Long-Term Effect of Lime Application on Quantity and Quality of Soil Organic Carbon in Double Rice Cropping System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sampling
2.4. Soil Physical Fractionation
2.5. Solid-State 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Analyses
2.6. Carbon Inputs
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Carbon Inputs
3.2. Concentration and Stocks of SOC
3.3. Physical Fractions of SOC
3.4. Chemical Composition of SOC
4. Discussion
4.1. SOC Stocks
4.2. Physical Fractions of SOC
4.3. Chemical Composition of SOC
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, C.; Tu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Deng, S.; Xia, Y.; Mao, W.; Chen, X. Soil acidification induced by intensive agricultural use depending on climate. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 2604–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterly, C.R.; Amado, T.J.C.; Tang, C. Soil acidity and acidification. In Subsoil Constraints for Crop Production; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 53–81. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, R.; Majumdar, A.; Sarkar, S.; Goswami, C.; Joardar, M.; Das, A.; Roychowdhury, T. An extensive review of arsenic dynamics and its distribution in soil-aqueous-rice plant systems in South and Southeast Asia with bibliographic and meta-data analysis. Chemosphere 2024, 141, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Huang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Shao, H.; Zhang, J.; Van Groenigen, K.J. Liming increases yield and reduces grain cadmium concentration in rice paddies: A meta-analysis. Plant Soil 2021, 465, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, J.; Burns, H. Soil Acidity—Its Stratification and Amelioration with Lime. Presented at the GRDC Grains Research Update, Jerilderie, July 2021. Available online: https://grdc.com.au/resources-and-publications/grdc-update-papers/tab-content/grdc-update-papers/2021/07/soil-acidity-its-stratification-and-amelioration-with-lime (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Paradelo, R.; Virto, I.; Chenu, C. Net effect of liming on soil organic carbon stocks: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 202, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, L.; Bell, S.M.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, S. Interaction of lime application and straw retention on ammonia emissions from a double-cropped rice field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 344, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, X.; Hartley, I.P. Long-term liming mitigates the positive responses of soil carbon mineralization to warming and labile carbon input. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Soussana, J.F.; Angers, D.; Schipper, L.; Chenu, C.; Rasse, D.P.; Klumpp, K. How to measure, report and verify soil carbon change to realize the potential of soil carbon sequestration for atmospheric greenhouse gas removal. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, M.; Yan, G.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Potential benefits of liming to acid soils on climate change mitigation and food security. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2807–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Liao, W.; Yin, L.; Zhou, W.; Cui, H.J. Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon fractions in paddy profiles with 40 years of fertilization under two groundwater levels. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Yue, S.C.; Li, S.Q. Chemical methods to determine soil organic carbon fractions and carbon indexes: A review. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cha, X.; Yang, W.; Zheng, M.; Liu, S.; Ren, C. Nitrogen addition-driven soil organic carbon stability depends on the fractions of particulate and mineral-associated organic carbon. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2024, 128, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Cui, X.; Chen, M.; Sang, Y. Forest conversion changes soil particulate organic carbon and mineral-associated organic carbon via plant inputs and microbial processes. Forests 2023, 14, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Huang, S.; Zeng, Y.; van Groenigen, K.J. Liming reduces nitrogen uptake from chemical fertilizer but increases that from straw in a double rice cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, A.; Blomquist, J.; Persson, L.; Olsson, Å.; Hamnér, K.; Berglund, K. Liming alkaline clay soils: Effects on soil structure, nutrients, barley growth and yield. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2022, 72, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, Y.; Rui, Y.; Ning, Z.; Hu, Y.; Tang, H.; Su, Y. Microbial carbon use efficiency, biomass turnover, and necromass accumulation in paddy soil depending on fertilization. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 292, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, C.; Rui, Y.; Su, Y. Contrasting pathways of carbon sequestration in paddy and upland soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, B.; Wilhelm, R.C.; Debenport, S.J.; Fahey, T.J.; Buckley, D.H.; Goodale, C.L. Microbial community shifts correspond with suppression of decomposition 25 years after liming of acidic forest soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5399–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liao, P.; Shao, H.; Liu, J.S.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y.J.; Huang, S. Interactive effects of liming and straw return on apparent soil potassium balance in a double rice cropping system. Acta Agron. Sin. 2021, 48, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hagedorn, F.; Guidi, C.; Yang, L. Limited soil carbon storage under long-term organic fertilization in solar greenhouses. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duddigan, S.; Shaw, L.J.; Alexander, P.D.; Collins, C.D. A comparison of physical soil organic matter fractionation methods for amended soils. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 3831241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonsri, K.; Naruse, H.; Watanabe, A. Mechanisms controlling the stabilization of soil organic matter in agricultural soils as amended with contrasting organic amendments: Insights based on physical fractionation coupled with 13C NMR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, N.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Siddique, K.H.; Feng, H. Ammoniated straw returning: A win-win strategy for increasing crop production and soil carbon sequestration. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 363, 108879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Kongsurakan, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Soil organic carbon in sandy paddy fields of Northeast Thailand: A review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Siddique, K.H. The responses of crop yield and greenhouse gas emissions to straw returning from staple crops: A meta-analysis. Agriculture 2025, 15, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil organic matter priming: The pH effects. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Liao, P.; van Gestel, N.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, S.; van Groenigen, K.J. Lime application lowers the global warming potential of a double rice cropping system. Geoderma 2018, 325, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoakwah, E.; Shim, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, S.; Sangho, J.; Park, S. Impact of silicate and lime application on soil fertility and temporal changes in soil properties and carbon stocks in a temperate ecosystem. Geoderma 2023, 433, 116431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Berns-Herrboldt, E.C.; Gu, B.; Wullschleger, S.D.; Graham, D.E. Quantifying pH buffering capacity in acidic, organic-rich Arctic soils: Measurable proxies and implications for soil carbon degradation. Geoderma 2022, 424, 116003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mao, N.; Liu, T.; Cheng, J.; Wei, X.; Shao, M.A. Effects of anecic Amynthas aspergillum on the proportion and depth of straw-derived carbon input into soil. Geoderma 2024, 452, 117114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanzolini, J.I.; Galantini, J.A.; Martínez, J.M.; Suñer, L. Changes in soil pH and phosphorus availability during decomposition of cover crop residues. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 1864–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, T.M.; de Moraes Sá, J.C.; Caires, E.F.; Gonçalves, D.R.P. Lime and gypsum application increases biological activity, carbon pools, and agronomic productivity in highly weathered soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, L. Continuous straw returning enhances the carbon sequestration potential of soil aggregates by altering the quality and stability of organic carbon. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, M.; Ahmad, S.J.; Rahman, T.; Joardar, J.C.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Islam, M.S.; Peng, X. Effects of straw incorporation and straw-burning on aggregate stability and soil organic carbon in a clay soil of Bangladesh. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 32, e00620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Fan, J.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Q.; Wang, T.; Meng, Y.; Hu, S. The accumulation of plant-and microbial-derived carbon and its contribution to soil organic carbon in reclaimed saline-sodic farmland. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscatelli, M.C.; Massaccesi, L.; Marabottini, R.; Primavera, F.; Riccini, A.; Marinari, S. The beneficial use of basalt flour combined to a microbial consortium to improve soil quality in basalt and carbonatic dismissed quarries. Catena 2024, 237, 107820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Huang, S.; Van Gestel, N.C.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Z.; van Groenigen, K.J. Liming and straw retention interact to increase nitrogen uptake and grain yield in a double rice-cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2018, 216, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tian, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Guo, P.; Wang, Q. Nitrogen deposition caused higher increases in plant-derived organic carbon than microbial-derived organic carbon in forest soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Huang, W.; Hall, S.J.; Hu, S. Association of organic carbon with reactive iron oxides driven by soil pH at the global scale. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2022, 36, e2021GB007128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kaye, J.P.; Bradley, B.A.; Amsili, J.P.; Suseela, V. Cover crop functional types differentially alter the content and composition of soil organic carbon in particulate and mineral-associated fractions. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5831–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Lv, J.; Peng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, X. Mechanisms controlling the stability and sequestration of mineral associated organic carbon upon erosion and deposition. Catena 2024, 242, 108119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Frouz, J.; Naveed, M.; Ping, Z.; Nan, S.; Minggang, X.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Stability of soil organic carbon under long-term fertilization: Results from 13C NMR analysis and laboratory incubation. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson, P.; Sterngren, A.E.; Rousk, J. Archaeal abundance across a pH gradient in an arable soil and its relationship to bacterial and fungal growth rates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5906–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puissant, J.; Jones, B.; Goodall, T.; Mang, D.; Blaud, A.; Gweon, H.S.; Malik, A.; Jones, D.L.; Clark, I.M.; Hirsch, P.R.; et al. The pH optimum of soil exoenzymes adapt to long term changes in soil pH. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Baldock, J.A.; Butterly, C.R.; Gazey, C. Long-term effect of lime application on the chemical composition of soil organic carbon in acid soils varying in texture and liming history. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, A.; Herburger, K. Precursor biosynthesis regulation of lignin, suberin and cutin. Protoplasma 2021, 258, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Ran, H.; Wang, F.; Ye, X.; Niu, L.; Schulin, R.; Wang, G. Conservation tillage facilitated soil carbon sequestration through diversified carbon conversions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 337, 108080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, M.; Yang, L.; Gu, X.; Jin, J.; Fu, M. Regulation of straw decomposition and its effect on soil function by the amount of returned straw in a cool zone rice crop system. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothe, S.; Polisetty, V.R. Review on anaerobic digestion of rice straw for biogas production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24455–24469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhaii, P.; Bohorc, B.; Schliedermann, U.; Griesinger, C. Efficient access to elusive 1D 13C NMR spectra through highly resolved 1H, 13C-long-range correlation spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 5843–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.S.; Ros, G.H.; Furtak, K.; Iqbal, H.M.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Soil carbon sequestration–An interplay between soil microbial community and soil organic matter dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plante, A.F.; Fernández, J.M.; Haddix, M.L.; Steinweg, J.M.; Conant, R.T. Biological, chemical and thermal indices of soil organic matter stability in four grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.P.; Butterly, C.R.; Wang, X.; Tang, C. The short-term effects of liming on organic carbon mineralisation in two acidic soils as affected by different rates and application depths of lime. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Source of Variations | Soil Organic Carbon Concentration (g kg−1) | Soil Organic Carbon Stocks (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Liming (L) | ||
| −L | 13.4 a | 24.4 a |
| +L | 13.7 a | 24.9 a |
| Straw retention (RS) | ||
| −RS | 13.1 b | 24.0 b |
| +RS | 14.0 a | 25.3 a |
| F-values | ||
| L | 0.94 | 0.79 |
| RS | 7.90 * | 6.36 * |
| L × RS | 1.37 | 0.11 |
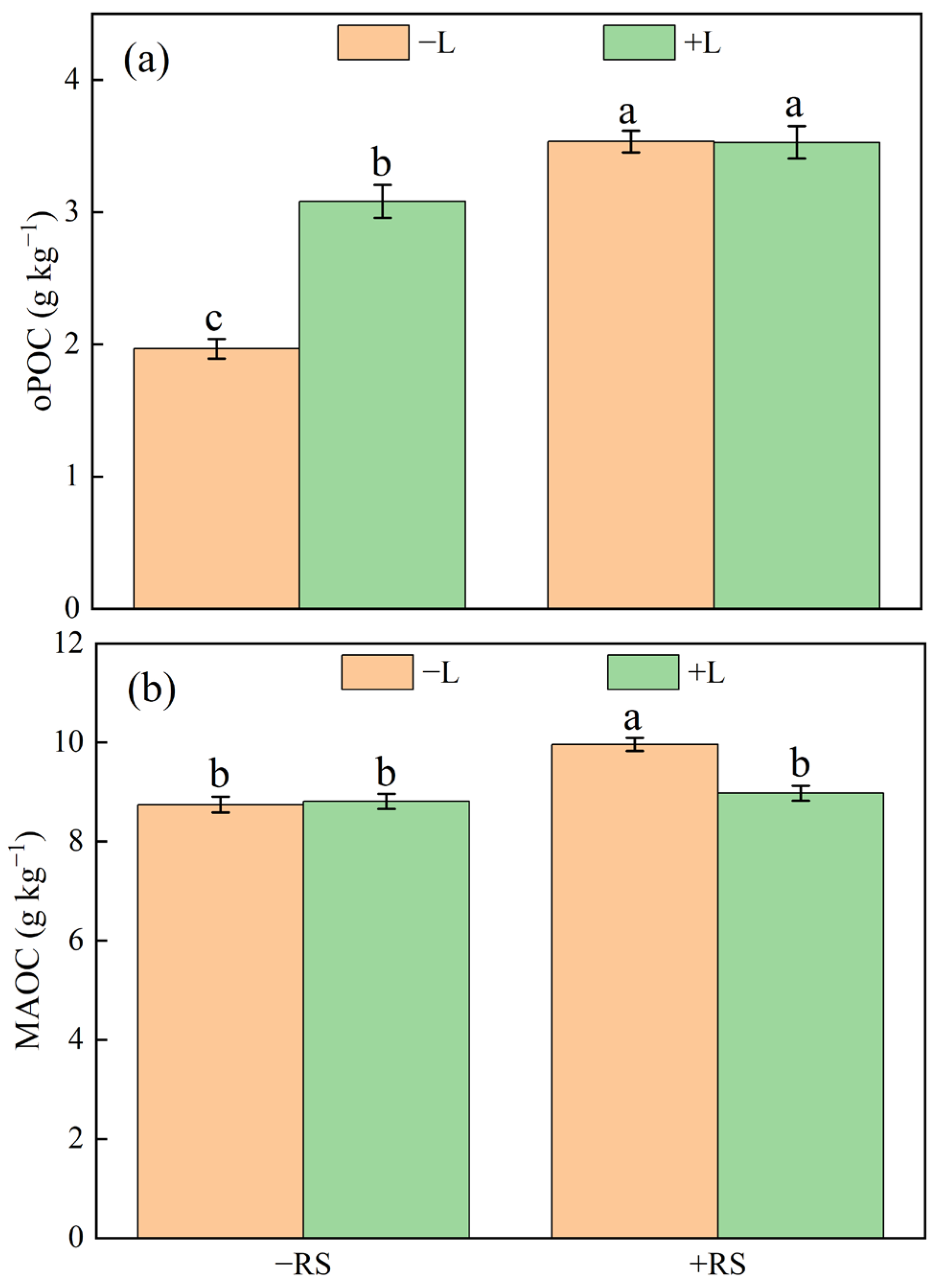
| Source of Variations | Free Particulate Organic Carbon (g kg−1) | Occluded Particulate Organic Carbon (g kg−1) | Mineral-Associated Organic Carbon (g kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liming (L) | |||
| −L | 0.3 a | 2.8 b | 9.4 a |
| +L | 0.1 b | 3.3 a | 8.9 b |
| Straw retention (RS) | |||
| −RS | 0.2 b | 2.5 b | 8.8 b |
| +RS | 0.3 a | 3.5 a | 9.5 a |
| F-values | |||
| L | 66.07 ** | 28.58 ** | 7.72 * |
| RS | 34.65 ** | 94.11 ** | 17.37 ** |
| L × RS | 2.03 | 29.21 ** | 10.04 ** |
| Source of Variations | Alkyl C (%) | O-Alkyl C (%) | Aromatic C (%) | Carbonyl C (%) | Alkyl C/O-Alkyl C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liming (L) | |||||
| −L | 26.73 a | 45.31 a | 16.27 a | 11.57 a | 58.99 a |
| +L | 25.36 b | 46.25 a | 16.82 a | 12.39 a | 54.83 b |
| Straw retention (RS) | |||||
| −RS | 25.40 b | 45.85 a | 16.64 a | 12.04 a | 55.40 a |
| +RS | 26.69 a | 45.70 a | 16.46 a | 11.93 a | 58.40 a |
| F-values | |||||
| L | 16.85 ** | 3.02 | 0.99 | 4.90 | 14.18 ** |
| RS | 14.95 ** | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 6.78 * |
| L × RS | 11.34 * | 0.06 | 3.10 | 0.08 | 5.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, S. Long-Term Effect of Lime Application on Quantity and Quality of Soil Organic Carbon in Double Rice Cropping System. Agriculture 2025, 15, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060650
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Sun Y, Zeng Y, Huang S. Long-Term Effect of Lime Application on Quantity and Quality of Soil Organic Carbon in Double Rice Cropping System. Agriculture. 2025; 15(6):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060650
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuxiang, Zhigang Wang, Yanni Sun, Yongjun Zeng, and Shan Huang. 2025. "Long-Term Effect of Lime Application on Quantity and Quality of Soil Organic Carbon in Double Rice Cropping System" Agriculture 15, no. 6: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060650
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, Z., Sun, Y., Zeng, Y., & Huang, S. (2025). Long-Term Effect of Lime Application on Quantity and Quality of Soil Organic Carbon in Double Rice Cropping System. Agriculture, 15(6), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060650






