Nondestructive Quality Detection of Characteristic Fruits Based on Vis/NIR Spectroscopy: Principles, Systems, and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Vis/NIR Spectroscopy for Quality Detection of Fruits
2.1. Fundamental Principles
2.2. Basic Procedure
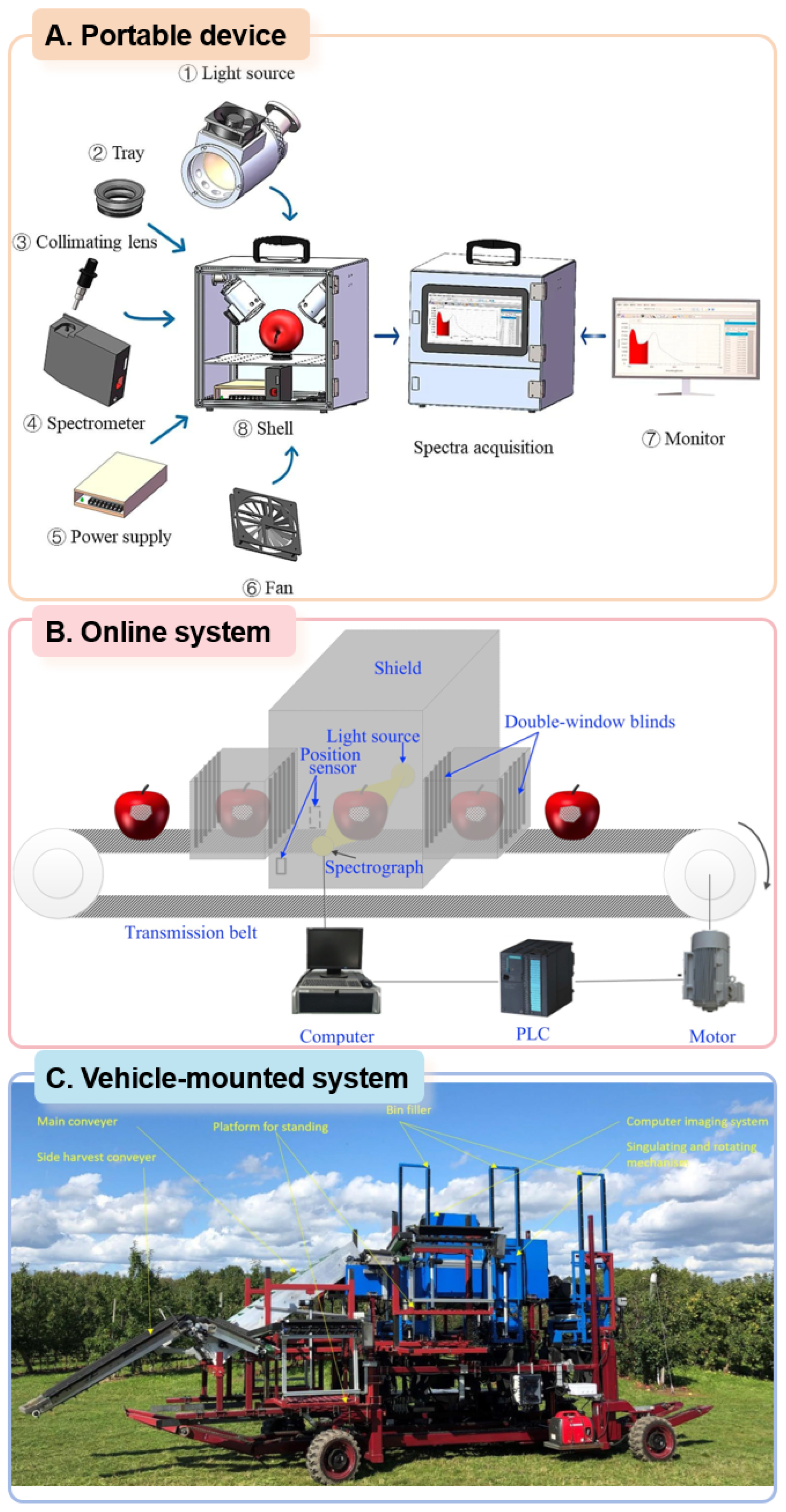
2.3. Typical Vis/NIR System
2.3.1. Portable Detection Equipment
2.3.2. Online Detection System
2.3.3. Vehicle-Mounted Detection System
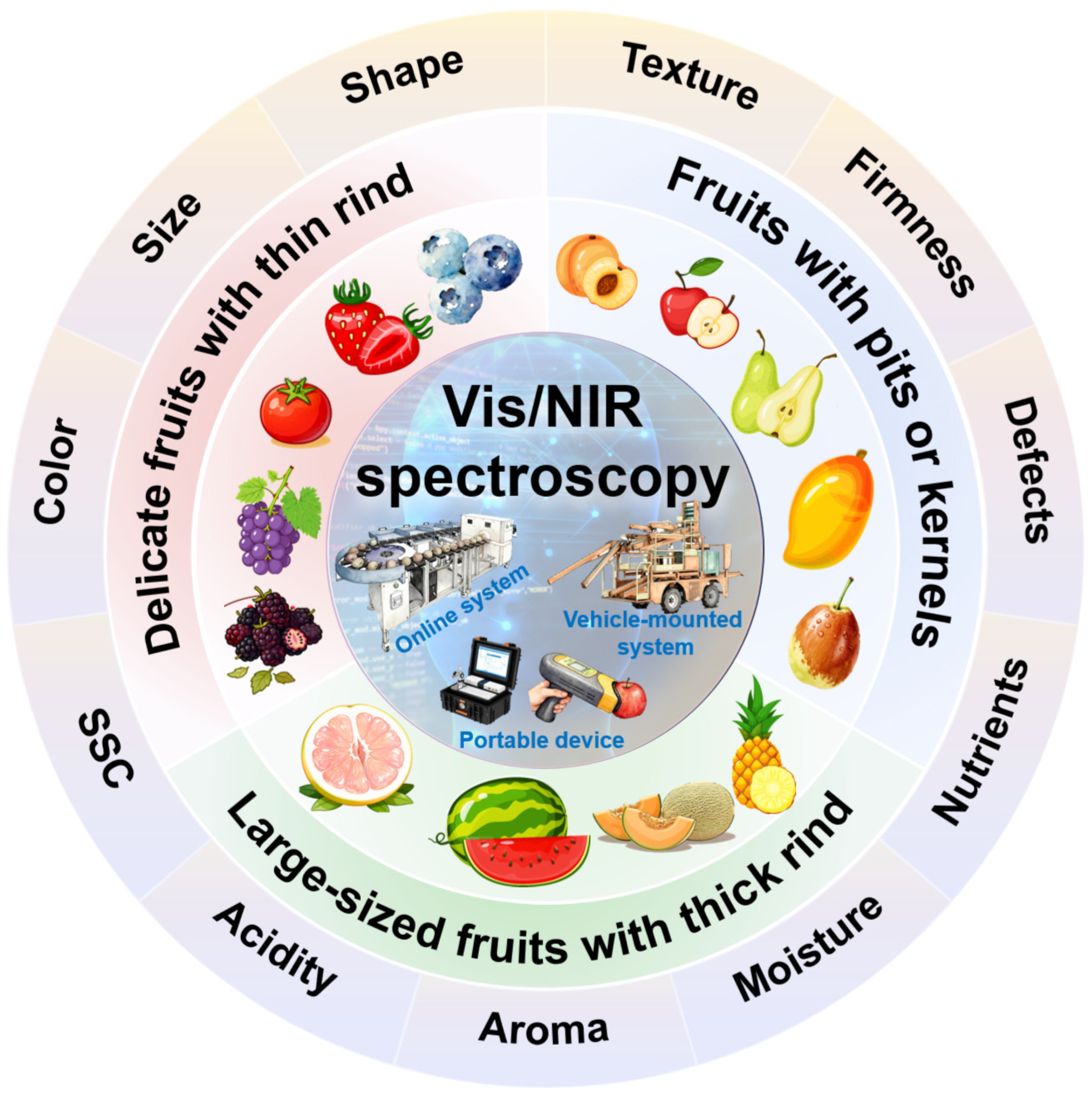
3. Influence of Fruit Characteristics on Quality Detection by Vis/NIR Spectroscopy
3.1. Fruit Pits, Kernel, and Cavity
3.2. Fruit Rind
3.3. Fruit Size and Shape
3.4. Spatial Distribution of the Component Within the Fruit
4. Applications of Vis/NIR Spectroscopy for Quality Evaluation
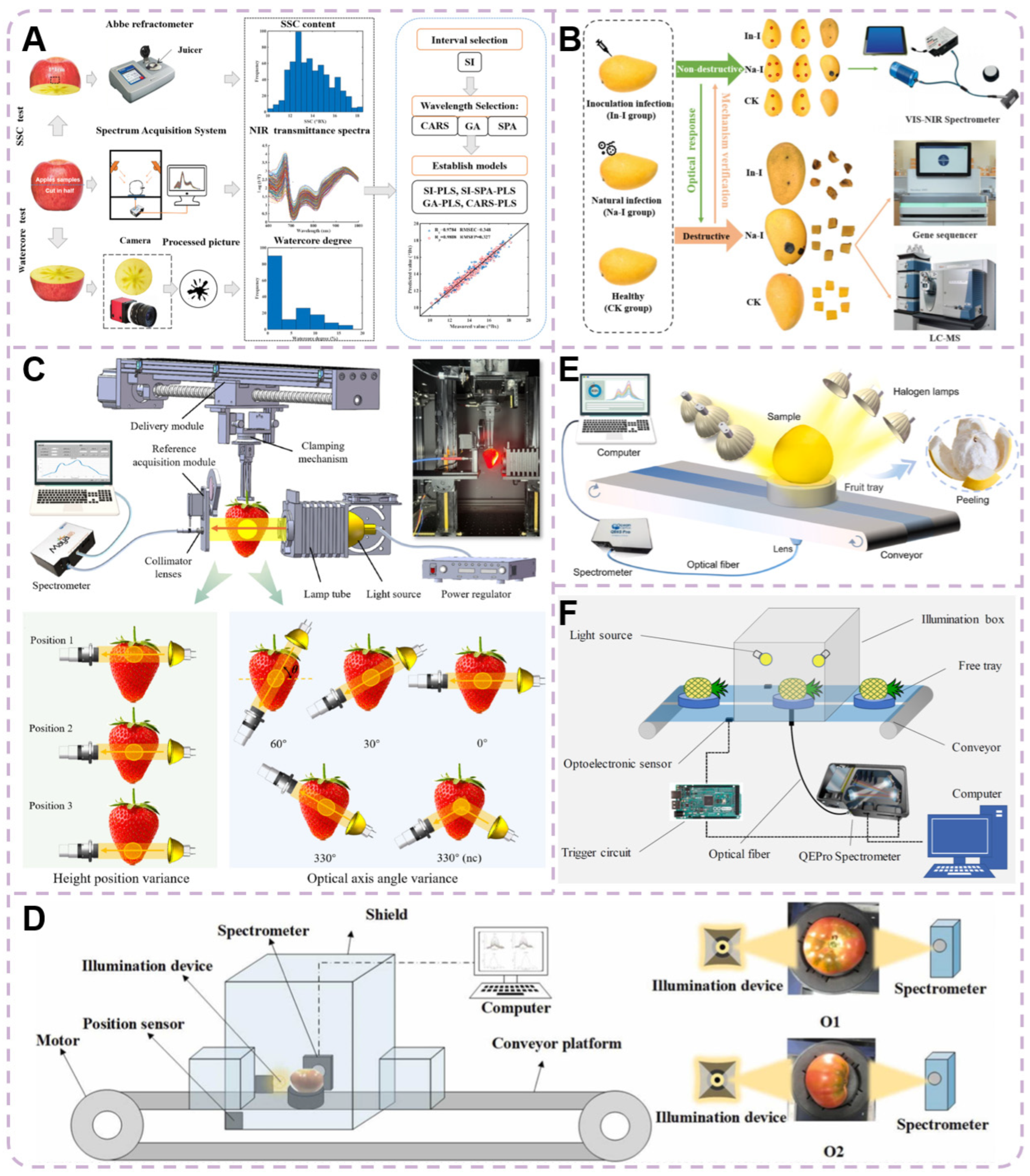
4.1. Fruits with Pits or Kernels
4.1.1. Peach
4.1.2. Apple
4.1.3. Pear
4.1.4. Mango
4.1.5. Fresh Jujube
4.2. Delicate Fruits with Thin Rind
4.2.1. Blueberry
4.2.2. Strawberry
4.2.3. Cherry Tomato
| Fruits | Detection Indexes | Data Acquisition Modes | Spectral Range | Models | Validation Approach | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orange | Freezing damage | Online transmission | 644–900 nm | DCM-1D-CNN | Internal validation, cross-validation | Accuracy = 91.96% | [74] |
| Orange | Sweetness classification | Interactance | 600–1050 nm | Ensemble classifier | Internal validation, cross-validation | Accuracy = 81.03% | [105] |
| Fig | Firmness, SSC | Diffuse reflectance | 545–1175 nm | SPA-RF | Internal validation, cross-validation | Firmness R2p = 0.9173, RMSEP = 19.9027, RPD = 2.24 | [37] |
| Strawberry | Cultivar classification | Integrating sphere | 1000–2500 nm | PLS-DA | Internal validation, cross-validation | Successful discrimination | [124] |
| Strawberry | SSC | Online transmission | 650–980 nm | 1D-CNN-LSTM | Internal validation, cross-validation | R2p = 0.963, RMSEP = 0.209°Brix, RPD = 5.332 | [88] |
| White strawberry, Red strawberry | SSC | Reflectance | 500–978 nm, 908–1676 nm | PLSR | Internal validation, cross-validation | White: R2p = 0.85–0.89, RMSEP = 0.40–0.43%, RPD = 2.64–2.98 Red: R2p = 0.89, RMSEP = 0.36%, RPD = 3.04–3.05 | [28] |
| Lime | TA | Integrating sphere | 833–2500 nm, 898–1720 nm | PLS, DT, XGBoost, FFNN | Internal validation, cross-validation | R2p = 0.66, RMSEP = 0.3896, RPD = 1.33 | [36] |
| Cherry tomato | Lycopene | Reflectance, transmittance | 200–1100 nm | PLSR | Internal validation, cross-validation | R2p = 0.91, RMSEP = 11.60 mg/kg, RPD = 3.28 | [129] |
| Navel orange | SSC | Online transmittance | 650–950 nm | PLSR | Internal validation, cross-validation | R2p = 0.9406, RMSEP = 0.442%, RPD = 2.77 | [55] |
| Nanguo pears | SSC | Portable reflectance | 900–1700 nm | Si-GA-PLS | Internal validation, cross-validation | R2p = 0.9406, RMSEP = 0.1655°Brix | [98] |
| Pears | Cork spot disorder | Portable reflectance | 900–1700 nm | SVM | Internal validation, cross-validation | Accuracy = 84.65% | [76] |
| Sugar orange | Granulation | Online transmittance | 400–1200 nm | PLS-DA | Internal validation, cross-validation | Accuracy = 94.00%, Class error = 5.84% | [73] |
| Pear | Sunburn severity | Reflectance | 400–1100 nm | iPLS, LDA | Internal validation, cross-validation | Accuracy = 83% | [69] |
| Mango | SSC | Reflectance | 900–1650 nm | SPA-PLSR | Internal validation, cross-validation | Rp = 0.78, SEP = 0.67°Brix, RPD = 2.12 | [87] |
| Mango | Anthracnose disease | Reflectance | 450–980 nm | LDA, QDA, PLS-DA | Internal validation | Accuracy = 90.9%, sensitivity = 0.929, specificity = 0.989 | [103] |
| Kiwifruit | Sweetness, firmness | Reflectance | 800, 810, 850, 880, 900, 940, 970, 1000, 1100 nm | SVM | Cross-validation, independent external validation | Sweetness accuracy = 82.0%, firmness accuracy = 74.0% | [50] |
| Apple | Moldy core | Online transmittance | 650–1000 nm | PLS-DA | Internal validation, independent external validation | Accuracy = 94.44%, recall = 92.59%, precision = 96.15% | [54] |
| Apple | SSC, firmness, pH, watercore degree | Transmittance | 700–1100 nm | CARS-CNN | Internal validation, independent external validation | Rp: 0.951 (SSC), 0.824 (firmness), 0.828 (pH), 0.943 (watercore) | [16] |
| Lemon | TSS, TA | Reflectance | 950–1700 nm | PLSR | Internal validation, independent external validation | R2p: 0.84 (TSS), 0.72 (TA); RMSEP: 0.42% (TSS), 0.45 g/100 mL (TA) | [66] |
| Avocado | DMC | Diffuse reflectance, interaction | 350–2500 nm 310–1135 nm | PLSR | Internal validation, cross-validation | RMSECV: 1.02% dw/fw (non-dehydrated), 1.49% dw/fw (dehydrated) | [19] |
| Pomegranate | Juice percentage, TSS, TA, Taste, pH, vitamin C | Interactance | 400–1000 nm | PLSR | Internal validation | Rp = 0.95–0.98, RMSEP = 0.036–0.583 | [33] |
| Tomato | Lycopene | Transmission | 560–1072 nm | PLSR | Internal validation, cross-validation | Rp = 0.95–0.96, RMSEP = 7.43–13.44 mg kg−1 | [130] |
| Banana | SSC, ripeness | Reflectance | 610, 680, 730, 760, 810, 860 nm | MLR | Internal validation | SSC: R2p = 0.9915, RMSEP = 0.38%, Ripeness: Avg. accuracy 97% | [75] |
| Apricot | TSS, TA, DMC | Reflectance | 310–1100 nm | ANN-MLP | Internal validation, independent external validation | R2: 0.855 (TSS), 0.681 (TA), 0.857 (DMC) | [17] |
| Pomelo | SSC | Transmission | 400–1100 nm | SNV-CARS-PLSR | Internal validation | R2c = 0.98, RMSEC = 0.46, R2v = 0.89, RMSEV = 0.87 | [15] |
| Barhi dates | TSS, hardness | Reflectance | 285–1200 nm | ANN | Internal validation, cross-validation | R2c = 0.912, RMSEC = 0.308, RMSECV = 0.308 | [113] |
4.2.4. Grape
4.2.5. Mulberry
4.3. Large-Sized Fruits with Thick Rind
4.3.1. Pomelo
4.3.2. Watermelon
4.3.3. Hami Melon
4.3.4. Pineapple
5. Critical Considerations in Model Development and Validation
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, P.P.; Sun, J.; Cong, S.L.; Dai, C.X.; Cai, Z.T.; Yao, K.S.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.H.; Liu, J.Y. Detection of early damage in kiwifruit based on near-infrared technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2025, 48, e70130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; He, W.L.; Lin, M.H.; Fu, X.H.; Li, Y.H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y. Comprehensive analysis of volatile flavor components in pear fruit spanning the entire development stages. Food Chem. 2025, 485, 144493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.; Zou, X.B.; Tahir, H.E.; Xuetao, H.; Rakha, A.; Basheer, S.; Hao, Z. Near-infrared spectroscopy coupled chemometric algorithms for prediction of antioxidant activity of black goji berries (Lycium ruthenicum Murr.). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 2366–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.N.; Zareef, M.; Liu, L.H.; Din, Z.U.; Chen, Q.S.; Ouyang, Q. Application of portable Vis-NIR spectroscopy for rapid detection of myoglobin in frozen pork. Meat Sci. 2023, 201, 109170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Adade, S.Y.-S.S.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, T.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Deep learning and feature reconstruction assisted vis-NIR calibration method for on-line monitoring of key growth indicators during kombucha production. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.L.; Tian, Y.L.; Lu, D.L.; Chen, B. Research progress of applying infrared spectroscopy technology for detection of toxic and harmful substances in food. Foods 2022, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Liang, Z.N.; Qi, W.L.; Zheng, X.H.; Lu, D.L.; Chen, B. Application of NIR spectral standardization based on principal component score evaluation in wheat flour crude protein model sharing. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 9009756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.M.; Huang, W.Q.; Peng, Y.K.; Chen, Q.S.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J.W. Color compensation and comparison of shortwave near infrared and long wave near infrared spectroscopy for determination of soluble solids content of ‘Fuji’ apple. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 115, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, T.; Wang, D.; Guo, Z.; Gao, S.; Zou, X. Advances in molecular vibrational spectroscopy for foodborne pathogen detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 25756–25779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.X.; Li, J.B.; Xia, Y.; Tian, X.; Guo, Z.M.; Huang, W.Q. Long-term evaluation of soluble solids content of apples with biological variability by using near-infrared spectroscopy and calibration transfer method. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 151, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Fu, H.J. Non-destructive detection of fruit quality: Technologies, applications and prospects. Foods 2025, 14, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.H.; Wu, B.; Sun, J.; Yang, N. Classification of apple varieties using near infrared reflectance spectroscopy and fuzzy discriminant c-means clustering model. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.T.; Zou, X.B.; Shi, J.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Huang, X.W.; Xu, Y.W.; Chen, W. Determination geographical origin and flavonoids content of Goji berry using near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasampalis, D.S.; Tsouvaltzis, P.; Siomos, A.S. Assessment of melon fruit nutritional composition using vis/nir/swir spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H.; He, Z.; Liang, X. Non-destructive determination of internal soluble solid content in pomelo using visible/near infrared full-transmission spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 214, 112990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zou, Y.; Sun, C.; Jayan, H.; Jiang, S.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X. Nondestructive determination of edible quality and watercore degree of apples by portable Vis/NIR transmittance system combined with CARS-CNN. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 4058–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoriello, T.; Ciorba, R.; Ruggiero, G.; Masciola, F.; Scutaru, D.; Ciccoritti, R. Vis/NIR spectroscopy and Vis/NIR hyperspectral imaging for non-destructive monitoring of apricot fruit internal quality with machine learning. Foods 2025, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.H.; Yang, Z.T.; Yang, Y.L.; Wu, B.; Sun, J. Geographical origin identification of Chinese red jujube using near-infrared spectroscopy and Adaboost-CLDA. Foods 2025, 14, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Paillart, M.; Meesters, L.; Woltering, E.; Chauhan, A. Avocado dehydration negatively affects the performance of visible and near-infrared spectroscopy models for dry matter prediction. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 183, 111739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.G.; Jiao, T.H.; Adade, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.X.; Li, H.H.; Chen, Q.S. Based on vis-NIR combined with ANN for on-line detection of bacterial concentration during kombucha fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Z.; Zareef, M.; Chen, Q.S.; Ouyang, Q. Application of visible-near infrared spectroscopy in tandem with multivariate analysis for the rapid evaluation of matcha physicochemical indicators. Food Chem. 2023, 421, 136185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.H.; Zhou, H.X.; Wu, B.; Fu, H.J. Determination of apple varieties by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy coupled with improved possibilistic Gath-Geva clustering algorithm. J. Food Process. Pres. 2020, 44, e14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Lin, H.; Xu, P.T.; Bi, X.K.; Sun, L. Egg freshness evaluation using transmission and reflection of NIR spectroscopy coupled multivariate analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Luo, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, R.; Cai, J. Influence of the peel on online detecting soluble solids content of pomelo using Vis-NIR spectroscopy coupled with chemometric analysis. Food Control 2025, 167, 110777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghooshkhaneh, N.G.; Golzarian, M.R.; Mollazade, K. VIS-NIR spectroscopy for detection of citrus core rot caused by Alternaria alternata. Food Control 2023, 144, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Wu, X.H.; Wu, B.; Zhou, H.X. Detection of apple varieties by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy coupled with SPSO-PFCM. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Guo, T.H.; Sun, X.L.; Lian, K.X.; Tian, K.; Wang, A.C.; Sun, T. Internal quality evaluation of ‘Fuji’ apples during storage based on bulk optical properties or diffuse reflection and transmission spectra. LWT 2024, 200, 116202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, H.; Murakami, H.; Ma, T.; Tsuchikawa, S.; Inagaki, T. Evaluating soluble solids in white strawberries: A comparative analysis of Vis-NIR and NIR spectroscopy. Foods 2024, 13, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.; Recasens, I.; Alegre, S. Potential of VIS/NIR spectroscopy to detect and predict bitter pit in ‘Golden Smoothee’ apples. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2021, 19, e1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, M.; Zuo, C.; Song, J.; Tu, K.; Lan, W.; Pan, L. Comparing visible and near infrared ‘point’ spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging techniques to visualize the variability of apple firmness. Spectrochim. Acta A 2024, 316, 124344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, M.J.; Fan, W.P.; Liu, J.Z. State-of-the-art techniques for fruit maturity detection. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Ding, J.; Yuan, S.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Yao, W. Benchtop Vis-NIR spectroscopy meets machine learning for multi-task analysis in Hongmeiren citrus: Geographical origin identification and antioxidant component quantification. Food Chem. 2025, 489, 145007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, A.; Mahmoudi, A.; Jamshidi, B.; Ghaffari, H. Assessment of Persian export pomegranate quality: A reliable non-destructive method based on spectroscopy and chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 131, 106202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Le, D.; Zhang, T.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Song, Y.; Chen, N. Detection of apple moldy core disease by fusing vibration and Vis/NIR spectroscopy data with dual-input MLP-Transformer. J. Food Eng. 2024, 382, 112219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.M.; Wang, M.M.; Shujat, A.; Wu, J.Z.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Shi, J.Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q.S.; Zou, X.B. Nondestructive monitoring storage quality of apples at different temperatures by near-infrared transmittance spectroscopy. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3793–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, L.; Du, G.; Shan, Y. Nondestructive prediction of lime acidity with a single scan using two types of near infrared spectrometers and ensemble learning strategy. J. Food Eng. 2024, 368, 111917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, R.; Sun, L. Rapid nondestructive detection of the pulp firmness and peel color of figs by NIR spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2575–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Fan, S.; Li, J. Online detection of apples with moldy core using the Vis/NIR full-transmittance spectra. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 168, 111269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareef, M.; Chen, Q.S.; Hassan, M.M.; Arslan, M.; Hashim, M.M.; Ahmad, W.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Agyekum, A.A. An overview on the applications of typical non-linear algorithms coupled with NIR spectroscopy in food analysis. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.M.; Barimah, A.O.; Shujat, A.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Qin, O.Y.; Shi, J.Y.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X.B.; Chen, Q.S. Simultaneous quantification of active constituents and antioxidant capability of green tea using NIR spectroscopy coupled with swarm intelligence algorithm. LWT 2020, 129, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Tian, X.; Hu, D.Y.; Yuan, X.C.; Ma, X.L.; Xiang, P.W.; Liao, S.M. Utilizing full transmittance Vis/NIR spectroscopy for online detection of soluble solids and anthocyanin content in blood oranges. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 145, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zuo, W.D.; Ding, J.J.; Yuan, S.F.; Qian, H.; Cheng, Y.L.; Guo, Y.H.; Yu, H.; Yao, W.R. Machine learning driven benchtop Vis/NIR spectroscopy for online detection of hybrid citrus quality. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareef, M.; Arslan, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Ali, S.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, H.H.; Wu, X.Y.; Hashim, M.M.; Javaria, S.; Chen, Q.S. Application of benchtop NIR spectroscopy coupled with multivariate analysis for rapid prediction of antioxidant properties of walnut (Juglans regia). Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.K.; Xu, S.; Lu, H.Z.; Liang, X.; Feng, H.L.; Li, W.J. Nondestructive detection of litchi stem borers using multi-sensor data fusion. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi-Amoghin, M.; Abbaspour-Gilandeh, Y.; Tahmasebi, M.; Kisalaei, A.; Hernández-Hernández, J.L.; Hernández-Hernández, M.; De La Cruz-Gámez, E. Analyzing the nitrate content in various bell pepper varieties through non-destructive methods using Vis/NIR spectroscopy enhanced by metaheuristic algorithms. Processes 2025, 13, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.R.; Li, Q.Q.; An, C.Q.; Tao, K.; Yu, Y.D.; Xu, H.R. Improving the prediction performance of soluble solid content in bagged “Cuiguan” pear using Vis/NIR spectroscopy with spectral correction. Food Control 2026, 179, 111596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, B.Y.; Hwan, L.J.; Yang, H.E.; Kim, M.S.; Hwang, I.G.; Jeong, C.S.; Mo, C. Evaluating ripeness in post-harvest stored kiwifruit using VIS-NIR hyperspectral imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 225, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Pan, T.H.; Li, Y.Q.; Chen, S.; Li, G.Q. Development of analytical method associating near-infrared spectroscopy with one-dimensional convolution neural network: A case study. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 2963–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Liu, L.H.; Zareef, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.S. Application of portable visible and near-infrared spectroscopy for rapid detection of cooking loss rate in pork: Comparing spectra from frozen and thawed pork. LWT 2022, 160, 113304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Guo, W.; Huang, X.; Du, R.; Liu, Z. A portable, low-cost and sensor-based detector on sweetness and firmness grades of kiwifruit. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 179, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, W.; Yang, B.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhu, X. A novel noninvasive and cost-effective handheld detector on soluble solids content of fruits. J. Food Eng. 2019, 257, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.X.; Wu, X.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Wu, B.; Fu, H.J. Discrimination of the red jujube varieties using a portable NIR spectrometer and fuzzy improved linear discriminant analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borba, K.R.; Aykas, D.P.; Milani, M.I.; Colnago, L.A.; Ferreira, M.D.; Rodriguez-Saona, L.E. Portable near infrared spectroscopy as a tool for fresh tomato quality control analysis in the field. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Pu, Y.; Wu, W.; Pan, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J. Online detection of moldy apple core based on diameter and SSC features. Food Control 2025, 168, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ying, J.; Wan, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, X.; Liu, B. Non-destructive evaluation of soluble solids content in navel orange by an on-line visible near-infrared system with four parallel spectrometers. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 4225–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xie, L. Design of a multi-function experimental system for online internal quality evaluation of fruits. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 18, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J. Measurement orientation compensation and comparison of transmission spectroscopy for online detection of moldy apple core. Infrared Phys. Techn. 2020, 111, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Mishra, A.; Maja, J.M.; Ehsani, R. Visible-near infrared spectroscopy for detection of Huanglongbing in citrus orchards. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 77, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Pothula, A.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, R. Evaluation of a new apple in-field sorting system for fruit singulation, rotation and imaging. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 208, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.H.; Lu, B.; Dai, C.X. Research on apple origin classification based on variable iterative space shrinkage approach with stepwise regression-support vector machine algorithm and visible-near infrared hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Tian, Y.; Yao, K.S.; Xu, M. Visualization of heavy metal cadmium in lettuce leaves based on wavelet support vector machine regression model and visible-near infrared hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.L.; Sun, C.J.; He, Y.; Zhu, F.L.; Li, X.L. Cross-cultivar prediction of quality indicators of tea based on VIS-NIR hyperspectral imaging. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 202, 117009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, L.; Shen, T.; Cai, J.; Zou, X.; Guo, Z. Automatic early bruise detection in strawberry fruit by hyperspectral imaging and deep learning techniques. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2026, 232, 113966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Jifan, Y.; Hao, T.; Jinshan, Y.; Huirong, X. Evaluation of the optical layout and sample size on online detection of apple watercore and SSC using Vis/NIR spectroscopy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magwaza, L.S.; Opara, U.L.; Cronjé, P.J.R.; Nieuwoudt, H.H.; Landahl, S.; Terry, L.A. Quantifying the effects of fruit position in the canopy on physical and biochemical properties and predicting susceptibility to rind breakdown disorder of ‘Nules Clementine’ mandarin (Citrus reticulate Blanco) using Vis/NIR spectroscopy. Acta Hort. 2013, 1007, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Escolano, V.; Giménez, M.J.; Zapata, P.J.; Cubero, S.; Blasco, J.; Munera, S. Non-destructive assessment of ‘Fino’ lemon quality through ripening using NIRS and chemometric analysis. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 212, 112870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, W.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Ma, H.L.; Tuly, J.A. Physicochemical indicators coupled with statistical tools for comprehensive evaluation of the novel infrared peeling on tomatoes. LWT 2024, 191, 115634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magwaza, L.S.; Opara, U.L.; Terry, L.A.; Landahl, S.; Cronje, P.J.; Nieuwoudt, H.; Mouazen, A.M.; Saeys, W.; Nicolaï, B.M. Prediction of ‘Nules Clementine’ mandarin susceptibility to rind breakdown disorder using Vis/NIR spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Torres, C.A.; Mogollon, R. Characterization of sun-injury and prediction of sunscald on ‘Packham’s Triumph’ pears using Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 184, 111776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckena, L.; Alksnis, R.; Erdberga, I.; Alsina, I.; Dubova, L.; Duma, M. Non-destructive quality evaluation of 80 tomato varieties using Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Foods 2023, 12, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, A.; Dorais, M.; Vernon, M. Nondestructive measurement of fresh tomato lycopene content and other physicochemical characteristics using visible–NIR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9813–9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.A.; Bureau, S.; Renard, C.M.-G.C.; Pereira-Netto, A.B.; de Castilhos, F. Comparison of NIRS approach for prediction of internal quality traits in three fruit species. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, S.; Xie, L. Improving the identification accuracy of sugar orange suffering from granulation through diameter correction and stepwise variable selection. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 200, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. Early detection of freezing damage in oranges by online Vis/NIR transmission coupled with diameter correction method and deep 1D-CNN. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripaurya, T.; Sengchuai, K.; Booranawong, A.; Chetpattananondh, K. Gros Michel banana soluble solids content evaluation and maturity classification using a developed portable 6 channel NIR device measurement. Measurement 2021, 173, 108615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Gu, S.; Xu, J.; Jia, B.; Ye, Z.; Heng, W.; Jin, X. An early asymptomatic diagnosis method for cork spot disorder in ‘Akizuki’ pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) using micro near infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogollón, M.R.; Contreras, C.; de Freitas, S.T.; Zoffoli, J.P. NIR spectral models for early detection of bitter pit in asymptomatic ‘Fuji’ apples. Sci. Hort. 2021, 280, 109945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, F.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Su, Y.; Ju, Y.; Fang, Y.; Bai, X.; Liu, W. Quality assessment and ripeness prediction of table grapes using visible-near-infrared spectroscopy. Foods 2023, 12, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Li, K.; Lu, D.; Su, Y.; Ju, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, J. Discrimination of maturity stages of cabernet sauvignon wine grapes using visible-near-infrared spectroscopy. Foods 2023, 12, 4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Sun, Y. Measurement of early disease blueberries based on Vis/NIR hyperspectral imaging system. Sensors 2020, 20, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, P.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, L. Improving SSC detection accuracy of cherry tomatoes by feature synergy and complementary spectral bands combination. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 213, 112922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, T. Intelligent evaluation of stone cell content of Korla fragrant pears by Vis/NIR reflection spectroscopy. Foods 2022, 11, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Ma, B.; Li, Y.; Dong, F. Quality detection of watermelons and muskmelons using innovative nondestructive techniques: A comprehensive review of novel trends and applications. Food Control 2024, 165, 110688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Yao, Y.; Hu, D.; Ying, Y.; Guo, J.; Xie, L. Knowledge-guided temperature correction method for soluble solids content detection of watermelon based on Vis/NIR spectroscopy. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2025, 15, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semyalo, D.; Kwon, O.; Wakholi, C.; Min, H.J.; Cho, B.-K. Nondestructive online measurement of pineapple maturity and soluble solids content using visible and near-infrared spectral analysis. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 209, 112706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Luo, J.; Tian, Q.; Li, J.; Cao, M.; Yang, S.; Guo, W. Nondestructive detection of internal quality in multiple peach varieties by Vis/NIR spectroscopy with multi-task CNN method. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 227, 113579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, M.S.; Masum, A.A.; Islam, M.H.; Ashik-E-Rabbani, M.; Rahman, A. Short wave-near infrared spectroscopy for predicting soluble solid content in intact mango with variable selection algorithms and chemometric model. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 136, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, W.; Sun, L.; Bai, J.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, Z.; Cai, J. Online assessment of soluble solids content in strawberries using a developed Vis/NIR spectroscopy system with a hanging grasper. Food Chem. 2025, 478, 143671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Bao, Y.; He, Y. Visible/near-infrared spectra for linear and nonlinear calibrations: A case to predict soluble solids contents and pH value in peach. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2009, 4, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharabiani, V.R.; Saadati, N.; Alizadeh, F.; Szymanek, M. Non-destructive assessment of quality parameters in Javadi cv. Peach fruits using Vis/NIR spectroscopy and multiple regression analysis. Food Chem. 2025, 495, 146401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwadaira, Y.; Sekiyama, Y.; Ikehata, A. An examination of the principle of non-destructive flesh firmness measurement of peach fruit by using VIS-NIR spectroscopy. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Tian, S.; Xu, H. Identification of the geographic origin of peaches by VIS-NIR spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy and image processing technology. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y. Research on prediction of yellow flesh peach firmness using a novel acoustic real-time detection device and Vis/NIR technology. LWT 2024, 209, 116772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Guo, Z.M.; Zou, C.X.; Jiang, S.Q.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X.B. General model of multi-quality detection for apple from different origins by Vis/NIR transmittance spectroscopy. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 2582–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourdarbani, R.; Sabzi, S.; Arribas, J.I. Nondestructive estimation of three apple fruit properties at various ripening levels with optimal Vis-NIR spectral wavelength regression data. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, J.E.; Perkins-Veazie, P.; Ma, G.; Kon, T.M. Quantification and prediction with near infrared spectroscopy of carbohydrates throughout apple fruit development. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, M.; Agyekum, A.A.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Zuo, M.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Tao, F.; Shi, J.; Ouyang, Q.; et al. Quantitative detection of apple watercore and soluble solids content by near infrared transmittance spectroscopy. J. Food Eng. 2020, 279, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yao, M. A portable NIR system for nondestructive assessment of SSC and firmness of Nanguo pears. LWT 2022, 167, 113809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, A. Nondestructive determination of pear internal quality indices by visible and near-infrared spectrometry. LWT 2008, 41, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Fang, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z. Determination of soluble solids content and firmness of pears during ripening by using dielectric spectroscopy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 117, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, C.; Yang, G. Development of a non-destructive method for detection of the juiciness of pear via Vis/NIR spectroscopy combined with chemometric methods. Foods 2020, 9, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Nondestructive detection of SSC in multiple pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) cultivars using Vis-NIR spectroscopy coupled with the Grad-CAM method. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, C.; Prieto, F.; Palou, L.; Cubero, S.; Blasco, J.; Aleixos, N. New model for the automatic detection of anthracnose in mango fruits based on Vis/NIR hyperspectral imaging and discriminant analysis. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 18, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Leardi, R.; Self, G.; Luciano, G.; Pain, J.P. Multivariate calibration of mango firmness using Vis/NIR spectroscopy and acoustic impulse method. J. Food Eng. 2009, 94, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Qureshi, W.S.; Ghafoor, A.; Malik, A.; Imran, M.; Mirza, A.; Tiwana, M.I.; Alanazi, E. Towards sweetness classification of orange cultivars using short-wave NIR spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogollón, R.; Contreras, C.; da Silva Neta, M.L.; Marques, E.J.N.; Zoffoli, J.P.; de Freitas, S.T. Non-destructive prediction and detection of internal physiological disorders in ‘Keitt’ mango using a hand-held Vis-NIR spectrometer. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 167, 111251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zuo, C.; García-Martín, J.F.; Ge, Y.; Tu, K.; Peng, J.; Xiao, H.; Lan, W.; Pan, L. Non-invasive prediction of mango quality using near-infrared spectroscopy: Assessment on spectral interferences of different packaging materials. J. Food Eng. 2023, 357, 111653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liang, D.; Zhou, D.; Wang, N.; Cui, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y. Using Vis-NIR spectroscopy and multi-omics analysis to compare mango anthracnose under natural and inoculated conditions. Food Res. Int. 2025, 211, 116492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.C.; Sheng, R.; Li, H.H.; Agyekum, A.A.; Hassan, M.M.; Chen, Q.S. Development of near-infrared online grading device for long jujube. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.; Zou, X.B.; Tahir, H.E.; Hu, X.T.; Rakha, A.; Zareef, M.; Seweh, E.A.; Basheer, S. NIR spectroscopy coupled chemometric algorithms for rapid antioxidants activity assessment of Chinese dates (Zizyphus jujuba Mill.). Int. J. Food Eng. 2019, 15, 20180148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; He, Y. Building kinetic models for determining vitamin C content in fresh jujube and predicting its shelf life based on near-infrared spectroscopy. Sensors 2013, 13, 15673–15681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, S.; Ren, R.; Xue, J.; Zhao, H. Detection of soluble solids content in different cultivated fresh jujubes based on variable optimization and model update. Foods 2022, 11, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamdan, A.M. Utilizing Vis-NIR technology to generate a quality index (Q(i)) model of Barhi date fruits at the Khalal stage stored in a controlled environment. Foods 2024, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.Y.; Aheto, J.H.; Bai, J.W.; Dai, C.X.; Ren, Y.; Chang, X.H. Quantitative analysis and visualization of moisture and anthocyanins content in purple sweet potato by Vis-NIR hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process. Pres. 2021, 45, e15128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Guo, Z.; Fernandes Barbin, D.; Dai, Z.; Watson, N.; Povey, M.; Zou, X. Hyperspectral imaging and deep learning for quality and safety inspection of fruits and vegetables: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 10019–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, F.; He, Y. Identification of crack features in fresh jujube using Vis/NIR hyperspectral imaging combined with image processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, L.; Bai, B.; Tu, K.; Lan, W.; Pan, L. Study on black spot disease detection and pathogenic process visualization on winter jujubes using hyperspectral imaging system. Foods 2023, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Tao, Y.; Maimaiti, X.; Su, W.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Fan, L. Investigation on the exopolysaccharide production from blueberry juice fermented with lactic acid bacteria: Optimization, fermentation characteristics and Vis-NIR spectral model. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinelli, N.; Spinardi, A.; Di Egidio, V.; Mignani, I.; Casiraghi, E. Evaluation of quality and nutraceutical content of blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) by near and mid-infrared spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 50, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera-Fonseca, A.; Noferini, M.; Rombolá, A.D. Non-destructive assessment of highbush blueberry fruit maturity parameters and anthocyanins by using a visible/near infrared (Vis/NIR) spectroscopy device: A preliminary approach. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2016, 15, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhai, L.; Zou, Y.; Sun, C.; Jayan, H.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Jiang, S.; Cai, J.; Zou, X. Comparative study of Vis/NIR reflectance and transmittance method for on-line detection of strawberry SSC. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, N.S.; Miyashita, K.; Araki, T. Development of non-contact strawberry quality evaluation system using visible–near infrared spectroscopy: Optimization of texture qualities prediction model. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2022, 28, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabasco-Vílchez, L.; Jiménez-Jiménez, F.; Possas, A.; Brunner, M.; Fleck, C.; Pérez Rodríguez, F. Evaluating the shelf life of strawberries using a portable Vis-NIR spectrophotometer and a reflectance quality index (RQI). Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2024, 218, 113189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Mazzoni, L.; Leoni, E.; Tonanni, V.; Gagliardi, F.; Qaderi, R.; Capocasa, F.; Toscano, G.; Mezzetti, B. Application of near infrared spectroscopy for the rapid assessment of nutritional quality of different strawberry cultivars. Foods 2023, 12, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, R.; Cheng, W.; Li, H.H.; Ali, S.; Agyekum, A.A.; Chen, Q.S. Model development for soluble solids and lycopene contents of cherry tomato at different temperatures using near-infrared spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 156, 110952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Mo, X.; Ruan, S.; Yan, T.; Xing, P.; Gao, P.; Xu, W.; Ye, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; et al. Combining Vis-NIR and NIR spectral imaging techniques with data fusion for rapid and nondestructive multi-quality detection of cherry tomatoes. Foods 2023, 12, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egei, M.; Takacs, S.; Palotas, G.; Palotas, G.; Szuvandzsiev, P.; Daood, H.G.; Helyes, L.; Pek, Z. Prediction of soluble solids and lycopene content of processing tomato cultivars by Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 845317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brito, A.A.; Campos, F.; Nascimento, A.D.; Damiani, C.; da Silva, F.A.; Teixeira, G.H.D.; Cunha, L.C., Jr. Non-destructive determination of color, titratable acidity, and dry matter in intact tomatoes using a portable Vis-NIR spectrometer. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 107, 104288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Luo, X.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Huang, K.; Gao, W.; Xu, H.; Xie, L. Lycopene detection in cherry tomatoes with feature enhancement and data fusion. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, R.; Li, J. Online detection of lycopene content in the two cultivars of tomatoes by multi-point full transmission Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 211, 112813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovenzana, V.; Beghi, R.; Tugnolo, A.; Brancadoro, L.; Guidetti, R. Comparison of two immersion probes coupled with visible/near infrared spectroscopy to assess the must infection at the grape receiving area. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 146, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Feng, L.; Song, D.; Tu, K.; Peng, J.; Pan, L. Grading and sorting of grape berries using visible-near infrared spectroscopy on the basis of multiple inner quality parameters. Sensors 2019, 19, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherbiny, O.; El-Hendawy, S.; Elsayed, S.; Elwakeel, A.E.; Alebidi, A.; Yue, X.; Elmessery, W.M.; Galal, H. Incorporation of visible/near-infrared spectroscopy and machine learning models for indirect assessment of grape ripening indicators. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, R.A.; Ayepa, E.; Fometu, S.S.; Shittu, S.; Davids, J.S.; Wang, J. Mulberry fruit post-harvest management: Techniques, composition and influence on quality traits—A review. Food Control 2022, 140, 109126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, D.; Jin, H.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Lou, C. Internal quality determination of fruit with bumpy surface using visible and near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics: A case study with mulberry fruit. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 109, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, L.; Wu, D.; He, Y. Comparison of different CCD detectors and chemometrics for predicting total anthocyanin content and antioxidant activity of mulberry fruit using visible and near infrared hyperspectral imaging technique. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xu, Y.-C.; Siesler, H.W.; Han, B.-X.; Zhang, G.-Z. Hand-held near-infrared spectroscopy for authentication of fengdous and quantitative analysis of mulberry fruits. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanikazemi, M.; Abdanan Mehdizadeh, S.; Heydari, M. Non-destructive evaluation of the internal fruit quality of black mulberry (Morus nigra L.) using visible-infrared spectroscopy and genetic algorithm. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Z.; Xu, L.-L.; Tang, G.-Q.; Song, Q.-Q.; Feng, Q.-X. Rapid detection of surface color of Shatian pomelo using vis-nir spectrometry for the identification of maturity. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 9, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H.; Ference, C.; Qiu, G.; Liang, X. Rapid nondestructive detection of water content and granulation in postharvest “Shatian” pomelo using visible/near-infrared spectroscopy. Biosensors 2020, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Ference, C.M.; Liang, X.; Qiu, G. Nondestructive detection of internal flavor in ‘Shatian’ pomelo fruit based on visible/near infrared spectroscopy. HortScience 2021, 56, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, H.; Xie, L.; Rao, X. Assessing the temperature influence on the soluble solids content of watermelon juice as measured by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.; George, S.; Devassy, B.M.; George, S.N. Development of a unified framework of low-rank approximation and deep neural networks for predicting the spatial variability of SSC in ‘Spania’ watermelons using Vis/NIR hyperspectral imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 219, 113222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Daood, H.G.; Égei, M.; Takács, S.; Helyes, L. A comparative study between Vis/NIR spectroradiometer and NIR spectroscopy for the non-destructive quality assay of different watermelon cultivars. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Tian, X.; Li, J. The optimal local model selection for robust and fast evaluation of soluble solid content in melon with thick peel and large size by Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 12, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Zhang, R. Optimization of soluble solids content prediction models in ‘Hami’ melons by means of Vis-NIR spectroscopy and chemometric tools. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 102999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Ma, B.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y. Discrimination of pesticide residue levels on the Hami melon surface using multiscale convolution. Foods 2022, 11, 3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Ma, B.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Nondestructive identification of pesticide residues on the Hami melon surface using deep feature fusion by Vis/NIR spectroscopy and 1D-CNN. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 44, 13602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Liang, X.; Fan, C. Nondestructive detecting maturity of pineapples based on visible and near-infrared transmittance spectroscopy coupled with machine learning methodologies. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ren, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Liang, X. Nondestructive detection and grading of flesh translucency in pineapples with visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 192, 112029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantinantrakun, A.; Sukwanit, S.; Thompson, A.K.; Teerachaichayut, S. Nondestructive evaluation of SW-NIRS and NIR-HSI for predicting the maturity index of intact pineapples. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 195, 112141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamptey, F.P.; Amuah, C.L.Y.; Boadu, V.G.; Abano, E.E.; Teye, E. Smart classification of organic and inorganic pineapple juice using dual NIR spectrometers combined with chemometric techniques. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivichien, S.; Terdwongworakul, A.; Teerachaichayut, S. Quantitative prediction of nitrate level in intact pineapple using Vis–NIRS. J. Food Eng. 2015, 150, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fruit Morphological Feature | Typical Examples | Recommended Optical Mode | Common Preprocessing Methods | Suitable Modeling Strategies | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin rind (<1 mm), small size | Grape, blueberry, cherry | Transmittance or reflectance | SG smoothing, standard normalization, SNV, or MSC to reduce scatter | PLSR, MLR | [78,79,80,81] |
| Thin-to-medium rind (1–3 mm), medium size | Apple, pear, orange | Transmittance or reflectance | SNV or MSC to reduce scatter, SG + 1st derivative for baseline shift removal | PLSR, SVR | [30,54,73,82] |
| Thick rind (>3 mm), large size | Watermelon, pomelo, pineapple | Transmittance or interactance | MSC + detrend to reduce scatter and baseline drift, SG smoothing + 2nd derivative to enhance weak absorbance bands | CNN, PLSR, SVR | [24,83,84,85] |
| Presence of pits/kernels/cavities | Peach, mango, cherry | Interactance or reflectance | SNV to reduce scatter, SG smoothing + 2nd derivative for feature enhancement | PLSR, ANN, RF | [86,87] |
| Significant non-uniform distribution of quality attribute | Strawberry, melon | Multi-point reflectance or transmittance | Model the local areas, respectively, and perform weighted fusion, MSC, SNV | Local PLSR, CNN | [28,88] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, X.; Cai, J.; Wang, A. Nondestructive Quality Detection of Characteristic Fruits Based on Vis/NIR Spectroscopy: Principles, Systems, and Applications. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202167
Wang C, Li X, Zhang Z, Luo X, Cai J, Wang A. Nondestructive Quality Detection of Characteristic Fruits Based on Vis/NIR Spectroscopy: Principles, Systems, and Applications. Agriculture. 2025; 15(20):2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202167
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Xiaonan Li, Zijuan Zhang, Xuan Luo, Jianrong Cai, and Aichen Wang. 2025. "Nondestructive Quality Detection of Characteristic Fruits Based on Vis/NIR Spectroscopy: Principles, Systems, and Applications" Agriculture 15, no. 20: 2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202167
APA StyleWang, C., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Luo, X., Cai, J., & Wang, A. (2025). Nondestructive Quality Detection of Characteristic Fruits Based on Vis/NIR Spectroscopy: Principles, Systems, and Applications. Agriculture, 15(20), 2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202167