Stratified Nitrogen Application Enhances Subsoil Carbon Sequestration via Enzyme-Mediated Pathways in Straw-Incorporated Croplands of North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Determination
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
2.4.1. CPMI Calculation
2.4.2. C Input Calculation
2.4.3. Calculation of SQI
2.4.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SOC and TN Content
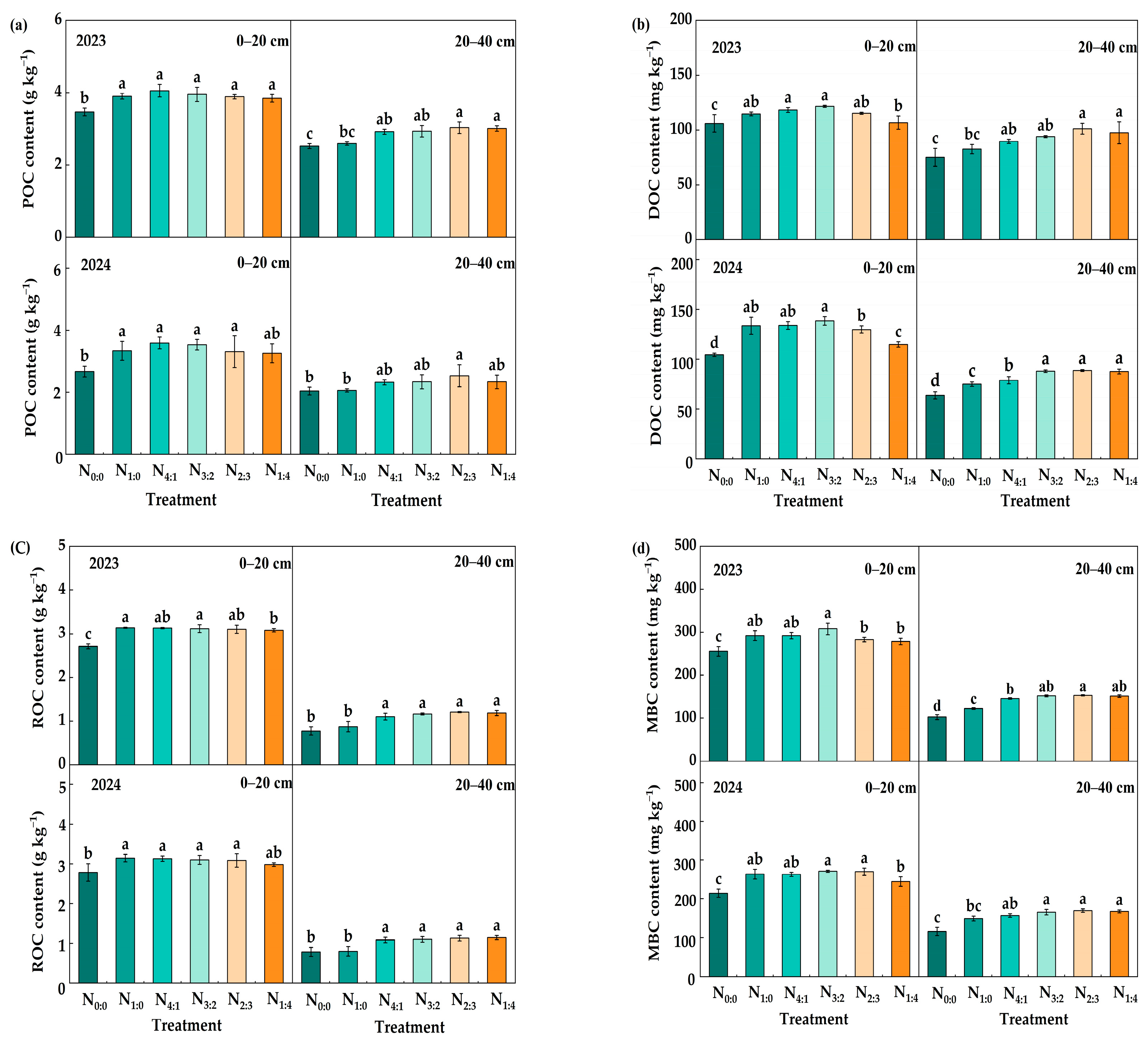
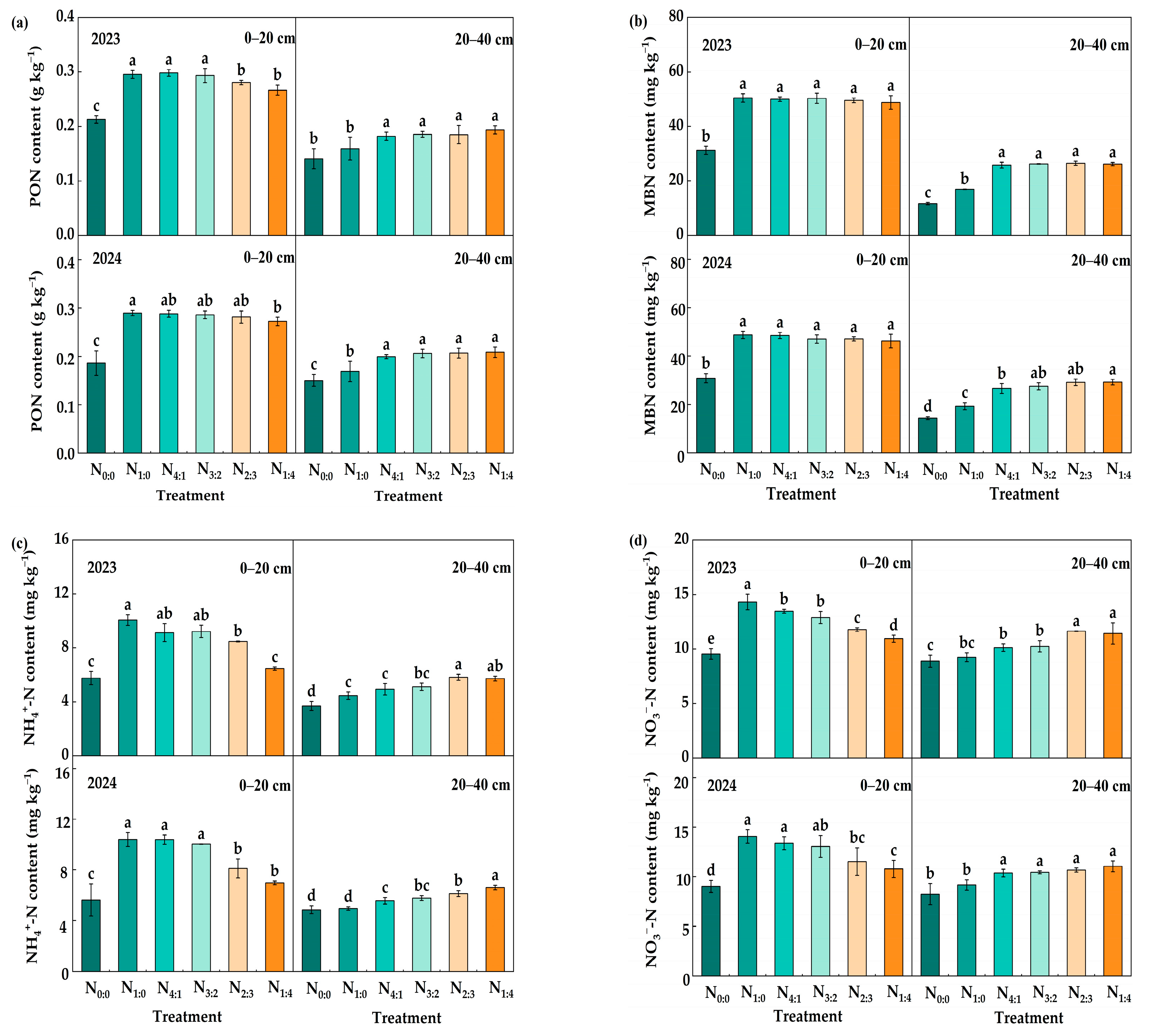
3.2. Labile Organic C and N Fractions
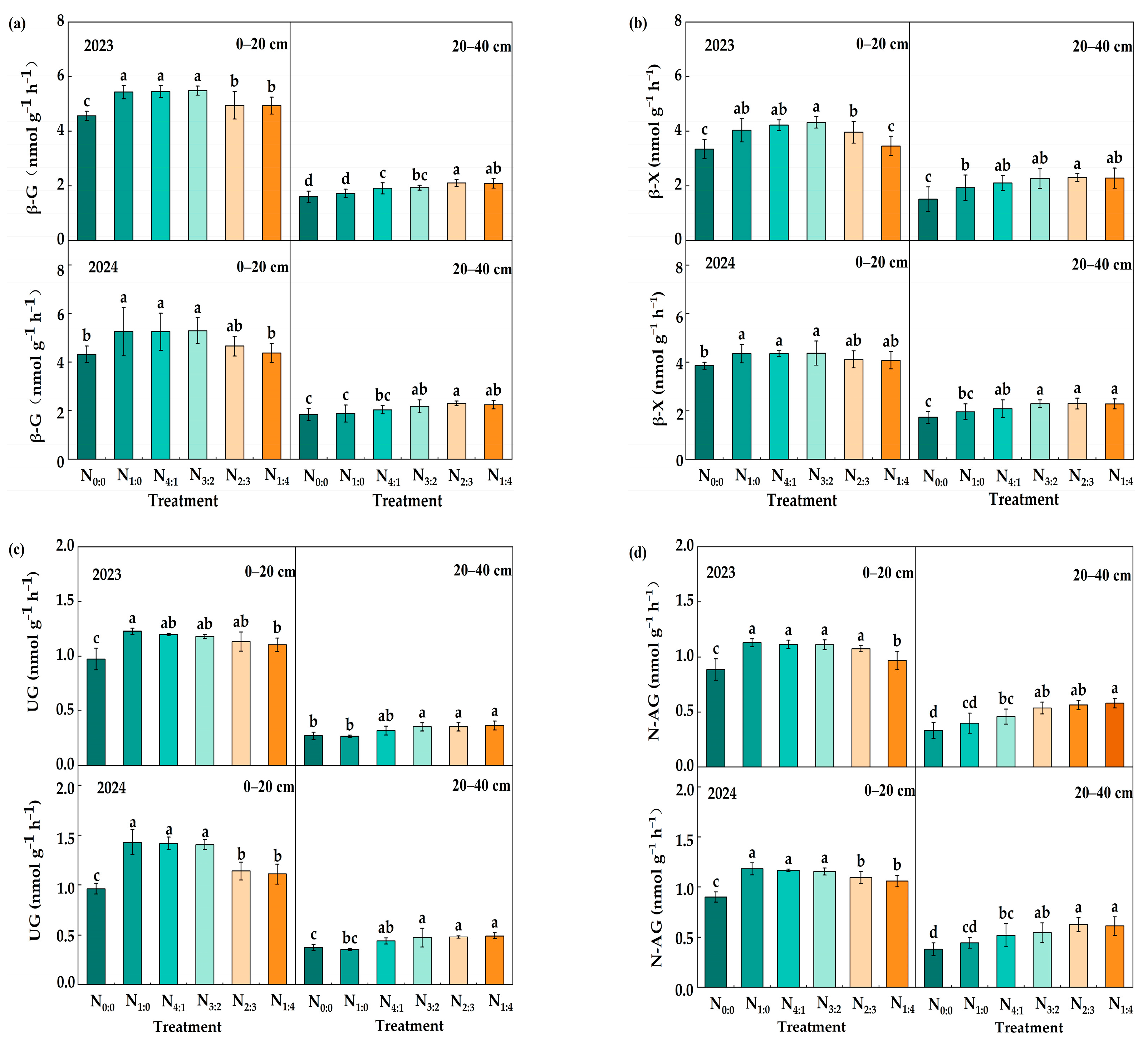
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activities
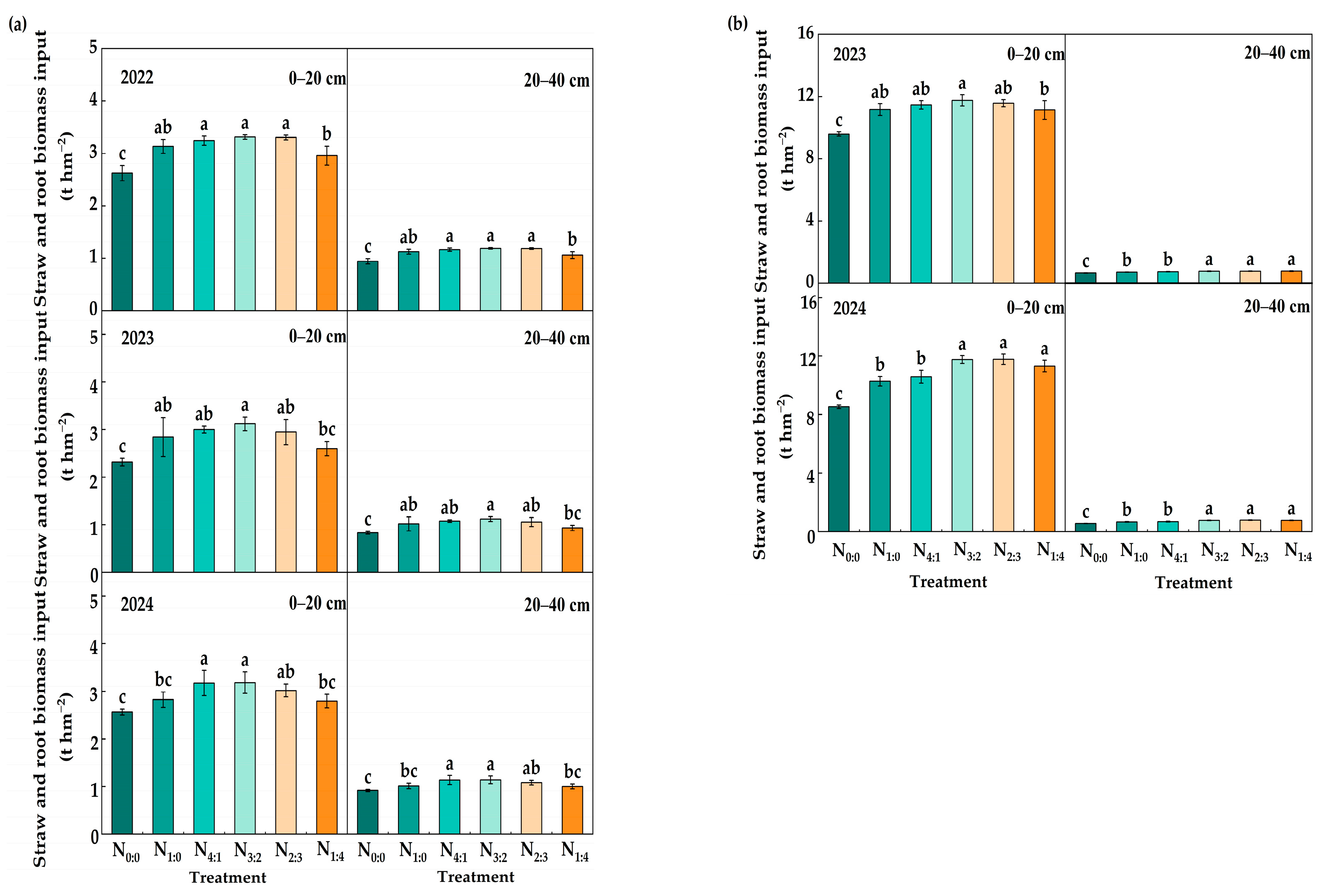
3.4. The Amount of Straw and Root Returning to the Field
3.5. Stoichiometric Ratio
3.6. Soil C Pool Management Index and Quality Index
3.7. Correlation Between Indicators
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Stratified Application of N Fertilizer on SOC Pools
4.2. Effects of Stratified Application of N Fertilizer on N Pools
4.3. Effect of Stratified Application of N Fertilizer on Soil Enzyme Activities
4.4. Effects of Stratified Application of N Fertilizer on CPMI and SQI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; He, C.H.; Chang, S.X.; Chen, X.L.; An, S.S.; Wang, D.W.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, P. Fertilization and tillage influence on soil organic carbon fractions: A global meta-analysis. Catena 2024, 246, 108404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, L.C.; Qiu, T.Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.X.; Yi, J.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, C.; Sardans, J.; et al. Crop residue return achieves environmental mitigation and enhances grain yield: A global meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.; Hati, K.M.; Dalal, R.C.; Dang, Y.P.; Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W. Soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a Vertisol following 50 years of no-tillage, crop stubble retention and nitrogen fertilization. Geoderma 2020, 358, 113996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, I.; Hooker, D.C.; Deen, B.; Janovicek, K.; Van Eerd, L.L. Long-term effects of crop rotation, tillage, and fertilizer nitrogen on soil health indicators and crop productivity in a temperate climate. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, C.; Cai, G.; Sauheitl, L.; Xiao, M.L.; Shibistova, Q.; Ge, T.; Guggenberger, G. Meta-analysis on the effects of types and levels of N, P, and K fertilization on organic carbon in cropland soils. Geoderma 2023, 437, 116580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.H.; Yao, X.B.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.J.; Qi, J.Y. Effects of Deep Application of Fertilizer on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Functions in Rice Paddies. Agronomy 2025, 15, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.M.; Xu, X.N.; Xia, J.Y. Different impacts of external ammonium and nitrate addition on plant growth in terrestrial ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.Y.; Liu, X.Y. Combined application of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers increases soil organic carbon storage in cropland soils. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 168, 127607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.J.; Song, J.H.; Xu, W.; Gao, G.X.; Bai, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.H.; Yu, Q.; Hao, J.Q.; Yang, G.H.; Ren, G.X.; et al. Straw return with fertilizer improves soil CO2 emissions by mitigating microbial nitrogen limitation during the winter wheat season. Catena 2024, 241, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Fornara, D.A.; Yang, W.Q.; Peng, Y.; Peng, C.H.; Liu, Z.L.; Wu, F.Z. Influence of multiple global change drivers on terrestrial carbon storage: Additive effects are common. Ecolo Lett. 2017, 20, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cao, J.J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Moorhead, D.L.; Bardgett, R.D.; Fanin, N.; Nottingham, A.T.; Zheng, X.H.; Chen, J. Soil extracellular enzymes as drivers of soil carbon storage under nitrogen addition. Biol. Rev. 2025, 100, 1716–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.F.; Sun, J.T.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Wang, C.Y. Influence of nitrogen addition on the changes in nitrogen and carbon fractions in soil profiles of wheat fields. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anning, D.K.; Ghanney, P.; Qiu, H.Z.; Abalori, T.A.; Zhang, C.H.; Luo, C.Y. Stimulation of soil organic matter fractions by maize straw return and nitrogen fertilization in the Loess Plateau of Northwest China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 191, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yao, Y.L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, B.; Tian, Y.H.; Yin, B.; Zhu, Z.L. Integration of urea deep placement and organic addition for improving yield and soil properties and decreasing N loss in paddy field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassink, J.; Whitmore, A.P.; Kubát, J. Size and density fractionation of soil organic matter and the physical capacity of soils to protect organic matter. Eur. J. Agron. 1997, 7, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.M.; Cao, M.K.; Liu, J.Y.; Tao, B. Potential and sustainability for carbon sequestration with improved soil management in agricultural soils of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battye, W.; Aneja, V.P.; Schlesinger, W.H. Is nitrogen the next carbon? Earths Future 2017, 5, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Z.; Zhang, L.L.; Lin, Y.D.; Wen, D.Z.; Hou, E.Q. Nitrogen availability mediates soil organic carbon cycling in response to phosphorus supply: A global meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 185, 109158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.Z.; Wang, D.J.; Yang, L.Z. Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure on labile organic matter fractions in a paddy soil. Biolog. Fert. Soils. 2007, 44, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, R.; Vanlauwe, B.; Chivenge, P.; Six, J. Trade-offs between the short- and long-term effects of residue quality on soil C and N dynamics. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, H.; Han, M.; Yang, L. Soil metagenomics reveals the effect of nitrogen on soil microbial communities and nitrogen-cycle functional genes in the rhizosphere of Panax ginseng. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1411073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.F.; Qiao, Y.C.; Wanek, W.; Moorhead, D.L.; Cui, Y.X.; Peng, Y.J.; Song, L.Q.; Hu, B.Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.L. Nitrogen input decreases microbial nitrogen use efficiency in surface soils of a temperate forest in northeast China. Geoderma 2025, 453, 117159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Pang, S.Y.; Li, X.F.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, J.W.; Ma, R.L.; Lin, X.; Wang, D. Nitrogen losses trade-offs through layered fertilization to improve nitrogen nutrition status and net economic benefit in wheat-maize rotation system. Field Crops Res. 2024, 312, 109406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, L.X.; Li, T.; Dou, Y.X.; Qiao, J.B.; Wang, Y.Q.; An, S.S.; Chang, S.X. Nitrogen fertilization weakens the linkage between soil carbon and microbial diversity: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 6446–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Zhang, H.P.; Wang, Q.X.; Zhu, W.D.; Kang, Y.H. Soil extracellular enzyme activity linkage with soil organic carbon under conservation tillage: A global meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 155, 127135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.K.; Fang, Y.Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, S.L.; Li, Y.F.; Li, B.Z.; Gao, W.; Yuan, H.Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. Stoichiometric regulation of priming effects and soil carbon balance by microbial life strategies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 169, 108669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. A theoretical model of litter decay and microbial interaction. Ecol. Monogr. 2006, 76, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.C.; Wood, M.; Jarvis, S.C. A microplate fluorimetric assay for the study of enzyme diversity in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.T.; Zhang, X.C.; Li, Y.N.; Jiao, Y.P.; Fan, L.C.; Jiang, Y.J.; Qu, C.Y.; Filimonenko, E.; Jiang, Y.H.; Tian, X.H.; et al. Nitrogen fertilizer builds soil organic carbon under straw return mainly via microbial necromass formation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 188, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Pang, S.Y.; Li, X.F.; Liu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, X.; Gu, S.B.; Wang, D. Layered nitrogen fertilization regulates root morphology to promote synergistic nitrogen and phosphorus absorption in maize (Zea mays L.). Field Crops Res. 2025, 322, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.J.; Li, C.F.; Cao, G. Effects of nitrogen deep placement on chemical properties of soil organic matter and extracellular enzyme activity in no-tillage paddy fields. J. Agron. Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 621–630. [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.G.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil quality-a critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Ma, J.W.; Li, Y.Q.; Jia, Q.M.; Shen, X.Y.; Xia, X.H. Spatiotemporal variations in the soil quality of agricultural land and its drivers in China from 1980 to 2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Z.; Lu, R.J.; Wu, Y.Q.; Zhao, T.J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, L. Spatiotemporal dynamics and influencing factors of soil quality in aeolian desertified lands of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Li, H.; Chai, X.T.; Zhao, S.; Li, L.W.; Jia, L.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, G.Y. Effects of fertilization with subsoiling of maize and limited irrigation of wheat on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and enzymes activities. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Y. Effects of Location and Rate of Mechanized Application of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Fertilizers on Growth and Soil Properties of Maize. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.C.; Zhang, X.F.; Xin, X.L.; Yang, W.L.; Zhu, A.N.; Yang, J.; Li, M.R. Soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions as affected by straw and nitrogen management on the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Song, Z.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Yu, C.X.; Fang, Y.Y.; Hartley, I.P.; Chen, J.; Xia, S.P.; et al. Patterns and drivers of soil organic carbon fractions and persistence in coastal wetlands of China. Catena 2025, 257, 109186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, J.N.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.X.; Gao, Y.H. The Effects of Localized Plant-Soil-Microbe Interactions on Soil Nitrogen Cycle in Maize Rhizosphere Soil under Long-Term Fertilizers. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.G.; Hu, X.; Ma, J.W.; Ye, J.; Sun, W.C.; Wang, Q.; Lin, H. Effects of long-term organic material applications on soil carbon and nitrogen fractions in paddy fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, L.H.; Chu, J.C.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhao, J.; Zang, H.D.; Yang, Y.D.; Zeng, Z.H. Improving soil quality and wheat yield through diversified crop rotations in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Bao, L.; Zhou, J. Crop yields and soil organic carbon fractions as influenced by straw incorporation in a rice-wheat cropping system in southeastern China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 112, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Jahangir, M.M.R.; Jahiruddin, M.; Islam, M.R.; Bokhtiar, S.M.; Islam, K.R. Reduced tillage with residue retention improves soil labile carbon pools and carbon lability and management indices in a seven-year trial with wheat-mung bean-rice rotation. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, X.; Sainju, M.U.; Zhao, F.Z. Soil carbon fractions in response to straw mulching in the Loess Plateau of China. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2018, 54, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.L.; Zhang, E.H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.H.; Liu, C.W.; Wang, T.T.; Yin, H. Effects of irrigation and N supply levels on soil organic carbon, total nitrogen and grain yield of spring wheat on no-tillage farmland with standing stubble. Acta Prat. Sci. 2013, 22, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P. A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 90, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ni, B.; Xu, X.C.; Yang, X.; Meng, F.Q. Impacts of Nitrogen Application on Ammonia Volatilization During Maize Season in Northern China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 5176–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.R.; Li, Z.Z.; Amelung, F.; Zhang, H.L.; Lal, R.; Bol, R.; Bian, X.M.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.G.; Li, F.M.; et al. Soil carbon accrual and crop production enhanced by sustainable subsoil management. Nat. Geosci. 2025, 18, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Li, S.H.; Guo, L.G.; Cao, C.G.; Li, C.F.; Zhai, Z.B.; Zhou, J.Y.; Mei, Y.M.; Ke, H.J. Advantages of nitrogen fertilizer deep placement in greenhouse gas emissions and net ecosystem economic benefits from no-tillage paddy fields. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 263, 121322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhu, X.F. The soil microbial carbon pump as a new concept for terrestrial carbon sequestration. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, F.A.; Zhu, B.; Cheng, W.X. Root effects on soil organic carbon: A double-edged sword. New Phytol. 2020, 230, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Li, J.M. Are there links between nutrient inputs and the response of microbial carbon use efficiency or soil organic carbon? A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 201, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Schimel, J.P.; Jastrow, J.D. The importance of anabolism in microbial control over soil carbon storage. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.G.; Chen, Y.L.; Ma, J.P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Pang, D.D.; Li, X.B. Soil microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation constraints soil organic carbon stability in arid and semi-arid grasslands. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Chavez, H.M.; Fierer, N.; van Bodegom, P.M. Global drivers and patterns of microbial abundance in soil. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Hu, N.; Li, Z.F.; Feng, L.S.; Zhang, W.D.; Preez, G.D.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, D.C.; Lu, S.B.; Chang, S.X.; et al. Soil enzyme profile analysis for indicating decomposer micro-food web. IMeta 2024, 3, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, P.P.; Sun, H.; Jia, X.X.; Zhang, C.C.; Liu, S.Z.; Shao, M.A. Vertical patterns and controlling factors of soil nitrogen in deep profiles on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2022, 215, 106318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Sun, X.; Du, L.N.; Sun, W.L.; Wang, X.L.; Gaafar, A.R.Z.; Zhang, P.; Cai, T.; Liu, T.N.; Jia, Z.K.; et al. Appropriate fertilization increases carbon and nitrogen sequestration and economic benefit for straw-incorporated upland farming. Geoderma 2024, 441, 116743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Evans, S.E.; Friesen, M.L.; Tiemann, L.K. Root exudates shift how N mineralization and N fixation contribute to the plant-available N supply in low fertility soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, J.D. Microbial extracellular enzymes in biogeochemical cycling of ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Dippold, M.A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Razavi, B.S. Spatial pattern of enzyme activities depends on root exudate composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 133, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; Calderón, F.; Jackson, L.E. Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, C.J.; Lacey, C.; Armstrong, S. The synchrony of cover crop decomposition, enzyme activity, and nitrogen availability in a corn agroecosystem in the Midwest United States. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Y.; Dolfing, J.; Guo, Z.Y.; Chen, R.R.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.P.; Lin, X.G.; Feng, Y.Z. Important ecophysiological roles of non-dominant in plant residue decomposition, especially in less fertile soils. Microbiome 2021, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.L.; Zhao, L.; Tan, W.B.; Wang, G.A.; Xi, B.D. Discrepant responses of soil organic carbon dynamics to nitrogen addition in different layers: A case study in an agroecosystem. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Cui, Z.L.; Zhou, R.R.; Zhang, W.S.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Yue, S.C.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. Soil organic carbon thresholds control fertilizer effects on carbon accrual in croplands worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Z.T.; Wang, L.A.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, M.Y.; Jin, W.; Hu, W.; Meng, Y.L.; Yang, H.S.; Zhou, Z.G. Enhancement joint fertilization efficacy of straw and nitrogen fertilizer on soil quality and seedcotton yield for sustainable cotton farming. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2025, 20, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhou, J.B.; Xu, X.P.; Zhu, Y.J. Long-term straw mulching with nitrogen fertilization increases nutrient and microbial determinants of soil quality in a maize–wheat rotation on China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Ma, Y.Q.; He, W.H.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Chen, H.Q.; Fan, M.S. Soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality after 13-year of organic and nitrogen fertilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Y.; Lu, S.X.; Wang, C.G.; Mu, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, X.D. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities in response to tillage practices in the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Yang, H.L.; Zhao, M.L.; Monaco, T.A.; Rong, Y.P.; Huang, D.; Song, Q.; Zhao, K.; Wang, D.P. Soil extracellular enzyme activities and the abundance of nitrogen-cycling functional genes responded more to N addition than P addition in an Inner Mongolian meadow steppe. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


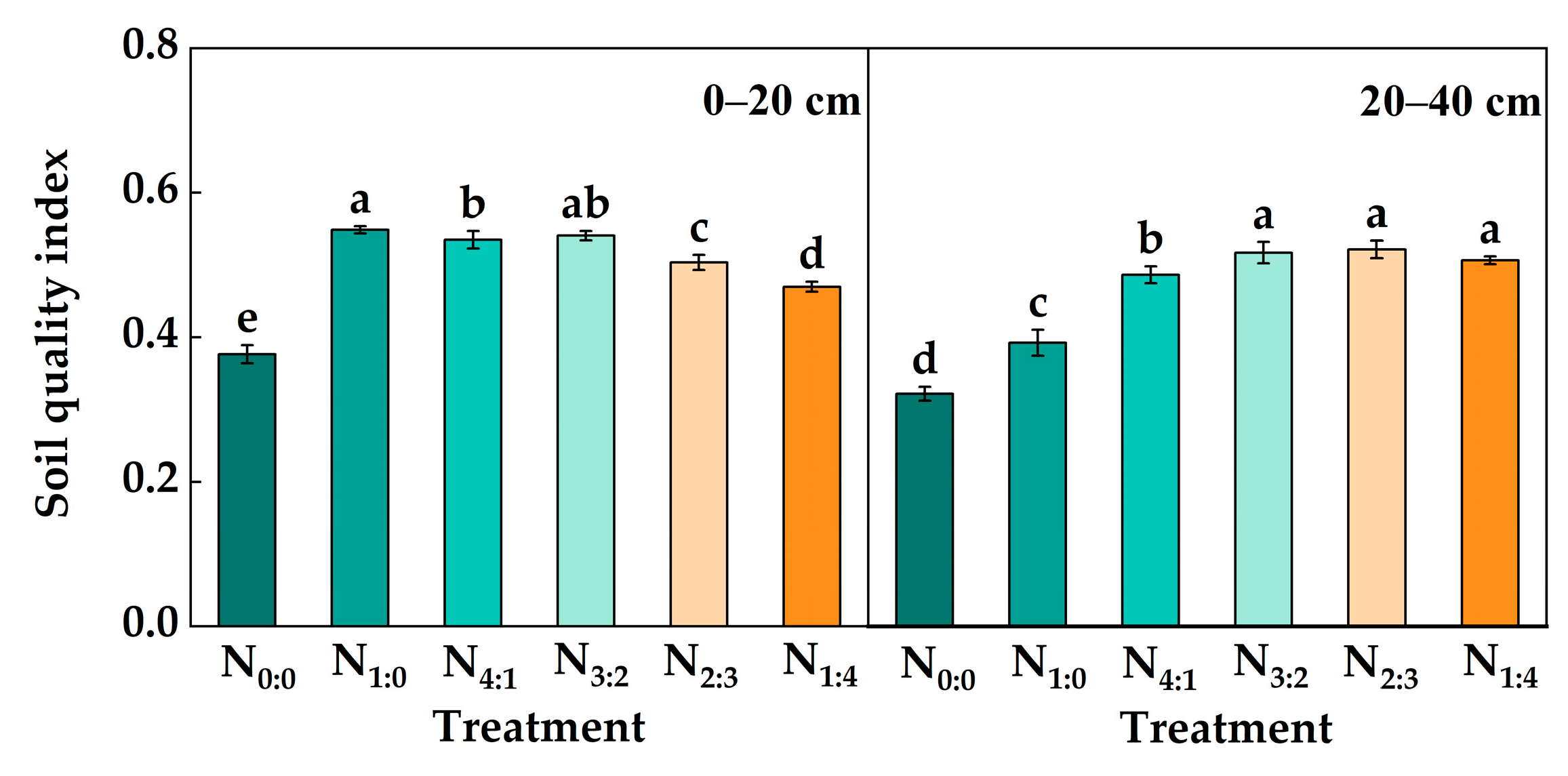
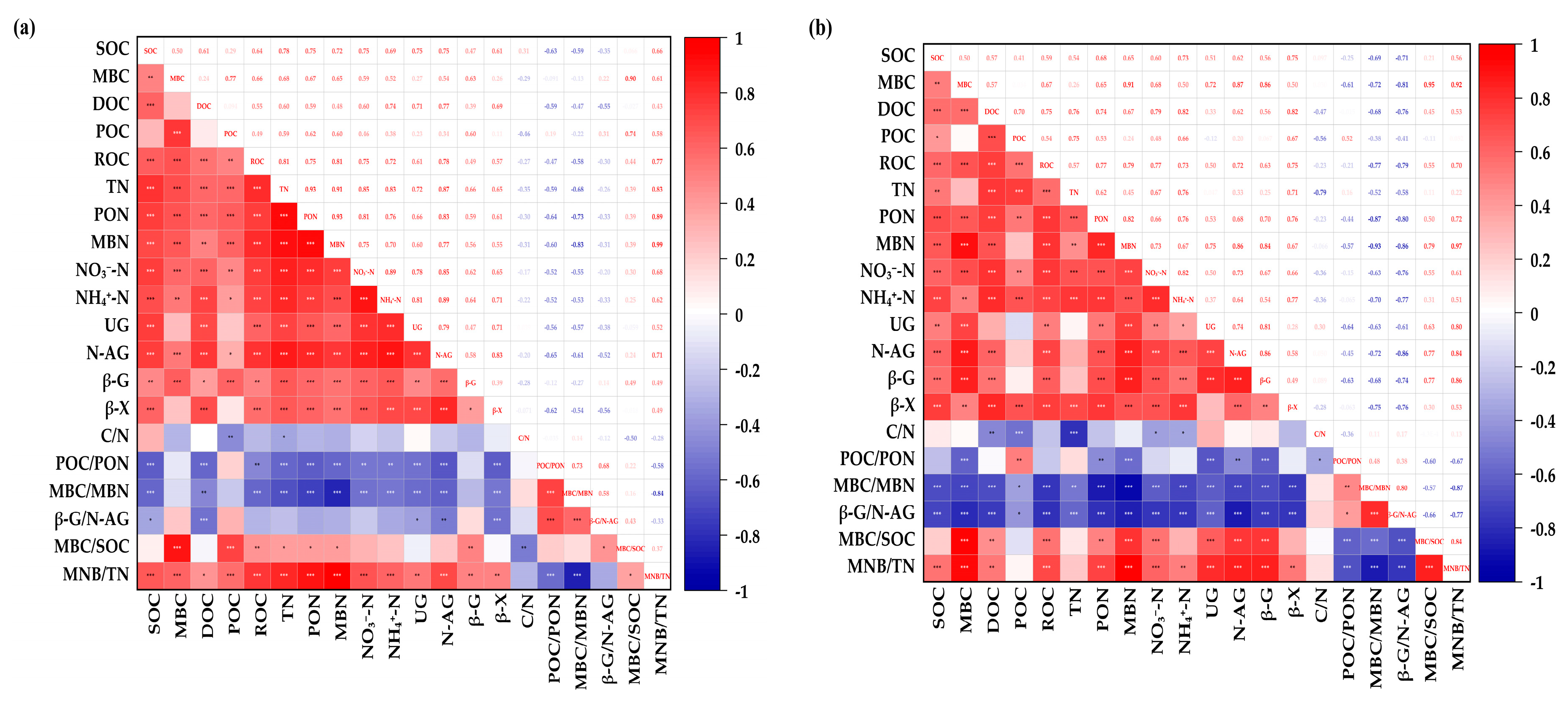
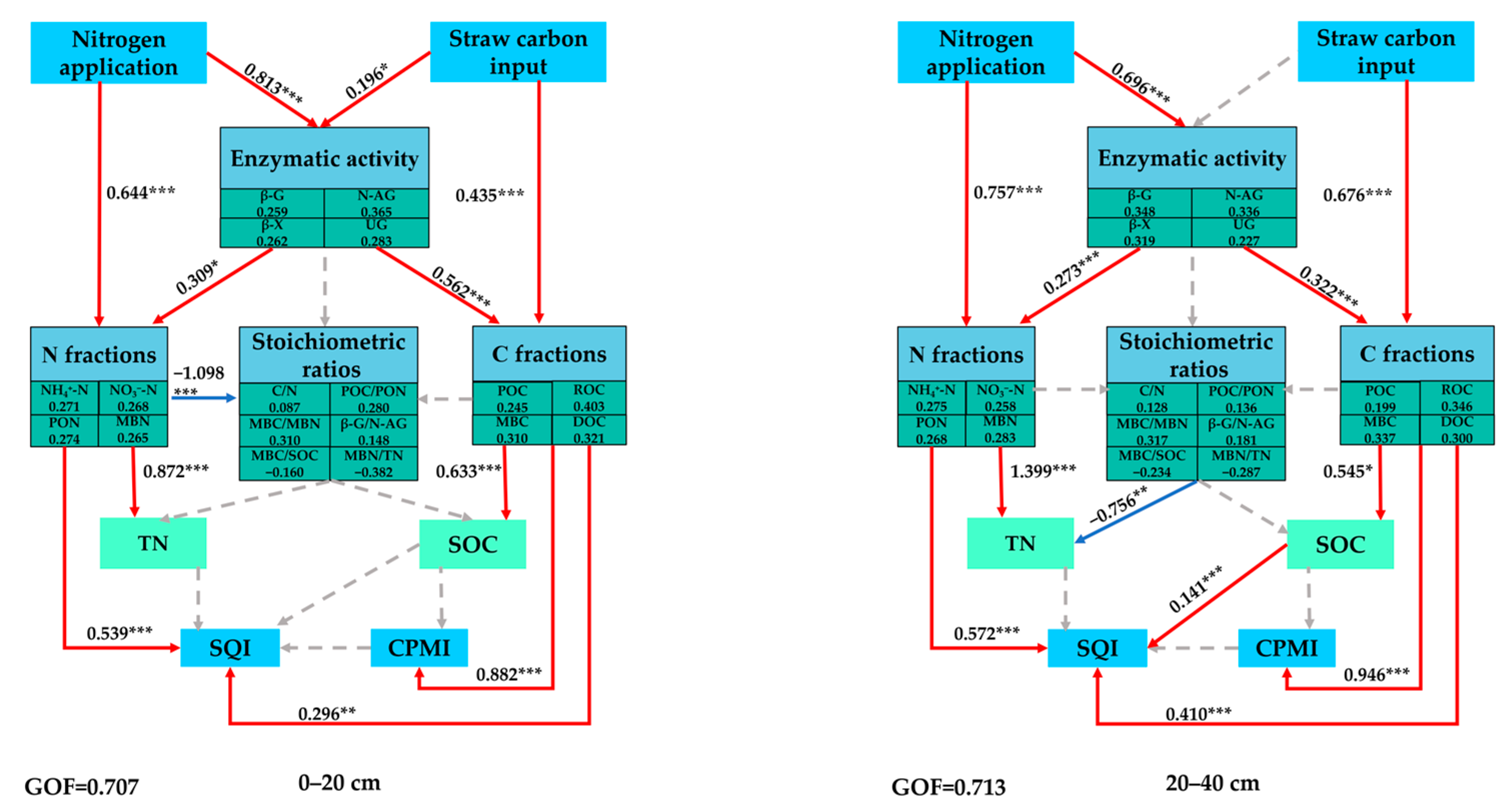
| Treatment | Proportion | Application of Pure N Amount at 0–20 cm (kg hm−2) | Application of Pure N Amount at 20–40 cm (kg hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N0:0 | 0:0 | 0 | 0 |
| N1:0 | 1:0 | 225 | 0 |
| N4:1 | 4:1 | 180 | 45 |
| N3:2 | 3:2 | 135 | 90 |
| N2:3 | 2:3 | 90 | 135 |
| N1:4 | 1:4 | 45 | 180 |
| Year | Treatment | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPI | A | AI | CPMI(%) | CPI | A | AI | CPMI(%) | ||
| 2023 | N0:0 | 1.000 0.000 d | 0.362 0.019 c | 1.000 0.000 c | 100.00 0.00 b | 1.000 0.000 b | 0.171 0.029 b | 1.000 0.000 b | 100.00 0.00 b |
| N1:0 | 1.090 0.019 ab | 0.390 0.021 b | 1.078 0.058 b | 117.48 5.02 a | 1.002 0.042 b | 0.199 0.042 b | 1.161 0.246 b | 115.66 19.74 b | |
| N4:1 | 1.099 0.011 a | 0.389 0.006 b | 1.076 0.018 b | 118.19 0.92 a | 1.052 0.032 ab | 0.248 0.029 a | 1.446 0.168 a | 151.81 13.91 a | |
| N3:2 | 1.104 0.018 a | 0.385 0.005 b | 1.065 0.014 b | 117.56 1.19 a | 1.080 0.033 a | 0.255 0.010 a | 1.487 0.056 a | 160.48 3.60 a | |
| N2:3 | 1.034 0.021 c | 0.417 0.006 a | 1.152 0.017 a | 119.15 4.13 a | 1.082 0.043 a | 0.269 0.016 a | 1.567 0.092 a | 169.29 3.62 a | |
| N1:4 | 1.068 0.010 b | 0.395 0.011 ab | 1.091 0.030 b | 116.48 2.28 a | 1.077 0.035 a | 0.262 0.025 a | 1.531 0.148 a | 164.53 11.09 a | |
| 2024 | N0:0 | 1.000 0.000 b | 0.374 0.034 a | 1.000 0.000 a | 100.00 0.00 b | 1.000 0.000 c | 0.175 0.031 b | 1.000 0.000 b | 100.00 0.00 b |
| N1:0 | 1.106 0.055 a | 0.380 0.033 a | 1.051 0.091 a | 115.94 6.16 a | 1.016 0.024 bc | 0.176 0.034 b | 1.027 0.196 b | 104.06 17.99 b | |
| N4:1 | 1.106 0.043 a | 0.388 0.037 a | 1.071 0.102 a | 118.25 6.66 a | 1.021 0.022 bc | 0.251 0.021 a | 1.463 0.125 a | 149.29 11.86 a | |
| N3:2 | 1.119 0.022 a | 0.378 0.016 a | 1.044 0.044 a | 116.81 3.72 a | 1.067 0.032 a | 0.241 0.013 a | 1.407 0.077 a | 150.12 10.70 a | |
| N2:3 | 1.110 0.013 a | 0.375 0.027 a | 1.036 0.075 a | 114.96 8.42 a | 1.073 0.025 a | 0.248 0.015 a | 1.444 0.089 a | 154.99 11.12 a | |
| N1:4 | 1.057 0.058 b | 0.383 0.021 a | 1.058 0.058 a | 111.66 0.04 a | 1.060 0.031 ab | 0.256 0.023 a | 1.493 0.131 a | 158.10 9.94 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, R.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Men, J.; Li, Y.; Peng, Z. Stratified Nitrogen Application Enhances Subsoil Carbon Sequestration via Enzyme-Mediated Pathways in Straw-Incorporated Croplands of North China Plain. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192098
Wang B, Wang Y, Li J, Hou R, Liu Y, Fu X, Men J, Li Y, Peng Z. Stratified Nitrogen Application Enhances Subsoil Carbon Sequestration via Enzyme-Mediated Pathways in Straw-Incorporated Croplands of North China Plain. Agriculture. 2025; 15(19):2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192098
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bin, Yanqun Wang, Jingyu Li, Rui Hou, Yulong Liu, Xin Fu, Jie Men, Yingchun Li, and Zhengping Peng. 2025. "Stratified Nitrogen Application Enhances Subsoil Carbon Sequestration via Enzyme-Mediated Pathways in Straw-Incorporated Croplands of North China Plain" Agriculture 15, no. 19: 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192098
APA StyleWang, B., Wang, Y., Li, J., Hou, R., Liu, Y., Fu, X., Men, J., Li, Y., & Peng, Z. (2025). Stratified Nitrogen Application Enhances Subsoil Carbon Sequestration via Enzyme-Mediated Pathways in Straw-Incorporated Croplands of North China Plain. Agriculture, 15(19), 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192098





