Long Non-Coding RNA lncXIRP1 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Pig Leydig Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.4. Isolation and Conversion of RNA into cDNA
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.7. Cell Counting Kit 8 (CCK-8)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
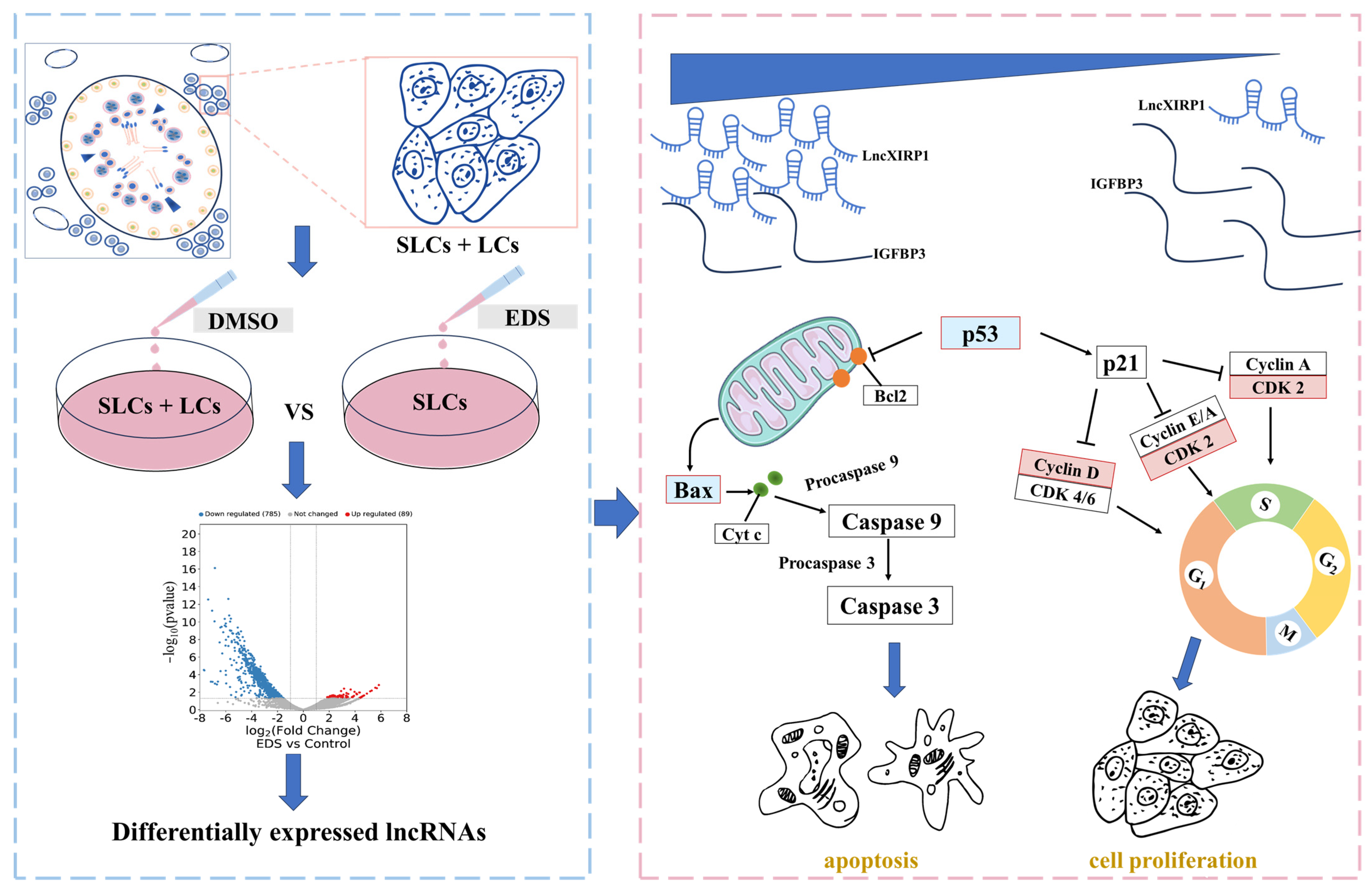
3. Results
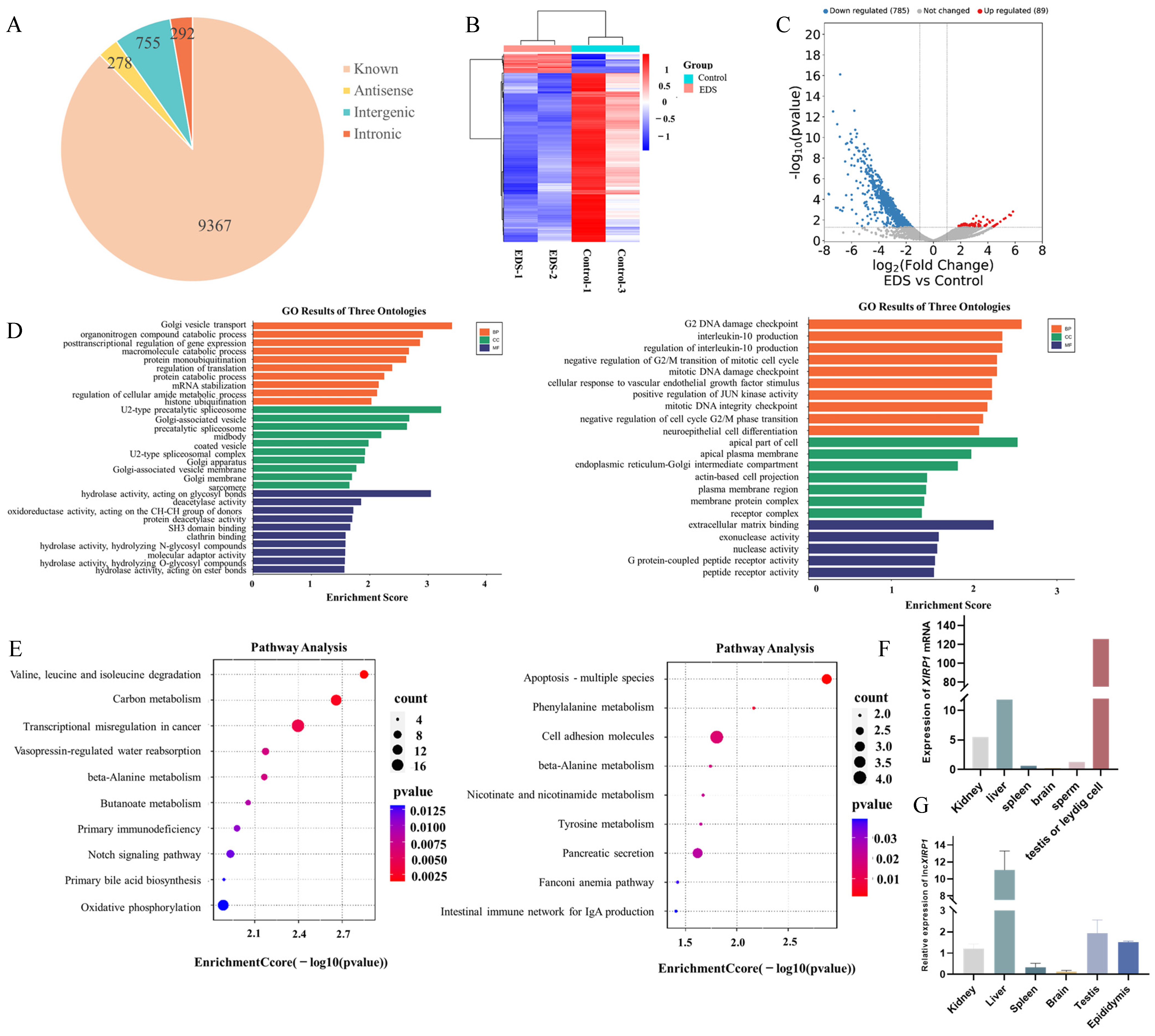
3.1. RNA-Seq Data Analysis and Differential Expression lncRNAs Screening
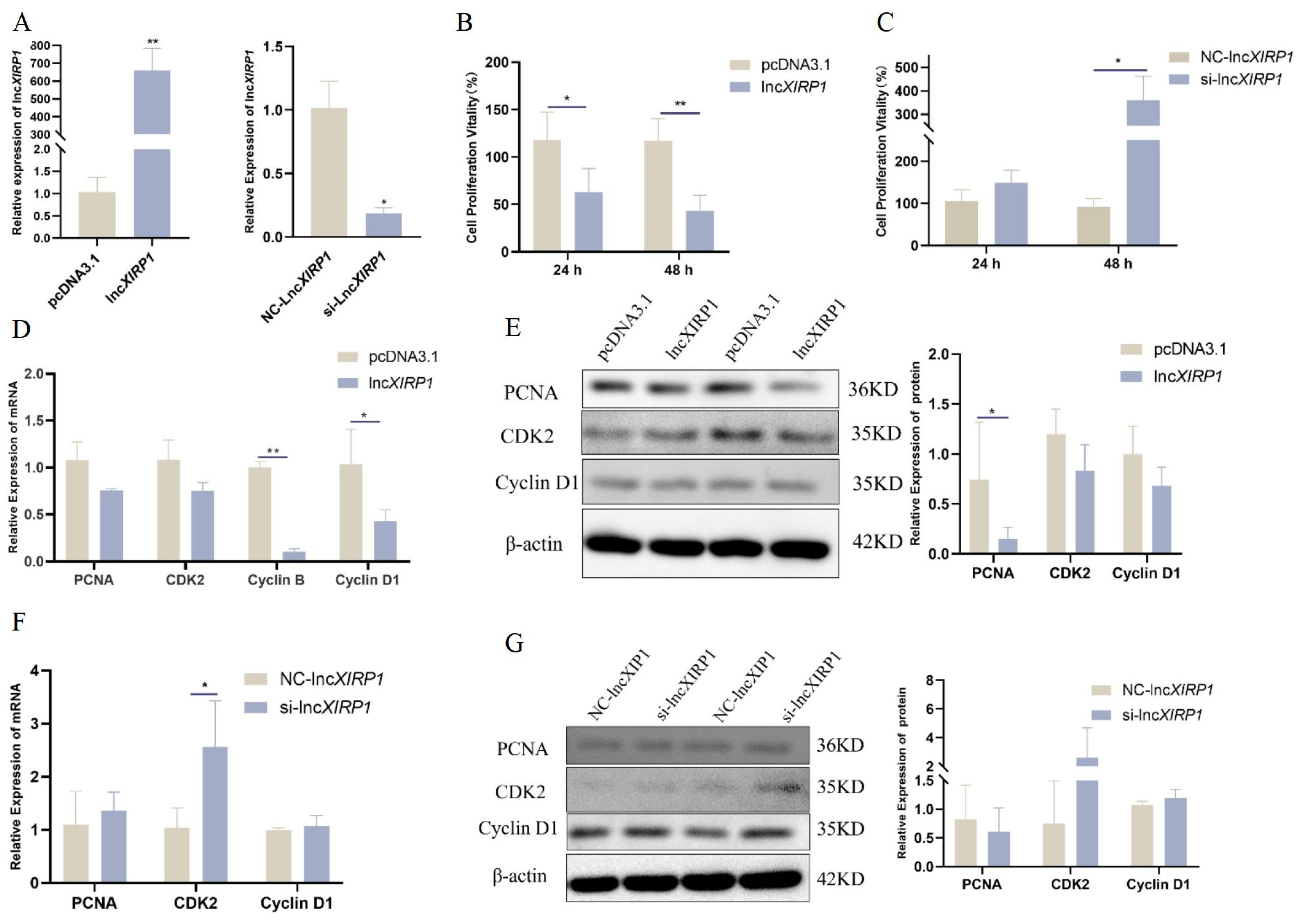
3.2. The Effect of lncXIRP1 on the Proliferation of Pig LCs
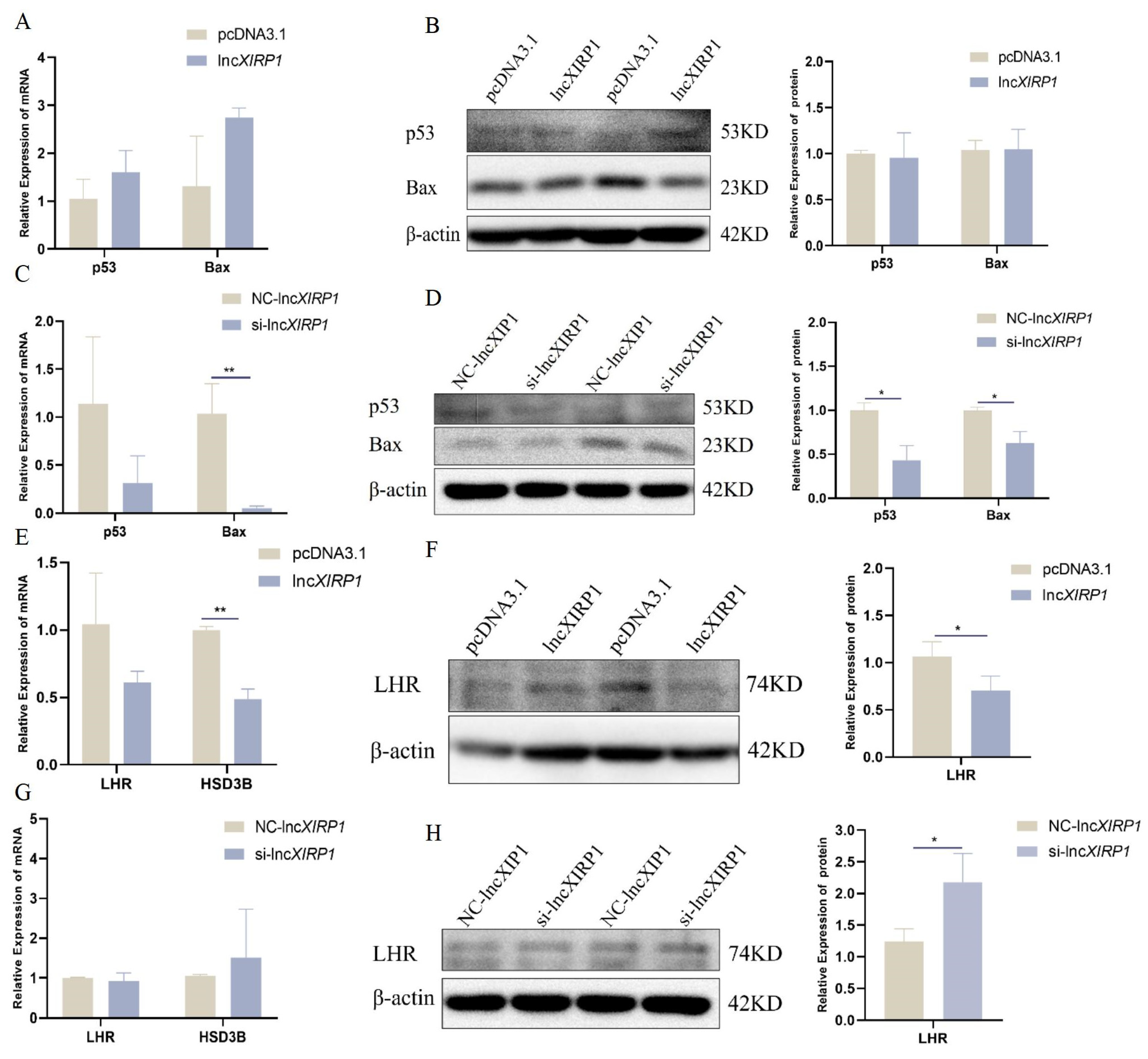
3.3. The Effect of lncXIRP1 on Apoptosis and Testosterone Synthesis in LCs
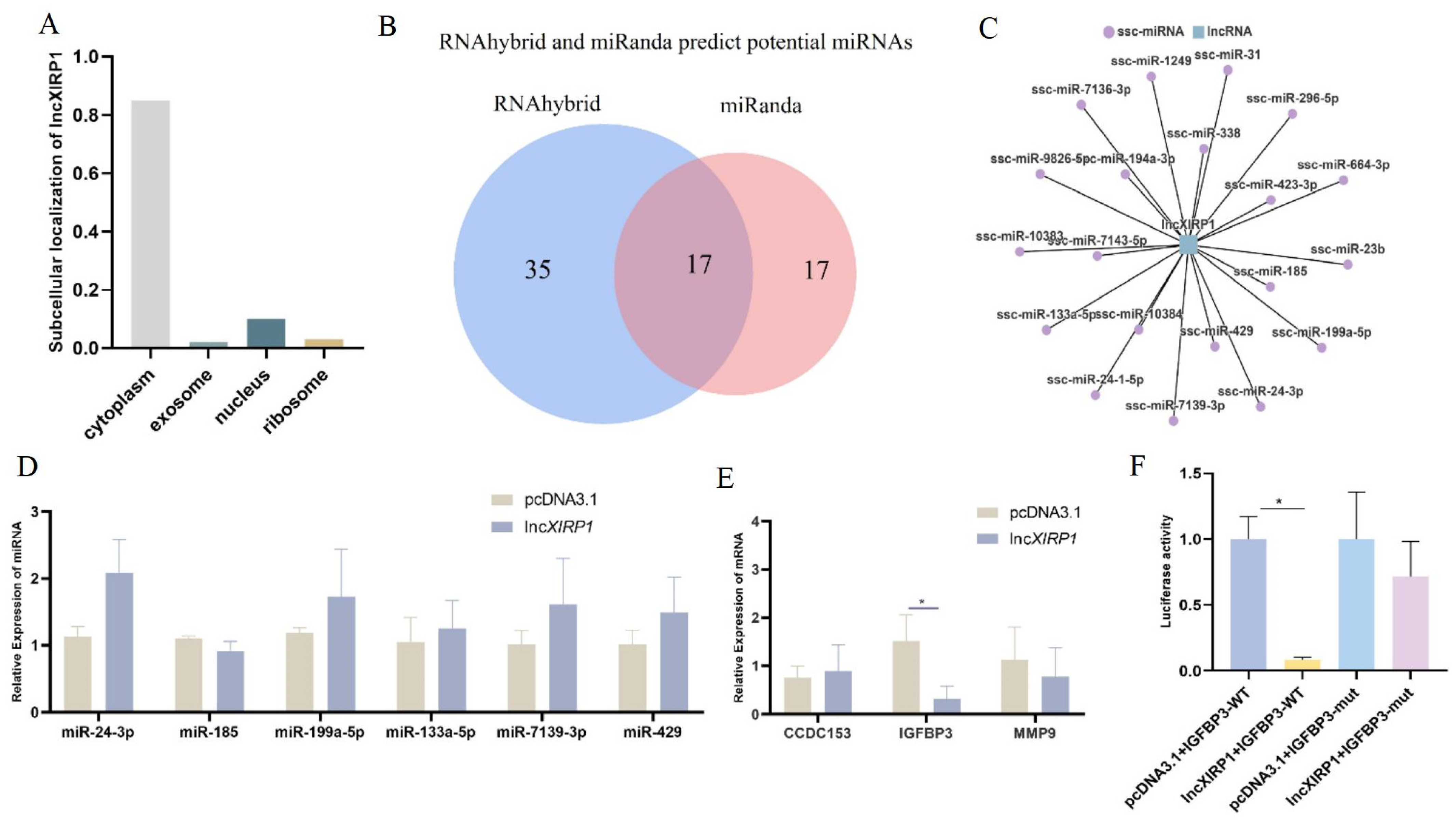
3.4. The Molecular Regulatory Mechanism of lncXIRP1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; He, Q.; He, Z. The roles and mechanisms of Leydig cells and myoid cells in regulating spermatogenesis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2681–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.H.; Cai, B.; Tuo, Y.; Wang, J.; Zang, Z.J.; Tu, X.; Gao, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, W.; Li, G.; et al. Characterization of Nestin-positive stem Leydig cells as a potential source for the treatment of testicular Leydig cell dysfunction. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1466–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zirkin, B.R.; Chen, H. Stem Leydig Cells in the Adult Testis: Characterization, Regulation and Potential Applications. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, R.; Zirkin, B.R. Leydig cell stem cells: Identification, proliferation and differentiation. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 445, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, P.; Zhao, X.; Mei, H.; Liu, J.; Lian, Q.; Zirkin, B.R.; Chen, H. Effects of spermatogenic cycle on Stem Leydig cell proliferation and differentiation. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2019, 481, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begolli, R.; Sideris, N.; Giakountis, A. LncRNAs as Chromatin Regulators in Cancer: From Molecular Function to Clinical Potential. Cancers 2019, 11, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; El-Samahy, M.A.; Li, X.; Bao, Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F. LncRNA-412.25 activates the LIF/STAT3 signaling pathway in ovarian granulosa cells of Hu sheep by sponging miR-346. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.W.; Yang, J.H.; Tsitsipatis, D.; Yang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; Munk, R.; Pandey, P.R.; Banskota, N.; Romero, B.; Batish, M.; et al. Enhanced myogenesis through lncFAM-mediated recruitment of HNRNPL to the MYBPC2 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 13026–13044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przanowska, R.K.; Weidmann, C.A.; Saha, S.; Cichewicz, M.A.; Jensen, K.N.; Przanowski, P.; Irving, P.S.; Janes, K.A.; Guertin, M.J.; Weeks, K.M.; et al. Distinct MUNC lncRNA structural domains regulate transcription of different promyogenic factors. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Anderson, K.M.; Chang, C.L.; Makarewich, C.A.; Nelson, B.R.; McAnally, J.R.; Kasaragod, P.; Shelton, J.M.; Liou, J.; Bassel-Duby, R.; et al. A micropeptide encoded by a putative long noncoding RNA regulates muscle performance. Cell 2015, 160, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi Karoii, D.; Azizi, H. Functions and mechanism of noncoding RNA in regulation and differentiation of male mammalian reproduction. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2023, 41, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; He, C.; Wang, K.; Li, L.; Liao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, M. Overexpression of lncRNA-Gm2044 in spermatogonia impairs spermatogenesis in partial seminiferous tubules. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Tan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Huang, S.; Mao, F.; Lian, J. LOC102549726/miR-760-3p network is involved in the progression of ISO-induced pathological cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Mol. Histol. 2023, 54, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, P.; Dong, W.; Zeng, W.; Pan, C. Identification of Stem Leydig Cells Derived from Pig Testicular Interstitium. Stem. Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 2740272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, R.; Ma, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Dong, W.; Zeng, W.; Lan, X.; et al. miR-205 Expression Elevated With EDS Treatment and Induced Leydig Cell Apoptosis by Targeting RAP2B via the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, F.; Condorelli, R.A.; Mongioi, L.M.; Cannarella, R.; Aversa, A.; Calogero, A.E.; La Vignera, S. Effects of Bisphenols on Testicular Steroidogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.H.; Chu, E.T.; Spektor, R.; Soloway, P.D. Long non-coding RNA regulation of reproduction and development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 82, 932–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ren, W.; Han, D.; Zhao, G.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, Z.; Gao, W.; Yuan, B. LncRNA-m18as1 competitively binds with miR-18a-5p to regulate follicle-stimulating hormone secretion through the Smad2/3 pathway in rat primary pituitary cells. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2022, 23, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Duan, C.; Li, J.; Ji, S.; Yan, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. LncGSAR Controls Ovarian Granulosa Cell Steroidogenesis via Sponging MiR-125b to Activate SCAP/SREBP Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.H.; Youngblood, G.L. Regulation of expression of steroidogenic enzymes in Leydig cells. Biol. Reprod. 1995, 52, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.J.; Tay, Y. Noncoding RNA:RNA Regulatory Networks in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, P.; Chen, X.; Xie, R.; Xie, W.; Huang, L.; Dong, W.; Han, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Huang, J.; et al. A novel AR translational regulator lncRNA LBCS inhibits castration resistance of prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; He, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, D.; Cai, H.; et al. lncRNA LINC00665 Stabilized by TAF15 Impeded the Malignant Biological Behaviors of Glioma Cells via STAU1-Mediated mRNA Degradation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, H.; Niu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, H.; Kong, J.; Ding, K.; Shen, H.M.; Wu, H.; et al. Long non-coding RNA linc00673 regulated non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-150-5p. Mol Cancer 2017, 16, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Du, Q.; Zhao, Q. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 inhibits the proliferation and migration of bladder cancer cells by modulating the microRNA-34a/cyclin D1 axis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L. Steroid hormone synthesis in mitochondria. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2013, 379, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence | Tm Value | GC% | PCR Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCNA | F: AATGCAGACACCTTGGCACT | 60.18 | 50.00 | 154 |
| R: GTGCAAATTCACCAGAAGGCA | 59.66 | 47.62 | ||
| CDK2 | F: GAGCCTTTGGAGTCCCTGTTC | 60.61 | 57.14 | 148 |
| R: CGGGTCACCATCTCAGCAAAG | 61.28 | 57.14 | ||
| Cyclin B | F: AATCCCTTCTTGTGGTTA | 49.94 | 38.89 | 104 |
| R: CTTAGATGTGGCATACTTG | 50.60 | 42.11 | ||
| Cyclin D | F: TACACCGACAACTCCATCCG | 59.47 | 55.00 | 224 |
| R: GAGGGCGGGTTGGAAATGAA | 60.61 | 55.00 | ||
| Bax | F: GCTGACGGCAACTTCAACTG | 60.04 | 55.00 | 202 |
| R: GCGTCCCAAAGTAGGAGAGG | 59.82 | 60.00 | ||
| Bcl-2 | F: CATGTGTGTGGAGAGCGTCA | 60.32 | 55.00 | 135 |
| R: TCTACCATGGACTTCCCCCA | 59.58 | 55.00 | ||
| Caspase 3 | F: TCAGAGGGGACTGCTGTAGA | 59.30 | 55.00 | 81 |
| R: AGTCCAATTCTGTGCCTCGG | 60.04 | 55.00 | ||
| GAPDH | F: TCGGAGTGAACGGATTTGGC | 60.67 | 55.00 | 95 |
| R: GAAGGGGTCATTGATGGCGA | 60.11 | 55.00 | ||
| LHR | F: TCTCCCTATCAAAGTAATCC | 51.00 | 40.00 | 148 |
| R: GTTCTGGATCAGTATTTCAG | 50.99 | 40.00 | ||
| HSD3B | F: GCTGGAGGAGAAGGATCTGC | 59.89 | 60.00 | 89 |
| R: TGCTCTGGAGCTTAGAAAATTCC | 58.73 | 43.48 | ||
| CCDC153 | F: TCATCCCCTGGAAGTGTGTGG | 61.73 | 57.14 | 205 |
| R: GGAAAGAGCGGTGGAGAATGG | 61.01 | 57.14 | ||
| IGFBP3 | F: TGCCTGACTCCAAACTCCAC | 59.89 | 55.00 | 199 |
| R: AACTTGAGGTGGTTCAGCGT | 59.82 | 50.00 | ||
| MMP9 | F: CGCCGACATCGTTATCCAGT | 60.25 | 55.00 | 153 |
| R: TTGCCCAGAGACCACAACTC | 59.89 | 55.00 |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| lncXIRP1 | F: TGAAAGTGGAGGGTGACTCAA |
| R: CTTATGGCTACCAGTGGAGGCTAT | |
| miR-24-3p | RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACCTGTTC |
| F: TGCGTCCGTGGCTCAGTTCAGCAG | |
| miR-185 | RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTCAGGA |
| F: TGCGTCTTGGAGAGAAAGGCAGT | |
| miR-199a-5p | RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGAACAG |
| F: TGCGTCCGCCCAGTGTTCAGACTAC | |
| miR-133a-5p | RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACATTTGG |
| F: TGCGTCCGAGCTGGTAAAATGGAA | |
| miR-7139-3p | RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACCCTCAT |
| F: TCGAGATAGGGCACAGGATGGG | |
| miR-429 | RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACACGGCA |
| F: GCGGTCGCTAATACTGTCTGGTAA | |
| GPR | GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT |
| Antibody Name | Dilution Ratio | Protein Molecular Weight | Brand Name | Serial Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCNA | 1:500 | 36 KD | WanleiBio, Shenyang, China | WL02208 |
| CDK2 | 1:500 | 35 KD | WanleiBio, Shenyang, China | WL02028 |
| Cyclin D1 | 1:500 | 35 KD | WanleiBio, Shenyang, China | WL01435a |
| P53 | 1:500 | 53 KD | WanleiBio, Shenyang, China | WL01919 |
| Bax | 1:500 | 23 KD | WanleiBio, Shenyang, China | WL01637 |
| LHR | 1:500 | 74 KD | Bioss, Beijing China | BS-6431R |
| β-actin | 1:5000 | 42 KD | Proteintech, Rosemont, Illinois, USA | 66009-Hg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Tang, Q.; Lan, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Pan, C. Long Non-Coding RNA lncXIRP1 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Pig Leydig Cells. Agriculture 2025, 15, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080802
Yang H, Lu X, Zhang S, Tang Q, Lan X, Wang J, Chen X, Pan C. Long Non-Coding RNA lncXIRP1 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Pig Leydig Cells. Agriculture. 2025; 15(8):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080802
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Haiyan, Xianzhao Lu, Shan Zhang, Qi Tang, Xianyong Lan, Jing Wang, Xiaolei Chen, and Chuanying Pan. 2025. "Long Non-Coding RNA lncXIRP1 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Pig Leydig Cells" Agriculture 15, no. 8: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080802
APA StyleYang, H., Lu, X., Zhang, S., Tang, Q., Lan, X., Wang, J., Chen, X., & Pan, C. (2025). Long Non-Coding RNA lncXIRP1 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Pig Leydig Cells. Agriculture, 15(8), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080802






