Effects of Different Nitrogen Substitution Practices on Nitrogen Utilization, Surplus, and Footprint in the Sweet Maize Cropping System in South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Plant Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis
2.5. Calculation Methods for Nitrogen Management Indicators
2.5.1. Nitrogen Use Efficiency
2.5.2. Partial Productivity of Nitrogen Fertilizer
2.5.3. Nitrogen Surplus
2.5.4. Nitrogen Footprint
| Item | Emission Coefficient (g N-eq·kg−1) | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Diesel | 0.08 | [50] |
| Diesel combustion | 4.58 | [50] |
| Synthetic N fertilizer (N) | 0.89 | [50] |
| Synthetic P fertilizer (P2O5) | 0.54 | [50] |
| Synthetic K fertilizer (K2O) | 0.03 | [50] |
| Insecticides | 3.53 | [50] |
| Herbicides | 4.49 | [50] |
| Fungicides | 7.00 | [50] |
2.6. Economic Benefits
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nitrogen Uptake
3.2. Nitrogen Use Efficiency
3.3. Partial Productivity of Nitrogen Fertilizer
3.4. Nitrogen Surplus and Loss
3.5. Nitrogen Footprint
3.6. Economic Benefit
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Nitrogen Substitution on Nitrogen Utilization
4.2. Effect of Nitrogen Substitution on Nitrogen Surpluses
4.3. Effect of Nitrogen Substitution on Nitrogen Loss
4.4. Potential Uncertainty and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruber, N.; Galloway, J.N. An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 2008, 451, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.Y.; Xia, L.L.; Ti, C.P. Win-win Nitrogen Management Practices for Improving Crop Yield and Environmental Sustainability. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2018, 33, 177–183, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Zhang, C. The Principles and Indicators of Rational N Fertilization. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2021, 58, 1–13, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT Database. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Statistics Division. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Wright, J.S.; Hall, J.W.; Gong, P.; Ni, S.; Qiao, S.; Huang, G.; et al. Managing nitrogen to restore water quality in China. Nature 2019, 567, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, I.O.; Gitari, H.I.; Mochoge, B.; Rezaei-Chiyaneh, E.; Gweyi-Onyango, J.P. Optimizing Maize Yield, Nitrogen Efficacy and Grain Protein Content under Different N Forms and Rates. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1867–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reay, D.S.; Davidson, E.A.; Smith, K.A.; Smith, P.; Melillo, J.M.; Dentener, F.; Crutzen, P.J. Global agriculture and nitrous oxide emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakidou, M. China’s nitrogen management. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhong, X.; Pan, J.; Liang, K.; Liu, Y.; Peng, B.; Hu, X.; Huang, N. QTLs identification for nitrogen and phosphorus uptake-related traits using ultra-high density SNP linkage. Plant Sci. 2019, 288, 110209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.; Diwan, H. Assessing fertilizer use behaviour for environmental management and sustainability: A quantitative study in agriculturally intensive regions of Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 5822–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; Xie, R.; Wang, K.; Ming, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, W.; et al. How to increase maize production without extra nitrogen input. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 160, 104913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Xu, M.; Li, R.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Reis, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; et al. Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer use for more grain and less pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 132180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Liang, G.; Hou, E.; Luo, Y. Manure acts as a better fertilizer for increasing crop yields than synthetic fertilizer does by improving soil fertility. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 189, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ti, C.; Xia, L.; Xia, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yan, X. Ecosystem services of partial organic substitution for chemical fertilizer in a peri-urban zone in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Zhou, P.; Li, Z.; Smith, P.; Li, L.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Shen, S.; Chen, X. Combined inorganic/organic fertilization enhances N efficiency and increases rice productivity through organic carbon accumulation in a rice paddy from the Tai Lake region, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 131, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Chu, H. Bacterial diversity in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization can be more stably maintained with the addition of livestock manure than wheat straw. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J.J.; de Visser, W.; Assinck, F.B.T.; Velthof, G.L. Effects of short-term nitrogen supply from livestock manures and cover crops on silage maize production and nitrate leaching. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Ju, X.; Shen, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Fan, M.; et al. Chapter one—Integrated Nutrient Management for Food Security and Environmental Quality in China. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 116, pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.B.; Yuan, M.M.; Wang, P.X.; Zhang, X.M.; Shu, X.H. Combined Application of Different Proportions of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers: Effects on Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2022, 38, 1–5, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Ma, Y.J.; Chen, S.W.; Zhang, K.Q.; Wang, F.; Shen, S.Z. Effects of different ratios of organic fertilizers replacing chemical fertilizers on nitrogen and phosphorus utilization ratio of rice and nitrogen and phosphorus balance in rice fields. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 93–98, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Han, X.; Li, N.; Chen, K.; Yang, J.; Zhan, X.; Luo, P.; Liu, N. Combined application of biochar with fertilizer promotes nitrogen uptake in maize by increasing nitrogen retention in soil. Biochar 2021, 3, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Shangguan, Z. Combined biochar and nitrogen fertilization at appropriate rates could balance the leaching and availability of soil inorganic nitrogen. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 276, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Tan, S.; Chen, Y.; Yan, P.; Wang, X. Effects of substituting synthetic nitrogen with organic amendments on crop yield, net greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint: A global meta-analysis. Field Crop Res. 2023, 301, 109035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, J.R.; Lu, B.S.; Shi, Y.X.; Fan, Y.L. Current situation and development trend of fresh corn seed industry in China. China Seed Ind. 2020, 10, 14–18, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, C.; Nagy, J.; Huzsvai, L.; Zelenák, A.; Szabó, A.; Széles, A. Analysis of the Content Values of Sweet Maize (Zea mays L. Convar Saccharata Koern) in Precision Farming. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Huang, C.L. Current Production Status, Problem and Countermeasure on Sweet Corn Industry in China. Sugar Crops China 2021, 43, 67–71, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Song, Z.; Shi, S.; Bai, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, A.; Huang, W.; Chen, N.; Chen, F. Developments and prospects of multiple cropping in China. Farming Syst. 2024, 2, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.G.; Li, Q.; Chen, Q.X.; Luo, S.B.; Cao, J.; Zhong, Y.J.; Yang, Q. Research on index system for sweet maize fertilization in Guangdong. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2013, 40, 67–70, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Y.; Tang, S.H.; Zhang, F.B.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.; Pang, Y.W.; Li, P.; Fu, H.T. Effect of the blending ratio of controlled-release urea and conventional urea on yield and nitrogen utilization efficiency of sweet corn. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2017, 23, 622–631, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heumann, S.; Fier, A.; Haßdenteufel, M.; Höper, H.; Schäfer, W.; Eiler, T.; Böttcher, J. Minimizing nitrate leaching while maintaining crop yields: Insights by simulating net N mineralization. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2013, 95, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Gao, C.; Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Ammonia volatilization in Chinese double rice-cropping systems: A 3-year field measurement in long-term fertilizer experiments. Biol. Fert. Soils 2014, 50, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M.; Mulvaney, C.S. Nitrogen—Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 9.2.2, 2nd ed.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; pp. 595–624. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhai, L.; Yang, B.; Wu, S.; Ren, T.; Lei, Q.; Wang, H. Long-term benefits of combining chemical fertilizer and manure applications on crop yields and soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Y.; Tian, C.Y.; Yin, H.J.; Xu, J.K.; Zhao, B.Q.; Tang, J.W. Long-term effect of organic fertilizer on soil system nitrogen surplus and nitrogen loss in winter wheat-summer maize rotation system. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2022, 3, 21–28, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Gu, B.J. Indexes of Nitrogen Management. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 281–296, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mori, T.; Mao, Q.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, H.; Lu, X.; Mo, J. Long-term phosphorus addition downregulates microbial investments on enzyme productions in a mature tropical forest. J. Soil Sediment. 2020, 20, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, L.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Van Der Hoek, K.W.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Van Vuuren, D.P.; Willems, J.; Rufino, M.C.; Stehfest, E. Exploring global changes in nitrogen and phosphorus cycles in agriculture induced by livestock production over the 1900–2050 period. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20882–20887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Luo, X.S.; Pan, Y.P.; Zhang, L.; Tang, A.H.; Shen, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.H.; Wu, Q.H.; Yang, D.W.; et al. Quantifying atmospheric nitrogen deposition through a nationwide monitoring network across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12345–12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.X.; Han, L.L.; He, J.Z.; Luo, F.; Zhang, L.M. Research advance on molecular ecology of asymbiotic nitrogen fixation microbes. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 3440–3450, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Huang, G.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.; Huo, Z. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on grain yield, water and nitrogen dynamics and their use efficiency of spring wheat farmland in an arid agricultural watershed of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 260, 107277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, L.M.; He, P.; Zhao, T.K.; Xu, X.P.; Zheng, H.G. Nitrogen cycling and balance for wheat in China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 76–86, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, X.; Reis, S.; Wang, S.; Jin, J.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. Climate change unequally affects nitrogen use and losses in global croplands. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.N.; Winiwarter, W.; Leip, A.; Leach, A.M.; Bleeker, A.; Erisman, J.W. Nitrogen footprints: Past, present and future. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendia, E.; Tanabe, K.; Kranjc, A.; Jamsranjav, B.; Fukuda, M.; Ngarize, S.; Osako, A.; Pyrozhenko, Y.; Shermanau, P.; Federici, S. 2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guinee, J.B. Handbook on life cycle assessment operational guide to the ISO standards. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2002, 7, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Li, Y.E.; Jiang, D.F.; Zou, X.X. Life Cycle Assessment on Carbon Footprint of Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Cropping System Based on Survey Data of Gaomi in Shandong Province, China. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2017, 34, 473–482. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.D.; Xu, C.C.; Ji, L.; Fang, F.P. Comprehensive evaluation for carbon and nitrogen footprints of rice–wheat rotation system in Middle Yangtze River Basin. J. Plant. Nutr. Fertil. 2019, 25, 1125–1133, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Cao, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. Effects of equal chemical fertilizer substitutions with organic manure on yield, dry matter, and nitrogen uptake of spring maize and soil nitrogen distribution. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e219512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, S.Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.B. Effect of combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers on nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency by paddy rice. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 2021, 41, 1–6, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wang, J.P.; Liang, B.; Li, J.L. Effects of Different Organic Materials on Nitrogen Leaching Loss in Greenhouse. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2020, 35, 256–261, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.K.; Shi, W.M.; Xu, Y.H.; Min, J. Effects of Long-term Different Chemical Nitrogen Rates on Soil Nitrogen Mineralization and Nitrification in Greenhouse Vegetable Field. Soils 2021, 53, 1160–1166, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.M.; Zhang, F.S.; Ma, W.Q.; Xu, W.H. Change of farmyard manure application in Shaanxi Province. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 10, 1669–1672, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.L.; Liu, L.; Qiu, H.H. Effects of different organic resources application combined with chemical fertilizer on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of main grain crops in China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 1384–1394, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Xu, C.; Tahmasbian, I.; Che, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wallace, H.M.; Bai, S.H. Effects of biochar on soil available inorganic nitrogen: A review and meta-analysis. Geoderma 2017, 288, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Baruah, K.K. Organic substitution in fertilizer schedule: Impacts on soil health, photosynthetic efficiency, yield and assimilation in wheat grown in alluvial soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q. Effects of organic–inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice–wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fungo, B.; Lehmann, J.; Kalbitz, K.; Thion, O.M.; Okeyo, I.; Tenywa, M.; Neufeldt, H. Aggregate size distribution in a biochar-amended tropical Ultisol under conventional hand-hoe tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Hong, M.; Wen, X.; Pei, Z.F.; Zhao, H.X.; Chen, C.; Wen, X.L. Effect of Different Organic Amendments on Soil Organic Carbon Pool and Chemical Properties in Soda Alkaline Soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 311–318, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sui, P.; Lian, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Gong, X.; Qi, H.; et al. Tillage with straw incorporation? Reduces the optimal nitrogen rate for maize production by affecting crop uptake, utility efficiency, and the soil balance of nitrogen. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2825–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Liang, W. Organic substitutions improve soil quality and maize yield through increasing soil microbial diversity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Yan, C.; Mei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, T. Long-Term Effect of Manure and Fertilizer on Soil Organic Carbon Pools in Dryland Farming in Northwest China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siedt, M.; Sch Ffer, A.; Smith, K.E.C.; Nabel, M.; Ro Nickoll, M.; van Dongen, J.T. Comparing straw, compost, and biochar regarding their suitability as agricultural soil amendments to affect soil structure, nutrient leaching, microbial communities, and the fate of pesticides. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of anaerobic digestion on digestate nutrient availability and crop growth: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K. Effects of anaerobic digestion on soil carbon and nitrogen turnover, N emissions, and soil biological activity. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1021–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.Q.; Wu, L.S.; Hu, C.X. Effects of N rate on application rate on N utilization and yield of vegetable and soil residual NO3--N under drip irrigation system. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2017, 11, 2535–2545, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Ju, X.T.; Zhang, L.J.; Li, X.; Yuan, L.J.; Liu, N. Effects of different N rates on fate of N fertilizer and balance of soil N of winter wheat. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2010, 16, 296–303, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.J.; Ren, Q.R.; Jiao, X.Q. Nitrogen flow characteristics and management of wheat-maize system in Quzhou. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 51, 1422–1429, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.F.; Ai, S.Y.; Li, M.J.; Yao, J.W.; Yu, D.N.; Wang, S.Y.; Shen, J. Impacts of Reduced Fertilizer Application with Organic N on Vegetable Growth and Soil N Balance in Vegetable Fields in Latosolic Red Soil Zones. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2019, 40, 1008–1014, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, B.H.; de Willigen, P. Ideal and saturated soil fertility as bench marks in nutrient management: II. Interpretation of chemical soil tests in relation to ideal and saturated soil fertility. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 116, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Du, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, T.; Sui, P.; Gao, W.; Chen, Y. Different organic material amendments effects soil nitrogen utilization and crop yield in the North China Plain. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 3473–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.R.; Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.R.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.L.; Zhu, J.Q.; Xu, M.G. Swine manure as part of the total N source improves red soil resistance to acidification. J. Plant. Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 2052–2059, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wu, K.; Sun, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, W.; Li, X.; Hu, C. Effect of partial replacement of mineral fertilizer by manure on nitrogen losses and balance from wheat-maize farmland in North China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2025, 33, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Kalbitz, K.; Zhou, J. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on the composition of maize roots and their decomposition at different soil depths. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2015, 67, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, M.G.; Zhao, H.L.; Duan, Y.H. Decomposition Characteristics and Driving Factors of Organic Materials in Typical Farmland Soils in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2019, 52, 1564–1573, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcińczyk, M.; Oleszczuk, P. Biochar and engineered biochar as slow- and controlled-release fertilizers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, V.; Rütting, T.; Huygens, D.; Staelens, J.; Ruysschaert, G.; Boeckx, P. Maize biochars accelerate short-term soil nitrogen dynamics in a loamy sand soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 55, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakawa, R.; Ohte, N.; Shibata, H.; Isobe, K.; Tateno, R.; Oda, T.; Hishi, T.; Fukushima, K.; Inagaki, Y.; Hirai, K.; et al. Factors contributing to soil nitrogen mineralization and nitrification rates of forest soils in the Japanese archipelago. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 361, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthurson, V. Closing the Global Energy and Nutrient Cycles through Application of Biogas Residue to Agricultural Land—Potential Benefits and Drawback. Energies 2009, 2, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghball, B.; Power, J.F. Phosphorus- and Nitrogen-Based Manure and Compost Applications Corn Production and Soil Phosphorus. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.K.; Chang, C.; Clayton, G.W.; Carefoot, J.P. Cattle Manure Amendments Can Increase the pH of Acid Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Hu, K.; Batchelor, W.D.; Liang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, J.; Cui, X.; Zhou, F. Exploring optimal nitrogen management strategies to mitigate nitrogen losses from paddy soil in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, O.; Gu, B. Nitrogen management across croplands. Nat. Food 2024, 5, 974–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Liang, X.; Lam, S.K.; Chen, D.; Malik, A.; Li, M.; Lenzen, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; et al. Localized nitrogen management strategies can halve fertilizer use in Chinese staple crop production. Nat. Food 2024, 5, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Riaz, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, B.; El-Desouki, Z.; Jiang, C. Biochar increases nitrogen use efficiency of maize by relieving aluminum toxicity and improving soil quality in acidic soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Tong, C.; Hu, K.; Zhou, B.; Xing, S.; Mao, Y. Biochar-fertilizer interaction modifies N-sorption, enzyme activities and microbial functional abundance regulating nitrogen retention in rhizosphere soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, É.M.G.; Reis, M.M.; Frazão, L.A.; Da Mata Terra, L.E.; Lopes, E.F.; Dos Santos, M.M.; Fernandes, L.A. Biochar increases enzyme activity and total microbial quality of soil grown with sugarcane. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G. Effects of biochar on nitrification and denitrification-mediated N2O emissions and the associated microbial community in an agricultural soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6649–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Xiong, Z. Biochar reduces yield-scaled emissions of reactive nitrogen gases from vegetable soils across China. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2851–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Liu, Q.; Shao, Y.; Li, S.S.; Li, X.B.; Weng, Z.P. Effects of organic material returning and nitrogen fertilizer reduction on the economic yields and carbon, nitrogen, and water footprints of wheat-maize annual farmland in China. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2020, 37, 527–536, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, B.; Xia, L.; Fan, C.; Xiong, Z. Organic-substitute strategies reduced carbon and reactive nitrogen footprints and gained net ecosystem economic benefit for intensive vegetable production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, Z.; Hu, J.; Yaa, O.; Wu, J. Decomposition Characteristics, Nutrient Release, and Structural Changes of Maize Straw in Dryland Farming under Combined Application of Animal Manure. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloukounon Goubalan, A.Y.; Aliou, S.; Obognon, N.; Amadji, G.; IGUE, A.; Clottey, V.; Kenis, M. Decomposition and nutrient release pattern of animal manures biodegraded by fly larvae in Acrisols. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 99, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Ou, J.; Liu, F.; Cai, G.; Tan, K.; Wang, X. Nitrogen substitution practice improves soil quality of red soil (Ultisols) in South China by affecting soil properties and microbial community composition. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 240, 106089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ros, G.H.; Xu, M.; Cai, Z.; Sun, N.; Duan, Y.; de Vries, W. Long-term impacts of mineral and organic fertilizer inputs on nitrogen use efficiency for different cropping systems and site conditions in Southern China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 146, 126797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
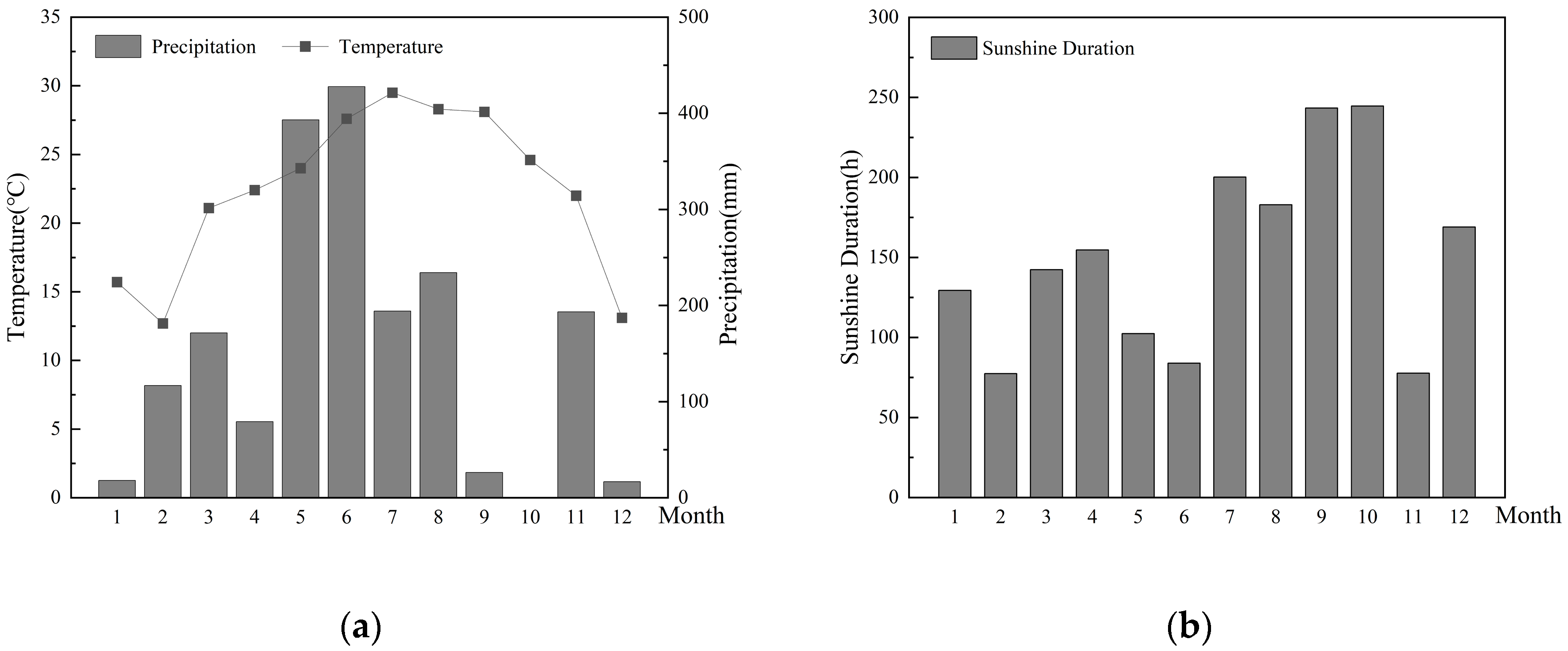
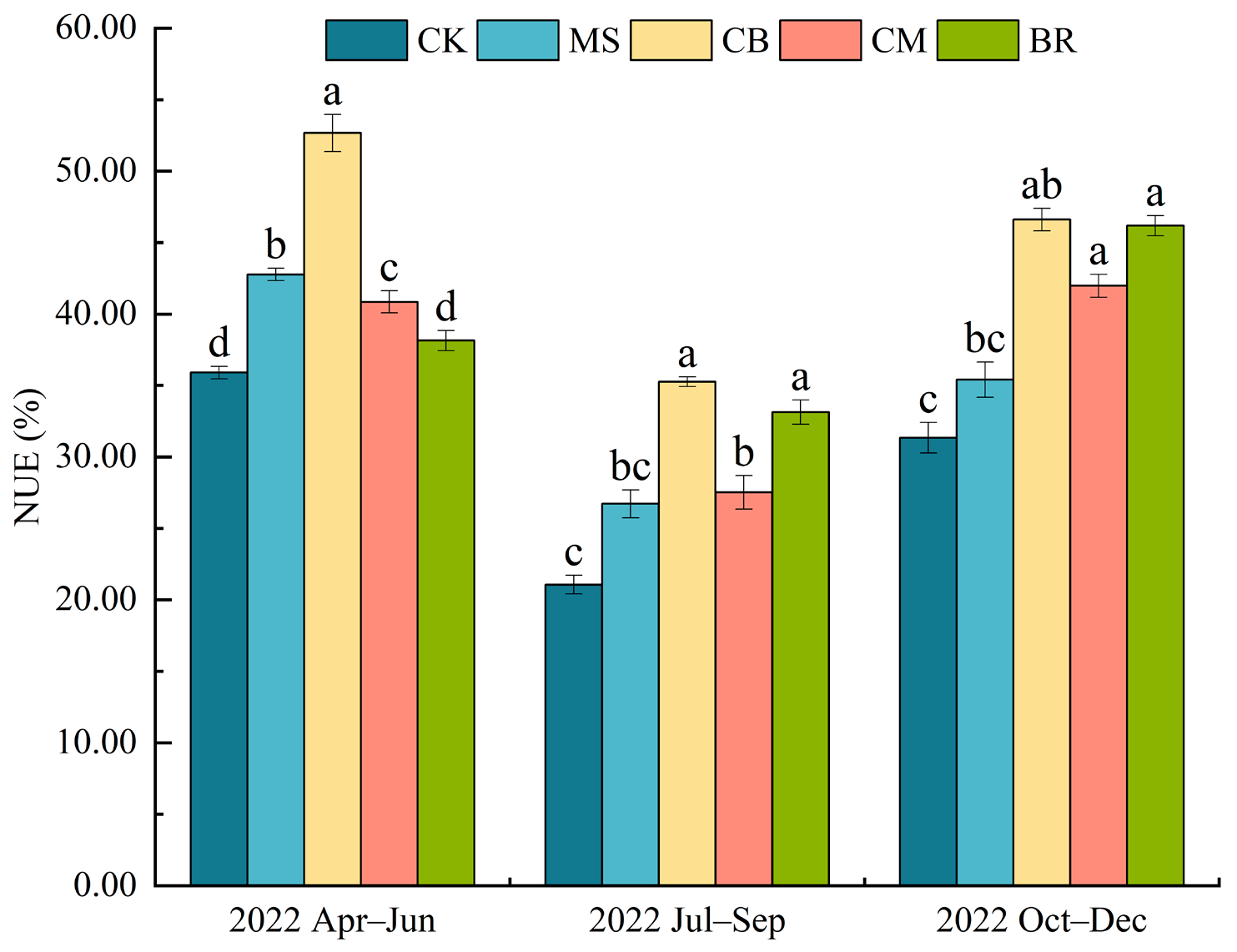
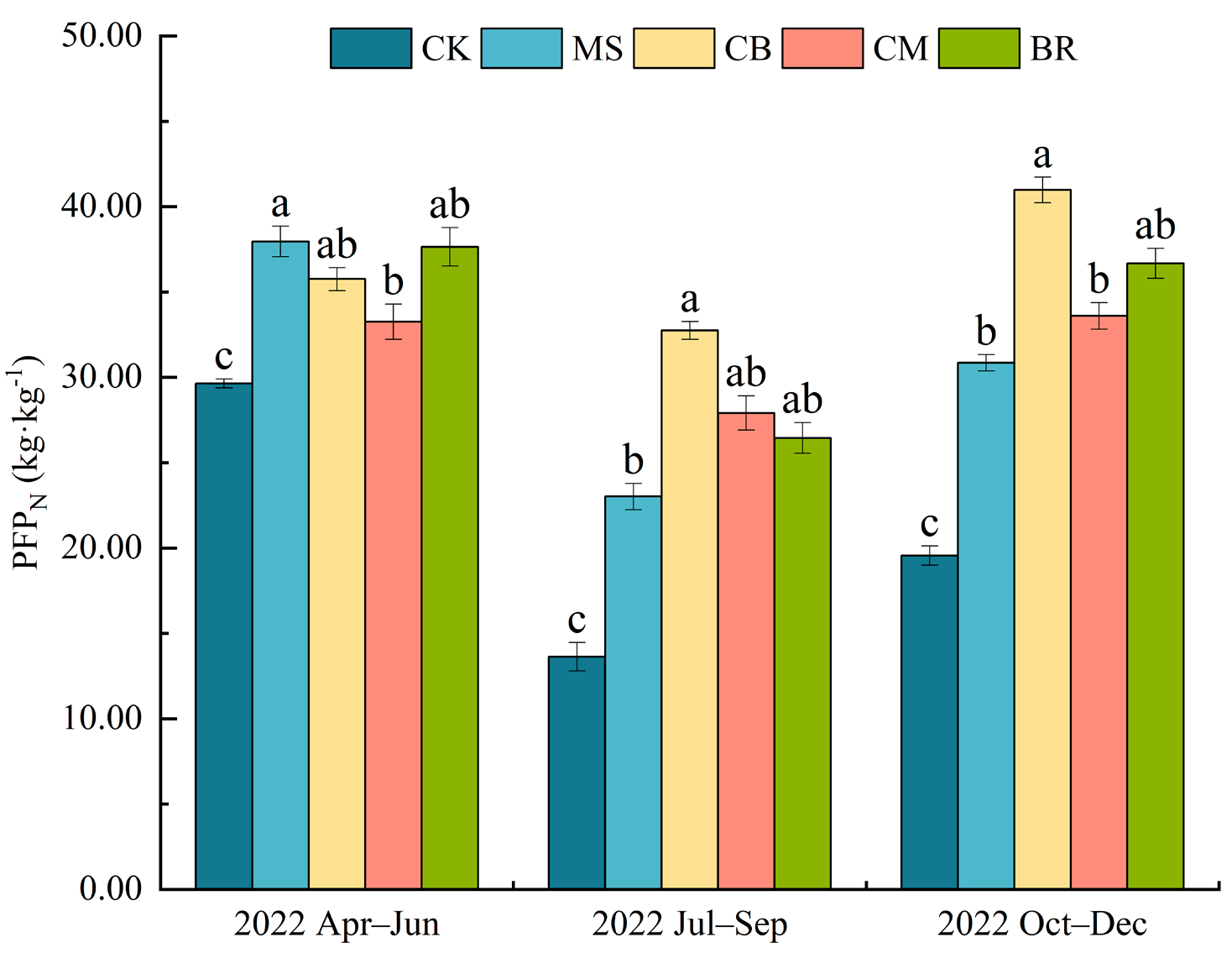
| Treatment | Organic Material 1 | Synthetic Fertilizer (kg·ha−1) | Total N Input | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount (kg·ha−1) | Total N content (%) | N | P2O5 | K2O | (kg·ha−1) | |
| Conventional N input (CK) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 300.00 | 150.00 | 300.00 | 300.00 |
| Substituting 20% synthetic N with crop straw (MS) | 7091.36 | 1.40 | 240.00 | 150.00 | 300.00 | 300.00 |
| Substituting 20% synthetic N with biochar (CB) | 12,485.04 | 0.77 | 240.00 | 150.00 | 300.00 | 300.00 |
| Substituting 20% synthetic N with cow manure (CM) | 18,117.79 | 1.85 | 240.00 | 150.00 | 300.00 | 300.00 |
| Substituting 20% synthetic N with biogas residue (BR) | 17,251.67 | 1.46 | 240.00 | 150.00 | 300.00 | 300.00 |
| Organic Material | TOC (g·kg−1) | TN (g·kg−1) | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maize straw | 385.10 | 14.00 | 27.51 |
| Biochar | 536.00 | 7.70 | 69.61 |
| Cow manure | 265.50 | 18.45 | 14.39 |
| Biogas residue | 305.95 | 14.60 | 20.96 |
| Season | Treatment | Maize Grain | Maize Cob | Maize Straw | N Uptake in Crops (kg·ha−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (kg·ha−1) | N Content (%) | N Uptake (kg·ha−1) | Yield (kg·ha−1) | N Content (%) | N Uptake (kg·ha−1) | Yield (kg·ha−1) | N Content (%) | N Uptake (kg·ha−1) | |||
| 2022 April–June | CK | 1762.23 ab | 1.51 a | 26.61 b | 1063.03 a | 0.58 a | 6.20 a | 5951.58 ab | 1.82 b | 95.81 bc | 128.62 bc |
| MS | 1987.93 a | 1.45 ab | 29.42 a | 1044.33 a | 0.52 a | 5.48 a | 6467.75 a | 1.67 b | 119.54 b | 153.23 b | |
| CB | 1854.03 ab | 1.42 ab | 28.76 a | 990.07 ab | 0.55 a | 5.46 a | 6387.57 a | 2.19 a | 154.48 a | 188.69 a | |
| CM | 1666.87 b | 1.34 b | 27.57 b | 977.17 ab | 0.57 a | 5.45 a | 6332.00 a | 1.50 bc | 113.34 b | 145.23 b | |
| BR | 1927.03 a | 1.50 ab | 30.66 a | 993.10 ab | 0.59 a | 5.81 a | 5875.73 ab | 1.20 c | 70.14 c | 106.61 c | |
| 2022 July–September | CK | 1064.61 d | 1.56 b | 16.62 d | 743.46 c | 1.12 a | 8.36 bc | 3187.50 b | 1.58 b | 50.49 b | 75.47 d |
| MS | 1449.18 c | 1.63 ab | 23.62 c | 867.24 b | 1.03 c | 8.91 bc | 4023.17 ab | 1.57 b | 63.21 ab | 95.74 cd | |
| CB | 2002.29 a | 1.69 a | 33.91 a | 1124.23 a | 0.98 d | 11.01 a | 5246.33 a | 1.55 b | 81.42 a | 126.34 a | |
| CM | 1553.69 c | 1.62 ab | 25.23 c | 1041.34 a | 1.03 c | 10.69 a | 4029.83 ab | 1.56 b | 62.7 ab | 98.61 bc | |
| BR | 1696.54 b | 1.65 a | 27.98 b | 918.60 b | 1.07 b | 9.81 b | 4603.56 a | 1.75 a | 80.95 a | 118.74 ab | |
| 2022 October–December | CK | 1303.14 d | 2.45 a | 31.93 c | 862.03 c | 0.71 a | 6.15 b | 4556.00 b | 1.63 a | 74.19 b | 112.27 c |
| MS | 1565.64 c | 2.35 b | 36.72 bc | 953.33 bc | 0.68 ab | 6.46 b | 6452.67 ab | 1.30 d | 83.68 ab | 126.86 bc | |
| CB | 1988.00 a | 2.34 b | 46.56 a | 1229.96 a | 0.64 b | 7.85 a | 8369.83 a | 1.34 c | 112.57 a | 166.99 a | |
| CM | 1737.50 bc | 2.29 b | 39.89 b | 1068.78 b | 0.71 a | 7.55 a | 7886.67 a | 1.30 d | 102.96 ab | 150.40 ab | |
| BR | 1797.93 ab | 2.30 b | 41.34 b | 953.53 bc | 0.70 a | 6.66 b | 7626.00 a | 1.54 b | 117.49 a | 165.48 a | |
| Average | CK | 1376.66 c | 1.84 a | 25.05 d | 889.51 b | 0.80 a | 6.90 b | 4565.03 d | 1.68 a | 73.50 b | 105.45 d |
| MS | 1667.58 b | 1.81 ab | 29.92 c | 954.97 ab | 0.74 ab | 6.95 b | 5647.86 bc | 1.51 b | 88.81 ab | 125.27 c | |
| CB | 1948.11 a | 1.82 a | 36.40 a | 1114.75 a | 0.72 b | 8.11 a | 6667.91 a | 1.69 a | 116.16 a | 160.67 a | |
| CM | 1652.69 b | 1.75 b | 30.89 c | 1029.10 a | 0.77 a | 7.90 a | 6082.83 ab | 1.45 c | 93.00 ab | 131.79 b | |
| BR | 1807.17 ab | 1.82 a | 33.32 b | 955.08 ab | 0.79 a | 7.43 ab | 6035.10 ab | 1.50 b | 89.53 ab | 130.27 b | |
| Season | Nitrogen Budget (kg·ha−1) | CK | MS | CB | CM | BR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 April–June | Nitrogen fertilizer | 300.00 a | 240.00 b | 240.00 b | 240.00 b | 240.00 b |
| Organic material | 0.00 a | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | |
| Seed | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | |
| Biological nitrogen fixation | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | |
| Nitrogen deposition | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | |
| Soil non-symbiotic nitrogen fixation | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | |
| Nitrogen input | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | |
| Nitrogen uptake in crops | 128.62 c | 153.23 b | 188.69 a | 145.23 b | 136.65 bc | |
| Soil nitrogen pool increment | −33.51 d | 14.54 c | 42.38 a | −25.73 e | 23.40 b | |
| Nitrogen surplus | 229.68 a | 205.07 ab | 169.61 b | 211.93 ab | 221.65 a | |
| Nitrogen loss | 263.19 a | 190.53 c | 127.23 d | 237.66 ab | 198.25 c | |
| 2022 July–September | Nitrogen fertilizer | 300.00 a | 240.00 b | 240.00 b | 240.00 b | 240.00 b |
| Organic material | 0.00 a | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | |
| Seed | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | |
| Biological nitrogen fixation | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | |
| Nitrogen deposition | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | |
| Soil non-symbiotic nitrogen fixation | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | |
| Nitrogen input | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | |
| Nitrogen uptake in crops | 75.47 d | 95.74 cd | 126.34 a | 98.61 bc | 118.74 ab | |
| Soil nitrogen pool increment | −56.70 b | −59.76 bc | −36.31 a | −52.24 b | −34.37 a | |
| Nitrogen surplus | 282.83 a | 262.56 ab | 231.96 c | 259.69 ab | 239.56 bc | |
| Nitrogen loss | 339.53 a | 322.32 ab | 268.27 c | 311.93 ab | 273.93 c | |
| 2022 October–December | Nitrogen fertilizer | 300.00 a | 240.00 b | 240.00 b | 240.00 b | 240.00 b |
| Organic material | 0.00 a | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | 60.00 b | |
| Seed | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | 0.50 a | |
| Biological nitrogen fixation | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | 5.00 a | |
| Nitrogen deposition | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | 37.80 a | |
| Soil non-symbiotic nitrogen fixation | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | 15.00 a | |
| Nitrogen input | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | 358.30 a | |
| Nitrogen uptake in crops | 112.27 c | 126.86 bc | 166.99 a | 150.40 ab | 165.48 a | |
| Soil nitrogen pool increment | 87.88 cd | 75.35 d | 144.56 a | 102.58 c | 131.81 ab | |
| Nitrogen surplus | 246.03 a | 231.44 ab | 191.31 c | 207.9 bc | 192.82 c | |
| Nitrogen loss | 158.15 a | 156.09 ab | 46.75 de | 105.32 c | 61.01 d |
| Treatment | Direct RN Emissions (kg N-eq·ha−1) | Indirect RN Emissions (kg N-eq·ha−1) | NFA (kg N-eq·ha−1) | NFY (kg N-eq·kg−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2O Emissions | NH3 Volatilization | N Leaching | Diesel | Fertilizer | Pesticides | |||
| CK | 0.87 a | 74.29 a | 304.09 a | 0.05 a | 0.36 a | 0.08 a | 379.75 a | 0.0426 a |
| MS | 0.87 a | 74.29 a | 252.36 a | 0.05 a | 0.30 b | 0.08 a | 327.95 a | 0.0280 b |
| CB | 0.87 a | 74.29 a | 181.73 b | 0.05 a | 0.30 b | 0.08 a | 257.33 b | 0.0223 b |
| CM | 0.87 a | 74.29 a | 237.80 ab | 0.05 a | 0.30 b | 0.08 a | 313.40 ab | 0.0225 b |
| BR | 0.87 a | 74.29 a | 240.96 ab | 0.05 a | 0.30 b | 0.08 a | 316.55 ab | 0.0272 b |
| Treatments | Total Input (CNY·ha−1) | Revenue (CNY·ha−1) | Net Revenue (CNY·ha−1) | Input–Output Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Material (CNY·ha−1) | Fertilizer (CNY·ha−1) | Other Costs (CNY·ha−1) | ||||
| CK | 0 | 2130 | 10,891 | 34,150 | 21,129 | 2.62 bc |
| MS | 0 | 1974 | 11,276 | 40,382 | 27,132 | 3.05 ab |
| CB | 49,940 | 1974 | 11,251 | 44,921 | −18,244 | 0.71 d |
| CM | 0 | 1974 | 11,251 | 41,596 | 28,371 | 3.15 a |
| BR | 3450 | 1974 | 11,251 | 42,460 | 25,784 | 2.55 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lai, J.; Chen, K.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of Different Nitrogen Substitution Practices on Nitrogen Utilization, Surplus, and Footprint in the Sweet Maize Cropping System in South China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080800
Hu H, Chen Y, Zhang L, Lai J, Chen K, Xie Y, Wang X. Effects of Different Nitrogen Substitution Practices on Nitrogen Utilization, Surplus, and Footprint in the Sweet Maize Cropping System in South China. Agriculture. 2025; 15(8):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080800
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Hongyan, Yun Chen, Luyu Zhang, Jiajun Lai, Ke Chen, Yuna Xie, and Xiaolong Wang. 2025. "Effects of Different Nitrogen Substitution Practices on Nitrogen Utilization, Surplus, and Footprint in the Sweet Maize Cropping System in South China" Agriculture 15, no. 8: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080800
APA StyleHu, H., Chen, Y., Zhang, L., Lai, J., Chen, K., Xie, Y., & Wang, X. (2025). Effects of Different Nitrogen Substitution Practices on Nitrogen Utilization, Surplus, and Footprint in the Sweet Maize Cropping System in South China. Agriculture, 15(8), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080800






