WGMG-Net: A Wavelet-Guided Real-Time Instance Segmentation Framework for Automated Post-Harvest Grape Quality Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Instance Segmentation Models for Agricultural Vision
2.2. Feature Enhancement for Detail Preservation and Occlusion Handling
2.3. Multi-Parameter Phenotyping and Multi-Task Learning
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
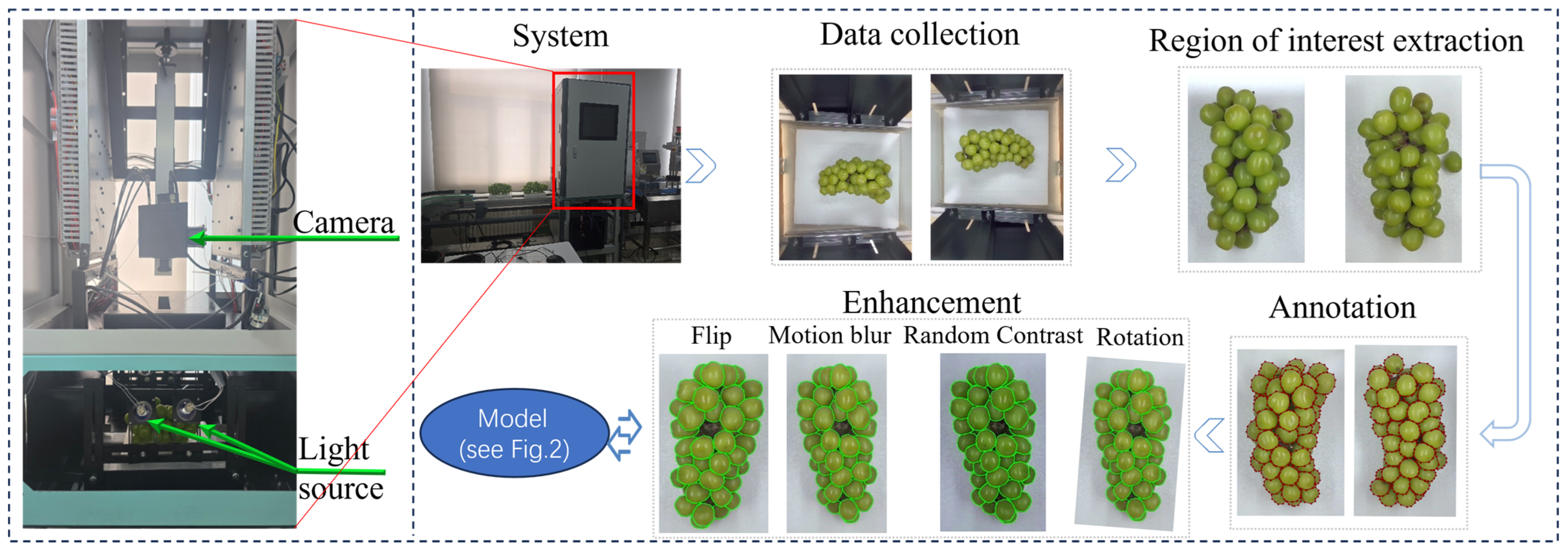
3.1.1. Image Acquisition Setup
3.1.2. Dataset Curation and Preprocessing
3.2. The Integrated Phenotyping Pipeline
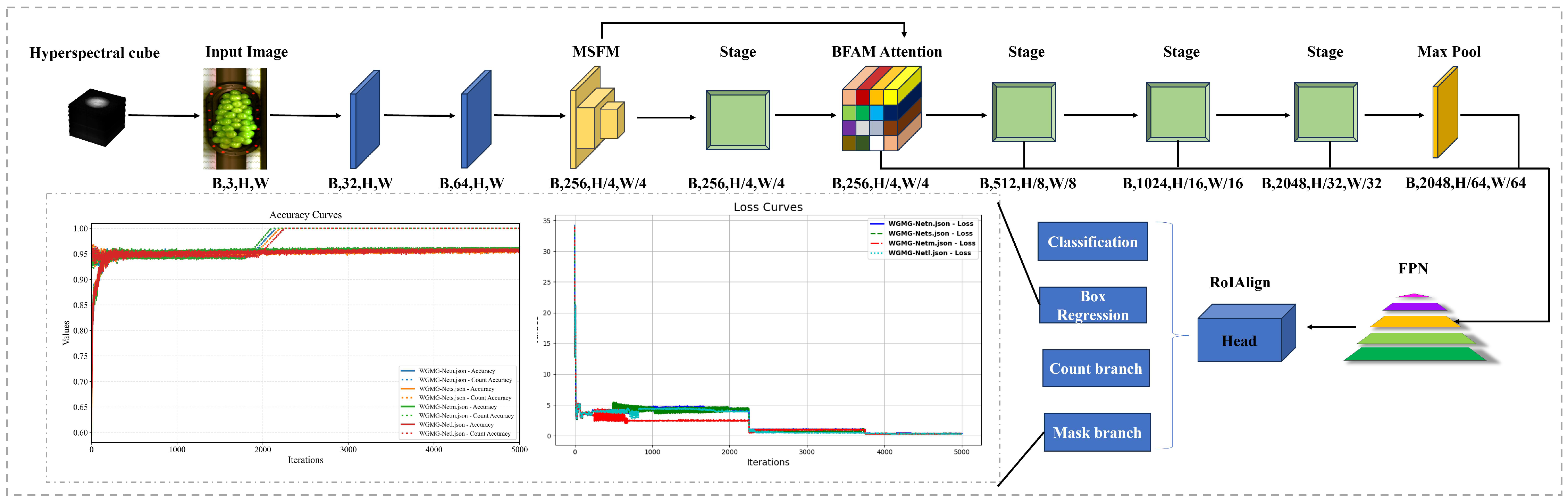
3.3. WGMG-Net Architecture
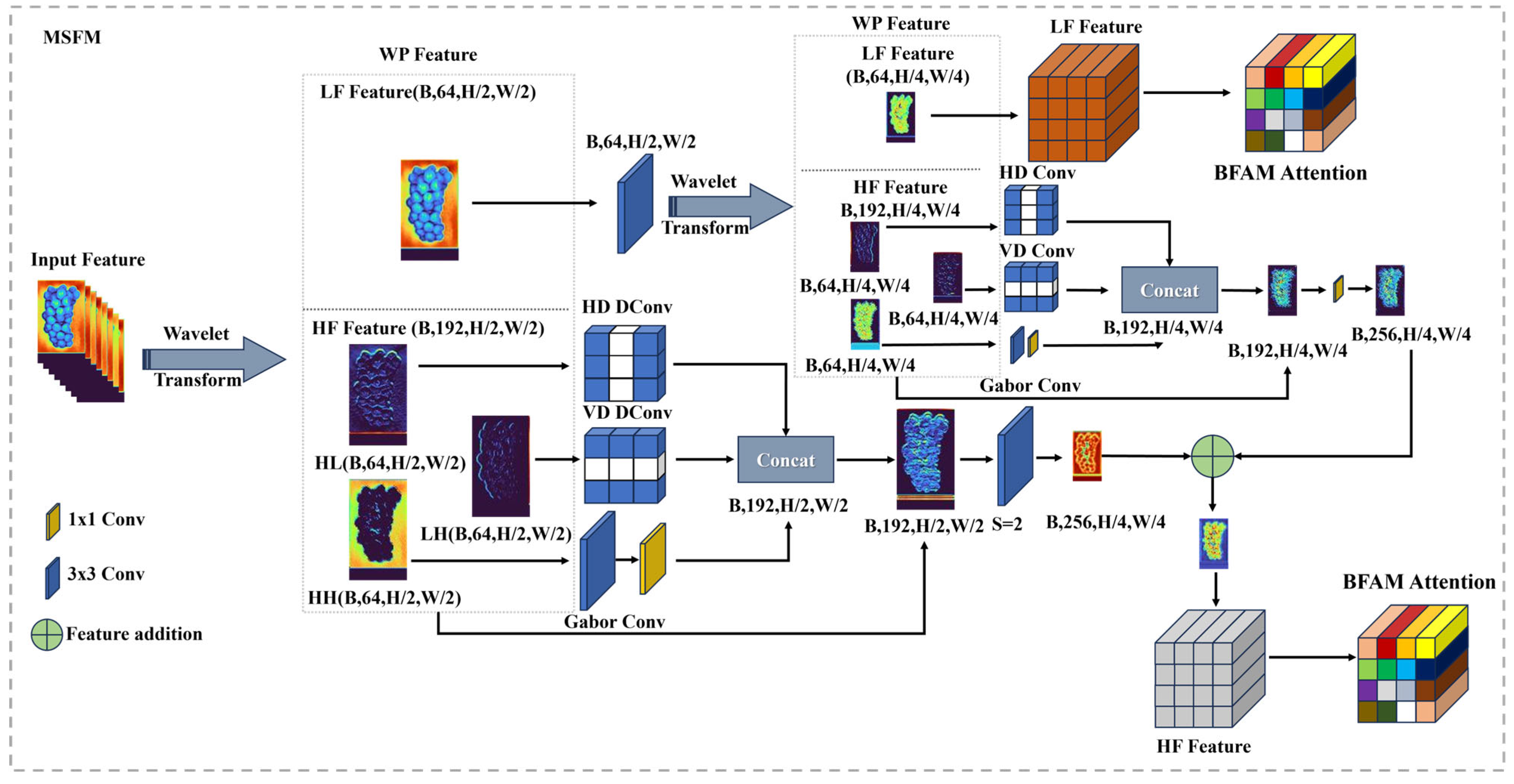
3.3.1. Multi-Scale Feature Merging Module (MSFM)
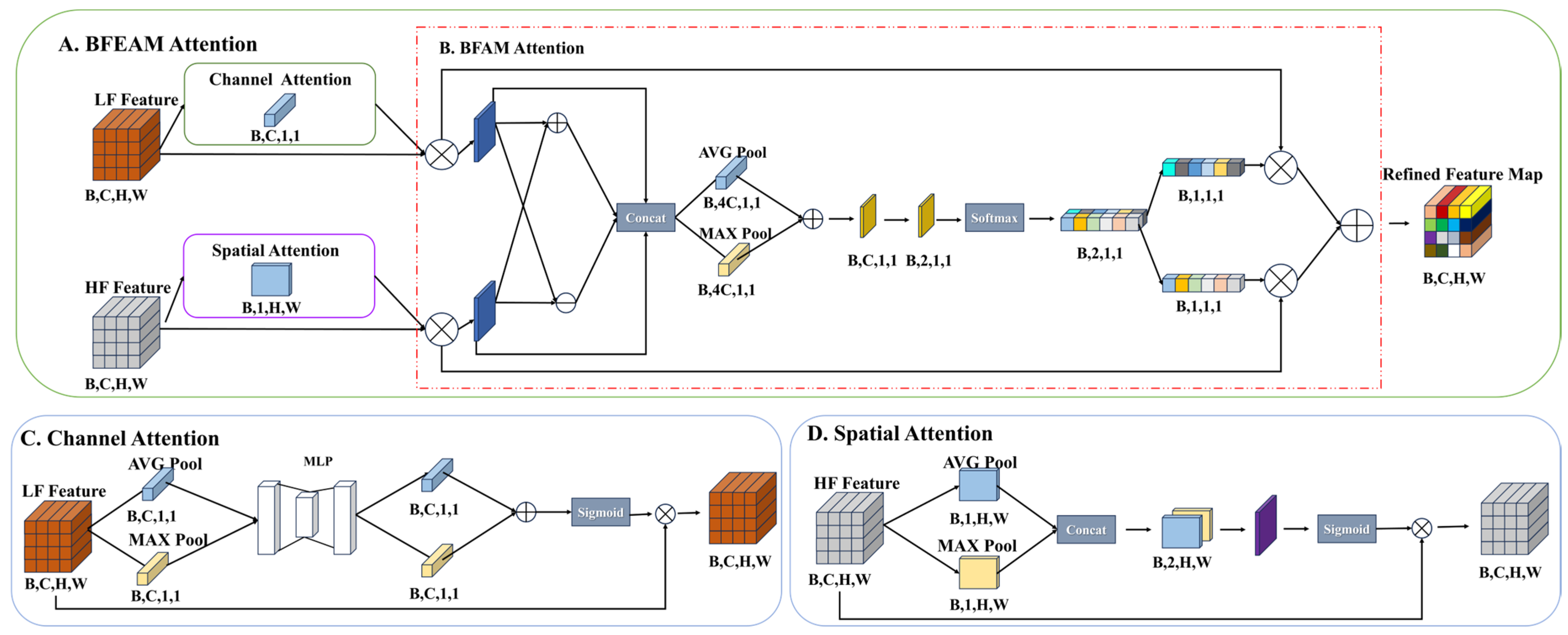
3.3.2. Bivariate Fusion Enhanced Attention Mechanism
3.3.3. Network Task Heads
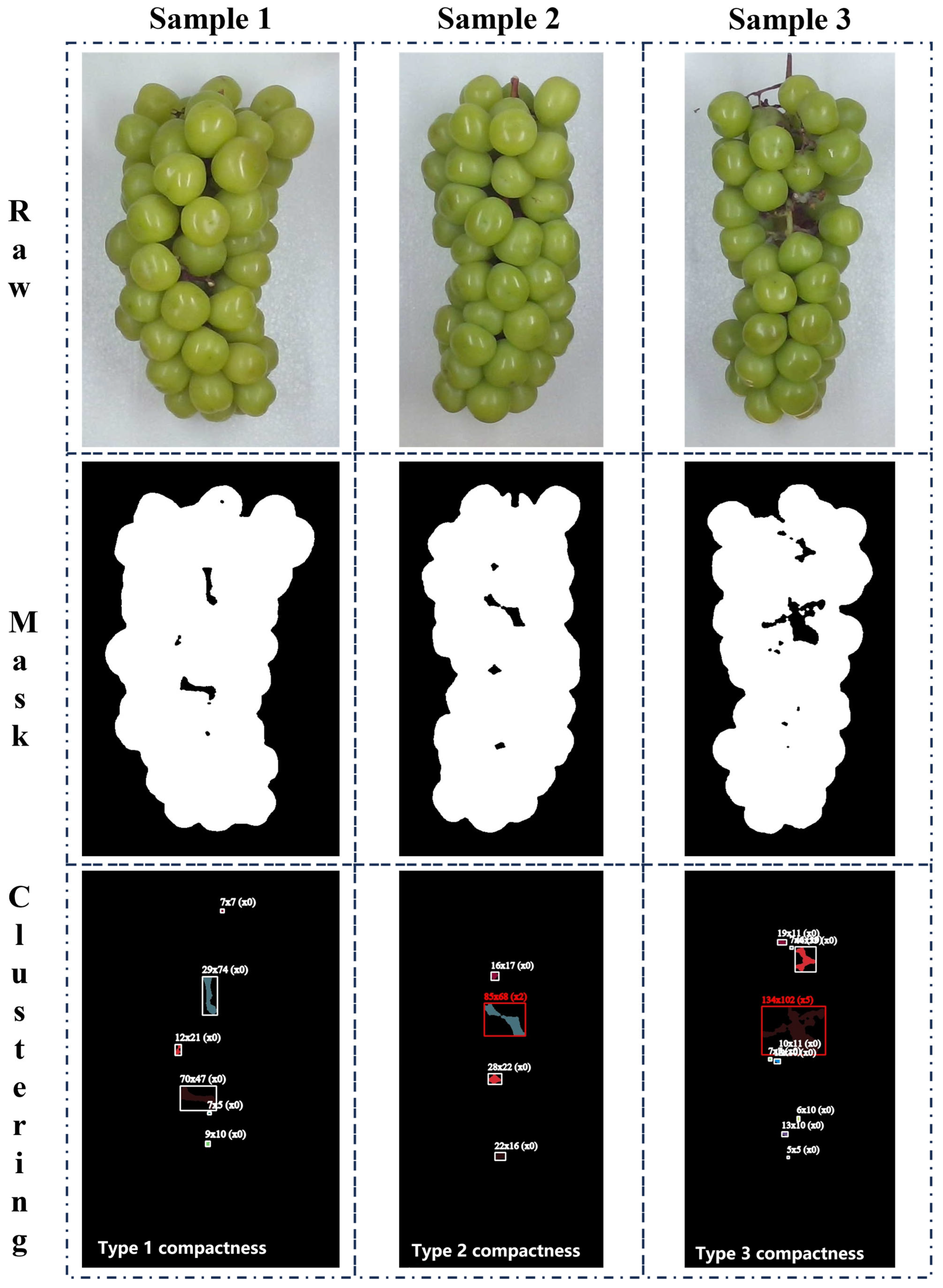
3.4. Morphological Compactness Classification
3.5. Network Loss Function
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.1.1. Experimental Environment
4.1.2. Implementation Details
4.1.3. Training Settings
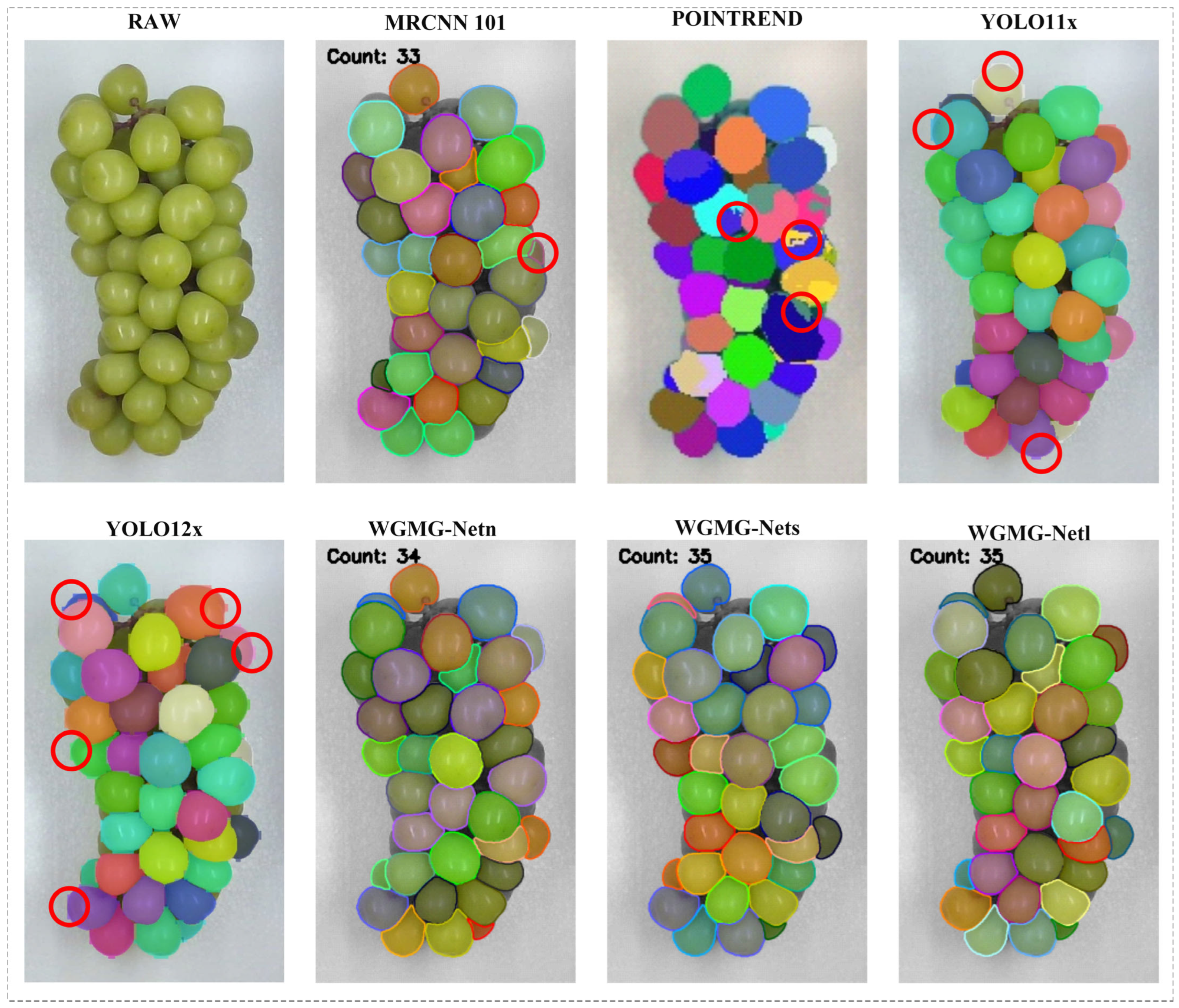
4.2. Analysis of Experimental Results
4.3. Ablation on Data Augmentation
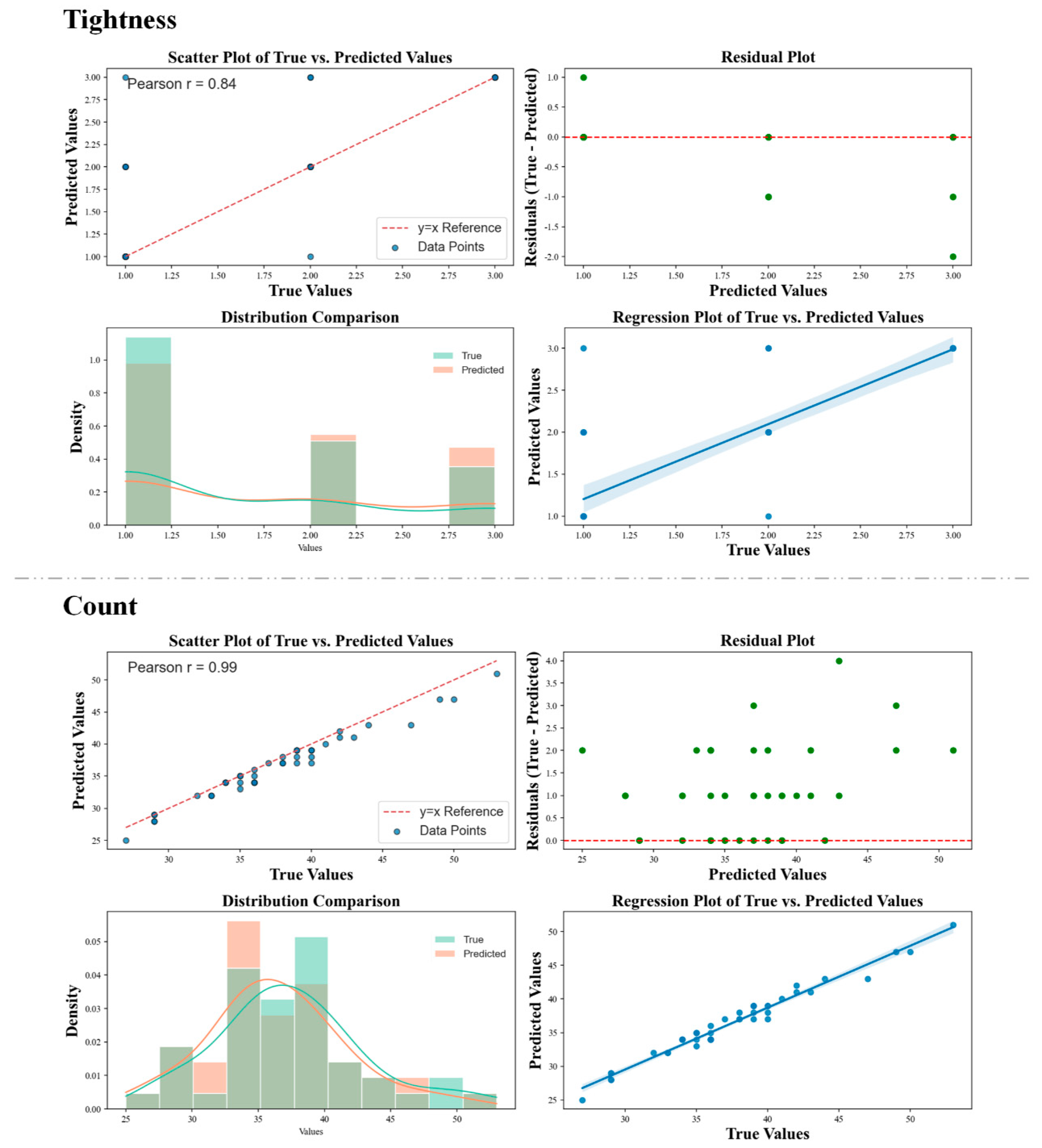
4.4. Phenotypic Analysis Results
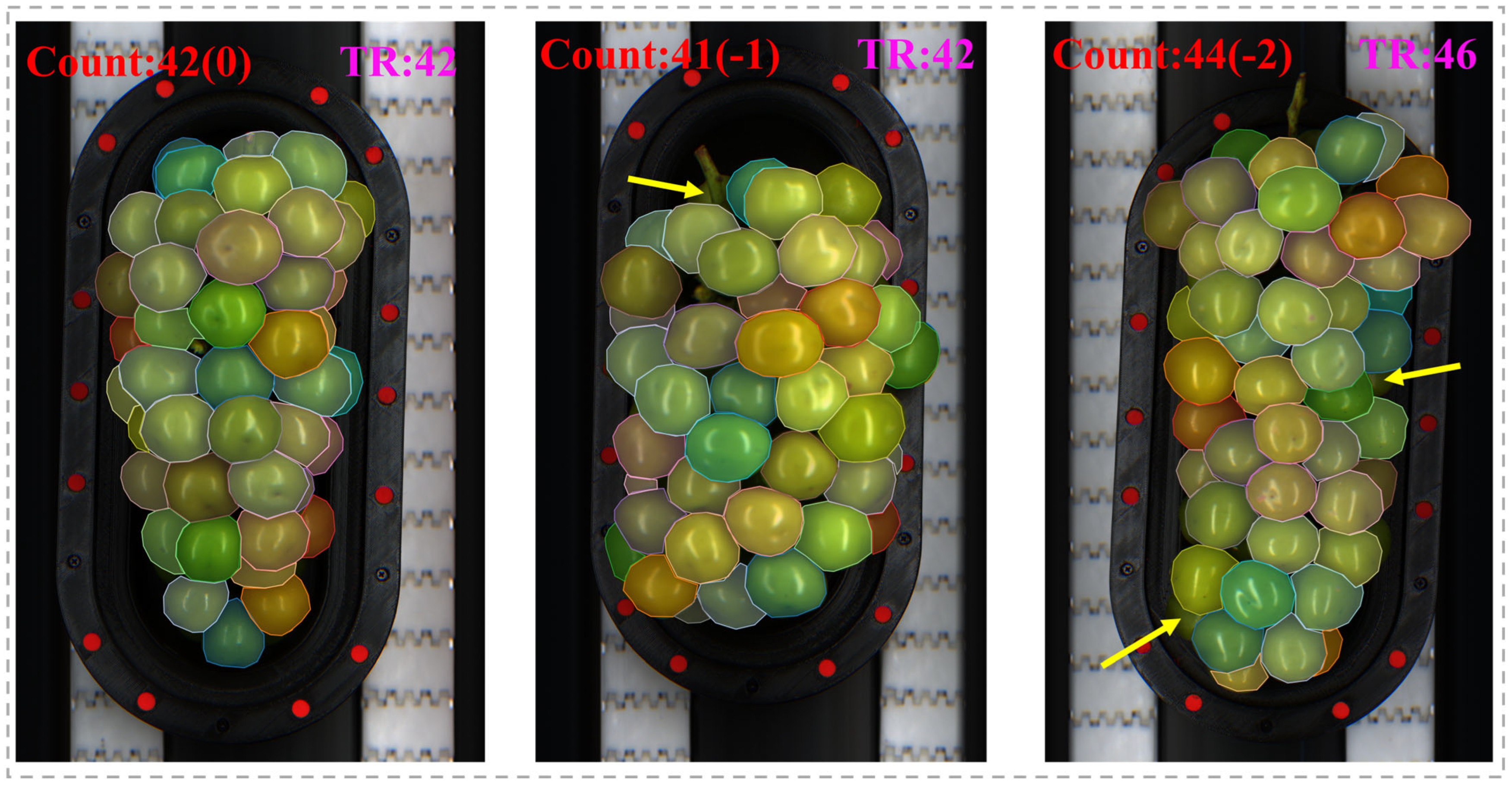
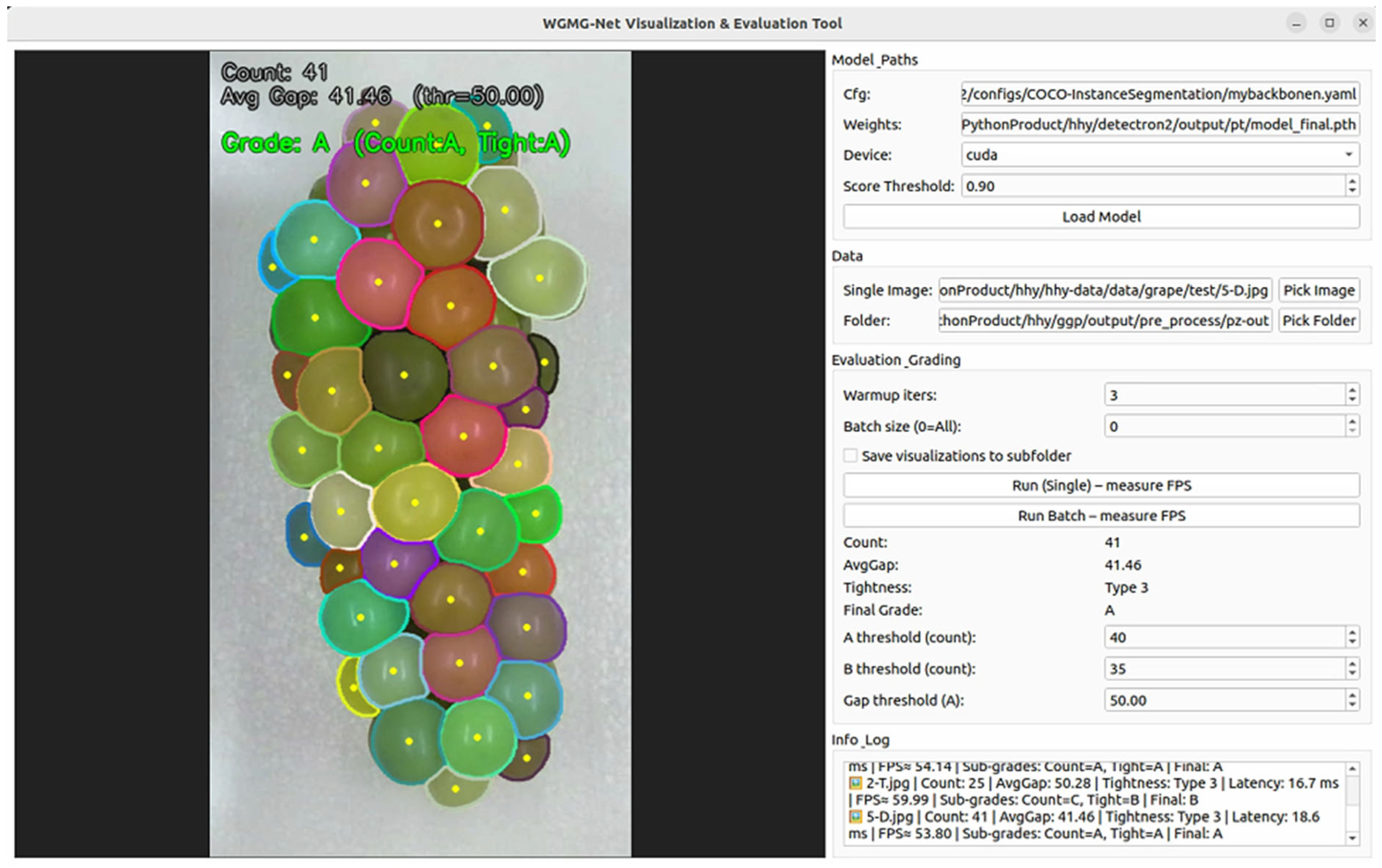
4.5. Practical Deployment and Evaluation
5. Discussion
5.1. Performance Advantages
5.2. Practical Acceptance Criteria
5.3. Integrated Grading Capability
5.4. Industrial Applicability
5.5. Scalability and Deployment Potential
5.6. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WGMG-Net | Wavelet-Guided Multi-Task Grape Network |
| MSFM | Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Module |
| BFEAM | Bivariate Fusion Enhanced Attention Mechanism |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| ACC | Accuracy |
| Pearson r | Pearson Correlation Coefficient |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| BCE | Binary Cross-Entropy Loss |
| Dice | Dice Loss |
| Lovász-Softmax | Lovász-Softmax Loss |
| mAP | mean Average Precision |
References
- Raheem, F.; Iqbal, N. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for the industrial internet of things (iiot). In Industrial Internet of Things; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Walas, F.; Redchuk, A. IIOT/IOT and Artificial Intelligence/machine learning as a process optimization driver under industry 4.0 model. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2021, 21, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, S.Z. Introductory Chapter: Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, and New Trends in Quality Control. In Quality Control-Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, and New Trends: Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, and New Trends; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2025; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Guo, L.; Xu, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 888–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Lu, H. Research Progress on Methods for Improving the Stability of Non-Destructive Testing of Agricultural Product Quality. Foods 2024, 13, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Lu, H. Application of nondestructive evaluation (NDE) technologies throughout cold chain logistics of seafood: Classification, innovations and research trends. LWT 2022, 158, 113127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, A.; Feroze, M.A.; Malik, S.N.; Zulfiqar, B.; Rafique, R.; Shah, M.H.; Javed, A.; Asif, M.; Ahmad, S.; Ayub, C.M.; et al. Yield and quality assessment of grapevine cultivar sultnina at different geographic locations of Punjab, Pakistan. CABI 2022, 10, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Meneses, M.; Muñoz-Espinoza, C.; Reyes-Impellizzeri, S.; Salazar, E.; Meneses, C.; Herzog, K.; Hinrichsen, P. Characterization of Bunch Compactness in a Diverse Collection of Vitis vinifera L. Genotypes Enriched in Table Grape Cultivars Reveals New Candidate Genes Associated with Berry Number. Plants 2025, 14, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Yan, L.; Liu, S.; Gao, T.; Han, L.; Jiang, X.; Jin, H.; Zhu, Y. Agricultural Image Processing: Challenges, Advances, and Future Trends. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Peng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Cen, J.; Jiang, D.; Xie, L.; Yang, X.; Tian, Q. A survey on label-efficient deep image segmentation: Bridging the gap between weak supervision and dense prediction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 9284–9305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Lin, G.; Xia, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y. Video object segmentation and tracking: A survey. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2020, 11, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Chandel, N.S.; Singh, K.P.; Chakraborty, S.K.; Nandede, B.M.; Kumar, M.; Subeesh, A.; Upendar, K.; Salem, A.; Elbeltagi, A. Deep learning and computer vision in plant disease detection: A comprehensive review of techniques, models, and trends in precision agriculture. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakuri, J.P.; Nkundineza, C.; Gatera, O.; Nkurikiyeyezu, K. State-of-the-art deep learning algorithms for internet of things-based detection of crop pests and diseases: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 169824–169849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, N.; Niu, Y.; Yin, X.; Ding, Y.; Ge, X. Accurate segmentation of green fruit based on optimized mask RCNN application in complex orchard. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 955256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Hicks, Y.; Sun, X.; Luo, C. Peach ripeness classification based on a new one-stage instance segmentation model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 214, 108369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, H.; Vatta, S. Occlusion detection and handling: A review. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 120, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Rathod, V.; Sun, C.; Zhu, M.; Korattikara, A.; Fathi, A.; Fischer, I.; Wojna, Z.; Song, Y.; Guadarrama, S.; et al. Speed/accuracy trade-offs for modern convolutional object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Wu, Y.; He, K.; Girshick, R. Pointrend: Image segmentation as rendering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Xia, L.; Gutierrez, B.; Gagne, I.; Munoz, A.; Eribez, K.; Jagnandan, N.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Waller, L.; et al. Low-latency label-free image-activated cell sorting using fast deep learning and AI inferencing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 220, 114865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurtsch, T.; Moryson, J.; Wiczyński, G. Machine vision-based detection of forbidden elements in the high-speed automatic scrap sorting line. Waste Manag. 2024, 189, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, W.; He, Z. Control Algorithms for Intelligent Agriculture: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions. Processes 2025, 13, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Lomas, E.; Lado-Bega, J.; Garcia-Zamora, G.; Diaz-Garcia, L. Segment Anything for comprehensive analysis of grapevine cluster architecture and berry properties. Plant Phenomics 2024, 6, 0202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, R.J.; Schapke, S.-E. A distributed multi-model-based management information system for simulation and decision-making on construction projects. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2011, 25, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, M.; Riomoros, I.; Pajares, G.; Zitinski, P. Discrete wavelets transform for improving greenness image segmentation in agricultural images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 118, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.D. Complex Wavelet Transforms and Their Applications. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J. HAF-YOLO: Dynamic Feature Aggregation Network for Object Detection in Remote-Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wan, Z.; Zhao, S.; Han, H.; Liu, Y. BFEA: A SAR ship detection model based on attention mechanism and multiscale feature fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 11163–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Gou, R.; Li, X. Semantic segmentation of agricultural images: A survey. Inf. Process. Agric. 2024, 11, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Shen, T.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Deep learning implementation of image segmentation in agricultural applications: A comprehensive review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.; Rodríguez, Í.; Rodríguez, N.; Usamentiaga, R.; García, D.F. Robot guidance using machine vision techniques in industrial environments: A comparative review. Sensors 2016, 16, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, C.S.; Lee, S. Low-complexity topological derivative-based segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 24, 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Su, J.; Huang, R.; Quan, W.; Song, Y.; Fang, Y.; Su, B. Fusing attention mechanism with Mask R-CNN for instance segmentation of grape cluster in the field. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 934450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M.; Hill, R.; Allen, P. A comprehensive review of convolutional neural networks for defect detection in industrial applications. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 94250–94295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. Yolact: Real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Kong, T.; Li, L.; Shen, C. Solov2: Dynamic and fast instance segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 17721–17732. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Elhilali, M.; Xiang, J.; Shamma, S.A.; Simon, J.Z. Interaction between attention and bottom-up saliency mediates the representation of foreground and background in an auditory scene. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Yu, Y. Efficient SonarNet: Lightweight CNN grafted vision transformer embedding network for forward-looking sonar image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, C.E.; Walnut, D.F. Continuous and discrete wavelet transforms. SIAM Rev. 1989, 31, 628–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T.; Burnett, C.; Pekkarinen, A. Image segmentation methods for object-based analysis and classification. In Remote Sensing Image Analysis: Including the Spatial Domain; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 211–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. An overview of multi-task learning. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K., VII. Mathematical contributions to the theory of evolution.—III. Regression, heredity, and panmixia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Or Phys. Character 1896, 187, 253–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Stage1-In-Out | Stage2-In-Out | Stage3-In-Out | Stage4-In-Out |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WGMG-Netn | 2-64-256 | 2-256-512 | 2-512-1024 | 2-1024-2048 |
| WGMG-Nets | 2-64-256 | 4-256-512 | 6-512-1024 | 3-1024-2048 |
| WGMG-Netm | 2-64-256 | 4-256-512 | 8-512-1024 | 3-1024-2048 |
| WGMG-Netl | 2-64-256 | 6-256-512 | 12-512-1024 | 3-1024-2048 |
| Model | mAP 50 | mAP 75 | mAP 50:95 | Param (M) | GFlops |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaskRCNN- Resnet50 | 98.81 | 93.60 | 82.33 | 43.98 | 75.81 |
| MaskRCNN- Resnet101 | 98.79 | 92.64 | 82.34 | 62.92 | 95.20 |
| PointRend | 98.52 | 89.63 | 80.52 | 55.71 | 75.81 |
| YOLOv11n | 96.62 | 92.21 | 84.35 | 2.87 | 10.5 |
| YOLOv11s | 96.65 | 92.20 | 84.36 | 10.11 | 35.8 |
| YOLOv11m | 96.98 | 92.64 | 84.56 | 22.42 | 123.9 |
| YOLOv11l | 97.21 | 93.02 | 85.12 | 27.67 | 143.0 |
| YOLOv11x | 98.52 | 95.34 | 85.65 | 62.14 | 320.2 |
| YOLOv12n | 98.20 | 95.64 | 85.60 | 2.85 | 10.6 |
| YOLOv12s | 98.20 | 95.67 | 85.60 | 9.94 | 35.7 |
| YOLOv12m | 98.61 | 96.21 | 85.92 | 22.51 | 123.5 |
| YOLOv12l | 98.96 | 96.50 | 86.31 | 28.76 | 145.1 |
| YOLOv12x | 98.97 | 97.25 | 86.86 | 64.39 | 324.6 |
| WGMG-Netn(Ours) | 98.94 | 97.84 | 87.59 | 36.91 | 116.38 |
| WGMG-Nets(Ours) | 98.94 | 97.88 | 87.60 | 46.40 | 124.39 |
| WGMG-Netm(Ours) | 98.98 | 97.82 | 87.70 | 48.63 | 126.68 |
| WGMG-Netl(Ours) | 98.98 | 97.90 | 87.76 | 53.60 | 133.55 |
| Attention | Model | mAP50 | mAP75 | mAP50:90 | Flops |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| / | WGMG | 98.926 | 97.805 | 87.221 | 0 |
| Channel Attention | 98.930 | 96.822 | 87.294 | 66,560 | |
| Spatial Attention | 98.927 | 96.812 | 87.211 | 100,352 | |
| Self Attention | 98.939 | 97.790 | 87.394 | 80,740,352 | |
| CBAM | 98.927 | 97.818 | 87.481 | 166,912 | |
| SE | 98.939 | 97.794 | 87.210 | 66,048 | |
| BFEAM(Ours) | 98.94 | 97.84 | 87.59 | 75,776,128 |
| Models | mAP 50 | mAP 75 | mAP 50:95 | RMSE (Count) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WGMG-Netn(Ours) | 98.14 | 97.04 | 86.79 | 1.96 |
| WGMG-Nets(Ours) | 98.34 | 97.58 | 87.32 | 1.82 |
| WGMG-Netm(Ours) | 98.68 | 97.65 | 87.46 | 1.76 |
| WGMG-Netl(Ours) | 98.88 | 97.84 | 87.71 | 1.53 |
| Type | / | Flip | Rotation | Gaussian Blur | Random Contrast | mAP@50:95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | - | - | - | - | 84.350 | |
| - | √ | - | - | - | 85.352 | |
| - | √ | √ | - | - | 85.653 | |
| - | √ | √ | √ | - | 86.678 | |
| - | √ | √ | √ | √ | 87.59 |
| Methods | MAE | RMSE | MAPE (%) | Acc@2 (%) | Pearson r | Time-Consuming |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaskCount | 1.10 | 1.48 | 2.82 | 92.86 | 0.986 | 3 ms |
| DensityMap | 1.68 | 2.12 | 4.01 | 90.12 | 0.951 | 2.6 ms |
| Ours | 1.10 | 1.48 | 2.82 | 92.86 | 0.986 | 0.5 ms |
| Phenotype | MAE | RMSE | MAPE (%) | ACC@1 (%) | Acc@2 (%) | Pearson r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 1.10 | 1.48 | 2.82 | 66.67 | 92.86 | 0.986 |
| Compactness | 0.18 | 0.46 | 14.71 | 98.04 | 100 | 0.844 |
| Test Mode | Total Number of Images | Average Latency (ms) | FPS | Average Counting Error | Grade Distribution (A/B/C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-frame inference | 43 | 11.7 | 54.4 | 0.89 | 23/18/2 |
| Batch inference | 43 | 26.8 | 37.25 | 0.89 | 23/18/2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Hao, H.; Zhuang, L.; Yang, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, X.; Li, J. WGMG-Net: A Wavelet-Guided Real-Time Instance Segmentation Framework for Automated Post-Harvest Grape Quality Assessment. Agriculture 2026, 16, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010121
Hao H, Zhuang L, Yang Y, Yu C, Yang X, Li J. WGMG-Net: A Wavelet-Guided Real-Time Instance Segmentation Framework for Automated Post-Harvest Grape Quality Assessment. Agriculture. 2026; 16(1):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010121
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Haoyuan, Lvhan Zhuang, Yi Yang, Chongchong Yu, Xinting Yang, and Jiangbo Li. 2026. "WGMG-Net: A Wavelet-Guided Real-Time Instance Segmentation Framework for Automated Post-Harvest Grape Quality Assessment" Agriculture 16, no. 1: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010121
APA StyleHao, H., Zhuang, L., Yang, Y., Yu, C., Yang, X., & Li, J. (2026). WGMG-Net: A Wavelet-Guided Real-Time Instance Segmentation Framework for Automated Post-Harvest Grape Quality Assessment. Agriculture, 16(1), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010121







