Fertilization Effects of Solid Digestate Treatments on Earthworm Community Parameters and Selected Soil Attributes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Digestate
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Earthworm and Soil Sampling
2.4. Soil Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Earthworm Species Found in the Studied Plots
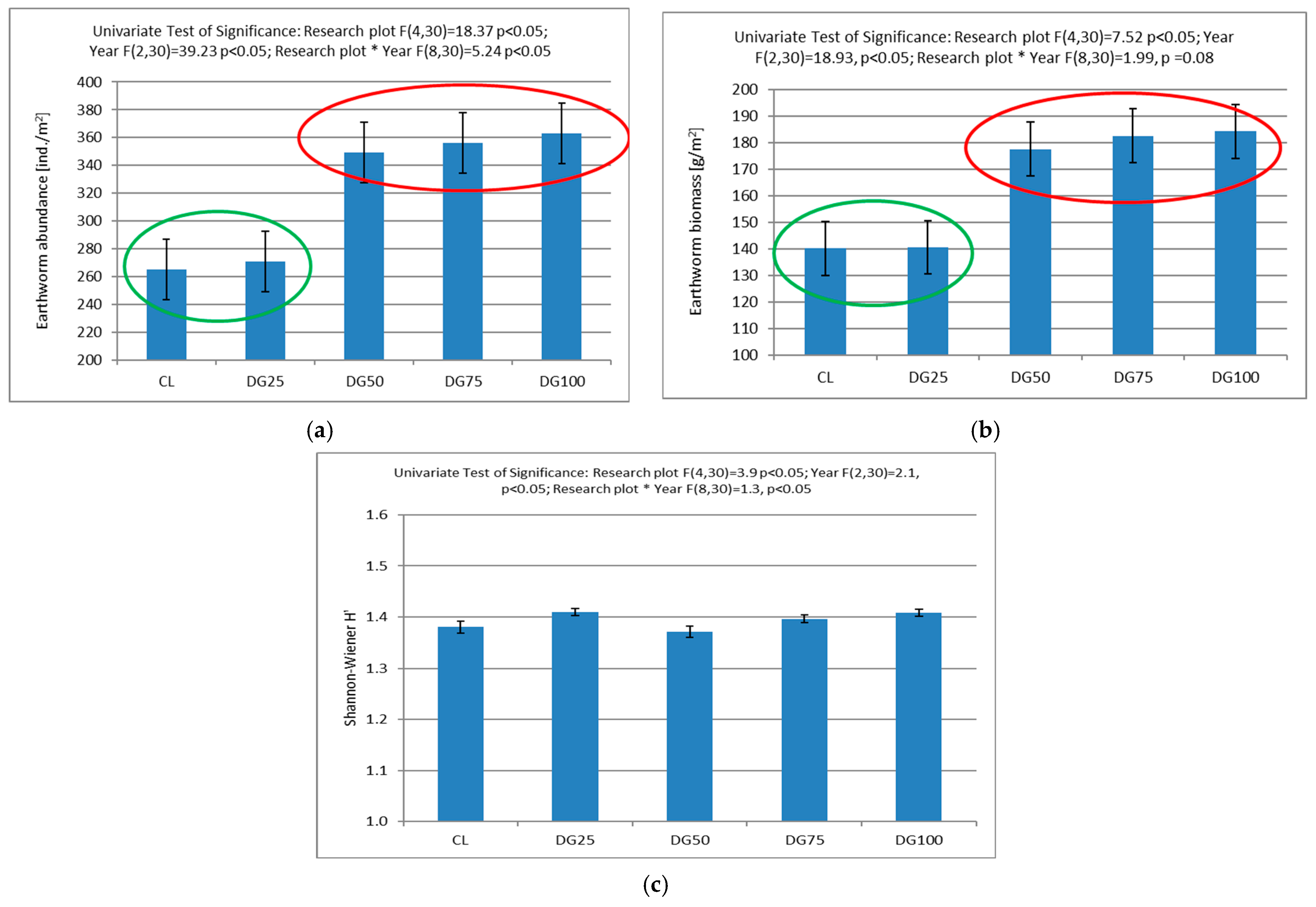
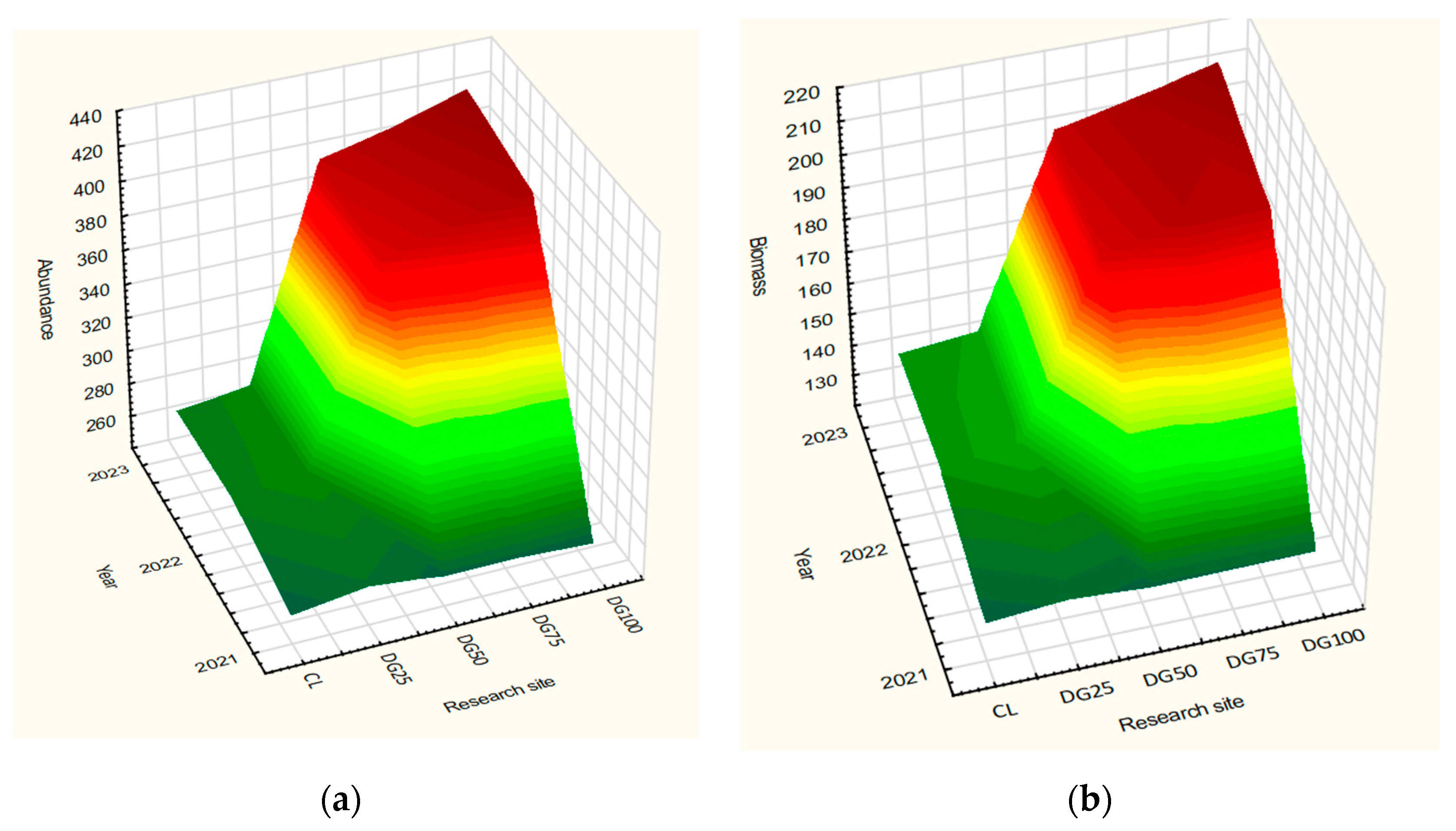
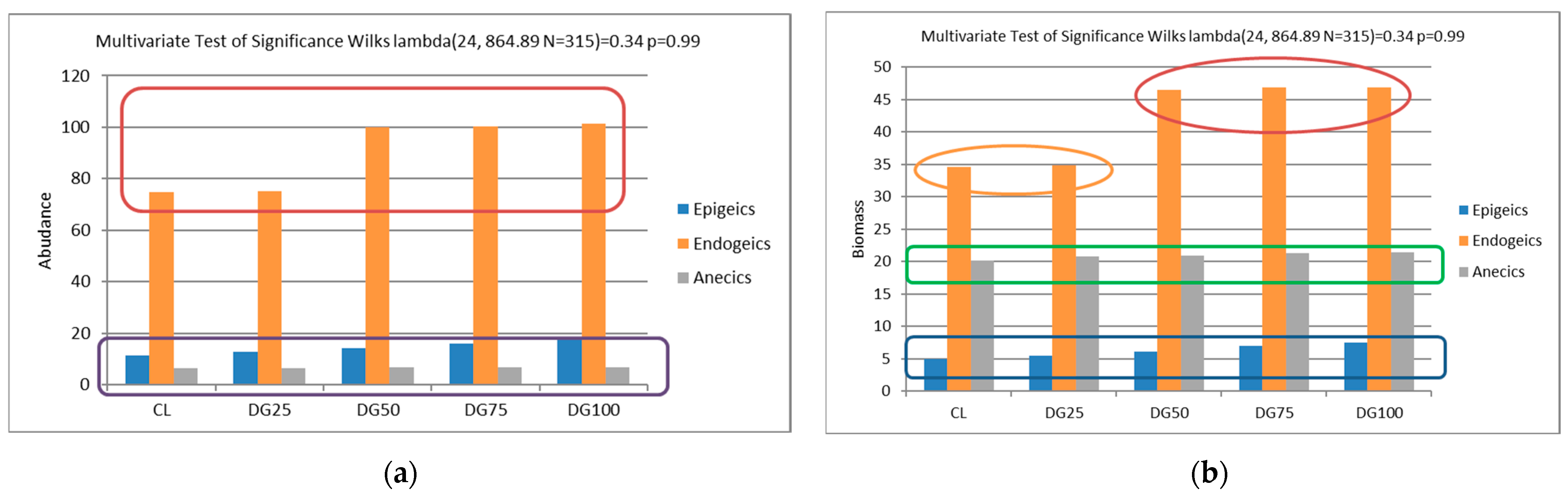
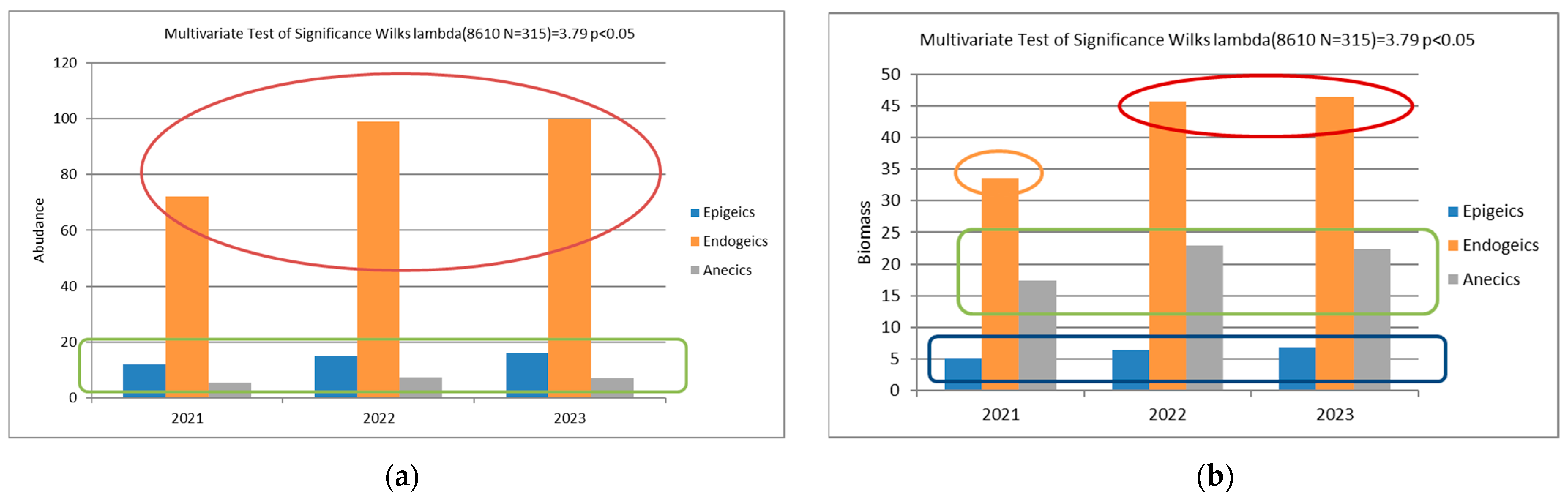
3.2. Effect of Applied Fertilization on Earthworm Abundance and Biomass
3.3. Effect of Different Doses of Digestate on Selected Soil Physicochemical Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Möller, K.; Stinner, W. Effects of organic wastes digestion for biogas production on mineral nutrient availability of biogas effluents. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2010, 87, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, K.; Łapczyńska-Kordon, B.; Jurczyk, M.; Arczewska, M.; Wróbel, M.; Jewiarz, M.; Mudryk, K.; Pająk, T. Solid digestate—Physicochemical and thermal study. Energies 2021, 14, 7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.R.; Cavallo, O.; Malerba, A.D.; Fabbri, C.; Zaccone, C. Unravelling (maize silage) digestate features throughout a full-scale plant: A spectroscopic and thermal approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamatia, S.K.S.; Chaudhuri, P.S. Earthworm community structure under tea plantations (Camellia sinensis) of Tripura (India). Trop. Ecol. 2017, 58, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Xiao, J.; Liu, D.; Ye, G.; Luo, J.; Houlbrooke, D.; Laurenson, S.; Yan, J.; Chen, L.; Tian, J.; et al. Effect of application of dairy manure, effluent and inorganic fertilizer on nitrogen leaching in clayey fluvo-aquic soil: A lysimeter study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Pączka, A.; Butt, K.R.; Garczyńska, M.; Jaromin, M.; Hajduk, E.; Kostecka, J.; Pączka, G. Comparative effects of no-dig and conventional cultivation with vermicompost fertilization on earthworm community parameters and soil physicochemical condition. Agriculture 2024, 14, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Loh, K.C.; Lee, J.; Wang, C.H.; Dai, Y.; Tong, Y.W. Thre-estage anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and horse manure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Escalante, H.; Jaimes-Estevez, J.; Díaz, L.J.; Vecino, K.; Rojas, G.; Mantilla, L. Low cost digester monitoring under realistic conditions: Rural use of biogas and digestate quality. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 239, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive (EU) 2018/851 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 amending Directive 2008/98/EC on waste (Text with EEA relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32018L0851 (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Nkoa, R. Agricultural benefits and environmental risks of soil fertilization with anaerobic digestates: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; de la Fuente, C.; Campoy, M.; Carrasco, L.; Nájera, I.; Baixauli, C.; Caravaca, F.; Roldán, A.; Cegarra, J.; Bernal, M.P. Agricultural use of digestate for horticultural crop production and improvement of soil properties. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 43, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, L.J.; Salter, A.M.; Banks, C.J.; Poppy, G.M. The usability of digestate in organic farming. Water Sci. 2012, 66, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Midden, C.; Harris, J.; Shaw, L.; Sizmur, T.; Pawlett, M. The impact of anaerobic digestate on soil life: A review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 191, 105066, ISSN 0929-1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, M.G. The role of earthworms for assessment of sustainability and as bioindicators. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 74, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, A.; Pommeresche, R.; Riley, H.; Løes, A.K. Anaerobic digestion of animal manure—Implications for crop yields and soil biota in organic farming. In Proceedings of the Nordic View to Sustainable Rural Development 25th Congress, Riga, Latvia, 16–18 June 2015; pp. 2011–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Curry, J.P. Factors affecting the abundance of earthworms in soils. In Earthworm Ecology, 2nd ed.; Edwards, C.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 91–113. ISBN 978-042-912-904-9. Available online: https://llufb.llu.lv/conference/NJF/NJF_2015_Proceedings_Latvia-97-102.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Blouin, M.; Hodson, M.E.; Delgado, E.A.; Baker, G.; Brussaard, E.; Butt, K.R.; Dai, J.; Dendooven, L.; Peres, G.; Tondoh, J.E.; et al. A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015, International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jadczyszyn, T.; Winiarski, R. Use of digestate from agricultural biogas plants for fertilization. Stud. I Rap. IUNG-PIB 2017, 53, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieleman, U. Elektrischer regenwurmfang mit der oktett-methode. Pedobiologia 1986, 29, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Pączka, A.; Pączka, G.; Kostecka, J.; Podolak, A.; Garczyńska, M. Effectiveness of Lumbricidae extracting with an environmentally friendly method. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, K. Soil Oligochaeta III. The Family of Earthworms (Lumbricidae), the Keys to Indicate the Invertebrates of Poland; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1986; 187p. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowska, A.; Gawliński, S.; Szczubiałka, Z. The Soil and Plants Method of Analysis and Evaluation; IOŚ Publishing: Warsaw, Poland, 1991; 334p. [Google Scholar]
- PN ISO 11465:1999; Soil Quality—Determination of Dry Matter Content of Soil and Water in Soil in Terms of Dry Mass—Weight Method. Polish Standardization Committee: Warsaw, Poland, 1999; pp. 1–3.
- Southwood, T.R.E. Ecological Methods, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1978; ISBN 978-0-412-30710-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kasprzak, K.; Niedbała, W. Biocenotic indices used for data organisation and analysis in the quantitative studies. In Methods Used in Soil Zoology; Górny, M., Grüm, L., Eds.; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1981; pp. 397–416. [Google Scholar]
- Górny, M.; Grüm, L. Methods Used in Soil Zoology; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1981; 483p. [Google Scholar]
- Bouché, M.B. Strategies lombriciennes. In Soil Organisms as Components of Ecosystems; Lohm, U., Persson, T., Eds.; Ecological Bulletins: Stockholm, Sweden, 1977; Volume 25, pp. 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Koblenz, B.; Tischer, S.; Rücknagel, J.; Christen, O. Influence of biogas digestate on density, biomass and community composition of earthworms. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 66, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, K.R.; Putwain, P.D. Earthworm community development in organic matter-amended plots on reclaimed colliery spoil. North West Geogr. 2017, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, B.L.M.; Van den Bossche, A.; De Neve, S.; Reheul, D.; Moens, M. The quality of exogenous organic matter: Short-term influence on earthworm abundance. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2007, 43, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, A.; Bos, D.; Ouwehand, J.; de Goede, R.G.M. Long-term effects of fertilisation regime on earthworm abundance in a semi-natural grassland area. Pedobiologia 2006, 50, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, G.; Bhardwaj, P. Earthworm diversity and habitat preferences in arid regions of Rajasthan. ZOOS Print J. 2004, 19, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adigun, M.O.; Akinbola, G.E.; Olaleye, A.O.; Obuh, J. Variability of soil properties across planted fallows under earthworm casts on an alfisols in South Western Nigeria. World J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 4, 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Rollett, A.J.; Bhogal, A.; Scullion, J.; Nicholson, F.A.; Taylor, M.J.; Williams, J.R. The effect of field application of food-based anaerobic digestate on earthworm populations. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 37, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, J.; Walter, R.; Fritz, M. Auswirkung der Düngung MIT Biogasgärresten auf die Bodentiere. Munich: Bayern Forum Biogas 2015. Available online: https://www.biogas-forum-bayern.de/media/files/0001/Auswirkung-der-Dungung-mit-Biogasgarresten-auf-die-Bodentiere.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Moinard, V.; Redondi, C.; Etiévant, V.; Savoie, A.; Duchene, D.; Pelosi, C.; Houot, S.; Capowiez, Y. Short- and long-term impacts of anaerobic digestate spreading on earthworms in cropped soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 168, 104149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogerkamp, M.; Rogaar, H.; Eijsackers, H.J.P. Effect of earthworms on grassland on recently reclaimed polder soils in the Netherlands. In Earthworm Ecology: From Darwin to Vermiculture; Satchell, J.E., Ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1983; pp. 85–105. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C.A.; Bohlen, P.J. Biology and Ecology of Earthworms, 3rd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1996; ISBN 041-256-160-3. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C.A.; Lofty, J.R. The effects of straw residues and their disposal on the soil fauna. In Proceedings of the a Symposium on Straw Decay and Workshop on Assessment Techniques, Hatfield, UK, 10–11 April 1979; Grossbard, E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1979; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix, P.J.; Mueller, B.R.; Bruce, R.R.; Langdale, G.W.; Parmelee, R.W. Abundance and distribution of earthworms in relation to landscape factors on the Georgia Piedmont, U.S.A. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivato, A.; Vanin, S.; Raga, R.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Barausse, A.; Rieple, A.; Laurent, A.; Cossu, R. Use of digestate from a decentralized on-farm biogas plant as fertilizer in soils: An ecotoxicological study for future indicators in risk and life cycle assessment. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.-L.; Wilken, V.; Krück, S.; Nielsen, K.; Sensel-Gunke, K.; Ellmer, F. Assessing the impact of soil amendments made of processed biowaste digestate on soil macrofauna using two different earthworm species. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, G.; Müller, A.; Göhler, H.; Emmerling, C. C and N turnover of fermented residues from biogas plants in soil in the presence of three different earthworm species (Lumbricus terrestris, Aporrectodea longa, Aporrectodea caliginosa). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.K.; Parmelee, R.W.; Edwards, C.A. Population dynamics of earthworm communities in corn agroecosystems receiving organic or inorganic fertilizers amendments. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1998, 27, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, S.; Tischer, S.; Hofmann, B.; Christen, O. Biological soil properties in a long-term tillage trial in Germany. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2010, 173, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadi, M.; Tomocsik, A.; Lengyel, J.; Marton, A. Problems and successess of digestate utilization on crops. In Proceedings of the Internationale Conference ORBIT 2008, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 13–15 October 2008; European Compost Network ECN e.V. 13–16 October 2008. ISBN 3-935974-19-1. [Google Scholar]
- Odlare, M.; Arthurson, V.; Pell, M.; Svensson, K.; Nehrenheim, E.; Abubaker, J. Land application of organic waste—Effects on the soil ecosystem. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villario, S.H.; McDaniel, M.D.; Blauwet, M.J.; Sievers, J.; Sievers, L.; Schulte, L.A.; Miguez, F.E. Adding anaerobic digestate to commercial farm fields increases soil organic carbon. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 21, 101942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, A.; Carter, M.S.; Jensen, E.S.; Hauggard-Nielsen, H.; Ambus, P. Effects of digestate from anaerobically digested cattle slurry and plant materials on soil microbial community and emission of CO2 and N2O. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 63, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Tiwari, K.; Upadhyay, R. Effect of crop residues and biogas slurry incorporation in wheat on yield and soil fertility. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 2000, 48, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Farquharson, R.; Baldock, J. Concepts in modelling N2O emissions from land use. Plant Soil 2008, 309, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; de la Fuente, C.; Bernal, M.P. Chemical properties of anaerobic digestate affecting C and N dynamics in amended soils. Agri. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 160, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Adani, F. Nitrogen mineralization from digestate in comparison to sewage sludge, compost and urea in a laboratory incubated soil experiment. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2017, 180, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimon, T.; Kunzová, E.; Friedlová, M. The effect of digestate, cattle slurry and mineral fertilization on the winter wheat yield and soil quality parameters. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Nest, T.V.; Ruysschaert, G.; Vandecasteele, B.; Cougnon, M.; Merckx, R.; Reheul, D. P availability and P leaching after reducing the mineral P fertilization and the use of digestate products as new organic fertilizers in a 4-year field trial with high P status. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 202, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, K.; Muller, T. Effects of anaerobic digestion on digestate nutrient availability and crop growth: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.B.; Fan, J.B.; Zhou, J. Effects of biogas slurry on soil organic matter and characteristics of soil aggregates in upland red earth. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 3201–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, C. Effects of long-term (23 years) mineral fertilizer and compost application on physical properties of fluvo-aquic soil in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, A.; Sebag, D.; Turberg, P.; Verrecchia, E.P.; Guenat, C.; Brunner, P.; Adatte, T.; Schlaepfer, R.; Le Bayon, R.C. Composition and superposition of alluvial deposits drive macro-biological soil engineering and organic matter dynamics in floodplains. Geoderma 2019, 355, 113899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaša, S.; Badalíková, B.; Ćervinka, J. Influence of digestate on physical properties of soil in ZD Budišov. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2019, 67, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-López, A.M.; Delgado, A.; Anjos, O.; Horta, C. Digestate not only affects nutrient availability but also soil quality indicators. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Units | Digestate |
|---|---|---|
| OC | mg kg−1 (d.m.) | 99,086.4 ± 1283.7 |
| TN | 5621.3 ± 33.2 | |
| P | 1741.2 ± 82.5 | |
| K | 2557.2 ± 121.8 | |
| Ca | 2736.8 ± 163.1 | |
| Mg | 1659.4 ± 75.9 | |
| Cd | 0.4 ± 0.1 | |
| Pb | 1.4 ± 0.2 | |
| C/N ratio | - | 17.63 ± 1.3 |
| pH in H2O | - | 6.89 ± 0.2 |
| Electrical conductivity | mS-cm−1 | 1.25 ± 0.06 |
| Temp. | °C | - |
| Moisture | % | - |
| Species/Ecological Group * | Features | Digestate Treatments ** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL | DG25 | DG50 | DG75 | DG100 | ||
| Epigeics | ||||||
| Dendrodrilus rubidus | Abundance | 8.44 ± 1.21 d | 10.06 ± 1.46 c | 11.59 ± 2.33 b,c | 12.54 ± 3.02 a,b | 13.55 ± 4.12 a |
| Biomass | 1.05 ± 0.17 d | 1.23 ± 0.21 c | 1.43 ± 0.31 b,c | 1.53 ± 0.39 a,b | 1.66 ± 0.51 a | |
| Dominance % | 3.18 | 3.71 | 3.32 | 3.52 | 3.73 | |
| Lumbricus rubellus | Abundance | 10.98 ± 2.00 d | 12.12 ± 1.93 c | 13.22 ± 2.28 b,c | 15.64 ± 3.90 a,b | 16.47 ± 4.95 a |
| Biomass | 5.79 ± 1.16 d | 6.40 ± 1.06 c | 7.01 ± 1.22 b,c | 8.31 ± 2.09 a,b | 8.78 ± 2.69 a | |
| Dominance % | 4.14 | 4.47 | 4.79 | 4.39 | 4.53 | |
| Dendrobaena octaedra | Abundance | 15.26 ± 1.74 c | 16.52 ± 1.03 c | 18.21 ± 1.86 b,c | 20.19 ± 3.41 a,b | 21.99 ± 5.42 a |
| Biomass | 8.12 ± 0.93 c | 8.86 ± 0.54 c | 9.74 ± 0.98 b,c | 10.91 ± 1.83 a,b | 11.87 ± 2.95 a | |
| Dominance % | 5.76 | 6.09 | 5.22 | 5.67 | 6.06 | |
| Endogeics | ||||||
| Aporrectodea caliginosa | Abundance | 122.96 ± 9.18 b | 122.76 ± 9.04 b | 157.58 ± 32.16 a | 158.16 ± 36.44 a | 159.75 ± 37.16 a |
| Biomass | 55.78 ± 5.69 b | 55.24 ± 5.33 b | 71.65 ± 15.71 a | 71.89 ± 17.68 a | 71.20 ± 18.34 a | |
| Dominance % | 46.37 | 45.29 | 45.13 | 44.39 | 44.01 | |
| Aporrectodea rosea | Abundance | 85.47 ± 7.57 b | 87.07 ± 9.94 b | 119.50 ± 29.61 a | 119.89 ± 28.85 a | 121.16 ± 31.59 a |
| Biomass | 40.23 ± 4.77 b | 41.22 ± 5.92 b | 56.47 ± 14.61 a | 56.93 ± 14.29 a | 57.49 ± 15.59 a | |
| Dominance % | 32.23 | 32.13 | 34.23 | 33.65 | 33.38 | |
| Octolasion lacteum | Abundance | 15.67 ± 1.61 b | 15.87 ± 1.53 b | 22.38 ± 5.92 a | 23.11 ± 6.55 a | 23.27 ± 6.02 a |
| Biomass | 7.88 ± 1.09 b | 8.01 ± 1.12 b | 11.35 ± 3.25 a | 11.66 ± 3.53 a | 11.76 ± 3.19 a | |
| Dominance % | 5.91 | 5.86 | 6.41 | 6.48 | 6.41 | |
| Anecics | ||||||
| Lumbricus terrestris | Abundance | 6.39 ± 2.24 a | 6.63 ± 1.95 a | 6.65 ± 1.84 a | 6.79 ± 2.02 a | 6.81 ± 1.62 a |
| Biomass | 20.09 ± 7.11 b | 20.82 ± 6.21 b | 20.87 ± 5.85 b | 21.32 ± 6.44 b | 21.39 ± 5.16 b | |
| Dominance % | 2.41 | 2.45 | 1.90 | 1.90 | 1.88 | |
| Substrate Characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Units | CL | DG25 | DG50 | DG75 | DG100 |
| OC | mg kg−1 (d.m.) | 13,119.6 ± 19.2 e | 14,104 ± 833.6 d | 14,990.3 ± 833.8 c | 15,867.3 ± 762.6 b | 16,797.7 ± 713.3 a |
| TN | 1303.2 ± 13.1 d | 1349.1 ± 88.9 c,d | 1391.0 ± 87.5 b,c | 1449.4 ± 86.7 a,b | 1486.1 ± 80.9 a | |
| P | 223.7 ± 13.5 e | 249.7 ± 14.2 d | 264.3 ± 14.0 c | 279.6 ± 16.9 b | 299.5 ± 16.7 a | |
| K | 238.4 ± 11.6 e | 260.3 ± 13.3 d | 273.1 ± 13.9 c | 288.8 ± 13.1 b | 320.7 ± 12.8 a | |
| Ca | 1491.7 ± 24.0 b | 1492.6 ± 71.3 b | 1528.3 ± 72.9 a | 1552.8 ± 71.5 a | 1587.8 ± 71.1 a | |
| Mg | 83.1 ± 6.7 d | 97.0 ± 11.2 c | 103.9 ± 9.9 c | 124.8 ± 11.9 b | 139.1 ± 12.4 a | |
| Cd | 0.6 ± 0.1 a | 0.6 ± 0.0 a | 0.6 ± 0.0 a | 0.6 ± 0.0 a | 0.6 ± 0.1 a | |
| Pb | 18.9 ± 0.2 a | 18.9 ± 0.1 a | 19.2 ± 0.1 a | 19.3 ± 0.2 a | 19.0 ± 0.2 a | |
| C/N ratio | - | 10.07 ± 0.1 e | 10.46 ± 0.2 d | 10.78 ± 0.1 c | 10.95 ± 0.1 b | 11.30 ± 0.2 a |
| pH in H 02 | - | 7.21 ± 0.1 a | 7.26 ± 0.0 a | 7.18 ± 0.1 a | 7.33 ± 0.1 a | 7.20 ± 0.1 a |
| Electrical conductivity | mS-cm−1 | 0.28 ± 0.04 b | 0.29 ± 0.00 b | 0.30 ± 0.01 a | 0.35 ± 0.02 a | 0.39 ± 0.03 a |
| Temp. | °C | 13.7 ± 1.6 a | 13.7 ± 1.5 a | 13.8 ± 1.4 a | 13.8 ± 1.9 a | 13.6 ± 1.5 a |
| Moisture | % | 24.6 ± 2.9 b | 24.9 ± 2.8 b | 27.3 ± 2.7 a | 27.9 ± 2.7 a | 28.3 ± 2.7 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazur-Pączka, A.; Butt, K.R.; Jaromin, M.; Hajduk, E.; Garczyńska, M.; Kostecka, J.; Pączka, G. Fertilization Effects of Solid Digestate Treatments on Earthworm Community Parameters and Selected Soil Attributes. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141511
Mazur-Pączka A, Butt KR, Jaromin M, Hajduk E, Garczyńska M, Kostecka J, Pączka G. Fertilization Effects of Solid Digestate Treatments on Earthworm Community Parameters and Selected Soil Attributes. Agriculture. 2025; 15(14):1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141511
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazur-Pączka, Anna, Kevin R. Butt, Marcin Jaromin, Edmund Hajduk, Mariola Garczyńska, Joanna Kostecka, and Grzegorz Pączka. 2025. "Fertilization Effects of Solid Digestate Treatments on Earthworm Community Parameters and Selected Soil Attributes" Agriculture 15, no. 14: 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141511
APA StyleMazur-Pączka, A., Butt, K. R., Jaromin, M., Hajduk, E., Garczyńska, M., Kostecka, J., & Pączka, G. (2025). Fertilization Effects of Solid Digestate Treatments on Earthworm Community Parameters and Selected Soil Attributes. Agriculture, 15(14), 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141511






