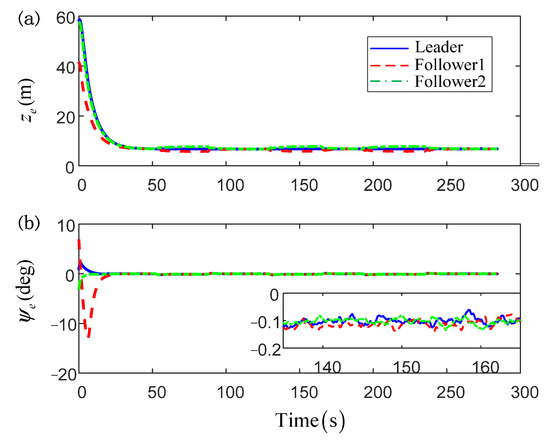
Figure 5.
The position and heading angle errors for USVs: (a) error curves of position; (b) error curves of heading angle.
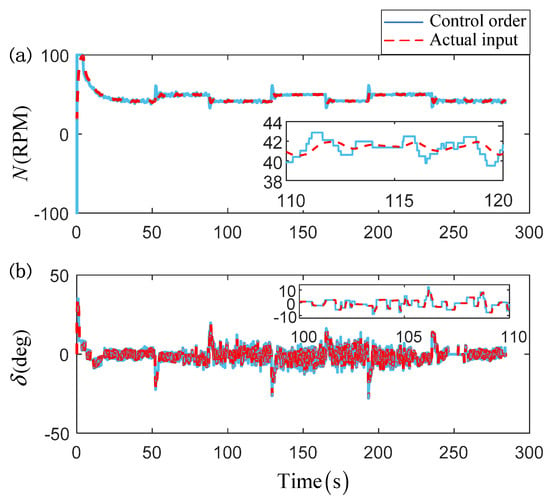
Figure 6.
The control input for follower 1: (a) control input of the propeller; (b) control input of the rudder.
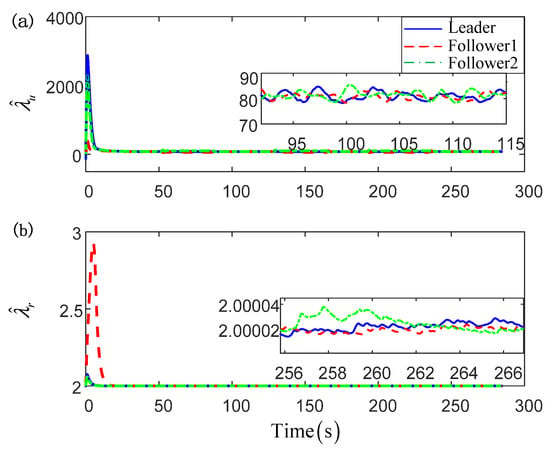
Figure 7.
The composite adaptive parameters for USVs: (a) adaptive parameters for surge motion; (b) adaptive parameters for yaw motion.
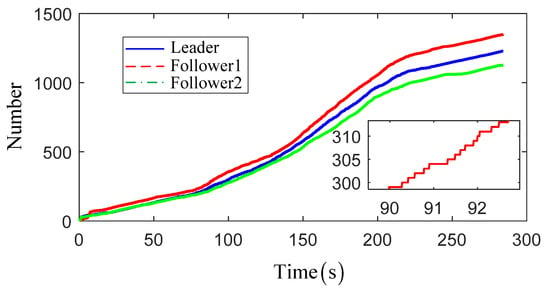
Figure 8.
The event-triggered cumulative number for USVs.
For more intuitive exhibition, the curves of the tracking errors are given in Figure 5, and both the position and heading angle errors have also illustrated the effectiveness of the proposed control scheme. For the purpose of clarity, the control input effect of only follower1 is provided in Figure 6. From this figure, one can find that the control orders are in a stair-stepping form, which is benefited by the designed dynamic event-triggered mechanism. That means that the control orders can be transmitted to the actuators only when it is necessary. In this way, the communication channel occupancy can be released, and the further excessive wear and chattering phenomenon of actuators can be effectively avoided. Besides, benefiting from the executive serve system, the actual input is presented as a smooth signal, which can guarantee the tracking accuracy of the proposed control scheme. Figure 7 presents the curves of the composite adaptive learning parameters of USVs. Note that, differing from the traditional neural approximation methods, only two adaptive parameters for each USV are required to be updated online rather than the enormous NN weight matrix. That can effectively reduce the calculated burden of the closed-loop control system. Moreover, Figure 8 presents the number of trigger instants that have occurred with respect to the total number of sampling instants. It is worth noting that the triggering number of every USV is lower than 1500, while the traditional continuous control scheme samples about 30,000 times (i.e., the simulation total time is about 300 s and the sampling step is 0.01 s). That means that the communication burden from the controller to the actuators can be largely reduced.
5.2. The Comparative Simulation
In this subsection, a comparative simulation has been employed to further illustrate the robustness and the superiority of the proposed control scheme. For this consideration, the proposed robust composite dynamic event-triggered control algorithm is compared with the static event-triggered control without the SPEM and robust neural damping technique. Without loss of generality, we consider one USV of the formation, i.e., follower1, to carry out the path-following task between the two algorithms. For the RBF NNs, the neural weight matrix includes eight neural nodes with width 2 and their centers evenly spaced in . The external disturbances and the corresponding control parameters are set to be the same as in Section 5.1, and the static trigger scheme has the fixed threshold parameter for the sake of fairness. Besides, the simulated total time is set as 120 s, and the initial states are selected as .
Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 describe the main comparative results of the path-following task under the proposed robust composite dynamic event-triggered control scheme and the static one. Figure 9 is the comparative results of the path-following trajectories under the 2-D platform. It is obvious that, although both schemes have satisfactory tracking accuracy, the proposed control scheme has more superior tracking performance. To show the control effect more intuitively, the output error curves are given in Figure 10, and the preferable tracking accuracy can be seen clearly under the proposed scheme. Figure 11 displays the comparative results of the control orders. Compared with the static trigger scheme, the proposed control scheme has a more flexible triggering manner, and thus a longer trigger interval and small buffeting can be achieved. Moreover, the triggered time and triggered interval under different schemes have been presented in Figure 12. From the enlarged detail, the proposed scheme has a superior triggering performance, and the dense accumulation of triggered time in a short time can be effectively avoided. Besides, to show the control effect more intuitively, we introduce three evaluation indexes to compare the two algorithms in Table 3. From Table 3, we can know that the proposed control scheme has fewer adaptive laws required to be updated online, and thus the low computational burden of a personal computer can be attained. The corresponding total number of triggering times can illustrate that the proposed scheme can achieve a more superior communication economizing effect.
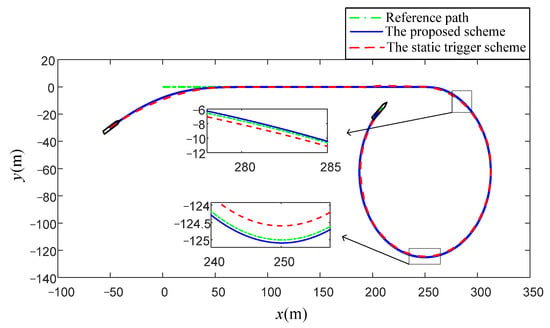
Figure 9.
The comparative results under the 2-D platform.
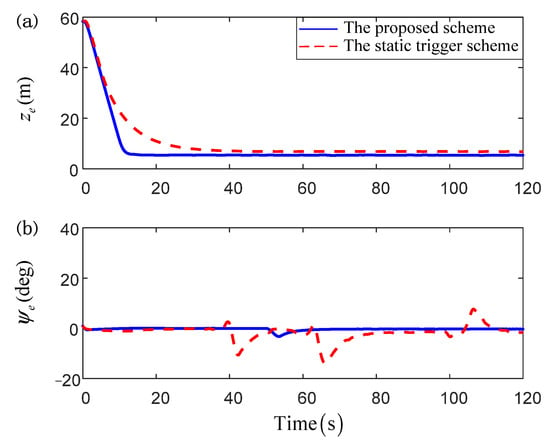
Figure 10.
The comparison of output errors: (a) error curves of position; (b) error curves of heading angle.
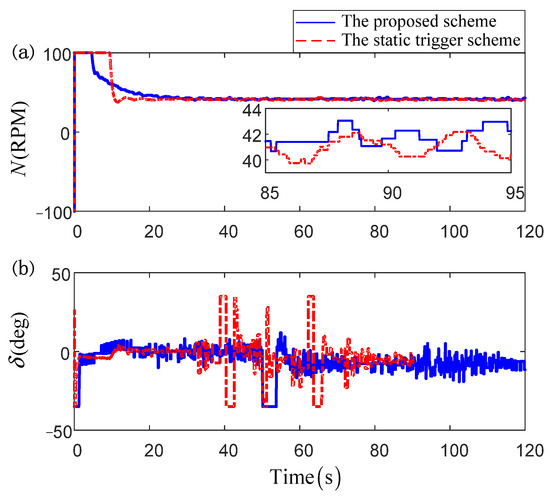
Figure 11.
The comparison of control orders: (a) the control order of propeller; (b) the control order of rudder.
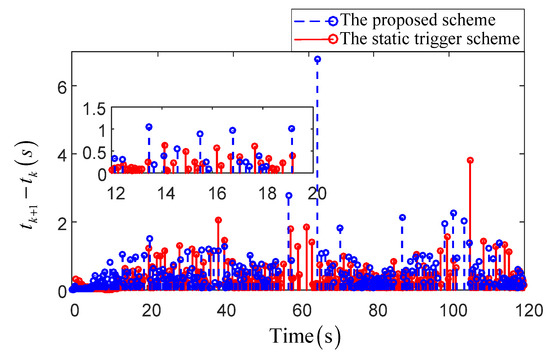
Figure 12.
The comparison of the triggered time and triggered interval.

Table 3.
The main comparison results for two algorithms.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, a robust composite dynamic event-triggered control scheme has been developed for USV formations to execute a waypoints-based auto-navigation mission. For this consideration, a novel DLLOS guidance principle has been developed in the leader–follower framework, and a smooth reference route can be generated by using the derived guidance law. As for the followers, a virtual ship strategy with a speed controller is designed to address the problem of the leader’s unobtainable velocity. Based on the proposed guidance principle, a robust control scheme is proposed by using the RBF NN approximation, the DSC method, the robust neural damping technique and the SPEM prediction. In this way, the model system uncertainty and ocean environmental disturbances can be remodeled and effectively compensated for. Differing from the traditional neural approximation methods, only two composite adaptive learning parameters are required to be updated online rather than an enormous weight matrix. Then, the SGUUB stability of the closed-loop control system was proofed via the Lyapunov theorem. Finally, two simulations, i.e., the guidance-based simulated example and the comparative one, have illustrated the effectiveness and the superiority of the proposed control scheme. Though meaningful results have been acquired in this paper, there are still several problems that are required to be solved in the future. For example, a dynamic event-triggered control to economize the communication burden in the sensor-to-controller channel should be further investigated. Besides, this work has not been verified by real testing, which will be the authors’ following direction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z. and S.L.; methodology, G.Z.; software, G.Z. and S.L.; validation, G.Z. and S.L.; formal analysis, S.L.; investigation, B.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.; writing—review and editing, G.Z.; supervision, G.Z.; project administration, G.Z. and X.Z.; funding acquisition, G.Z. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The paper is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52171291, 51909018), the Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program (No. 2021BQWB64), the Science and Technology Innovation Foundation of Dalian City (No. 2019J12GX026), the Dalian Innovation Team Support Plan in the Key Research Field (2020RT08) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 3132021132, 3132021340). The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the fundings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fossen, T.I.; Pettersen, K.Y. On Uniform Semiglobal Exponential Stability (USGES) of Proportional Line-of-Sight Guidance Laws. Automatica 2014, 50, 2912–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Ki Ahn, C. Hyperbolic-Tangent LOS Guidance-Based Finite-Time Path Following of Underactuated Marine Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 8566–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Peng, Z. ESO-Based Line-of-Sight Guidance Law for Path Following of Underactuated Marine Surface Vehicles with Exact Sideslip Compensation. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 42, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, A.M.; Fossen, T.I. Integral LOS Path Following for Curved Paths Based on a Monotone Cubic Hermite Spline Parametrization. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 2287–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X. Uniformly Globally Asymptotically Stable Path Following with Integral Gain-Variable Guidance Law for Ships. Control Theory Appl. 2015, 32, 850–858. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Sun, L.; Xie, L. Error-Constrained LOS Guidance Path Following of a Surface Vessel with Actuator Saturation and Faults. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, X. Improved Integral LOS Guidance and Path-Following Control for an Unmanned Robot Sailboat via the Robust Neural Damping Technique. J. Navig. 2019, 72, 1378–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Peng, Z.; Wang, H. Predictor-Based LOS Guidance Law for Path Following of Underactuated Marine Surface Vehicles with Sideslip Compensation. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 124, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xiang, X.; Lapierre, L.; Zhang, Q. Nonlinear guidance and fuzzy control for three-dimensional path following of an underactuated autonomous underwater vehicle. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 146, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Han, Q.L. An Overview of Recent Advances in Coordinated Control of Multiple Autonomous Surface Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, X. A novel DVS guidance principle and robust adaptive path-following control for underactuated ships using low frequency gain-learning. ISA Trans. 2015, 56, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Tong, S. Neural-Network-Based Adaptive Event-Triggered Consensus Control of Non-Strict Feedback Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 1750–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, G. Event-Triggered Adaptive Control of a Class of Nonlinear Systems. ISA Trans. 2019, 94, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Li, Y. Fuzzy Adaptive Event-Triggered Output Feedback Control for Nonlinear Systems with Tracking Error Constrained and Unknown Dead-Zone. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2021, 52, 2918–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wen, C.; Liu, Z.; Su, H.; Cai, J. Adaptive Compensation for Actuator Failures with Event-Triggered Input. Automatica 2017, 85, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, G. Model-Based Adaptive Event-Triggered Control of Strict-Feedback Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wen, C.; Huang, J.; Zhou, J. Adaptive Consensus of Uncertain Nonlinear Systems with Event-Triggered Communication and Intermittent Actuator Faults. Automatica 2020, 111, 108667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W. Event-Triggered Control for Unmanned Sailboat with Actuator Failures. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2021, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Nie, Z.; Yu, Y.; Hu, S.; Peng, Z. Event-Triggered Fuzzy Control of Networked Nonlinear Underactuated Unmanned Surface Vehicle. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 213, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, X. LVS Guidance Principle and Adaptive Neural Fault-Tolerant Formation Control for Underactuated Vehicles with the Event-Triggered Input. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 229, 108927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Wang, G. Event-triggered Trajectory Tracking Control Approach for Full Actuated Surface Vessel. Neurocomputing 2016, 182, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Malekian, R.; Sotelo, M. Event-Triggered Adaptive Neural Fault-Tolerant Control of Underactuated MSVs with Input Saturation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, C.L. Philip. Reduced-Order Observed-Based Dynamic Event-Triggered Adaptive NN Control for Stochastic Nonlinear Systems Subject to Unknown Input Saturation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 34, 1678–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tong, S. Fuzzy Adaptive Control Design Strategy of Nonlinear Switched Large-Scale Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, D.; Feng, G.; Tong, S. A DSC Approach to Robust Adaptive NN Tracking Control for Strict-Feedback Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2010, 40, 915–928. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, X. Concise Robust Adaptive Path-Following Control of Underactuated Ships Using DSC and MLP. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 39, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Shou, Y. Composite Learning Control of MIMO Systems with Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6414–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tong, S.; Li, T. Hybrid Fuzzy Adaptive Output Feedback Control Design for Uncertain MIMO Nonlinear Systems with Time-Varying Delays and Input Saturation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 24, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, W. Leader-Follower Formation Control of Underactuated Surface Vehicles Based on Sliding Mode Control and Parameter Estimation. ISA Trans. 2018, 72, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G. Improved Decentralized Finite-Time Formation Control of Underactuated USVs via a Novel Disturbance Observer. Ocean Eng. 2019, 174, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, C.; Li, W. Computationally Efficient MPC for Path Following of Underactuated Marine Vessels Using Projection Neural Network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 7455–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossion, T.I. Handbook of Marine Craft Hydrodynamics and Motion Control; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 112–124. [Google Scholar]
- Do, K.D. Practical Control of Underactuated Ships. Ocean. Eng. 2010, 37, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, K.D.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, J. Robust Adaptive Path Following Control of Underactuated Ships. Automatica 2004, 40, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).