Abstract
Chicken farming plays a crucial role in the global food supply; however, the frequent occurrence of chicken diseases presents a substantial challenge to the industry’s sustainable development. This study introduces an enhanced YOLOv11 model, DOSA-YOLO, designed to detect four prevalent chicken diseases: avian pox, coccidiosis, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, and Newcastle disease. The research team developed an intelligent inspection robot to capture multi-angle images in intensive farming environments, constructing a five-class dataset comprising 8052 images. These images were categorized based on phenotypic features such as comb, eyes, and wattles, as well as pathological anatomical characteristics. To address challenges such as complex backgrounds, multi-scale lesions, and occlusion interference, three attention-enhancement modules—MSDA, MDJA, and SEAM—were integrated into the YOLOv11. The model was trained and validated using the constructed dataset and compared against seven other algorithms, including YOLOv5n, YOLOv7tiny, YOLOv8n, YOLOv9t, YOLOv10n, YOLOv11n, YOLOv12n, and Faster R-CNN. Experimental results demonstrated that DOSA-YOLO achieved a mean Average Precision (mAP) of 97.2% and an F1-score of 95.0%, outperforming the seven other algorithms while maintaining a balance between lightweight design and performance with GFLOPs of 6.9 and 2.87 M parameters. The model provides strong support for real-time chicken health monitoring in intensive farming environments.
1. Introduction
The global chicken farming industry, due to its large scale and significant economic role, is a vital component of the global food supply. However, the frequent occurrence of chicken diseases has caused substantial economic losses and raised food safety concerns, making early detection and prevention of chicken diseases an urgent need [1]. With the advancement of digital transformation, efficient disease detection and accurate diagnosis have become central tasks for improving production efficiency and ensuring food safety. Disease outbreaks not only increase mortality rates but also cause significant economic losses annually, due to impacts on production performance, rising treatment costs, and food safety risks. Chicken diseases caused by pathogens are numerous, with common examples including avian pox, coccidiosis, Mycoplasma gallisepticum (MG), and Newcastle disease. Avian pox, caused by the Avian poxvirus, primarily spreads through direct contact or mechanical transmission by insects [2], and lesions mainly occur on the comb, wattle, and facial areas of chickens, leading to reduced egg production and stunted growth [3,4]. Coccidiosis, an intestinal disease caused by Eimeria, affects chickens over three months old and spreads through contaminated feed, water, or the environment. Infected chickens suffer from diarrhea, weight loss, and high mortality rates [5]. MG infections, more prevalent in colder seasons, present respiratory symptoms such as coughing, nasal discharge, and conjunctivitis, and long-term effects on chicken growth [6]. Newcastle disease (ND), a viral infection with high mortality, commonly affects chickens aged 20 to 60 days, leading to anorexia, weight loss, and severely impacting poultry productivity [7,8]. These diseases not only threaten poultry health but also result in significant economic losses for the farming industry [9]. In response to these threats, traditional chicken disease detection methods include clinical observation, laboratory testing, and post-mortem examination [10]. While machine learning techniques [11] have been explored for classifying avian disease characteristics, current methods still face challenges such as time consumption, complexity, high reliance on expertise, and limited accuracy, making them inadequate for meeting the urgent need for real-time, efficient diagnosis in modern intensive poultry farming.
The rapid development of digital image processing and deep learning technologies has propelled deep learning-based chicken disease detection methods into a research hotspot, achieving significant progress [12,13]. Zhuang et al. achieved 99.7% accuracy in broiler health identification using an improved feature fusion single-shot multi-box detector (IFSSD), establishing the feasibility of the technology [14]. Subsequently, the extraction of pathological features became a key breakthrough. Quach et al. utilized SURF-Kmeans to reconstruct ResNet-50 inputs, focusing on disease phenotype areas such as the head, wings, and legs, demonstrating that local pathological features significantly enhance model sensitivity [15]. Serbessa et al. noted that visible morphological changes, such as abnormal comb color, movement disorders, and feather condition changes, are core to clinical diagnosis, aligning well with the “three looks and one listen” diagnostic principle in veterinary practice [16]. Notably, traditional machine learning methods are limited by shallow structures and have restricted capability in expressing multi-source phenotypic features [17]. In contrast, combining IoT-based multi-source sensing data with deep generative networks (GANs) can enable precise classification of poultry health [18]. Breakthroughs in poultry disease detection using infrared thermal imaging and deep learning have also been achieved. Pei Li and colleagues successfully implemented non-contact health monitoring by analyzing temperature features in the head, body, and leg regions of chickens [19]. Additionally, research based on fecal visual features has enhanced early detection capabilities, achieving a 99.99% recognition accuracy using an ensemble fine-tuned convolutional neural network via smartphone images [20]. Zhang et al. combined quantum dot fluorescence labeling with the YOLOv5 model to develop a rapid diagnostic system with a detection accuracy of 92.7%, making a significant contribution to the field [21]. Furthermore, Qin et al. developed a YOLOv5-based model for detecting digestive tract diseases in laying hens, achieving an accuracy rate of over 95% and implementing traceability through the SuperPoint-SuperGlue model [22]. Elmessery et al. proposed a YOLO algorithm based on visual and thermal images, successfully developing a system for automatic detection of broiler pathological phenomena, enabling efficient detection of pathological conditions [23]. The application of deep learning in video analysis has also seen remarkable results. Scheidwasser et al. proposed an unlabeled video tracking method to analyze behavior patterns in flocks, identifying behavioral differences between E. coli-infected and healthy chickens [24].
In summary, significant progress has been made in deep learning for chicken disease detection, achieving high-precision recognition of key phenotypic features such as comb color, movement behavior, body temperature, and excrement. However, current research still faces the following limitations: (1) The robustness and generalization ability of models in complex real-world scenarios need improvement; (2) The computational overhead and parameter limitations of high-performance models restrict real-time performance and model deployment feasibility; (3) Research on the recognition and utilization mechanisms of core diagnostic phenotypic features such as combs, eyes, and wattles remains insufficient. Therefore, this study aims to deeply integrate deep learning methods with key phenotypic features to further optimize the detection of common chicken diseases. To this end, we propose an improved YOLOv11 model, DOSA-YOLO, focusing on the automatic detection of common chicken diseases such as avian pox, coccidiosis, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, and Newcastle disease. To address the challenges, this study introduces three attention-enhanced modules: MSDA, MDJA, and SEAM. These modules significantly improve the model’s feature extraction and discrimination capabilities, enabling it to more effectively overcome complex backgrounds, multi-scale lesions, and occlusion interference, resulting in more accurate and robust performance in phenotypic feature-based chicken disease detection. The main contributions of this study are as follows:
- This study employed an intelligent inspection robot for routine inspections and data collection. By integrating image data and pathological anatomical features for annotation, a high-quality dataset was constructed, containing five disease states: avian pox, coccidiosis, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, Newcastle disease, and healthy chickens.
- To address the challenges of multi-scale lesion recognition, partial occlusion interference, and real-time detection in farming scenarios, MDJA, SEAM, and MSDA attention mechanisms were incorporated into the YOLOv11 architecture. The innovative DOSA-YOLO model was proposed, and the improvements in performance brought by different modules to the YOLOv11 model were explored and validated.
- The performance of DOSA-YOLO model was compared with seven mainstream algorithms: Faster R-CNN, YOLOv5n, YOLOv7tiny, YOLOv8n, YOLOv9t, YOLOv10n, and YOLOv12n. The evaluation demonstrated that DOSA-YOLO outperforms other models in chicken disease detection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Data Acquisition
Data collection for this study was conducted at two egg-laying poultry farms in Shanxi Province, China: Nanguang Village, Taigu District, Jinzhong City (112°30′57″ E, 37°22′43″ N) and the Shennong Technology Group in Yangqu County (112°71′ E, 38°12′ N). Approximately 20,000 Roman, Beijing Red, Bian, and Hy-Line Brown hens were housed across two poultry houses. All chickens involved in data collection were aged between 25 and 70 weeks, within the laying period. During the data collection, multiple batches of chickens within the laying period of the poultry house were sampled. The poultry houses, measuring 55 m × 12 m × 4 m, followed a standardized four-layer A-type stacked cage design. Each cage, sized 380 mm × 400 mm × 250 mm (L × W × H), accommodated 3–4 chickens, with aisle widths of 90 cm.
Accounting for variations in the incubation and peak periods of different diseases, a disease data of chicken was comprehensively collected using an intelligent inspection robot developed by the team. The robot was equipped with a UV-SH08-HD Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) camera (1920 × 1080 at 30 fps), developed by Shenzhen Uvsion Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China, with a resolution of 1920 × 1080 at 30 fps. It was mounted on an electric lift system for automatic adjustment of camera height between 1163 mm and 1663 mm. This ensured precise adaptation to the varying heights of poultry cages. The camera supported a 360-degree horizontal rotation and a vertical tilt range of −90 to 90 degrees, enabling multi-angle (overhead and side) imaging.
The data collection period, from October 2022 to June 2025, encompassed diverse scenarios including occlusion, density, posture variations, lighting fluctuations, and varying disease states. This ensured a comprehensive video record of sick chickens. Camera height was adjusted based on the layer of the cages: 1163 mm for the 1st and 2nd layers, and 1663 mm for the 3rd and 4th layers, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of data acquisition for the inspection robot.
The poultry house employed mixed light, primarily consisting of variable daytime natural light and constant-intensity supplemental lighting. Since lighting conditions varied over time, the cameras were equipped with an automatic exposure adjustment to accommodate different light intensities. This ensured stable image quality and provided accurate and reliable image data for subsequent analysis.
During data collection, preliminary screenings were conducted by farm veterinarians through daily clinical observations, focusing on the chickens’ mental state, feeding and water intake, respiratory symptoms, fecal characteristics, and body surface abnormalities of chickens. Suspected diseased chickens showing typical symptoms were then selectively necropsied. Based on their characteristic pathological changes, a differential diagnosis was made in conjunction with clinical symptoms. Although other common diseases, such as avian influenza, infectious bronchitis, and necrotic enteritis, may present similar symptoms, they were distinguished and excluded through the typical pathological features of each disease. The four poultry breeds involved in this study exhibited essentially consistent disease phenotypes. Throughout the data collection period, video data was collected from fifty-six target chickens diagnosed by comprehensive diagnosis, including five categories: avian pox, coccidiosis, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, Newcastle disease, and healthy chickens. Frame extraction technology was employed to sample every 15th frame. After preliminary screening, 4072 image data were ultimately obtained.
This study adhered to the relevant guidelines set forth by the Animal Ethics Committee of Shanxi Agricultural University and had been approved by the committee (Approval No. SXAU-EAW-2022P.GT.0070080141; Date: 10 September 2022).
2.1.2. Data Classification Standards and Annotations
Chickens exhibited distinct phenotypic changes and corresponding organ lesions following infection. Phenotypic characteristics were integrated with pathological anatomical features to assess the disease status of chickens. Based on this approach, a dataset was constructed with five categories: avian pox, coccidiosis, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, Newcastle disease, and healthy status. This comprehensive diagnostic strategy, grounded in objective phenotypic and pathological anatomical features, ensured reliable and reproducible disease diagnostic criteria for disease categorization, establishing a robust data foundation for subsequent deep learning model training.
Infected chickens with avian pox developed pox lesions on featherless areas such as the comb, wattles, face, and legs. The lesions initially appeared as small, grayish-white nodules that rapidly enlarged, forming warts that protruded from the skin or mucosal surfaces. These warts had an uneven surface and were hard and dry. Thus, the avian pox diagnosis was based on skin lesions [25]. In chickens infected with coccidiosis, damage to the intestinal wall impaired nutrient absorption, resulting in a pale comb and retracted head. Pathological features included intestinal mucosal hemorrhage, thickening of the intestinal wall, ulcers or necrosis, hepatomegaly, splenic congestion, and bloody intestinal contents [26], as shown in Figure 2a. The phenotypic characteristics of Mycoplasma gallisepticum (MG) [27] infection included swelling of the comb and wattles, which turned purple, as well as bubble-like fluid in the eyes. Pathological features included excessive mucous fluid or catarrhal exudates in the nasal air sacs, trachea, and bronchi, with edema of the tracheal walls. In early stages, the air sac membranes thickened and became gray-white and opaque, while later stages showed cheesy exudates on the air sac walls, as depicted in Figure 2b. Chickens infected with Newcastle disease (ND) developed neurological symptoms such as torticollis, neck twisting, and circling after several days [28], accompanied by mucosal and serous discharge, open-mouthed neck stretching, and a purple comb and wattles. Post-mortem examination revealed hemorrhaging in the proventriculus, swollen lymphoid follicles, hemorrhagic trachea and larynx, and hepatomegaly [29], as shown in Figure 2c. Therefore, chickens exhibiting torticollis and purple combs and wattles were diagnosed with Newcastle disease. The relationships between the phenotypic features and diagnostic criteria for each disease are summarized in Table 1.


Figure 2.
Phenotypic and pathological anatomical features of each disease. (a) Coccidiosis phenotypic and pathological anatomical features. (b) Mycoplasma gallisepticum phenotypic and pathological anatomical features. (c) Newcastle disease phenotypic and pathological anatomical features.

Table 1.
Relationship between phenotypic features of chicken disease and diagnostic criteria.
2.1.3. Dataset Construction
SSIM is a metric used to measure the structural similarity between two images. analyzing their similarity in terms of luminance, contrast, and structural content. In this study, the Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) [30] was employed to eliminate similar images. The computational process is given by Equation (1):
where is luminance comparison, represents contrast comparison, and is structural comparison. When α = β = γ = 1 and , SSIM can be simplified to Equation (2):
where and are corresponding blocks of two images, and are the mean values of and , respectively, and are the variances of and , respectively, and is the covariance between and . and are small constants used to stabilize the calculations.
During the imaging process, some images were difficult to distinguish clearly and label accurately due to motion blur, camera malfunctions, extreme lighting conditions in the poultry house, and chicken occlusion. These images were classified as abnormal samples and manually excluded. After screening, 2684 valid images were retained. To increase dataset diversity, data augmentation methods were employed, including enhancing brightness and contrast, as well as applying random rotations and flips (with crops), which tripled the size of the original dataset. The detailed effect is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Data augmentation. (a) Original image; (b) Brightness enhancement; (c) Contrast enhancement; (d) Random rotation (flip).
After augmentation, a dataset consisting of 8052 images of chicken disease states was constructed. This dataset included images of five disease states: avian pox, coccidiosis, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, Newcastle disease, and healthy chickens, corresponding to five labeled categories: “AP” (avian pox), “AC” (coccidiosis), “MG” (Mycoplasma gallisepticum), “ND” (Newcastle disease), and “HL” (healthy). The images of chickens in each state, along with their pathological anatomical images, are presented in Figure 2. Annotations were performed using the LabelImg tool, version 1.8.6., and the results were saved in YOLO format as TXT files. The annotation boxes were carefully drawn to include key features such as the comb, wattle, eyes, head, and neck. Annotation boxes were designed to cover as many characteristic parts of the chicken as possible, including the comb, wattles, eyes, beak, head, and neck, as shown in Figure 4. To ensure effective model training and accurate evaluation, the dataset was randomly split into training, validation, and testing sets in a 7:1:2 ratio, ensuring balanced class distribution in each subset. The distribution of the chicken disease state dataset is shown in Table 2.

Figure 4.
Image Labeled Process. (a) Original image; (b) Annotation image.

Table 2.
Distribution of the disease dataset.
2.2. Chicken Disease Detection Model
YOLOv11, an advanced object detector developed by Ultralytics, has become a benchmark in the field of object detection due to its exceptional real-time performance. Compared to earlier versions of YOLO, YOLOv11 improved the backbone and neck architecture, enhancing feature extraction capabilities. These improvements allowed more accurate object detection in complex scenarios, while also achieving gains in model efficiency and speed. YOLOv11 introduced two new modules, C3k2 and C2PSA, and continued the YOLOv10 strategy of training without Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) achieving end-to-end object detection and further enhancing both performance and flexibility [31].
Test results from related studies indicated that YOLOv11n significantly increased computational efficiency without sacrificing detection accuracy [32]. Based on this model, the model architecture was refined, and a new enhanced model—DOSA-YOLO—was introduced. This model combined phenotypic features and deep learning techniques and was specifically optimized to address the challenges of complex backgrounds, multi-scale lesions, and occlusion interference in chicken disease detection.
2.2.1. MSDA Module
An efficient Multi-Scale Dilated Attention (MSDA) mechanism was introduced to address the computational redundancy in the global attention mechanism in Vision Transformer (ViT), particularly the redundant spatial dependencies in shallow features, as illustrated in Figure 5. The channels of the feature map are divided into different heads. Sliding Window Dilated Attention (SWDA) is applied with varying dilation rates (r = 1, 2, and 3) in each head to focus on different receptive fields, represented by the colored blocks around the red query region. Additionally, features from different branches are concatenated and subsequently passed through a linear layer. This module achieved multi-scale feature fusion through structured sparse perception [33].

Figure 5.
MSDA module.
The MSDA module adopted a multi-head design. By controlling the dilation rate, each head adaptively captured local details and enhanced focus on the lesion regions. Moreover, SWDA calculated sparse attention weights within the sliding window, avoiding the complexity of global computations. This significantly reduced FLOPs while maintaining real-time performance, improved detection accuracy in complex scenarios, and enhanced the model’s robustness and generalization across different contexts.
2.2.2. MDJA Module
The Multi-dimensional Joint Attention (MDJA) module, as shown in Figure 6, leveraged dilated convolutions to capture features at multiple scales, thereby enhancing the model’s receptive field and multi-scale processing capabilities. The core concept of this module was to integrate multi-dimensional information and perform joint attention calculations. In real-world farm environments, the complex scenes often resulted in occlusions between chickens, and the phenotypic features of chickens were typically presented at different scales within the images. This presented a challenge for traditional models. The joint attention mechanism not only effectively resisted background interference but also addressed the occlusion issues. The model focused on key local regions and performed more precise feature extraction and inference in these areas by applying weighted processing to features at different scales. Furthermore, the joint attention mechanism enhanced the expression of important features, enabling the model to make more reliable and accurate inferences when confronted with varying disease manifestations across different chickens. This approach improved the model’s adaptability to complex environments, ensuring higher accuracy and practicality in real-world farm applications.

Figure 6.
MDJA module.
2.2.3. SEAM Module
In response to the issues of phenotype feature disappearance and localization distortion caused by the dense occlusion in chicken farming scenarios, the Separated and Enhancement Attention Module (SEAM) was introduced, as shown in Figure 7. This module addressed two key challenges: chicken-to-chicken occlusion and environmental object occlusion, using a dual-path feature optimization mechanism to enhance the response capability of the partially occluded objects in the Head layer output.

Figure 7.
SEAM module.
The feature separation path of SEAM utilized depth wise separable convolutions with residual connections. Depth wise separable convolution performed channel-wise separation, independently extracting spatial features from each channel, enhancing local lesion details while reducing the parameter count. However, this approach overlooked inter-channel relationships. To compensate for this loss, pointwise convolution layers were applied to dynamically fuse cross-channel semantic information and established lesion associations. The feature enhancement path built a global channel attention unit, suppressing occluding area noise and enhancing the features of key lesion channels.
2.2.4. DOSA-YOLO Module
In this study, the MSDA (Multi-Scale Dilated Attention) module, the MDJA (Multi-dimensional Joint Attention) module, and the SEAM (Spatial-Enhanced Attention Mechanism) module were introduced into the YOLOv11 model to construct an improved model named DOSA-YOLO. The overall architecture is shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8.
The overall architecture of the DOSA-YOLO model.
These three modules collectively constituted a collaborative attention-enhanced mechanism that spanned various stages of the model. Specifically, the MSDA module was embedded into the backbone network, and the multi-scale dilated attention mechanism extensively captured multi-scale features at shallow layers of the image, ranging from local details to intermediate semantics, generating rich and low-redundancy feature representations. These features were then passed to the Neck layer and further processed by the MDJA module. This module enhanced the integration and discrimination ability of multi-scale pathological features by fusing multi-dimensional information and performing joint attention calculation. Finally, at the Head layer, the SEAM module refined high-level features, focusing on handling occlusion and environmental interference. Through a dual-path mechanism, it separated and enhanced key features while suppressing irrelevant noise, thereby optimizing the feature quality of the input detection head. This significantly improved the localization accuracy and classification robustness for disease phenotype regions.
By embedding these three attention modules into different levels of YOLOv11, DOSA-YOLO achieved progressive processing from feature encoding and multi-scale fusion to occlusion robustness enhancement. This enabled it to gradually focus on the most critical pathological information, demonstrating stronger robustness and detection accuracy in complex scenarios.
2.3. Experimental Platform and Training Parameters
The experiments were conducted on a server equipped with an Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8358P processor and an NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU, running Ubuntu 22.04 as the operating system. PyTorch 2.1.0 was adopted as the deep learning framework, accelerated by CUDA 12.1. The development environment was PyCharm 2025.1.2, with Python 3.10 as the programming language. All algorithms were executed in the same environment to ensure consistency of the comparison experiment.
During the training phase, input images were uniformly resized to 640×640 pixels. The Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) was selected as the optimizer, with an initial learning rate set to 0.01 to balance training efficiency and model robustness. The weight decay coefficient and momentum factors were set to 0.0005 and 0.937, respectively, to enhance convergence speed and control overfitting. Cross Entropy Loss was employed as the loss function to measure the discrepancy between the model prediction and the ground truth. The batch size was 32, and the training epoch was 200.
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
A comprehensive evaluation of the model’s performance is essential for the neural network-based recognition of chicken diseases. Therefore, a set of commonly used performance metrics was selected for model evaluation. The metrics applied in this study include:
(1) Accuracy
Accuracy quantifies the fraction of correct predictions over the total predictions. It is computed as shown in Equation (3):
where P represents the number of true positive samples, and N indicates the number of true negative samples. The calculation of P and N is detailed in Equation (4).
(2) Precision
Precision is the ratio of correctly predicted positive samples to all samples predicted as positive. The formula for precision is shown in Equation (5):
where TP represents true positives (correctly identified positives), and indicates false positives (incorrectly identified positives).
(3) Recall
Recall, also known as true positive rate, evaluates the model’s capability to capture actual positive instances. The formula is shown in Equation (6):
where FN represents false negatives (incorrectly identified negatives).
(4) F1-score
The F1-score provides a harmonic means of recall and precision, balancing the trade-off between detection accuracy and comprehensive coverage. The formula is given in Equation (7):
(5) GFLOPs
GigaFLOPs (GFLOPs) denote the number of floating-point operations per second performed. It is an important metric for evaluating the computational load. Lower GFLOPs generally indicate faster inference, reduced hardware demands, and lower energy usage.
(6) Parameters
Parameters represent the total number of trainable weights and biases. More parameters enable the model to learn more complex features but also increase calculative cost and memory requirements. More parameters typically require more data and training time to generalize well and avoid overfitting. In resource-constrained environments, the number of parameters serves as a key factor in balancing model accuracy, efficiency, and feasibility of deployment.
3. Results
3.1. DOSA-YOLO Model Results
The average loss during the training and validation of the DOSA-YOLO model is shown in Figure 9. The reduction in the average loss indicates that the improved model enhances both localization accuracy and disease recognition efficacy.

Figure 9.
Training process curves.
The trends of train/box_loss and val/box_loss reflect improvement in localization accuracy. During training, train/box_loss decreased from 3.35 to 0.63, demonstrating good convergence in localizing different chicken diseases. The val/box_loss exhibited a similar trend and remained relatively stable, indicating strong generalization ability. The cls_loss, representing the difference between predicted and true classes, stabilized at approximately 0.40 after 200 iterations, confirming the model’s accuracy in detecting subtle phenotypic characteristics of chickens with various diseases. The distribution focal loss (DFL), which addresses class imbalance, showed a steady decline in train/dfl_loss and val/dfl_loss, confirming the model’s ability to minimize misclassification impacts. Both training and validation sets displayed smooth loss reduction, validating the method’s effectiveness in optimizing precision. Additionally, the metrics/precision (B) and metrics/recall (B) curves revealed a gradual increase in both precision and recall throughout training. Notably, on the validation set, both precision and recall reached high levels, indicating the model’s capability to effectively balance false positives and false negatives during disease detection.
After initialization, the metrics/mAP 50 quickly increased to 0.89 and gradually stabilized around 0.97. In particular, the metrics/mAP 50–95 started from the initial value and steadily rose to 0.77, remaining stable across different IoU thresholds, which demonstrates the robustness and accuracy of the model in detection of chicken disease. Figure 10 shows the P-R curve and normalized confusion matrix of the DOSA-YOLO model training results, demonstrating the recognition performance for different disease phenotypes. Model detection effect is shown as Figure 11.
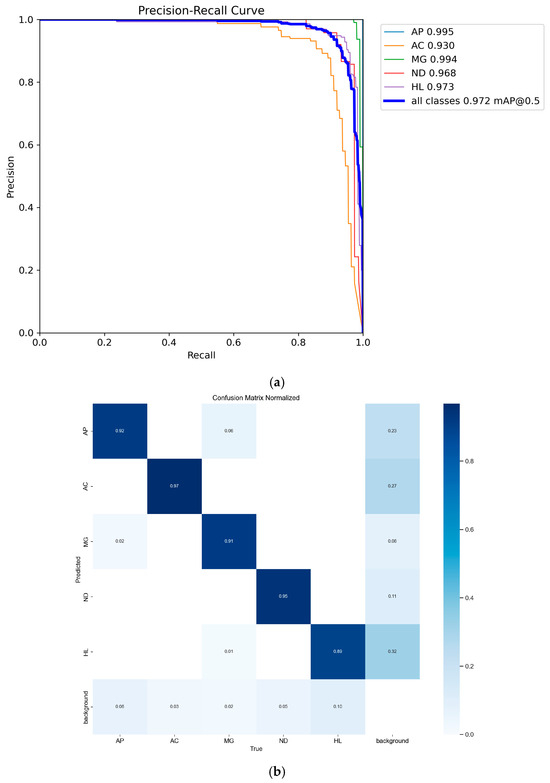
Figure 10.
P-R curves and normalized confusion matrix. (a) P-R Curves; (b) Normalized Confusion Matrix.
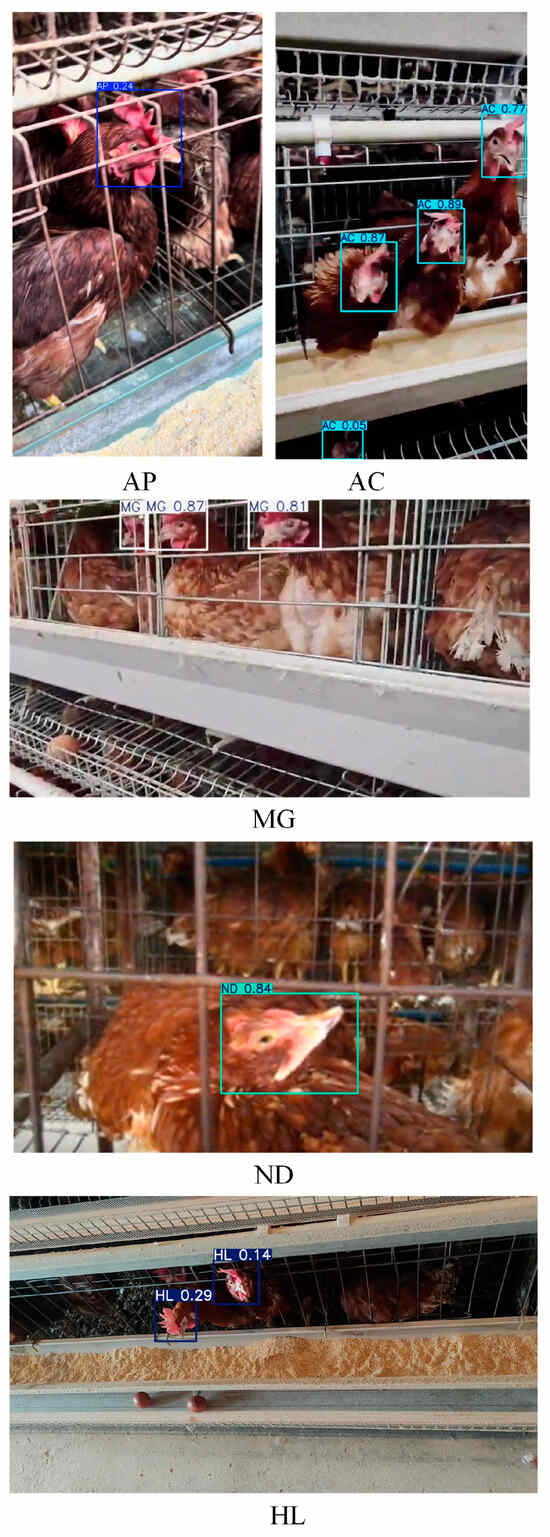

Figure 11.
Model Detection Effect.
3.2. Ablation Study
The ablation study was designed to evaluate the contribution of the improved modules to the model’s overall performance. Using YOLOv11 as the baseline, a series of ablation experiments were conducted by incrementally incorporating the three modules introduced in Section 2.2. The performance of individual components is as shown in Table 3, while the effects of various combinations on algorithm performance are as shown in Figure 12.

Table 3.
Ablation study results.
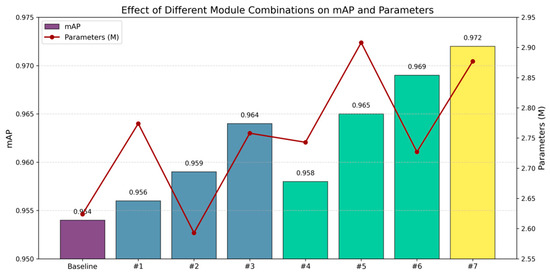
Figure 12.
Performance enhancement of various combinations on algorithm efficiency.
When MSDA was integrated into the backbone network, the mAP increased by 1.0% with only a 0.134 M increase in parameters compared to the baseline. This indicates that by controlling the dilation rate, MSDA can adaptively capture local details, enhancing the focus on lesion areas. Compared to the baseline, when only the MDJA module was used to improve the neck layer, the mAP increased by 0.5%, while the parameters reduced 0.031 M. This demonstrated that optimizing the neck layer effectively enhances the discrimination between lesions and background, achieving a synergy between computational efficiency and accuracy. The introduction of the SEAM module was not ideal; however, when combined with MSDA and MDJA modules, the mAP increased by 1.8% with only a 0.253 M increase in parameter compared to the baseline. This suggested that the combination of SEAM with the other two modules effectively optimizes the network’s feature extraction ability, enhancing the overall model’s capacity to recognize complex disease features and improving computational efficiency. Particularly, in the context of chicken phenotypic features, where lesions often exhibited dense occlusion and complex local variations, the synergistic effect of the SEAM module enhanced the model’s multi-level feature learning capability, thereby improving overall detection accuracy.
3.3. Comparison with Similar Models
This study compares the performance of eight object detection models on the same chicken disease dataset, with the training results shown in Table 4. All models were trained from scratch without using pre-trained weights.

Table 4.
Training results of eight object detection models.
As shown in Table 4, YOLOv11 achieved an F1-Score of 0.92, improving by 0.01 compared to YOLOv12. Additionally, YOLOv11n reduced GFLOPs by 1.5% compared to YOLOv12n. Therefore, YOLOv11 was chosen as the baseline algorithm for further optimization.
The improved model, DOSA-YOLO, exceled in both accuracy and computational efficiency. DOSA-YOLO achieved a mAP of 97.2%, an increase of 1.8% over YOLOv11n. The model’s GFLOPs and parameters were 6.9 and 2.877 M, respectively, showing increases of 0.3% and 0.253 M compared to YOLOv11n. Despite the increase in computational complexity and parameters, DOSA-YOLO’s F1-Score of 0.950 improved by 3% over YOLOv11n’s 0.920.
Compared to YOLOv5n, YOLOv7tiny, YOLOv8n, YOLOv9t, YOLOv12n, and Faster R-CNN, DOSA-YOLO achieved increases in mAP of 4.0%, 4.0%, 3.0%, 4.0%, 4.0%, and 13.0%, respectively. While GFLOPs and parameter count increased by 0.003% and 0.195 M compared to the latest YOLO12, the detection accuracy and F1-Score improved by 1.7% and 0.4. This highlights the advantage of DOSA-YOLO in detection accuracy and efficiency.
The precision, recall, and mAP curves of iterative processes for the eight algorithms are shown in Figure 13. These curves further demonstrate the superior performance of the DOSA-YOLO model.

Figure 13.
Precision, recall, and mAP curves of iterative processes for eight algorithms.
Table 5 presents the average precision values for different diseases, indicating that DOSA-YOLO outperforms the other seven models in disease recognition. Specifically, compared to Faster R-CNN, DOSA-YOLO improved the detection accuracy of AP, AC, MG, ND, and HL by 5.4%, 11.4%, 5.5%, 17.2%, and 14.7%, respectively. However, the mAP for AC is lower than that of other models. Table 6 details the AP improvement rates for each category. Figure 14 shows the recognition accuracy and average precision values for all categories across algorithms, while Figure 15 illustrates the loss curves for different algorithms during the iterative process.

Table 5.
Average precision of each algorithm across all categories.

Table 6.
AP Improvement Rates of DOSA-YOLO Compared to Other Algorithms Across Categories.


Figure 14.
Average precision in each category for eight algorithms.

Figure 15.
Loss curves during the iteration process of several algorithms.
To visually compare the overall performance of each algorithm, a radar chart was created, as shown in Figure 16. To ensure unified comparison, GFLOPs and parameter count were normalized and inverted. In the chart, values closer to 0 indicate higher computational complexity and parameter count, reflecting worse performance, while values closer to 1 indicate better performance. This normalization helps highlight the relative strengths and weaknesses of the algorithms in different performance metrics. As seen in the chart, despite slightly higher computational complexity and parameter count, DOSA-YOLO covers a larger area in the radar chart, with more evenly distributed metrics, indicating a significant advantage in overall performance.
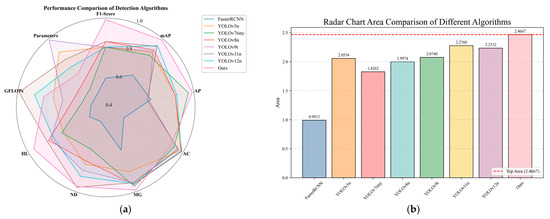
Figure 16.
Radar chart of algorithm performance. (a) Radar chart performance comparison; (b) Area covered by each algorithm in the radar chart.
Disease detection results using YOLOv5n, YOLOv7tin, YOLOv8n, YOLOv9t, YOLOv11n, YOLOv12n, Faster R-CNN, and DOSA-YOLO are presented in Figure 17.
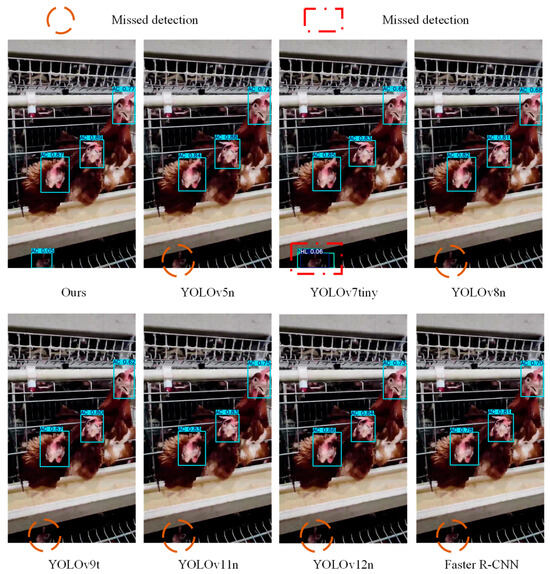
Figure 17.
Detection results of different models.
3.4. Scene Evaluation
To demonstrate the applicability of DOSA-YOLO in practical scenarios, this study conducted model validation in Shanxi Province, China. The purpose of the validation was to explore the model’s performance across various breeding environments. The data were collected from chicken farms located in Nanguang Village, Taigu District, and Shennong Technology Group in Yangqu County, Shanxi Province, as shown in Table 7. These data were exclusively used to validate the performance of DOSA-YOLO in diverse real-world settings. The validation dataset included data from four different breeds of laying hens collected from two distinct test locations. It also accounted for variations in hen postures, angles, and lighting conditions at different times of the day, maximizing the complexity and diversity of the test data. As shown in Figure 18, using the intelligent inspection robot described in Section 2.1.1, which operated in multi-tiered poultry housing, video streams captured by the UV-SH08-HD PTZ camera were wirelessly transmitted to the monitoring room for image data extraction. The data collection process is illustrated in Figure 16. To ensure the reliability and accuracy of the validation results, professional veterinarians performed pathological dissections on sick chickens during the model verification, with these findings serving as a benchmark for evaluating the model’s recognition accuracy.

Table 7.
Data collection for validation.

Figure 18.
Data collection process for chicken farms.
3.5. Expert Collaboration and Model Validation
The veterinary expert team from Shanxi Agricultural University was involved in model validation, addressing challenges such as variations in chicken breeds, environmental conditions, and posture angles across different locations. Statistical analysis was conducted on model predictions, expert evaluations, and pathological anatomy results. Each expert assigned each image into one of the predefined categories. The final classification was determined based on pathological anatomical findings. The quantitative results from the model, experts, and pathological anatomical findings are summarized in Table 8.

Table 8.
Comparison of model scores and expert evaluation results.
As shown in Table 8 the model’s recognition performance is approaching expert level. It is expected that further optimization will enhance its recognition accuracy.
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion of Current Chicken Disease Detection Methods
Current early detection of chicken diseases primarily relies on clinical symptom observation, while accurate diagnosis often depends on invasive or costly laboratory tests. Additionally, challenges such as variability in disease phenotypes, environmental interference, and individual differences among chickens complicate the data collection and annotation process. The scarcity of publicly available chicken disease datasets further limits the development of current detection methods. Recent advancements in deep learning-based chicken disease detection are summarized in Table 9.

Table 9.
Recent advances in chicken disease detection based on deep learning.
Current research on chicken disease detection primarily focused on early diagnosis and classification utilizing image processing, deep learning, and smart devices. Although these technologies had considerably improved detection efficiency and accuracy, existing methods still encountered difficulties in complex environments, model generalization, and accurate multi-disease diagnosis. For instance, Banakar et al. achieved 91.15% classification accuracy for Newcastle disease, bronchitis, and avian influenza by analyzing chicken sound signals with a support vector machine (SVM) classifier [29]. Chidziwisano et al. evaluated the generalizability of deep learning models such as MobileNet and DenseNet for disease prediction, but the models showed average performance in unfamiliar environments [35]. While effective in controlled settings, these approaches face limitations when dealing with multiple disease types and variable environmental conditions.
Ansarimovahed et al. improved classification accuracy for avian influenza and Newcastle disease by segmenting chicken heads and legs based on thermal images combined with the YOLOv8 model, showing that focusing on critical areas significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy [34]. Additionally, Qin et al. proposed an early warning model based on YOLOv5, which efficiently located diseased chicken cages using fecal images and successfully provides early warnings for gastrointestinal diseases [22]. In contrast, an innovative attention mechanism was introduced to the YOLOv11 in this study. It focused on precise detection of key phenotypic features of the chicken head and maintained an average accuracy of 97.2% while detecting multiple chicken diseases. Compared to the improved SSD model proposed by Zhuang et al. [14] for diseased chicken recognition, DOSA-YOLO enhances the model structure with minimal increase in computational complexity, making it more suitable for practical deployment.
Overall, the DOSA-YOLO model, through its attention mechanism and high-quality dataset, provides an effective solution for detecting various chicken diseases, and provides a scientific approach to disease detection based on chicken phenotypic features.
4.2. Model Performance Analysis
As illustrated in Figure 10a, the DOSA-YOLO model achieved AP values exceeding than 0.93 across all five chicken disease categories, demonstrating high effectiveness and strong generalization capability. The model performed particularly well in detecting diseases with distinct external lesions, such as avian pox and Mycoplasma gallisepticum. This indicates its robustness in effectively capturing and distinguishing lesions with obvious skin surface features. In contrast, Newcastle disease detection relied on comb color and specific posture features. Therefore, the complexity of such symptoms presented greater recognition challenges, resulting in relatively lower accuracy. Although detection accuracy of the coccidiosis is high, but slightly lower than other types of diseases as its less apparent external phenotypic.
As shown in Table 4, DOSA-YOLO achieved superior overall performance, achieving the highest mAP with lower GFLOPs and parameters compared to other models. According to Table 5 and Table 6, although YOLOv12n performed slightly better in parameter and computational efficiency, DOSA-YOLO improved mAP and F1-Score by 1.7% and 0.04, respectively. This indicated that it achieved higher accuracy without significantly increasing computational burden. Under the synergy of the MSDA, MDJA, and SEAM modules, the model exhibited strong robustness in real-world scenarios involving multi-scale, high occlusion, and complex backgrounds, as shown in Figure 11. Furthermore, DOSA-YOLO yielded higher confidence in disease classification compared to other models, as shown in Figure 17. Compared with existing methods, the proposed approach enables more accurate multi-disease detection while maintaining lower computational cost, providing a feasible solution for the field application of poultry farms. It should be noted that the detection accuracy for coccidiosis (AC) remained relatively low, as shown in Table 5. As analyzed in Section 2.1.2, the “pale comb” symptom caused by coccidiosis closely resembled the color of light-colored combs and wattles, and the lesion area exhibited smooth texture, making it challenging to capture distinctive features, thus affecting classification performance.
4.3. Model Limitation Analysis
Although the incorporation of three attention mechanism modules improved the model’s contextual feature extraction and detection under partial occlusion, its accuracy may decline in heavily occluded or highly complex environments. For instance, in low-light conditions or when the chicken’s comb and head are severely occluded, model precision may decrease, leading to misclassification or detection failures. The model faces limitations due to cage obstructions, blurred images, and complex environments, including too many chickens in the same cage or individual targets becoming too small to discern the head’s appearance changes, as shown in Figure 19. The model will be restricted in these extreme conditions.

Figure 19.
Scenarios lead to model limitations. (a) Cage obstructions; (b) Blurred images; (c) Complex environments.
Furthermore, the introduction of the MSDA, MDJA, and SEAM modules increased model parameters and FLOPs by approximately 9.6% and 4.5%, respectively, compared to the baseline YOLOv11. This increase may pose challenges to real-time inference efficiency when deployed on edge devices with limited computational resources. Therefore, improving computational efficiency and reducing resource consumption while maintaining accuracy remain key issues for future practical applications. Although multiple chicken breeds were included to enhance model generalization, performance across different farming modes, such as free-range, growth stages, and other poultry breeds requires further validation. Future research could focus on collecting more diverse and multi-scenario data to comprehensively evaluate the adaptability and robustness of the model in real complex scenarios from multiple dimensions, such as environment, breed, and growth cycle.
4.4. Discussion on the Impact of Confidence Threshold on DOSA-YOLO Performance
The balance between detection efficiency and confidence threshold plays a critical role in object detection algorithms, as its choice directly affects model performance. Analysis of Figure 20a,b reveals that with increasing confidence, precision improves, reaching a maximum of 1 at a threshold of approximately 0.826, reflecting enhanced prediction reliability and a lower false positive rate. On the other hand, recall decreases as confidence rises, meaning the model becomes stricter and misses some true positives. The maximum recall occurs at a confidence of 0, at 0.99, but it sharply drops after exceedingly approximately 0.7, indicating an increased number of missed detections. These analyses indicate that in practical chicken disease detection, the confidence threshold can serve as a performance metric. A lower threshold reduces missed detections, while a higher one minimizes false positives. The confidence threshold can be adjusted according to specific operational requirements to achieve different detection purposes. By selecting an appropriate threshold, a balance between precision and recall can be effectively achieved, thereby enhancing the applicability and practicality of the model in real-world environments.
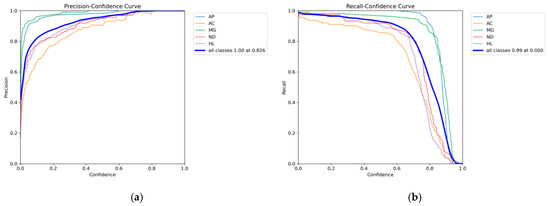
Figure 20.
Precision and Recall Curves. (a) Precision Curve; (b) Recall Curve.
4.5. Economic Benefit Analysis
The DOSA-YOLO model demonstrates not only technical strengths but also potential economic benefits. Firstly, the model maintains high detection accuracy in complex scenarios, helping to reduce both false positives and false negatives, thereby improving the reliability of automated inspections. This is not only expected to reduce the cost of manual inspection but also may further promote the stability of chicken health and production performance by minimizing unnecessary chicken stress. Secondly, although the introduction of new modules in DOSA-YOLO resulted in a slight increase in computational load and parameter count compared to YOLOv11, the overall computational cost remains significantly lower than that of two-stage detectors and is competitive among other comparable mainstream models. This indicates that the model still maintains a low deployment threshold while considering the accuracy, making it feasible for small and medium-sized farms to achieve cost-effective intelligent upgrades. Moreover, the high robustness and stability of the model make it have a long-life cycle in practical applications, potentially reducing long-term costs related to frequent updates and maintenance. In summary, the DOSA-YOLO model demonstrates strong economic potential and application value in terms of improving detection accuracy, optimizing operation costs, and enhancing system efficiency.
5. Conclusions
This study proposes DOSA-YOLO, an advanced object detection model based on YOLOv11, for the automated detection and identification of common diseases in chickens. DOSA-YOLO addresses challenges such as dense occlusion in flocks, multi-scale variations in phenotypic characteristics, and complex background interference by introducing three modules: MDJA, SEAM, and MSDA. Through analysis of key phenotypic features including comb, eyes, wattles, and neck, the model accurately identifies avian pox, coccidiosis, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, Newcastle disease and healthy status, meeting the requirements for all-weather real-time detection. Experimental results demonstrate that DOSA-YOLO significantly improves detection accuracy and robustness compared to the original YOLOv11 model when handling multiple common chicken diseases, achieving a mAP of 97.2% and an F1-Score of 95.0%. With only 2.877 M parameters and 6.9 GFLOPs, it maintains low computational complexity. Compared to Faster R-CNN and other YOLO models, DOSA-YOLO achieves optimal recognition accuracy while maintaining a lightweight design, enhancing real-time detection capabilities. This offers a new scientific approach for modern non-contact chicken disease detection.
The research team will further explore the impact of factors such as breed and age on phenotypic characteristics in chickens. Existing methodologies will be optimized to enhance model robustness and processing efficiency, with validation across multiple pilot farms. Additionally, the team will focus on exploring biomarkers based on vocal and fecal characteristics for disease detection, employing a multimodal approach that combines visual, acoustic, and fecal features to enhance the accuracy and reliability of early disease diagnosis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: X.G. and Z.L.; methodology, X.G. and Y.W.; software, X.G. and Y.W.; formal analysis, X.G.; investigation, Q.L. and Z.Z.; data curation, J.L. and Z.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.G.; writing—review and editing, X.G. and Z.L.; visualization, Y.W.; supervision, Z.L.; project administration, Y.W., J.L. and Q.L.; funding acquisition, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Key R&D program of Shanxi Province, funded by the Shanxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology. (grant number: 202302010101002) and Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China, funded by Shanxi Provincial Education Department (project number 2023-092).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol has been reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanxi Agricultural University (protocol code: NO.SXAU-EAW-2022H.AE.009012314; approval date: 15 September 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
The study involves the poultry farm owner and the chickens under his care, with written informed consent obtained from the animal owners.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available due to privacy and confidentiality. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is it under review by another journal or other publishing venue. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Zhuang, X.; Bi, M.; Guo, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, T. Development of an early warning algorithm to detect sick broilers. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 144, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.A.; Laidlaw, S.M.; Eldaghayes, I.; Kaiser, P.; Cottingham, M.G. Fowlpox virus as a recombinant vaccine vector for use in mammals and poultry. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2005, 4, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.A.; Laidlaw, S.M. Advances in fowlpox vaccination. CABI Rev. 2009, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Panghal, R.; Mehtani, R.; Yadav, R.; Kalonia, S.; Gowthaman, V. Fowl pox virus: A minireview. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2023, 80, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.P.; McKenzie, M.E. Poultry Coccidiosis: Diagnostic and Testing Procedures; John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Glisson, J.R. Bacterial respiratory disease of poultry. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganar, K.; Das, M.; Sinha, S.; Kumar, S. Newcastle disease virus: Current status and our understanding. Virus Res. 2014, 184, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D. Newcastle disease and other avian paramyxoviruses. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2000, 19, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akidarju, M.; Onyemaechi, E.; Dauda, M. An assessment of some poultry management practices and disease recognition by poultry farmers in Maiduguri arid zone, Nigeria. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2010, 66, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhart, D.; Bilic, I.; Grafl, B.; Hess, C.; Hess, M. Diagnosing infectious diseases in poultry requires a holistic approach: A review. Poultry 2023, 2, 252–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, S.; Maheswaran, R. Recognition of poultry disease in real time using extreme learning machine. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Disciplinary Research in Engineering and Technology (ICIDRET2014), Coimbatore, India, 21–22 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Zou, X. DualHet-YOLO: A Dual-Backbone Heterogeneous YOLO Network for Inspection Robots to Recognize Yellow-Feathered Chicken Behavior in Floor-Raised House. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakrosis, A.; Paulauskaite-Taraseviciene, A.; Raudonis, V.; Narusis, I.; Gruzauskas, V.; Gruzauskas, R.; Lagzdinyte-Budnike, I. Towards early poultry health prediction through non-invasive and computer vision-based dropping classification. Animals 2023, 13, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Zhang, T. Detection of sick broilers by digital image processing and deep learning. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 179, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, L.-D.; Quoc, N.P.; Thi, N.H.; Tran, D.C.; Hassan, M.F. Using surf to improve resnet-50 model for poultry disease recognition algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence (ICCI), Bandar Seri Iskandar, Malaysia, 8–9 October 2020; IEEE: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Serbessa, T.A.; Geleta, Y.G.; Terfa, I.O. Review on diseases and health management of poultry and swine. Int. Int. J. Avian Wildl. Biol. 2023, 7, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Akter, J. Machine learning techniques to precaution of emerging disease in the poultry industry. In Proceedings of the 2021 24th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 18–20 December 2021; IEEE: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, G.; Malick, R.A.S.; Akhunzada, A.; Zahid, S.; Sagri, M.R.; Gani, A. An approach towards IoT-based predictive service for early detection of diseases in poultry chickens. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lu, H.; Wang, F.; Zhao, S.; Wang, N. Detection of sick laying hens by infrared thermal imaging and deep learning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2025, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Salsabil, U.S.; Syeed, M.M.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Fatema, K.; Uddin, M.F. Smartpoultry: Early detection of poultry disease from smartphone captured fecal image. In Proceedings of the 2023 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE), Phitsanulok, Thailand, 28 June–1 July 2023; IEEE: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. Converge of coordinate attention boosted YOLOv5 model and quantum dot labeled fluorescent biosensing for rapid detection of the poultry disease. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 206, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Zheng, W. A deep learning method based on YOLOv5 and SuperPoint-SuperGlue for digestive disease warning and cage location backtracking in stacked cage laying hen systems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 222, 108999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmessery, W.M.; Gutiérrez, J.; El-Wahhab, G.G.A.; Elkhaiat, I.A.; El-Soaly, I.S.; Alhag, S.K.; Al-Shuraym, L.A.; Akela, M.A.; Moghanm, F.S.; Abdelshafie, M.F. YOLO-Based Model for Automatic Detection of Broiler Pathological Phenomena through Visual and Thermal Images in Intensive Poultry Houses. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidwasser, N.; Poulsen, L.L.; Leow, P.R.; Khurana, M.P.; Iglesias-Carrasco, M.; Laydon, D.J.; Donnelly, C.; Bojesen, A.M.; Bhatt, S.; Duchene, D.A. Deep learning from videography as a tool for measuring E. coli infection in poultry. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv:2024.11.20.624075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giotis, E.S.; Skinner, M.A. Spotlight on avian pathology: Fowlpox virus. Avian Pathol. 2018, 48, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, E.; Gugsa, G. A review on poultry coccidiosis. Abyssinia J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Feberwee, A.; de Wit, S.; Dijkman, R. Clinical expression, epidemiology, and monitoring of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma synoviae: An update. Avian Pathol. 2021, 51, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzogbema, K.F.-X.; Talaki, E.; Batawui, K.B.; Dao, B.B. Review on Newcastle disease in poultry. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2021, 15, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakar, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Shushtari, A. An intelligent device for diagnosing avian diseases: Newcastle, infectious bronchitis, avian influenza. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakurov, I.; Buzzelli, M.; Schettini, R.; Castelli, M.; Vanneschi, L. Structural similarity index (SSIM) revisited: A data-driven approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 189, 116087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhou, H.; Xie, H.; Wang, B. YOLO-CE: An underwater low-visibility environment target detection algorithm based on YOLO11. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Tang, Y.-M.; Lin, K.-Y.; Gao, Y.; Ma, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.-S.; Ma, J. Dilateformer: Multi-scale dilated transformer for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2023, 25, 8906–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansarimovahed, A.; Banakar, A.; Li, G.; Javidan, S.M. Separating Chickens’ Heads and Legs in Thermal Images via Object Detection and Machine Learning Models to Predict Avian Influenza and Newcastle Disease. Animals 2025, 15, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidziwisano, G.; Samikwa, E.; Daka, C. Deep learning methods for poultry disease prediction using images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 230, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).