The V-Type H+-Transporting ATPase Gene PoVHA-a3 from Portulaca oleracea Confers Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana Through the Modulation of BR-ABA Signaling Balance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Cloning and Bioinformatic Characterization of PoVHA-a3
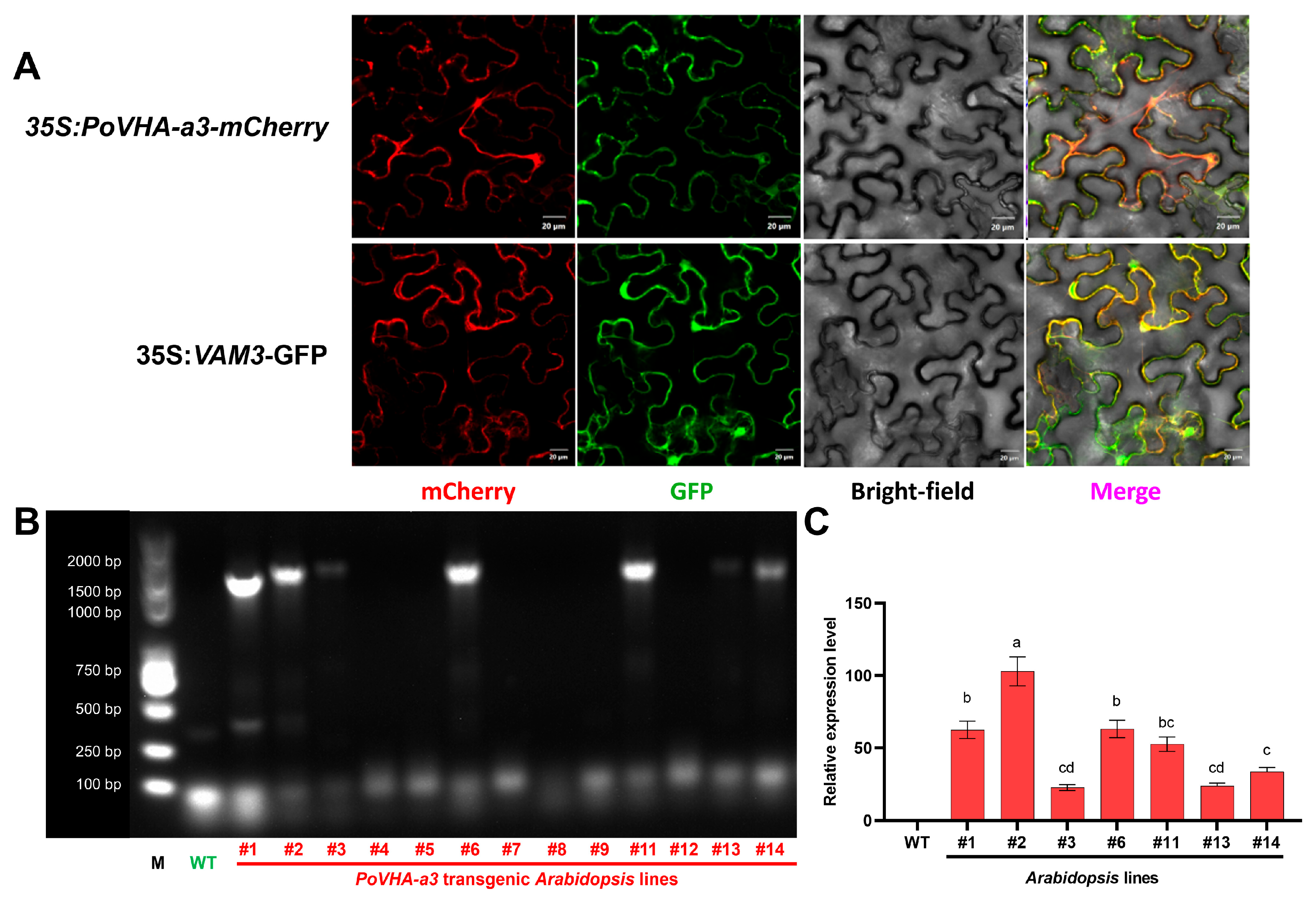
2.3. Subcellular Localization of PoVHA-a3 and Selection of Transgenic Lines
2.4. Salt Tolerance Analysis of PoVHA-a3 Expression Arabidopsis Plants
2.5. Analysis of Physiological Indices and Gene Expression in Arabidopsis Under Salt Stress
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
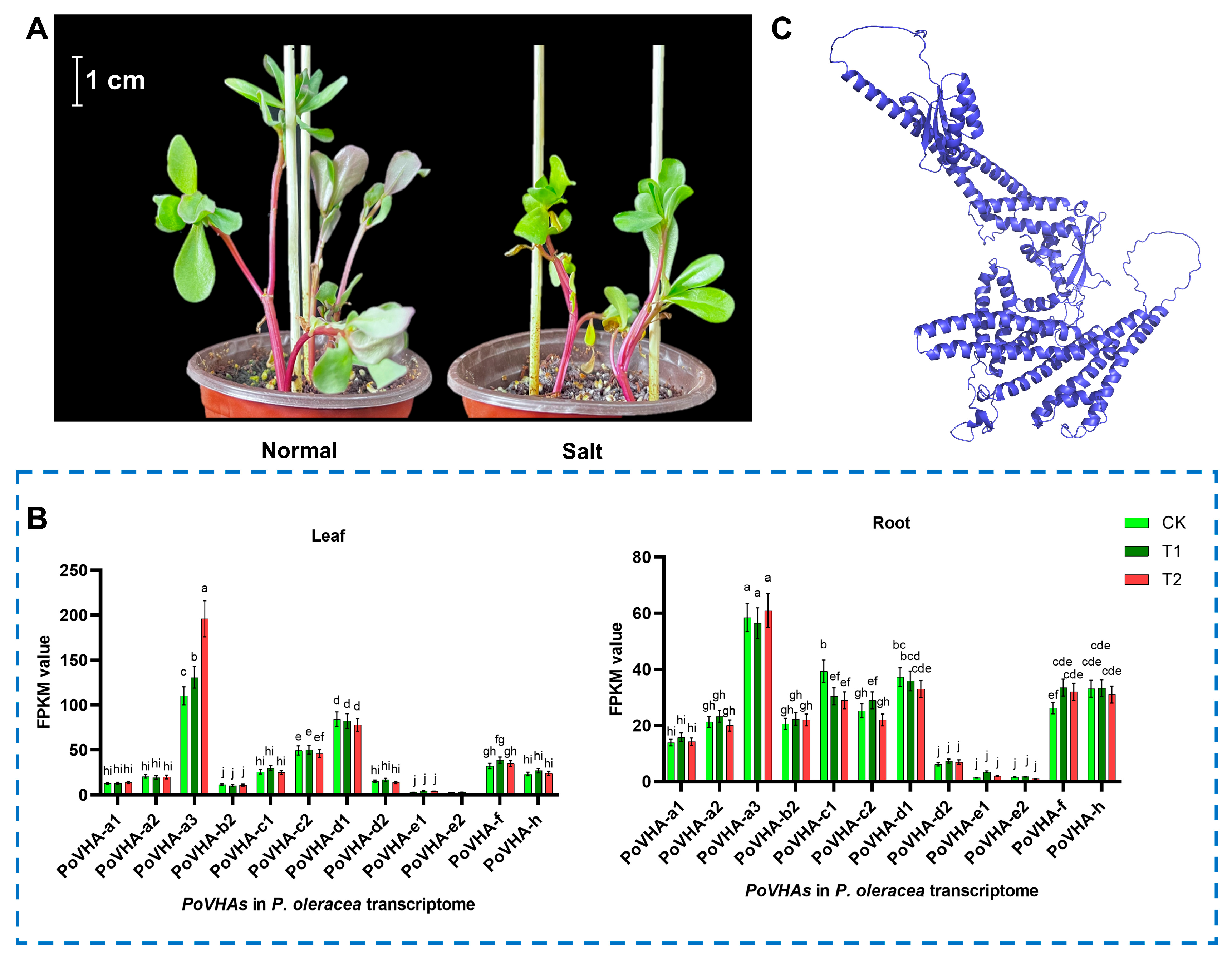
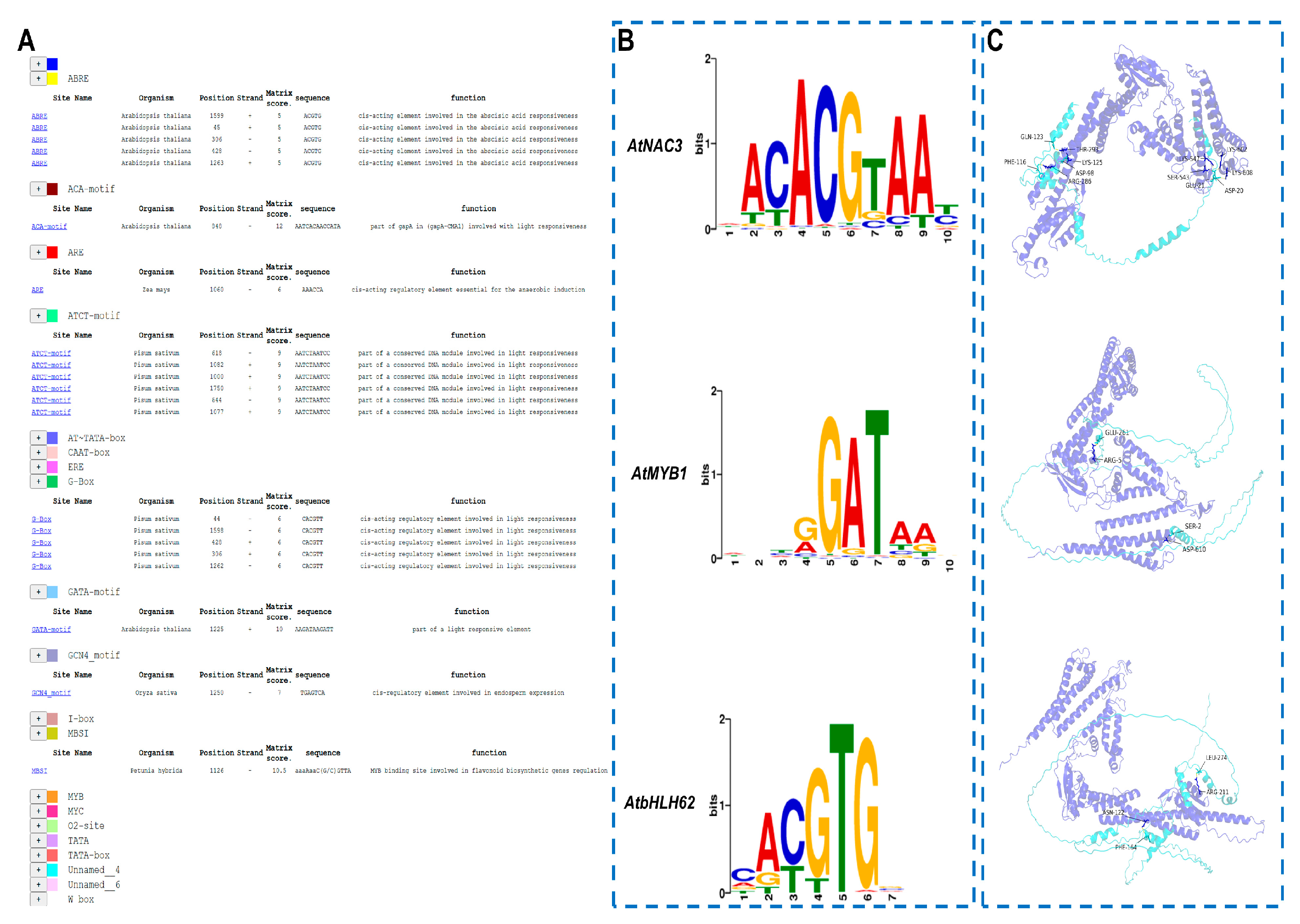
3.1. Identification and Bioinformatic Analysis of PoVHA-a3
3.2. Subcellular Localization and Functional Characterization of PoVHA-a3 in Salt Tolerance
3.3. The Effect of PoVHA-a3 on Energy Production of Arabidopsis Under Salt Stress
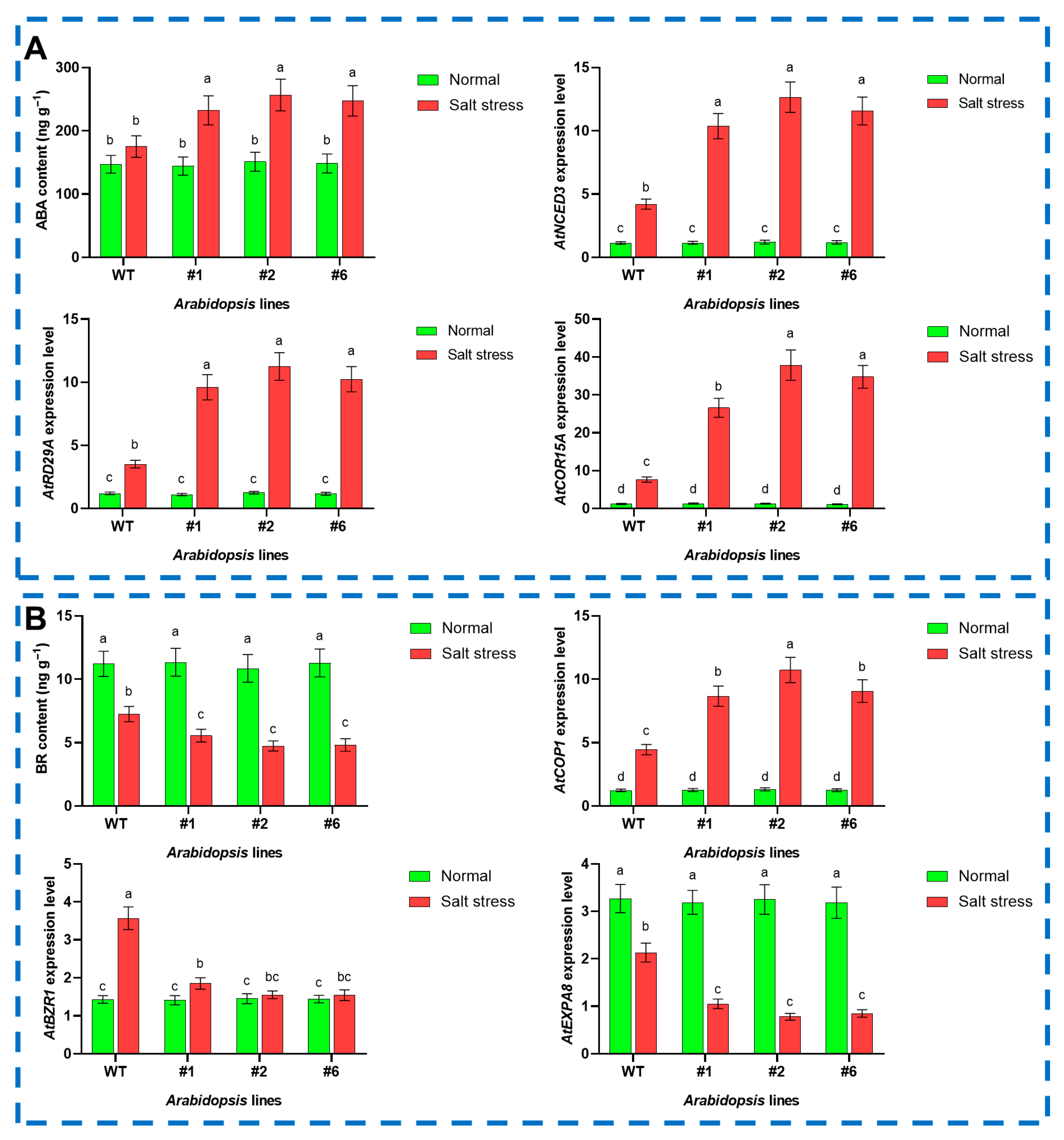
3.4. The Effect of PoVHA-a3 on Aba-Br Antagonism in Arabidopsis Under Salt Stress
3.5. The Effect of PoVHA-a3 on Ros Scavenging in Arabidopsis Under Salt Stress
4. Discussion
4.1. Synergistic Regulation of PoVHA-a3 Expression by TFs in Response to Salt Stress
4.2. PoVHA-a3 Enhanced Ion Compartmentalization and Osmotic Adjustment Capacity by Optimizing Energy Metabolism
4.3. PoVHA-a3 Modulates the Aba-Br Antagonistic Balance to Attenuate Ros Accumulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Hu, W.; Yu, A.; Tang, H.; Li, J.; Kuang, H.; Zhang, H. Extraction, Purification, Structural Characteristics, Biological Activity and Application of Polysaccharides from Portulaca oleracea L. (Purslane): A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, A.; Pascual, J.A.; Ros, M.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Alguacil, M.D.M. Agronomical Practices and Management for Commercial Cultivation of Portulaca oleracea as a Crop: A Review. Plants 2023, 12, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranshahy, M.; Javadi, B.; Iranshahi, M.; Jahanbakhsh, S.P.; Mahyari, S.; Hassani, F.V.; Karimi, G. A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Portulaca oleracea L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 205, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, J.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M. Ameliorative effects of Portulaca oleracea L. (purslane) on the metabolic syndrome: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 299, 115672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, H.; Xu, F.; Yan, F.; Xu, W. H+-ATPases in Plant Growth and Stress Responses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 495–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falhof, J.; Pedersen, J.T.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Palmgren, M. Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase Regulation in the Center of Plant Physiology. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, H.; Chanroj, S. Plant Endomembrane Dynamics: Studies of K+/H+ Antiporters Provide Insights on the Effects of pH and Ion Homeostasis. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 875–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.Z.; Shimazaki, T.; Gulzar, S.; Kikuchi, A.; Gul, B.; Khan, M.A.; Koyro, H.W.; Huchzermeyer, B.; Watanabe, K.N. The influence of genes regulating transmembrane transport of Na+ on the salt resistance of Aeluropus lagopoides. Funct. Plant Biol. 2013, 40, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, C.; Di Silvestre, D.; Fischer-Schliebs, E.; Homann, U.; De Palma, A.; Comunian, C.; Mauri, P.L.; Thiel, G. Proteomic analysis of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum leaf microsomal fractions finds an imbalance in V-ATPase stoichiometry during the salt-induced transition from C3 to CAM. Biochem. J. 2013, 450, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.; Gerós, H. Regulation by salt of vacuolar H+-ATPase and H+-pyrophosphatase activities and Na+/H+ exchange. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidhi; Iqbal, N.; Khan, N.A. Synergistic effects of phytohormones and membrane transporters in plant salt stress mitigation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 221, 109685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G. The walnut JrVHAG1 gene is involved in cadmium stress response through ABA-signal pathway and MYB transcription regulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, R.; Russinova, E.; Rodriguez, P.L. Tripartite hormonal regulation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, Y.; Peng, J.; Dong, M.; Yang, G. Characterization of a vacuolar H+-ATPase G subunit gene from Juglans regia (JrVHAG1) involved in mannitol-induced osmotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xing, D. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Promotes Activation and Vacuolar Acidification and Delays Methyl Jasmonate-Induced Leaf Senescence. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1714–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gong, P.; Li, K.; Huang, F.; Cheng, F.; Pan, G. A single cytosine deletion in the OsPLS1 gene encoding vacuolar-type H+-ATPase subunit A1 leads to premature leaf senescence and seed dormancy in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 2761–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.T.; Yang, L.H.; Zheng, J.X.; Geng, X.C.; Bai, Y.X.; Wang, Y.C.; Xue, H.W.; Lin, W.H. Vacuolar H+-ATPase and BZR1 form a feedback loop to regulate the homeostasis of BR signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1976–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, F.; Xie, Q. Balancing growth and adaptation to stress: Crosstalk between brassinosteroid and abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 2325–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.M.; Vukašinović, N.; Liu, D.; Russinova, E.; Yin, Y. Brassinosteroids: Multidimensional Regulators of Plant Growth, Development, and Stress Responses. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, V.P.; Wu, H.C.; Jinn, T.L. Coordination of ABA and Chaperone Signaling in Plant Stress Responses. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Walley, J.W. Unveiling a new regulator: Vacuolar V-ATPase mediates brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.C.; Zhao, B.Q.; Dong, J.; Liu, C.; Wen, Z.G.; Zhu, X.M.; Ding, H.R.; He, T.T.; Yang, H.; Wang, M.W.; et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Profiles Revealed Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Tolerance of Portulaca oleracea to Saline Stress. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 67, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Qiao, H.X.; Yang, T.; Zhao, P.; Zhao, J.H.; Luo, J.M.; Liu, F.F.; Xiong, A.S. DcMYB62, a transcription factor from carrot, enhanced cadmium tolerance of Arabidopsis by inducing the accumulation of carotenoids and hydrogen sulfide. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 216, 109114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottanelli, F.; Foresti, O.; Hanton, S.; Denecke, J. Vacuolar transport in tobacco leaf epidermis cells involves a single route for soluble cargo and multiple routes for membrane cargo. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3007–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Qiao, J.; Quan, R.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Qin, H. SALT AND ABA RESPONSE ERF1 improves seed germination and salt tolerance by repressing ABA signaling in rice. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 1110–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gan, L.; Peng, X.; Peng, X.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, F.; Wei, M. Overexpression of cassava MeAMY1 and MeBAM3 genes enhance drought and salt stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 226, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, C.; Luo, S.; Singh, R.M.; Li, Y.; Kim, C.; et al. FERONIA regulates salt tolerance in Arabidopsis by controlling photorespiratory flux. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 4732–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Xu, Q.Y.; Zhu, Z.P.; Liu, P.Z.; Yu, J.X.; Guo, Y.X.; Tang, S.; Yu, Z.F.; Xiong, A.S. AgMYB5, an MYB transcription factor from celery, enhanced β-carotene synthesis and promoted drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuria, M.; Goel, P.; Kumar, S.; Singh, A.K. AtUSP17 negatively regulates salt stress tolerance through modulation of multiple signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2022, 174, e13635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Yang, G.; Yan, K.; Zheng, C.; Huang, J. CYSTM3 negatively regulates salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 99, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabała, K.; Janicka-Russak, M.; Kłobus, G. Different responses of tonoplast proton pumps in cucumber roots to cadmium and copper. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Pang, H.; Jia, L.; Sun, K.; Zhang, J.; Du, J.; Feng, H. Extracellular ATP sensing in living plant tissues with a genetically encoded, ratiometric fluorescent sensor. New Phytol. 2023, 238, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Khanna, K.; Landi, M.; Prasad, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Zheng, B. Brassinosteroids and metalloids: Regulation of plant biology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Rejeb, K.; Lefebvre-De Vos, D.; Le Disquet, I.; Leprince, A.S.; Bordenave, M.; Maldiney, R.; Jdey, A.; Abdelly, C.; Savouré, A. Hydrogen peroxide produced by NADPH oxidases increases proline accumulation during salt or mannitol stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Admas, T.; Shu, J.; Shalmani, A.; Pan, R.; Zhang, W. Salt stress-responsive transcription factors provide insights to enhance barley improvement: A review. Planta 2025, 262, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Jian, C.; Mei, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, N.; Li, T.; Du, L.; et al. Variation in cis-regulation of a NAC transcription factor contributes to drought tolerance in wheat. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Y. The Physiological and Molecular Mechanism of Abscisic Acid in Regulation of Fleshy Fruit Ripening. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 619953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Sun, F.; Yan, L.; Li, R.; Bai, J.; Caetano-Anollés, G. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Vacuolar H+-ATPase Subunit H Gene Family in Crop Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, L. Overexpression of Arachis hypogaea NAC3 in tobacco enhances dehydration and drought tolerance by increasing superoxide scavenging. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 70, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Tohge, T.; Ivakov, A.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Fernie, A.R.; Mutwil, M.; Schippers, J.H.; Persson, S. Salt-Related MYB1 Coordinates Abscisic Acid Biosynthesis and Signaling during Salt Stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Q.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, L.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Xiao, L.H.; Wu, Z.G.; Zheng, Y.H.; Jin, P. Phytosulfokine α treatment induces osmotic regulation to alleviate postharvest chilling injury of peach fruit by PpbHLH62. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 230, 113746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, L.; Gu, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, Y.; Li, L. Vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit VAB3 regulates cell growth and ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2022, 112, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Takano, T.; Liu, S. The role of endomembrane-localized VHA-c in plant growth. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, e1382796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Duan, W.; Ma, C.; Zhao, M.; Gu, J.; Du, X.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, K. Overexpression of TaNHX3, a vacuolar Na⁺/H⁺ antiporter gene in wheat, enhances salt stress tolerance in tobacco by improving related physiological processes. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Jiang, P.; Tai, F.; Wang, D.; Feng, J.; Fan, P.; Bao, H.; Li, Y. The V-ATPase subunit A is essential for salt tolerance through participating in vacuolar Na+ compartmentalization in Salicornia europaea. Planta 2017, 246, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Deng, S.; Zhao, N.; Deng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sa, G.; Yao, J.; Wu, C.; et al. Salt-Sensitive Signaling Networks in the Mediation of K+/Na+ Homeostasis Gene Expression in Glycyrrhiza uralensis Roots. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.E.; Savouré, A.; Szabados, L. Proline metabolism as regulatory hub. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Per, T.S.; Khan, N.A.; Reddy, P.S.; Masood, A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Khan, M.I.R.; Anjum, N.A. Approaches in modulating proline metabolism in plants for salt and drought stress tolerance: Phytohormones, mineral nutrients and transgenics. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Das, P.; Parida, A.K.; Agarwal, P.K. Proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics perspectives of salinity tolerance in halophytes. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhanian, H.; Motamed, N.; Jazii, F.R.; Nakamura, T.; Komatsu, S. Salt stress induced differential proteome and metabolome response in the shoots of Aeluropus lagopoides (Poaceae), a halophyte C(4) plant. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 2882–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, F.; Lin, H.; Guo, Y. Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steber, C.M.; McCourt, P. A role for brassinosteroids in germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, P.; Ma, X.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Mishev, K.; Lu, D.; Kumar, R.; Vanhoutte, I.; et al. Regulation of Arabidopsis brassinosteroid receptor BRI1 endocytosis and degradation by plant U-box PUB12/PUB13-mediated ubiquitination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1906–E1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Fujita, Y.; Sayama, H.; Kidokoro, S.; Maruyama, K.; Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. Plant J. 2010, 61, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, F.; Chen, Z.; Teng, Z.; Sun, K.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, G.; Liang, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. Synergistic interplay of ABA and BR signal in regulating plant growth and adaptation. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alché, J.D. A concise appraisal of lipid oxidation and lipoxidation in higher plants. Redox Biol. 2019, 23, 101136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Xing, J.; Sun, G.; He, S.; Dong, J.; He, T.; Zhu, X.; Hong, L.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z. The V-Type H+-Transporting ATPase Gene PoVHA-a3 from Portulaca oleracea Confers Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana Through the Modulation of BR-ABA Signaling Balance. Agriculture 2026, 16, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010010
Xing J, Sun G, He S, Dong J, He T, Zhu X, Hong L, Qian Y, Zhang Z. The V-Type H+-Transporting ATPase Gene PoVHA-a3 from Portulaca oleracea Confers Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana Through the Modulation of BR-ABA Signaling Balance. Agriculture. 2026; 16(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Jincheng, Guoli Sun, Sunan He, Jing Dong, Tingting He, Xiaomei Zhu, Lizhou Hong, Yexiong Qian, and Zhenhua Zhang. 2026. "The V-Type H+-Transporting ATPase Gene PoVHA-a3 from Portulaca oleracea Confers Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana Through the Modulation of BR-ABA Signaling Balance" Agriculture 16, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010010
APA StyleXing, J., Sun, G., He, S., Dong, J., He, T., Zhu, X., Hong, L., Qian, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2026). The V-Type H+-Transporting ATPase Gene PoVHA-a3 from Portulaca oleracea Confers Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana Through the Modulation of BR-ABA Signaling Balance. Agriculture, 16(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010010






