Preparation of Phosphogypsum–Bentonite-Based Slow-Release Potassium Magnesium Sulfate Fertilizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PVA–SA
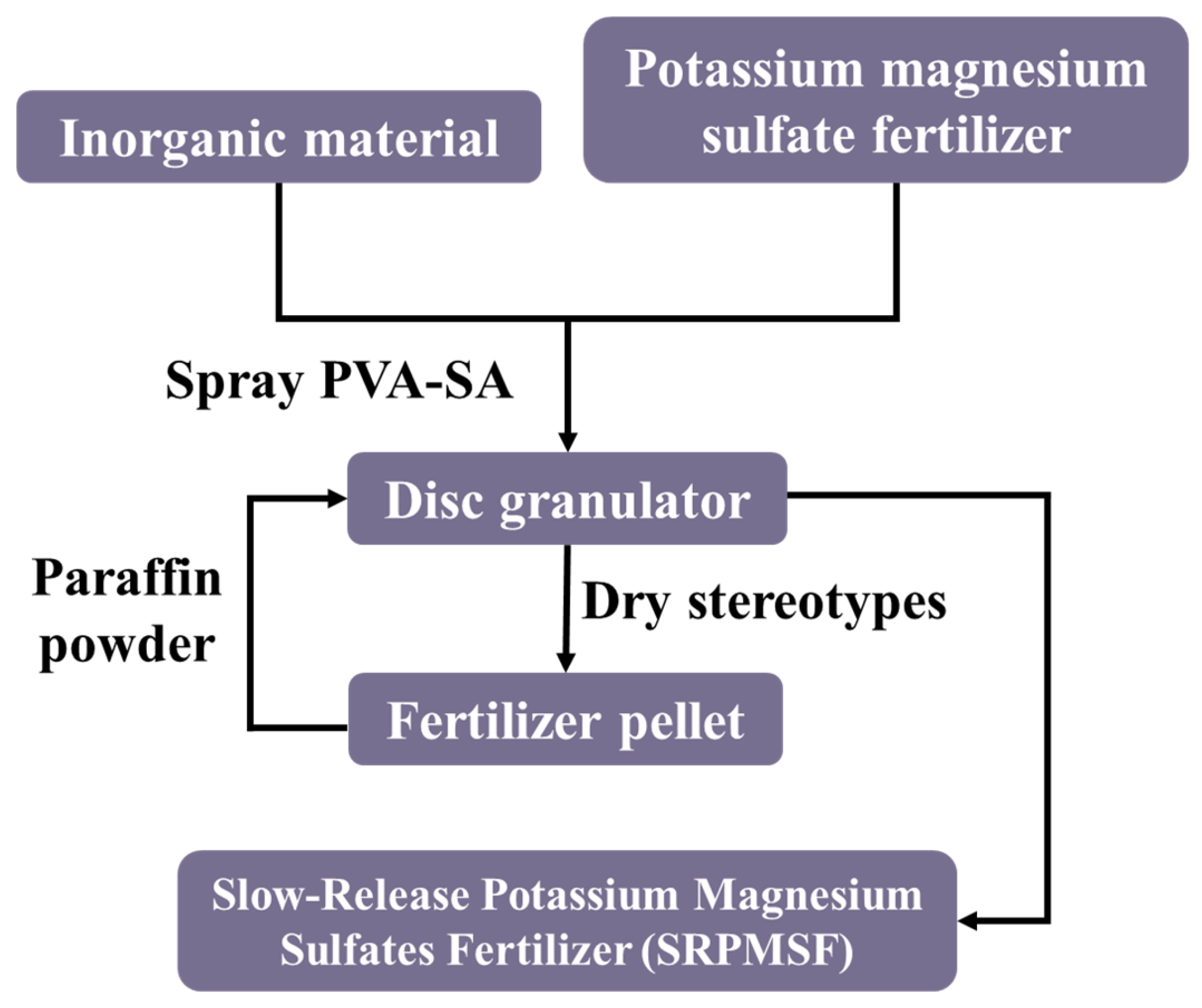
2.2. Preparation of the SRPMSF
2.3. Characterization of PVA–SA
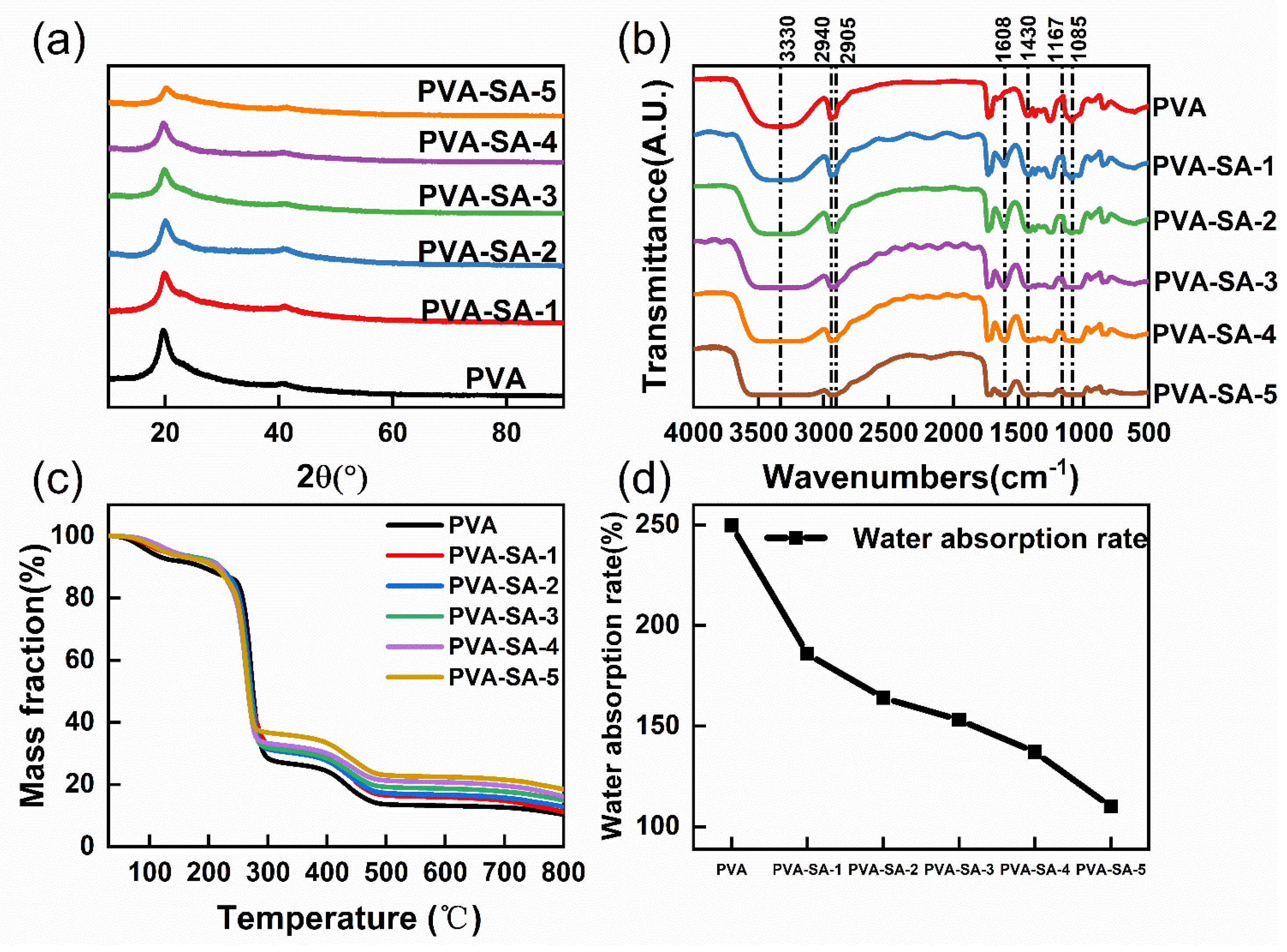
2.3.1. XRD Analysis
2.3.2. FTIR Analysis
2.3.3. TGA Analysis
2.3.4. Water Absorption Test
2.4. Determination of the SRPMSF Fertilizer Performance
2.4.1. Particle Size Distribution
2.4.2. Compressive Strength and Wear Resistance Test
2.4.3. Soil Column Leaching Experiments
2.5. Method for Fitting Nutrient Release Kinetics
2.5.1. First-Order Kinetic Release Kinetics
2.5.2. Langmuir Release Kinetics
2.5.3. Elovich Release Kinetics
2.5.4. Weibull Release Kinetics
2.5.5. Higuchi Release Kinetics
2.6. Description of Garlic Sprout Growth Experiment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Modification Analysis of Polyvinyl Alcohol by Sodium Alginate
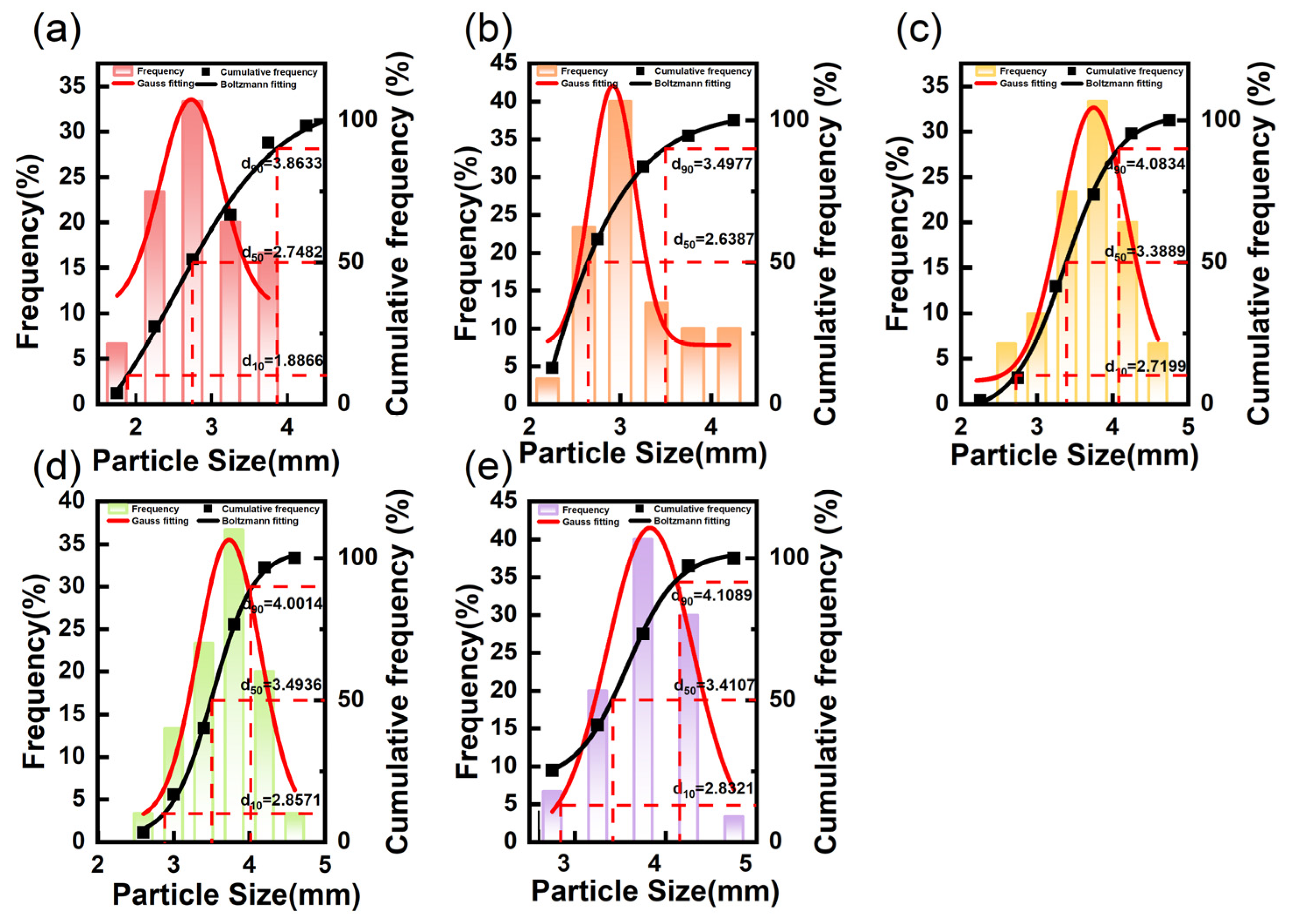
3.2. Particle Size Distribution of the SRPMSF
3.3. Wear Resistance and Compressive Strength Test
3.4. Potassium Magnesium Sulfate Fertilizer Release Behavior in the Column Leaching Study
3.5. Simulation of Nutrient Release Kinetics
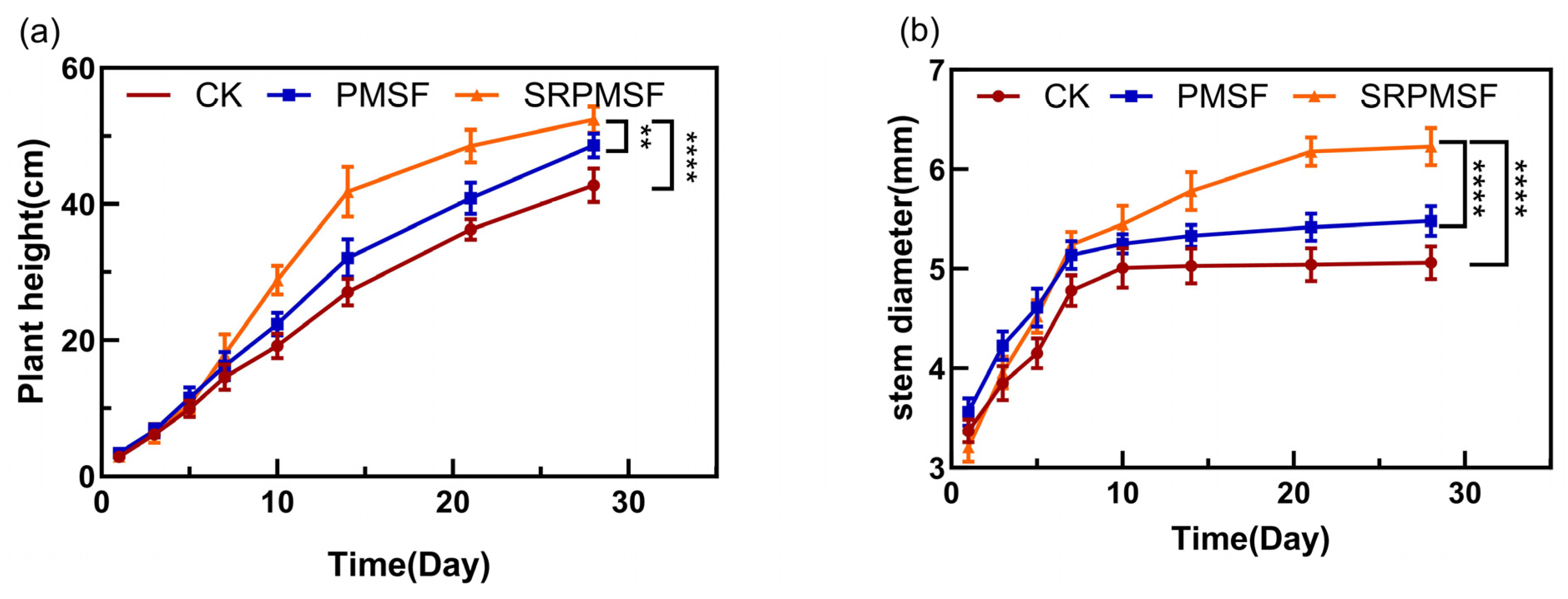
3.6. Pot Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vermoesen, E.; Bodé, S.; Brosens, G.; Boeckx, P.; Van Vlierberghe, S. Chemical Strategies Towards Controlled Release in Agriculture. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2024, 2, 247–277. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, C.; Li, B.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Q.; Hassan, M. Application of lignin in preparation of slow-release fertilizer: Current status and future perspectives. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 176, 114267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, C.J.; Cui, S.Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, A.Y.; Huang, Z.P.; Cheng, Y.J. Development status of slow/controlled release fertilizers and their application prospects in agricultural production. J. Agric. 2022, 12, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.; Jiang, L.; Tan, S.; Zheng, F.; Xu, Y.; Cui, R.; Wang, M.; Shi, J.; Li, G.; Liu, Z. An in situ study of inorganic nitrogen flow under different fertilization treatments on a wheat-maize rotation system surrounding Nansi Lake, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 123, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Tahir, M.M.; Rahim, N. Effect of N fertilizer source and timing on yield and N use efficiency of rainfed maize (Zea mays L.) in Kashmir—Pakistan. Geoderma 2013, 195–196, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.C.; He, P.; Zhou, W. Development strategies of the new-type fertilizer industry in China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertilizers 2023, 29, 201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, C.; Su, Y.; Peng, W.; Lu, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; He, X.; Yang, M.; Zhu, S. Soil acidification caused by excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer aggravates soil-borne diseases: Evidence from literature review and field trials. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 340, 108176. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.D.; Zhao, G.Z.; Bai, T.; Liu, Y.Q. Preparation and nutrient release mechanism of a polymer as slow-release compound fertilizer. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2014, 36, 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Su, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B. Characterization, swelling, and slow-release properties of a new controlled release fertilizer based on wheat straw cellulose hydrogel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 56, 564–572. [Google Scholar]
- Boonsuk, P.; Sukolrat, A.; Kaewtatip, K.; Chantarak, S.; Kelarakis, A.; Chaibundit, C. Modified cassava starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend films plasticized by glycerol: Structure and properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, M.A. A review of polyvinyl alcohol derivatives: Promising materials for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 8, 674–684. [Google Scholar]
- Sau, S.; Pandit, S.; Kundu, S. Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol): Structural, optical, and mechanical properties. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 25, 101198. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, P.K.; Sadeghi, K.; Seo, J. Recent advances in poly(vinyl alcohol)/natural polymer based films for food packaging applications: A review. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Garg, S.; Premi, A.; Premi, A.; Sekhar Giri, A. Synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol/modified starch-based biodegradable nanocomposite films reinforced with starch nanocrystals for packaging applications. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, Y.H.; Shaaban, A.; Mohamad, N.; Dimin, F.; Yatim, N.M. Boric acid modified starch polyvinyl alcohol matrix for slow release fertilizer. e-Polymers 2016, 16, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, N.; Niazi, M.B.; Sher, F.; Khalid, U.; Jahan, Z.; Shah, G.A.; Zia, M. Starch and polyvinyl alcohol encapsulated biodegradable nanocomposites for environment-friendly slow release of urea fertilizer. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 7, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofyane, A.; Ablouh, E.; Lahcini, M.; Elmeziane, A.; Khouloud, M.; Kaddami, H.; Raihane, M. Slow-release fertilizers based on starch acetate/glycerol/polyvinyl alcohol biocomposites for sustained nutrient release. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 36, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Wu, Z.; Yu, J.; Cravotto, G.; Liu, X.; Yu, B. Copyrolysis of biomass, bentonite, and nutrients as a new strategy for the synthesis of improved biochar-based slow-release fertilizers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3181–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, Z.; Cao, Y.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.; Han, G. Characterization of sodium alginate-carrageenan films prepared by adding peanut shell flavonoids as an antioxidant: Application in chilled pork preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131081. [Google Scholar]
- Bierhalz, A.C.K.; Silva, M.A.D.; Braga, M.E.M.; Hermínio, J.C.S.; Kieckbusch, T.G. Effect of calcium and/or barium crosslinking on the physical and antimicrobial properties of natamycin-loaded alginate films. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.; Dini, G.; Vaezifar, S.; Mehdikhani, M.; Movahedi, B. Preparation and characterization of sodium alginate/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel containing drug-loaded chitosan nanoparticles as a drug delivery system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101530. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, L.; Johnston, A.E.; Goulding, K.W.T. Mobilization of aluminium in soil by acid deposition and its uptake by grass cut for hay—A chemical time bomb. Soil Use Manag. 1994, 10, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Deng, Z. Research hotspots and trends of comprehensive utilization of phosphogypsum: Bibliometric analysis. J. Environ. Radioact. 2022, 242, 106778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouray, M.; Moir, J.; Condron, L.; Lehto, N. Impacts of phosphogypsum, soluble fertilizer, and lime amendment of acid soils on the bioavailability of phosphorus and sulphur under lucerne (Medicago sativa). Plants 2020, 9, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.G.; Garrido, F.; Illera, V.; Garcia-Gonzalez, M.T. Transport of Cd, Cu, and Pb in an acid soil amended with phosphogypsum, sugar foam, and phosphoric rock. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 21, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, Y.D.; Komarneni, S.; Park, M. Mineral-based slow-release fertilizers: A review. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2015, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pliaka, M.; Gaidajis, G. Potential uses of phosphogypsum: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 57, 746–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akfas, F.; Elghali, A.; Aboulaich, A.; Munoz, M.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bodinier, J.L. Exploring the potential reuse of phosphogypsum: A waste or a resource. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, V.A.; Smirnov, Y.D.; Suchkov, D.V. Industrial processing of phosphogypsum into organomineral fertilizer. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trots, N.M.; Borovkova, N.V.; Soloviev, A.A. Efficiency of phosphogypsum in agrocenosis of spring barley. Bull. Samara State Agric. Acad. 2022, 7, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, K.; Yu, M.; Dong, X.; Sarwar, M.T.; Yang, H. Facet-engineering strategy of phosphogypsum for production of mineral slow-release fertilizers with efficient nutrient fixation and delivery. Waste Manag. 2024, 182, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhantasov, K.; Ziyat, A.; Sarypbekova, N.; Kirgizbayeva, K.; Iztleuov, G.; Zhantasov, M.; Sagitova, G.; Aryn, A. Ecologically friendly, slow-release granular fertilizers with phosphogypsum. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 2935–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbunov, A.V.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Gundorina, S.F.; Onischenko, T.L.; Maksjuta, B.B.; Pal, C.A. Effect of agricultural use of phosphogypsum on trace elements in soils and vegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 122, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. Phosphogypsum as a construction material. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, J. Phosphogypsum—Management and opportunities for use: Resolving a conflict between negative externality and public good. Int. Fertil. Soc., Proc. 2006, 587, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Mesić, M. Korekcija suvišne kiselosti tla različitim vapnenim materijalima. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2001, 66, 75–93. [Google Scholar]
- Soratto, R.P.; Crusciol, C.A.C. Dolomite and phosphogypsum surface application effects on annual crops nutrition and yield. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, N.; Alkaraki, M. Wheat response to phosphogypsum and mycorrhizal fungi in alkaline soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 873–883. [Google Scholar]
- Michalovicz, L.; Müller, M.M.L.; Tormena, C.A.; Dick, W.A.; Vicensi, M.; Meert, L. Soil chemical attributes, nutrient uptake, and yield of no-till crops as affected by phosphogypsum doses and parceling in southern Brazil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Choi, C.L.; Choi, J.; Lee, S.R.; Choy, J.H. Intercalation of magnesium-area complex into swelling clay. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2004, 65, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tu, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, C. Encapsulation and characterization of slow-release microbial fertilizer from the composites of bentonite and alginate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 109, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Pamungkas, R.B.; Jos, B.; Djaeni, M.; Saputri, K.A.D. Granulation processing variables on the physical properties of granule slow-release urea fertilizer. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2197, 100001. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarkar, R.; Patel, J. Polyvinyl alcohol: A comprehensive study. Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 3, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Saarai, A.; Kasparkova, V.; Sedlacek, T.; Saha, P. On the development and characterization of crosslinked sodium alginate/gelatine hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 18, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xie, W.; Long, Z.; Zhou, J. Synthesis and anticoagulant activity of sodium alginate sulfates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, W.; Zhang, W. Preparation and characterization of chitosan coating of slow-release fertilizers. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2005, 21, 216. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Yang, A. Preparation and characterization of nano-hydroxyapatite/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel biocomposite. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 5669–5672. [Google Scholar]
- Korbag, I.; Mohamed Saleh, S. Studies on the formation of intermolecular interactions and structural characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/lignin film. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 73, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Gao, X.; Fan, H.; Zhang, M.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhu, S. Green and recyclable graphitic carbon nitride/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol photocatalytic films with efficient antibacterial activity for fruit packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123974. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, K.R.M.; Babadi, F.E.; Yunus, R. Comparative performance of different urea coating materials for slow release. Particuology 2014, 17, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Babadi, F.E.; Yunus, R.; Rashid, S.A.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Ali, A. New coating formulation for the slow release of urea using a mixture of gypsum and dolomitic limestone. Particuology 2015, 23, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Tzika, M.; Alexandridou, S.; Kiparissides, C. Evaluation of the morphological and release characteristics of coated fertilizer granules produced in a Wurster fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 2003, 132, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C.; Jacobsen, J. Commercial fertilizers and soil amendments. Nutrient Manag. Module 2009, 10, 4449–4410. [Google Scholar]
- Azeem, B.; KuShaari, K.Z.; Man, Z.; Trinh, T.H. Nutrient release characteristics and coating homogeneity of biopolymer-coated urea as a function of fluidized bed process variables. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 95, 849–862. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, J. Fertilizer strength prediction model based on shape characteristics. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 87007–87023. [Google Scholar]
- Avsar, C.; Ulusal, A. Granular fertilizer caking: A research on the performance evaluation of coating agents. Eur. J. Chem. 2021, 12, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, R.M.; Siyal, A.A.; Luukkonen, T.; Shamsuddin, R.M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Fly ash geopolymer as a coating material for controlled-release fertilizer based on granulated urea. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 33187–33199. [Google Scholar]
- Shavit, U.; Shaviv, A.; Shalit, G.; Zaslavsky, D. Release characteristics of a new controlled release fertilizer. J. Control. Release 1997, 43, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Azeem, B.; KuShaari, K.Z.; Man, Z.B.; Basit, A.; Thanh, T.H. Review on materials & methods to produce controlled release coated urea fertilizer. J. Control. Release 2014, 181, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Helal, M.I.D.; Tong, Z.; Khater, H.A.; Fathy, M.A.; Ibrahim, F.E.; Li, Y.; Abdelkader, N.H. Modification of fabrication process for prolonged nitrogen release of lignin–montmorillonite biocomposite encapsulated urea. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.A.A.; de Macedo, O.F.L.; Cunha, G.C.; Oliveira, R.V.M.; Romão, L.P.C. Using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) biomass and humic substances to produce urea-based multi-coated slow-release fertilizer. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3691–3701. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Wang, Z. Release characteristics of different N forms in an uncoated slow/controlled release compound fertilizer. Agric. Sci. China 2007, 6, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Ganetri, I.; Essamlali, Y.; Amadine, O.; Danoun, K.; Aboulhrouz, S.; Zahouily, M. Controlling factors of slow or controlled-release fertilizers. In Controlled Release Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhmad, F.; Dyah, T.S. Release pattern of ammonium, nitrate, and potassium from Slow-Release Fertilizer (SRF) in the soil. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 383, 012037. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.; He, X.; Duan, H.; Han, L.; Huang, G. Evaluation of controlled release urea on the dynamics of nitrate, ammonium, and its nitrogen release in black soils of northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, P.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Trinh, H.T.; Nguyen, V.M.; Le, A.T.; Tran, H.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.T. The nitrogen slow-release fertilizer based on urea incorporating chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol) blend. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101528. [Google Scholar]
- Abedi-Koupai, J.; Varshosaz, J.; Mesforoosh, M. Controlled release of microcapsule fertilizer using ethylene vinyl acetate polymer. In Proceedings of the XVIth International Conference on Bioencapsulation, Dublin, Ireland, 4–6 September 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]



| Treatments | PVA (%) | SA (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PVA | 8.00 | 0 |
| PVA–SA-1 | 8.00 | 0.80 |
| PVA–SA-2 | 8.00 | 1.20 |
| PVA–SA-3 | 8.00 | 1.60 |
| PVA–SA-4 | 8.00 | 2.00 |
| PVA–SA-5 | 8.00 | 2.40 |
| Treatments | PMSF (g) | Phosphogypsum (g) | Bentonite | Mass Ratio Phosphogypsum/Bentonite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMSF | - | - | - | |
| SRPMSF-1 | 125 | 54.0 | 0 | - |
| SRPMSF-2 | 125 | 43.2 | 10.8 | 4:1 |
| SRPMSF-3 | 125 | 32.4 | 21.6 | 3:2 |
| SRPMSF-4 | 125 | 21.6 | 32.4 | 2:1 |
| SRPMSF-5 | 125 | 10.8 | 43.2 | 1:4 |
| Phosphogypsum particle size (mm) | <1.00 |
| Usage amount of PMSF (g) | 125 |
| Drum speed (rpm) | 40 |
| Spray PVA–SA (mL) | 10 |
| Paraffin wax (g) | 15 |
| Duration time (min) | 15 |
| Drying temperature after granulation (°C) | 60 |
| Drying temperature after paraffin sealing | room temperature |
| Full Name | Source |
|---|---|
| Potassium magnesium of sulphate fertilizer | SDIC Xinjiang Luobupo Postash Co., Ltd. (Hami, China) |
| Phosphogypsum | Hubei Xingfa Co., Ltd. (Yidu, China) |
| Bentonite | Xincheng Mineral Resources Co., Ltd. (Shijiazhuang, China) |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | MACKLIN Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Chongqing, China) |
| Sodium alginate | MACKLIN Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Chongqing, China) |
| Paraffin wax | Zhengmei Engineering Plastic Co., Ltd. (Ningbo, China) |
| No. | Potassium Magnesium Sulfate Fertilizer (g/g) | The Amount of Fertilizer Used (g) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0 |
| PMSF | 1.00 | 5.00 |
| SRPMSF-3 | 0.61 | 8.20 |
| No. | Particle Size Distribution | |
|---|---|---|
| Average/ mm | Variation Coefficient | |
| SRPMSF-1 | 2.856 ± 0.57 c | 19.75 |
| SRPMSF-2 | 3.142 ± 0.54 b | 16.92 |
| SRPMSF-3 | 3.634 ± 0.52 a | 12.61 |
| SRPMSF-4 | 3.668 ± 0.45 a | 12.12 |
| SRPMSF-5 | 3.731 ± 0.44 a | 11.83 |
| No. | Wear Resistance | Compression Resistance Strength (N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | Residual Weight Ratio (%) | ||
| SRPMSF-1 | 95.62 | 96.76 | 96.31 ± 0.49 d | 20.85 ± 3.41 b |
| SRPMSF-2 | 98.27 | 99.34 | 98.79 ± 0.44 c | 38.75 ± 6.32 a |
| SRPMSF-3 | 99.08 | 99.50 | 99.32 ± 0.17 b | 40.71 ± 5.71 a |
| SRPMSF-4 | 99.38 | 99.53 | 99.45 ± 0.06 b | 42.52 ± 8.20 a |
| SRPMSF-5 | 99.89 | 99.96 | 99.93 ± 1.33 a | 43.78 ± 8.97 a |
| Model | Simultaneous Equations | Parameters | SRPMSF-2 | SRPMSF-3 | SRPMSF-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| first-order kinetic | k | 0.1907 | 0.1464 | 0.1199 | |
| N0 | 0.8014 | 0.8095 | 0.8085 | ||
| R2 | 0.9836 | 0.9792 | 0.9873 | ||
| Langmuir | a | 0.9695 | 0.9459 | 0.9445 | |
| b | 0.2031 | 0.1657 | 0.1360 | ||
| R2 | 0.9631 | 0.9614 | 0.9749 | ||
| Elovich | a | 0.1230 | 0.0750 | 0.0451 | |
| b | 0.2169 | 0.2097 | 0.2065 | ||
| R2 | 0.9477 | 0.9496 | 0.9674 | ||
| Weibull | a | 0.2101 | 0.1869 | 0.1645 | |
| b | 0.6772 | 0.6398 | 0.6382 | ||
| R2 | 0.9332 | 0.9246 | 0.9432 | ||
| Higuchi | a | 0.1692 | 0.1424 | 0.1310 | |
| R2 | 0.8100 | 0.7960 | 0.8340 |
| No. | Soluble Sugar (%) | Soluble Protein (mg/g) | Free Amino Acid (mg/g) | Vitamin C (µg/g) | Allicin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.72 ± 0.13 c | 4.05 ± 0.22 c | 2.05 ± 0.08 c | 142.56 ± 3.61 b | 6.16 ± 0.33 b |
| PMSF | 1.96 ± 0.06 b | 6.64 ± 0.57 b | 3.19 ± 0.72 b | 178.77 ± 4.61 a | 8.73 ± 0.37 a |
| SRPMSF | 2.47 ± 0.11 a | 8.06 ± 0.51 a | 5.54 ± 0.14 a | 184.39 ± 5.91 a | 9.03 ± 0.13 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Han, C.; Tao, C.; Fan, X.; Liu, R. Preparation of Phosphogypsum–Bentonite-Based Slow-Release Potassium Magnesium Sulfate Fertilizer. Agriculture 2025, 15, 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070692
Zhang Z, Han C, Tao C, Fan X, Liu R. Preparation of Phosphogypsum–Bentonite-Based Slow-Release Potassium Magnesium Sulfate Fertilizer. Agriculture. 2025; 15(7):692. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070692
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhizhi, Chunxiao Han, Changyuan Tao, Xing Fan, and Renlong Liu. 2025. "Preparation of Phosphogypsum–Bentonite-Based Slow-Release Potassium Magnesium Sulfate Fertilizer" Agriculture 15, no. 7: 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070692
APA StyleZhang, Z., Han, C., Tao, C., Fan, X., & Liu, R. (2025). Preparation of Phosphogypsum–Bentonite-Based Slow-Release Potassium Magnesium Sulfate Fertilizer. Agriculture, 15(7), 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070692







