Rostral Geometric Morphometrics in a Hippolytid Shrimp: Are There Elements That Reflect the Homozygous/Heterozygous State of Its Morphotypes?
Abstract
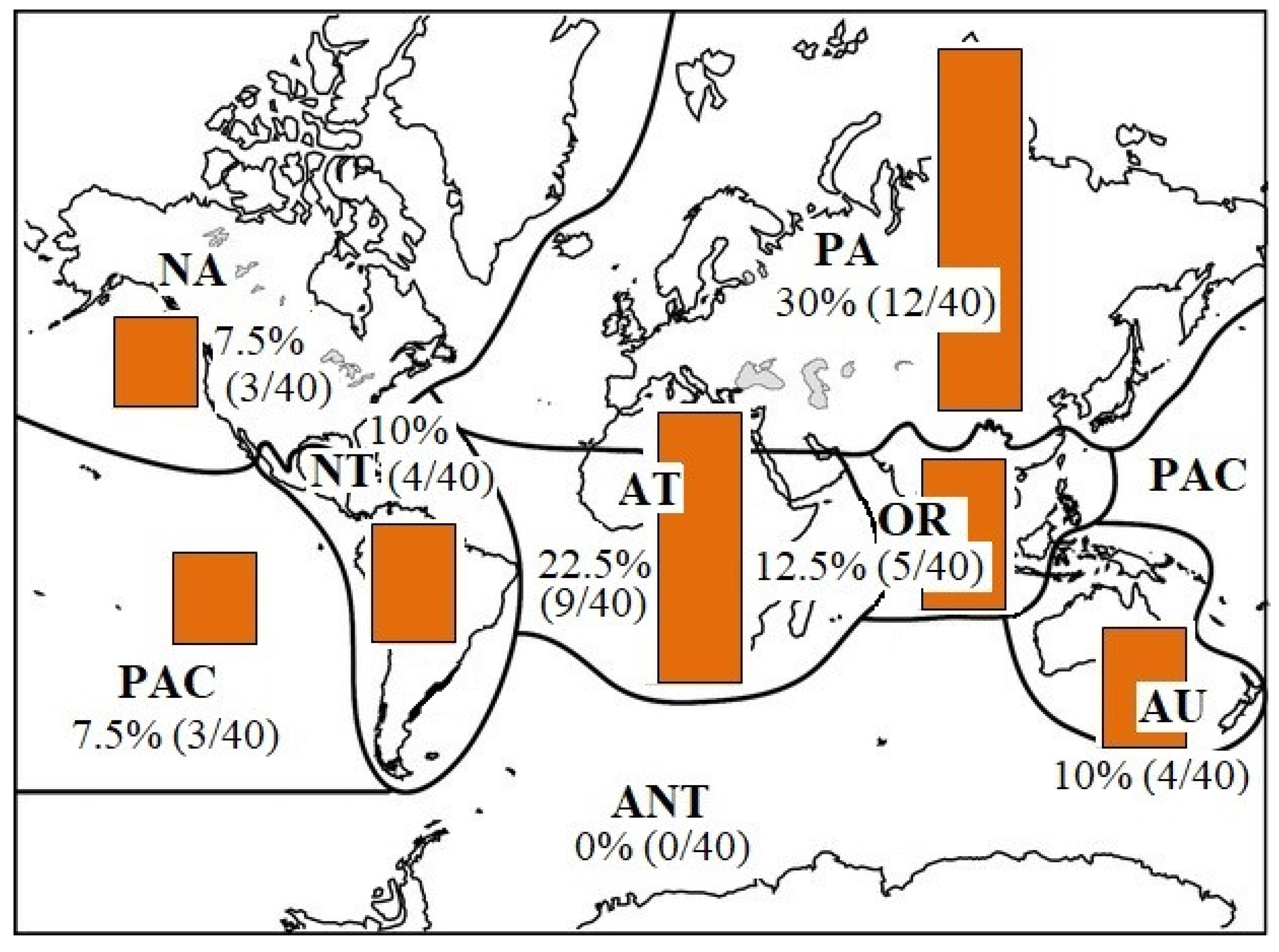
1. Introduction
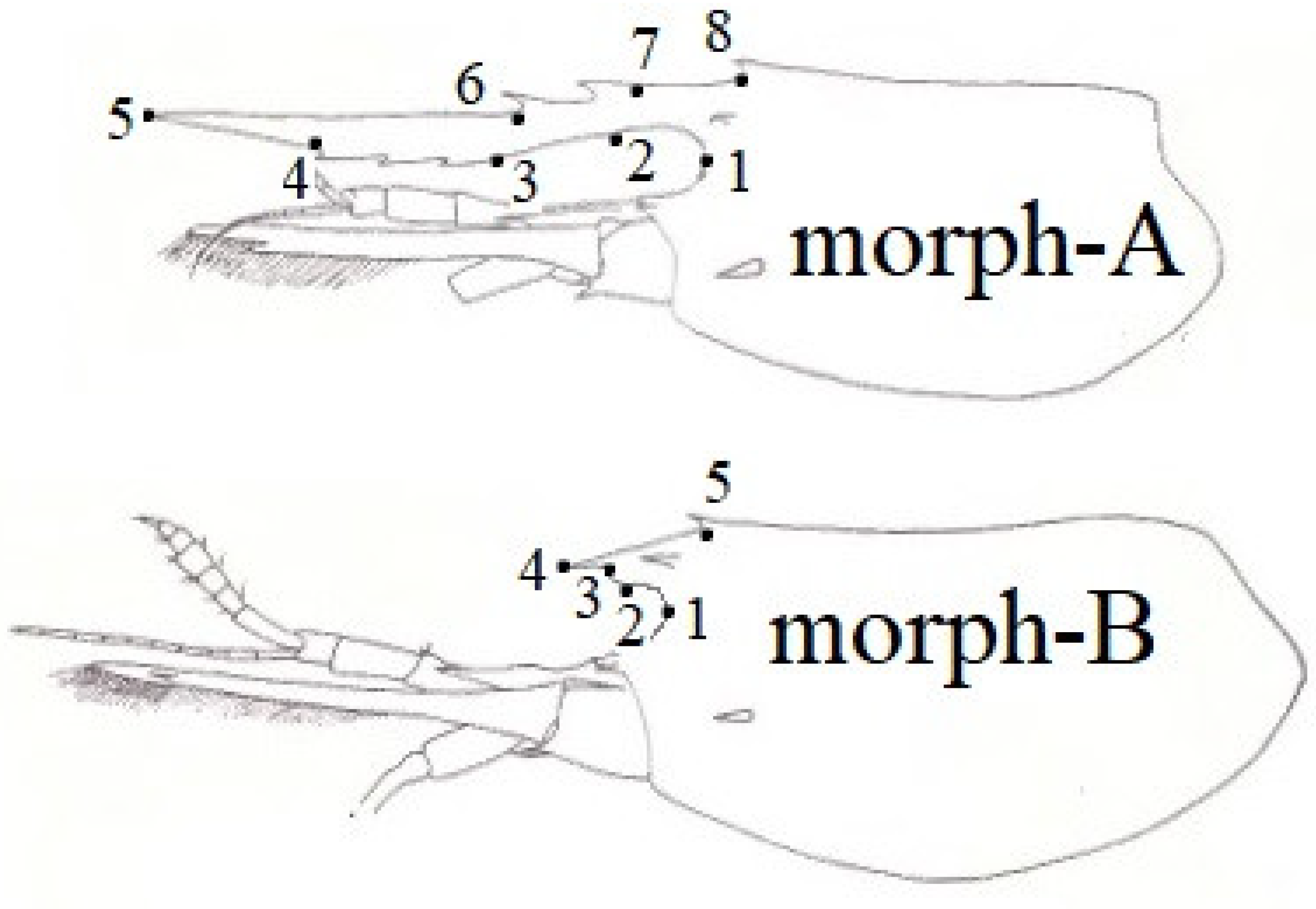
2. Material and Methods
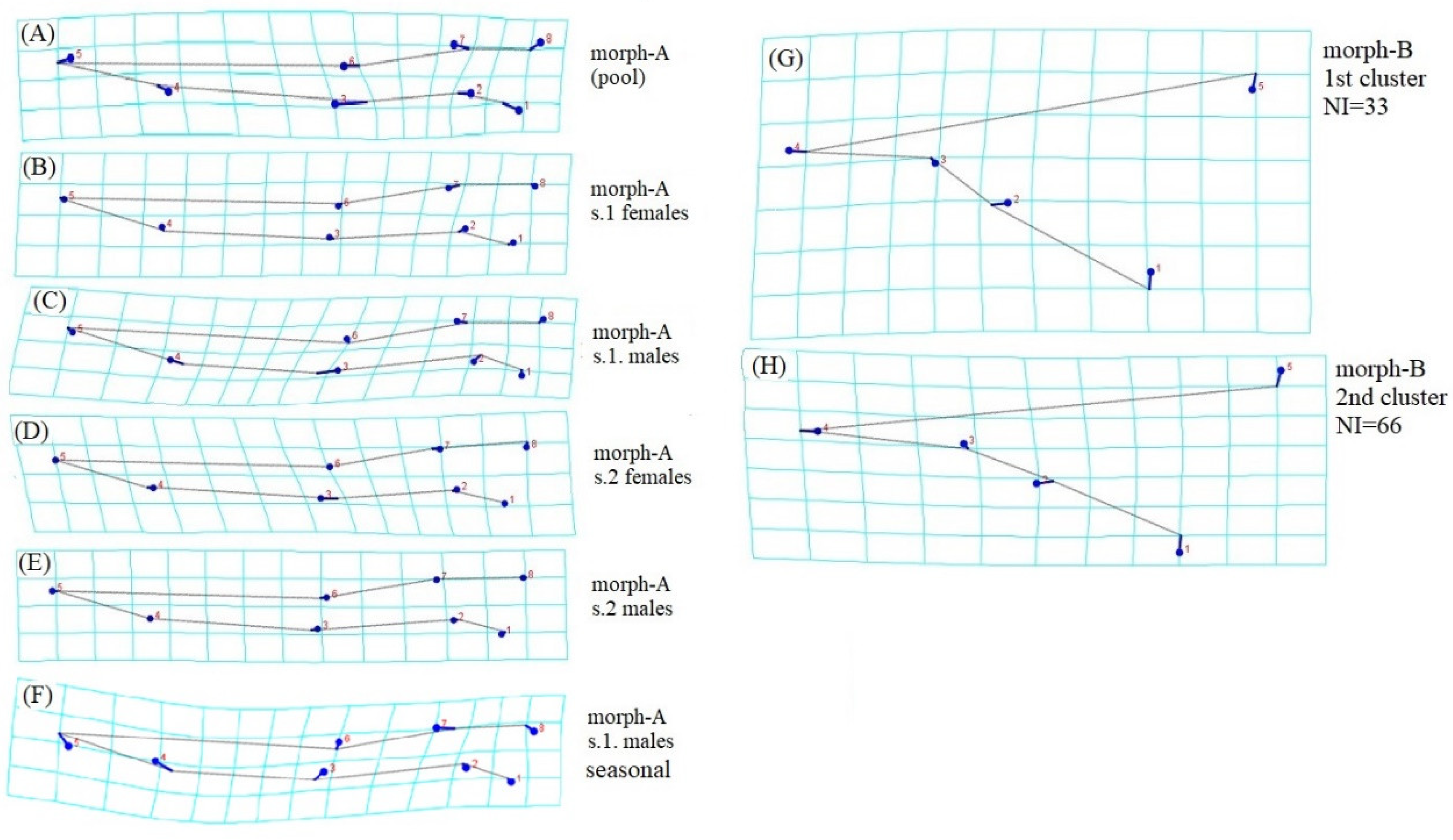
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohlf, F.J.; Marcus, L.F. A Revolution in Morphometrics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C.; Rohlf, F.J.; Slice, D.E. A field comes of age: Geometric morphometrics in the 21st century. Hystrix 2013, 24, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg, C.P. Evolution and development of shape: Integrating quantitative approaches. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, C.P. Size, shape, and form: Concepts of allometry in geometric morphometrics. Develop. Genes Evol. 2016, 226, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, F.; Collins, P. A geometric morphometric analysis of two sympatric species of the family Aeglidae (Crustacea, Decapoda, Anomura) from the La Plata basin. Ital. J. Zool. 2004, 71, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, F.; Loy, A. Size and shape variation of two freshwater crabs in Argentinean Patagonia: The influence of sexual dimorphism, habitat, and species interactions. J. Crust. Biol. 2008, 28, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idaszkin, Y.L.; Marquez, F.; Nocera, A.C. Habitat-specific shape variation in the carapace of the crab Cyrtograpsus angulatus. J. Zool. 2013, 290, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.V.; Giri, F.; Collins, P.A. Geometric morphometric analysis of the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium borellii (Decapoda: Palaemonidae) at a microgeographical scale in a floodplain system. Ecol. Res. 2014, 29, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liasko, R.; Anastasiadou, C.; Ntakis, A. Eco-morphological consequences of the “rostal loss” in the intertidal marine shrimp Hippolyte sapphica morphotypes. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2017, 98, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, G.I. Effect of geographic location and sexual dimorphism on shield shape of the Red Sea hermit crab Clibanarius signatus using the geometric morphometric approach. Can. J. Zool. 2018, 96, 667–679. [Google Scholar]
- Grinang, J.; Das, I.; Ng, P.K.L. Geometric morphometric analysis in female freshwater crabs of Sarawak (Borneo) permits addressing taxonomy-related problems. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Udekem d’Acoz, C. The genus Hippolyte Leach, 1814 (Crustacea, Decapoda, Caridea: Hippolytidae) in the East Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, with a checklist of all species in the genus. Zool. Verh. 1996, 303, 1–133. [Google Scholar]
- D’Udekem d’Acoz, C. Inventaire et distribution des Crustacés Décapodes de l’ Antlantique nord-oriental, de la Méditerranée et des eaux continentales adjacentes au nord de 25 N. Collect. Patrim. Nat. 1999, 40, 1–383. [Google Scholar]
- Rafinesque, C.S. Précis des Découvertes et Travaux somiologiques de Mr. C. S. Rafinesque Schmaltz Entre 1800 et 1814. Ou Choix Raisonné de Ses Principales Découvertes en Zoologie et en Botanique, Pour Servir D’ Introduction à Ses Ouvrages Futurs; BHL: Palermo, Italy, 1814; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Fabricius, J.C. Systema Entomologiae, Sistens Insectorum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, Adiectis Synonymis, Locis, Descriptionibus, Observationibus; BHL: Aachen, Germany, 1775; pp. 1–832. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, W.E. Malacostraca Podophthalmata Britanniae, Descriptions of Such British Species of the Linnean Genus Cancer as Have Their Eyes Elevated on Footstalks: 124 Unnumbered Pages; BHL: London, UK, 1815; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fransen, C.H.J.M.; De Grave, S. Two new species of Hippolyte from the Tropical Central and East Atlantic (Crustacea, Decapoda, Caridea). Zootaxa 2019, 4550, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Li, X. A new species of the genus Hippolyte (Decapoda: Caridea: Hippolytidae) from South China Sea and Singapore. Zootaxa 2017, 4258, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Terossi, M.; De Grave, S.; Mantelatto, F.L. Global biogeography, cryptic species and systematic issues in the shrimp genus Hippolyte Leach, 1814 (Decapoda: Caridea: Hippolytidae) by multimarker analyses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthuis, L.B. The Recent Genera of the Caridean and Stenopodidean Shrimps (Crustacea, Decapoda): With an Appendix on the Order Amphionidacea; Fransen, C.H.J.M., van Achterberg, C., Eds.; Nationaal Natuurhistorisch Museum: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 1–328. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, M.; Antoniou, A.; Magoulas, A.; Koukouras, A. Revision of the freshwater genus Atyaephyra (Crustacea, Decapoda, Atyidae) based on morphological and molecular data. ZooKeys 2012, 229, 53–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugovic, J.; Prevorcnik, S.; Aljancic, G.; Sket, B. The atyid shrimp (Crustacea: Decapoda: Atyidae) rostrum: Phylogeny versus adaptation, taxonomy versus trophic ecology. J. Nat. Hist. 2010, 44, 2509–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocasio-Torres, M.E.; Crowl, T.A.; Sabat, A.M. Allometric differences between two phenotypes of the amphidromous shrimp Xiphocaris elongata. J. Crust. Biol. 2015, 35, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, J.T.; Waloszek, D.; Maas, A.; Liu, Y.; Hayg, C. Functional morphology, ontogeny and evolution of mantis shrimp-like predators in the Cambrian. Palaeontology 2012, 55, 369–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grave, S. Variation in rostral dentition and telson setation in a saltmarsh population of Palaemonetes varians (Leach) (Crustacea: Decapoda: Palaemonidae). Hydrobiologia 1999, 397, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapiris, K.; Thessalou-Legaki, M. Sex related variability of rostrum morphometry of Aristeus antennatus (Decapoda: Aristeidae) from the Ionian Sea (Eastern Mediterranean, Greece). Hydrobiologia 2001, 449, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardà, F.; Demestre, M. Shortening of the rostrum and rostral variability in Aristeus antennatus (Risso, 1816) (Decapoda: Aristeidae). J. Crust. Biol. 1989, 9, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grave, S.; Cai, Y.; Anker, A. Global diversity of shrimps (Crustacea: Decapoda: Caridea) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Kim, J.N. New records of Hippolytid shrimps (Crustacea: Decapoda: Caridea) from Korea. Korean J. Syst. Zool. 2004, 20, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Davie, P.J.F. Hippolytidae. Crustacea: Malacostraca: Phyllocarida, Hoplocarida, Eucarida (Part 1). Zoological Catalogue of Australia. 19.3A; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Z.; Li, X. Recognizing two new Hippolyte species (Decapoda, Caridea, Hippolytidae) from the South China Sea based on integrative taxonomy. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, W.L. The Marine Decapod Crustacea of California with Special Reference to the Decapod Crustacea Collected by the United States Bureau of Fisheries Steamer “Albatross” in Connection with the Biological Survey of San Francisco Bay during the Years 1912–1913; University of California Pubs in Zoology: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1921; Volume 23, pp. 1–470. [Google Scholar]
- Schram, F.; von Vaupel Klein, C.; Charmantier-Daures, M.; Forest, J. Treatise on Zoology—Anatomy, Taxonomy, Biology. The Crustacea, Volume 9, Part A: Eucarida: Euphausiacea, Amphionidacea, and Decapoda (partim) (BRILL EDS). J. Crust. Biol. 2010, 33, 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- D’ Udekem d’ Acoz, C. New records of Atlantic Hippolyte, with the description of two new species, and a key to all Atlantic and Mediterranean species (Crustacea, Decapoda, Caridea). Zoosystema 2007, 1, 183–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff, E.N. Marine Invertebrates of the Pacific Northwest; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, I.; Okuno, J.; Chan, T.Y. On the “Hippolyte commensalis Kemp, 1925” species complex (Decapoda, Caridea, Hippolytidae), with the designation of a new genus and description of two new species from the Indo-West Pacific. Zootaxa 2011, 2768, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.I. The Central Pacific Shrimps of the Genus Hippolyte, with a Description of Two New Species (Decapoda, Caridea, Hippolytidae). Pac. Sci. 1981, 35, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zariquieyi Alvarez, R. Decápodos españoles VII. In Algo Sobre Hippolytidae de las Costas N.E. de España; CSIC-UBG-Instituto de Biología Aplicada: Barcelona, Spain, 1953; Volume 13, pp. 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Koukouras, A.; Anastasiadou, C. The genus Hippolyte (Decapoda, Caridea) in the Aegean and Ionian Seas. Crustaceana 2002, 75, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.; Penha-Lopes, G.; Macia, A.; Paula, J. Population structure and egg production of the seagrass shrimp Hippolyte kraussiana Stimpson, 1860 (Decapoda: Hippolytidae) at Inhaca island, Mozambique. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2007, 50, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaldwyn, J.C. Preliminary descriptions of a new genus and twelve new species of natant Decapod Crustacea from New Zealand. Rec. Dom. Mus. 1971, 7, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- D’Udekem d’Acoz, C. Redescription of Hippolyte obliquimanus Dana, 1852, and comparison with Hippolyte williamsi Schmitt, 1924 (Decapoda, Caridea). Crustaceana 1997, 70, 369–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terossi, M.; Mantelatto, F.L. Morphological and genetic variability in Hippolyte obliquimanus Dana, 1852 (Decapoda, Caridea, Hippolytidae) from Brazil and Caribbean Sea. Crustaceana 2012, 85, 685–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Udekem d’Acoz, C. Redescription of Hippolyte ventricosa H. Milne Edwards, 1837 based on syntypes, with remarks on Hippolyte orientalis Heller, 1862 (Crustacea, Decapoda, Caridea). Zoosystema 1999, 2, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Román-Contreras, R.; Martínez-Mayén, M. Shallow water hippolytid shrimps (Crustacea: Decapoda: Caridea) from the Mexican Caribbean coast. Hidrobiológica 2009, 19, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, G.; López-Duarte, P.C.; Able, K.W. Composition, Seasonality, and Life History of Decapod Shrimps in Great Bay, New Jersey. Northeast. Nat. 2019, 26, 817–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Udekem d’Acoz, C. Description d’une nouvelle crevette de l’île de Lesbos: Hippolyte sapphica sp. nov. (Crustacea, Decapoda, Caridea: Hippolytidae). Belg. J. Zool. 1993, 123, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ntakis, A.; Anastasiadou, C.; Liasko, R.; Leonardos, I. Larval development of the shrimp Hippolyte sapphica d’Udekem d’Acoz, 1993 forma A and B (Decapoda: Caridea: Hippolytidae) reared in the laboratory, confirmation of the conspecific status of the two forms. Zootaxa 2010, 2579, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liasko, R.; Anastasiadou, C.; Ntakis, A.; Leonardos, I.D. How a sharp rostral dimorphism affects the life history, population structure and adaptability of a small shrimp: The case study of Hippolyte Sapphica. Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, C.; Papathanasiou, V.; Kamidis, N.; Gubili, C. Crustacean decapod diversity associated with four shallow meadows of Cymodocea nodosa meadows from the North Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). J. Wildl. Biodivers. 2020, 4, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg, C.P. MorphoJ: An integrated software package for geometric morphometrics. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, W.; Miesen, F.W.; Hüllen, S.; Herder, F. Two Asian fresh water shrimp species found in a thermally polluted stream system in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Aquat. Invasions 2013, 8, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, M. Investigation of the Taxonomy, Zoogeography and Phylogeny of the Shrimps of the Genus Atyaephyra, in the Circum-Mediterranean Freshwaters. Ph.D. Thesis, Aritotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, M.; Anastasiadou, C. Sexual dimorphism in the shrimp genus Atyaephyra De Brito, 1867 (Caridea: Atyidae): The case study of Atyaephyra thyamisensis Christodoulou, Antoniou, Magoulas & Koukouras, 2012. J. Crust. Biol. 2017, 37, 588–601. [Google Scholar]
- De Mazancourt, V.; Marquet, G.; Keith, P.H. The “Pinocchio-shrimp effect”: First evidence of variation in rostrum length with the environment in Caridina H. Milne-Edwards, 1837 (Decapoda: Caridea: Atyidae). J. Crust. Biol. 2017, 37, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasser, A.G.; Sheldon, F.; Hughes, J.M. Spatial distributions and environmental relationships of two species complexes of freshwater atyid shrimps. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sars, G.O. Account of the post-embryonal development of Hippolyte varians Leach. Arch. Math. Nat. 1912, 32, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gurney, R. Notes on some decapod Crustacea of Bermuda II. The species of Hippolyte and their larvae. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1936, 106, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shield, P.D. Larval Development of the Caridean Shrimp, Hippolyte pleuracanthus (Stimpson), reared in the Laboratory. Estuaries 1978, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnich, R. The Larvae of the Crustacea Decapoda (excl. Brachyura) in the Plankton of the French Mediterranean Coast (Identification Keys and Systematics Review). Ph.D. Thesis, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Göttingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
| Taxa | Distribution | Depth Range (m) | Habitat | TL (mm) | RL/CL | Rostral Formula | Rostral Variability | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hippolyte acuta (Stimpson, 1860) | Pacific Ocean (N, S japan, Korea) | 2 to 5 | eelgrass bed | DD | 1.03–1.36 | 1(0)/0–4 (usually 1–2) | no | [12,29] |
| Hippolyte australiensis (Stimpson, 1860) | Australia | 0 to 15 | tufted algae | 18 to 25 | 1 | 0(0)/4–6 (rarely 3) | no | [12,30] |
| Hippolyte bifidirostris (Miers, 1876) | New Zealand | 18 to 36 | DD | DD | 1 | rostrum very long, strongly dentate, with bifid/trifid rostral apex | no | [12,30,31] |
| Hippolyte californiensis Holmes, 1895 | Northeastern Pacific Ocean | intertidal | seagrass, gorgonians | 38 | 1.16 | 3(0)/4–5 | no | [32,33] |
| Hippolyte caradina Holthuis, 1947 | Pacific Ocean | DD | DD | DD | DD | 2(1)/1 | no | [12,30] |
| Hippolyte catagrapha d ‘Udekem d’ Acoz, 2007 | S. Aftrica | 6 to 8 | Tropiometra carinata | 22 | 0.9 | 1(0)/2–3 | no | [34] |
| Hippolyte cedrici Fransen & De Grave, 2019 | Gulf of Guinea, tropical E Atlantic Ocean | 34 to 37 | Tanacetipathes spinescens, Antipathella wollastoni, Muriceopsis tuberculata | DD | 1 | 3(0)/2 | yes, males with slender rostrum, rostral formula: 3(0)/0–1) | [17,34] |
| Hippolyte chacei Gan & Li, 2019 | Hainan Island, ΝS China Sea | 1 to 3 | Sargassum sp. | DD | 0.9 | 0(0)/4 | yes, male rostral formula:1(0)/4 | [31] |
| Hippolyte clarki Chace, 1951 | NE Pacific Ocean | intertidal to 30 | seagrass, gorgonians | 28 | 0.8 to 1.4 | 3(0)/4 | no | [35] |
| Hippolyte coerulescens (J.C. Fabricius, 1775) | Atlantic Ocean | sublittoral | Drifting substrates, mud-sand flats, Sargassum natans | 16.5 | 0.7–0.9 | 1(0–2)(0)/1(3) | no | [12] |
| Hippolyte commensalis Kemp, 1925 | Indo-Pacific Ocean | 0.5 to 30 | Xenia sp. | DD | 0.7 | 0(0)/1 | no | [36] |
| Hippolyte dossena (Marin et al. 2011) | Izu Islands, Japan, Bali, and Ν Great Barrier Reef of Australia | 5 to 8 | Stereonephthea japonica, Efflatounaria sp. | DD | 0.5 | 0(0)/1 | no | [36] |
| Hippolyte edmondsoni Hayashi, 1981 | Indo-Pacific Oceanu, Hawaiian Islands | DD | DD | 10.3 | <0.5 | 0(1)/0 | no | [12,37] |
| Hippolyte garciarasoi d’ Udekem d’ Acoz, 1996 | Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea | 0 to 15 | photofilous algae, Posidonia oceanica | 15 | 0.6–0.8 | 2(1–3)(1)/1–4 | yes, in shape and dentition | [12] |
| Hippolyte holthuisi Zariquiey Alvarez, 1953 | Mediterranean Sea | 7 to 50 | Deep photophile algae, Coralligen, marine caves, coastal detritical bottoms | 19 | 0.9 | 2(0)/2 | no | [38,39] |
| Hippolyte inermis Leach, 1815 | Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea | 1 to 30 | Posidonia oceanica, Cymodocea nodosa, Zostera marina, Zostera noltii, and photophilous algae (Ulva spp.) | Atlantic: to 50.1 Mediterranean: to 39.5 | 1.1 | 0–1(2)(0)/2–3(0–6) | no | [12] |
| Hippolyte jarvinensis Hayashi, 1981 | Central Pacific Ocean, Jarvis and Line Islands, Solomon Islands | DD | DD | 8 | 0.7 | 1(0)/1 | no | [12,37] |
| Hippolyte karenae Fransen & De Grave, 2019 | St. Helena in the tropical South-Central Atlantic Ocean | 15 to 20.4 | Macrorhynchia filamentosa, Plumapathes pennacea | DD | <1 | 3(0)/2 | yes, males with slender rostrum, rostral formula: 1–3(0)/0–1) | [17] |
| Hippolyte kraussiana (Stimpson, 1860) | Indo-Pacific Ocean, Mozambique | 50 | Zostera capensis, Thalassodendron ciliatum, Halodule uninervis, Thalassia hemprichii, Halodule wrightii | DD | DD | DD | DD | [40] |
| Hippolyte lagarderei d’ Udekem d’ Acoz, 1995 | Atlantic Ocean | intertidal | Photophile algae: Laurencia pinnatifida, Gelidium sesquipetale | 22 | 0.67 to 0.78 | 0–2(0)/0–3 | yes, in shape inclination | [12] |
| Hippolyte leptocerus (Heller, 1863) | Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea | intertidal to 30 | Photophil algae:small seagrasses, Posidonia oceanica | Atlantic: 17.7 to 22.4 Mediterranean: 11 to 15 | 0.4–0.5 | 2–3(1–6)(1)/0–2(0–4) | yes, in shape and dentition | [12] |
| Hippolyte leptometrae Ledoyer, 1969 | Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea | 95 to 130 | Leptometra phalangium, L. celtica | 18 | 1.4 | 2(0)/2 | no | [12,34] |
| Hippolyte longiallex d ‘Udekem d’ Acoz, 2007 | NE Atlantic Ocean | 35 to 40 | Muriceopsis tuberculata | 8 | 0.7 | 2–3(0)/1–2 | no | [34] |
| Hippolyte multicolorata Yaldwyn, 1971 | Pacific Ocean | intertidal | algae | 8.5 | 1.1 | 0(0)/4–9, trifid apex | no | [41] |
| Hippolyte nanhaiensis Gan & Li, 2019 | Xisha Islands, South China Sea | 1 to 3 | Galaxaura sp., Halimeda sp. | DD | 0.7 | 2(0)/1 | no | [31] |
| Hippolyte ngi Gan & Li, 2017 | Subar Laut Island, St. John’s Island and Hainan Island, ΝS China Sea | 1 to 5 | Sargassum sp. | DD | 0.73 | 1(0)/2 | no | [18] |
| Hippolyte nicholsoni Chace, 1972 | Caribbean Sea | 2 to 12 | Pseudopterogorgia acerosa | DD | 0.3–0.5 | 1–2(0)/1–3 | no | [12] |
| Hippolyte niezabitowskii d’ Udekem d’ Acoz, 1996 | Mediterranean Sea | 0.5 to 5 | sheltered meadows, seagrasses | 10 to 20 | 0.8 | 0–2(0–4)(0)/0–4 | yes, in dorsal dentition | [12] |
| Hippolyte obliquimanus Dana, 1852 | NW Atlantic Ocean: U.S.A., Cuba, Saint Christopher, Antigua, Carriacou, Tobago, Guadeloupe, Curaqao, Puerto Rico, Venezuela, Brazil | intertidal | Thalassia testudinum, Syringodium filiforme | 15 | 1 | 3–4(0)/4, bifid apex | yes, shape and dentition | [42,43] |
| Hippolyte orientalis Heller, 1861 | Red Sea, Suez Canal, Gulf of Aden | intertidal | DD | DD | 1 | 1(0)/3 | no | [44] |
| Hippolyte palliola Kensley, 1970 | Atlantic Ocean | Intertidal to 25 | amongst algae on buttom with shells and hydroids | 10 | 0.3 | 1(0)/0 | no | [12] |
| Hippolyte pleuracanthus (Stimpson, 1871) | W Atlantic Ocean | 0.4 to 0.8 | sublittoral, turte-grass flatsmuddy substrate with T. testudinum, Zostera, Diplanthera | 12 to 18 | 0.5 | 2(0)/1 | no | [12,45,46] |
| Hippolyte prideauxiana Leach, 1817 (in Leach, 1815–1875) | Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea | intertidal to 60 | Antedon bifida and Antedon mediterranea | 10.4 to 21.7 | 0.6 | 0(0)/1–7 | yes, in ventral dentition | [12] |
| Hippolyte proteus (Paulson, 1875) | Red Sea, Suez Canal | DD | DD | 13 | 1.1 | 2(1–4)(0)/2(1–4) | no | [12] |
| Hippolyte sapphica d’ Udekem d’Acoz, 1993, “forma A” d’ Udekem d’ Acoz, 1996 | Mediterranean Sea | 0 to 1.5 | Zostera marina, Cymodocea nodosa | 12 to 27 | 1.1 | 2(1–3)(1–2)/ 2–3(1–4) | sharp dimorphic | [12,47] |
| Hippolyte sapphica d’ Udekem d’Acoz, 1993, “forma B” d’ Udekem d’ Acoz, 1996 | Mediterranean Sea | 0 to 1.5 | Zostera marina, Cymodocea nodosa, Cystoseira spp. | 15 | 0.25 | 0(1)/0 | sharp dimorphic | [12,47] |
| Hippolyte singaporensis Gan & Li, 2017 | Singapore | 0 to 1.5 | Enhalus acoroides, Sargassum spp., Padina spp. | DD | 1 | 0(0)/1 | no | [18] |
| Hippolyte varians Leach, 1814 (in Leach, 1813–1815) | Atlantic Ocean | 7 to 60 (mainly 20 to 40) | deep photophile algae, Coralligen, marine caves, coastal detritical bottoms | 20.1 to 32.2 | 0.8 | 2(0)/2(0–4) | yes in dentition | [12] |
| Hippolyte ventricosa H. Milne Edwards, 1837 (in H. Milne Edwards, 1834–1840) | Red Sea, Suez Canal, Indian Ocean | 1 to 3 | Thalassia sp., Sargassum sp. | 13 to 24 | 1.1 | 1–3(0)/1–5 | no | [12,31,37] |
| Hippolyte williamsi Schmitt, 1924 | E Pacific Ocean | intertidal | Sargassum sp. | 20 | 1 | 3(0)/4 | no | [12,42] |
| Hippolyte zostericola (Smith, 1873) | W Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean | 0.5 to 1.5 | sublittoral, soft substrata, turte-grass flats, T. testudinum, Halodule wrightii, Syringodium filiforme | DD | 0.5–0.7 | 2(0)/3 | no | [12,45] |
| Belong to | Classified in | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| February | November | Total | |
| February | 22 | 2 | 24 |
| November | 4 | 16 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anastasiadou, C.; Liasko, R.; Kallianiotis, A.A.; Leonardos, I. Rostral Geometric Morphometrics in a Hippolytid Shrimp: Are There Elements That Reflect the Homozygous/Heterozygous State of Its Morphotypes? J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111687
Anastasiadou C, Liasko R, Kallianiotis AA, Leonardos I. Rostral Geometric Morphometrics in a Hippolytid Shrimp: Are There Elements That Reflect the Homozygous/Heterozygous State of Its Morphotypes? Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(11):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111687
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnastasiadou, Chryssa, Roman Liasko, Athanasios A. Kallianiotis, and Ioannis Leonardos. 2022. "Rostral Geometric Morphometrics in a Hippolytid Shrimp: Are There Elements That Reflect the Homozygous/Heterozygous State of Its Morphotypes?" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 11: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111687
APA StyleAnastasiadou, C., Liasko, R., Kallianiotis, A. A., & Leonardos, I. (2022). Rostral Geometric Morphometrics in a Hippolytid Shrimp: Are There Elements That Reflect the Homozygous/Heterozygous State of Its Morphotypes? Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(11), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111687









