Does Environmental Regulation Affect China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity? Considering the Role of Technological Innovation
Abstract
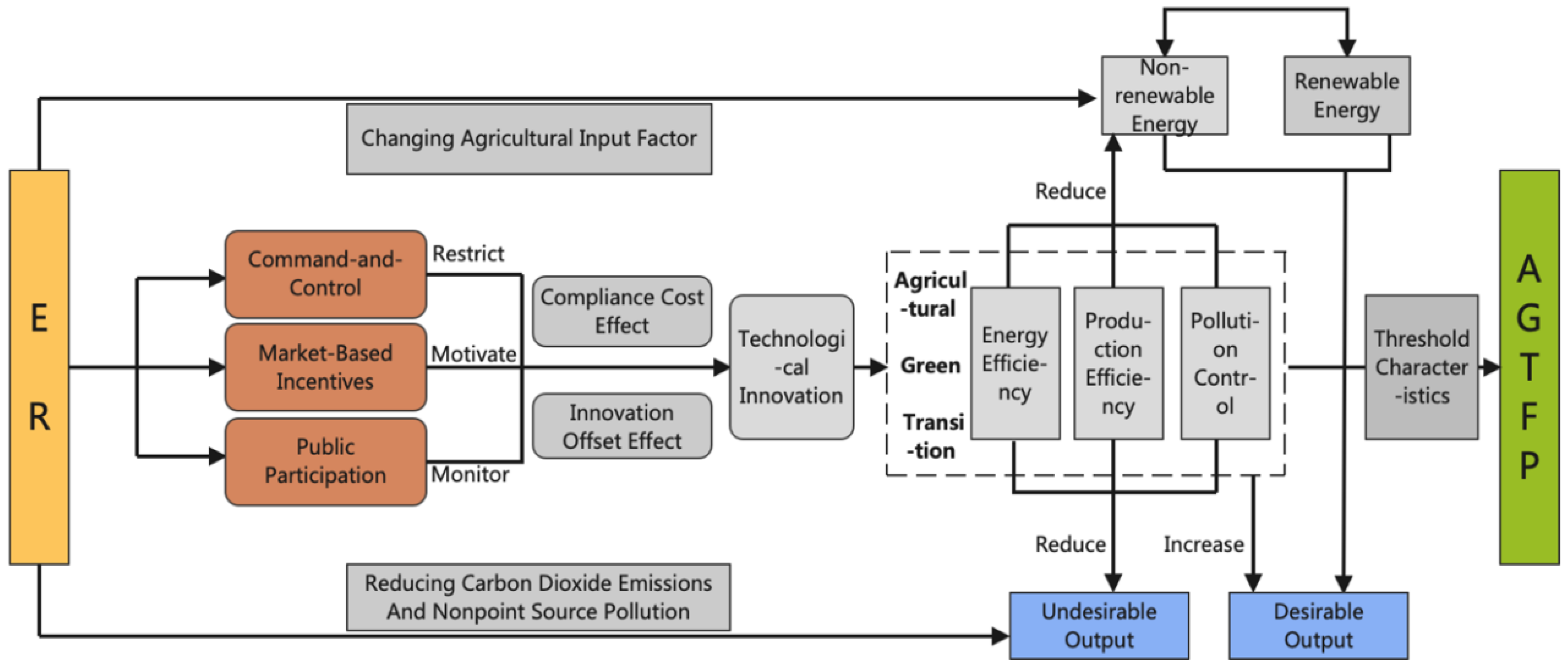
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis
2.1. Impact of ER on AGTFP
2.2. Mediating and Threshold Effects of TI
3. Research Methodology, Variables, and Data
3.1. Research Methodology
3.1.1. Benchmark Regression Model
3.1.2. Mediated Effects Model
3.1.3. Panel Threshold Model
3.2. Variable Selection and Data Sources
3.2.1. The Dependent Variable: AGTFP
3.2.2. The Core Independent Variable: ER
3.2.3. The Control Variables
3.2.4. Mechanism Variables: Technological Innovation (TI)
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Estimation Results of AGTFP
4.2. Benchmark Regression Results
4.3. Endogeneity Treatment and Robustness Tests
4.3.1. Endogenous Processing
4.3.2. Robustness Test
4.3.3. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.4. Mechanism Analysis
4.4.1. Analysis of Mediating Effect of TI
4.4.2. Analysis of Threshold Effect of TI
- (1)
- Threshold Existence Test
- (2)
- Threshold value estimation
- (3)
- Results and analysis of threshold regression
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Research Conclusions
5.2. Recommendations
5.3. Theoretical Contributions
- (1)
- Expanding the Theoretical Framework of AGTFP Analysis. The existing literature on agricultural total factor productivity (TFP) has largely neglected the undesirable outputs inherent in agricultural production, such as resource, energy, and environmental constraints. Additionally, the selection of undesirable outputs has often been narrow. Failure to fully account for environmental issues like agricultural non-point source pollution and carbon emissions during production may lead to biased assessments of agricultural performance. This paper addresses this gap by incorporating both non-point source pollution and carbon emissions as undesirable outputs. It constructs a unified theoretical framework that integrates resources, energy, environment, and agricultural economy. This approach offers distinct advantages in accurately assessing agricultural TFP under environmental regulation, while better reflecting the current state of China’s AGTFP.
- (2)
- Enriching Research on Environmental Governance and Agricultural Sustainability. Most existing studies have focused on the impact of environmental regulation on the broader economy and industrial sectors. However, the agricultural sector, as a fundamental industry, also deserves more attention. In the limited literature addressing environmental regulation and agricultural sustainability, few scholars have considered the heterogeneous effects of environmental regulations on AGTFP. This oversight limits the ability to evaluate the differential impacts of various regulatory approaches. This study seeks to fill this gap by exploring how environmental regulation influences AGTFP through the lens of technological innovation. It aims to provide a scientifically rigorous measure of AGTFP while exploring the interrelationships and mechanisms among environmental regulation, technological innovation, and AGTFP.
- (3)
- Constructing a Unified Analytical Framework for Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation, and AGTFP. The existing literature typically examines the relationships among “environmental regulation—AGTFP”, “environmental regulation—technological innovation”, and “technological innovation—AGTFP” in isolation. Few studies have integrated all three variables into a single framework. This paper, therefore, adopts a technological innovation perspective to explore the interactions and impact mechanisms among environmental regulation, technological innovation, and AGTFP. It identifies technological innovation pathways within AGTFP under environmental regulation and, by considering the current state of regional technological innovation, discusses the innovation thresholds for different types of environmental regulation in promoting agricultural green development. This contribution offers a valuable addition to the existing research on environmental regulation and AGTFP and provides a more comprehensive research foundation for implementing environmental policies, fostering agricultural technological innovation, and advancing SAD in China.
5.4. Research Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, W.; Wang, R.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, S. Study on connotation and evaluation of the agricultural green development. J. China Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2019, 40, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarin, T. The Concept of Sustainable Development: From its Beginning to the Contemporary Issues. Zagreb Int. Rev. Econ. Bus. 2018, 21, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Hu, R.; Mao, H.; Chen, S.J. How crop insurance influences agricultural green total factor productivity: Evidence from Chinese farmers. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 12, 128977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Q.; Feng, C.; Qin, J.H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Measuring China’s agricultural green total factor productivity and its drivers during 1998–2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Miao, J.F.; Zhu, Z.T. Measuring green total factor productivity of China’s agricultural sector: A three-stage SBM-DEA model with non-point source pollution and CO2 emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.F.; Cai, T.; Deng, W.; Zheng, R.; Jiang, Y.H.; Bao, H.J. Indicators for Evaluating High-Quality Agricultural Development: Empirical Study from Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Soc. Indic. Res. 2022, 164, 1101–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.F. China’s agricultural green total factor productivity based on carbon emission: An analysis of evolution trend and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manioudis, M.; Meramveliotakis, G. Broad strokes towards a grand theory in the analysis of sustainable development: A return to the classical political economy. New Political Econ. 2022, 27, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Boussemart, J.P.; Hao, Y. Digital transition and green growth in Chinese agriculture. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 181, 121742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.F.; Ji, X.; Cheng, C.M.; Liao, S.; Bright, O.; Zhang, Y.F. Digital economy empowers sustainable agriculture: Implications for farmers’ adoption of ecological agricultural technologies. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Zhang, J.W.; Song, J.F. Analysis of the threshold effect of agricultural industrial agglomeration and industrial structure upgrading on sustainable agricultural development in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Meng, J.X.; Cheng, B.D. How does improving agricultural mechanization affect the green development of agriculture? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 472, 143298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.H.; Mao, S.P.; Lin, Q.N. Has China’s Carbon Emissions Trading Pilot Policy Improved Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity? Agriculture 2022, 12, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhan, J.T.; Xu, Y.J.; Zuo, A.; Lv, X.Y. Challenges or drivers? Threshold effects of environmental regulation on China’s agricultural green productivity. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 429, 139503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.X.; He, Z.X.; Zhang, W.K.; Qin, X.M. The Agricultural Green Production following the Technological Progress: Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.G.; Zhang, B.C.; Wang, J.H.; Kwek, K. The impact of climate change on China’s agricultural green total factor. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 185, 122054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.Y.; Tian, M.J.; Wang, J. The impact of digital economy on green development of agriculture and its spatial spillover effect. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2023, 15, 708–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.F.; Deng, Y. Resource misallocation and unbalanced growth in green total factor productivity in Chinese agriculture. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2023, 68, 49–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, C. What drives the fluctuations of “green” productivity in China’s agricultural sector? A weighted Russell directional distance approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 147, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Zhang, Y.W. Administration or marketization: Environmental regulation, marketization and agricultural green total factor productivity. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.H.; Ping, Y. The Impact of Technological Innovation on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity: The Mediating Role of Environmental Regulation in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; She, Y.A.; Liu, S.; Lan, H.X. Supply-shock, demand-induced or superposition effect? The impacts of formal and informal environmental regulation on total factor productivity of Chinese agricultural enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhao, L.D.; Zhang, Y.B.; Sun, L.X.; Yu, X.; Yu, Y. Can climate change influence agricultural GTFP in arid and semi-arid regions of Northwest China? J. Arid. Land 2020, 12, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.M.; Hussain, S.; Yan, J.Y. Evaluating the interlinkage between pesticide residue regulation and agricultural green total factor productivity: Empirical insights derived from the threshold effect model. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.S.; Liu, L.X.; Gao, S.H.; Yuan, S.Y.; Shen, Q.L.; Chen, H.P. Impact of carbon trading on agricultural green total factor productivity in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 132789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Yang, Z.N.; Yu, M.R.; Watson, S.; Lovell, A. Can Market-Oriented Reform of Agricultural Subsidies Promote the Growth of Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity? Empirical Evidence from Maize in China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.F.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, T.T. Spatial Spillover Effects of Resource Misallocation on the Green Total Factor Productivity in Chinese Agriculture. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.H.; Yang, X.; Qin, J.H. Does agricultural factor misallocation hinder agricultural green production efficiency? Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.A. Local environmental regulation and plant-level productivity. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 2516–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, S. Environmental regulation, spatial effects and green development of agriculture. Res. Dev. Manag. 2022, 34, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.C.; Wheeler, R.; Winter, M.; Lobley, M.; Chivers, C.A. Agriculture 4.0: Making it work for people, production, and the planet. Land Use Policy 2021, 100, 104933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.C. Environmental regulation, agricultural green technology innovation, and agricultural green total factor productivity. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 955954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.Y.; Wang, B.; Yu, Z.G.; Cui, Z.D. Does seed industry innovation in developing countries contribute to sustainable development of grain green production? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 137029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coomes, O.T.; Barham, B.L.; MacDonald, G.K.; Ramankutty, N.; Chavas, J.P. Leveraging total factor productivity growth for sustainable and resilient farming. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piesse, J.; Thirtle, C. Agricultural R&D, technology and productivity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3035–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. Dealing with Undesirable Outputs in DEA: A Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) Approach; Grips Research Report Series; GRIPS: Tokyo, Japan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, D.H. A global Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index. J. Product. Anal. 2010, 34, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Fan, M.T.; Yang, L.L.; Shao, S. Heterogeneous green innovations and carbon emission performance: Evidence at China’s city level. Energy Econ. 2021, 99, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: Estimation, testing, and inference. J. Econom. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Hu, X.D. Assessment and analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution loads in China: 1978–2017. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Decomposition of spatial and temporal characteristics and factors affecting agricultural carbon emissions in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2011, 21, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Zhou, X. The double effect of environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China. Economist 2017, 9, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minten, B.; Randrianarison, L.; Swinnen, J. Spillovers from high-value agriculture for exports on land use in developing countries: Evidence from Madagascar. Agric. Econ. 2007, 37, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Li, C.F.; Li, Y.S. A study on the dynamic impact of industrial structure change on economic fluctuations. Ind. Econ. Res. 2013, 3, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variables | Variable Description | Sample Size | Average | Std. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGTFP | Agricultural green total factor productivity | 360 | 0.484 | 0.382 | −0.502 | 1.702 |
| ER | Environmental regulation | 360 | 7.146 | 0.734 | 4.928 | 8.634 |
| ERC | Command-and-control ER | 360 | 5.023 | 0.778 | 2.639 | 7.265 |
| ERM | Market-based incentives ER | 360 | 10.687 | 0.939 | 7.955 | 12.791 |
| ERP | Public participation ER | 360 | 5.857 | 0.967 | 3.219 | 8.673 |
| INS | Agricultural structure | 360 | 0.493 | 0.084 | 0.314 | 0.703 |
| ADR | Affected disaster rate | 360 | 0.181 | 0.135 | 0.006 | 0.695 |
| TI | Technological innovation | 360 | 1.823 | 2.628 | 0 | 16.780 |
| AE | Agricultural economic development | 360 | 0.102 | 0.054 | 0.003 | 0.300 |
| MAC | Agricultural machinery intensity | 360 | 0.618 | 0.243 | 0.245 | 1.386 |
| TRA | Trade dependence | 360 | 0.507 | 1.361 | 0.001 | 9.842 |
| Year | GTFPC | GTEC | GTC | Year | GTFPC | GTEC | GTC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007—2008 | 1.0445 | 1.0154 | 1.0287 | 2016—2017 | 1.0920 | 1.0580 | 1.0321 |
| 2008—2009 | 1.0742 | 1.0299 | 1.0430 | 2017—2018 | 1.1529 | 1.0316 | 1.1175 |
| 2009—2010 | 1.1762 | 0.9266 | 1.2693 | 2018—2019 | 1.1384 | 1.0120 | 1.1249 |
| Average of 2007 to 2010 | 1.0969 | 0.9896 | 1.1085 | Average of 2015 to 2019 | 1.0707 | 0.9911 | 1.0803 |
| 2010—2011 | 1.0624 | 0.9834 | 1.0802 | Average of the eastern region | 1.0776 | 1.0070 | 1.0701 |
| 2011—2012 | 1.1034 | 1.0098 | 1.0926 | Average of the central region | 1.0718 | 0.9813 | 1.0922 |
| 2012—2013 | 1.1007 | 0.9974 | 1.1035 | Average of the western region | 1.0837 | 0.9799 | 1.1059 |
| 2013—2014 | 1.0495 | 0.9727 | 1.0650 | Average of main grain-producing areas | 1.0779 | 0.9738 | 1.1069 |
| 2014—2015 | 1.0534 | 0.9727 | 1.0830 | Average of main grain-marketing area | 1.0763 | 1.0278 | 1.0472 |
| Average of 2010 to 2015 | 1.0737 | 0.9897 | 1.0848 | Average of grain-balancing area | 1.0782 | 0.9873 | 1.0974 |
| 2015—2016 | 0.9170 | 0.8735 | 1.0497 | National average | 1.0784 | 0.9901 | 1.0892 |
| AGTFP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REM (1) | FEM (2) | REM (3) | FEM (4) | |
| ER | 0.325 *** | 0.428 *** | 0.227 *** | 0.274 *** |
| (0.040) | (0.072) | (0.036) | (0.073) | |
| INS | 1.560 *** | 4.817 * | ||
| (0.440) | (2.717) | |||
| ADR | −0.964 *** | −0.663 *** | ||
| (0.179) | (0.206) | |||
| AE | −0.040 | −2.639 | ||
| (1.310) | (2.868) | |||
| MAC | 0.383 ** | 0.636 * | ||
| (0.160) | (0.321) | |||
| TRA | −0.029 | −0.050 ** | ||
| (0.026) | (0.022) | |||
| Constant variable | −1.839 *** | −2.570 *** | −1.947 *** | −3.823 ** |
| (0.290) | (0.515) | (0.397) | (1.765) | |
| Fixed Effects | NO | YES | NO | YES |
| Hausman Test | 8.67 | 44.16 | ||
| [0.013] | [0.000] | |||
| Sample size | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| R2 | 0.178 | 0.178 | 0.375 | 0.421 |
| ER | AGTFP | ER | AGTFP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Z1 | 0.928 *** | |||
| (0.020) | ||||
| Z2 | 0.913 *** | |||
| (0.025) | ||||
| ER | 0.249 *** | 0.265 *** | ||
| (0.027) | (0.032) | |||
| INS | 0.068 | 1.233 *** | 0.080 | 1.243 *** |
| (0.173) | (0.179) | (0.216) | (0.180) | |
| ADR | −0.113 | −0.980 *** | 0.246 * | −0.961 *** |
| (0.110) | (0.150) | (0.144) | (0.174) | |
| AE | 0.453 | 1.916 *** | 0.747 * | 2.243 *** |
| (0.326) | (0.459) | (0.443) | (0.481) | |
| MAC | 0.138 ** | 0.229 *** | 0.268 *** | 0.220 *** |
| (0.063) | (0.062) | (0.079) | (0.065) | |
| TRA | 0.012 | 0.029 | 0.030 ** | 0.034 |
| (0.011) | (0.021) | (0.013) | (0.022) | |
| Constant variable | 0.397 ** | −2.052 *** | 0.347 ** | −2.177 *** |
| (0.183) | (0.249) | (0.233) | (0.281) | |
| Fixed Effects | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| KP rk LM-statistic | 105.599 | 94.885 | ||
| LM p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| KP rk wald F-statistic | 2125.512 | 1338.657 | ||
| Sample size | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| R2 | 0.178 | 0.178 | 0.375 | 0.421 |
| Replacing the Measurement of AGTFP | Replacing the Measurement of ER | Dynamic Effect | Classifying Types of ER | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |||
| ER | 0.140 *** | 0.098 *** | 0.042 * | |||
| (0.038) | (0.026) | (0.023) | ||||
| ERC | 0.139 *** | |||||
| (0.042) | ||||||
| ERM | 0.102 * | |||||
| (0.051) | ||||||
| ERP | 0.085 ** | |||||
| Ln.AGTFP | 0.780 *** | |||||
| (0.072) | (0.032) | |||||
| INS | 2.661 * | 1.662 *** | −0.680 ** | 3.710 | 5.420 * | 4.769 |
| (1.423) | (0.487) | (0.309) | (2.846) | (2.775) | (4.043) | |
| ADR | −0.409 *** | −1.080 *** | −0.188 * | −0.746 *** | −0.774 *** | −0.713 *** |
| (0.131) | (0.200) | (0.104) | (0.215) | (0.218) | (0.212) | |
| AE | −1.573 | −0.417 | 0.447 | −2.986 | −3.718 | −3.412 |
| (1.559) | (1.250) | (0.380) | (2.792) | (2.918) | (2.948) | |
| MAC | 0.331 * | 0.377 * | 0.051 * | 0.619 * | 0.665 * | 0.741 * |
| (0.181) | (0.200) | (0.065) | (0.337) | (0.356) | (0.366) | |
| TRA | −0.017 * | −0.041 | −0.013 | −0.042 * | −0.044 | −0.045 * |
| (0.009) | (0.028) | (0.008) * | (0.023) | (0.026) | (0.025) | |
| Constant variable | −1.979 * | −0.308 | 0.174 | −1.962 | −3.148 * | −2.321 |
| (0.981) | (0.354) | (0.159) | (1.570) | (1.657) | (1.780) | |
| Fixed Effects | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| AR(1) | 0.017 | |||||
| AR(2) | 0.775 | |||||
| Hansen | 0.827 | |||||
| Sample size | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| R2 | 0.408 | 0.331 | 0.402 | 0.372 | 0.378 | |
| AGTFP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern (1) | Central (2) | Western (3) | Main Grain-Producing Area (4) | Main Grain- Marketing Area (5) | Grain-Balancing Area (6) | |
| ER | 0.318 *** | 0.419 ** | 0.079 | 0.336 *** | 0.303 ** | 0.104 |
| (0.097) | (0.168) | (0.120) | (0.096) | (0.115) | (0.010) | |
| INS | 3.997 | −6.039 | 5.916 * | 3.169 | 0.930 | 6.245 |
| (2.970) | (4.627) | (2.880) | (4.553) | (3.944) | (5.141) | |
| ADR | 0.063 | −0.697 ** | −1.111 *** | −0.455 * | −0.079 | −1.2873 *** |
| (0.095) | (0.235) | (0.254) | (0.236) | (0.134) | (0.160) | |
| AE | −8.835 * | 0.679 | −3.986 | −1.166 | −12.186 * | −2.592 |
| (4.115) | (3.595) | (3.826) | (3.939) | (6.159) | (3.016) | |
| MAC | 0.567 | 0.100 | 0.932 | 0.847 | −0.224 | 0.594 ** |
| (0.401) | (0.513) | (0.895) | (0.633) | (0.458) | (0.248) | |
| TRA | −0.052 ** | −5.474 ** | −1.791 *** | −0.853 ** | −0.0436 ** | −1.885 ** |
| (0.022) | (2.208) | (0.351) | (0.327) | (0.017) | (0.589) | |
| Constant variable | −3.323 | 0.701 | −2.938 | −3.681 | −1.009 | −3.421 |
| (1.869) | (2.705) | (2.374) | (2.438) | (2.308) | (3.293) | |
| Fixed Effects | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Sample size | 132 | 96 | 132 | 156 | 84 | 120 |
| R2 | 0.558 | 0.412 | 0.627 | 0.419 | 0.554 | 0.589 |
| Number of num | 11 | 8 | 11 | 13 | 7 | 10 |
| Variables | AGTFP | TI | AGTDP |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
| ER | 0.274 *** | 1.094 ** | 0.235 *** |
| (0.073) | (0.528) | (0.070) | |
| TI | 0.035 ** | ||
| (0.015) | |||
| INS | 4.817 * | 13.21 | 4.354 |
| (2.717) | (8.584) | (2.579) | |
| ADR | −0.663 *** | −0.775 | −0.636 *** |
| (0.206) | (0.479) | (0.198) | |
| AE | −2.639 | −26.93 *** | −1.696 |
| (2.868) | (9.043) | (2.862) | |
| MAC | 0.636 * | 1.852 * | 0.571 * |
| (0.321) | (1.068) | (0.309) | |
| TRA | −0.050 ** | −0.051 | −0.048 ** |
| (0.022) | (0.064) | (0.021) | |
| Constant variable | −3.823 ** | −10.74 ** | −3.447 ** |
| (1.765) | (5.017) | (1.680) | |
| Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sample size | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| R2 | 0.421 | 0.207 | 0.451 |
| [95% Conf. Interval] | [0.065, 0.142] | ||
| Threshold Variables | Threshold Model | F-Value | p-Value | 10% Threshold Level | 5% Threshold Level | 1% Threshold Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | Single | 72.61 | 0.000 | 23.09 | 27.49 | 35.32 |
| Double | 19.73 | 0.093 | 19.13 | 22.62 | 30.53 | |
| Triple | 19.58 | 0.793 | 49.05 | 54.87 | 65.64 | |
| ERC | Single | 65.76 | 0.000 | 25.41 | 30.72 | 40.77 |
| Double | 19.22 | 0.089 | 18.29 | 21.93 | 30.38 | |
| Triple | 21.59 | 0.659 | 44.75 | 55.75 | 61.93 | |
| ERM | Single | 76.45 | 0.001 | 26.29 | 31.41 | 39.40 |
| Double | 20.16 | 0.084 | 19.22 | 23.46 | 32.81 | |
| Triple | 17.87 | 0.744 | 43.40 | 49.97 | 63.09 | |
| ERP | Single | 74.72 | 0.000 | 25.09 | 29.12 | 38.55 |
| Double | 17.46 | 0.161 | 20.18 | 24.64 | 32.79 | |
| Triple | 21.09 | 0.744 | 53.24 | 59.81 | 72.17 |
| Type of Regulation | Number of Thresholds | Threshold Value | 95% Conf. Interval (Lower Limit) | 95% Conf. Interval (Upper Limit) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | The First Threshold | 0.530 | 0.500 | 0.540 |
| The Second Threshold | 1.650 | 1.615 | 1.680 | |
| ERC | The First Threshold | 0.120 | 0.100 | 0.130 |
| The Second Threshold | 0.530 | 0.500 | 0.540 | |
| ERM | The First Threshold | 0.530 | 0.500 | 0.540 |
| The Second Threshold | 1.650 | 1.580 | 1.680 | |
| ERP | The First Threshold | 0.530 | 0.500 | 0.540 |
| Variables | AGTFP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | ||
| ER | (TI ≤ 0.530) | 0.170 *** | |||
| (0.061) | |||||
| (0.530 < TI ≤ 1.650) | 0.210 *** | ||||
| (0.061) | |||||
| (TI > 1.65) | 0.235 *** | ||||
| (0.061) | |||||
| ERC | (TI ≤ 0.120) | −0.007 | |||
| (0.041) | |||||
| (0.120 < TI ≤ 0.530) | 0.050 | ||||
| (0.034) | |||||
| (TI > 0.53) | 0.108 *** | ||||
| (0.033) | |||||
| ERM | (TI ≤ 0.530) | 0.058 | |||
| (0.043) | |||||
| (0.530 < TI ≤ 1.650) | 0.086 * | ||||
| (0.042) | |||||
| (TI > 1.65) | 0.104 ** | ||||
| (0.042) | |||||
| ERP | (TI ≤ 0.530) | 0.038 | |||
| (0.024) | |||||
| (TI > 0.53) | 0.091 *** | ||||
| (0.026) | |||||
| TI | 0.018 | 0.033 ** | 0.024 * | 0.036 ** | |
| (0.013) | (0.014) | (0.013) | (0.014) | ||
| INS | 3.230 | 2.683 | 3.611 | 3.578 | |
| (2.213) | (2.443) | (2.209) | (2.551) | ||
| ADR | −0.463 *** | −0.472 *** | −0.515 *** | −0.486 *** | |
| (0.158) | (0.149) | (0.160) | (0.160) | ||
| AE | 0.965 | −0.337 | 0.438 | −0.330 | |
| (2.146) | (2.237) | (2.219) | (2.268) | ||
| MAC | 0.594 ** | 0.567 ** | 0.603 ** | 0.673 ** | |
| (0.253) | (0.255) | (0.262) | (0.253) | ||
| TRA | −0.038 * | −0.042 * | −0.032 | −0.045 * | |
| (0.022) | (0.023) | (0.025) | (0.024) | ||
| Constant variable | −2.965 ** | −1.535 | −2.524 * | −2.047 | |
| (1.307) | (1.253) | (1.278) | (1.383) | ||
| Fixed Effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| Sample size | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 | |
| R2 | 0.569 | 0.549 | 0.548 | 0.524 | |
| Year | Low-Level Technological Innovation Regions (TI ≤ 0.120) | Low- to Medium-Level TI Region (0.120 < TI ≤ 0.530) | Medium- to High-Level TI Region (0.530 < TI ≤ 1.650) | High-Level TI Regions (TI > 1.650) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Qinghai, Hainan, Gansu, Guizhou, Jilin, Xinjiang | Jiangxi, Chongqing, Anhui, Shanxi, Guangxi, Yunnan, Heilongjiang, Fujian, Sichuan, Hebei, Henan, Tianjin, Liaoning | Hubei, Hunan, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Shaanxi, Guangdong, Shandong | Jiangsu, Beijing |
| 2019 | Qinghai, Ningxia, Jilin | Inner Mongolia, Hainan, Xinjiang, Shanxi, Chongqing, Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Tianjin, Gansu | Yunnan, Guizhou, Hebei, Guangxi, Shaanxi, Jiangxi, Fujian, Hubei, Hunan, Sichuan, Shanghai, Henan, Beijing, Anhui, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Shandong, Jiangsu |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Lu, W.; Lin, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, H. Does Environmental Regulation Affect China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity? Considering the Role of Technological Innovation. Agriculture 2025, 15, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060649
Shi Y, Lu W, Lin L, Li Z, Chen H. Does Environmental Regulation Affect China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity? Considering the Role of Technological Innovation. Agriculture. 2025; 15(6):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060649
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yi, Wencong Lu, Li Lin, Zenghui Li, and Huangxin Chen. 2025. "Does Environmental Regulation Affect China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity? Considering the Role of Technological Innovation" Agriculture 15, no. 6: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060649
APA StyleShi, Y., Lu, W., Lin, L., Li, Z., & Chen, H. (2025). Does Environmental Regulation Affect China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity? Considering the Role of Technological Innovation. Agriculture, 15(6), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060649






