Abstract
Big data approaches are rapidly expanding across many fields of science and are seeing increasing application, yet the use of big data in research related to invasive species lags. Big data can play a key role in predicting, detecting, preventing, controlling, and eradicating biological invasions. Here, we assess terms in the literature related to big data, biological invasions, and agriculture and review sources of big data, including museum records, crowdsourcing observations, natural history collections, and DNA-based information. These sources can be combined with environmental data to build models, predict the origins of invasive species, and develop control methods. To harness the power of data for agricultural biological invasions, several action areas are recommended to streamline processes and improve data sources.
1. Introduction
Big data, defined here as data large in volume (too large to process with commodity methods), collected or accessed with increased velocities, existing in a variety of data formats, and with varying reliability, are revolutionizing the way societies address global challenges [1,2]. Increasingly, big data are being produced, combined, and analyzed to provide insights and solutions across diverse fields, including business [3], finance [4], healthcare [2], city planning [5], and transportation [6]. Agricultural stakeholders have also begun to see the potential value of using big data for decision-making; estimates suggest that the implementation of big data planting practices in agriculture will increase annual global profits from crops by $20 billion USD [7], and additional applications can lead to agricultural sustainability, provide solutions to address the global food security crisis, and contribute to conservation objectives. However, implementation of such efforts lags behind that of other sectors (Figure 1A) [8,9], including efforts in biological invasions, which cause between $83 and 300 billion USD in damages annually [10,11,12].
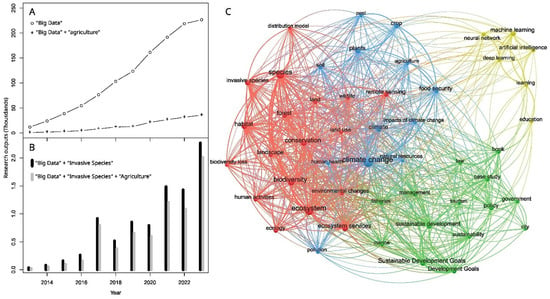
Figure 1.
Trends in “Big Data” research with subcategories of “Agriculture” and “Invasive Species”. (A) Number of research products that include the term “Big Data” with or without the term “Agriculture”; (B) Within “Big Data” publications, number per year that include the terms “Invasive Species” with or without the term “Agriculture”; (C) Concept co-occurrence graph for the top 50 concepts in papers that include “Big Data”, “Agriculture”, and “Invasive Species”. Node size corresponds to the number of papers, connections indicate co-occurrence, and thickness increases with frequency. Distance between nodes is not meaningful. Four clusters were identified by color. All data are from dimensions.ai (search conducted in March 2024) for publications appearing from 2013 to 2023. (A,B) was generated using R version 4.3.3 with the code available in Supplemental File S2 trace.txt.
Invasive species, defined as harmful organisms introduced into a novel area that then become established, increase in number, and spread to other areas [13], cause tremendous ecological and environmental damage. However, where big data are being used to address invasive species [14], it is most often in an agricultural context (Figure 1B), including farming crops, livestock, or fish [15]. Big data discussions occur across varying fields and disciplines of invasive species and agriculture.
Invasive species become problematic in agriculture when their numbers are high enough to damage, ruin, or spread diseases in crops or livestock. Although insects are perhaps the most notorious invasive pests of agriculture (including the invasive boll weevil, Anthonomus grandis Boheman, 1843 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), which almost decimated US cotton crops in the early 19th century [16], and aphids (Figure 2A), which account for 26% of all invasive insects [17]), they are only one part of the agricultural invasive landscape (Figure 2). Pathogens, such as the causal agent of olive quick decline syndrome (Figure 2B), which, depending on transmission mechanism, can be spread by wind, water, animal vectors, or global trade, can cause significant damage to agriculture. Similarly, invasive weeds can cost billions of dollars per year to control, increase fire frequency (e.g., cheatgrass, Bromus tectorum L. (Asterales: Asteraceae)), impact rangeland quality (e.g., Canada thistle, Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop (Asterales: Asteraceae)), and impact water quality and quantity (e.g., water hyacinth, Pontederia crassipes Mart. (Commelinales: Pontederiaceae)) [16]. Across systems and sectors of agriculture, integrating data and computational methods that intersect with when, where, and how invasive species occur will help drive scientific discovery and inform policy-based decision-making for how to approach and combat invasives.

Figure 2.
Many taxa of invasive species affect agriculture across the world. (A) The milkweed aphid, Aphis nerii Boyer de Fonscolombe (Hemiptera: Aphididae), is native to Mediterranean climates but is now common across the Western hemisphere, spreading several mosaic viruses. (B) Olive trees in Italy are impacted by olive quick decline syndrome, a disease caused by Xylella fastidiosa Wells et al. (Xanthomonadales: Xanthomonadaceae), an invasive bacterial pathogen transmitted by spittlebugs (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae). (C) The glassy-winged sharpshooter Homalodisca vitripennis Germar (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) also transmits X. fastidiosa and is responsible for Pierce’s disease epidemics in grapevines in southern California. Photo credits: RAC (A), USDA-ARS (B,C).
To lessen the consequences of biological invasions on agriculture, there are several actions governments and stakeholders can implement. First, surveys provide a baseline of local flora, fauna, and environmental variables before and after the detection of an invasive species. Surveillance mechanisms can include generalized plant, insect, or soil surveys performed by scientists or members of the public or targeted surveillance programs for a specific pest but also include measurements of temperature, rainfall, soil pH, or weather events that can allow prediction of future invasions. Then, detections from survey data can be used to identify high-risk locations where species are likely to invade. With these predictions, many biological invasions can be prevented. If prevention is impossible, existing invasives can be controlled, eradicated, or monitored. In turn, each action against invasion results in data about success rates, future invasions, or further action.
Surveillance, prediction, and data-driven action align well with the objectives of big data analysis. In descriptive analytics, data are aggregated and visualized to observe trends or patterns (as in Figure 1C), such as dispersal rate and distance [18]. Predictive analytics uses machine learning methods (Section 2.1.3) to build models to predict outcomes [19], such as which invasive species may be of most concern. Diagnostic analytics examines the data to determine why an event such as an invasion happened, and prescriptive analytics determines the best course of action [19]. Though we do not address detailed analytics methods here, their utility is clear in their application to address species invasions in an agricultural setting.
To examine recent research activity, we produced an analysis of research outputs for an eleven-year period ending in 2023 (peer-reviewed publications, conference proceedings, datasets, research proposals, and patent applications, among other sources) that included the terms “big data”, “agriculture”, and “invasive species” and grouped the top (most frequent) 50 concepts into four “co-occurring concept” clusters; i.e., ideas or topics that most often occur together in the research output (Figure 1C, Supplemental Figures S1–S5, Tables S1–S5). One cluster (marked in yellow) is clearly related to computational methods, likely focused on how to harness the power of big datasets (Figure 1C). A central cluster (in blue) is heavily connected to climate change; this co-occurring concept group probably focuses on resilience and management via the application of big data to invasive species issues (Figure 1C). A third cluster (in red) is highly focused on conservation and ecosystem issues and includes some of the largest nodes (indicating more common concepts) (Figure 1C). Finally, the fourth cluster (in green) includes concepts such as management, development, and policy issues (Figure 1C). Each of these topics prioritizes distinctive data types and applies them with unique techniques. The relatively few per-node connections between concepts in the computational methods cluster and nodes in the other clusters suggest an opportunity for increased application of these methods across invasive species research, a key motivation for this review.
Here, we discuss how big data are used to discern or predict species distributions in space and time (Section 2.1), identify invasion pathways (Section 2.2), understand the invasion process (Section 2.3), and evaluate current control methods (Section 2.4). We examine these tasks and the following generalized data types relevant to agriculture: species occurrences, environmental variables, images, intercept/trade data, species life histories, and genetic data (Figure 3). For each data type, we identify common data sources and big data methods. We then recommend key actions for overcoming obstacles and challenges in integrating big data platforms into current use systems (Section 3).
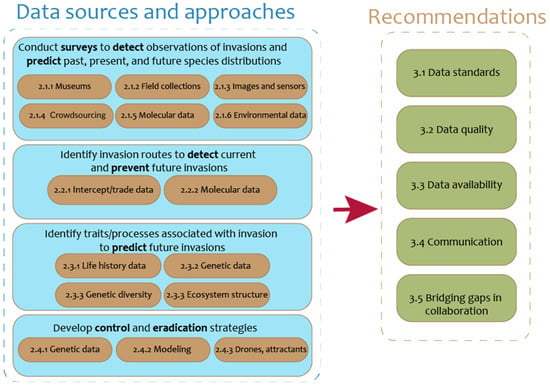
Figure 3.
Data may be used to address the spread of invasive species and its effects on agriculture. Data sources and approaches discussed in this manuscript include (1) surveying to detect the presence of invasive species and predict the current, past, and future distributions; (2) identifying invasion routes to prevent future invasions; (3) identifying traits or processes associated with invasion; and (4) identifying management or eradication strategies. Several data recommendations will make these tasks more feasible, as demonstrated in Section 3.
2. Data Are Used to Predict, Detect, Prevent, Control, and Eradicate Biological Invasions in Agriculture
2.1. Reconstructing Species Distributions with Occurrence Data
To assess the risk of species invasion, a baseline understanding of the biotic and abiotic components of a landscape is needed, i.e., which species are native to a range and what are the normal fluxes in the range for a native species. In the following subsections, we detail various sources of occurrence data and their specific contributions to invasion modeling, including from museums (Section 2.1.1), field sampling/traps (Section 2.1.2), remote and smart trap image data (Section 2.1.3), crowdsourcing (Section 2.1.4), and molecular data (Section 2.1.5). Using biodiversity observations and environmental data (Section 2.1.6), we can build models of current and past species distributions, predict species abundance, and identify likely invaders or high-risk locations to help stop, manage, or control biological invasions.
The basic unit of biodiversity is a species. A minimum of three pieces of data are essential for each species observation: (1) the taxonomic identity of the organism, (2) the collection location, and (3) the date of collection. While abundance is an important measure for determining the impact of invasive species, effective population sizes cannot be directly assessed from a single observation. Nonetheless, observation data are often accompanied by estimates of abundance. Species occurrence databases are maintained by global, continental, country, and state-level organizations [20]. One of the largest, the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), is funded by governments around the world; it is a database that provides >2.5 billion species occurrence records informed by a variety of sources, including fossils, natural history collections, university and government researchers, citizen scientists, camera traps, and remote sensing [21]. The GBIF provides species presence records collected from various sources (e.g., iNaturalist, CSIRO, and museums worldwide) that may be combined to inform assessments of a species’ range.
2.1.1. Museum Collections Are Key to Taxonomy and Occurrence Data
Through hundreds of years of thoughtful curation, museums have preserved locality, temporal, and taxonomic information about biodiversity, providing an idea of how species distributions have changed over the years, including for agricultural pests. Collaborative efforts from organizations like the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS) work to offer a database of taxonomy that is updated as new species are described, and museum workers assign universally unique identifiers to each species record, which is also given a Digital Object Identifier to reference the exact information source [22]. Invasive species researchers need reliable taxonomy to focus their efforts on the correct species or must be aware of shortcomings of the current taxonomy, and museums offer those data and literature resources.
Museums also include physical evidence of occurrence data. Traditionally, museum specimens were only available to morphologists and taxonomists, but today, many museums and universities have digitized their animal and plant collections [20], making these occurrence data widely accessible as a big data source that is accumulating substantial organism image data with millions of observations (see https://www.idigbio.org/, accessed on 21 May 2025). The Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History has contributed over 9 million occurrence records to the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF, https://www.gbif.org/dataset/821cc27a-e3bb-4bc5-ac34-89ada245069d, accessed on 21 May 2025). Likely, only 2% of museum specimen occurrence records have been digitized, and that digitization can also include images and genomic data [23].
Occurrence data from museum specimens can be put into ecological niche models to predict distributions of pests, as was demonstrated with rodent pests in crops in Veracruz, Mexico [24]. In some cases, museum specimen abundance may reflect population size. However, most collections aim to maximize species coverage and thus may overrepresent species-rich or rare taxa [25]. Museum collections often also show bias in locations and taxa sampled depending on taxonomist preference. Many models account for these biases.
In addition to their value in occurrence data, museum collections have been used to show the morphological evolution of invasive species, determine source populations, and reconstruct geographic expansion through time [26].
2.1.2. Monitoring with Field Sampling, Surveys, and Traps
Through field sampling and traps, researchers can also make predictions about species distributions or the population size of invasive organisms, though bias may still occur if there are not enough sampling locations or effort. Field observations are also necessary for determining invasive species’ host plants, natural predators, or competitors. However, with the urgency required for invasive species monitoring and management and limited field expertise and funding, such opportunistic surveys are not enough on their own. Early detection of invasive organisms is essential for effectively responding to biological invasions [27]. Early detection utilizes both active surveillance, which monitors for specific target species (i.e., traps with species-specific attractants), and passive monitoring systems, which allow general monitoring without targeting specific species (i.e., remote sensing, camera traps, acoustic sensors, and any traps without attractants or with a general [e.g., food-based] lure). Note that many methods may be used for both active and passive monitoring, and in crowdsourcing and eDNA research, active and passive monitoring differ in their definitions (see glossary). Regardless of whether active or passive monitoring occurs, rapid identification and taxonomic confirmation of the organisms is essential. The earlier detection and identification occur, the more feasible effective control or eradication of the invasive organisms becomes [28]. To enable early detection of invasions, regular surveys are conducted in high-risk areas (e.g., environmentally suitable areas, ports, airports, and species boundaries), and species with a high potential for invasion are identified for targeted monitoring. However, monitoring large areas frequently and the accompanying taxonomic identification of the organisms requires extensive time and resources. Various university and government research programs regularly conduct field surveys for emerging invasive organisms. Communication between such entities and aggregation of their data are required to apply big data methods.
2.1.3. Occurrence Data and Taxonomy from Image and Sensor Data
While human field sampling and inspection stations remain important, big data approaches for surveillance can amplify the ability to monitor and identify invasive organisms. Rapid image analysis systems have been developed for invasive pest monitoring requiring extensive sampling. Image recognition software has the potential to alleviate the bottleneck often imposed by few taxonomic experts for some taxa, as long as collection methods preserve specimens and the models have been appropriately trained [29].
For surveillance systems using traps, attaching cameras to periodically and automatically store and transmit images or developing integrated traps with embedded image classification systems enables automated monitoring [28]. The advantages of such systems include reducing the need for “trap servicing” (checking for captures), thus saving costs, and quicker or even real-time notification of capture. The principal disadvantages are increased trap cost and potential system complexity (reliability). Automated systems utilizing various camera-equipped traps have been developed for monitoring diverse species in the field [30]. For instance, Diller et al. [31] developed an electronic version of the McPhail trap (a funnel-pheromone trap used with wasps and flies) and tested the field performance of the trap for monitoring three major invasive fruit fly species that damage hundreds of agricultural crop species (Ceratitis capitata Wiedemann, Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel, and Bactrocera zonata Saunders (Diptera: Tephritidae)). The e-trap attracted and retained male flies on a sticky card inside the trap. A high-resolution camera automatically took pictures of the sticky card and sent the images to a remote server, where a deep learning algorithm was applied to identify the species. In the field tests, the algorithm was able to correctly identify the three target fruit fly species with 93 to 95% accuracy on average [26]. Other electronic traps have become commercial products, like RapidAIM (https://rapidaim.io/, RapidAIM PTY LTD, West End, QLD, Australia), SemiosBio Technologies Inc. (https://semios.com, Almanac Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada), and TrapView (https://trapview.com/, EFOS d.o.o., Hruševje, Slovenia). These smart trap platforms offer real-time wireless monitoring of organisms and help make data-driven management decisions, though obstacles remain to their wide deployment, principally cost, as mentioned above.
Other smart trap systems have addressed the cost issue by avoiding the use of an imaging sensor. An early example with fruit flies is the smart trap developed by Jiang and colleagues [32]. This utilized photo-interrupters, where dual infrared light beams were used to ensure accurate counts of pests entering the trap. The system was deployed over a wide area and allowed real-time monitoring and surveillance of the pest [33,34]. The specificity of the lure enabled a simpler counting mechanism; in situations where the trap includes a bycatch, such an approach would be less practical. Similar approaches have continued to be pursued, with considerable success for research applications [35].
Additionally, because image recognition analyses are computationally expensive and storing large numbers of photos requires considerable infrastructure, alternative methods for remotely quantifying organism abundance are being explored. For winged insects, optoelectronic sensors, which detect non-visible light, can be used to identify specific wing beat frequencies, providing a method for quantifying specific species in proximity to the sensor with lower data requirements [36]. Optoelectronic sensors can be inexpensive and hold the potential for species identification [37], thus enabling large-scale research on insect abundance and diversity [38]. Newer systems are now incorporating multiple inputs from simple sensors in addition to wing-beat data, such as melanization and flight direction [39]. An excellent review of various techniques currently in use is given by Lello et al. [40]. The challenge for these smart trap systems remains their application in programs.
Accumulating image data from smart traps, remote cameras, sticky cards, etc., is primarily in RGB format, with three color filters that mimic the way that humans perceive color [41]. RGB images can be particularly useful for the automated identification of large organisms with distinct morphological traits or species selectively captured by active traps. However, since RGB images are suitable for characterizing objects based on their shape and color, species that are difficult to identify morphologically may not be classifiable from RGB images alone. To address this, multi/hyper-spectral imaging can also be used for species identification by recording four to hundreds of spectral bands. Although hyperspectral images require large data storage and a more precisely controlled lighting system, they encompass a broader range of information than RGB images, offering diverse utility. Hyperspectral imaging enables discrimination and identification of cryptic species previously only distinguishable via molecular markers, such as ants identified by their cuticular compounds [42], and even allows visualization of parasites inside the eggs of hosts [43].
Remote sensing is another valuable surveillance tool that produces occurrence data used to monitor and specify control methods for invasions. Drone-based aerial remote sensing can be used to survey fields or orchards and find signs of invasives or plants with disease from a less remote setting [44]. Additionally, imaging can provide information about crop damage (e.g., chlorophyll content, biomass, and leaf nitrogen content) used to determine the severity of an invasion or predict damage from future invasions [45].
The large number of photographs assembled by remote cameras and rapid image analysis systems requires tabulation of metadata that are common to all pictures to ease image analysis and later retrieval [46]. Image data are generally larger in size compared to typical ecological data (e.g., date, coordinates, and density) and constitute big data when sufficient volumes accumulate. With such data accumulating, work in computer vision and machine learning has led to many studies introducing and evaluating techniques for automatically identifying species [47].
Machine learning techniques improve in performance as more image data are aggregated, owing to their data-driven nature (Figure 4). In supervised learning, an expert must first label each image (i.e., weed vs. plant), whereas, in unsupervised learning, a machine finds categorizations on its own based on patterns in the images. Several deep learning algorithms have demonstrated their ability to successfully detect and classify insects on traps based on images, with developments in various methods improving the outcomes of these tasks [48]. Similar techniques can be used to detect plant diseases or weeds across landscapes.

Figure 4.
Image analysis: a pragmatic explanation for biologists. Graphic: Taina Litwak, USDA. Photos: USDA-ARS.
While remote sensing, camera traps, and acoustic sensors can be used to detect the presence of invasive species, the data must then be analyzed for detection to occur, and methods of analysis are still in development for many invasive species [49]. Some datasets likely contain taxonomic errors in the original data [50] and lack standardized data collection protocols (e.g., resolution, lighting, and posture). While remote sensing provides the ability for continuous monitoring, cloud cover and obstructing vegetation may interfere with data collection [51]. The technological advancement in automated image capturing and species identification has enhanced the quality of observation submissions, including accounting for biases [52,53], but there is still work to be completed. Various image-based species identification systems enable rapid processing of vast image datasets gathered through field observations but also make citizen science projects and crowdsourcing methods like iNaturalist possible, allowing early detection of invasive organisms.
2.1.4. Crowdsourcing Observation Data
With the advent of artificial intelligence algorithms to identify objects in images and the wide availability of cell phone cameras, invasive species occurrences can be identified and reported in real-time with crowdsourcing through iNaturalist, citizen science, and social media/news. iNaturalist is an online social network that uses an application or a website to allow universal access to photograph and report occurrences of organisms. It sources hundreds of millions of global ecological observations tabulated for biodiversity assessments, taxonomic classification, phenology, and population dynamic modeling [54,55]. With almost 8 million registered users—350,000 of whom were active in the past 30 days—there are over 200 million observations from people all over the world [56]. iNaturalist datasets may be used to identify patterns associated with both native and non-native species, especially in urban settings [57], but are also applicable to natural and agricultural areas. However, information about invasive species spread is often based on opportunistic information acquired from publicly derived observations, causing disproportionate distribution and abundance rates for the targeted species [58].
One limitation of the crowdsourcing approach is that it is often biased towards large, visible, abundant invasive species and misses things like very tiny invasive insects, fungi, or plant pathogens. Observations are also highly congregated in densely populated areas with more access to the platform and limited in inaccessible areas [59]. Although opportunistic crowdsourcing surveillance of invasive organisms presents challenges with sampling coverage, these concerns can be mitigated through active volunteer recruitment, educating volunteers, and funding citizen science projects in less-explored areas [60,61]. BioBlitzes invite citizen science participation to target specific groups of organisms during a short time period, often educating members of the public as well [62]. iNaturalist offers accessible guides to educate participants interested in contributing observations to large datasets used in peer-reviewed research publications [63]. Education programs combined with the ability to submit suspected identifications either through photographic or sample evidence increase the network of people involved. For example, Carney et al. [64] demonstrated the important role of citizen science in monitoring invasive mosquitos. Their team developed artificial intelligence software from multiple international citizen science apps that can automatically identify mosquito species.
Social media platforms, i.e., Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), and Instagram, are also useful for accessing novel pest observations in agriculture [65]. In one case, tweet frequencies mentioning Emerald Ash Borer corresponded to annual life cycles over a three-year period [66]. Tateosian et al. [67] examined the real-world aspects of utilizing three online data collection tools—the Global Database of Events, Language and Tone (GDELT), Google News, and the commercial platform Brandwatch—to assist with monitoring invasive organisms. They showed that online news and social media offer useful supplemental data streams in addition to official reports about invasions. In South Korea, Cryptotermes domesticus Haviland (Blattodea: Kalotermitidae) termites introduced via imported lumber were first detected through an online community, enabling subsequent joint field surveys and eradication by relevant agencies [68]. In this case, species identification was initially carried out via photographs, which can be challenging when invasive organisms are small, image resolution or quality is low, or species lack morphologically distinct identification keys.
Leveraging citizen science allows research professionals to use external resources through partnerships with volunteers and generate data for science-based initiatives [69]. Agricultural stakeholders are concerned about the risks of pest and disease introduction in farming, and crowdsourcing programs encourage collaboration between agriculture stewards, scientists, and volunteers willing to close the knowledge gaps in invasive species research [70]. Crowdsourcing provides an excellent opportunity to involve more people in science while also expanding the reach and real-time abilities to detect species. However, most iNaturalist efforts have been directed toward identifying organisms in natural areas. Interfaces like PestTracker [71], EDDMapS [72], and the Cooperative Agricultural Pest Survey (CAPS) are specifically geared toward use for invasive species and agriculture but have far fewer users and observations. Citizen science is an integral aspect of protecting agriculture-related resources from biological invasions due to the limited number of professionally trained taxonomists and the minimal amount of available funds to support survey fieldwork and maintenance of museum collections [73,74]. Integrating large datasets derived from experts and non-experts can improve sample coverage and identify species dispersal patterns using multiple web-based platforms [75].
Citizen science and crowdsourcing initiatives have increased the volume of observations available for biodiversity research and improved time constraints of data collection in the academic community [72,76]. However, the standardization of protocols is crucial to integrate observations and evaluate the data quality from multiple sample sources [61]. To fully harness digital data from web pages, social media, Flickr, or other online sources, a framework for collecting and processing these data must include web scraping, filtering, extraction, quality checking, and harmonization [77]. Data access is crucial for scientific research, and tools have been built around the iNaturalist Application Programming Interface (API) to facilitate these endeavors. Command-line interface tools eliminate the redundancy of point-and-click with a mouse or keyboard; instead, data can be accessed, filtered, and downloaded with just a few commands. For example, pyinaturalist (https://github.com/pyinat/pyinaturalist, accessed 21 May 2025) and rinat (https://github.com/ropensci/rinat, accessed 21 May 2025) are computing libraries to access these data in Python and R, respectively.
Along with awareness of data bias, organization, and data availability, standardization also comprises data quality assurance [78]. Crowdsourcing efforts face challenges in effectively monitoring the presence of invasive species in a location due to observation biases such as selective reporting, inaccurate details, and varying identification methods. For example, in avian species, behavioral characteristics and phenotypic features can validate an observation; however, the verification inconsistencies create datasets with observation biases and increase the likelihood of sample errors [79]. Some organisms are traditionally more difficult to identify morphologically, which is amplified with crowdsourcing. For example, McMullin and Allen [80] noted that species that require microscopy or chemical analysis for confirmation, such as lichen or fungi, are seldom accurately identified. To help alleviate this issue, an observation in iNaturalist obtains “research grade” classification once the qualifications are evaluated based on the image, date, coordinates, and verified identification supported by a specified number of members of the iNaturalist community [81]. Multiple iNaturalist users may label an image as a particular species, but that does not always mean they are correct. In some organismal groups, such as termites, there is no difference in accuracy between research-grade and non-research-grade observations [82], and in non-native marine organisms, this metric was also found to be an inadequate proxy for accuracy compared to confidence scores based on visibility of diagnostic features, photo quality, and georeferencing [83]. Thus, filtering for accuracy based on “research grade” can add false confidence while limiting the number of observations. Additional citizen science or crowdsourcing platforms should prioritize improving standardizing practices to maintain the efficiency and quality of observation submissions and to ensure the viability of crowdsourcing as an appropriate tool for the surveillance of biological invasions in agriculture.
2.1.5. Observation Through Molecular Taxonomy and Sampling eDNA
Another way that technology has improved our ability to detect and survey invasive species is through environmental DNA (eDNA) and molecular markers. After obtaining biological material from the environment or possible invasive specimens, large-scale genomic and genetic sequence data can be used to detect and monitor biological invasions in several ways. Genetic material can be compared to reference sequences to identify organisms thought to be invasive. Common molecular markers are referred to as barcode sequences, like the mitochondrial gene Cytochrome c oxidase I (COI) for animals, the ribosomal gene for the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) for fungi, or the RuBisCo gene from the chloroplast for plants. If sequences are highly similar between a potentially invasive species and a confirmed reference for an invasive species, the taxonomic identity can be confirmed [84]. Molecular markers enable the identification of individuals that are small or morphologically ambiguous. Although this process is relatively time-consuming and cost-inefficient for processing large numbers of samples, advances in technology are dealing with these constraints in several ways. With bulk trap samples, assays like the droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) can be used to detect a single individual of Old World Bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera Hübner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)) from a pool of 999 individuals of similarly looking Helicoverpa zea Boddie (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), allowing for quick detection and response [85]. Additionally, updates in nanopore technology make it possible to sequence barcode DNA samples in bulk for as low as $0.01 per specimen [86]. Recently, CRISPR-based diagnostics have been used to identify commonly mistaken organisms with even greater accuracy [87]. Invasive insects, viruses, fungi, or nematodes can also be discovered in the field with approaches like Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP), which can detect highly specific targets in less than 30 min [88]. Molecular identification is straightforward for a single organism already in hand, but with the use of eDNA and metabarcoding, an invasive species can also be detected in complex communities from residual DNA in the environment, either with active surveys to detect a single invasive species or through passive surveys that can indicate the presence of many species [89].
However, barcode genes offer a limited perspective on invasive species compared to other molecular tools. Genomic data can be isolated from organic material through various protein or nucleic acid extraction and sequencing/analysis techniques to produce genomes (full complement of genetic information from a single organism), transcriptomes (mRNA that is expressed in an organism/cell), reduced-representation sequencing (like RAD-seq used to subsample only specified sites), microbiomes (snapshot of DNA from microorganisms in a community), and various other data collections [90]. Additionally, genetic material for single genes can be collected from individual or environmental samples, providing a snapshot of organisms in an environment (metabarcoding). Raw sequence data are often accompanied by additional data, including metadata, annotations, alignments, chromosomal information, genotype data, or SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms or differences in genetic material from reference genomes).
Because molecular datasets have always been large, the field of molecular biology confronted issues related to making robust, flexible, and sharable tools earlier than other fields. Various databases exist for the storage and sharing of sequences and additional data. Notably, the United States National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), established in 1988, has operated its GenBank DNA sequence database since 1992. Together with the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) and the DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ), the NCBI collaborates via the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC) [91]. Increasing volumes of data in ecological research, discussed below, seem to be necessitating similar developments.
Some view molecular data as a silver bullet in biodiversity research, yet like other data, molecular markers are only as good as their reference databases. The Barcode of Life Data System (BOLD) has over 9.7 million records of more curated barcode sequences but is biased towards common or large-bodied organisms and still contains errors. Studies that evaluated taxonomic accuracy found as low as 20% of sampled sequences from GenBank and 30% from BOLD were accurate at the species level [92,93]. Furthermore, many samples were not accompanied by valuable metadata, including locality data. Many journals require submission of molecular data to GenBank before publication, which can result in a rushed submission process or the publication of low-quality sequences.
In an agricultural context, the AgBioData consortium provides 44 agricultural databases related to the genetics, genomics, and breeding of many agricultural organisms, including pests [94]. Similarly, InvasionDB is a database of well-curated invasive species that includes genomes, assemblies, and information about gene families related to invasiveness [95]. The Ag100Pest initiative is a USDA-ARS-driven effort to sequence, assemble, and make available agricultural pest genomes via NCBI, ensuring high quality [96]. Other useful databases for specific groups of invasive species include VectorBase [97], Aphidbase [98], InsectBase [99], WhiteflyDB [100], and PlantGDB [101]. Notwithstanding, fewer than 50% of invasive species on the “worst list” have publicly available reference genomes, an important step for being able to detect their presence via their DNA from natural populations and performing downstream genomic analyses (Figure 5) [102].
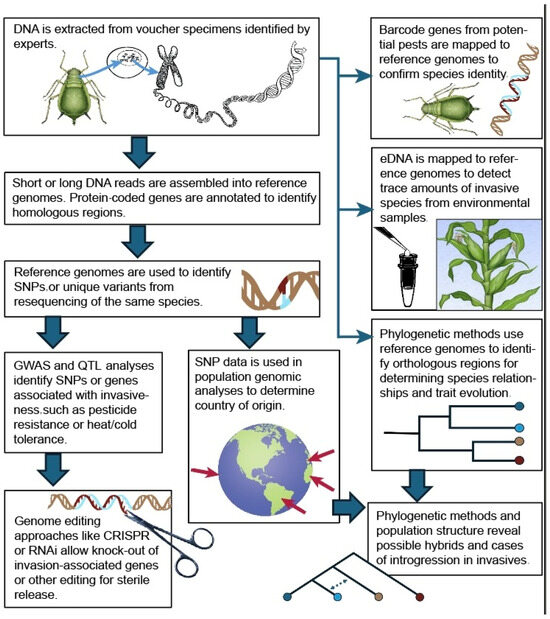
Figure 5.
Processes involving reference genomes in invasive species research. Graphic and illustrations: Taina Litwak, USDA.
Biological invasions cause ecological disturbances, altering the biosecurity and biodiversity in agricultural production on a spatiotemporal scale [61]. Early detection of invasive species distribution acquired through extensive database collaboration, observations, and modernized technological advancements, including photo recognition and genetic tools, provides a basis to classify biological invasions prior to establishment [55,89].
2.1.6. Combining Occurrence and Environmental Data to Predict Species Distributions and Abundance
While species occurrence data from DNA, crowdsourcing, citizen science, individual collections, and museums can inform where invasive species are now, it is by combining these data with environmental and climate data that modelers can make predictions about where the next invasions will occur or which areas are at risk. An important part of knowing which areas will be invaded and building models of species distribution is understanding the forces shaping communities within the environment.
Historical and current records for climate variables such as temperature and rainfall are found in the WorldClim dataset [103] and others and are key determinants of species distributions [104]. However, many other environmental factors, such as vegetation cover, nutrient availability, organismal counts, extreme weather events, and topological features, also affect species distributions. For example, hurricanes have been used to predict outbreaks of the cattle fever tick (Rhipicephalus (boophilus) annulatus Say and R. (B.) microplus Canestrini (Acari: Ixodidae)) in the US [105]. Environmental big data include both historical data and data that are continuing to be collected. Many organizations have set up long-term ecological monitoring networks to record these measurements, including the Long-Term Ecological Network (LTER), National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON), Critical Zone Observatory, Terrestrial Ecosystem Research Network, South African Environmental Observation Network, and FLUXNET. At a smaller scale, many researchers have set up their own temperature and humidity loggers, which are recorded across various platforms. For data currently being collected, the easiest way to ensure that data are collected in a manner that allows combining into larger global datasets is to plan data collection protocols ahead of time. For example, the Nutrient Network, which collects data on interactions between environment, productivity, and diversity, outlays specific protocols for plot layout, experimental treatments, and data collection with ~130 collection sites worldwide (e.g., [106]). Similarly, NEON obtains time-series data by sampling for the same organismal groups over a long period [107]. While such preplanned coordination is ideal, experimental designs and sampling protocols depend on the primary purpose of the study, often precluding this degree of coordination [108].
Usable datasets arise from sequential data acquisition, information extraction, and cleaning processes before being used for modeling and analysis [109]. Then, modelers can predict current distributions and future invaders with occurrence and environmental data. Using Species Distribution Models (SDMs) and Species Abundance Models (SAMs), data on species occurrence may be combined with geo-referenced data to identify biotic and abiotic components of the environment that are associated with a species occurrence (e.g., [110,111]). In turn, uninhabited areas with similar biotic and abiotic conditions may be identified [112]. For example, occurrence data from citizen science and the GBIF were combined with environmental data to build an SDM for the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys Stål, 1855 (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), a pest to many fruit trees and other agricultural crops, across Europe for the next 40 years, resulting in predictions of future areas of suitable and marginal habitats [113]. Mapping occurrence data points acquired from the GBIF using spatial analysis tools improves the confidence level of prediction models by establishing the species’ habitat range and accounting for redundancy [114]. As ranges can shift due to climate change or anthropogenic forces, having data depicting species range shifts is also important [115]. Using occurrence and climate data, multiple SDMs predicted the range expansion of the Asian hornet (Vespa velutina nigrithorax Lepeletier 1836 (Hymenoptera: Vespidae)) across France with some accuracy; however, evolutions of these methods are still being developed [116].
Given the appropriate data, models can also predict species abundance. Presence–absence databases can be used to develop SDMs, whereas abundance databases may be used to develop SAMs [117]. While many data sources provide information on organism abundance along with presence in a specific location, datasets are often reduced to presence/absence, as it is the simplest method for handling differences in sampling methodology [118]. Datasets that provide measures of abundance are more difficult to combine, but methods to combine datasets that include evaluations of abundance have been developed [118]. Note that sampling methodology often does not provide a true assessment of absence but rather documents presence in specific geographic locations [119,120,121]. If a dataset does not show the presence of a species in a certain location, this could indicate either a true absence, lack of sampling effort, or presence in low numbers. Nearly all collections have some sort of inherent bias, whether because of the collector (geographic or taxonomic bias) or preservation mode (degradation, decoloration, pest damage), but there are also many computational tools for assessing bias, and such bias can be incorporated into models using covariates [122].
Numerous platforms are available for developing SDMs and SAMs that use a wide array of statistical procedures and machine learning algorithms [123]. Similarly, there are a variety of tools available to help prepare data for evaluation (e.g., [121,124]). Model choice and routine decisions regarding model development may affect the outcomes of an SDM [125,126,127]. As a result, ensemble forecasting approaches that combine or analyze results from multiple SDMs have been developed [128]. For example, biomod2 is an R-based platform that combines algorithms such as artificial neural networks, generalized linear models, and random forests and was used to predict ecological niches for invasive plants and determine suitable habitats in China [129]. However, ensemble models do not always provide better predictive value than individual SDMs [130,131]. When navigating the modeling landscape, it is helpful to collaborate with experts from the field, as there are many options and parameters.
While SDMs provide an estimate of the geographic range suitable for an invasive organism, not all climatically suitable regions are equally likely to be invaded because of geographic barriers or passageways, dispersal trends, and association with agricultural commodities. Accordingly, when resources are limited, surveillance efforts often target high-risk locations based on invasion routes. While species distribution models and occurrence data form the basis for surveying, detecting, and predicting future invasions, identifying invasion routes and life history traits can help develop plans to control or stop invasions.
2.2. Identifying Invasion Routes
Because resources for surveillance are limited, preventing future invasions requires robust risk assessments to identify species most likely to invade (e.g., [132,133]), areas most likely to be invaded, and invasion routes [134]. A species can spread to a new area due to international or interstate trade, hitchhiking in the luggage of careless travelers, climate change making new areas available, or phytosanitary breakdowns [135,136]. Meurisse et al. identified major pathways (i.e., imports) in which non-native insects move; this included wood products, plants, and containers as major pathways for Coleoptera, Hemiptera, and Lepidoptera, which are all significant agricultural pests [137]. Mitigating economic damage from invasive organisms requires monitoring these imports and planning at multiple phases. Invasions are most successfully eradicated if detected before the organism has spread from the point of entry [138,139]. Accordingly, optimal surveillance strategies and methodology for delineating the extent of the invaded area and the invasion route are needed. Invasion routes can be detected through the use of trade route data or DNA data.
2.2.1. Intercept/Trade Route Data
Several factors are associated with an increased risk of biological invasions. First, meta-analyses and modeling studies indicate that one of the primary factors driving biological invasions is propagule pressure, or the rate of introduction [140]. Analysis of interception data of arthropod contaminants recorded on plant imports arriving in southern Africa from 2005 to 2019 found that of 29 tested predictor variables, only inspection volume was correlated with detection, demonstrating this trend [141]. Thus, focusing on trade routes associated with high volumes of high-risk commodities can aid in identifying areas at high risk for invasion. For example, studies often show that the main entrance of invasive species is through ports with subsequent road transportation (e.g., [142]). Wang et al. [143] used invasion networks to determine two bioinvasion risk-intensive port regions at greatest risk of invasion by invasive marine organisms due to the movement of container ships among ports and the changing of ballast water. For terrestrial pests and diseases of trees, entry may occur through ports, but their establishment is facilitated by the presence of ornamental trees in greenbelts and backyards in proximity to ports [144]. Thus, knowledge of the distribution of landscape features in proximity to high-traffic ports will facilitate identifying areas at greatest risk for invasion. Once these areas are identified, resources can be devoted to surveillance to detect new potential invasions.
Data are collected at inspection stations along shipping routes, but there is no standardized, systematic approach to collecting and sharing data associated with interceptions [145]. International interception data can provide valuable insights into which organisms are being transported and from where, yet access to many of these data is limited due to privacy concerns or data agreements [146]. Additionally, although ports can limit the spread of invasive organisms on commercial crafts, they have little control over private vessels such as yachts [147]. Being able to monitor ports is key to identifying invasion routes, and data about routes and intercepts are integral to making predictions about invasive species relevant to agriculture.
2.2.2. DNA Data for Population Genetics
Without direct evidence from ports, molecular data can also be used to reconstruct invasion routes [148]. Molecular data (usually microsatellite or mitochondrial DNA, but also genomic data for greater confidence and accuracy [149,150]) are collected from invasive pest populations as well as potential source populations, and population genetic and phylogenetic methods can be used to determine the source population. Today, at least 82 of the world’s 100 worst invasive species have been examined using population genetics, and the use of genomics in invasion science continues to become more prevalent [102]. For example, the initial introduction event of the tobacco aphid Myzus persicae nicotianae Blackman, 1987 (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to the New World via Chile, along with subsequent introductions in both North and South America, was detected using microsatellite data [151]. Although applying genetics to biological invasions has been important for decades, most studies restrict their approach to a few loci and describe patterns rather than processes [152]. With big data and genomic resources, these studies can be more accurate at identifying invasion routes. Knowing the invasion history allows for the building of predictive models for preventing secondary spread [88].
2.3. Traits and Processes Associated with Invasion
In addition to occurrence data and invasion route data, another important facet of invasion biology data is biological information about specific invasive species. Data measurements from primary observations or Essential Biodiversity Variables (EBVs) related to species traits and populations, community and genetic composition, and ecosystem structure/function are important for determining indicators of biodiversity [153]. Specifically for invasive species, Latombe et al. identified essential variables for invasion monitoring, which include the occurrence of invasive species in a defined area, knowledge of the historical species range, and the detrimental impact of the species [145]. These variables can help predict whether an invasion will succeed or fail and the impacts of the invasion, but cooperation is needed both to identify important EBVs and standardize sampling protocols, especially as they can be computed from both physical observations/measurements as well as DNA.
2.3.1. Life History Data
Traits associated with invasiveness may be identified using datasets on successful invasions and life history traits like dispersal ability, diapause dates, and population sizes. Analysis of trait data can contribute to risk assessments and help identify invasive organisms of greatest concern. For example, Liu et al. [154] analyzed 6293 freshwater fishes and found that invasion success was associated with larger body size, greater longevity, delayed maturation, and higher fecundity. Similarly, Capellini et al. [155] evaluated databases on invasions by mammals and found that invasion success was associated with high reproductive capacity. Fournier et al. [156] identified the ant species at greatest risk of becoming invasive by analyzing databases on ant traits and successful ant introductions. Finally, Philibert et al. [157] found that seven traits were correlated with the invasion success of forest pathogenic fungi. The fungi examined included the causal agents of Dutch elm disease and chestnut blight, which devastated their respective host plant populations when introduced in Europe [158]. Current distributions combined with environmental data can also give information about species’ thermal tolerances or suitable habitats and ranges for invasives [159]. Understanding these traits associated with invasion success can allow the prediction of other potential invasive organisms. Trait data can come from trait databases assembled by natural history experts or museums, though there is not currently a platform for all types of trait data. Plazi TreatmentBank takes advantage of one powerful data source: taxonomic publications [160]. By extracting information like scientific names, geographic locations, and traits from species descriptions and linking them to the corresponding GBIF data, Plazi enables open access to these data.
In addition to trait data about invasives, trait data pertaining to potential hosts are essential. One study found that host tree traits related to wood density, shade, and drought tolerance were important predictors of invasive insect impact [161]. Invasive insect herbivores can follow invasions of plant hosts that provide them with ecological niches [162]. Many invasive species are specialists; therefore, knowing information about an organism’s food web is essential.
Life history data are also key for noting the impact of potential invasives. For example, horizon scans give each possible invasive an impact score based on how it will affect the economy, human health, and ecosystems [163]. Life history data can also include information about how to combat invasives, such as natural predators used for biological controls, biochemistry information for making pheromone traps, and response to pesticides.
As a result of the number and diversity of invasive organisms, ranging from insects to plants to viruses, a unified trait database may seem incomprehensible. For trees, functional traits like photosynthetic ability and leaf shape promote invasion success [164], yet these are hardly applicable to nematodes or fruit flies. Within some insect orders, there are impressive trait databases (CONUS for freshwater insects, GlobalAnts, ITT for insects in Europe), yet a unified trait database has not yet been developed for insects and other invasive organisms.
2.3.2. Genetic Traits from DNA Data
Phenotypic traits associated with invasiveness can also be inferred from genotypic data. Genetic and genomic methods can be used to identify adaptive loci in either a forward genetic or reverse genetic approach [150]. With a forward method, Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) analysis can be used to map traits associated with invasion to chromosomes when invasive species can be reared in a lab [165]. In an agricultural context, knowing the locations of the genes associated with invasive traits can let you know if weedy traits have evolved in weedy populations through similar genetic mechanisms as their agricultural counterparts [166] and help to generate populations of crops resistant to pests [167]. A reverse selection approach like Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) can be used with genomic data to identify regions of the genome or candidate genes associated with invasion by comparing genomes from populations that have invaded to their native counterparts [168,169]. For example, a GWAS study of 532 genomes from the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella L. (lepidoptera: Plutellidae) showed a very large effective population size and identified three variants associated with insecticide resistance [170]. Correlating gene family diversification with invasiveness or positively selected genes with invasion success is key to determining the risk of invasiveness and preventing and controlling future invasions [171].
Phylogenetic methods are also used to predict traits in invasives based on their relatedness to other pests. Evolutionary history has been shown to predict the trait of invasiveness based on an organism’s sibling relationship to a known pest if their close relatives cause damage [172]. Combining phylogenetic comparative methods with traditional statistical approaches can illuminate trait evolution and its related genetic variation [173]. For example, a phylogeny of mammals was combined with data about lifespan and body size and revealed associations with these traits and tumor suppression, p53 regulation, and telomere maintenance [174]. Similar methods can be used to identify genes associated with temperature tolerance, pesticide resistance, and invasiveness across taxa.
2.3.3. Importance of Genetic Diversity in Invaders
Along with invasion success, phylogenetic and genetic methods can inform the maintenance of genetic diversity after a bottleneck and hybridization, which can influence invasion potential [150]. Molecular data can be used to detect the genetic diversity of an invading population and if the change in genetic diversity occurred before or after an introduction [150]. Most species introductions are associated with a bottleneck event, which can severely restrict genetic diversity, leading to inbreeding depression or limited natural selection ability; however, not all invasions are accompanied by diversity loss because of multiple invasions or large invading populations [175]. Yet the paradox of biological invasions suggests that introduced species can be successful with minimal genetic diversity [148], explained by preadapted genomes [176], demographic or environmental stochasticity [177], the bridgehead effect [13], or hybridization or introgression with local populations or species [178]. For example, introgression between three fungal lineages of Ophiostoma Syd. & P. Syd. (Ophiostomatales: Ophiostomataceae) responsible for Dutch elm disease has resulted in fungi with higher growth rates in high temperatures and higher pathogenicity [179]. In a genomic study on the fall webworm Hyphantria cunea (Drury, 1773; Lepidoptera: Erebidae), genetic bottlenecks were identified in invasive populations; however, increased functional polymorphisms were also identified in these populations, suggesting adaptation [180]. Population genetic or genomic data can illuminate the timing and extent of bottleneck events and hybridization and measure genetic diversity across loci [150]. Molecular tools allow the detection of genetic variation in ploidy, genome size, or chromosomal rearrangements [181], as well as transposable elements or epigenetic changes leading to gene expression modification [182], all of which may be mechanisms related to invasiveness. Identifying genetic characteristics in current populations can provide insight into their probability of a successful invasion.
2.3.4. Ecosystem Structure and Function
A species’ ability to successfully invade an area is also determined by the overall proceeding ecosystem structure and function. Areas that are species-rich and have a healthy balance of producers and consumers are more likely to be resilient to invaders, and in forest areas, structural diversity is associated with increased resistance to invasion [183]. Invaders often take advantage of ecosystems that lack functionally similar species and fill empty niches [184]. Therefore, the ability to predict invasions requires data about ecosystem function and structure, which is where data-collecting organizations like NEON and LTER are very useful. NEON documents the presence and abundance of terrestrial and aquatic communities as well as abiotic factors across North America over the long term [185], while sites in the LTER are used for long-term ecological experiments on processes like nutrient cycling, hydrology, or changes in forest structure from disturbance [186]. Data from both of these organizations can be used to link native diversity and environmental parameters to invasions and predict how invasions may differentially impact ecosystems with variable environmental conditions [185].
2.4. Developing and Evaluating Control and Eradication Methods
Finally, big data can be used to identify and implement remedial strategies with the greatest chance of success. Big data approaches facilitate comprehensive invasive species management across the invasion continuum. Through systematic monitoring of high-risk areas (Section 2.1), these methodologies enable early detection of potential invasions, significantly increasing the probability of successful intervention. When invasions are confirmed, big data analytics can elucidate invasion pathways (Section 2.2), informing targeted interception strategies that disrupt dispersal routes. Furthermore, the integration of species trait information with environmental data (Section 2.3) allows for a robust assessment of invasion success probability, enhancing prioritization efforts. Thus, a coordinated implementation of these diverse big data resources creates a multifaceted framework for pre-invasion preparedness, active invasion response, and post-invasion management strategies.
Although big data are most commonly employed for predictive and surveillance purposes, there are many ways that big data strategies are being implemented to develop control methods. After a successful eradication, data can then be used to identify factors related to invasion success. Genetic data and technology can be used to engineer invasives for sterile release in addition to modeling, drones, and other control methods.
2.4.1. Genetic Data for Control Methods
Genetic and genomic big data have been shown to be effective data types applied to control and eradicate biological invasions. One technique that leverages genetic and genomic big data is the Sterile Insect Technique (SIT). It consists of releasing a large number of sterile males to reduce female fecundity in the next generation of the pest, and this technique has been used for more than 50 years, but the use of transposable elements and CRISPR has increased the applicability and ease of SIT [187]. CRISPR genome editing, accompanied by gene drives, can be used to reduce the abundance of a pest species or minimize the environmental impact [188] by efficiently transmitting genetic elements to offspring. This technology can be used to cause the extinction of an invasive pest if used over a large portion of the breeding population; although, the ethics of purposely causing extinction that may have unintended ecological consequences needs more exploration [189]. RNA interference (RNAi) technology provides the ability to knock down genes related to mortality and has successfully been applied to agriculturally important thrips and delivered via symbiont gut bacteria [190]. With RNAi technology, Eastern Ash Borer mortality can be achieved without harming non-target organisms [191]. Together, advanced molecular techniques and increased genetic and genomic data can provide crucial information about genetic variation, dispersal patterns, and populations to provide targeted frameworks for control and eradication plans [192].
Although eradication is ideal for many agricultural invasives, it is usually only possible if the species has low density and high visibility or if Allee effects reduce population viability at low densities [193]. After an eradication event, genomic data can be used to predict which factors led to the extirpation. For example, population genetic analyses found that the eradication success of the Northern Giant Hornet (Vespa mandarinia Smith 1852) was facilitated by local eradication efforts and inbreeding [194].
2.4.2. Modeling for Control Methods
Quantitative modeling and optimization approaches can predict the efficacy of eradication actions and strategies, which can be implemented in decision-support tools. For example, models can evaluate factors such as the likelihood of successful eradication, reinvasion probability, and resource allocation to determine if eradication will be successful or when it can be declared [195]. Where eradication is not feasible, models and simulations may also enable the development of better guidelines for the management of spread after establishment. For example, computational modeling can quantitatively assess the trap density required for effective pest control at the landscape level [196] and the optimal release rates for sex attractants used for pest control, though chemical and biological sensors are still in development [197]. Control methods can be built into species distribution models to predict how a given species might react to a certain control measure in forecasting methods like the Pest or Pathogen Spread (PoPS) forecasting platform [198]. Recently, Lampert [193] developed an algorithm that determined the optimum treatment timeline for the spongy moth using population dynamics, cost, and response to treatment as factors. In the Netherlands, an application called NemaDecide uses population dynamics of nematodes and information about crop rotation, soil analysis, and control efficacy to make management decisions [199].
2.4.3. Use of Drones and AI for Detecting and Controlling Invasive Species
Where manpower is not available for eradication or control of invasive species, drones prove useful. For example, drones can use artificial intelligence (AI) and image recognition to find invasive weeds, but they can also be used for purposes such as deploying “bug pods” (small biodegradable packages of specialist biocontrol agents) for the mile-a-minute weed (Persicaria perfoliata (L.) H. Gross), which can be hard to reach on foot [200].
Traditional control methods use known biochemistry to design lures and traps or develop new molecules for attractants. Generative AI can be adapted to develop new molecules for attractants or pest deterrents with this type of information [201]. Databases for olfactomes that record comparative olfactory responses for these uses are in development for several species of fruit flies, although only that of Drosophila melanogaster is well-developed [202].
3. Moving Forward: Key Tools, Obstacles, and Challenges
The field of biological invasions merges several wide and heterogeneous fields, including ecology, entomology, plant pathology, virology, genomics, and natural history, making a single approach or toolkit elusive. Yet each field produces data that can function to predict species distributions, identify invasion routes, link associated traits and processes, and develop control and eradication methods. There is a growing recognition in these fields that the data themselves are a product, not merely a step on the way to answering a scientific question or publishing a paper [203]. However, several obstacles limit the usefulness of these data. Farley et al. [204] provide a helpful framework for understanding the issues of big data, categorizing data sources as having varying degrees of the “4 V’s”: volume, velocity, veracity, and variety. Different “data systems” may be particularly challenging along one or more of these dimensions; for example, remote sensing produces large datasets (high volume), distributed networks of cheap sensors might have high velocity, citizen science might be challenging on the veracity dimension, and datasets produced because of individual research projects might be highly variable. The following priorities address these data issues and will improve invasive species research with big data: data standards (3.1), data quality (3.2), data storage and availability (3.3), communication (3.4), and bridging gaps in collaboration (3.5) (Figure 3).
3.1. Data Standards
Risk assessments may be informed by combining data from a range of sources. For example, the fundamental data required to assess the risk of invasion are data on species occurrences, with the designation of a species as native or invasive depending on its historical and current range. Similarly, citizen science programs such as field surveys and the submission of wildlife photographs contribute information on a species’ occurrence [64,205,206]. The presence of an organism in a geographic area can also be assessed by collecting and sequencing environmental DNA [207] or via remote sensing [208]. Finally, university and government research programs conduct field research that directly or indirectly reports on species occurrences. Combining data from disparate sources requires that one or more data fields be shared across datasets. As we have demonstrated, combining data from different sources and utilizing big data sources and technologies gives power and insight to biological invasion research. However, for the data to be useful, they must be standardized and formatted with shared data fields across datasets.
Similarly, data ontologies, or standardized definitions of associated data fields and how they relate to each other, are needed. Defining universal fields that inform biodiversity research will aid in the ability to combine and share data. Darwin Core is the primary data standard used in the field of biological invasions, and Darwin Core defines data fields related to taxon (specimen identity), identification (data associated with the identification), occurrence (abundance, life history information), record level (institutional information), location (descriptors of the collection location), and event (relationship to larger research objectives) [209]. In addition to data on species occurrence, the study of invasive species requires the use of Geographic Information System (GIS) data. Data standards for GIS metadata are provided by ISO 19116 [210], and standards for data quality are provided by ISO 19157 [211]. Genetic and genomic data have standard formats, including FASTA and FASTQ files for DNA sequences.
Just as data standards facilitate combining independent datasets, a standardized protocol for reporting methods and results from SDMs would be eased if a standard reporting system were adopted [212]. We also need standardized trait databases and a way of reporting the results of control methods.
3.2. Data Quality, Taxonomic Accuracy, and Awareness of Data Bias
Provided that each data source includes the minimum fields recorded in a standardized format such as Darwin Core, combining data sources should be straightforward. However, the risk of propagating errors present in original datasets is a concern. Inaccurate taxonomy can lead to poorly conceived control or eradication methods. Although certain observations from iNaturalist can obtain ‘grades’ that are associated with higher confidence, this comes at the cost of limiting the total amount of data. Ultimately, groups that are difficult to taxonomically identify may be associated with data that are of little use, and how far that extends into agriculturally important organisms has not been explored. Goodwin et al. [50] also determined that misclassification of museum specimens is common; thus, it is possible to spread taxonomic errors present in original datasets. The same applies to DNA data—errors may arise through contamination or misidentification [92], though metazoan identifications have very low error rates, at least at the genus level [213]. In addition, there may be errors associated with the reporting of collection locations, which may affect the outcome of subsequent analyses [214,215]. Big data sources must be aware of potential errors and screen for quality without removing too much valuable information.
Additionally, as discussed by Beck et al. [216], many databases suffer from spatial bias, with some locations intensively sampled and other locations rarely or never sampled. The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is the largest known database with observations of invasive species, with over 2.2 billion records, yet this covers only 1% of global climate variability [217]. The taxonomic bias is also clear. The GBIF receives taxonomically focused data from ecological monitoring applications with extensive geographic scopes, which can be subjected to data overlapping [53,72]. Therefore, concerns with repetitive data may be a hindrance when sorting large datasets from multiple sources. To make these data most valuable in invasive species research, users must be aware of biases and variable taxonomic accuracy and address them in their work.
3.3. Proper Data Storage and Data Availability
While data standards and error reduction improve quality, this is of little use if data are not stored somewhere where they can be preserved and made available to users. Wilkinson recommends following the FAIR Data principles; data should be Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable, and storage methods need to reflect these principles [218]. The fields of genetics and genomics have been established as big data sources for decades, and at this point, GenBank is a useful open-access data storage platform with a recognized standard workflow. Increasing volumes of data in ecological research and other fields related to invasive species seem to be necessitating similar developments in both technology and culture [203,219].
Extensive open-access databases and contemporary observations are vital to controlling the spread of current invasive species, such as the spotted lanternfly (e.g., [220]), and stopping the spread of others. Yet, it is not always clear who “owns” the big data that has been generated. Issues regarding ownership of big data limit its application. For example, Monsanto Corporation (now Bayer) developed a suite of digital tools that farmers use to help identify weeds and make decisions based on weather and soil conditions [221]. Likewise, several agricultural businesses have successfully monetized similar machine learning-based tools for weed identification through targeted marketing and precision recommendations [222]. If a company pays for the collection, storage, and analysis of data, the data belong to the company in question. However, in many cases, big data may be repurposed. While privacy issues may be a concern, as some data may include sensitive information, harnessing the full potential of big data that has already been collected is improved by providing open access. Ultimately, if agri-businesses view big data as proprietary, the usefulness of the collected data will be more limited [223].
Increased understanding of the value of big data is leading to increased efforts toward availability. For example, the United States 2018 Geospatial Data Act specifies that “open and publicly available data is essential to the successful operation of the GeoPlatform” and prohibits federal funds for entities that do not follow the established guidelines [224]. This guideline includes making data machine-readable. Increasing data availability also means educating a task force of future workers who understand the storage management and analysis methods and are prepared to adapt to the next data revolution when the time comes.
3.4. Communication About and Between Data Sources
Combining data from different sources requires awareness of their existence. In our review, we found many data sources we did not realize were available. Some sources are subsets of other datasets. A centralized reference repository for relevant data on invasive species might be helpful. The GBIF, the Ocean Biodiversity Information System, and the Global Register of Introduced and Invasive Species [225] are examples of these efforts.
Communication is needed for awareness of data sources, and there can be linguistic barriers to accessing information on invasive species, which affects people globally. Since one of the best predictors of a species becoming invasive in a new location is it already being invasive elsewhere, it is important to incorporate local invasive records and information into the global context [226].
While data may be the lingua franca of ecology, many dialects are spoken, so comparing datasets and combining them in analyses has historically been very difficult. The problem may be worse than dialectical differences since datasets are collected for specific and varying reasons, with different instrumentation, methods, and conventions. Before rapid electronic dissemination and the sharing of these data, these differences mattered less since a combined analysis would become cumbersome or logistically impossible. At the turn of the 21st century, ecologists had already been working on data and metadata standards to allow the documentation, dissemination, and reuse of data, such as the “Ecological Metadata Language” and the DataONE investigator toolkit [227,228]. These efforts to standardize, document, and share are ongoing [229].
3.5. Bridging Gaps in Collaboration
In this review, we have discussed many sources of missing data, whether due to sampling bias or lack of genomic resources. A recurring issue is an avenue for centralized reporting from those most directly involved with agriculture. By involving farmers, on-the-ground insight can be paired with the needs of the communities and workforce. There is variation in agricultural data depending on what the data are collected for and by whom. Individual scientists or farmers may each have their own goals and methods; how these might be integrated into a comparable dataset that can be used for biosecurity is not clear, but it is evident that collaboration between researchers and farmers is necessary.
As demonstrated in Figure 1C, a gap also exists between those using big data within a computational framework (in yellow) and those working on other aspects of invasive species and agriculture. This gap may be due to a cultural divide between computational and other scientists. Advancing computational training for upcoming invasion scientists and providing training opportunities for those looking to incorporate big data into their research will increase utilization and cooperative ability as well. Online platforms like Kaggle (https://www.kaggle.com/) allow machine learning practitioners to work with real-world data and collaborate with others in the field. Specifically, Kaggle provides large datasets, coding competitions, community forums, and computing resources to scientists looking to solve problems, sharpen skills, and share knowledge. These platforms enable hands-on learning of image-based species identification methods using real-world data, as well as practice with uploaded image datasets and codes from others. With a collaborative effort on open access work and a willingness to incorporate difficult technical concepts into all aspects of invasive species research, we will be better equipped to stop invasions worldwide.
4. Conclusions
Here, we have outlined some of the main ways that big data are used to detect, predict, prevent, and control biological invasions. We showed where the data gaps are for using big data for invasive species in agriculture and summarized some main sources of big data, including observation data from museums, online databases, social media, and DNA databases. To enhance the utility of big data in the fields of agriculture and invasive species, we indicate the possibility of improved and extended data standards, assurance of data quality, proper data storage and availability, better communication about and between data sources, increased involvement of those on the ground, and use of open access data.
The diverse forms of big data now being collected offer significantly more efficient approaches to addressing biological invasions compared to traditional methods. While these individual data sources are valuable on their own, there is untapped potential in their integration. By fostering collaboration among experts from various disciplines to combine insights from different data types, we can develop more responsive and sustainable invasion management strategies. Such integration, though challenging, represents an important step toward protecting agricultural systems and ecological integrity from invasive threats.
We hope that the reader comes away with a new awareness of novel big data sources outside of their core expertise and perhaps with ideas on how to combine them to address particular challenges. Though the volume of data continues to grow, as does our ability to process, integrate, and understand them, solutions to problems facing agriculture due to invasive species may remain limited by our experience and imagination.
5. Glossary Terms
Active versus passive surveillance with reference to eDNA: Active surveillance monitors and samples for specific species. For example, testing water samples for eDNA using species-specific primers. In contrast, passive surveillance collects and monitors samples without a species-specific target. For example, testing water samples for eDNA using high-throughput sequencing [230].
Active versus passive surveillance with reference to citizen science: Active surveillance involves programs that monitor and survey invasive species and are conducted by commodity, state, and federal organizations. In contrast, passive surveillance includes reports outside the official regulatory survey network, such as land users (e.g., farmers, land managers, and homeowners), citizen scientists, and concerned members of the public [231].
Barcode sequence: A region of DNA common across all taxa that can be used to differentiate between organisms. In animals, this is most commonly the COX1 region of the mitochondria [232].
Big data: Data that are large in volume, collected or accessed with increased velocities, existing in a variety of formats, and with varying reliability (veracity) [1,2].
Data standards: Stable terms and vocabularies for collecting and sharing data. For example, the Darwin Core is a body of standards for biodiversity [209].
eDNA: DNA captured from an environmental sample without first isolating any target organisms [233].
Ensemble forecast: Ensembles of forecasts are produced by making multiple simulations across more than one set of initial conditions, model classes, model parameters, and boundary conditions [128].
Essential Biodiversity Variables (EBVs): EBVs are defined as the measurements required for the study, reporting, and management of biodiversity change [153].
Insect smart trap: Traps that can autonomously report when insects are detected [36].
Invasive species: Harmful groups of organisms introduced into a new area that then become established, increase in numbers, and spread to other areas [13].
Invasion route: The geographic pathways followed by propagules between the source and invading populations [234].
Machine learning: Algorithms designed to identify patterns from data [235].
Metabarcoding: Taxonomic identification of multiple species extracted from a mixed sample of eDNA that have been PCR-amplified and sequenced [236].
Occurrence record: The scientific evidence that a specific species was observed at a particular place on a specified date [237].
Optoelectronic sensor: Monitors the disruption of light to detect wing-beat frequency and insect movement, which is useful for identification. It can be attached to traps [238].
Species Abundance Model (SAM): A species distribution model (SDM) built with count data that can quantify indices of abundance and density rather than occurrence [239].
Species Distribution Model (SDM): A model that relates species distribution data with information on the environmental and/or spatial characteristics of those locations. Also referred to as Ecological Niche Models (ENMs) [240].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15111157/s1, File S1: Metadata file describing the dimensions.ai analysis; File S2: See “trace.txt” for the R commands used to generate panels A and B of Figure 1. Panel C was created using a JSON file from dimensions.ai and loaded into VOSViewer for export as a vector graphic (pdf); File S3: Data used to create concept co-occurrence with the top 25 research concepts; File S4: Data used to create concept co-occurrence with the top 50 research concepts; File S5: Data used to create concept co-occurrence with the top 100 research concepts; Figure S1: Overall trends in “big data” over the last 10 years generated using dimensions.ai; Figure S2: Top 20 research categories within “big data” ranked by number of publications in each category; Figure S3: Overall trends in “big data” and “agriculture” over the last 10 years generated using dimensions.ai; Figure S4: Overall trends in “big data” and “invasive species” over the last 10 years generated using dimensions.ai; Figure S5: Overall trends in “big data”, “invasive species”, and “agriculture” over the last 10 years generated using dimensions.ai; Table S1: Data used to generate Figure S1; Table S2: Data used to generate Figure S2; Table S3: Data used to generate Figure S3; Table S4: Data used to generate Figure S4; Table S5: Data used to generate Figure S5.
Author Contributions
Review conception and design were performed by R.A.C., C.L.O., N.C.M., F.R. and M.S.S. The first draft of the manuscript was assembled by R.A.C. with the supervision of C.L.O., with portions written by R.A.C., C.L.O., N.C.M., F.R., M.S.S., H.L. and Y.M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Rebecca Clement was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship funded by the USDA Agricultural Research Service’s SCINet Program and AI Center of Excellence, ARS project numbers 0201-88888-003-000D and 0201-88888-002-000D, and administered by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education (ORISE) through an interagency agreement between the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Hyoseok Lee was also supported by an appointment to the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) Research Participation Program administered by ORISE. ORISE is managed by ORAU under DOE contract number DE-SC0014664. All opinions expressed in this paper are the author’s and do not necessarily reflect the policies and views of USDA, DOE, or ORAU/ORISE.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The findings and conclusions in this publication have not been formally disseminated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and should not be construed to represent any Agency determination or policy. Any mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely to provide specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Data Availability Statement
The data for Figure 1 were produced using data from dimensions.ai spanning the last ten years and are available in Supplementary Materials. Descriptions of Supplementary Materials can be found in File S1 meta.txt. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Laney, D. 3D Data Management: Controlling Data Volume, Velocity and Variety. META Group Res. Note 2001, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.; Shakyawar, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Kaushik, S. Big Data in Healthcare: Management, Analysis and Future Prospects. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalkrishnan, V.; Steier, D.; Lewis, H.; Guszcza, J. Big Data, Big Business: Bridging the Gap. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Big Data, Streams and Heterogeneous Source Mining: Algorithms, Systems, Programming Models and Applications, Beijing, China, 12 August 2012; ACM: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.M.; Popp, J.; Oláh, J. Current Landscape and Influence of Big Data on Finance. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z.; Dhunny, Z.A. On Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Smart Cities. Cities 2019, 89, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, A.; Indratmo; Daniel, B.; Tjandra, S. Systematic Review of the Literature on Big Data in the Transportation Domain: Concepts and Applications. Big Data Res. 2019, 17, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, J. Big Data Comes to the Farm, Sowing Mistrust. Wall Str. J. 2014. Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424052702304450904579369283869192124 (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Lokers, R.; Knapen, R.; Janssen, S.; van Randen, Y.; Jansen, J. Analysis of Big Data Technologies for Use in Agro-Environmental Science. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 84, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Kartakoullis, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. A Review on the Practice of Big Data Analysis in Agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 143, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, R.I. Invasive Species Research in the United States Department of Agriculture–Agricultural Research Service. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, R.N.; Diagne, C.; Haubrock, P.J.; Turbelin, A.J.; Courchamp, F. Are the “100 of the World’s Worst” Invasive Species Also the Costliest? Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagne, C.; Leroy, B.; Vaissière, A.-C.; Gozlan, R.E.; Roiz, D.; Jarić, I.; Salles, J.-M.; Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Courchamp, F. High and Rising Economic Costs of Biological Invasions Worldwide. Nature 2021, 592, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemaud, T.; Ciosi, M.; Lombaert, É.; Estoup, A. Biological Invasions in Agricultural Settings: Insights from Evolutionary Biology and Population Genetics. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2011, 334, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandy, A.S.; Wieder, W.R.; Wickings, K.; Kyker-Snowman, E. Beyond Microbes: Are Fauna the next Frontier in Soil Biogeochemical Models? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 102, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paini, D.R.; Sheppard, A.W.; Cook, D.C.; De Barro, P.J.; Worner, S.P.; Thomas, M.B. Global Threat to Agriculture from Invasive Species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7575–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziska, L.H.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Runion, G.B.; Hunt, E.R.; Diaz-Soltero, H. Invasive Species and Climate Change: An Agronomic Perspective. Clim. Change 2011, 105, 13–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedryver, C.-A.; Le Ralec, A.; Fabre, F. The Conflicting Relationships between Aphids and Men: A Review of Aphid Damage and Control Strategies. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2010, 333, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clubley, C.H.; Firth, L.B.; Wood, L.E.; Bilton, D.T.; Silva, T.A.M.; Knights, A.M. Science Paper or Big Data? Assessing Invasion Dynamics Using Observational Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, M.; Jeon, G.; Piccialli, F. A Framework for Pandemic Prediction Using Big Data Analytics. Big Data Res. 2021, 25, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenova, S.; Bartley, T.J.; Bohan, D.A.; Boutain, J.R.; Colautti, R.I.; Domaizon, I.; Fontaine, C.; Lemainque, A.; Le Viol, I.; Mollot, G.; et al. Chapter Three—Invasions Toolkit: Current Methods for Tracking the Spread and Impact of Invasive Species. In Advances in Ecological Research; Bohan, D.A., Dumbrell, A.J., Massol, F., Eds.; Networks of Invasion: A Synthesis of Concepts; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 56, pp. 85–182. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, T.; Döring, M.; Guralnick, R.; Bloom, D.; Wieczorek, J.; Braak, K.; Otegui, J.; Russell, L.; Desmet, P. The GBIF Integrated Publishing Toolkit: Facilitating the Efficient Publishing of Biodiversity Data on the Internet. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.D.; Bargeron, C.T.; Reaser, J.K. Enabling Decisions That Make a Difference: Guidance for Improving Access to and Analysis of Invasive Species Information. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, A.E.Z.; Dikow, T.; Moreau, C.S. Entomological Collections in the Age of Big Data. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Cordero, V.; Martínez-Meyer, E. Museum Specimen Data Predict Crop Damage by Tropical Rodents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7074–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guralnick, R.; Van Cleve, J. Strengths and Weaknesses of Museum and National Survey Data Sets for Predicting Regional Species Richness: Comparative and Combined Approaches. Divers. Distrib. 2005, 11, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, A.V.; Tsutsui, N.D. The Value of Museum Collections for Research and Society. BioScience 2004, 54, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaser, J.K.; Burgiel, S.W.; Kirkey, J.; Brantley, K.A.; Veatch, S.D.; Burgos-Rodríguez, J. The Early Detection of and Rapid Response (EDRR) to Invasive Species: A Conceptual Framework and Federal Capacities Assessment. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanes, F. Visual and Acoustic Sensors for Early Detection of Biological Invasions: Current Uses and Future Potential. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 42, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batz, P.; Will, T.; Thiel, S.; Ziesche, T.M.; Joachim, C. From Identification to Forecasting: The Potential of Image Recognition and Artificial Intelligence for Aphid Pest Monitoring. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1150748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisle, Z.J.; Flaherty, E.A.; Nobbe, M.R.; Wzientek, C.M.; Swihart, R.K. Next-Generation Camera Trapping: Systematic Review of Historic Trends Suggests Keys to Expanded Research Applications in Ecology and Conservation. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 617996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, Y.; Shamsian, A.; Shaked, B.; Altman, Y.; Danziger, B.-C.; Manrakhan, A.; Serfontein, L.; Bali, E.; Wernicke, M.; Egartner, A.; et al. A Real-Time Remote Surveillance System for Fruit Flies of Economic Importance: Sensitivity and Image Analysis. J. Pest. Sci. 2023, 96, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-A.; Tseng, C.-L.; Lu, F.-M.; Yang, E.-C.; Wu, Z.-S.; Chen, C.-P.; Lin, S.-H.; Lin, K.-C.; Liao, C.-S. A GSM-Based Remote Wireless Automatic Monitoring System for Field Information: A Case Study for Ecological Monitoring of the Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 62, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-A.; Lin, T.-S.; Yang, E.-C.; Tseng, C.-L.; Chen, C.-P.; Yen, C.-W.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Liu, R.-H.; Chen, Y.-F.; et al. Application of a Web-Based Remote Agro-Ecological Monitoring System for Observing Spatial Distribution and Dynamics of Bactrocera dorsalis in Fruit Orchards. Precis. Agric. 2013, 14, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.-S.; Chuang, C.-L.; Lin, T.-S.; Chen, C.-P.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Chen, P.-T.; Liao, K.-C.; Jiang, J.-A. Development of an Autonomous Early Warning System for Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) Outbreaks in Remote Fruit Orchards. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshtein, E.; Cohen, Y.; Hetzroni, A.; Gazit, Y.; Timar, D.; Rosenfeld, L.; Grinshpon, Y.; Hoffman, A.; Mizrach, A. Development of an Automatic Monitoring Trap for Mediterranean Fruit Fly (Ceratitis capitata) to Optimize Control Applications Frequency. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 139, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, T.J.; Bentall, D.; Kwon, C.; Mas, F. Automated Surveillance of Lepidopteran Pests with Smart Optoelectronic Sensor Traps. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Why, A.; Batista, G.; Mafra-neto, A.; Keogh, E. Flying Insect Classification with Inexpensive Sensors. J. Insect Behav. 2014, 27, 657–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydhmer, K.; Eckberg, J.O.; Lundgren, J.G.; Jansson, S.; Still, L.; Quinn, J.E.; Jr, R.W.; Lemmich, J.; Nikolajsen, T.; Sheller, N.; et al. Automating an Insect Biodiversity Metric Using Distributed Optical Sensors: An Evaluation across Kansas, USA Cropping Systems. eLife 2024, 13, RP92227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydhmer, K.; Bick, E.; Still, L.; Strand, A.; Luciano, R.; Helmreich, S.; Beck, B.D.; Grønne, C.; Malmros, L.; Poulsen, K.; et al. Automating Insect Monitoring Using Unsupervised Near-Infrared Sensors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lello, F.; Dida, M.; Mkiramweni, M.; Matiko, J.; Akol, R.; Nsabagwa, M.; Katumba, A. Fruit Fly Automatic Detection and Monitoring Techniques: A Review. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.-H. Advanced Machine Learning in Point Spectroscopy, RGB- and Hyperspectral-Imaging for Automatic Discriminations of Crops and Weeds: A Review. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 767–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarica, J.; Bittner, L.; Pallua, J.; Pezzei, C.; Huck-Pezzei, V.; Dowell, F.; Schied, J.; Bonn, G.K.; Huck, C.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; et al. Near-Infrared Imaging Spectroscopy as a Tool to Discriminate Two Cryptic Tetramorium Ant Species. J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansen, C.; Coelho, A., Jr.; Vieira, J.M.; Parra, J.R.P. Reflectance-Based Identification of Parasitized Host Eggs and Adult Trichogramma Specimens. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iost Filho, F.H.; Heldens, W.B.; Kong, Z.; de Lange, E.S. Drones: Innovative Technology for Use in Precision Pest Management. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Dao, P.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Shang, J. Recent Advances of Hyperspectral Imaging Technology and Applications in Agriculture. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, B.; Tuia, D.; Morris, D. AIDE: Accelerating Image-Based Ecological Surveys with Interactive Machine Learning. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wäldchen, J.; Mäder, P. Machine Learning for Image Based Species Identification. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 2216–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.C.; Ribeiro, J.; Morais, R.; Sousa, J.J.; Cunha, A. A Systematic Review on Automatic Insect Detection Using Deep Learning. Agriculture 2023, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuia, D.; Kellenberger, B.; Beery, S.; Costelloe, B.R.; Zuffi, S.; Risse, B.; Mathis, A.; Mathis, M.W.; van Langevelde, F.; Burghardt, T.; et al. Perspectives in Machine Learning for Wildlife Conservation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, Z.A.; Harris, D.J.; Filer, D.; Wood, J.R.I.; Scotland, R.W. Widespread Mistaken Identity in Tropical Plant Collections. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R1066–R1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wang, L.; Yin, D.; Li, X.; Diao, C.; Gong, H.; Shi, C.; Menenti, M.; Ge, Y.; Nie, S.; et al. Development of Spectral-Phenological Features for Deep Learning to Understand Spartina alterniflora Invasion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- August, T.; Fox, R.; Roy, D.B.; Pocock, M.J.O. Data-Derived Metrics Describing the Behaviour of Field-Based Citizen Scientists Provide Insights for Project Design and Modelling Bias. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllerová, J.; Brundu, G.; Große-Stoltenberg, A.; Kattenborn, T.; Richardson, D.M. Pattern to Process, Research to Practice: Remote Sensing of Plant Invasions. Biol. Invasions 2023, 25, 3651–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, C.T.; Mesaglio, T.; Ascher, J.S.; Brooks, T.M.; Cabras, A.A.; Chandler, M.; Cornwell, W.K.; Ríos-Málaver, I.C.; Dankowicz, E.; Dhiya’ulhaq, N.U.; et al. The Benefits of Contributing to the Citizen Science Platform iNaturalist as an Identifier. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putman, B.J.; Williams, R.; Li, E.; Pauly, G.B. The Power of Community Science to Quantify Ecological Interactions in Cities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Site Stats · iNaturalist. Available online: https://www.inaturalist.org/stats (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Callaghan, C.T.; Ozeroff, I.; Hitchcock, C.; Chandler, M. Capitalizing on Opportunistic Citizen Science Data to Monitor Urban Biodiversity: A Multi-Taxa Framework. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 251, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocock, M.J.O.; Tweddle, J.C.; Savage, J.; Robinson, L.D.; Roy, H.E. The Diversity and Evolution of Ecological and Environmental Citizen Science. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botan, A.L.M.; Heringer, G.; de Matos, A.C.L.; Oliveira, D.L.; de Alvarenga, D.R.; Almeida, J.W.; Tavares, K.P.; Bueno, M.L.; Lopes, V.H.; Zenni, R.D. Use of a Citizen Science Tool for the Determination of Biological Invasions in Urban Areas. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulbert, J.M.; Hallett, R.A.; Roy, H.E.; Cleary, M. Citizen Science Can Enhance Strategies to Detect and Manage Invasive Forest Pests and Pathogens. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1113978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelling, S.; Johnston, A.; Bonn, A.; Fink, D.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Bonney, R.; Fernandez, M.; Hochachka, W.M.; Julliard, R.; Kraemer, R.; et al. Using Semistructured Surveys to Improve Citizen Science Data for Monitoring Biodiversity. BioScience 2019, 69, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiago, P.; Evaristo, I.; Pinto, B. The Role of BioBlitzes in Citizen Science: Insights from Participants and Experts. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1347428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiller, K.D.K.; Davis, M.A.; Niemiller, M.L. Addressing ‘Biodiversity Naivety’ through Project-Based Learning Using iNaturalist. J. Nat. Conserv. 2021, 64, 126070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, R.M.; Mapes, C.; Low, R.D.; Long, A.; Bowser, A.; Durieux, D.; Rivera, K.; Dekramanjian, B.; Bartumeus, F.; Guerrero, D.; et al. Integrating Global Citizen Science Platforms to Enable Next-Generation Surveillance of Invasive and Vector Mosquitoes. Insects 2022, 13, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.F.; Frei, R.J.; Lee, R.M.; Maxwell, J.D.; Shoemaker, R.; Follett, A.P.; Lawson, G.M.; Malmfeldt, M.; Watts, R.; Aanderud, Z.T.; et al. Citizen Science Reveals Unexpected Solute Patterns in Semiarid River Networks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daume, S. Mining Twitter to Monitor Invasive Alien Species—An Analytical Framework and Sample Information Topologies. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 31, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateosian, L.G.; Saffer, A.; Walden-Schreiner, C.; Shukunobe, M. Plant Pest Invasions, as Seen through News and Social Media. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2023, 100, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-B.; Lee, H.; Song, J.; Jang, B.; Cho, S.M.; Yum, J.; Ahn, N.-H.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Choi, Y.-S.; et al. A Post in an Internet Forum Led to a Discovery of an Invasive Drywood Termite in Korea, Cryptotermes domesticus (Haviland) (Blattodea: Kalotermitidae). J. Integr. Pest. Manag. 2024, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encarnação, J.; Baptista, V.; Teodósio, M.A.; Morais, P. Low-Cost Citizen Science Effectively Monitors the Rapid Expansion of a Marine Invasive Species. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 752705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, J.; Curnel, Y.; Gobin, A.; Goffart, J.-P.; Mélard, F.; Tychon, B.; Wellens, J.; Defourny, P. Crowdsourcing for Agricultural Applications: A Review of Uses and Opportunities for a Farmsourcing Approach. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 142, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paini, D.R.; Worner, S.P.; Cook, D.C.; De Barro, P.J.; Thomas, M.B. Threat of Invasive Pests from within National Borders. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Mader, A.D.; Dasgupta, R.; Kumar, P. Citizen Science and Invasive Alien Species: An Analysis of Citizen Science Initiatives Using Information and Communications Technology (ICT) to Collect Invasive Alien Species Observations. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebach, M.C.; Valdecasas, A.G.; Wheeler, Q.D. Impediments to Taxonomy and Users of Taxonomy: Accessibility and Impact Evaluation. Cladistics 2011, 27, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, E. Shuttered Natural History Museums Fight for Survival. Science 2020, 368, 1042–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crall, A.W.; Jarnevich, C.S.; Young, N.E.; Panke, B.J.; Renz, M.; Stohlgren, T.J. Citizen Science Contributes to Our Knowledge of Invasive Plant Species Distributions. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 2415–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, F.; Franco, S.; Rosso, F. Citizens and Cities: Leveraging Citizen Science and Big Data for Sustainable Urban Development. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 648–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Redondo, A.; Correia, R.A.; Barve, V.; Brooks, T.M.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Jarić, I.; Kulkarni, R.; Ladle, R.J.; Vaz, A.S.; Minin, E.D. Harnessing Online Digital Data in Biodiversity Monitoring. PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinga, S.A.; Paudel, D.; Mouzakitis, S.A.; Athanasiadis, I.N. Big Data in Agriculture: Between Opportunity and Solution. Agric. Syst. 2022, 195, 103298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cecco, G.J.; Barve, V.; Belitz, M.W.; Stucky, B.J.; Guralnick, R.P.; Hurlbert, A.H. Observing the Observers: How Participants Contribute Data to iNaturalist and Implications for Biodiversity Science. BioScience 2021, 71, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullin, R.T.; Allen, J.L. An Assessment of Data Accuracy and Best Practice Recommendations for Observations of Lichens and Other Taxonomically Difficult Taxa on iNaturalist. Botany 2022, 100, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- iNaturalist Research-Grade Observations. 2024. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/dataset/50c9509d-22c7-4a22-a47d-8c48425ef4a7 (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Hochmair, H.H.; Scheffrahn, R.H.; Basille, M.; Boone, M. Evaluating the Data Quality of iNaturalist Termite Records. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackland, S.J.; Richardson, D.M.; Robinson, T.B. A Method for Conveying Confidence in iNaturalist Observations: A Case Study Using Non-Native Marine Species. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, M.E. Genetic Reconstructions of Invasion History. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2212–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, F.A.; Tembrock, L.R.; Timm, A.E.; Farris, R.E.; Perera, O.P.; Gilligan, T.M. A Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Assay to Detect Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Bulk Trap Samples. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Floyd, R.; Jafarpour, S.; Prosser, S.W. Barcode 100 K Specimens: In a Single Nanopore Run. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 25, e14028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashank, P.R.; Parker, B.M.; Rananaware, S.R.; Plotkin, D.; Couch, C.; Yang, L.G.; Nguyen, L.T.; Prasannakumar, N.R.; Braswell, W.E.; Jain, P.K.; et al. CRISPR-Based Diagnostics Detects Invasive Insect Pests. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 24, e13881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villari, C.; Mahaffee, W.F.; Mitchell, T.K.; Pedley, K.F.; Pieck, M.L.; Hand, F.P. Early Detection of Airborne Inoculum of Magnaporthe oryzae in Turfgrass Fields Using a Quantitative LAMP Assay. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.R.; Graham, B.M.; Achury, R.; Coon, J.J.; Daniels, M.K.; Gambrell, D.K.; Jonasen, K.L.; King, G.D.; LaRacuente, N.; Perrin-Stowe, T.I.; et al. From eDNA to Citizen Science: Emerging Tools for the Early Detection of Invasive Species. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 18, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, D.; Luscombe, N.M.; Jansen, R.; Qian, J.; Gerstein, M. Interrelating Different Types of Genomic Data, from Proteome to Secretome: ’Oming in on Function. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Cochrane, G. The International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D121–D124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiklejohn, K.A.; Damaso, N.; Robertson, J.M. Assessment of BOLD and GenBank—Their Accuracy and Reliability for the Identification of Biological Materials. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Bejarano, N.; Reina, C.; Martínez-Revelo, D.E.; Medina, C.A.; Tovar, E.; Uribe-Soto, S.; Neita-Moreno, J.C.; Gonzalez, M.A. Taxonomic Identification Accuracy from BOLD and GenBank Databases Using over a Thousand Insect DNA Barcodes from Colombia. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.L.; Cooper, L.D.; Poelchau, M.F.; Berardini, T.Z.; Elser, J.; Farmer, A.D.; Ficklin, S.; Kumari, S.; Laporte, M.-A.; Nelson, R.T.; et al. Data Sharing and Ontology Use among Agricultural Genetics, Genomics, and Breeding Databases and Resources of the Agbiodata Consortium. Database 2023, 2023, baad076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lang, K.; Qian, W.; Wang, S.; Cao, X.; He, R.; Zhan, A.; Chen, M.; Yang, N.; Li, F. InvasionDB: A Genome and Gene Database of Invasive Alien Species. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, A.K.; Geib, S.M.; Sim, S.B.; Poelchau, M.F.; Coates, B.S.; Simmonds, T.J.; Scully, E.D.; Smith, T.P.L.; Childers, C.P.; Corpuz, R.L.; et al. The USDA-ARS Ag100Pest Initiative: High-Quality Genome Assemblies for Agricultural Pest Arthropod Research. Insects 2021, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo-Calderón, G.I.; Harb, O.S.; Kelly, S.A.; Rund, S.S.; Roos, D.S.; McDowell, M.A. VectorBase.Org Updates: Bioinformatic Resources for Invertebrate Vectors of Human Pathogens and Related Organisms. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 50, 100860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legeai, F.; Shigenobu, S.; Gauthier, J.-P.; Colbourne, J.; Rispe, C.; Collin, O.; Richards, S.; Wilson, A.C.C.; Tagu, D. AphidBase: A Centralized Bioinformatic Resource for Annotation of the Pea Aphid Genome. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Shen, G.; Guo, D.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Xiao, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. InsectBase: A Resource for Insect Genomes and Transcriptomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Kaur, N.; Kliot, A.; Pinheiro, P.V.; Luan, J.; Stensmyr, M.C.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, H.; et al. The Draft Genome of Whitefly Bemisia Tabaci MEAM1, a Global Crop Pest, Provides Novel Insights into Virus Transmission, Host Adaptation, and Insecticide Resistance. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvick, J.; Fu, A.; Muppirala, U.; Sabharwal, M.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Lawrence, C.J.; Lushbough, C.; Brendel, V. PlantGDB: A Resource for Comparative Plant Genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D959–D965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, P.; McGaughran, A. Genomic Data Is Missing for Many Highly Invasive Species, Restricting Our Preparedness for Escalating Incursion Rates. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-Km Spatial Resolution Climate Surfaces for Global Land Areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, M.P.; Van Niel, K.P. Improving Species Distribution Models for Climate Change Studies: Variable Selection and Scale. J. Biogeogr. 2011, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, A.; Perez De Leon, A.; Teel, P.; Manoukis, N.; Messenger, M.; Bonilla, D. Novel Hurricane Hypothesis Predicts U.S Cattle Fever Tick Outbreaks. 2020. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publication/?seqNo115=375172 (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Borer, E.T.; Grace, J.B.; Harpole, W.S.; MacDougall, A.S.; Seabloom, E.W. A Decade of Insights into Grassland Ecosystem Responses to Global Environmental Change. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Record, S.; Sokol, E.R.; Bitters, M.E.; Chen, M.Y.; Chung, Y.A.; Helmus, M.R.; Jaimes, R.; Jansen, L.; Jarzyna, M.A.; et al. Standardized NEON Organismal Data for Biodiversity Research. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.K.; Coddington, J.A. Estimating Terrestrial Biodiversity through Extrapolation. Philos. Trans. Biol. Sci. 1994, 345, 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadish, H.V.; Gehrke, J.; Labrinidis, A.; Papakonstantinou, Y.; Patel, J.M.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Shahabi, C. Big Data and Its Technical Challenges. Commun. ACM 2014, 57, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Thuiller, W.; Miaud, C. Prediction and Validation of the Potential Global Distribution of a Problematic Alien Invasive Species—The American Bullfrog. Divers. Distrib. 2007, 13, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlin, I.; Egizi, A.; Narvaez, Z.; Bonilla, D.L.; Gallagher, M.; Williams, G.M.; Rainey, T.; Price, D.C.; Fonseca, D.M. Microhabitat Modeling of the Invasive Asian Longhorned Tick (Haemaphysalis longicornis) in New Jersey, USA. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-H.; Song, J.-W.; Yoon, S.-H.; Jung, J.-M. Spatial Evaluation of Machine Learning-Based Species Distribution Models for Prediction of Invasive Ant Species Distribution. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streito, J.-C.; Chartois, M.; Pierre, É.; Dusoulier, F.; Armand, J.-M.; Gaudin, J.; Rossi, J.-P. Citizen Science and Niche Modeling to Track and Forecast the Expansion of the Brown Marmorated Stinkbug Halyomorpha halys (Stål, 1855). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.; Kumar, S.; Aguilar, G. Mapping the Potential Global Range of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug, Halyomorpha halys, with Particular Reference to New Zealand. Climate 2017, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, M.A.; Weiskopf, S.R.; Bertrand, R.; Carter, S.L.; Comte, L.; Eaton, M.J.; Johnson, C.G.; Lenoir, J.; Lynch, A.J.; Miller, B.W.; et al. Climate Change and the Global Redistribution of Biodiversity: Substantial Variation in Empirical Support for Expected Range Shifts. Environ. Evid. 2023, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbet-Massin, M.; Rome, Q.; Villemant, C.; Courchamp, F. Can Species Distribution Models Really Predict the Expansion of Invasive Species? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillero, N.; Arenas-Castro, S.; Enriquez-Urzelai, U.; Vale, C.G.; Sousa-Guedes, D.; Martínez-Freiría, F.; Real, R.; Barbosa, A.M. Want to Model a Species Niche? A Step-by-Step Guideline on Correlative Ecological Niche Modelling. Ecol. Model. 2021, 456, 109671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetz, W.; McGeoch, M.A.; Guralnick, R.; Ferrier, S.; Beck, J.; Costello, M.J.; Fernandez, M.; Geller, G.N.; Keil, P.; Merow, C.; et al. Essential Biodiversity Variables for Mapping and Monitoring Species Populations. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Franklin, J. Species Distribution Modelling. Encycl. Biodivers. 2013, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, H.L.; Montes, C.R.; Gandhi, K.J.K.; Poisson, M.A. A Comparison of Presence-Only Analytical Techniques and Their Application in Forest Pest Modeling. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 68, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavi, R.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; Elith, J. Predictive Performance of Presence-Only Species Distribution Models: A Benchmark Study with Reproducible Code. Ecol. Monogr. 2022, 92, e01486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meineke, E.K.; Daru, B.H. Bias Assessments to Expand Research Harnessing Biological Collections. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.B.; Anderson, R.P.; Márcia Barbosa, A.; Beale, C.M.; Dormann, C.F.; Early, R.; Garcia, R.A.; Guisan, A.; Maiorano, L.; Naimi, B.; et al. Standards for Distribution Models in Biodiversity Assessments. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaat4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.L. SDMtoolbox: A Python-Based GIS Toolkit for Landscape Genetic, Biogeographic and Species Distribution Model Analyses. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capinha, C.; Anastácio, P. Assessing the Environmental Requirements of Invaders Using Ensembles of Distribution Models. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 17, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merow, C.; Smith, M.J.; Silander, J.A., Jr. A Practical Guide to MaxEnt for Modeling Species’ Distributions: What It Does, and Why Inputs and Settings Matter. Ecography 2013, 36, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscatello, A.; Elith, J.; Kujala, H. How Decisions about Fitting Species Distribution Models Affect Conservation Outcomes. Conserv. Biol. 2021, 35, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.B.; New, M. Ensemble Forecasting of Species Distributions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, D.-M.; Sun, Y.; Long, L.-G.; Wang, J.-G.; Wu, J.-W.; Long, T.; Li, W.-J. Predicting the Suitable Habitat of the Invasive Alien Plant Lactuca serriola Using Biomod2 Model with ArcGIS. Environ. Res. Commun. 2025, 7, 045029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Elith, J.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J. A Review of Evidence about Use and Performance of Species Distribution Modelling Ensembles like BIOMOD. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Elith, J.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; Guillera-Arroita, G. Testing Whether Ensemble Modelling Is Advantageous for Maximising Predictive Performance of Species Distribution Models. Ecography 2020, 43, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboneras, C.; Genovesi, P.; Vilà, M.; Blackburn, T.M.; Carrete, M.; Clavero, M.; D’hondt, B.; Orueta, J.F.; Gallardo, B.; Geraldes, P.; et al. A Prioritised List of Invasive Alien Species to Assist the Effective Implementation of EU Legislation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.E.; Bacher, S.; Essl, F.; Adriaens, T.; Aldridge, D.C.; Bishop, J.D.D.; Blackburn, T.M.; Branquart, E.; Brodie, J.; Carboneras, C.; et al. Developing a List of Invasive Alien Species Likely to Threaten Biodiversity and Ecosystems in the European Union. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 1032–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeoch, M.A.; Genovesi, P.; Bellingham, P.J.; Costello, M.J.; McGrannachan, C.; Sheppard, A. Prioritizing Species, Pathways, and Sites to Achieve Conservation Targets for Biological Invasion. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, D.G.; Work, T.T.; Cavey, J.F.; Liebhold, A.M.; Marshall, D. Interceptions of Nonindigenous Plant Pests at US Ports of Entry and Border Crossings over a 17-Year Period. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 611–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venette, R.C.; Hutchison, W.D. Invasive Insect Species: Global Challenges, Strategies & Opportunities. Front. Insect Sci. 2021, 1, 650520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurisse, N.; Rassati, D.; Hurley, B.P.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Haack, R.A. Common Pathways by Which Non-Native Forest Insects Move Internationally and Domestically. J. Pest. Sci. 2019, 92, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, P.C.; Kean, J.M.; Suckling, D.M.; McCullough, D.G.; Herms, D.A.; Stringer, L.D. Determinants of Successful Arthropod Eradication Programs. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluess, T.; Cannon, R.; Jarošík, V.; Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P.; Bacher, S. When Are Eradication Campaigns Successful? A Test of Common Assumptions. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D. The Role of Propagule Pressure in Biological Invasions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccaggi, D.L.; Wilson, J.R.U.; Robinson, A.P.; Terblanche, J.S. Arthropods on Imported Plant Products: Volumes Predict General Trends While Contextual Details Enhance Predictive Power. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, e2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosuosso, U.; Cini, A.; Papini, A. Tracing Outliers in the Dataset of Drosophila Suzukii Records with the Isolation Forest Method. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Ma, L. Big Data Analysis for Evaluating Bioinvasion Risk. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnegie, A.J.; Eslick, H.; Barber, P.; Nagel, M.; Stone, C. Airborne Multispectral Imagery and Deep Learning for Biosecurity Surveillance of Invasive Forest Pests in Urban Landscapes. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 81, 127859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latombe, G.; Pyšek, P.; Jeschke, J.M.; Blackburn, T.M.; Bacher, S.; Capinha, C.; Costello, M.J.; Fernández, M.; Gregory, R.D.; Hobern, D.; et al. A Vision for Global Monitoring of Biological Invasions. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 213, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.M.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Bertelsmeier, C.; Blake, R.E.; Caton, B.; James, A.; MacLeod, A.; Nahrung, H.F.; Pawson, S.M.; Plank, M.J.; et al. Worldwide Border Interceptions Provide a Window into Human-Mediated Global Insect Movement. Ecol. Appl. 2021, 31, e02412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Sink, K.; Robinson, T.B. Aliens Cruising in: Explaining Alien Fouling Macro-Invertebrate Species Numbers on Recreational Yachts. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 182, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspers, C.; Ehrlich, M.; Pujolar, J.M.; Künzel, S.; Bayer, T.; Limborg, M.T.; Lombard, F.; Browne, W.E.; Stefanova, K.; Reusch, T.B.H. Invasion Genomics Uncover Contrasting Scenarios of Genetic Diversity in a Widespread Marine Invader. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2116211118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browett, S.S.; O’Meara, D.B.; McDevitt, A.D. Genetic Tools in the Management of Invasive Mammals: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives. Mammal. Rev. 2020, 50, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, H.L.; McGaughran, A.; Jiggins, C.D. Insights into Invasive Species from Whole-Genome Resequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 6289–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda-Paulo, F.A.; Simon, J.-C.; Ramírez, C.C.; Fuentes-Contreras, E.; Margaritopoulos, J.T.; Wilson, A.C.C.; Sorenson, C.E.; Briones, L.M.; Azevedo, R.; Ohashi, D.V.; et al. The Invasion Route for an Insect Pest Species: The Tobacco Aphid in the New World. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 4738–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius, M.; Bourne, S.; Hornsby, H.G.; Chapman, M.A. Applications of Next-Generation Sequencing to the Study of Biological Invasions. Curr. Zool. 2015, 61, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.; Ferrier, S.; Walters, M.; Geller, G.; Scholes, R.; Bruford, M.; Brummitt, N.; Butchart, S.; Cardoso, A.; Coops, N.; et al. Essential Biodiversity Variables. Science 2013, 339, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Comte, L.; Olden, J.D. Heads You Win, Tails You Lose: Life-History Traits Predict Invasion and Extinction Risk of the World’s Freshwater Fishes. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2017, 27, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capellini, I.; Baker, J.; Allen, W.L.; Street, S.E.; Venditti, C. The Role of Life History Traits in Mammalian Invasion Success. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, A.; Penone, C.; Pennino, M.G.; Courchamp, F. Predicting Future Invaders and Future Invasions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7905–7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, A.; Desprez-Loustau, M.-L.; Fabre, B.; Frey, P.; Halkett, F.; Husson, C.; Lung-Escarmant, B.; Marçais, B.; Robin, C.; Vacher, C.; et al. Predicting Invasion Success of Forest Pathogenic Fungi from Species Traits. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desprez-Loustau, M.-L.; Robin, C.; Buee, M.; Courtecuisse, R.; Garbaye, J.; Suffert, F.; Sache, I.; Rizzo, D. The Fungal Dimension of Biological Invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarnevich, C.S.; Young, N.E.; Talbert, M.; Talbert, C. Forecasting an Invasive Species’ Distribution with Global Distribution Data, Local Data, and Physiological Information. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosti, D.; Catapano, T.; Sautter, G.; Egloff, W. The Plazi Workflow: The PDF Prison Break for Biodiversity Data. Biodivers. Inf. Sci. Stand. 2019, 3, e37046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.N.; Mech, A.M.; Ayres, M.P.; Gandhi, K.J.K.; Havill, N.P.; Herms, D.A.; Hoover, A.M.; Hufbauer, R.A.; Liebhold, A.M.; Marsico, T.D.; et al. Predicting Non-Native Insect Impact: Focusing on the Trees to See the Forest. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 3921–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzihorský, V.; Trombik, J.; Mally, R.; Turčáni, M.; Liebhold, A.M. Insect Invasions Track a Tree Invasion: Global Distribution of Black Locust Herbivores. J. Biogeogr. 2023, 50, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieurance, D.; Canavan, S.; Behringer, D.C.; Kendig, A.E.; Minteer, C.R.; Reisinger, L.S.; Romagosa, C.M.; Flory, S.L.; Lockwood, J.L.; Anderson, P.J.; et al. Identifying Invasive Species Threats, Pathways, and Impacts to Improve Biosecurity. Ecosphere 2023, 14, e4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P.; Pati, P.K.; Khan, M.L.; Khare, P.K. Plant Functional Traits Best Explain Invasive Species’ Performance within a Dynamic Ecosystem—A Review. Trees For. People 2022, 8, 100260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.M.; Wayne, M. Quantitative Trait Locus (QTL) Analysis. Nat. Educ. 2008, 1, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Thurber, C.S.; Jia, M.H.; Jia, Y.; Caicedo, A.L. Similar Traits, Different Genes? Examining Convergent Evolution in Related Weedy Rice Populations. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widstrom, N.W.; Butron, A.; Guo, B.Z.; Wilson, D.M.; Snook, M.E.; Cleveland, T.E.; Lynch, R.E. Control of Preharvest Aflatoxin Contamination in Maize by Pyramiding QTL Involved in Resistance to Ear-Feeding Insects and Invasion by Aspergillus spp. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olazcuaga, L.; Loiseau, A.; Parrinello, H.; Paris, M.; Fraimout, A.; Guedot, C.; Diepenbrock, L.M.; Kenis, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; et al. A Whole-Genome Scan for Association with Invasion Success in the Fruit Fly Drosophila suzukii Using Contrasts of Allele Frequencies Corrected for Population Structure. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 2369–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; De Meyer, M.; Liao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Virgilio, M.; Feng, S.; Qin, Y.; Singh, S.; Wee, S.L.; et al. Genomes of the Cosmopolitan Fruit Pest Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) Reveal Its Global Invasion History and Thermal Adaptation. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 53, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Ke, F.; You, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Q.; He, W.; Baxter, S.W.; Yuchi, Z.; Vasseur, L.; Gurr, G.M.; et al. Variation among 532 Genomes Unveils the Origin and Evolutionary History of a Global Insect Herbivore. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, Y.; Guo, C.; Qu, W.; Yang, N.; Zhu, Y.; Jeong, I.; Li, X.; Ghanim, M.; et al. Invasion Genomics Uncover Complex Introduction Patterns of the Globally Invasive Whitefly, Bemisia tabaci MED. Divers. Distrib. 2023, 29, 1172–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uden, D.R.; Mech, A.M.; Havill, N.P.; Schulz, A.N.; Ayres, M.P.; Herms, D.A.; Hoover, A.M.; Gandhi, K.J.K.; Hufbauer, R.A.; Liebhold, A.M.; et al. Phylogenetic Risk Assessment Is Robust for Forecasting the Impact of Non-Native Insects on North American Trees. Ecol. Appl. 2023, 33, e2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.D.; Pennell, M.W.; Dunn, C.W.; Edwards, S.V. Phylogenetics Is the New Genetics (for Most of Biodiversity). Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmell, P.; Sackton, T.B.; Edwards, S.V.; Liu, J.S. A Phylogenetic Method Linking Nucleotide Substitution Rates to Rates of Continuous Trait Evolution. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1011995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoup, A.; Ravigné, V.; Hufbauer, R.; Vitalis, R.; Gautier, M.; Facon, B. Is There a Genetic Paradox of Biological Invasion? Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2016, 47, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gaughan, S.; Lamer, J.T.; Deng, C.; Hu, W.; Wachholtz, M.; Qin, S.; Nie, H.; Liao, X.; Ling, Q.; et al. Resolving the Genetic Paradox of Invasions: Preadapted Genomes and Postintroduction Hybridization of Bigheaded Carps in the Mississippi River Basin. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sax, D.F.; Brown, J.H. The Paradox of Invasion. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2000, 9, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chown, S.L.; Hodgins, K.A.; Griffin, P.C.; Oakeshott, J.G.; Byrne, M.; Hoffmann, A.A. Biological Invasions, Climate Change and Genomics. Evol. Appl. 2015, 8, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessenauer, P.; Fijarczyk, A.; Martin, H.; Prunier, J.; Charron, G.; Chapuis, J.; Bernier, L.; Tanguay, P.; Hamelin, R.C.; Landry, C.R. Hybridization and Introgression Drive Genome Evolution of Dutch Elm Disease Pathogens. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Hu, X.; Zhou, X.J.; et al. Fall Webworm Genomes Yield Insights into Rapid Adaptation of Invasive Species. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, D.G.; Caseys, C.; Cousens, R.D.; Hahn, M.A.; Heredia, S.M.; Hübner, S.; Turner, K.G.; Whitney, K.D.; Rieseberg, L.H. What We Still Don’t Know about Invasion Genetics. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2277–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, P.; Genitoni, J.; Barloy, D.; Maury, S.; Gibert, P.; Ghalambor, C.K.; Vieira, C. Biological Invasion: The Influence of the Hidden Side of the (Epi)Genome. Funct. Ecol. 2020, 34, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRue, E.A.; Hardiman, B.S.; Elliott, J.M.; Fei, S. Structural Diversity as a Predictor of Ecosystem Function. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Rakotoarivony, M.N.A.; Hassani, K.; Johnson, K.G.; Hamilton, R.G.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Schneider, F.D.; Bachelot, B. Advancing Our Understanding of Plant Diversity-Biological Invasion Relationships Using Imaging Spectroscopy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 304, 114028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, N.S.; Mahood, A.L.; Meier, C.L.; Muthukrishnan, R.; Nagy, R.C.; Stricker, E.; Duffy, K.A.; Petri, L.; Morisette, J.T. Six Central Questions about Biological Invasions to Which NEON Data Science Is Poised to Contribute. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, A.K.; Smith, M.D.; Hobbie, S.E.; Collins, S.L.; Fahey, T.J.; Hansen, G.J.A.; Landis, D.A.; La Pierre, K.J.; Melillo, J.M.; Seastedt, T.R.; et al. Past, Present, and Future Roles of Long-Term Experiments in the LTER Network. BioScience 2012, 62, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haymer, D. Genetics and Insect Pest Management in Agriculture. CABI Rev. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, D.; Byrne, M.; Kennedy, M.; Campbell, S.; Tizard, M. Identifying Knowledge Gaps for Gene Drive Research to Control Invasive Animal Species: The next CRISPR Step. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 13, e00363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.F. Gene Drives and the Management of Agricultural Pests. J. Responsible Innov. 2018, 5, S255–S262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, M.M.A.; Facey, P.D.; Del Sol, R.; Fernández-Martínez, L.T.; Evans, M.C.; Mitchell, J.J.; Bodger, O.G.; Dyson, P.J. Symbiont-Mediated RNA Interference in Insects. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampolini, F.; Rieske, L.K. Emerald Ash Borer Specific Gene Silencing Has No Effect on Non-Target Organisms. Front. Agron. 2020, 2, 608827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjodin, B.M.F.; Irvine, R.L.; Russello, M.A. RapidRat: Development, Validation and Application of a Genotyping-by-Sequencing Panel for Rapid Biosecurity and Invasive Species Management. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, A. Optimizing Strategies for Slowing the Spread of Invasive Species. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1011996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.A.; Tembrock, L.R.; Sankovitz, M.; Wilson, T.M.; Looney, C.; Takahashi, J.; Gilligan, T.M.; Smith-Pardo, A.H.; Harpur, B.A. Population Genomics of the Invasive Northern Giant Hornet Vespa mandarinia in North America and across Its Native Range. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.M.; Bode, M. Recent Advances of Quantitative Modeling to Support Invasive Species Eradication on Islands. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2021, 3, e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoukis, N.C.; Hall, B.; Geib, S.M. A Computer Model of Insect Traps in a Landscape. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaskovic, P.; Ainseba, B.; Nicolas, Y.; Toupance, T.; Tardy, P.; Thiéry, D. Sensing of Airborne Infochemicals for Green Pest Management: What Is the Challenge? ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3824–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.M.; Jones, S.; Petrasova, A.; Petras, V.; Gaydos, D.; Skrip, M.M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Bigsby, K.; Meentemeyer, R.K. Iteratively Forecasting Biological Invasions with PoPS and a Little Help from Our Friends. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 19, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Evert, F.K.; Fountas, S.; Jakovetic, D.; Crnojevic, V.; Travlos, I.; Kempenaar, C. Big Data for Weed Control and Crop Protection. Weed Res. 2017, 57, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Huebner, C.D.; Reardon, R.; Park, Y.-L. Spatially Targeted Biological Control of Mile-a-Minute Weed Using Rhinoncomimus latipes (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and an Unmanned Aircraft System. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maran, S.P.M. Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools in Integrated Pest Management (IPM)—An Insect—Plant Interaction Perspective. Acta Sci. Agric. 2022, 6, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasazin, T.D.; Larsson Herrera, S.; Kimbokota, F.; Dekker, T. Translating Olfactomes into Attractants: Shared Volatiles Provide Attractive Bridges for Polyphagy in Fruit Flies. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, S.E.; Strasser, C.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Gram, W.K.; Budden, A.E.; Batcheller, A.L.; Duke, C.S.; Porter, J.H. Big Data and the Future of Ecology. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, S.S.; Dawson, A.; Goring, S.J.; Williams, J.W. Situating Ecology as a Big-Data Science: Current Advances, Challenges, and Solutions. BioScience 2018, 68, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovos, I.; Kleitou, P.; Poursanidis, D.; Batjakas, I.; Bernardi, G.; Crocetta, F.; Doumpas, N.; Kalogirou, S.; Kampouris, T.E.; Keramidas, I.; et al. Citizen-Science for Monitoring Marine Invasions and Stimulating Public Engagement: A Case Project from the Eastern Mediterranean. Biol Invasions 2019, 21, 3707–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousteni, V.; Tsiamis, K.; Gervasini, E.; Zenetos, A.; Karachle, P.K.; Cardoso, A.C. Citizen Scientists Contributing to Alien Species Detection: The Case of Fishes and Mollusks in European Marine Waters. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e03875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ashton, L.; Pedley, S.M.; Edwards, D.P.; Tang, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Kitching, R.; Dolman, P.M.; Woodcock, P.; Edwards, F.A.; et al. Reliable, Verifiable and Efficient Monitoring of Biodiversity via Metabarcoding. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, E. Improved Prototypical Network Model for Forest Species Classification in Complex Stand. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocean Biodiversity Information System; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO. The OBIS Manual. 2024. Available online: https://obis.org (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- ISO 19116:2019(En); Geographic Information—Positioning Services. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:19116:ed-2:v1:en (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- ISO 19157-1:2023(En); Geographic Information—Data Quality—Part 1: General Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:19157:-1:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Zurell, D.; Franklin, J.; König, C.; Bouchet, P.J.; Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Fandos, G.; Feng, X.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Guisan, A.; et al. A Standard Protocol for Reporting Species Distribution Models. Ecography 2020, 43, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, M.; Knowlton, N.; Ho, S.-L.; Nguyen, B.N.; Machida, R.J. GenBank Is a Reliable Resource for 21st Century Biodiversity Research. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22651–22656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, C.; Molina, C.I.; Zizka, A.; Persson, C.; Taylor, C.M.; Albán, J.; Chilquillo, E.; Rønsted, N.; Antonelli, A. Estimating Species Diversity and Distribution in the Era of Big Data: To What Extent Can We Trust Public Databases? Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizka, A.; Silvestro, D.; Andermann, T.; Azevedo, J.; Duarte Ritter, C.; Edler, D.; Farooq, H.; Herdean, A.; Ariza, M.; Scharn, R.; et al. CoordinateCleaner: Standardized Cleaning of Occurrence Records from Biological Collection Databases. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Böller, M.; Erhardt, A.; Schwanghart, W. Spatial Bias in the GBIF Database and Its Effect on Modeling Species’ Geographic Distributions. Ecol. Inform. 2014, 19, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Roselló, E.; González-Dacosta, J.; Lobo, J.M. The Biased Distribution of Existing Information on Biodiversity Hinders Its Use in Conservation, and We Need an Integrative Approach to Act Urgently. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 283, 110118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.-W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for Scientific Data Management and Stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.-H.; Choi, M.J. Ecological Views of Big Data: Perspectives and Issues. Telemat. Inform. 2015, 32, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bona, S.D.; Barringer, L.; Kurtz, P.; Losiewicz, J.; Parra, G.R.; Helmus, M.R. Lydemapr: An R Package to Track the Spread of the Invasive Spotted Lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula, White 1845) (Hemiptera, Fulgoridae) in the United States. NeoBiota 2023, 86, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, K.; Knezevic, I. Big Data in Food and Agriculture. Big Data Soc. 2016, 3, 2053951716648174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackfort, S.; Marquis, S.; Bronson, K. Harvesting Value: Corporate Strategies of Data Assetization in Agriculture and Their Socio-Ecological Implications. Big Data Soc. 2024, 11, 20539517241234279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, I.M. The Ethics of Big Data in Big Agriculture. Internet Policy Rev. 2016, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folger, P. The Geospatial Data Act of 2018; FGDC: Reston, VA, USA, 2018.
- Pagad, S.; Genovesi, P.; Carnevali, L.; Schigel, D.; McGeoch, M.A. Introducing the Global Register of Introduced and Invasive Species. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 170202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Jarnevich, C.; Madsen, J.; Westbrooks, R.; Fournier, C.; Mehrhoff, L.; Browne, M.; Graham, J.; Sellers, E. Invasive Species Information Networks: Collaboration at Multiple Scales for Prevention, Early Detection, and Rapid Response to Invasive Alien Species. Biodiversity 2009, 10, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegraus, E.H.; Andelman, S.; Jones, M.B.; Schildhauer, M. Maximizing the Value of Ecological Data with Structured Metadata: An Introduction to Ecological Metadata Language (EML) and Principles for Metadata Creation. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2005, 86, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunia, B.; Sandusky, R.J. Designing Metadata for Long-Term Data Preservation: DataONE Case Study. Proc. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, J.; Bloom, D.; Guralnick, R.; Blum, S.; Döring, M.; Giovanni, R.; Robertson, T.; Vieglais, D. Darwin Core: An Evolving Community-Developed Biodiversity Data Standard. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, M.; Tucker, A.; Chadderton, W.L.; Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R. Active and Passive Environmental DNA Surveillance of Aquatic Invasive Species. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 73, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.; Pérez-Sierra, A.; Crow, P.; Parnell, S. The Role of Passive Surveillance and Citizen Science in Plant Health. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2020, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, K.F.; Ball, S.L. DNA Barcodes for Biosecurity: Invasive Species Identification. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoup, A.; Guillemaud, T. Reconstructing Routes of Invasion Using Genetic Data: Why, How and so What? Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 4113–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, G.L.W.; Seidl, R.; Bellvé, A.M.; Rammer, W. An Outlook for Deep Learning in Ecosystem Science. Ecosystems 2022, 25, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Bik, H.M.; Mächler, E.; Seymour, M.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Altermatt, F.; Creer, S.; Bista, I.; Lodge, D.M.; de Vere, N.; et al. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding: Transforming How We Survey Animal and Plant Communities. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5872–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data Quality Requirements: Occurrence Datasets. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/data-quality-requirements-occurrences (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Potamitis, I.; Rigakis, I.; Fysarakis, K. The Electronic McPhail Trap. Sensors 2014, 14, 22285–22299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, N.; Cumming, S.; Darveau, M. Models to Predict the Distribution and Abundance of Breeding Ducks in Canada. Avian Conserv. Ecol. 2014, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R. Species Distribution Models: Ecological Explanation and Prediction Across Space and Time. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 677–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).