Potential Use of Microalgae Isolated from the Natural Environment as Biofertilizers for the Growth and Development of Pak Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microalgae Isolation from the Natural Environment
2.2. Biofertilizers from Algal Cultures
2.3. Biofertilizer Analysis
2.4. Experimental Conditions
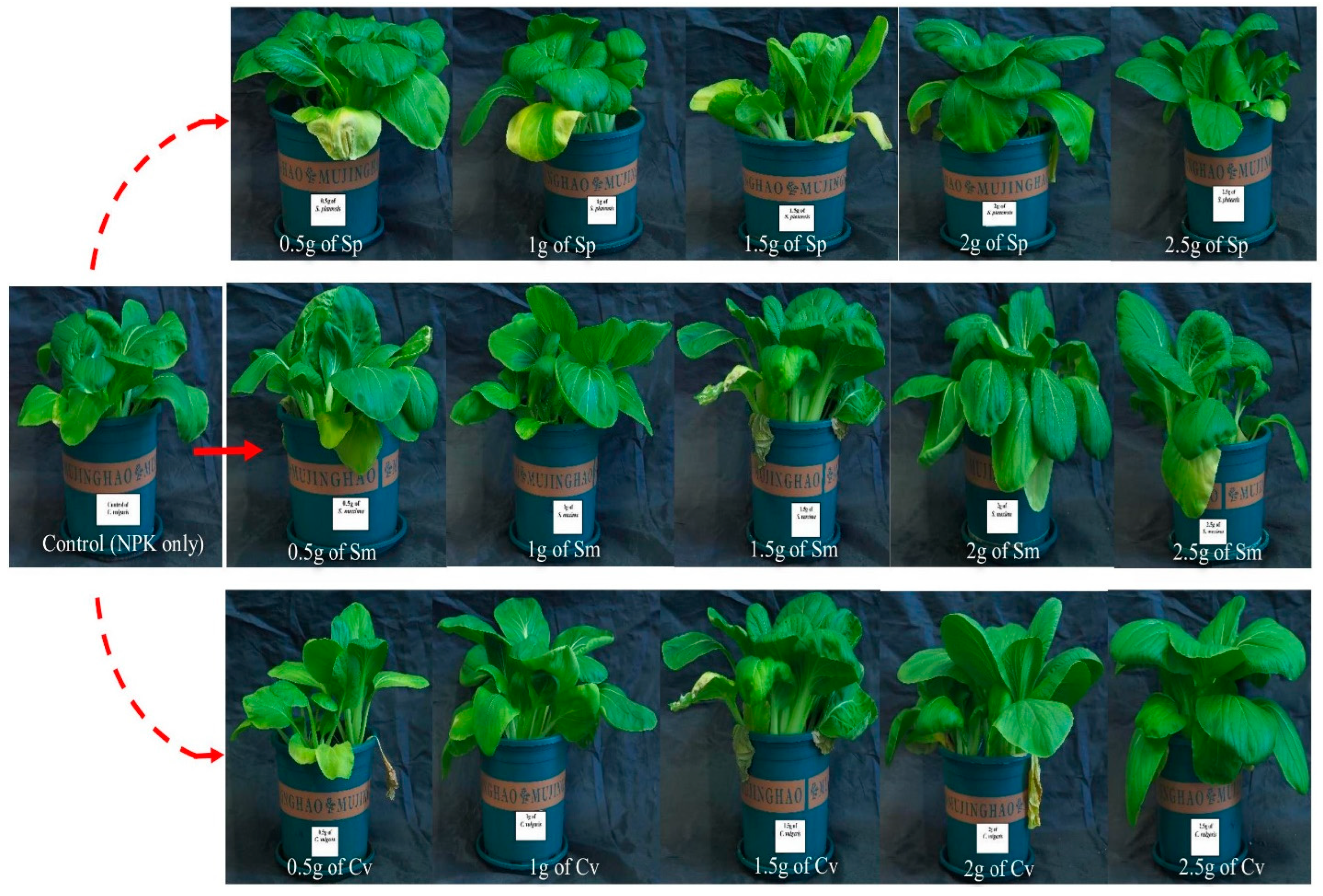
2.5. Treatment Plan
2.6. Plant Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
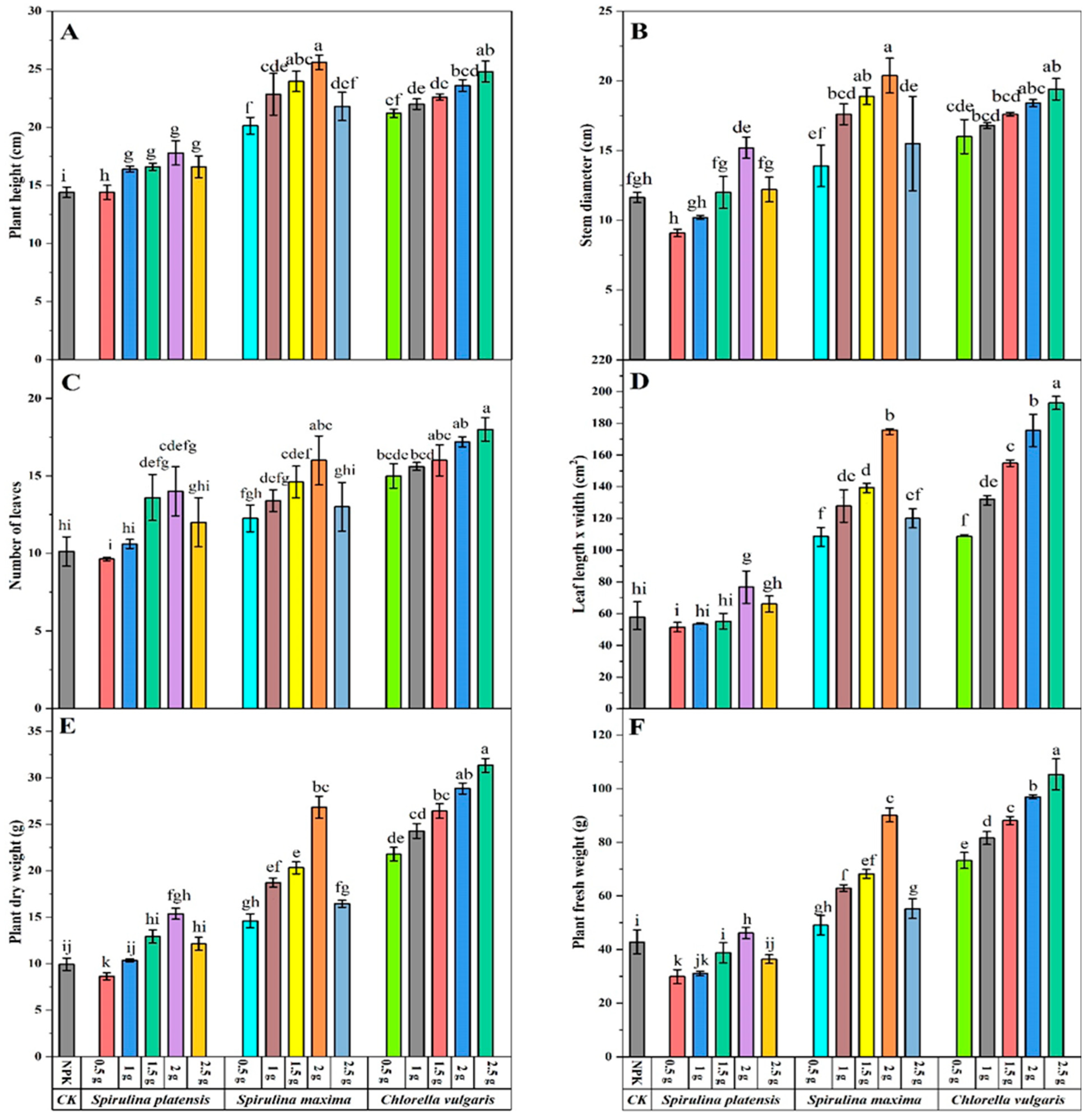
3.1. Effect of Biofertilizers on the Morphology of Above-Ground Biomass
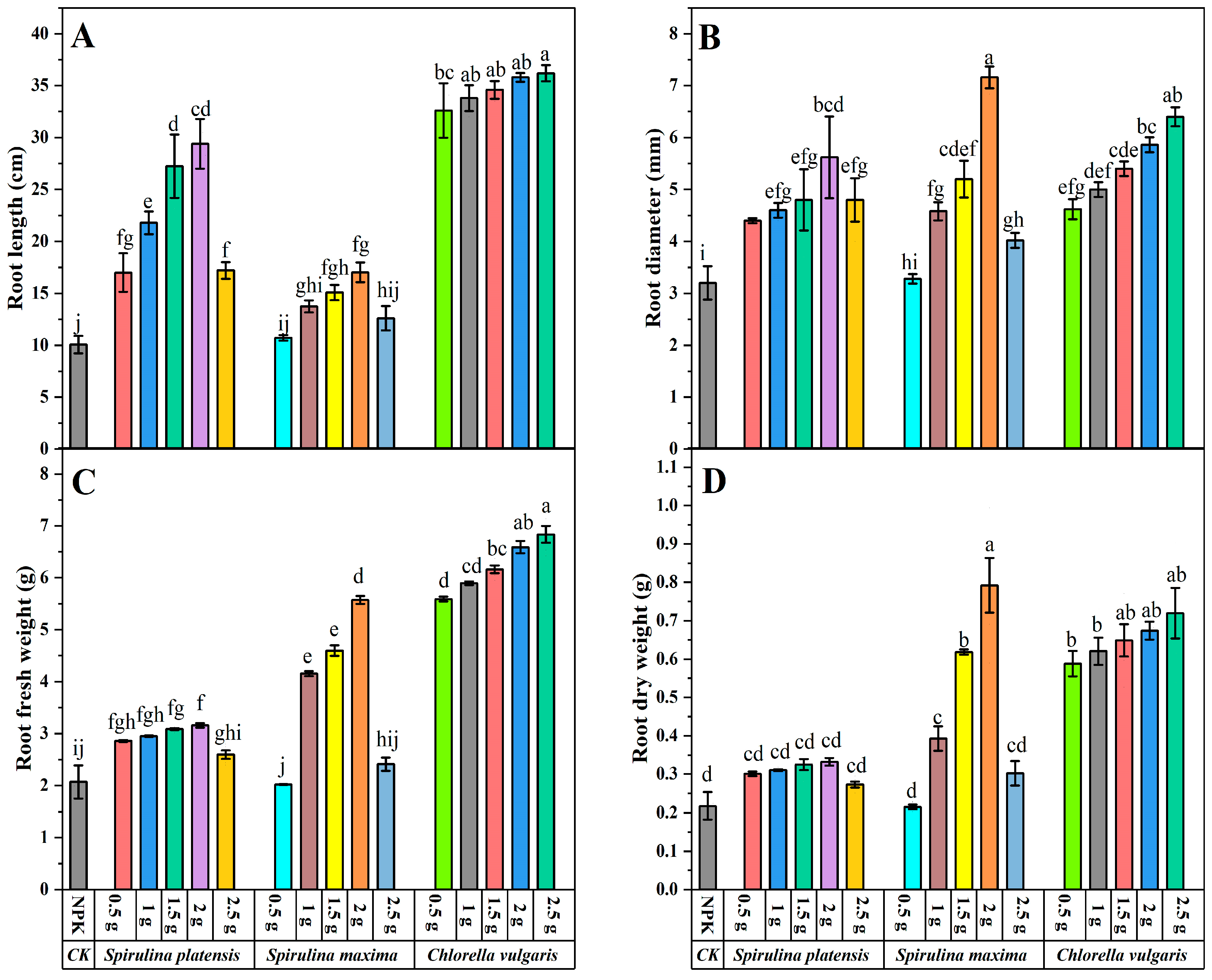
3.2. Effect of Biofertilizers on the Morphology of Below-Ground Biomass
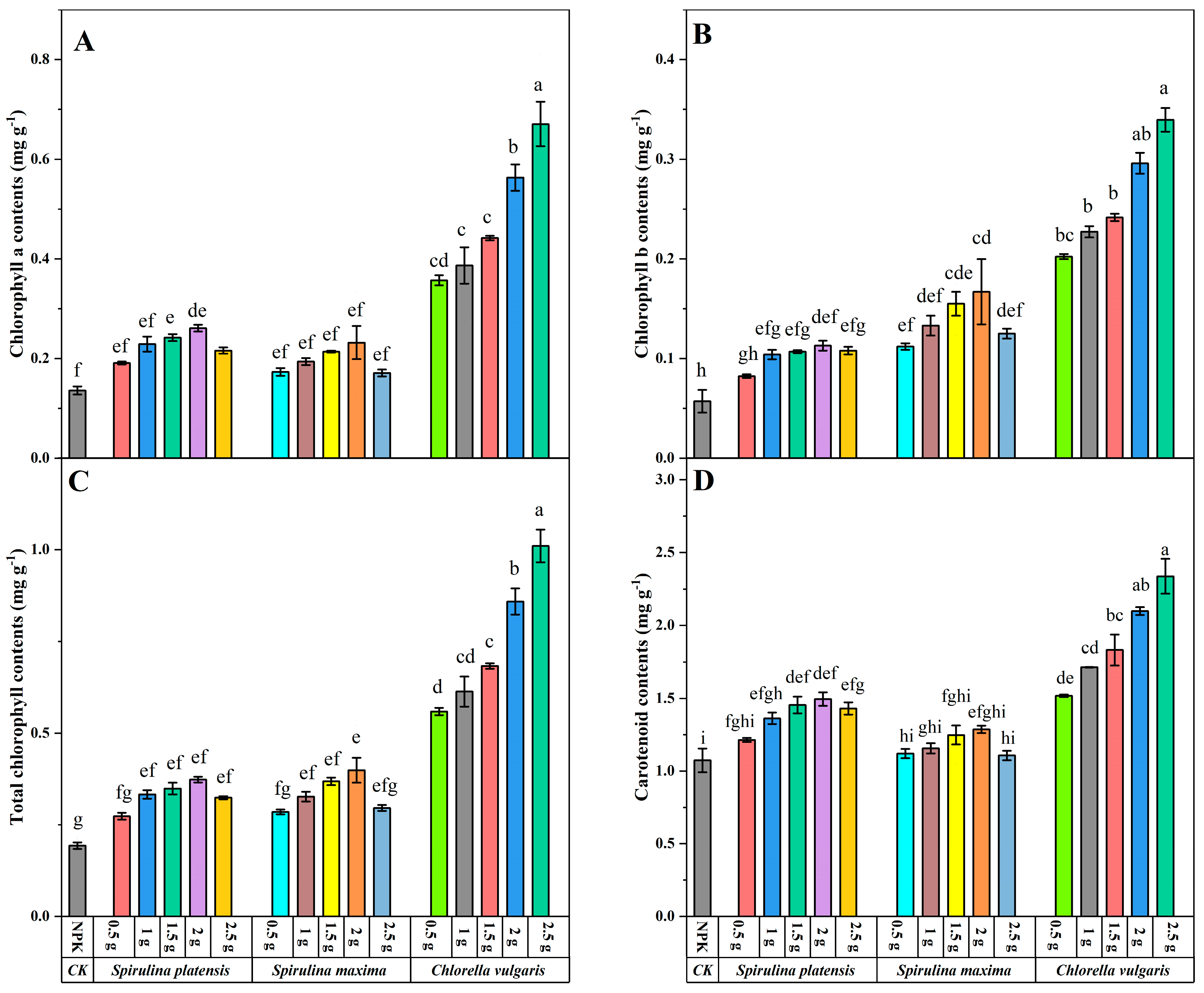
3.3. Effect of Biofertilizers on Chlorophyll and Carotenoid Contents
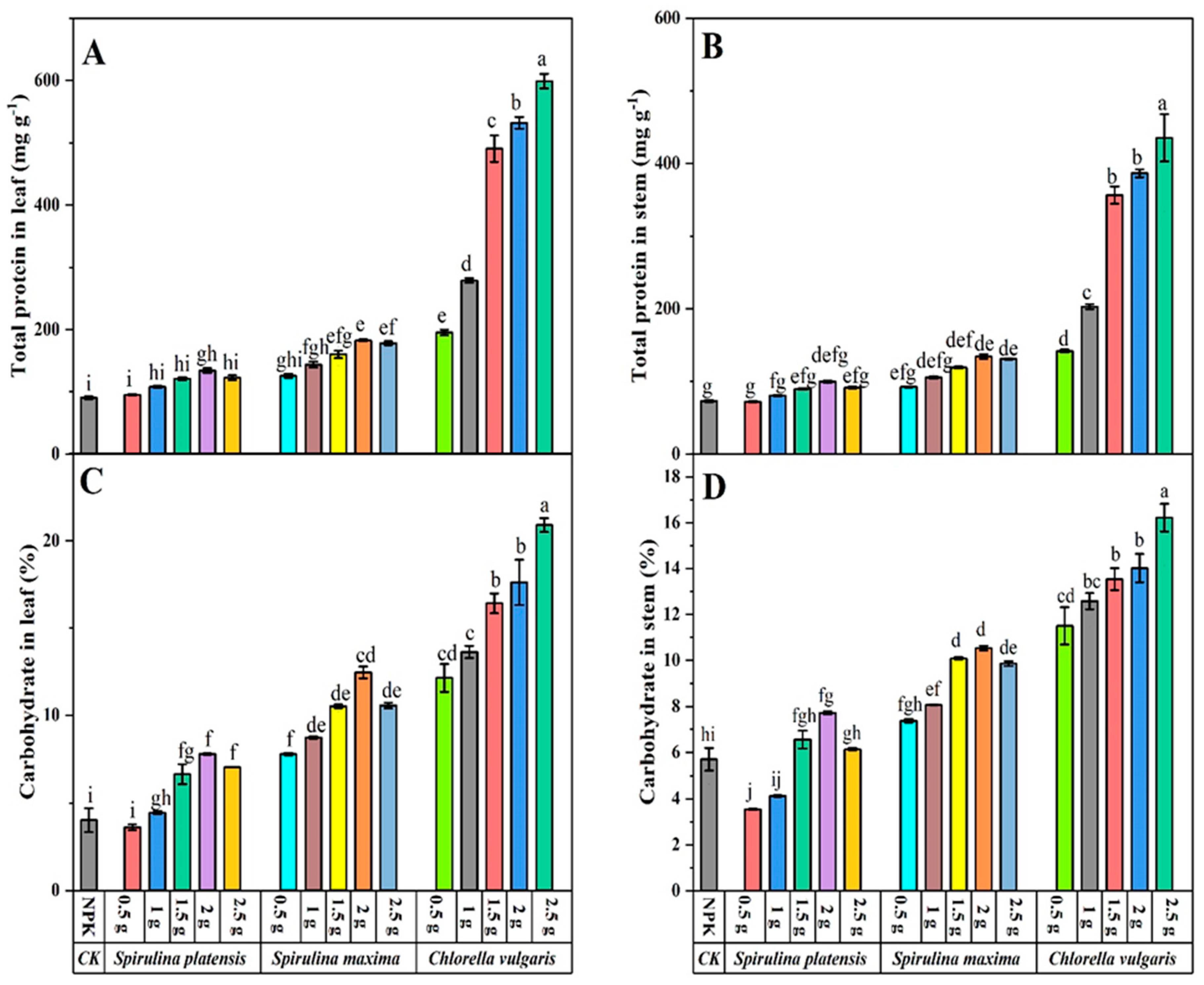
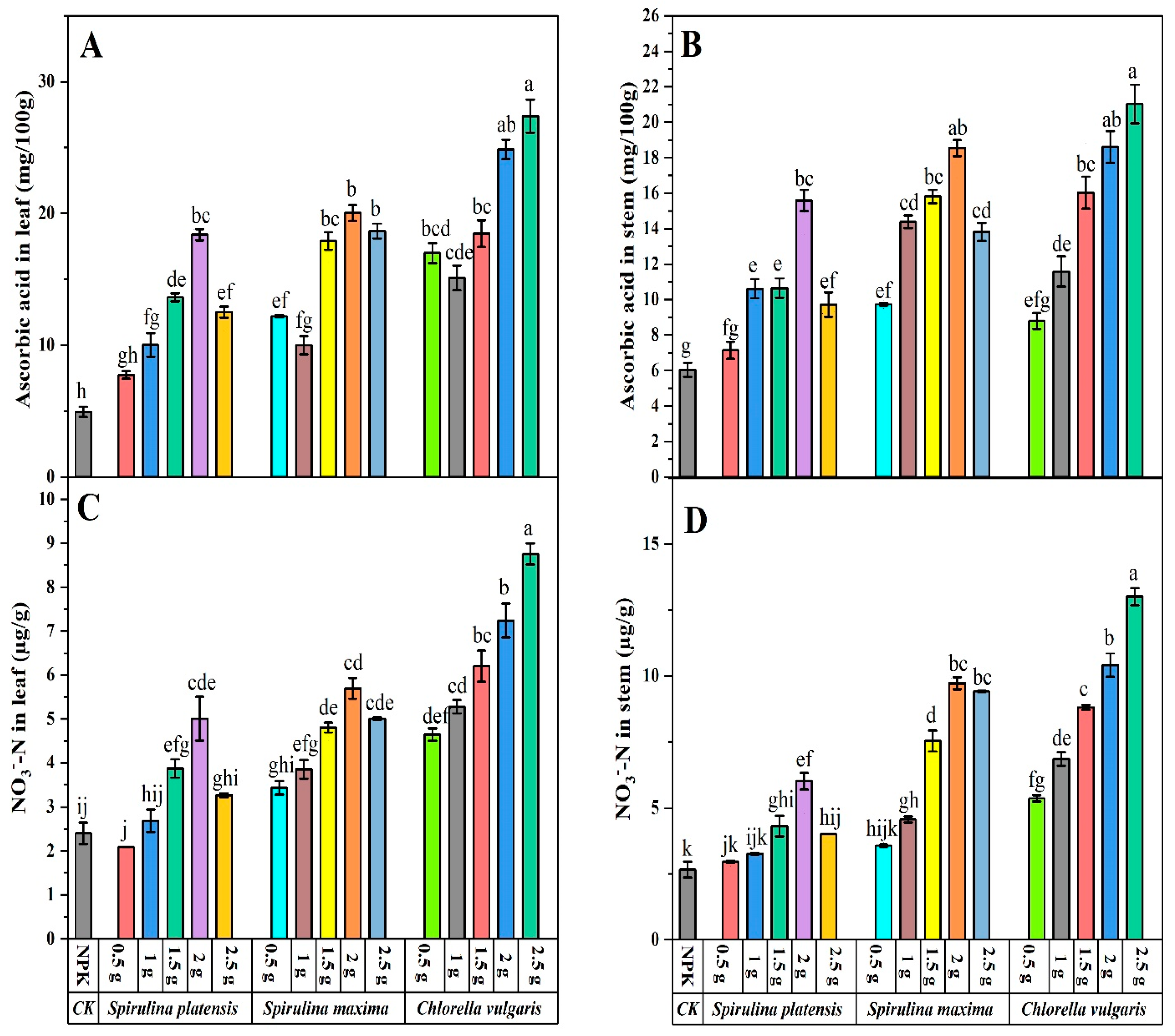
3.4. Effect of Biofertilizers on Biochemical Composition
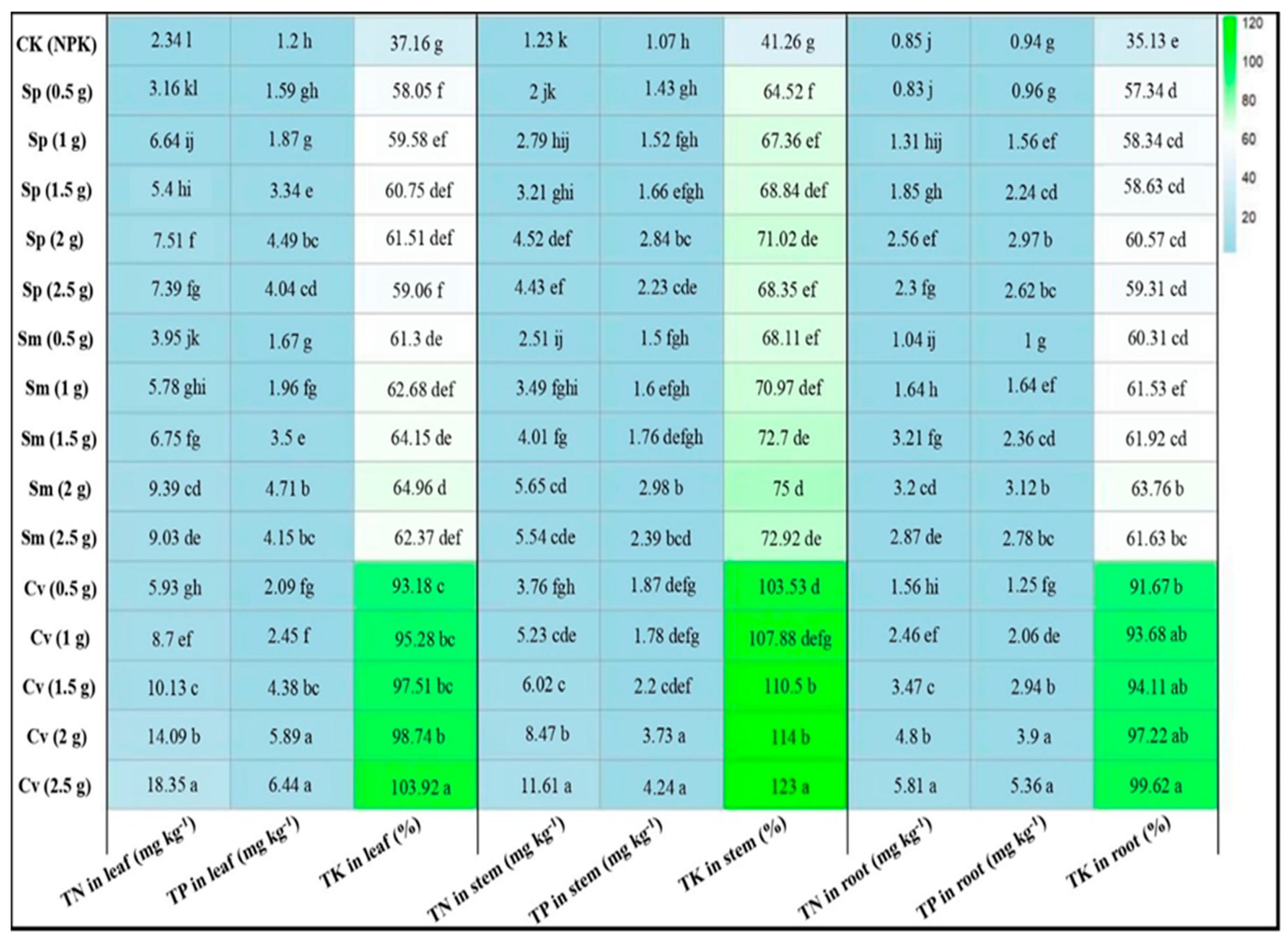
3.5. Effect of Biofertilizers on the Macronutrient Composition of Pak Choi Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Future Prospectus
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tchonkouang, R.D.; Onyeaka, H.; Nkoutchou, H. Assessing the vulnerability of food supply chains to climate change-induced disruptions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 171047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.M.; Demokritou, P.; Dokoozlian, N.; Hendren, C.O.; Karn, B.; Mauter, M.S.; Sadik, O.A.; Safarpour, M.; Unrine, J.M.; Viers, J. Nanotechnology for sustainable food production: Promising opportunities and scientific challenges. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Kong, F.; Zhang, N.; Ying, R. Knowledge training and the change of fertilizer use intensity: Evidence from wheat farmers in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řezbová, H.; Slaboch, J.; Mach, J. Emissions from managed agricultural soils in context of consumption of inorganic nitrogen fertilisers in selected EU Countries. Agronomy 2023, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, Y.; Bjørklund, G.; Bandpei, A.M.; Chirumbolo, S.; Keramati, H.; Pouya, R.H.; Asadi, A.; Amanidaz, N.; Sarafraz, M.; Sheikhmohammad, A. Concentrations of arsenic and lead in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Iran: A systematic review and carcinogenic risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannin, L.; Arkoun, M.; Etienne, P.; Laîné, P.; Goux, D.; Garnica, M.; Fuentes, M.; Francisco, S.S.; Baigorri, R.; Cruz, F. Brassica napus growth is promoted by Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. seaweed extract: Microarray analysis and physiological characterization of N, C, and S metabolisms. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 32, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobek, M.; Frąc, M.; Cybulska, J. Plant biostimulants: Importance of the quality and yield of horticultural crops and the improvement of plant tolerance to abiotic stress—A review. Agronomy 2019, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgotra, R.K.; Stewart, C.N., Jr. Genetic augmentation of legume crops using genomic resources and genotyping platforms for nutritional food security. Plants 2022, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Huang, J.; Feng, Y.; Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Yang, L. Ammonia volatilization mitigation in crop farming: A review of fertilizer amendment technologies and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigie, J.S. Seaweed extract stimuli in plant science and agriculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Quintero, Á.; Fernandes, S.C.; Beigbeder, J.-B. Overview of microalgae and cyanobacteria-based biostimulants produced from wastewater and CO2 streams towards sustainable agriculture: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 277, 127505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, E.E.; Aioub, A.A.; Elesawy, A.E.; Karkour, A.M.; Mouhamed, M.S.; Amer, A.A.; El-Shershaby, N.A. Algae as Bio-fertilizers: Between current situation and future prospective. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3083–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolisano, C.; Del Buono, D. Biobased: Biostimulants and biogenic nanoparticles enter the scene. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Xiao, Y. From manure to high-value fertilizer: The employment of microalgae as a nutrient carrier for sustainable agriculture. Algal Res. 2022, 67, 102855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.M.; Hernandez-Tenorio, F.; Villalta, F.; Vargas, G.J.; Sáez, A.A. Advances in the Development of Biofertilizers and Biostimulants from Microalgae. Biology 2024, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, D.F.; Puglisi, I.; Sicilia, A.; Baglieri, A.; La Bella, E.; Lo Piero, A.R. Transcriptomic profile of lettuce seedlings (Lactuca sativa) response to microalgae extracts used as biostimulant agents. AoB Plants 2023, 15, plad043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Ramsubhag, A.; Jayaraman, J. Transcriptome-wide modulation by Sargassum vulgare and Acanthophora spicifera extracts results in a prime-triggered plant signalling cascade in tomato and sweet pepper. AoB Plants 2022, 14, plac046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Using microalgae to reduce the use of conventional fertilizers in hydroponics and soil-based cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglisi, I.; Barone, V.; Fragalà, F.; Stevanato, P.; Baglieri, A.; Vitale, A. Effect of microalgal extracts from Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus quadricauda on germination of Beta vulgaris seeds. Plants 2020, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuang, S.C.; Khin, M.C.; Chua, P.Q.D.; Luo, Y.D. Use of Spirulina biomass produced from treatment of aquaculture wastewater as agricultural fertilizers. Algal Res. 2016, 15, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedeed, Z.A.; Gheda, S.; Elsanadily, S.; Alharbi, K.; Osman, M.E. Spirulina platensis biofertilization for enhancing growth, photosynthetic capacity and yield of Lupinus luteus. Agriculture 2022, 12, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchithra, M.; Muniswami, D.M.; Sri, M.S.; Usha, R.; Rasheeq, A.A.; Preethi, B.A.; Dineshkumar, R. Effectiveness of green microalgae as biostimulants and biofertilizer through foliar spray and soil drench method for tomato cultivation. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 146, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusvuran, S. Microalgae (Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck) alleviates drought stress of broccoli plants by improving nutrient uptake, secondary metabolites, and antioxidative defense system. Hortic. Plant J. 2021, 7, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaoui, F.; Hakkoum, Z.; Chabili, A.; Douma, M.; Mouhri, K.; Loudiki, M. Biostimulant effect of green soil microalgae Chlorella vulgaris suspensions on germination and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum var. Achtar) and soil fertility. Algal Res. 2024, 82, 103655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.Z.; Liu, X.J.; Hong, X.Y. Dynamics of pesticide residues in the autumn Chinese cabbage (Brassica chinensis L.) grown in open fields. Pest Manag. Sci. Former. Pest. Sci. 2006, 62, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantumar, G.; Jo, M.H.; Igori, D.; Ham, I.K.; Lee, E.M.; Lee, W.-H.; Lim, Y.; An, G.; Park, J.-T. Nutritional evaluation and comparison of new Pak Choi cultivars from China with Chinese cabbage cultivars popular in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 42, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Gruda, N.S. The potential of introduction of Asian vegetables in Europe. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tao, W.; Su, L. Effects of Oxygenated Brackish Water on Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) Growth Characteristics Based on a Logistic Crop Growth Model. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciferri, O. Spirulina, the edible microorganism. Microbiol. Rev. 1983, 47, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, C. Contribution a l’etude d’une Cyanophycee: Influence de Divers Facteurs Physiques et Chimiques sur la Croissance et la Photosynthese de Spirulina Mixima. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris, Paris, France, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Vonshak, A. Micro-algae: Laboratory growth techniques and outdoor biomass production. In Techniques in Bioproductivity and Photosynthesis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 188–200. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Patidar, S. Microalgae harvesting techniques: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Bashir, S.; Gulshan, A.B.; Khan, M.J.; Iqbal, J.; Sherani, J.; Husain, A.; Ahmed, N.; Shah, A.N.; Bukhari, M.A. The role of different organic amendments to improve maize growth in wastewater irrigated soil. J. King Saud Uni. Sci. 2021, 33, 101583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, M.S.; Altundağ, H. Determination of some major and trace elements in the lower Sakarya River water by ICP-MS. J. Chem. Metrol. 2018, 12, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.t.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, D.; Maroon, M.; Schrader, L.E.; Youngs, V.L. Rapid colorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissue by nitration of salicylic acid. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1975, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.B.; Stotz, E. The indophenolxylene extraction method for ascorbic acid and modifications for interfering substances. J. Biol. Chem. 1945, 160, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.G.; Torrie, J.H.; Dicky, D. Principles and Procedures of Statistics, A Biometrical Approach; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, NSA, 1997; pp. 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Cheng, K.; Huo, X.; Meng, P.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J. Bioorganic fertilizer promotes pakchoi growth and shapes the soil microbial structure. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1040437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Cao, X.; Xie, Y.; Gu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Mi, W.; Yang, X.; Wu, L. Effect of pH on the uptake and metabolism of glycine in pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 133, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Cao, X.; Wu, L.; Mi, W.; Feng, Y. Light intensity affects the uptake and metabolism of glycine by pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, P.; Kumar, R.; Neha, Y.; Srivatsan, V. Microalgae as next generation plant growth additives: Functions, applications, challenges and circular bioeconomy based solutions. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1073546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kholssi, R.; Lougraimzi, H.; Moreno-Garrido, I. Effects of global environmental change on microalgal photosynthesis, growth and their distribution. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 184, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renuka, N.; Prasanna, R.; Sood, A.; Bansal, R.; Bidyarani, N.; Singh, R.; Shivay, Y.S.; Nain, L.; Ahluwalia, A.S. Wastewater grown microalgal biomass as inoculants for improving micronutrient availability in wheat. Rhizosphere 2017, 3, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.M.P.; Rosa, A.; Borges, A.; Cunha, F.; Passos, F. The effects of microalgae use as a biofertilizer on soil and plant before and after its anaerobic (co-) digestion with food waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 934, 173301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Yang, Z.; Huang, L.; Sun, C.; Yu, X.; Zhao, M. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of the effects of relative air humidity on the morpho-physiological traits of Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) under high temperature. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohag, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Rychlik, M.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Genetic and physiological regulation of folate in pak choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis) germplasm. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 4914–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Srivastava, S.; Solomon, S.; Shrivastava, A.; Chandra, A. Impact of excess zinc on growth parameters, cell division, nutrient accumulation, photosynthetic pigments and oxidative stress of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickens, M.; Torralba, M.; Robinson, S.; Spencer, L.; Romeyn, M.; Massa, G.; Wheeler, R. Growth of red pak choi under red and blue, supplemented white, and artificial sunlight provided by LEDs. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 245, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, H.M.; Marrez, D.A.; Salama, A.B.; Wahba, H.E.; Khalid, K.A. Growth and chemical constituents of cardoon plant in response to foliar application of various algal extracts. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, M.; Romanowska-Duda, Z. Improvements in germination, growth, and metabolic activity of corn seedlings by grain conditioning and root application with cyanobacteria and microalgae. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Dineshkumar, R.; Subramanian, J.; Arumugam, A.; Ahamed Rasheeq, A.; Sampathkumar, P. Exploring the microalgae biofertilizer effect on onion cultivation by field experiment. Waste Biomass Valor. 2020, 11, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheed, F.A.; El-Fattah, Z. Effect of Chlorella vulgaris as bio-fertilizer on growth parameters and metabolic aspects of lettuce plant. J. Agric. Soc. Sci. 2008, 4, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- de Siqueira Castro, J.; Calijuri, M.L.; Mattiello, E.M.; Ribeiro, V.J.; Assemany, P.P. Algal biomass from wastewater: Soil phosphorus bioavailability and plants productivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.A.; Castro, J.S.d.; Ribeiro, V.J.; Ribeiro Júnior, J.I.; Tavares, G.P.; Calijuri, M.L. Microalgae biomass as a renewable biostimulant: Meat processing industry effluent treatment, soil health improvement, and plant growth. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 1334–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Metabolomics reveals the molecular mechanism of sewage sludge-derived nutrients and biostimulants stimulating resistance enhancement and the redistribution of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in pakchoi cabbage. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Jin, Q.; Lin, Y.; Lu, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, C.; Jin, J.; Jiang, Q.; Ling, L.; Xiao, M. Cell-free fermentation broth of Bacillus velezensis strain S3-1 improves pak choi nutritional quality and changes the bacterial community structure of the rhizosphere soil. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondonno, C.P.; Blekkenhorst, L.C.; Liu, A.H.; Bondonno, N.P.; Ward, N.C.; Croft, K.D.; Hodgson, J.M. Vegetable-derived bioactive nitrate and cardiovascular health. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 61, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luetic, S.; Knezovic, Z.; Jurcic, K.; Majic, Z.; Tripkovic, K.; Sutlovic, D. Leafy vegetable nitrite and nitrate content: Potential health effects. Foods 2023, 12, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Saadaoui, I.; Bibi, A.; Al-Ghouti, M.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.H. Applications, advancements, and challenges of cyanobacteria-based biofertilizers for sustainable agro and ecosystems in arid climates. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 25, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, G.; Chanda, U. Economic order quantity model for two generation consecutive technology products under permissible delay in payments. Int. J. Procure. Manag. 2021, 14, 93–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebers, N.; Hofmann, D.; Schiedung, H.; Landsrath, A.; Ackermann, B.; Gao, L.; Mojzeš, P.; Jablonowski, N.D.; Nedbal, L.; Amelung, W. Towards phosphorus recycling for agriculture by algae: Soil incubation and rhizotron studies using 33P-labeled microalgal biomass. Algal Res. 2019, 43, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alla, M.H.; Nafady, N.A.; Bashandy, S.R.; Hassan, A.A. Mitigation of effect of salt stress on the nodulation, nitrogen fixation and growth of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by triple microbial inoculation. Rhizosphere 2019, 10, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, B.R.; Bashan, Y.; Trejo, A.; de-Bashan, L.E. Amendment of degraded desert soil with wastewater debris containing immobilized Chlorella sorokiniana and Azospirillum brasilense significantly modifies soil bacterial community structure, diversity, and richness. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobwede, E.; Leake, J.R.; Pandhal, J. Circular economy fertilization: Testing micro and macro algal species as soil improvers and nutrient sources for crop production in greenhouse and field conditions. Geoderma 2019, 334, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.L.; Weyers, S.L.; Goemann, H.M.; Peyton, B.M.; Gardner, R.D. Microalgae, soil and plants: A critical review of microalgae as renewable resources for agriculture. Algal Res. 2021, 54, 102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulbry, W.; Westhead, E.K.; Pizarro, C.; Sikora, L. Recycling of manure nutrients: Use of algal biomass from dairy manure treatment as a slow release fertilizer. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupawalla, Z.; Robinson, N.; Schmidt, S.; Li, S.; Carruthers, S.; Buisset, E.; Roles, J.; Hankamer, B.; Wolf, J. Algae biofertilisers promote sustainable food production and a circular nutrient economy–An integrated empirical-modelling study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.K.; Khan, S.A.; Shrivastava, M.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, D.K.; Kishore, P.; Gupta, N. Circular economy fertilization: Phycoremediated algal biomass as biofertilizers for sustainable crop production. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, M.A.; Wagan, S.; Alam, I.; Hussain, A.; Ali, Q.; Saha, S.; Poudel, T.R.; Manghwar, H.; Liu, F. Impact of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on plant nutrition and root characteristics: Current perspective. Plant Stress 2023, 11, 100341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Bo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yan, X.; Ruan, R.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, P. Potential applications for multifunctional microalgae in soil improvement. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1035332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.; Yang, R.y.; Chang, L.c.; Ledesma, L.; Ledesma, D. Contents of carotenoids, ascorbic acid, minerals and total glucosinolates in leafy brassica pakchoi (Brassica rapa L. chinensis) as affected by season and variety. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Melkonyan, L.; Carapinha, S.; Ribeiro, B.; Figueiredo, D.; Avetisova, G.; Gouveia, L. Biostimulant and biopesticide potential of microalgae growing in piggery wastewater. Environ. Adv. 2021, 4, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Jiang, J.; He, M.; Zou, S.; Wang, C. Effect of kelp waste extracts on the growth and development of Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanick, B.; Brahmachari, K.; Ghosh, A. Effect of seaweed saps on growth and yield improvement of green gram. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Herrera, R.M.; Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, F.; Ruiz-López, M.A.; Norrie, J.; Hernández-Carmona, G. Effect of liquid seaweed extracts on growth of tomato seedlings (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almodares, A.; Hadi, M.; Dosti, B. Effects of salt stress on germination percentage and seedling growth in sweet sorghum cultivars. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 7, 1492–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
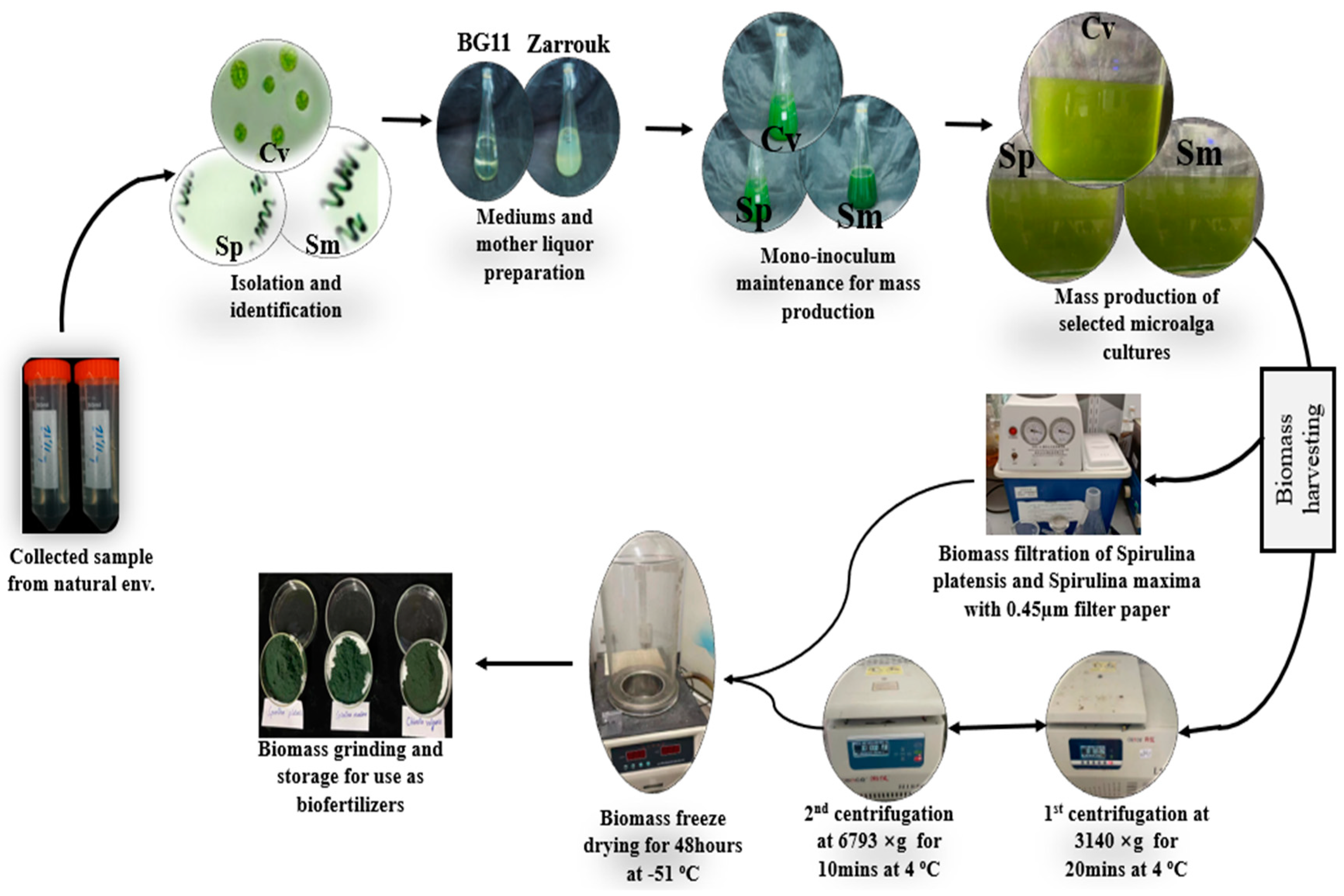

| Properties | Spirulina platensis | Spirulina maxima | Chlorella vulgaris |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.45 ± 0.69 | 6.40 ± 0.86 | 6.55 ± 0.58 |
| TN (mg/L) | 26.81 ± 1.26 | 38.54 ± 1.81 | 52.09 ± 2.44 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.599 ± 0.028 | 6.383 ± 0.065 | 2.061 ± 0.023 |
| TK (%) | 106.49 ± 4.20 | 98.53 ± 3.75 | 102.95 ± 4.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.; Yu, J.; Qu, Y.; Wang, T.; He, M.; Wang, C. Potential Use of Microalgae Isolated from the Natural Environment as Biofertilizers for the Growth and Development of Pak Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis). Agriculture 2025, 15, 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080863
Ali S, Yu J, Qu Y, Wang T, He M, Wang C. Potential Use of Microalgae Isolated from the Natural Environment as Biofertilizers for the Growth and Development of Pak Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis). Agriculture. 2025; 15(8):863. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080863
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Shahzad, Jiawen Yu, Yue Qu, Tiantian Wang, Meilin He, and Changhai Wang. 2025. "Potential Use of Microalgae Isolated from the Natural Environment as Biofertilizers for the Growth and Development of Pak Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis)" Agriculture 15, no. 8: 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080863
APA StyleAli, S., Yu, J., Qu, Y., Wang, T., He, M., & Wang, C. (2025). Potential Use of Microalgae Isolated from the Natural Environment as Biofertilizers for the Growth and Development of Pak Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis). Agriculture, 15(8), 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080863







