Effects of Different Operation Years of Photovoltaic Power Stations on Vegetation and Soil Characteristics in Temperate Deserts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Study Area
2.2. Site Selection and Experimental Design
2.2.1. Site Selection
2.2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.3. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
2.3.1. Species Importance Value
2.3.2. Biodiversity
2.3.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
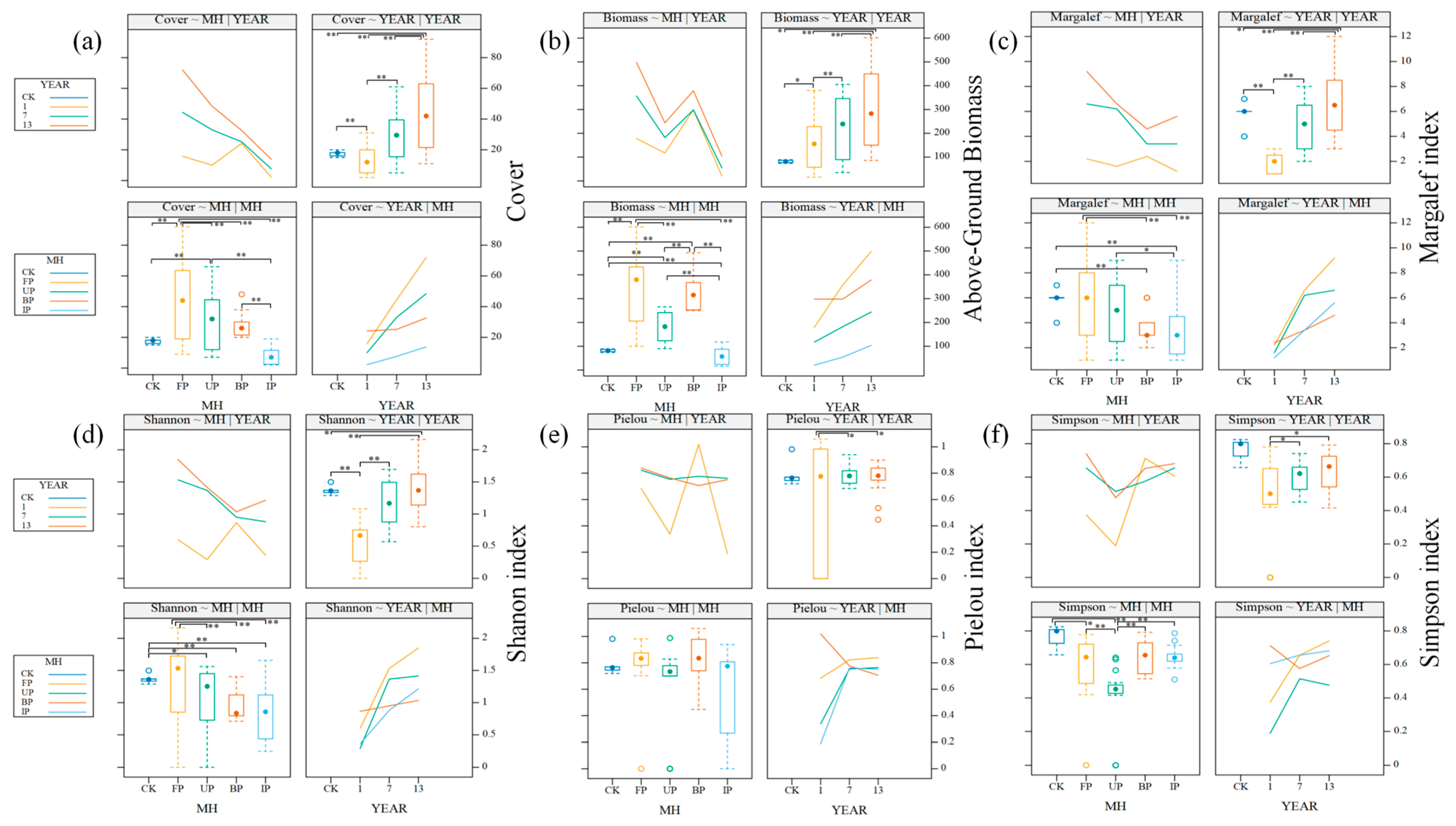
3.1. Community Characteristics
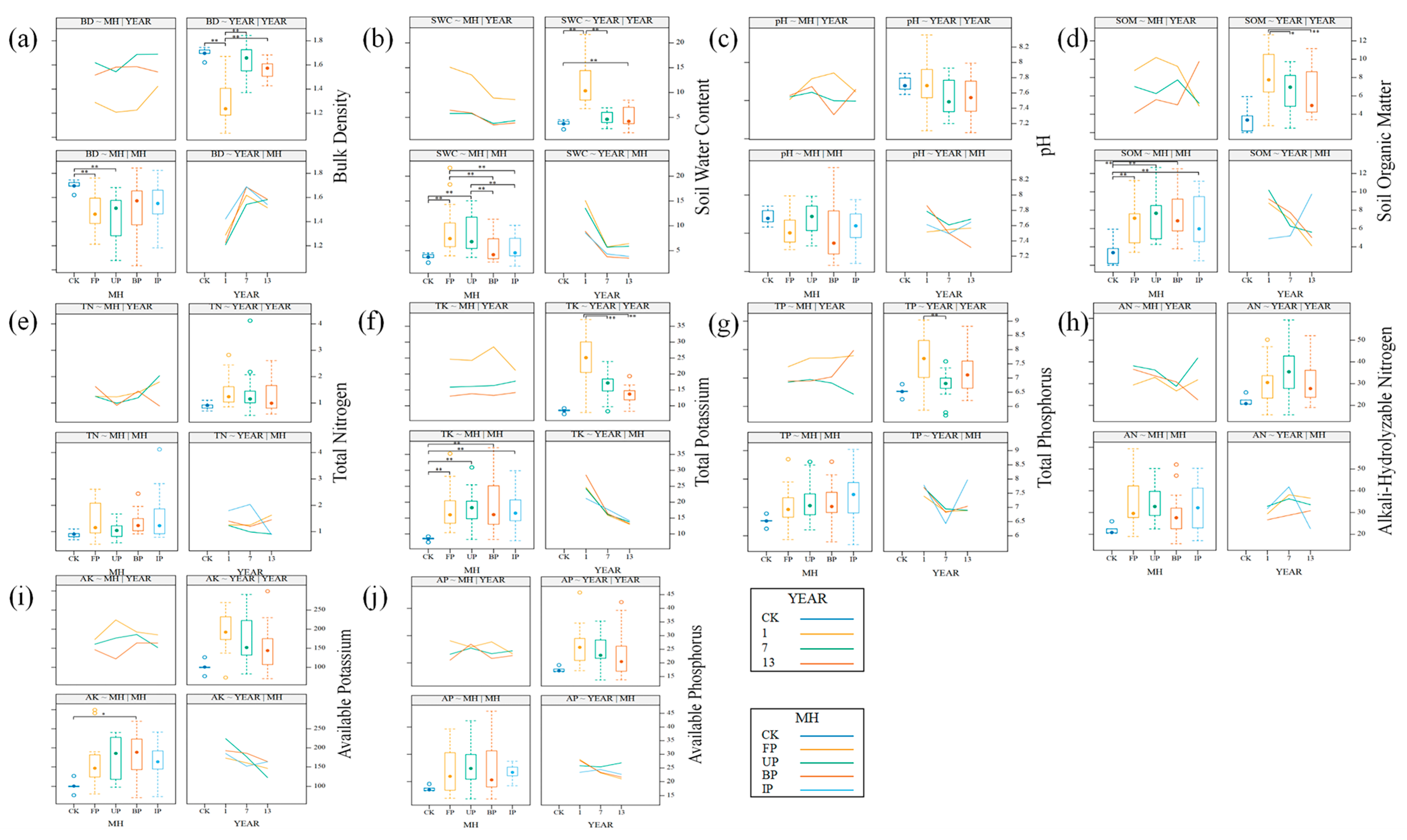
3.2. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
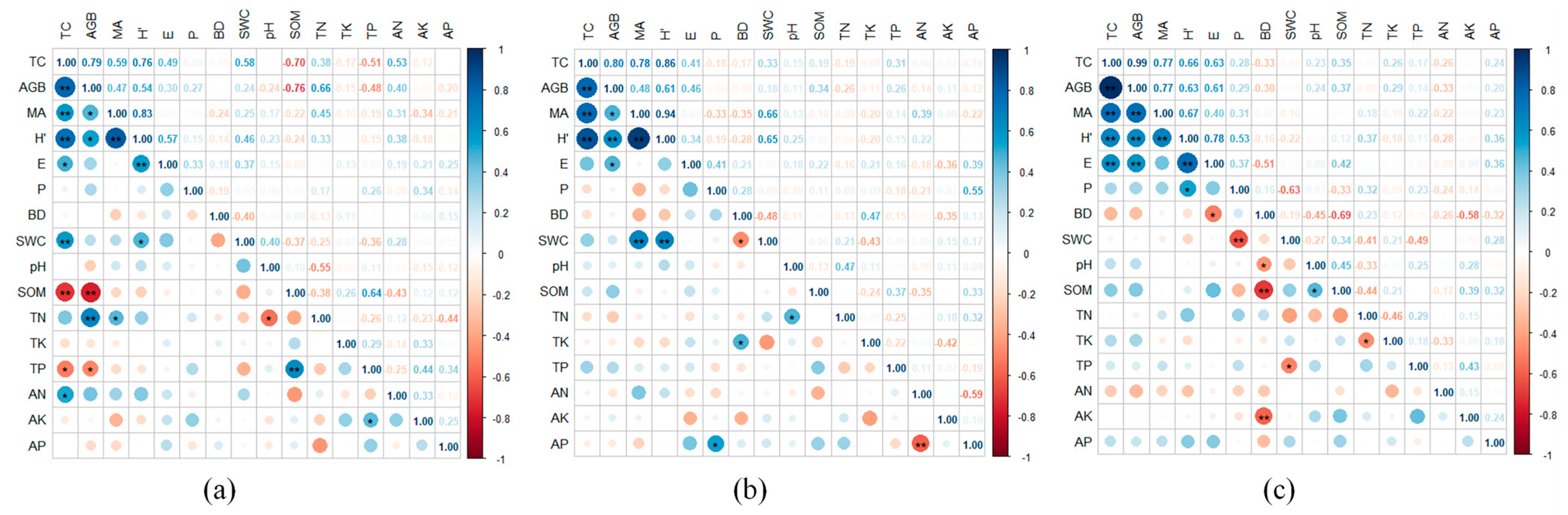
3.3. Relationship Between Community Characteristics and Soil Physical and Chemical Factors
3.3.1. Relevance Analysis
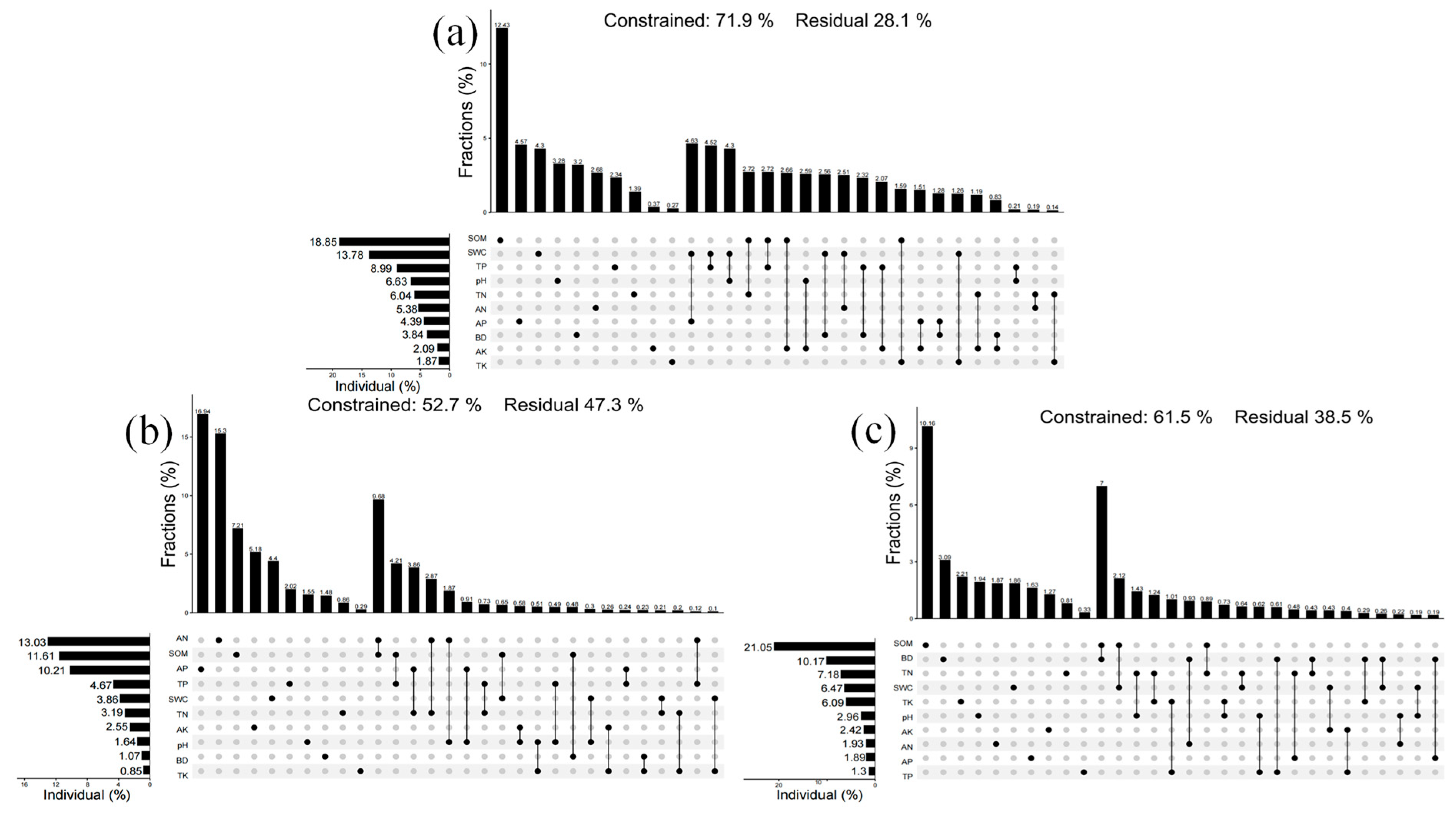
3.3.2. Variance Decomposition Analysis
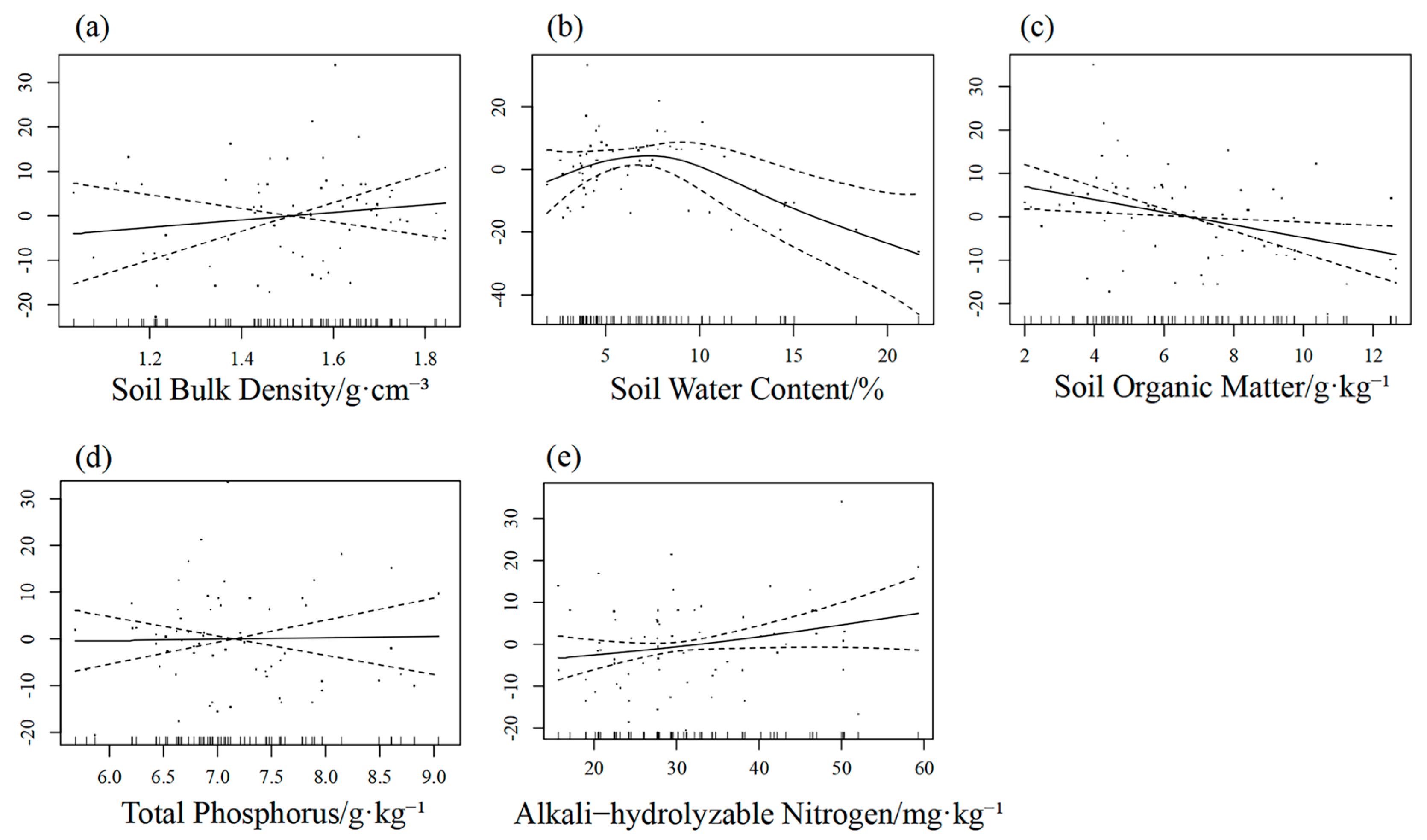
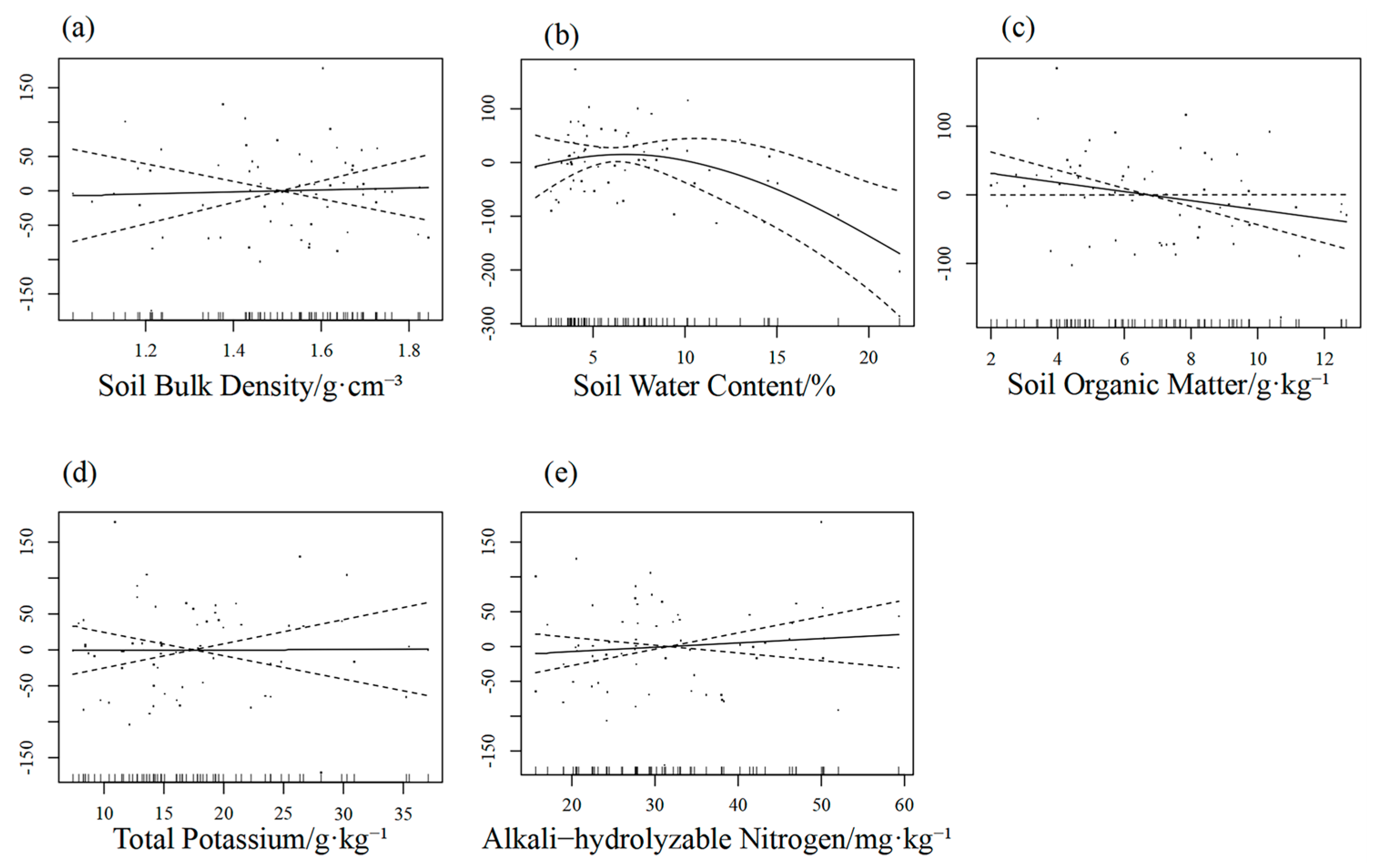
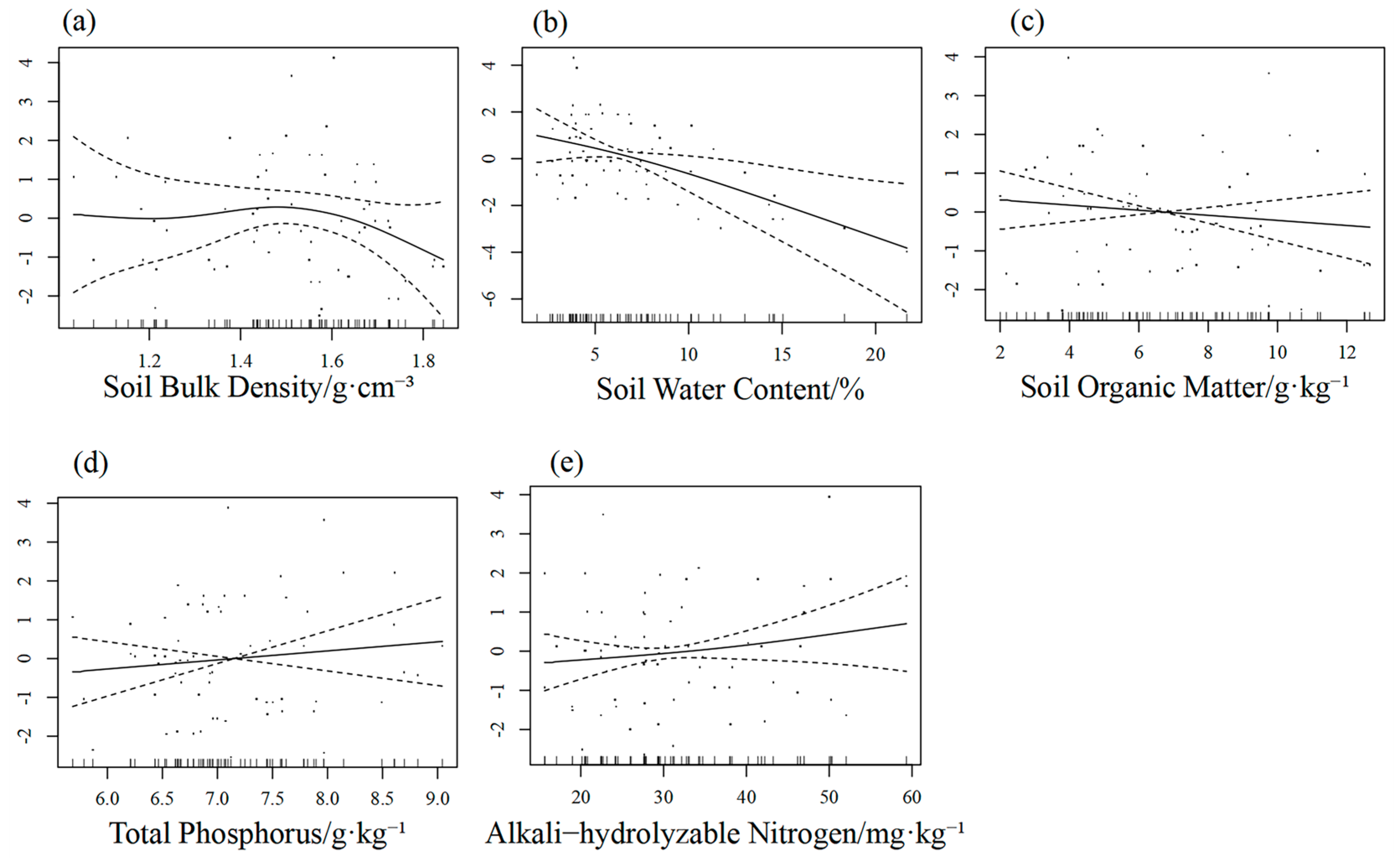
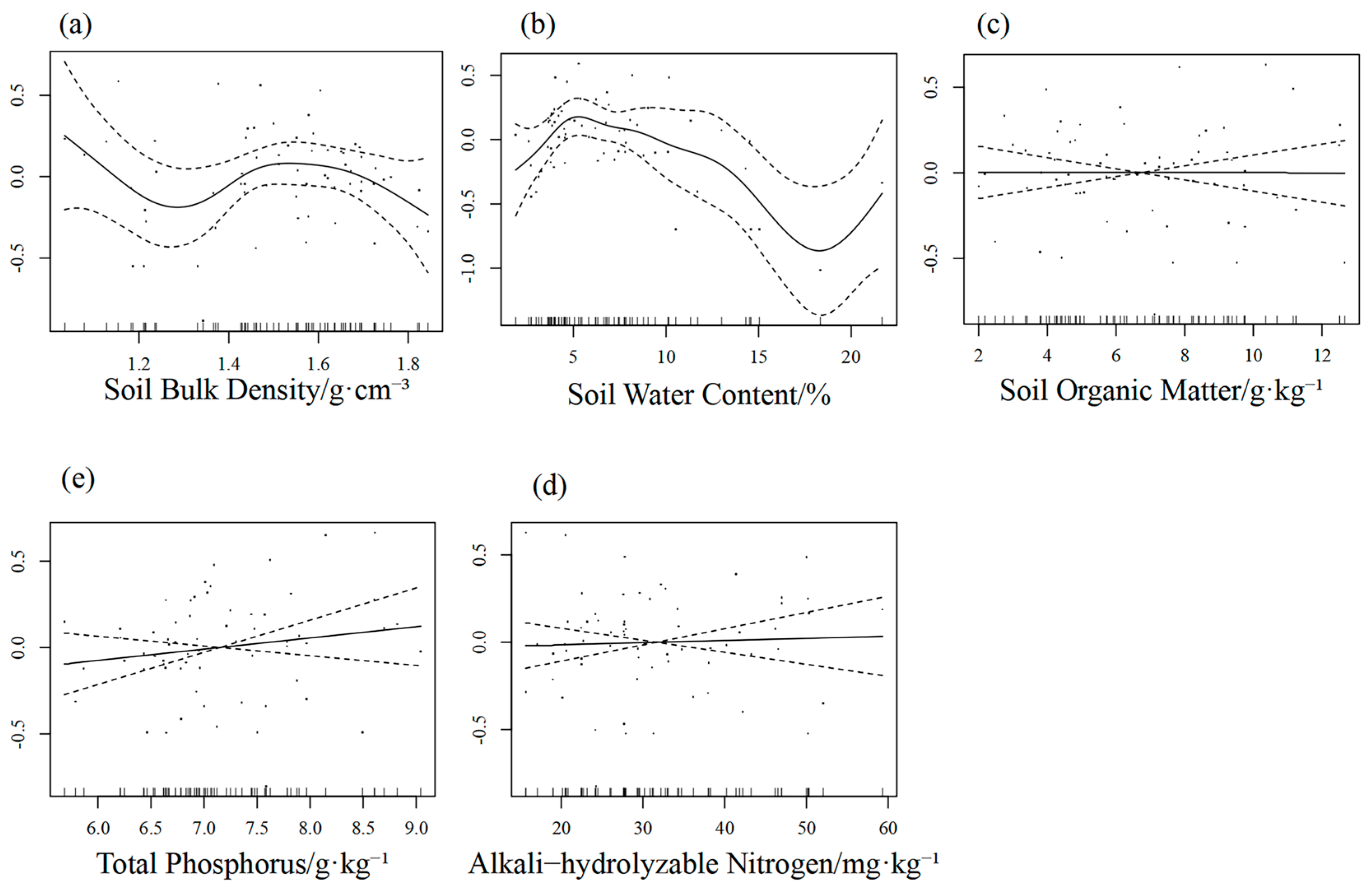
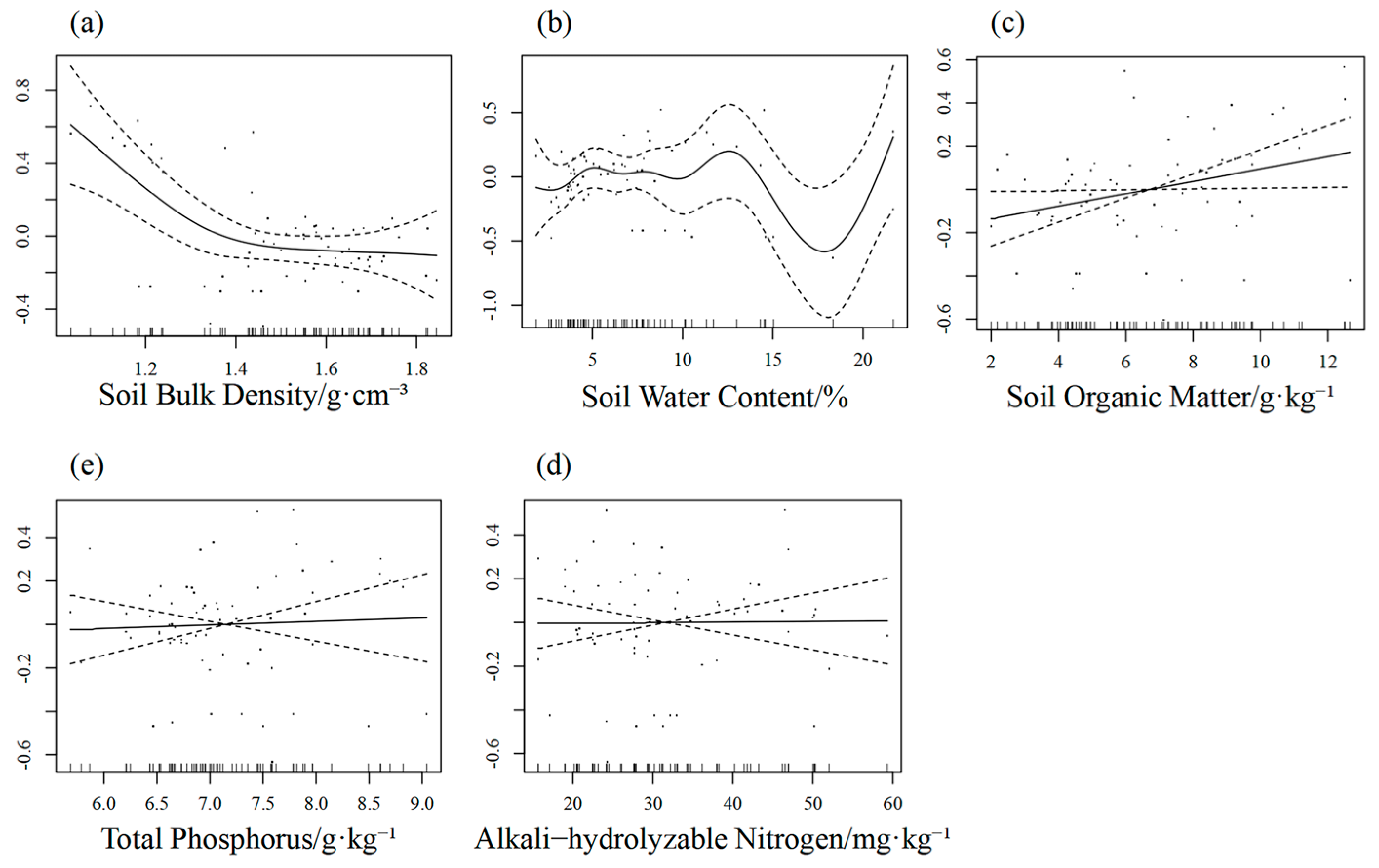
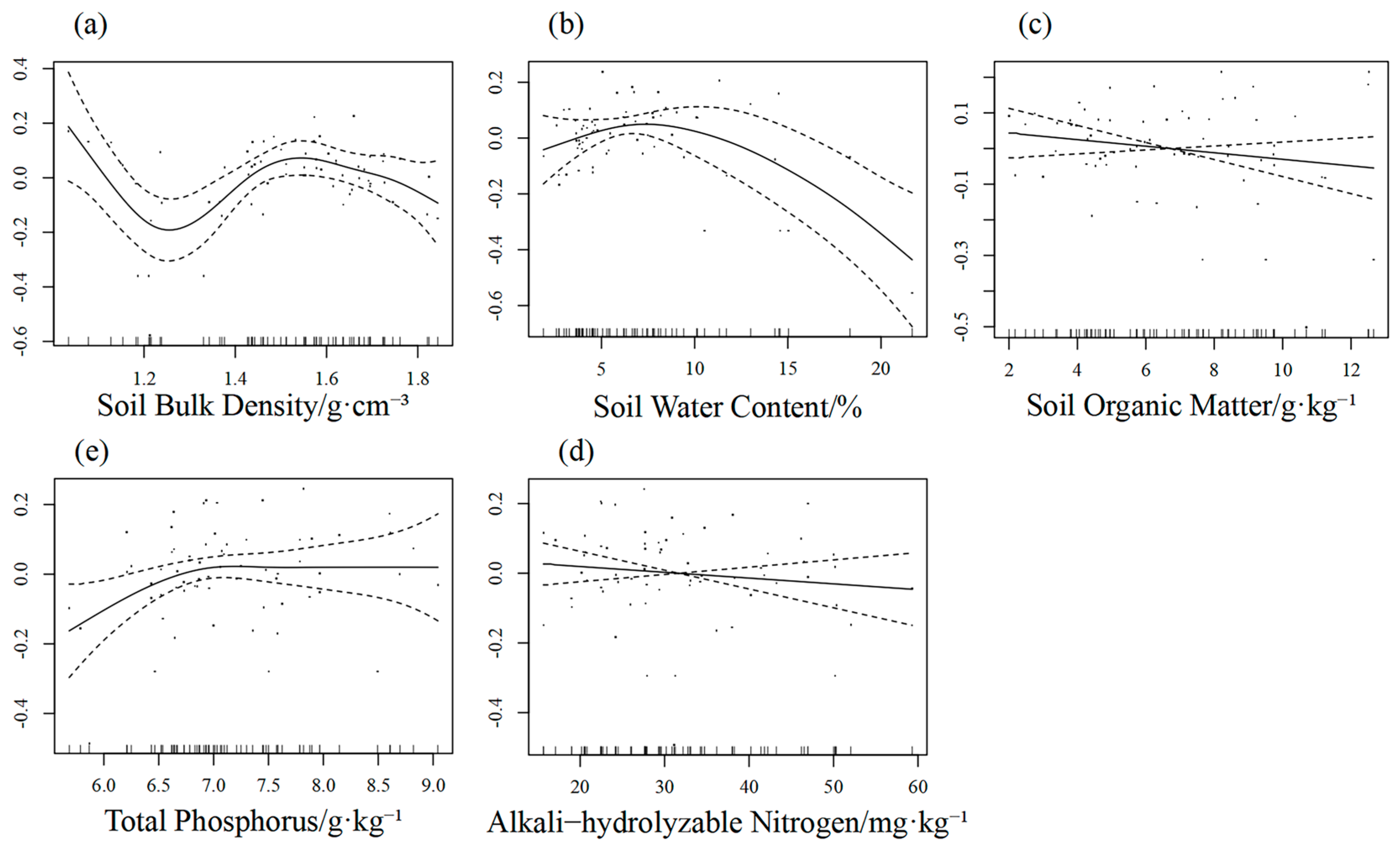
3.3.3. Generalised Additive Modelling
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of Different Operating Years and Microenvironments on Plant Community Characteristics
4.2. The Impact of Different Operating Years and Microenvironment Types on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
4.3. Relationship Between Plant Community Characteristics and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
5. Conclusions
- The long-term operation of photovoltaic power stations in temperate deserts promotes vegetation restoration, notably enhancing ground cover, aboveground biomass, and species diversity. In photovoltaic planning and management, full consideration should be given to ecological restoration potential, prioritising the protection and enhancement of vegetation structures in areas demonstrating long-term stability.
- Microenvironmental variations exert a pronounced regulatory effect on vegetation recovery, with the FP zone exhibiting superior restoration outcomes while vegetation in the IP zone remains constrained. Optimising inter-panel spacing, slope orientation, and drainage conditions within photovoltaic layout designs mitigates growth limitations in the inter-panel areas.
- Soil water content (SWC) and soil organic matter (SOM) are key factors in vegetation restoration. Combining water management strategies (such as interception, catchment, or recharge measures) with SOM accumulation approaches (such as mulching or localised fertilisation) can enhance the stability and sustainability of desert ecosystems.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prăvălie, R. Drylands Extent and Environmental Issues: A Global Approach. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 161, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, X.; Wei, Y.; Guo, R. Global Desertification Vulnerability to Climate Change and Human Activities. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Chen, L.; Li, X.B.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yang, X.G. Structural characteristics and ecological effects of shrub islands in desert grasslands. Grassl. Sci. 2018, 35, 2327–2335. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, X.Y. Soil Properties Following Cultivation and Non-Grazing of Desertified Sandy Grassland in Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 82, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.R.; Jia, X.H.; Long, L.Q.; Zerbe, S. Effects of Biological Soil Crusts on Seed Bank, Germination and Establishment of Two Annual Plant Species in the Tengger Desert (N China). Plant Soil 2005, 277, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, X.Y.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Review on Responses of Grassland Plant–Soil to Precipitation and Management Measures in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas of China. J. Desert Res. 2025, 45, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Shiroyama, H. Development of Photovoltaic Power Generation in China: A Transition Perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Peng, H.; Jiang, Y. Locating the Suitable Large-Scale Solar Farms in China’s Deserts with Environmental Considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turney, D.; Fthenakis, V. Environmental Impacts from the Installation and Operation of Large-Scale Solar Power Plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.S.; Cagle, A.E.; Macknick, J.; Bloom, D.E.; Caplan, J.S.; Ravi, S. Effects of Revegetation on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Solar Photovoltaic Infrastructure. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, S.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Su, J.; Hu, Y. Comparison of Tracking and Fixed Photovoltaic Systems for Soil Quality Improvement in Desert: A 5-Year Field Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 997, 180221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F.G.; Wu, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Jia, R.; Zhang, H.X.; Wei, L.; Dong, L.; et al. Ecological Effects of Photovoltaic Power Plant Construction: Progress and Prospects of Desert Photovoltaic Sand Control. China Deserts 2025, 45, 277–291. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, K.E.; Moore-O’Leary, K.A.; Parker, I.M.; Pavlik, B.M.; Hernandez, R.R. Simulated Solar Panels Create Altered Microhabitats in Desert Landforms. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walston, L.J.; Li, Y.; Hartmann, H.M.; Macknick, J.; Hanson, A.; Nootenboom, C.; Lonsdorf, E.; Hellmann, J. Modeling the Ecosystem Services of Native Vegetation Management Practices at Solar Energy Facilities in the Midwestern United States. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 47, 101227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.; Ostle, N.J.; Whitaker, J. Solar Park Microclimate and Vegetation Management Effects on Grassland Carbon Cycling. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 074016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnano, M.; Fiorentino, N.; Visconti, D.; Baldi, G.M.; Falce, M.; Acutis, M.; Genovese, M.; Di Blasi, M. Effects of a Photovoltaic Plant on Microclimate and Crops’ Growth in a Mediterranean Area. Agronomy 2024, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K. Mechanistic Insights into the Influences of Photovoltaic Panel Construction on Algal Crust Microbial Communities in Alpine Desert Grasslands. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1552071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, J.D.; Li, Z.D.; Zhang, F.; Bai, J.H.; Yang, X.H. Research Progress on Ecological Impacts of Photovoltaic Systems in Desert, Gobi, and Arid Regions. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2025, 15, 709–716. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Chen, R.; Zhang, W.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Du, P. Satellites Reveal Spatial Heterogeneity in Dryland Photovoltaic Plants’ Effects on Vegetation Dynamics. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, H.; Li, C.; Lu, G.; Ye, D.; Ma, C.; Ren, L.; Li, G. Assessment of the Ecological and Environmental Effects of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Development in Desert Areas. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Dong, B.; Xu, W.; Cai, L.; Wu, J. Evaluation of Farmland Quality Grades and Analysis of Soil Nutrients and Salinization in Arid Areas: A Case Study of Minqin Oasis. Arid. Zone Geogr. 2021, 44, 514–524. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, J.T.; McIntosh, R.P. The Interrelations of Certain Analytic and Synthetic Phytosociological Characters. Ecology 1950, 31, 434–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.A.; Qiu, K.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Cui, L.Y.; Luo, X.Y.; Yang, Y.T.; Xie, Y.Z. Leaf Functional Traits and Their Plasticity of Desert Grassland Plants under Nitrogen and Phosphorus Addition. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2024, 33, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Academy of Sciences Nanjing Institute of Soil Science. Physicochemical Analysis of Soil; Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1978; pp. 380–511. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 25–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.L.; Chen, F.; Yang, H.T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.L.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, X.R.; Yuan, H.B. Vegetation Characteristics of the Tengger Desert. China Deserts 2020, 40, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; He, K.N.; Hu, X.B.; Wang, W.W.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Effects of Different Tree Species Configurations on Understory Vegetation Diversity in Alpine Areas. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 19, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.P. Methods for Measuring Biodiversity of Biological Communities. I. Methods for Measuring α-Diversity (Part I). Biodiversity 1994, 2, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Catano, C.P.; Bassett, T.J.; Bauer, J.T.; Grman, E.; Groves, A.M.; Zirbel, C.R.; Brudvig, L.A. Soil resources mediate the strength of species but not trait convergence across grassland restorations. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huo, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X. Climatic and Ecological Impact Mechanisms and Vegetation Restoration Patterns of Cen-tralized Desert Photovoltaic Power Stations. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 23, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Bao, J.; Wu, T.; Chai, B. Effect of light heterogeneity caused by photovoltaic panels on the plant–soil–microbial system in solar park. Land 2023, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervloesem, J.; Marcheggiani, E.; Choudhury, M.A.M.; Muys, B. Effects of Photovoltaic Solar Farms on Microclimate and Vegetation Diversity. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Xie, Y.; Yue, S.; Yang, M.; Han, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. Plant species richness enhances aboveground primary productivity via net biodiversity effects and bacterial community interactions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 209, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Jia, A.; Bai, Z.; Qu, S.; Zhang, M.; Kong, L.; Sun, R.; Wang, M. Photovoltaic Panels Have Altered Grassland Plant Biodiversity and Soil Microbial Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1065899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafitte, A.; Sordello, R.; Ouédraogo, D.Y.; Thierry, C.; Marx, G.; Froidevaux, J.; Schatz, B.; Kerbiriou, C.; Gourdain, P.; Reyjol, Y. Existing Evidence on the Effects of Photovoltaic Panels on Biodiversity: A Systematic Map with Critical Appraisal of Study Validity. Environ. Evid. 2023, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo, V.M.; Rios, R.S.; Gianoli, E. Interactive effects of shading and disturbance on plant invasion in an arid shrubland: Assembly processes and CSR-strategies. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 2405–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, F.; Wei, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, Z.; Xu, D.; Haider, F.U.; Li, X.; Dong, Y. Ecological Restoration Increases the Diversity of Understory Vegetation in Secondary Forests: Evidence from 90 Years of Forest Closures. Forests 2024, 15, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, N.A.; Jones, H.P.; Duvall, M.R.; Wysocki, W.P.; Hansen, M.J.; Gibson, D.J. Phylogenetic Diversity Is Maintained Despite Richness Losses over Time in Restored Tallgrass Prairie Plant Communities. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscatelli, M.C.; Marabottini, R.; Massaccesi, L.; Marinari, S. Soil Properties Changes after Seven Years of Ground Mounted Photovoltaic Panels in Central Italy Coastal Area. Geoderma Reg. 2022, 29, e00500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Graciano, C.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, F.; Hughes, A.C.; Ahmed, Z.; Ullah, A.; Ali, S.; Gao, Y.; Peñuelas, J. Plant root mechanisms and their effects on carbon and nutrient accumulation in desert ecosystems under changes in land use and climate. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 916–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Chai, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, P. The Influences of the Desert Photovoltaic Power Station on Local Climate and Environment: A Case Study in Dunhuang Photovoltaic Industrial Park, Dunhuang City, China in 2019. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Guo, M.; Zou, P.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X. Effects of photovoltaic panels on soil temperature and moisture in desert areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 17506–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Meng, Z.; Jia, R.; Li, H.; Cai, J.; Gao, Y. Positive soil responses to different vegetation restoration measures in desert photovoltaic power stations. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1607404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Yetemen, O. Ecohydrological effects of photovoltaic solar farms on soil microclimates and moisture regimes in arid Northwest China: A modeling study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulla, D.; Galzki, J.; Hanson, A.; Šimůnek, J. Measuring and Modeling Soil Moisture and Runoff at Solar Farms Using a Disconnected Impervious Surface Approach. Vadose Zone J. 2024, 23, e20335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Leifheit, E.F.; Lehmann, A.; Rillig, M.C. Soil organic carbon stabilization is influenced by microbial diversity and temperature. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Fan, X.; Sun, L.; Sang, C.; Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Fang, Y.; Bai, E. Mineral composition controls the stabilization of microbially derived carbon and nitrogen in soils: Insights from an isotope tracing model. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, F.; Fu, B.; et al. Soil Microbial Networks’ Complexity as a Primary Driver of Multifunctionality in Photovoltaic Power Plants in the Northwest Region of China. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1579497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ai, N.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Qiang, F. Soil quality evaluation of various microtopography types at different restoration modes in the loess area of Northern Shaanxi. Catena 2021, 207, 105633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fu, L.; Ma, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, A. Effects of Microtopography on Soil Microbial Community Structure and Abundance in Permafrost Peatlands. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Fan, R.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, H.; Huang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, M. Field study of compound microbial agents for soil improvement and microbial community dynamics on rocky slopes in Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 33086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wu, W.; Yuan, B.; Ye, D.; Bai, W. Large-Scale Photovoltaic Farms Significantly Change the Vegetation Diversity and Biomass through Influencing Soil Moisture and Physiochemical Properties. Vadose Zone J. 2025, 24, e70002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.R.; Wang, X.J. Effects of Photovoltaic Power Station Construction on Soil and Vegetation: A Case Study in the Desert and Gobi Area of Hexi Corridor, Gansu. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 17, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, P.A.; Ji, B.; Sun, G.; Zhang, N.; Wu, X.D.; He, J.L.; Wang, Z.J.; Tian, Y. Effects of Photovoltaic Power Station Construction on Plant Communities and Soil Properties. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2024, 33, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Gong, J.; Zhang, W.; Dong, X.; Hu, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, T. Photovoltaic Systems Promote Grassland Restoration by Coordinating Water and Nutrient Uptake, Transport and Utilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Duan, H. Vegetation restoration increases soil carbon storage in land disturbed by a photovoltaic power station in semi-arid regions of Northern China. Agronomy 2023, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, B.J.; Briggs, J.M. Patch Dynamics of Soil Biotic Feedbacks in the Sonoran Desert. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Putten, W.H.; Bardgett, R.D.; Bever, J.D.; Bezemer, T.M.; Casper, B.B.; Fukami, T.; Kardol, P.; Klironomos, J.N.; Kulmatiski, A.; Schweitzer, J.A.; et al. Plant–soil feedbacks: The past, the present and future challenges. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Reynolds, J.F.; Cunningham, G.L.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jarrell, W.M.; Virginia, R.A.; Whitford, W.G. Biological Feedbacks in Global Desertification. Science 1990, 247, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Zhou, Z. Response of vegetation and soil property changes by photovoltaic established stations based on a comprehensive meta-analysis. Land 2024, 13, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


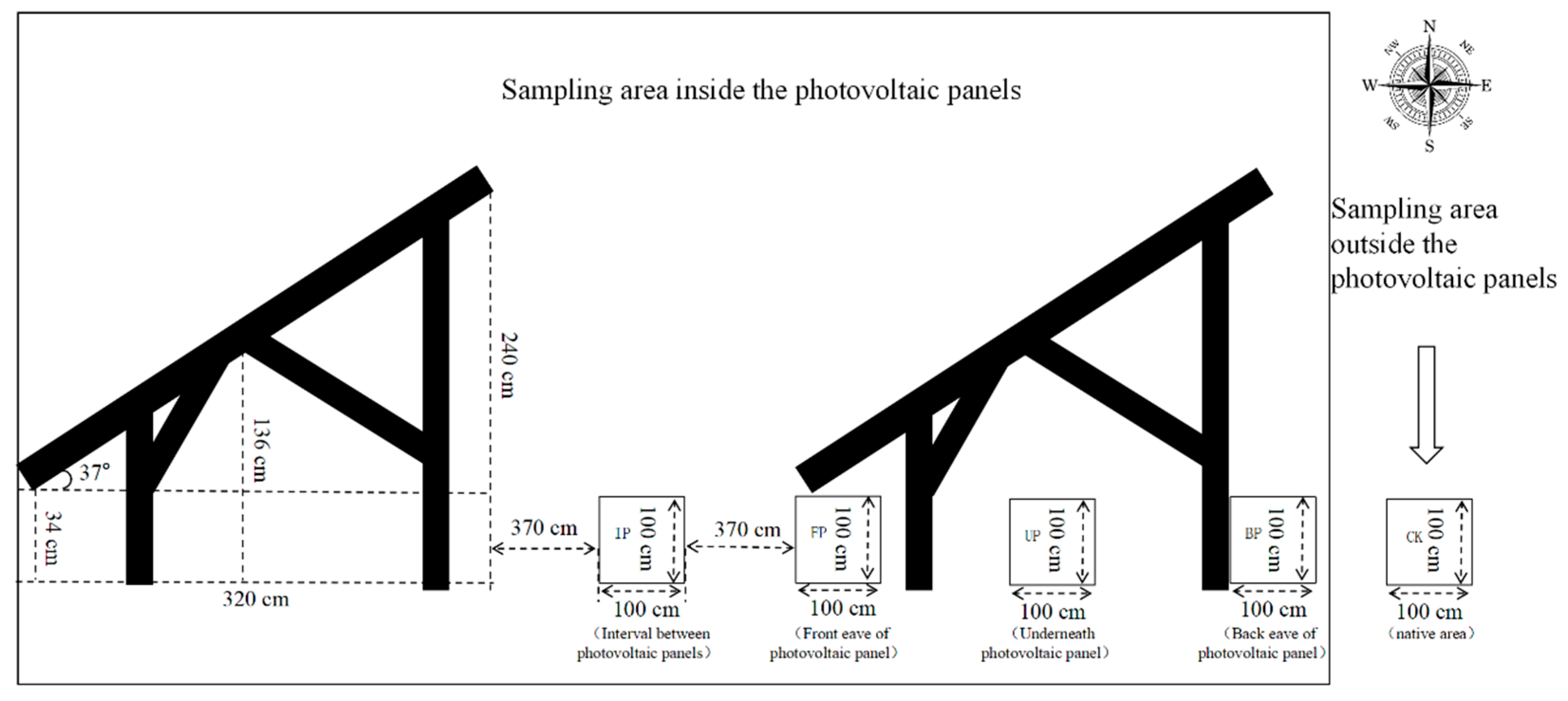
| Sample Type | Operation Duration /Year | Altitude | Elevation /m | Photovoltaic Power Plant Scale /MWP | Panel Tilt Angle /° | Panel Spacing /m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianhe Power Station | 13 | 38°57′10″ N, 102°28′06″ E | 1400 | 50 | 37 | 8 |
| Yineng Power Station | 7 | 38°55′25″ N, 102°34′05″ E | 1398 | 100 | 37 | 8 |
| Longyu Power Station | 1 | 38°53′12″ N, 102°32′53″ E | 1370 | 200 | 37 | 8 |
| Family | Species | Importance Value | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 7 | 1 | CK | |||||||||||
| FP | UP | BP | IP | FP | UP | BP | IP | FP | UP | BP | IP | CK | ||
| Asteracea | Echinops gmelinii | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Artemisia scoparia | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Heteropappus altaicus | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chenopodiaceae | Salsola collina | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 |
| Suaeda salsa | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.1 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.18 | |
| Halogeton glomeratus | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| Zygophyllaceae | Tribulus terrestris | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 |
| Zygophyllum mucronatum | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.09 | |
| Zygophyllum xanthoxylon | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.03 | |
| Nitraria tangutorum | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0 | 0.15 | |
| Nitraria sphaerocarpa | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | |
| Poaceae | Puccinellia distans | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Stipa glareosa | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cleistogenes songorica | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Amaryllidaceae | Allium mongolicum | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago minuta | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tamaricaceae | Reaumuria soongorica | 0.29 | 0.48 | 0.4 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.4 | 0.31 | 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Chen, T.; Ma, S.; Tian, Y.; Li, Q.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Xiao, J.; Shi, Y. Effects of Different Operation Years of Photovoltaic Power Stations on Vegetation and Soil Characteristics in Temperate Deserts. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192097
Yu Y, Chen T, Ma S, Tian Y, Li Q, Cai Z, Zhao L, Liu X, Xiao J, Shi Y. Effects of Different Operation Years of Photovoltaic Power Stations on Vegetation and Soil Characteristics in Temperate Deserts. Agriculture. 2025; 15(19):2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192097
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yaoxin, Tao Chen, Shijun Ma, Ya Tian, Qing Li, Zhaoshan Cai, Lijun Zhao, Xiaoni Liu, Jianhua Xiao, and Yafei Shi. 2025. "Effects of Different Operation Years of Photovoltaic Power Stations on Vegetation and Soil Characteristics in Temperate Deserts" Agriculture 15, no. 19: 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192097
APA StyleYu, Y., Chen, T., Ma, S., Tian, Y., Li, Q., Cai, Z., Zhao, L., Liu, X., Xiao, J., & Shi, Y. (2025). Effects of Different Operation Years of Photovoltaic Power Stations on Vegetation and Soil Characteristics in Temperate Deserts. Agriculture, 15(19), 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192097






