Lightweight SCD-YOLOv5s: The Detection of Small Defects on Passion Fruit with Improved YOLOv5s
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Dataset Preparation and Augmentation
2.3. Overview of Experimental Overall Stages
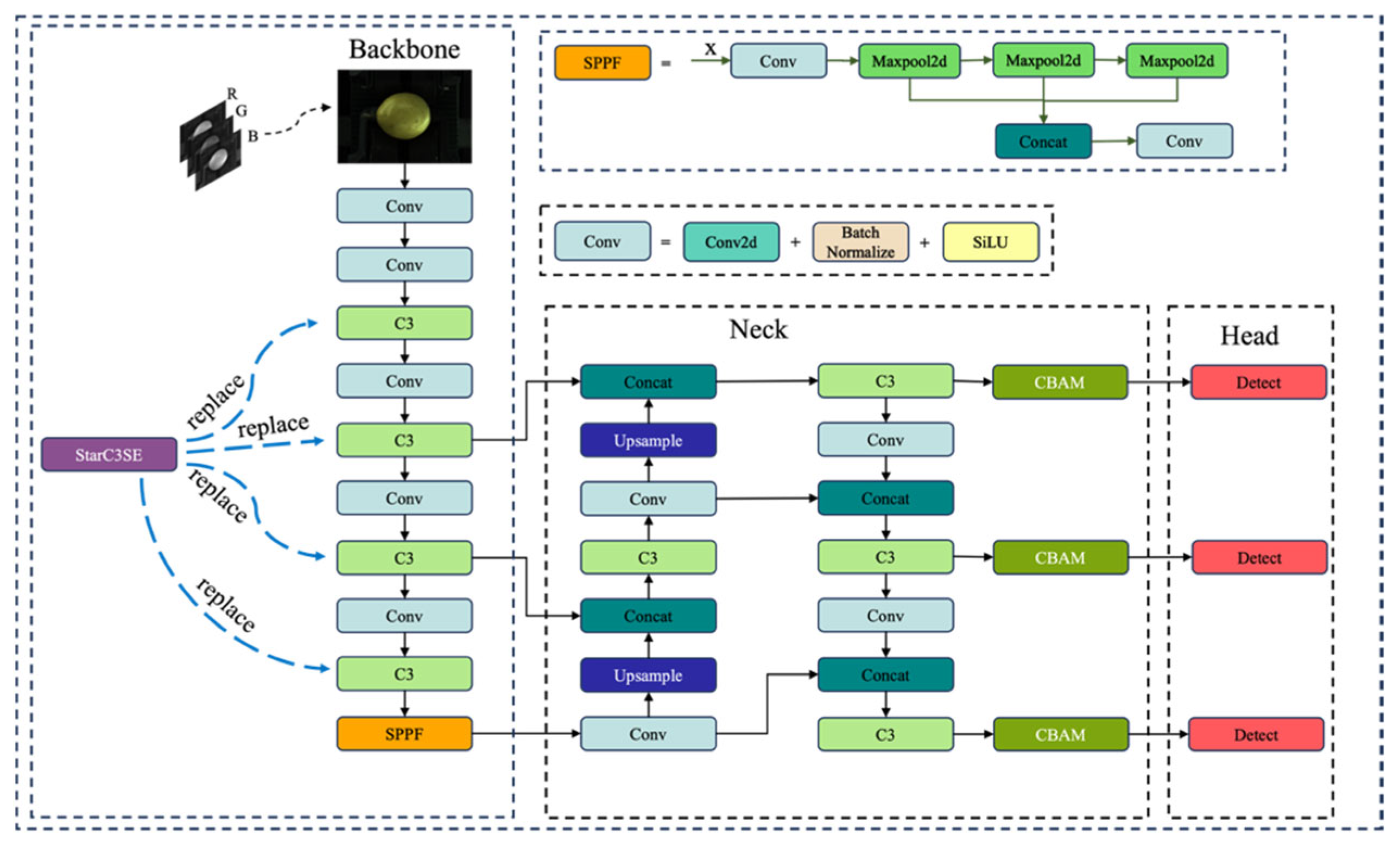
2.4. The Proposed SCD-YOLOv5s Network
2.4.1. Overview of the YOLOv5 Model
2.4.2. Enhanced Backbone with StarC3SE Module
SENet Channel Attention Mechanism
StarBlock
StarC3SE Module
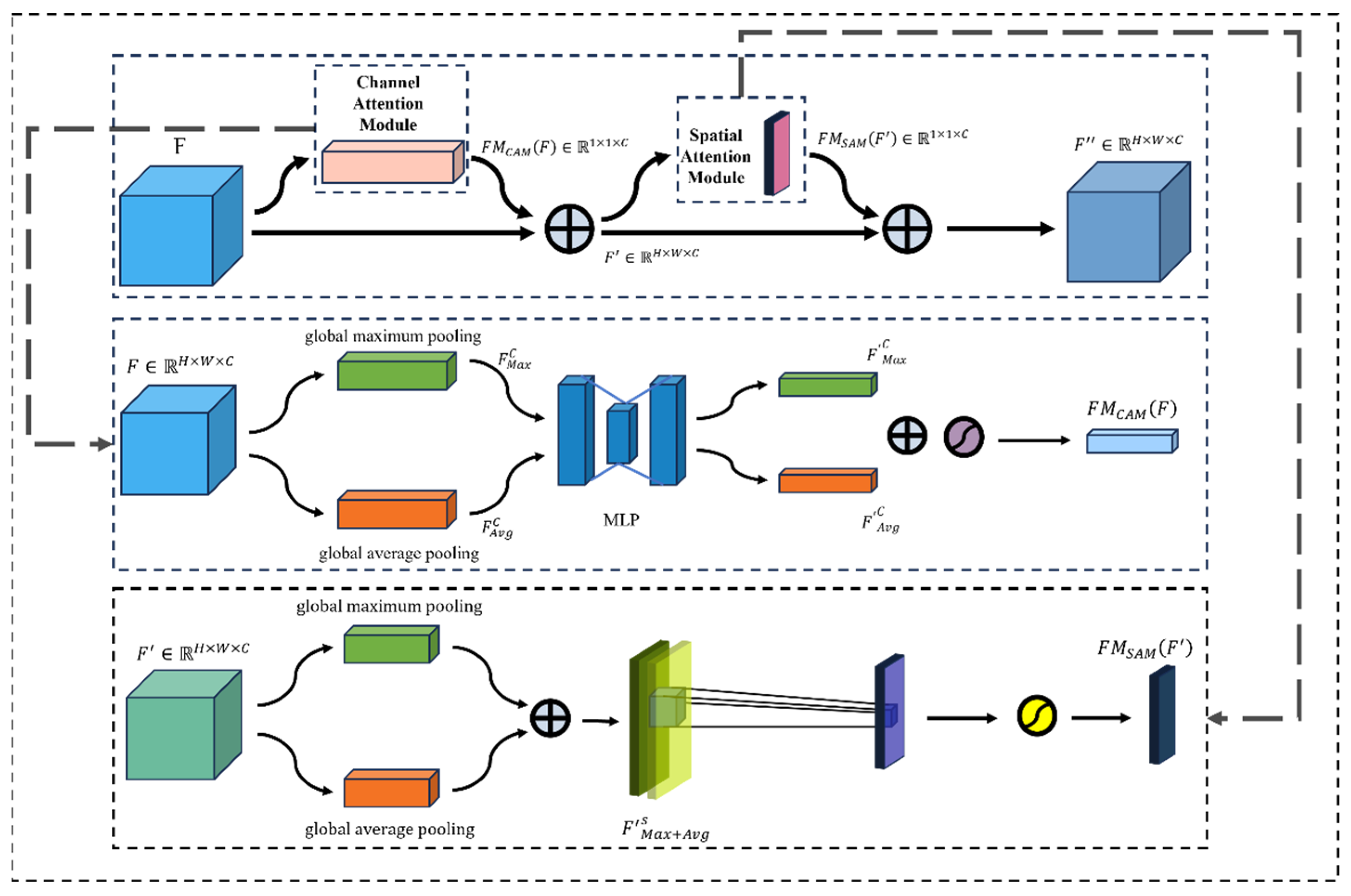
2.4.3. Enhanced Neck with CBAM Module
2.4.4. Enhanced Head with DIoU-NMS Loss Function
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Experimental Environment Configuration and Training Parameters Setting
3.2. Evaluation Metrics of YOLOv5
3.3. Results
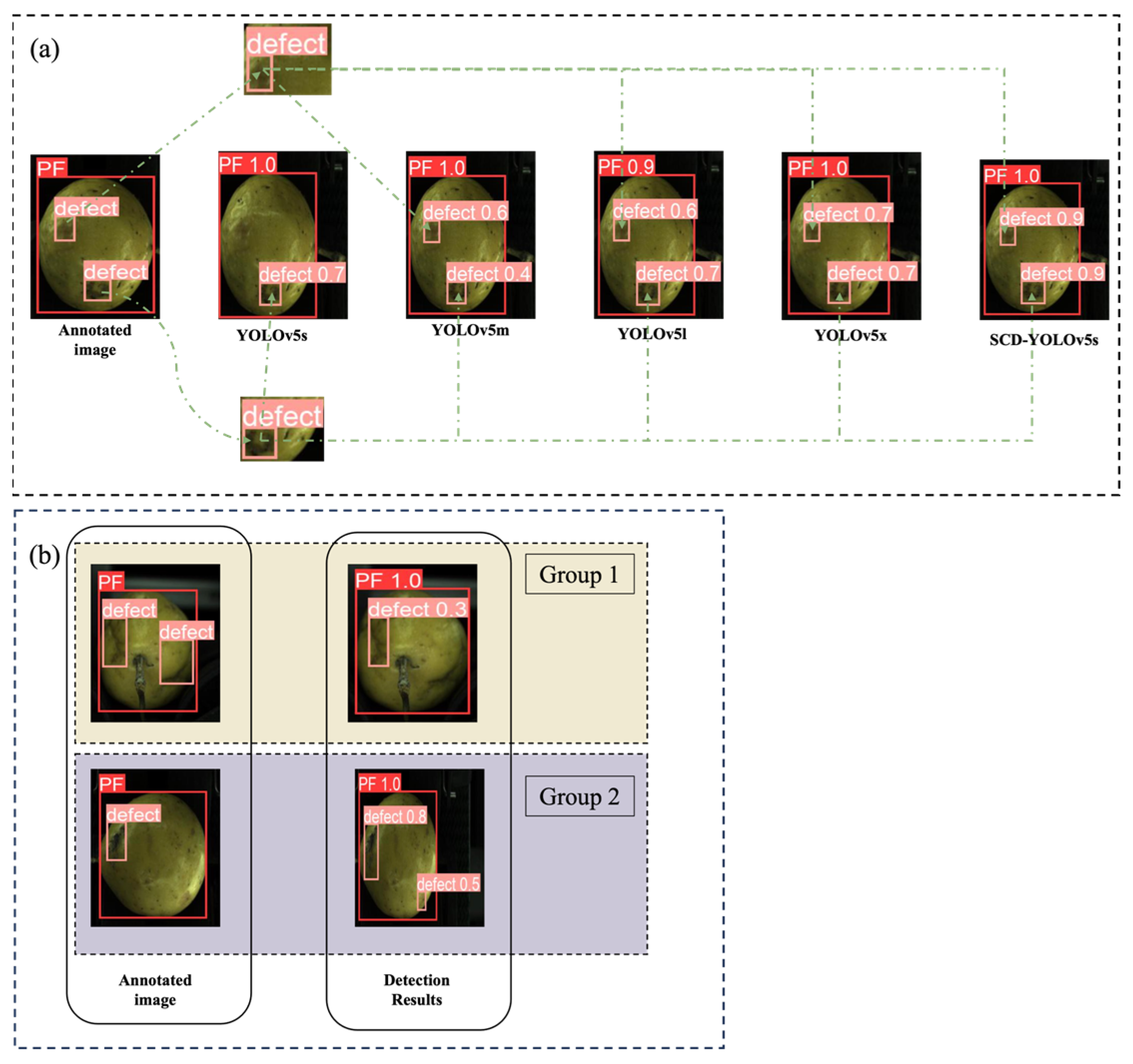
3.3.1. Comparison of Different Target Detection Models
3.3.2. Comparison of Different YOLO Network Versions
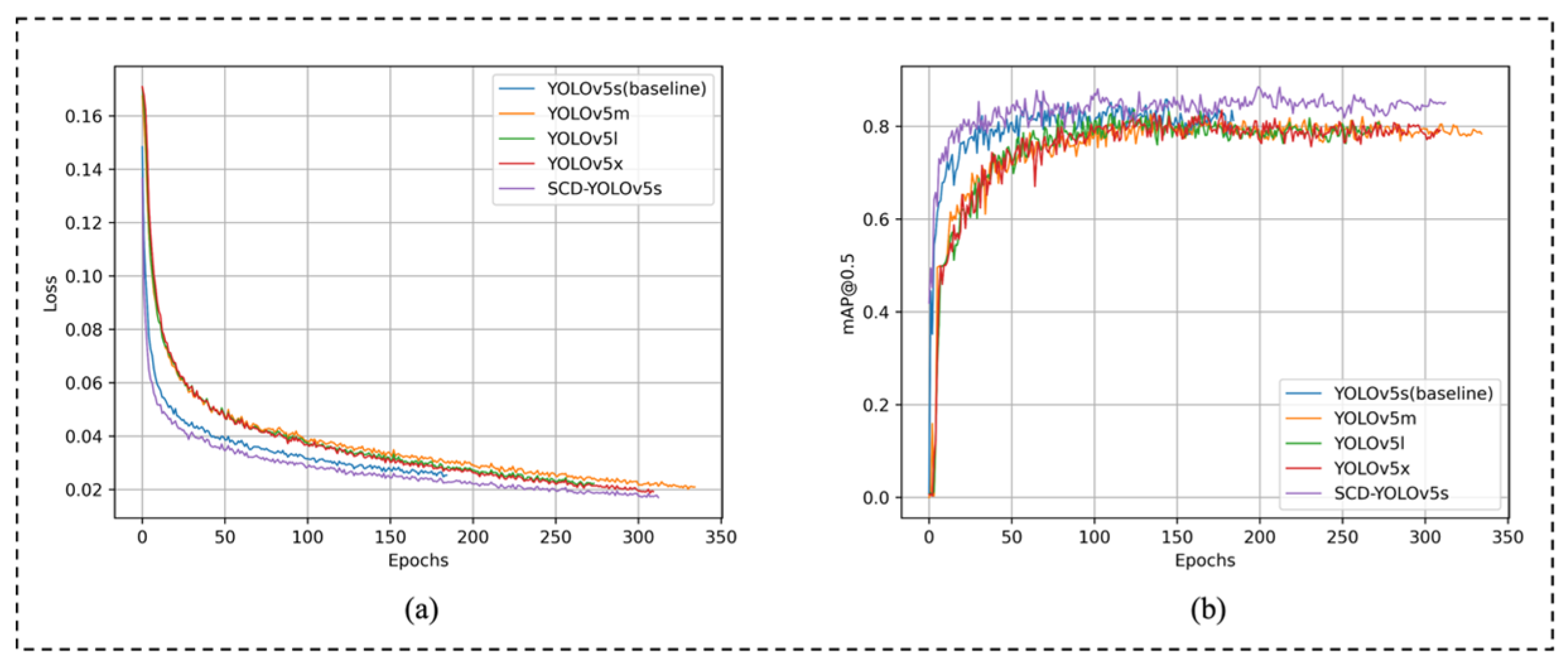
3.3.3. Comparison of Different YOLOv5 Sizes
3.3.4. Comparative Experiments of Different MODULES
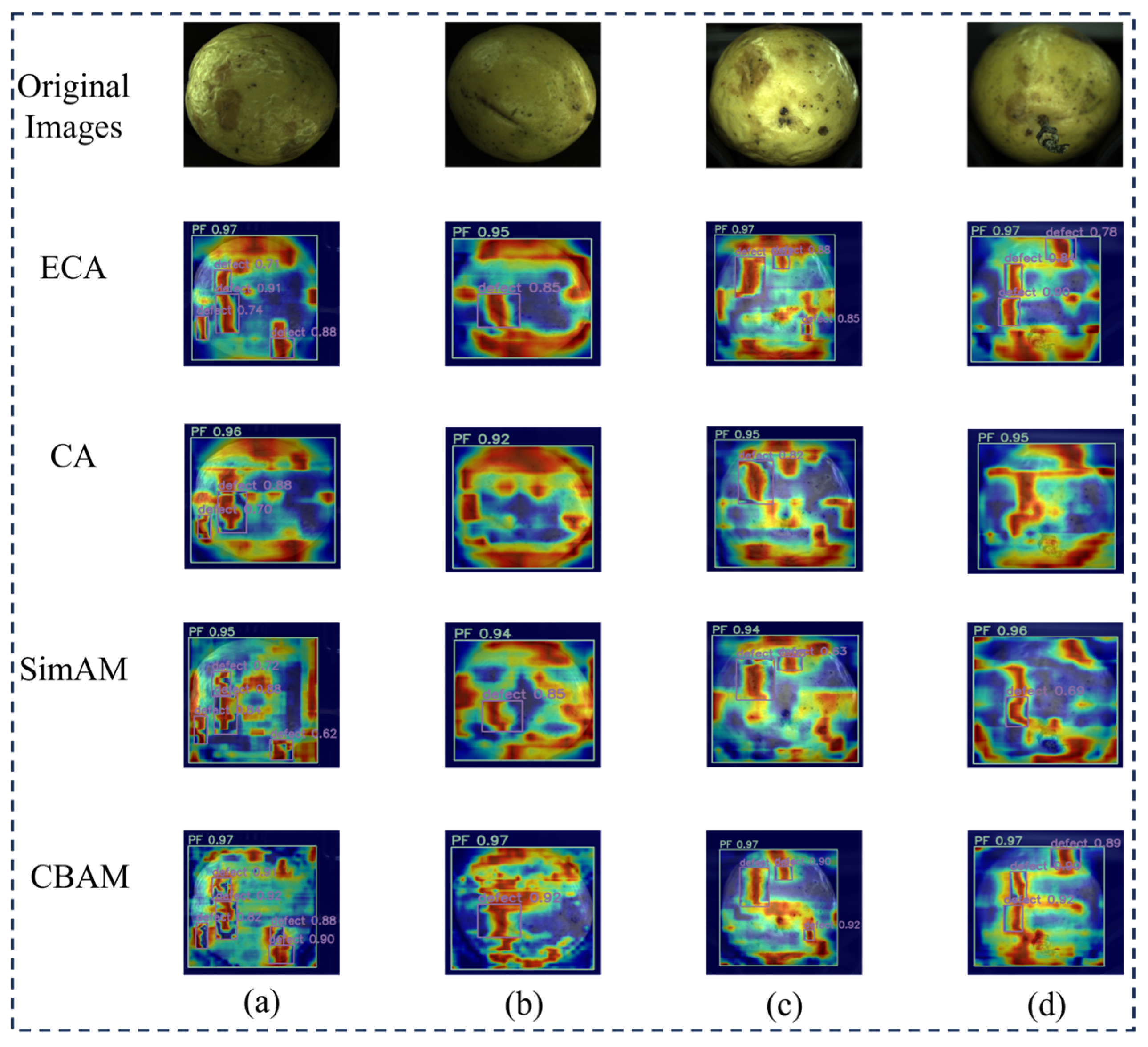
3.3.5. Comparative Experiments of Different Attention Mechanisms
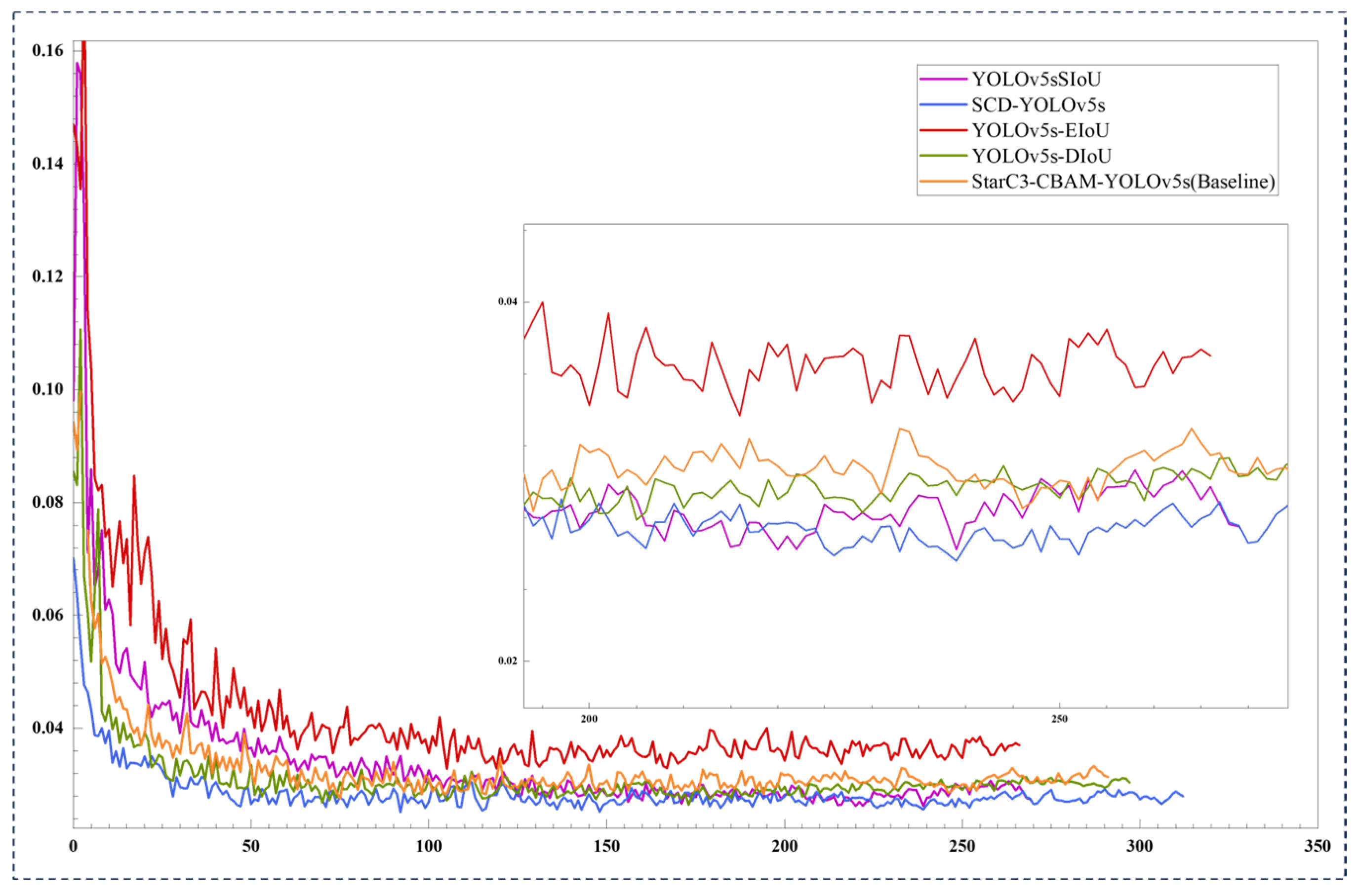
3.3.6. Comparative Experiments Using Different Bounding Box Loss Functions
3.3.7. Ablation Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| YOLOv5 | You only look once version 5 |
| SCD-YOLOv5s | StarC3SE-CBAM-DIoUNMS-YOLOv5s |
| DL | Deep learning |
| FPS | frames per second |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| ResNet | Residual Network |
| DCNN | Deep Convolutional Neural Networks |
| R-CNN | Region-based Convolutional Neural Network |
| mAP | mean Average Precision |
| CWD | Class Weight Distillation |
| M | Million |
| ELAN | Encoder-Label-Decoder Attention Network |
| CAA | Context Anchor Attention |
| DIoU | Distance-IoU |
| NMS | Non-maximum suppression |
| PF | Passion fruit |
| SENet | Squeeze-and-Excitation Network |
| FM | Feature map |
| CBAM | Convolutional Block Attention Module |
| CAM | Channel Attention Module |
| SAM | Spatial Attention Module |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| CIoU | Complete-IoU |
| EIoU | Expected-IoU |
| WIoU | Wise-IoU |
| SIoU | Soft-IoU |
| GLOPs | Giga Floating-point Operations Per Second |
| DSConv | Dynamic Snake Convolution |
| SAConv | Switchable Atrous Convolution |
| SPDConv | Spatial Pyramid Dilated Convolution |
| CA | Coordinate Attention |
| ECA | Efficient Channel Attention |
References
- Corrêa, R.C.G.; Peralta, R.M.; Haminiuk, C.W.I.; Maciel, G.M.; Bracht, A.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. The Past Decade Findings Related with Nutritional Composition, Bioactive Molecules and Biotechnological Applications of Passiflora Spp. (Passion Fruit). Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.d.A.E.; Milenkovic, D.; Borges, T.K.; Oliveira, L.d.L.d.; Costa, A.M. Brazilian Passion Fruit as a New Healthy Food: From Its Composition to Health Properties and Mechanisms of Action. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11106–11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.M.; Geraldi, M.V.; Junior, M.R.M.; Silvestre, A.J.; Rocha, S.M. Purple Passion Fruit (Passiflora Edulis f. Edulis): A Comprehensive Review on the Nutritional Value, Phytochemical Profile and Associated Health Effects. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, S.; Morinaga, M.; Tsukamoto-Sen, S.; Mori, S.; Matsui, Y.; Kawama, T. Constituent Characteristics and Functional Properties of Passion Fruit Seed Extract. Life 2022, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebet, D.; Savini, I.; Rimberia, F.K. Passion Fruits Resilience to Global Warming and Climate Change. In Cultivation for Climate Change Resilience, Volume 1; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 146–162. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, P.-H.; Huang, J.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Namisy, A.; Chen, C.Y.; Chung, W.-H. Diversity and Characteristics of Fusarium solani Species Complex (FSSC) Isolates Causing Collar Rot and Fruit Rot of Passion Fruit in Taiwan. Plant Dis. 2024, 109, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.K.S.; de Jesus, O.N.; Soares, T.L.; de Oliveira, S.A.S.; Haddad, F.; Girardi, E.A. Water Deficit Increases the Susceptibility of Yellow Passion Fruit Seedlings to Fusarium Wilt in Controlled Conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaruma, N.D.; Schmidt, F.L.; Duarte, M.C.T.; Figueira, G.M.; Delarmelina, C.; Benato, E.A.; Sartoratto, A. Control of Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides (Penz.) Sacc. in Yellow Passion Fruit Using Cymbopogon Citratus Essential Oil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Gupta, A.; Prusty, M.R.; Kumar, M. Elicitation of Fruit Fungi Infection and Its Protective Response to Improve the Postharvest Quality of Fruits. Stresses 2023, 3, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, Z.C.; dos Anjos Cruz, J.M.; Corrêa, R.F.; Sanches, E.A.; Campelo, P.H.; de Araújo Bezerra, J. Passion Fruit (Passiflora Spp.) Pulp: A Review on Bioactive Properties, Health Benefits and Technological Potential. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.P.; Peixoto, J.R.; Blum, L.E.B.; Pires, M.d.C. Standard Area Diagram Set for Scab Evaluation in Fruits of Sour Passion Fruit. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero, S.; Lee, W.S.; Aleixos, N.; Albert, F.; Blasco, J. Automated Systems Based on Machine Vision for Inspecting Citrus Fruits from the Field to Postharvest—A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ran, F.; Long, Y.; Mo, F.; Shu, R.; Yin, X. Evidences of Colletotrichum Fructicola Causing Anthracnose on Passiflora edulis Sims in China. Pathogens 2021, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Chen, D.; Liu, C.; He, J. Non-Destructive Detection of Golden Passion Fruit Quality Based on Dielectric Characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riascos, D.; Quiroga, I.; Gómez, R.; Hoyos-Carvajal, L. Cladosporium: Causal Agent of Scab in Purple Passion Fruit or Gulupa (Passiflora edulis Sims.). Agric. Sci. 2012, 3, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Long, X. Passion Fruit Plants Alter the Soil Microbial Community with Continuous Cropping and Improve Plant Disease Resistance by Recruiting Beneficial Microorganisms. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henila, M.; Chithra, P. Segmentation Using Fuzzy Cluster-based Thresholding Method for Apple Fruit Sorting. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 4178–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siridhara, A.L.; Manikanta, K.V.; Yadav, D.; Varun, P.; Saragada, J. Defect Detection in Fruits and Vegetables Using K Means Segmentation and Otsu’s Thresholding. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Networking and Communications (ICNWC), Chennai, India, 5–6 April 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chithra, P.; Henila, M. Apple Fruit Sorting Using Novel Thresholding and Area Calculation Algorithms. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, U.; Nagaveni, V. TomSevNet: A Hybrid CNN Model for Accurate Tomato Disease Identification with Severity Level Assessment. Neural Comput. Applic 2024, 36, 5165–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ge, X.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Kong, M.; Guo, Y.; Lv, C. Passion Fruit Disease Detection Using Sparse Parallel Attention Mechanism and Optical Sensing. Agriculture 2025, 15, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, R.; Santhi, B.; Manikandan, R.; Rahimi, M.; Gandomi, A.H. Computer Vision System for Mango Fruit Defect Detection Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Foods 2022, 11, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ni, X.; Liu, Y. Green Plums Surface Defect Detection Based on Deep Learning Methods. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 100397–100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Defect Classification of Green Plums Based on Deep Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, Q.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, W. On Line Detection of Defective Apples Using Computer Vision System Combined with Deep Learning Methods. J. Food Eng. 2020, 286, 110102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, A.Z.; Figueroa, H.E.; Fracarolli, J.A. Computer Vision Based Detection of External Defects on Tomatoes Using Deep Learning. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 190, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Alam, M.; Saugat, S.; Santosh, D.; Sarkar, M.I.; Al-Absi, A.A. Apple Defect Detection Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of International Conference on Smart Computing and Cyber Security; Pattnaik, P.K., Sain, M., Al-Absi, A.A., Kumar, P., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 149, pp. 215–223. ISBN 978-981-15-7989-9. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Huang, K.; Wei, S.; Yang, D. Extraction and Modeling of Carrot Crack for Crack Removal with a 3D Vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.H.; Kim, E.; Doan, T.N.N.; Han, D.; Yoo, S.J.; Kwak, J.T. Region-Aggregated Attention CNN for Disease Detection in Fruit Images. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Niu, T.; He, D. Tomato Young Fruits Detection Method under near Color Background Based on Improved Faster R-CNN with Attention Mechanism. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Lin, W.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xie, Z. ATC-YOLOv5: Fruit Appearance Quality Classification Algorithm Based on the Improved YOLOv5 Model for Passion Fruits. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, W.; Lan, Y.; Qiu, X.; Huang, J.; Luo, H. Design of Citrus Peel Defect and Fruit Morphology Detection Method Based on Machine Vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, H.; Yang, J.; Li, X. A Real-Time Detection Algorithm for Kiwifruit Defects Based on YOLOv5. Electronics 2021, 10, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Yao, Z.; Huang, Q.; Tang, K.; Jiang, D.; Yang, Z. A Fluorescence Detection Method for Postharvest Tomato Epidermal Defects Based on Improved YOLOv5m. J. Sci. Food Agric 2024, 104, 6615–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obsie, E.Y.; Qu, H.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Annis, S.; Drummond, F. Yolov5s-CA: An Improved Yolov5 Based on the Attention Mechanism for Mummy Berry Disease Detection. Agriculture 2022, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hua, J.; Xia, L.; Lu, F.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y.; Su, D. A Defect Detection Method for Akidzuki Pears Based on Computer Vision and Deep Learning. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 218, 113157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gao, S.; Xia, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, R.; Gao, J.; Zhu, W. Detection of Cigar Defect Based on the Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 4th International Conference on Software Engineering and Artificial Intelligence (SEAI), Xiamen, China, 21–23 June 2024; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, J.; Jalil, H.; Wang, H. A Fast and Lightweight Detection Algorithm for Passion Fruit Pests Based on Improved YOLOv5. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lin, F.; Lu, C.; Zhuang, J.; Su, H.; Zhang, D.; He, J. YOLOv8-MDN-Tiny: A Lightweight Model for Multi-Scale Disease Detection of Postharvest Golden Passion Fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 219, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Yilihamu, Y.; Ye, Y. Apple Surface Defect Detection Based on Lightweight Improved YOLOv5s. IJICT 2024, 24, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Kang, G.; Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Zeng, F.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, R.; Yue, X. Real-Time Lightweight Detection of Lychee Diseases with Enhanced YOLOv7 and Edge Computing. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yasenjiang, M. Defect Apple Detection Method Based on Lightweight YOLOv8. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering (CISCE), Guangzhou, China, 10–12 May 2024; pp. 1193–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Su, J. Research on Kiwi Surface Defect Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv7-Tiny. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering (CISCE), Guangzhou, China, 10–12 May 2024; pp. 1022–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Fu, R. Lightweight Yolov5s-Super Algorithm for Multi-Defect Detection in Apples. Eng. Agríc. 2024, 44, e20230175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Yin, C.; Xia, Y.; Fu, M.; Fu, W. Dragon Fruit Detection in Natural Orchard Environment by Integrating Lightweight Network and Attention Mechanism. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1040923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Lin, H.; Shi, X.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, B. MTS-YOLO: A Multi-Task Lightweight and Efficient Model for Tomato Fruit Bunch Maturity and Stem Detection. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekharamantry, P.K.; Melgani, F.; Malacarne, J. Deep Learning-Based Apple Detection with Attention Module and Improved Loss Function in YOLO. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, M.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. MTD-YOLO: Multi-Task Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Cherry Tomato Fruit Bunch Maturity Detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 216, 108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Mo, D.; Tian, X.; Tian, X. GSE-YOLO: A Lightweight and High-Precision Model for Identifying the Ripeness of Pitaya (Dragon Fruit) Based on the YOLOv8n Improvement. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; He, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G. Dynamic Snake Convolution Based on Topological Geometric Constraints for Tubular Structure Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 6070–6079. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, S.; Chen, L.-C.; Yuille, A. Detectors: Detecting Objects with Recursive Feature Pyramid and Switchable Atrous Convolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10213–10224. [Google Scholar]
- Sunkara, R.; Luo, T. No More Strided Convolutions or Pooling: A New CNN Building Block for Low-Resolution Images and Small Objects. In Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases; Amini, M.-R., Canu, S., Fischer, A., Guns, T., Kralj Novak, P., Tsoumakas, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 13715, pp. 443–459. ISBN 978-3-031-26408-5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.-Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. Simam: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and Efficient IOU Loss for Accurate Bounding Box Regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding Box Regression Loss with Dynamic Focusing Mechanism 2023. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar]
- Gevorgyan, Z. SIoU Loss: More Powerful Learning for Bounding Box Regression 2022. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12740. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Hu, T.; He, Q.; Chen, Z.S.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Fang, C.; Luo, J.; Fu, L. Nondestructive 3D Phenotyping Method of Passion Fruit Based on X-Ray Micro-Computed Tomography and Deep Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1087904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Lin, G. Research and Explainable Analysis of a Real-Time Passion Fruit Detection Model Based on FSOne-YOLOv7. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.; Hong, C.J.; Kuan, L.M.; Pauzi, M.M.; Sumari, P.; Abualigah, L.; Zitar, R.A.; Oliva, D. Markisa/Passion Fruit Image Classification Based Improved Deep Learning Approach Using Transfer Learning. In Classification Applications with Deep Learning and Machine Learning Technologies; Abualigah, L., Ed.; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 1071, pp. 143–189. ISBN 978-3-031-17575-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sidehabi, S.W.; Suyuti, A.; Areni, I.S.; Nurtanio, I. Classification on Passion Fruit’s Ripeness Using K-Means Clustering and Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communications Technology (ICOIACT), Online, 6–7 March 2018; pp. 304–309. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, S.; Pang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhuang, N.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, C.; Wan, H.; Xue, Y. Passion Fruit Detection and Counting Based on Multiple Scale Faster R-CNN Using RGB-D Images. Precis. Agric 2020, 21, 1072–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, P.; He, C.; Song, Q.; Chen, J.; Kong, X.; Luo, Z. A Lightweight and High-Precision Passion Fruit YOLO Detection Model for Deployment in Embedded Devices. Sensors 2024, 24, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


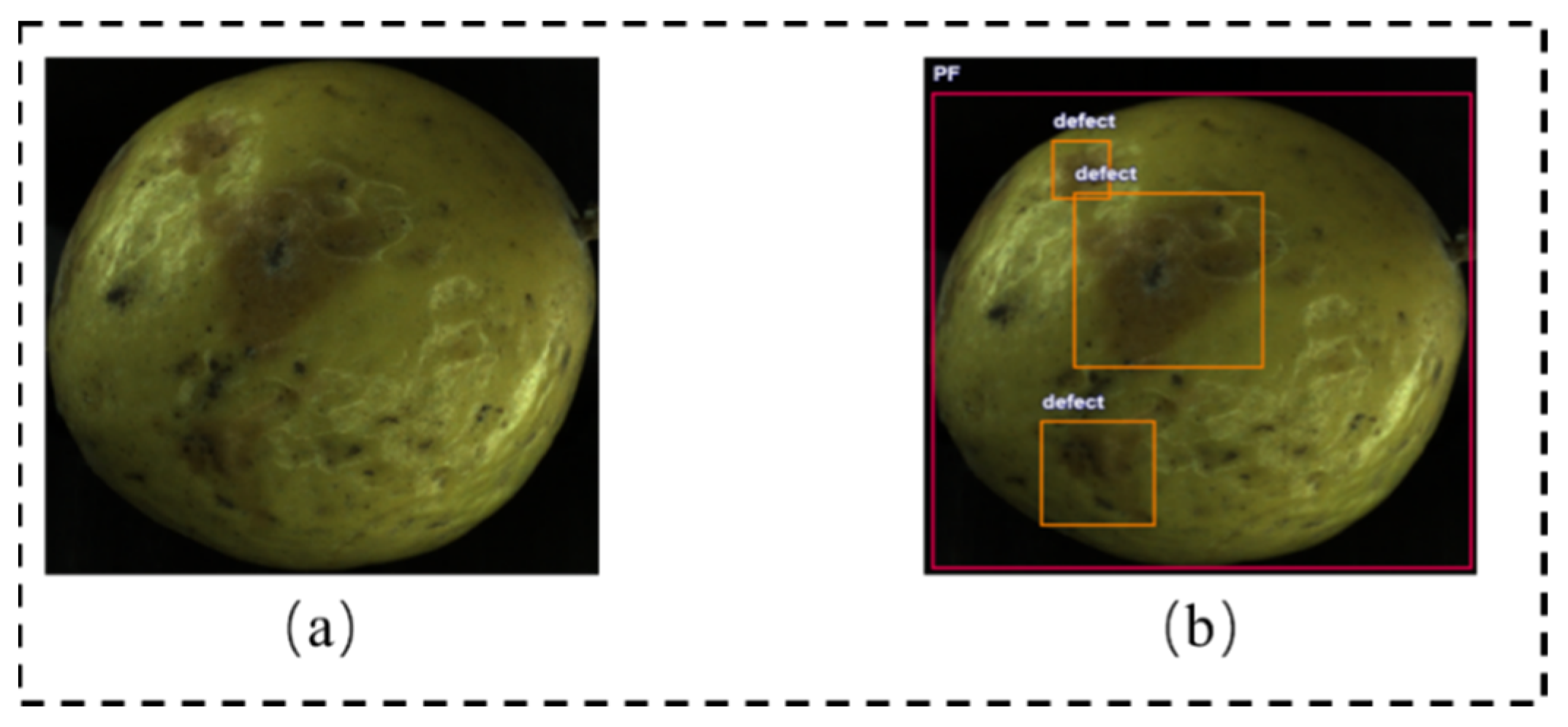



| Method | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Flipping | Horizon, vertical |
| Scaling | 0–16% |
| Rotation | 0–30° |
| Brightness | −21–+21% |
| Exposure | −11–+11% |
| Cropping | 0–10° |
| Name | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Random Access Memory | 30 GB |
| CPU | 7 vCPU Intel (R) Xeon (R) CPU E5-2680 v4 @ 2.40 GHz |
| Graphics Card | 2 (20 GB) |
| System | ubuntu20.04 |
| Pytorch Version | 1.10.0 |
| Cuda Version | 11.3 |
| Training Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Image size | 640 × 640 |
| Epochs | 400 |
| Batch-size | 16 |
| Initial learning rate | 0.01 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Models | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | GLOPs | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-CNN | 55.6 | 60.45 | 66.56 | 80.2 | 224.3 |
| Fast-RCNN | 59.8 | 58.7 | 70.12 | 52.3 | 125.7 |
| Faster-RCNN | 64.0 | 68.75 | 75.67 | 40.6 | 108.2 |
| Mask-RCNN | 60.5 | 72.12 | 73.88 | 70.2 | 187.5 |
| SCD-YOLOv5s | 95.9 | 84.7 | 88.4 | 14.3 | 12.6 |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.95 (%) | (%) | Parameters | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv7tiny | 83.3 | 77.9 | 81.6 | 64.62 | 80.0 | 6,017,694 | 12.3 |
| YOLOv7 | 85.5 | 77.9 | 80.4 | 64.84 | 81.0 | 37,201,950 | 74.8 |
| YOLOv7x | 85.8 | 80.9 | 84.2 | 64.87 | 78.0 | 70,821,830 | 142.1 |
| YOLOv8n | 80.3 | 76.7 | 79.4 | 66.59 | 79.0 | 3,011,238 | 6.3 |
| YOLOv8s | 88.4 | 71.2 | 79.3 | 66.63 | 78.0 | 11,136,374 | 22.5 |
| YOLO11s | 86.7 | 78.9 | 83.7 | 69.9 | 82.0 | 9,428,566 | 19.2 |
| SCD-YOLOv5s (Ours) | 95.9 | 84.7 | 88.4 | 71.2 | 93.0 | 6,408,833 | 12.6 |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.95 (%) | (%) | Parameters | Model Size (MB) | FPS ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 82.7 | 83.1 | 81.7 | 65.7 | 76.0 | 7,025,023 | 13.8 | 24.45 |
| YOLOv5m | 83.3 | 77.8 | 80.7 | 68.2 | 81.0 | 20,875,359 | 40.3 | 25.7 |
| YOLOv5l | 83.3 | 74.5 | 81.0 | 67.1 | 82.0 | 46,563,709 | 88.6 | 25.97 |
| YOLOv5x | 87.9 | 76.6 | 78.7 | 61.9 | 82.0 | 46,563,709 | 165.0 | 17.92 |
| SCD-YOLOv5s(Ours) | 95.9 | 84.7 | 88.4 | 71.2 | 93.0 | 6,408,833 | 12.6 | 26.66 |
| Index | Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.95 (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | YOLOv5s | 82.7 | 83.1 | 81.7 | 65.7 | 76.0 |
| 2 | YOLOv5s + DSConv [54] | 81.7 | 78.1 | 79.8 | 64.9 | 82.0 |
| 3 | YOLOv5s + SAConv [55] | 77.9 | 76.3 | 78.6 | 67.1 | 83.0 |
| 4 | YOLOv5s + SPDConv [56] | 82.6 | 78.8 | 79.7 | 68.5 | 81.0 |
| 5 | YOLOv5s + StarC3SE | 92.0 | 78.9 | 83.2 | 68.8 | 83.0 |
| Index | StarC3-YOLOv5s | ECA | SimAM | CA | CBAM | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.95 (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✔ | 92.0 | 78.9 | 83.2 | 68.8 | 83.0 | ||||
| 2 | ✔ | ✔ | 87.3 | 78.9 | 72.1 | 66.0 | 83.0 | |||
| 3 | ✔ | ✔ | 85.7 | 77.4 | 77.0 | 61.2 | 84.0 | |||
| 4 | ✔ | ✔ | 80.4 | 82.7 | 82.5 | 66.6 | 82.0 | |||
| 5 | ✔ | ✔ | 94.2 | 80.5 | 85.5 | 68.5 | 85.0 |
| Index | StarC3-CBAM-CIoU-YOLOv5s | EIoU | WIoU | SIoU | DIoU | DIoU-NMS | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.95 (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✔ | 94.2 | 80.5 | 85.5 | 68.5 | 85.0 | |||||
| 2 | ✔ | ✔ | 82.2 | 74.3 | 82.3 | 66.7 | 81.0 | ||||
| 3 | ✔ | ✔ | 68.3 | 44.6 | 25.2 | 66.8 | 26.0 | ||||
| 4 | ✔ | ✔ | 82.6 | 76.6 | 79.4 | 66.0 | 80.0 | ||||
| 5 | ✔ | ✔ | 94.2 | 78.5 | 81.7 | 64.7 | 86.0 | ||||
| 6 | ✔ | ✔ | 95.9 | 84.7 | 88.4 | 71.2 | 93.0 |
| Index | YOLOv5s | StarC3SE | DIoU-NMS | CBAM | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.95 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✔ | 82.7 | 83.1 | 81.7 | 65.7 | 76.0 | |||
| 2 | ✔ | ✔ | 92.0 | 78.9 | 83.2 | 68.8 | 83.0 | ||
| 4 | ✔ | ✔ | 86.6 | 77.9 | 81.1 | 64.8 | 79.0 | ||
| 5 | ✔ | ✔ | 89.4 | 78.7 | 85.1 | 68.6 | 83.0 | ||
| 6 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 89.1 | 79.9 | 84.8 | 67.7 | 84.0 | |
| 7 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 94.2 | 80.5 | 85.5 | 68.5 | 85.0 | |
| 8 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 87.3 | 75.7 | 82.8 | 68.0 | 81.0 | |
| 9 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 95.9 | 84.7 | 88.4 | 71.2 | 93.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Xue, S.; Wu, M.; Zhu, T.; Ni, C. Lightweight SCD-YOLOv5s: The Detection of Small Defects on Passion Fruit with Improved YOLOv5s. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101111
Zhou Y, Li Z, Xue S, Wu M, Zhu T, Ni C. Lightweight SCD-YOLOv5s: The Detection of Small Defects on Passion Fruit with Improved YOLOv5s. Agriculture. 2025; 15(10):1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101111
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yu, Zhenye Li, Sheng Xue, Min Wu, Tingting Zhu, and Chao Ni. 2025. "Lightweight SCD-YOLOv5s: The Detection of Small Defects on Passion Fruit with Improved YOLOv5s" Agriculture 15, no. 10: 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101111
APA StyleZhou, Y., Li, Z., Xue, S., Wu, M., Zhu, T., & Ni, C. (2025). Lightweight SCD-YOLOv5s: The Detection of Small Defects on Passion Fruit with Improved YOLOv5s. Agriculture, 15(10), 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101111





