Comprehensive Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element (PTE) Contamination in Honey from a Historically Polluted Agro-Industrial Landscape: Implications for Agricultural Sustainability and Food Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
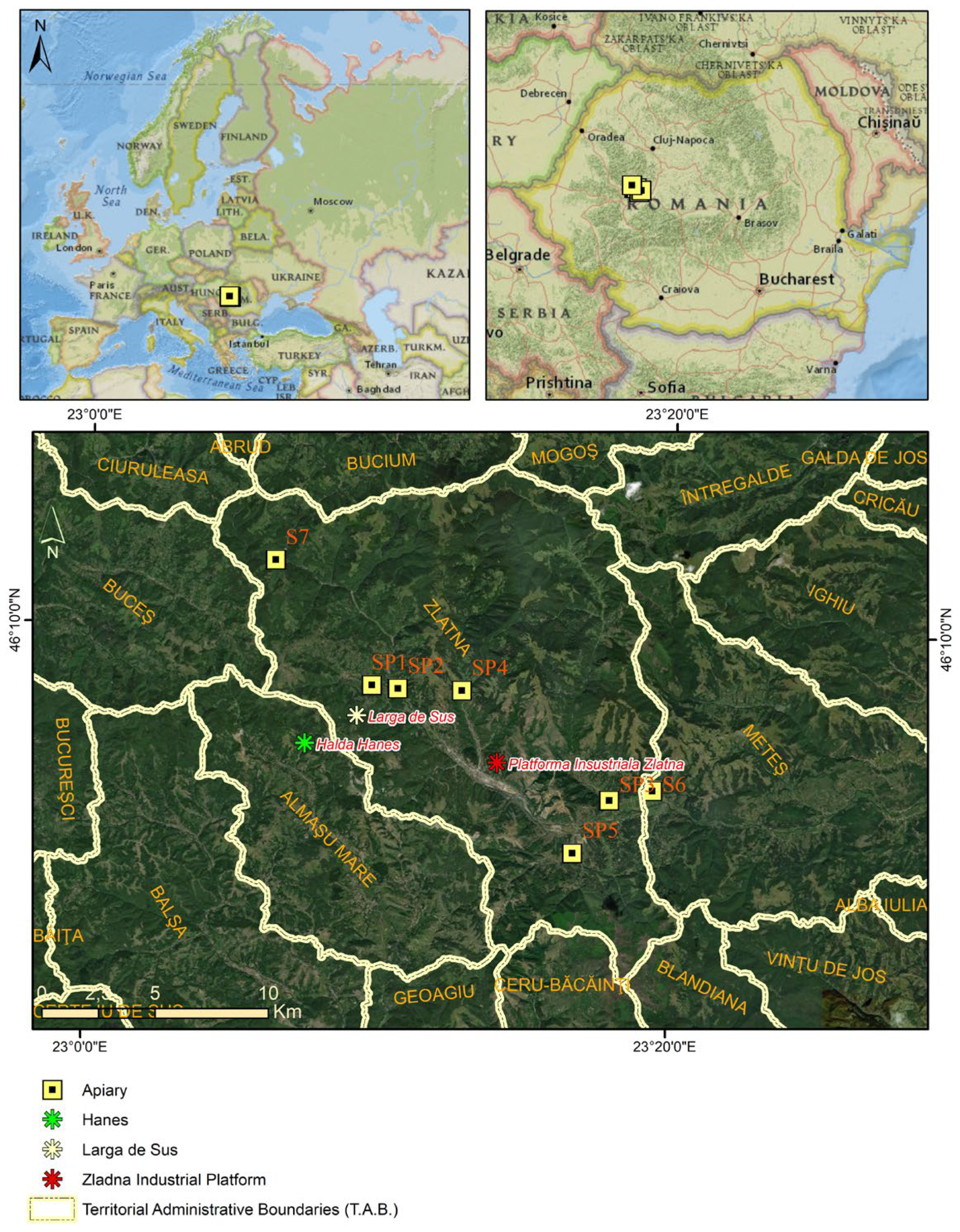
2.1. Study Area and Environmental Background
2.2. Honey Sampling and Storage Protocol
2.3. Sample Preparation and Microwave-Assisted Digestion
2.3.1. Analytical Approaches for Heavy Metal Analysis
2.3.2. The Microwave-Assisted Digestion Methodology
2.4. Instrumentation for FAAS and GFAAS
2.5. Reagents and Calibration
2.6. Analytical Validation and Quality Assurance
2.7. Statistical and Correlation Analysis
3. Results
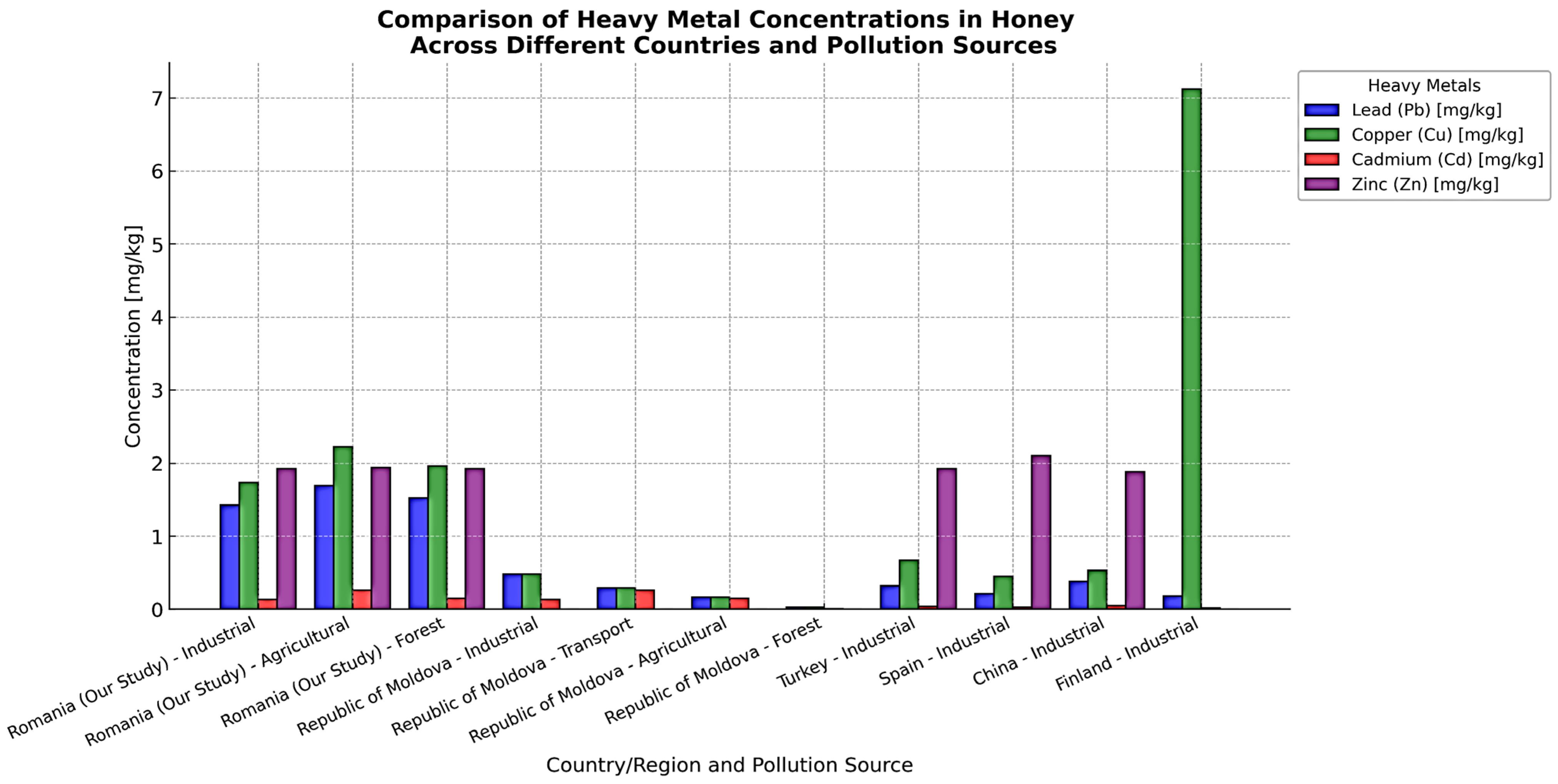
3.1. Spatial and Environmental Factors Influencing Heavy Metal Accumulation in Honey Samples
3.2. Spatial and Environmental Drivers of Risk in Beekeeping Zones
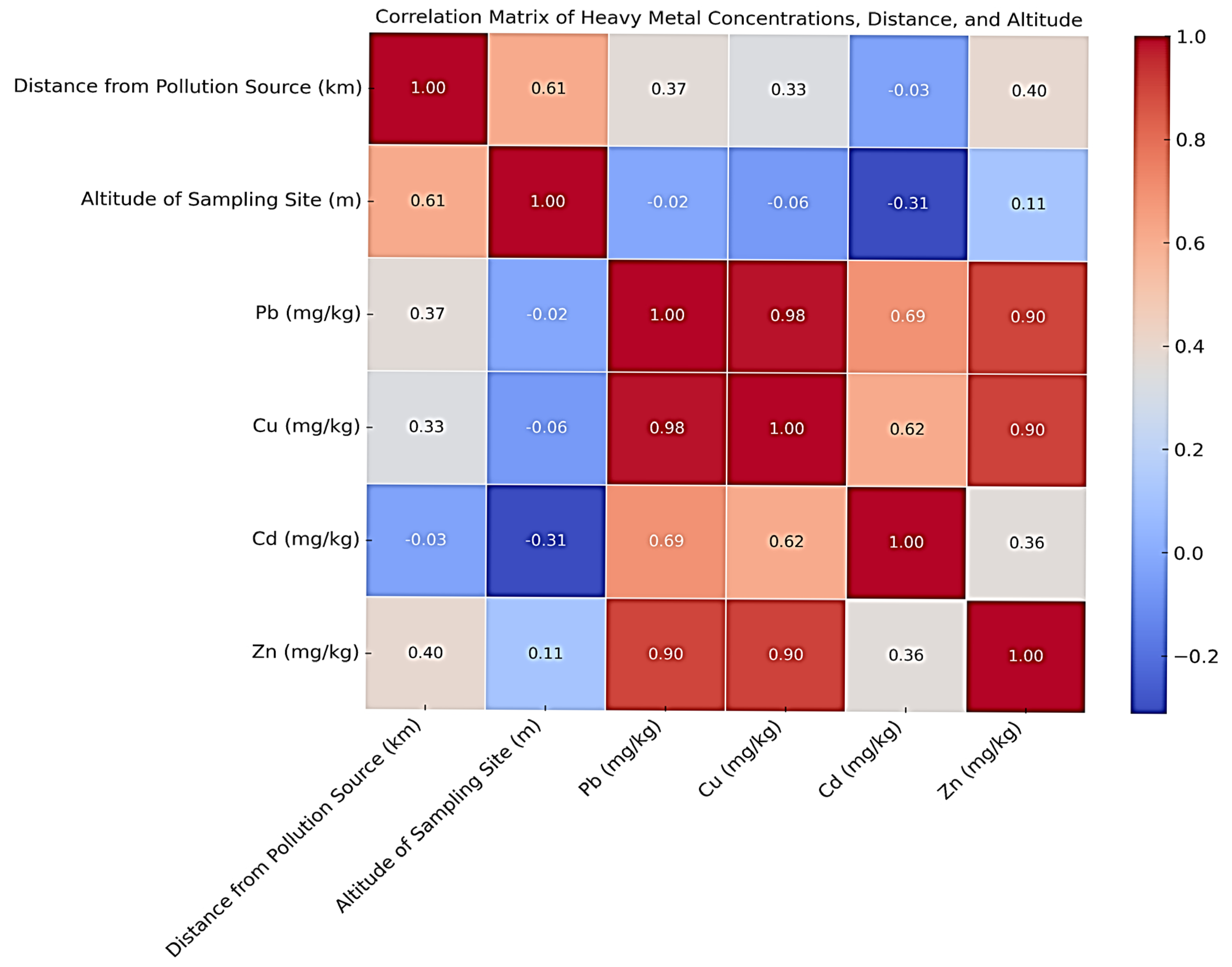
3.3. Correlation Between Heavy Metal Concentrations in Honey, Distance from Pollution Sources, and Altitude
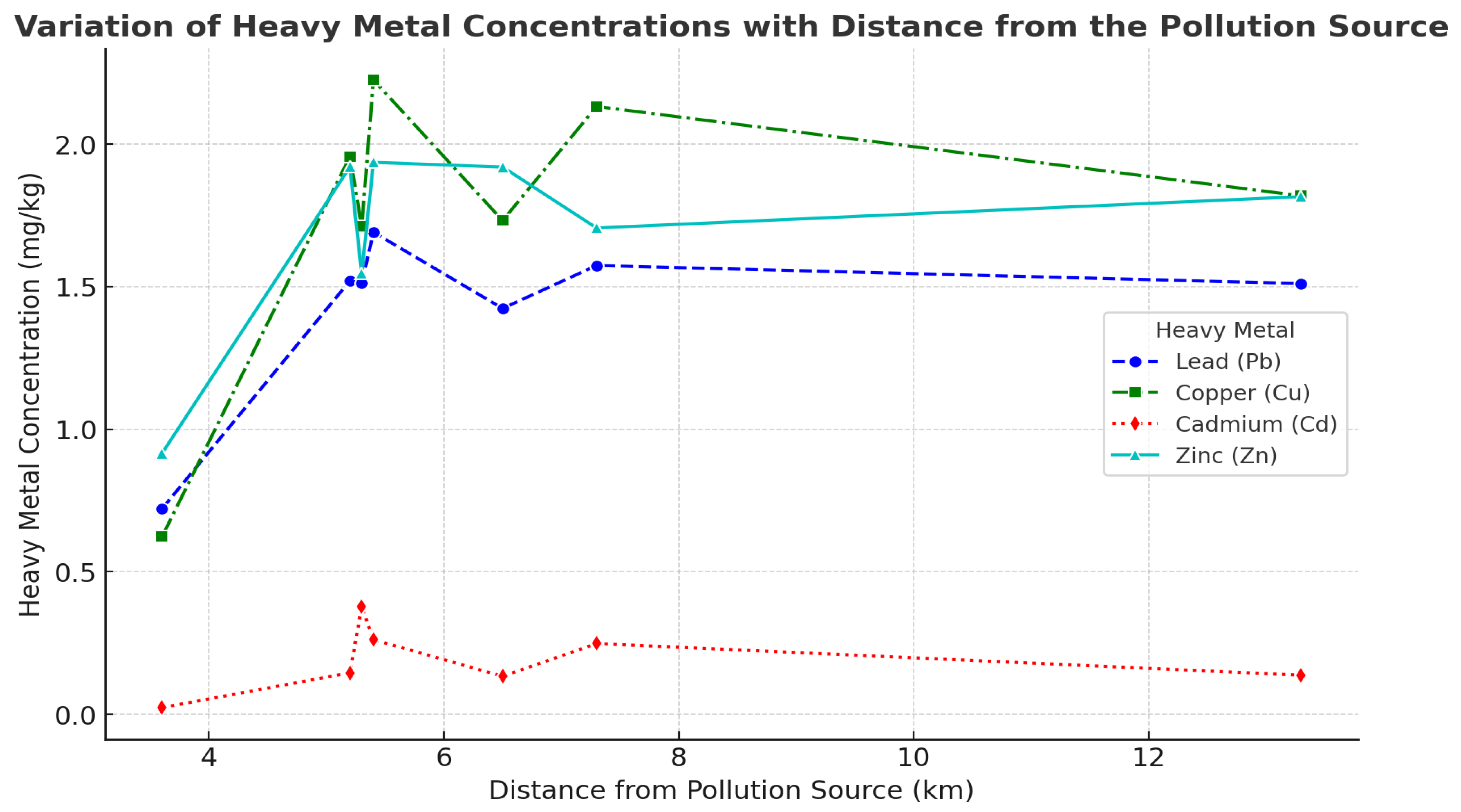
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metal Contamination in Relation to Distance from the Pollution Source
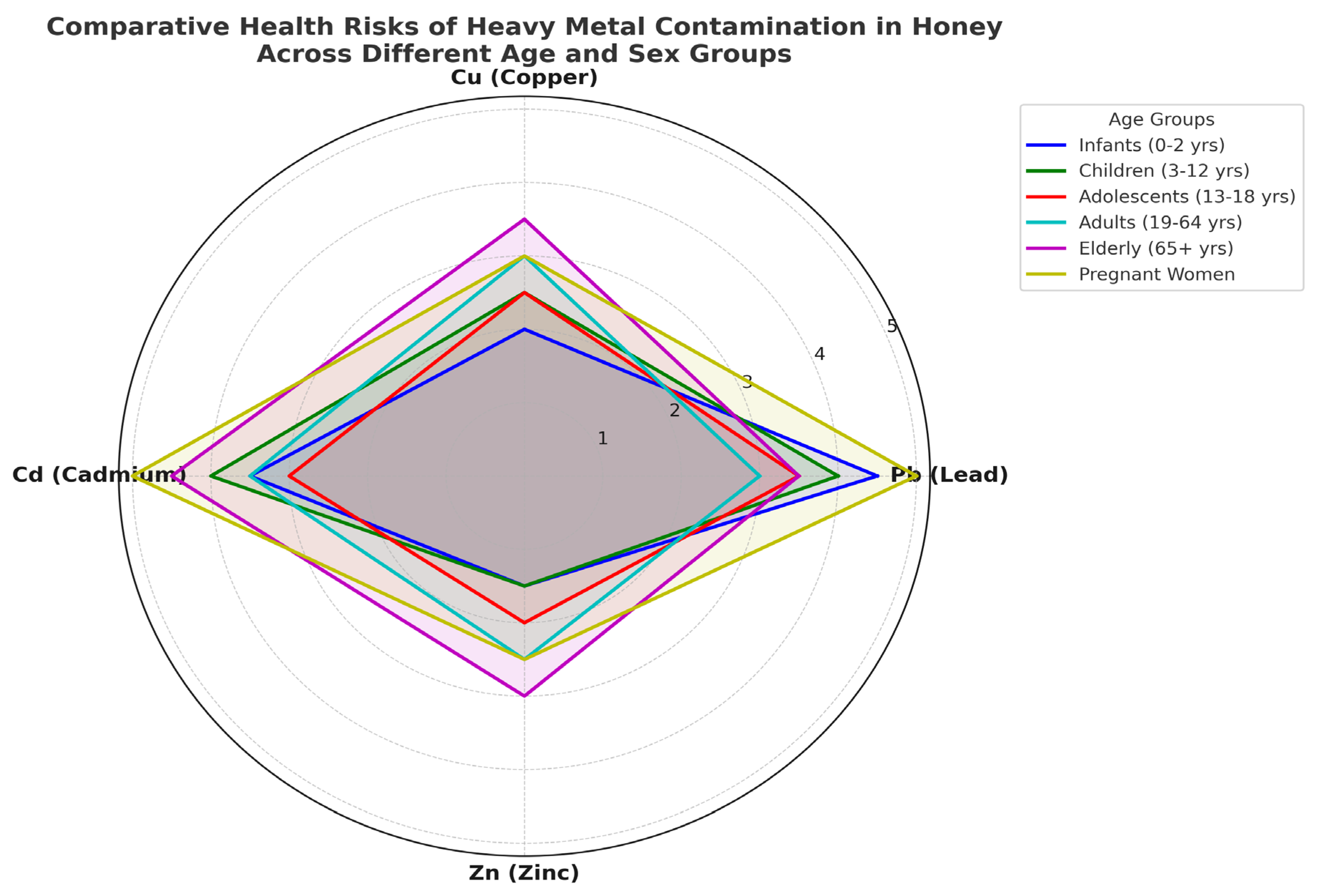
3.5. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Exposure Through Honey Consumption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAS | Atomic Absorption Spectrometry |
| Cd | Cadmium |
| Cu | Copper |
| FAAS | Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry |
| GFAAS | Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry |
| HNO3 | Nitric acid |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| ICP-OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| MRL | Maximum Residue Limit |
| NADESs | Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents |
| PAHs | Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons |
| Pb | Lead |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| Zn | Zinc |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| Na | Sodium |
| K | Potassium |
| Ca | Calcium |
| Fe | Iron |
| Ni | Nickel |
| Cr | Chromium |
| As | Arsenic |
| Mn | Manganese |
| Be | Beryllium |
| V | Vanadium |
| Co | Cobalt |
| B | Boron |
| Bi | Bismuth |
| Sb | Antimony |
| SiO2 | Silicon Dioxide |
| Pb3O4 | Lead(II,IV) oxide |
| PbO4 | Lead Tetroxide |
| TFM-PTFE | Modified Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| SAS | Societas Analytica Scientifica |
| SRB | Sulfate-reducing bacteria |
| EU | European Union |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| RSD% | Relative Standard Deviation Percentage |
| HorRat | Horwitz ratio |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| ppm | Parts per million |
| µg/L | Micrograms per liter |
| mg/kg | Milligrams per kilogram |
| PTEs | Potentially toxic elements |
| MLA | Maximum Legal Allowance |
References
- Bondurand, G.; Bosch, H. Honey: Production, Consumption, and Health Benefits; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés, M.E.; Vigil, P.; Montenegro, G. The medicinal value of honey: A review on its benefits to human health, with a special focus on its effects on glycemic regulation. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2011, 38, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltić, T.; Ćirić, J.; Simunović, S.; Branković-Lazić, I.; Đorđević, V.; Parunović, N.; Katanić, N. Bioactive compounds in honey: A literature overview. Meat Technol. 2023, 64, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, M.; Ahluwalia, P.; Dhandapani, K.M.; Vaibhav, K. Honey: A Sweet Way to Health. In Therapeutic Applications of Honey and Its Phytochemicals; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairan, K.; Mudatsir, M.; Diah, M.; Rizal, S.; Putra, M.I.A.; Jannah, S.M.; Chairani, I. Therapeutic activities of honey in wound care: A narrative review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1356, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, S.; Imtiyaz, Z.; Wali, A.F.; Khan, A.; Rashid, S.M.; Amin, I.; Arafah, A. Honey: A powerful natural antioxidant and its possible mechanism of action. In Therapeutic Applications of Honey and Its Phytochemicals; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S.; Jurendic, T.; Sieber, R.; Gallmann, P. Honey for nutrition and health: A review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2008, 27, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Yangchan, J.; Ahmad, A.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Vyawahare, A.; Khan, R. A mechanistic perspective on chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of phytochemicals in honey. In Therapeutic Applications of Honey and Its Phytochemicals; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 2, pp. 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeshu, M.A.; Geleta, B. Medicinal uses of honey. Biol. Med. 2016, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, S.; Taddeo, V.A.; Fiorito, S.; Epifano, F. Quantification of 4′-geranyloxyferulic acid (GOFA) in honey samples of different origin by validated RP-HPLC-UV method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 117, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, D.S.; Nanda, V. A Comprehensive Introduction to Honey Adulteration. In Advanced Techniques of Honey Analysis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 63–91. [Google Scholar]
- Angioi, R.; Morrin, A.; White, B. The rediscovery of honey for skin repair: Recent advances in mechanisms for honey-mediated wound healing and scaffolded application techniques. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyńska, A.; Żak, N. Polyphenols as the Main Compounds Influencing the Antioxidant Effect of Honey—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, S.A.; Al-Asiri, S.A.; Mahesar, A.L.; Ansari, M.J. Role of honey in modern medicine. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Honey in Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Guide to Future Applications of NADES to Medicines. Adv. Bot. Res. 2021, 97, 361–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Miranda, I.; Moguel-Ordoñez, Y.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Bioactive properties of honeys from stingless bees and Apis mellifera bees in the food industry. J. Apic. Res. 2023, 62, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Majid, S. Therapeutic Applications of Honey and Its Phytochemicals; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; p. 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheepa, F.F.; Liu, H.; Zhao, G. The natural cryoprotectant honey for fertility cryopreservation. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftikhar, A.; Nausheen, R.; Mukhtar, I.; Iqbal, R.K.; Raza, A.; Yasin, A.; Anwar, H. The regenerative potential of honey: A comprehensive literature review. J. Apic. Res. 2022, 62, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, M.; Zaguła, G.; Kaczmarski, M.; Puchalski, C.; Dżugan, M. The Negligible Effect of Toxic Metal Accumulation in the Flowers of Melliferous Plants on the Mineral Composition of Monofloral Honeys. Agriculture 2023, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, N.; Zhang, K.; Hladun, K.R.; Rust, M.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Liu, T.-X.; Trumble, J.T. Joint effects of cadmium and copper on Apis mellifera foragers and larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2020, 237, 108839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovrlić, Z.; Tošić, S.; Kovačević, R.; Jovanović, V.; Krstić, V. The Importance of Measuring Arsenic in Honey, Water, and PM10 for Food Safety as an Environmental Study: Experience from the Mining and Metallurgical Districts of Bor, Serbia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glevitzky, M.; Corcheş, M.T.; Popa, M.; Glevitzky, I.; Vică, M.L. Propolis: Biological Activity and Its Role as a Natural Indicator of Pollution in Mining Areas. Environments 2025, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuk, G.; Sulborska, A.; Stawiarz, E.; Olszewski, K.; Wiącek, D.; Ramzi, N.; Nawrocka, A.; Jędryczka, M. Capacity of honeybees to remove heavy metals from nectar and excrete the contaminants from their bodies. Apidologie 2021, 52, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladun, K.R.; Di, N.; Liu, T.-X.; Trumble, J.T. Metal contaminant accumulation in the hive: Consequences for whole-colony health and brood production in the honey bee (Apis mellifera L.). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvaggio, A.; Pecoraro, R.; Scalisi, E.M.; Tibullo, D.; Lombardo, B.M.; Messina, G.; Brundo, M.V. Morphostructural and immunohistochemical study on the role of metallothionein in the detoxification of heavy metals in Apis mellifera L., 1758. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadil, M.; Krasniqi, D.; Ahmet, M. Heavy metals in honey produced in some localities in Kosovo. Rasāyan J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2013–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădulescu, H.; Ciobanu, O. Impact of air pollution on heavy metals content of honey. In Proceedings of the 18th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM2018, Sofia, Bulgaria, 3–6 December 2018; Volume 18, pp. 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Musa, A.K.; Vanhaelewyn, L.; Hung, Y.; Adeboye, A.A.; Orijemie, E.A.; Popoola, F.A. Honey as a sustainable indicator of heavy metals in tropical rainforest vegetation zone: An early warning monitoring approach. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2023, 43, 1263–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, B.; Gharanfoli, F.; Khayyat, M.H.; Khashyarmanesh, Z.; Rezaee, R.; Karimi, G. Determination of heavy metals in different honey brands from Iranian markets. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2012, 5, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šerevičienė, V.; Zigmontienė, A.; Paliulis, D. Heavy metals in honey collected from contaminated locations: A case of Lithuania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mititelu, M.; Udeanu, D.I.; Docea, A.O.; Tsatsakis, A.; Calina, D.; Arsene, A.L.; Ghica, M. New method for risk assessment in environmental health: The paradigm of heavy metals in honey. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 115194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbilir, F.; Erdoğrul, Ö. Determination of heavy metals in honey in Kahramanmaraş City, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 109, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamminii, F.; Consalvo, A.; Cichelli, A.; Chiaudani, A. Assessing mineral content and heavy metal exposure in Abruzzo honey and bee pollen from different anthropic areas. Foods 2024, 13, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolelli, L.; Ferri, E.N.; Sangiorgi, S.; Porrini, C.; Ferrari, L.; Nenzioni, M.; Girotti, S. Honeybees as bioindicators in environmental monitoring: Practical applications and open online course. In Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, Y.; Mutlaq, A.; Al-Balas, Q.; Azzi, E.; Bouadjela, L.; Taïbi, N.; Bachari, K. Physicochemical characterization and determination of chloramphenicol residues and heavy metals in Algerian honeys. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 33322–33333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratu, I.; Georgescu, C. Chemical contamination of bee honey—Identifying sensor of the environment pollution. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2005, 6, 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Karabagias, I.K.; Louppis, A.P.; Kontakos, S.; Papastephanou, C.; Kontominas, M.G. Characterization and Geographical Discrimination of Greek Pine and Thyme Honeys Based on Their Mineral Content, Using Chemometrics. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Z.; Feng, Q.; Sun, P.L. Health risk assessment of six heavy metals in different sources of honey consumed in China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 680, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehri, A.; Pirhadi, M.; Shokri, S.; Khaniki, G.J. The possible effects of heavy metals in honey as toxic and carcinogenic substances on human health: A systematic review. Uludag Bee J. 2021, 21, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyńska, A.; Żak, N.; Stasiuk, E. Content of selected harmful metals (Zn, Pb, Cd) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in honeys from apiaries located in urbanized areas. Foods 2024, 13, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.; Cunningham, C.; Harper, S.; Ragazzon-Smith, A.; Lythgoe, P.R.; Walker, T.R. Biomonitoring of honey metal(loid) pollution in Northwest England by citizen scientists. Environ. Adv. 2023, 13, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, N.H.; Mok Sam, L.; Ador, K.; Binjamin, B.; Johny-Hasbulah, M.I.J.; Benedick, S. Linking measure of the tropical stingless bee (Apidae, Meliponini, and Heterotrigona itama) honey quality with hives distance to the source of heavy metal pollution in urban and industrial areas in Sabah, Borneo. J. Toxicol. 2022, 2022, 4478082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losfeld, G.; Saunier, J.B.; Grison, C. Minor and trace-elements in apiary products from a historical mining district (Les Malines, France). Food Chem. 2014, 146, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dżugan, M.; Wesołowska, M.; Zaguła, G.; Kaczmarski, M.; Czernicka, M.; Puchalski, C. Honeybees (Apis mellifera) as a biological barrier for contamination of honey by environmental toxic metals. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaku, S.; Aliu, A.; Sylejmani, D.; Ahmetaj, B.; Halili, J. Determination of heavy metals in bee honey as a bioindicator in the Istog, Drenas and Kastriot regions. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, F.D.; Babeș, A.C.; Călugăr, A.; Jitea, M.I.; Hoble, A.; Filimon, R.V.; Bunea, C.I. Unravelling heavy metal dynamics in soil and honey: A case study from Maramureș region, Romania. Foods 2023, 12, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastías, J.M.; Jambon, P.; Muñoz, O.; Manquián, N.; Bahamonde, P.; Neira, M. Honey as a bioindicator of arsenic contamination due to volcanic and mining activities in Chile. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 73, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, P.; Sergiel, I.; Stecka, H. Determination and fractionation of metals in honey. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 39, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goretti, E.; Pallottini, M.; Rossi, R.; La Porta, G.; Gardi, T.; Goga, B.C.; Cappelletti, D. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in honey bee matrix, an indicator to assess the contamination level in terrestrial environments. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereksi-Reguig, D.; Bouchentouf, S.; Allali, H.; Adamczuk, A.; Kowalska, G.; Kowalski, R. Trace elements and heavy metal contents in West Algerian natural honey. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2022, 2022, 7890856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciopec, M.; Pascu, B.; Negrea, P. Inductively coupled plasma optical spectroscopy and atomic absorption spectroscopy. In Microbial Electrochemical Technologies: Fundamentals and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 201–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliu, H.; Makolli, S.; Dizman, S.E.; Kadiri, S.; Hodolli, G. Impact of environmental conditions on heavy metal concentration in honey samples. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2020, 21, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Quinto, M.; Miedico, O.; Spadaccino, G.; Paglia, G.; Mangiacotti, M.; Li, D.; Chiaravalle, A.E. Characterization, chemometric evaluation, and human health-related aspects of essential and toxic elements in Italian honey samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 25374–25384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazeyad, A.Y.; Al-Sarar, A.S.; Rushdi, A.I.; Hassanin, A.S.; Abobakr, Y. Levels of heavy metals in a multifloral Saudi honey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3946–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, M.; Kiruthika, N.; Saranya, T.; Aravind, J. Bibliometric analysis and impact of heavy metals contamination in soils. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2025, 11, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godebo, T.R.; Stoner, H.; Taylor, P.; Jeuland, M. Metals in honey from bees as a proxy for environmental contamination in the United States. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 364, 125221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Raza, M.A.; Tariq, M.; Dai, Z.; Du, D. Heavy metal contamination and their remediation. In Metals Metalloids Soil Plant Water Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, A.; Khalid, S.; Noor, M.J.; Khanoranga. Honey bee products as bioindicator of heavy metals pollution and health risk assessment through the consumption of multifloral honey collected in Azad Kashmir, Pakistan. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 203, 2099–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilalov, F.; Skrebneva, L.; Nikitin, O.; Shuralev, E.A.; Mukminov, M. Seasonal variation in heavy-metal accumulation in honey bees as an indicator of environmental pollution. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Bartha, S.; Taut, I.; Goji, G.; Vlad, I.A.; Dinulică, F. Heavy metal content in polyfloral honey and potential health risk. A case study of Copșa Mică, Romania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; Zeng, L.; Peng, C.; Wang, J. Unlocking soil revival: The role of sulfate-reducing bacteria in mitigating heavy metal contamination. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhat, F.; Hagag, M.; Loutfy, N.; Ahmed, M.T. Contamination of honey with heavy metals, toxicity profile, and health hazards. Dtsch. Lebensm.-Rundsch. 2018, 114, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Olawade, D.B.; Wada, O.Z.; Egbewole, B.I.; Fapohunda, O.; Ige, A.O.; Usman, S.O.; Ajisafe, O. Metal and metal oxide nanomaterials for heavy metal remediation: Novel approaches for selective, regenerative, and scalable water treatment. Front. Nanotechnol. 2024, 6, 1466721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroian, M.; Prisacaru, A.; Hretcanu, E.C.; Stroe, S.G.; Leahu, A.; Buculei, A. Heavy metals profile in honey as a potential indicator of botanical and geographical origin. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcarea, C.; Dzugan, M.; Wesolowska, M.; Chis, A.M.; Zagula, G.; Teusdea, A.C.; Puchalski, C. A comparative study of metal content in selected Polish and Romanian honey samples. Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, F.D.; Andrecan, A.F.; Călugăr, A.; Bunea, C.I.; Popescu, M.; Petrescu-Mag, I.V.; Bunea, A. Comprehensive elemental profiling of Romanian honey: Exploring regional variance, honey types, and analyzed metals for sustainable apicultural and environmental practices. Foods 2024, 13, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludușan, N. Zăcăminte și Poluare pe Valea Ampoiului; Aeternitas: Alba Iulia, Romania, 2002; p. 198. [Google Scholar]
- Ludușan, N.; Dimen, L.; Popa, D.; Bara, A.M. A systematic analysis model for the environment components in metal mining areas. Pangeea 2022, 22, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Clepan, D. Poluarea Mediului; Altip: Alba Iulia, Romania, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, M.; Corcheș, M.; Popa, D.; Glevitzky, M. Educating future engineers for the prevention of heavy metals contamination of surface waters in mining areas: The case of Zlatna, Alba County. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 83, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, G.E.; Micle, V.; Sur, I.M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the soils nearby “Larga de Sus” mine (Romania). ProEnvironment Promediu 2019, 12, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Gurzău, E.S.; Ponoran, C.; Ponoran, S.; Micka, M.A.; Billig, P.; Silberschmidt, M. Zlatna case study. In Environment, Work & Health in the New Central and Eastern European Democracies; Euforie: Eforie, Romania, 24–26 October 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Weindorf, D.C.; Paulette, L.; Man, T. In-situ assessment of metal contamination via portable X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy: Zlatna, Romania. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed (CODEX STAN 193-1995); FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/fr/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B193-1995%252FCXS_193e.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Bayir, H.; Aygun, A. Heavy metal in honey bees, honey and pollen produced in different locations of Konya province in Turkey; (Version 1). Res. Sq. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.I.M.; Eding, E.H.; Verreth, J.A.J. The effect of recirculating aquaculture systems on the concentrations of heavy metals in culture water and tissues of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Scientific Opinion on Lead and Cadmium in Food. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Q.-M.; Feng, Q.; He, J.-Z. Risk assessment of heavy metals in honey consumed in Zhejiang province, southeastern China. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Paramás, A.M.; Gómez-Bárez, J.A.; García-Villanova, R.J.; Rivas-Palá, T.; Ardanuy-Albajar, R.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J. Geographical discrimination of honeys by using mineral composition and common chemical quality parameters. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç Altun, S.; Dinç, H.; Paksoy, N.; Karaçal Temamoğulları, F.; Savrunlu, M. Analyses of Mineral Content and Heavy Metal of Honey Samples from South and East Region of Turkey by Using ICP-MS. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 2017, 6391454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

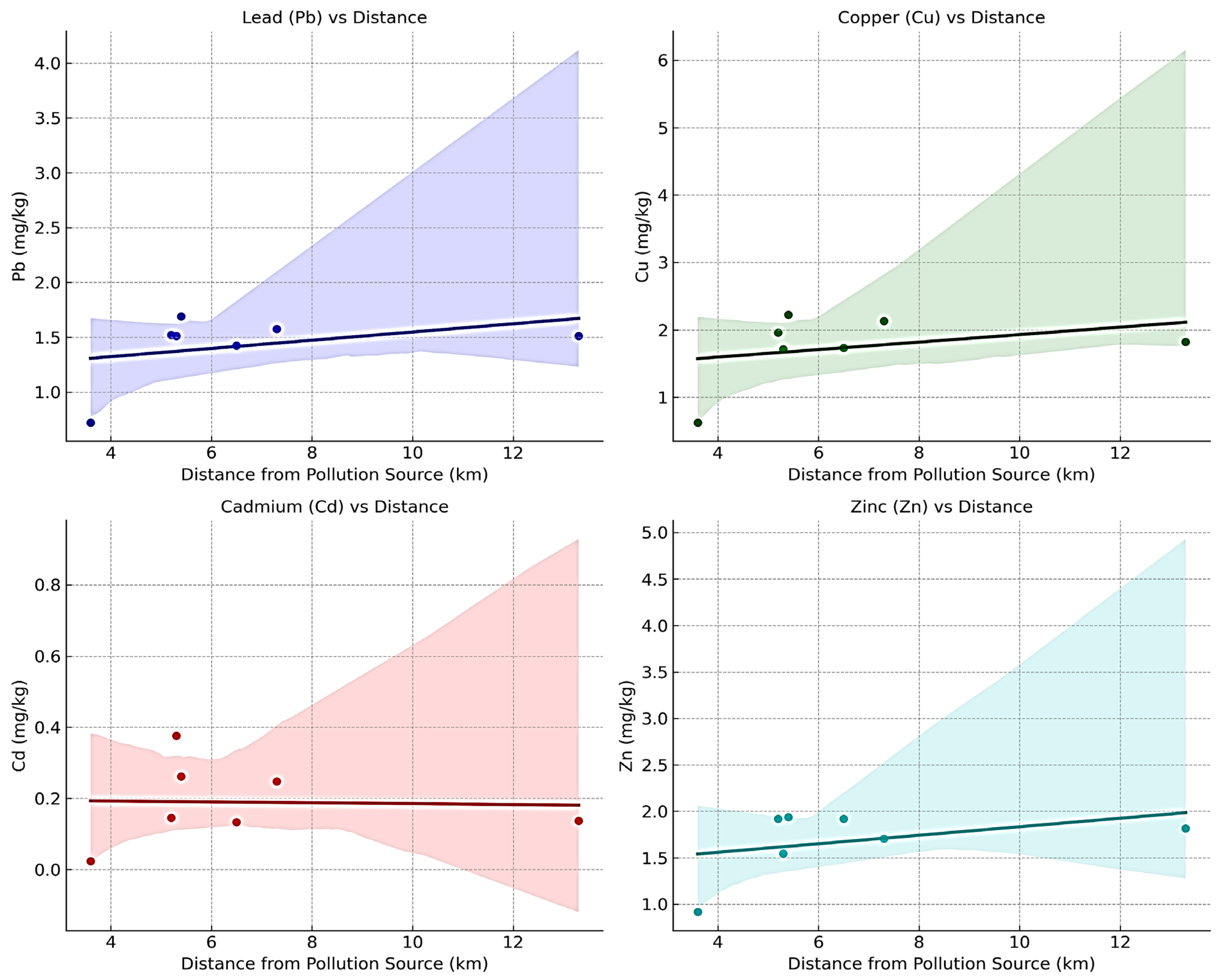
| Location | Altitude of the Sampling Area Above Sea Level (m) | Distance from the Pollution Source (km) | Altitude of the Pollution Source Above Sea Level (m) | Pb mg/kg | Cu mg/kg | Cd mg/kg | Zn mg/kg | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLA | MLA | MLA | MLA | |||||
| 0.10 mg/kg | 5.00 mg/kg | 0.01 mg/kg | 5.00 mg/kg | |||||
| Trâmpoiele | 534 | 6.5 Area I | 609 | 1.42 ± 0.39 a | 1.73 ± 0.21 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 b | 1.92 ± 0.01 a | 3.89 ± 0.01 ab |
| 1.5 Area II | 706 | |||||||
| 4.8 Area III | 715 | |||||||
| Izvorul Ampoiului | 582 | 5.4 Area I | 609 | 1.69 ± 0.19 a | 2.22 ± 0.24 a | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 1.93 ± 0.01 a | 3.76 ± 0.02 d |
| 2.2 Area II | 706 | |||||||
| 4.7 Area III | 715 | |||||||
| Feneș | 360 | 5.2 Area I | 609 | 1.52 ± 0.23 a | 1.95 ± 0.05 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 b | 1.92 ± 0.01 a | 3.93 ± 0.01 a |
| 11.8 Area II | 706 | |||||||
| 13.3 Area III | 715 | |||||||
| Vîltori | 502 | 3.6 Area I | 609 | 0.72 ± 0.23 b | 0.62 ± 0.03 b | 0.02 ± 0.001 c | 0.91 ± 0.01 b | 3.86 ± 0.01 bc |
| 4.8 Area II | 706 | |||||||
| 7.3 Area III | 715 | |||||||
| Valea Mică | 400 | 5.3 Area I | 609 | 1.51 ± 0.32 a | 1.71 ± 0.03 a | 0.37 ± 0.01 a | 1.54 ± 0.01 a | 3.88 ± 0.02 bc |
| 11.3 Area II | 706 | |||||||
| 12.7 Area III | 715 | |||||||
| Presaca Ampoiului | 373 | 7.3 Area I | 609 | 1.57 ± 0.62 a | 2.13 ± 0.03 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 1.70 ± 0.01 a | 3.81 ± 0.04 c |
| 13.6 Area II | 706 | |||||||
| 15.4 Area III | 715 | |||||||
| Budeni | 692 | 13.3 Area I | 609 | 1.51 ± 0.32 a | 1.81 ± 0.03 a | 0.13 ± 0.001 b | 1.81 ± 0.01 a | 3.9 ± 0.01 ab |
| 7.8 Area II | 706 | |||||||
| 8.1 Area III | 715 | |||||||
| F Value | 9.87 | 8.23 | 7.45 | 5.66 | 71.00 | |||
| p Value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.01 | |||
| Significance | ** | ** | * | * | *** | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlad, I.A.; Bartha, S.; Goji, G.; Tăut, I.; Rebrean, F.A.; Burescu, L.I.N.; Pășcuț, C.G.; Moțiu, P.T.; Tunduc, A.; Bunea, C.I.; et al. Comprehensive Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element (PTE) Contamination in Honey from a Historically Polluted Agro-Industrial Landscape: Implications for Agricultural Sustainability and Food Safety. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111176
Vlad IA, Bartha S, Goji G, Tăut I, Rebrean FA, Burescu LIN, Pășcuț CG, Moțiu PT, Tunduc A, Bunea CI, et al. Comprehensive Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element (PTE) Contamination in Honey from a Historically Polluted Agro-Industrial Landscape: Implications for Agricultural Sustainability and Food Safety. Agriculture. 2025; 15(11):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111176
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlad, Ioana Andra, Szilárd Bartha, Győző Goji, Ioan Tăut, Florin Alexandru Rebrean, Laviniu Ioan Nuțu Burescu, Călin Gheorghe Pășcuț, Petrică Tudor Moțiu, Adrian Tunduc, Claudiu Ion Bunea, and et al. 2025. "Comprehensive Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element (PTE) Contamination in Honey from a Historically Polluted Agro-Industrial Landscape: Implications for Agricultural Sustainability and Food Safety" Agriculture 15, no. 11: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111176
APA StyleVlad, I. A., Bartha, S., Goji, G., Tăut, I., Rebrean, F. A., Burescu, L. I. N., Pășcuț, C. G., Moțiu, P. T., Tunduc, A., Bunea, C. I., & Bora, F.-D. (2025). Comprehensive Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element (PTE) Contamination in Honey from a Historically Polluted Agro-Industrial Landscape: Implications for Agricultural Sustainability and Food Safety. Agriculture, 15(11), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111176







