Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Reveals Candidate Genes and Regulatory Pathways Shaping Duck Meat Color
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
2.3. Transcriptome Analysis of Pectoral Muscle Tissue
2.4. Metabolome Analysis of Pectoral Muscle Tissue
2.5. Comprehensive Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptions of Duck Meat Color
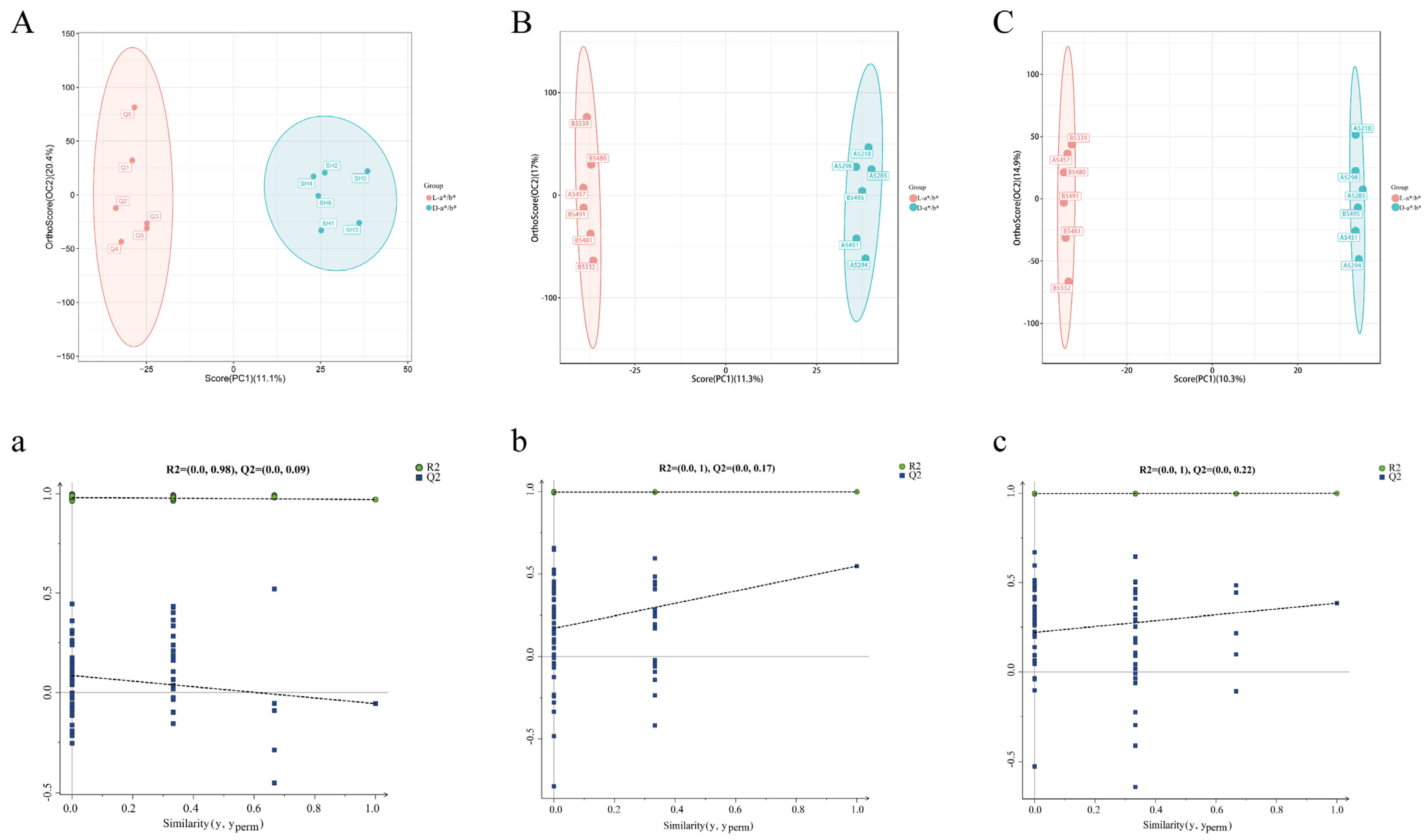
3.2. Overview of Transcriptome and Metabolome Dataset
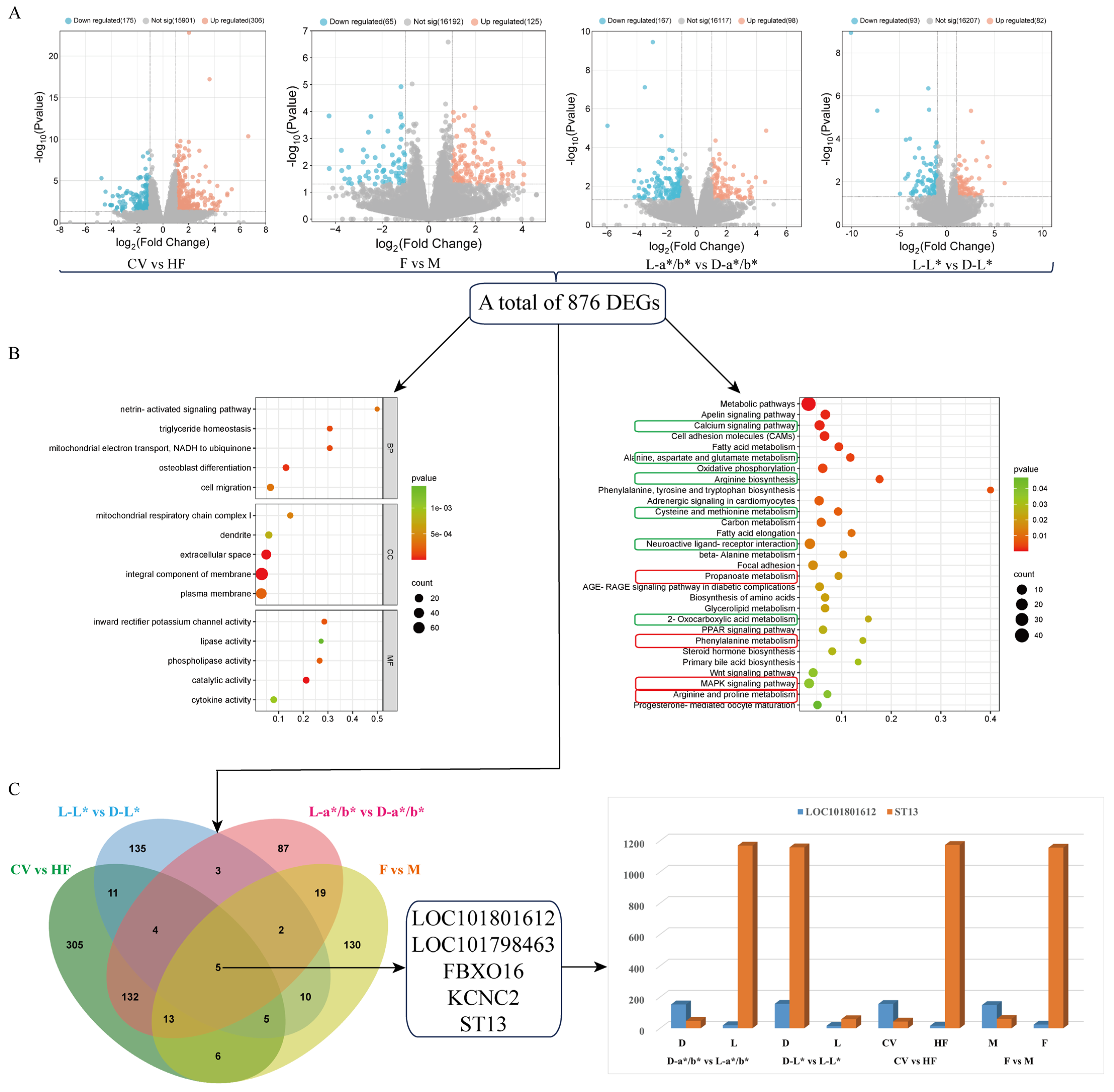
3.3. Comparative Analysis Based on the Pectoral Muscle Transcriptome
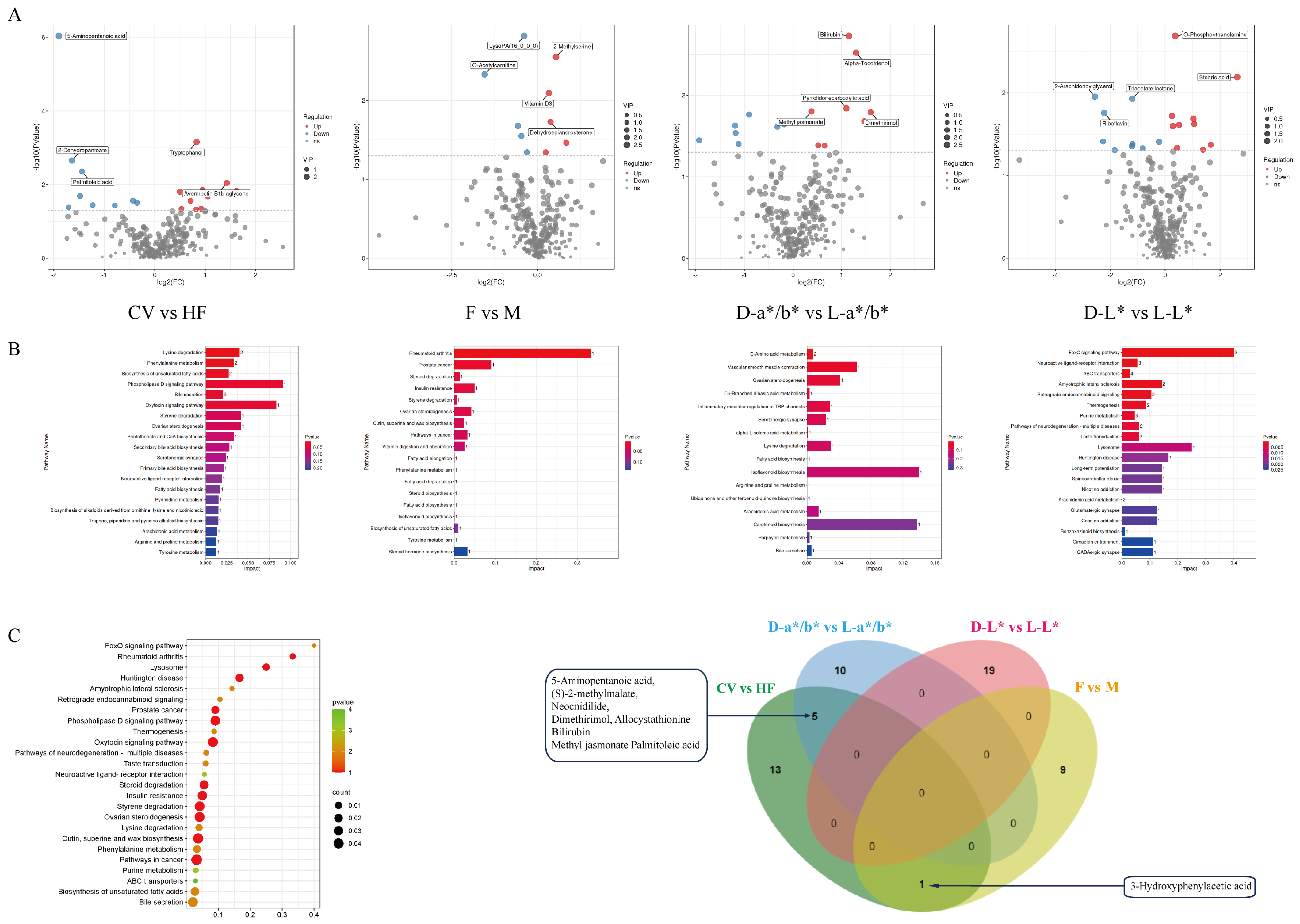
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Pectoral Muscle Metabolism
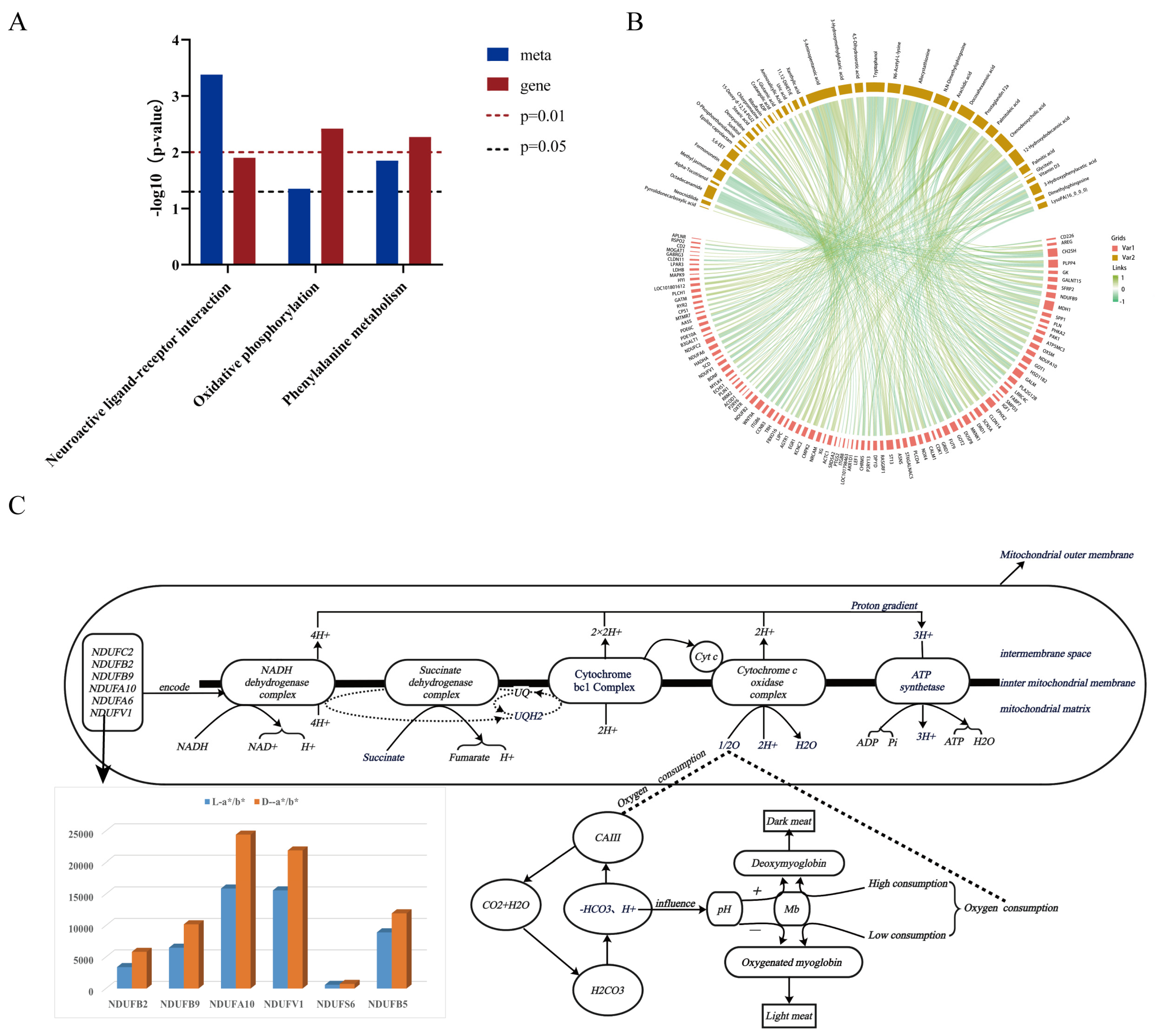
3.5. Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, X.; Chen, J. A Review of Hyperspectral Imaging for Chicken Meat Safety and Quality Evaluation: Application, Hardware, and Software. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri-Garavand, A.; Fatahi, S.; Omid, M.; Makino, Y. Meat quality evaluation based on computer vision technique: A review. Meat Sci. 2019, 156, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, R.; Kiyimba, F.; Suman, S.P.; Mafi, G.G. The potential of metabolomics in meat science: Current applications, trends, and challenges. J. Proteom. 2023, 283–284, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, R.A.; Hunt, M.C. Current research in meat color. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Hur, S.J.; Yang, H.S.; Moon, S.H.; Hwang, Y.H.; Park, G.B.; Joo, S.T. Discoloration characteristics of 3 major muscles from cattle during cold storage. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C1–C5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, R. Muscle fiber characteristics and apoptotic factor differences in beef Longissimus lumborum and Psoas major during early postmortem. Meat Sci. 2023, 198, 109092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Mitacek, R.M.; Abraham, A.; Mafi, G.G.; VanOverbeke, D.L.; DeSilva, U.; Ramanathan, R. Effects of Muscle-Specific Oxidative Stress on Cytochrome c Release and Oxidation-Reduction Potential Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7749–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wu, W.; Tian, X.; Jia, F.; Xu, L.; Dai, R.; Li, X. Comparative proteomics to reveal muscle-specific beef color stability of Holstein cattle during post-mortem storage. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Tian, X.; Shao, L.; Xu, L.; Dai, R.; Li, X. Label-free proteomic strategy to compare the proteome differences between longissimus lumborum and psoas major muscles during early postmortem periods. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.C.d.S.; Contreras-Castillo, C.J.; Santos-Donado, P.R.d.; Venturini, A.C. New alternatives for improving and assessing the color of dark–cutting beef—A review. Sci. Agric. 2021, 79, e20200079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hou, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, B.; Han, P.; Gao, C.; Niu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, R.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study and F(ST) Analysis Reveal Four Quantitative Trait Loci and Six Candidate Genes for Meat Color in Pigs. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 768710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, J.A.; Faucitano, L.; Laforest, J.P.; Rivest, J.; Marcoux, M.; Gariépy, C. Effects of slaughter weight on carcass composition and meat quality in pigs of two different growth rates. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Hu, J.; Qi, J.; Tang, Q.; Li, J.; Bai, L.; Tang, B.; Ouyang, Q.; Wu, T.; He, H.; et al. Research Note: Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals potential candidate genes and regulatory pathways associated with egg weight in ducks. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, C.; Liu, K.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Hou, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, R.; Wu, W. Combining genome-wide association study based on low-coverage whole genome sequencing and transcriptome analysis to reveal the key candidate genes affecting meat color in pigs. Anim. Genet. 2023, 54, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Panicker, D.; Wang, Q.; Kim, M.J.; Liu, J.; Yin, J.L.; Wong, L.; Jang, I.C.; Chua, N.H.; Sarojam, R. Next generation sequencing unravels the biosynthetic ability of spearmint (Mentha spicata) peltate glandular trichomes through comparative transcriptomics. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Kim, M.J.; Dhandapani, S.; Tjhang, J.G.; Yin, J.L.; Wong, L.; Sarojam, R.; Chua, N.H.; Jang, I.C. The floral transcriptome of ylang ylang (Cananga odorata var. fruticosa) uncovers biosynthetic pathways for volatile organic compounds and a multifunctional and novel sesquiterpene synthase. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3959–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Vieira, F.G.; Linderoth, T.; Nielsen, R. ngsTools: Methods for population genetics analyses from next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1486–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Kou, D.; Li, Z.; Ma, Q.; Hu, J.; Bai, L.; et al. Transcriptome-metabolome reveals the molecular changes in meat production and quality in the hybrid populations of Sichuan white goose. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, H.; Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Qiu, M.; Song, X.; Yu, C.; Jiang, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, C.; et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals regulators mediating breast muscle growth and development in three chicken breeds. Anim. Biotechnol. 2019, 30, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelena, E.; Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Carroll, K.M.; Begley, P.; O’Hagan, S.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Wilson, I.D.; et al. Development of a robust and repeatable UPLC-MS method for the long-term metabolomic study of human serum. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, B.; Gohlke, J.; Tonino, P.; Hourani, Z.; Kolb, J.; Strom, J.; Alekhina, O.; Smith, J.E., 3rd; Ottenheijm, C.; Gregorio, C.; et al. Nebulin and Lmod2 are critical for specifying thin-filament length in skeletal muscle. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yu, M.; Yu, D.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Du, W. Identification of the Differentially Expressed Genes of Muscle Growth and Intramuscular Fat Metabolism in the Development Stage of Yellow Broilers. Genes 2020, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, A.S.; Lin, S.; Tse, A.; Thürkauf, M.; Oliveri, F.; Ruegg, M.A. Single-nuclei sequencing of skeletal muscle reveals subsynaptic-specific transcripts involved in neuromuscular junction maintenance. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, J.; Hou, C.; Bao, B.; Wang, S.; Maté Sánchez de Val, J.E.; Wenhui, W. The Molecular Interaction of Collagen with Cell Receptors for Biological Function. Polymers 2022, 14, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, L.; Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Lv, M.; Zang, F.; Dai, R. Proteomic Changes in Sarcoplasmic and Myofibrillar Proteins Associated with Color Stability of Ovine Muscle during Post-Mortem Storage. Foods 2021, 10, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, M.W.; Suman, S.P.; Zhang, X.; Nair, M.N.; Desai, M.A.; Cai, K.; Ciaramella, M.A.; Allen, P.J. Proteomic approach to characterize biochemistry of meat quality defects. Meat Sci. 2017, 132, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilaki, A.; Simpson, D.; McArdle, F.; McLean, L.; Beynon, R.J.; Van Remmen, H.; Richardson, A.G.; McArdle, A.; Faulkner, J.A.; Jackson, M.J. Formation of 3-nitrotyrosines in carbonic anhydrase III is a sensitive marker of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2007, 1, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenberg, J.B. Myoglobin-facilitated oxygen diffusion: Role of myoglobin in oxygen entry into muscle. Physiol. Rev. 1970, 50, 559–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; Hunt, M.C.; Mancini, R.A.; Nair, M.N.; Denzer, M.L.; Suman, S.P.; Mafi, G.G. Recent updates in meat color research: Integrating traditional and high-throughput approaches. Meat Muscle Biol. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas Bervejillo, M.; Ferreira, A.M. Understanding Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors: From the Structure to the Regulatory Actions on Metabolism. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1127, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Index/Group | CV | HF | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | 75.86 ± 21.87 | 62.54 ± 21.26 | 0.0908 |
| G | 51.45 ± 17.83 | 39.31 ± 13 | 0.0356 * |
| B1 | 49.91 ± 15.73 | 48.36 ± 14.57 | 0.7745 |
| H | 118.88 ± 149.75 | 126.2 ± 166.21 | 0.8967 |
| S | 36.93 ± 5.13 | 36.68 ± 4.82 | 0.888 |
| B2 | 29.78 ± 8.53 | 29.11 ± 7.67 | 0.8189 |
| L* | 41.3 ± 3.46 | 41.22 ± 2.38 | 0.938 |
| a* | 14.58 ± 2.28 | 13.35 ± 1.48 | 0.0803 |
| b* | 5.04 ± 1.63 | 3.71 ± 1.23 | 0.0138 * |
| IMF (%) | 4.46 ± 0.48 | 4.18 ± 0.52 | 0.1308 |
| Index/Group | CV-M | CV-F | HF-M | HF-F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 89.7 ± 23.51 Ab | 62.03 ± 5.9 B | 68.8 ± 26.88 a | 56.23 ± 12.43 B |
| G | 63.03 ± 18.98 B | 39.88 ± 3.85 A | 41.73 ± 16.24 A | 36.9 ± 9.21 A |
| B1 | 59.4 ± 17.77 a | 40.43 ± 2.96 b | 48.9 ± 17.18 | 47.83 ± 12.61 |
| H | 41.8 ± 62.9 | 195.95 ± 174.7 | 117.88 ± 162.86 | 134.53 ± 180.33 |
| S | 35.7 ± 5.76 | 38.15 ± 4.44 | 37.95 ± 5.27 | 35.4 ± 4.29 |
| B2 | 35.15 ± 9.2 a | 24.4 ± 2.33 b | 29.65 ± 9.64 | 28.58 ± 5.7 |
| L* | 42.54 ± 3.93 | 40.06 ± 2.58 | 40.21 ± 1.42 | 42.23 ± 2.79 |
| a* | 14.57 ± 2.48 | 14.59 ± 2.24 | 14.04 ± 1.49 | 12.65 ± 1.16 |
| b* | 5.66 ± 1.72 Ab | 4.43 ± 1.37 | 3.98 ± 1.29 a | 3.43 ± 1.19 B |
| IMF (%) | 4.44 ± 0.66 | 4.48 ± 0.25 | 4.19 ± 0.47 | 4.17 ± 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xu, M.; Han, X.; Tao, Q.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Han, B.; et al. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Reveals Candidate Genes and Regulatory Pathways Shaping Duck Meat Color. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101059
Jiang S, Yang Z, Lu Y, Zhang T, Xu M, Han X, Tao Q, Bai Y, He X, Han B, et al. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Reveals Candidate Genes and Regulatory Pathways Shaping Duck Meat Color. Agriculture. 2025; 15(10):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101059
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shuaixue, Zhao Yang, Yinjuan Lu, Tao Zhang, Mengru Xu, Xu Han, Qiuyu Tao, Yuan Bai, Xinxin He, Bo Han, and et al. 2025. "Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Reveals Candidate Genes and Regulatory Pathways Shaping Duck Meat Color" Agriculture 15, no. 10: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101059
APA StyleJiang, S., Yang, Z., Lu, Y., Zhang, T., Xu, M., Han, X., Tao, Q., Bai, Y., He, X., Han, B., Zhu, J., Li, L., Huang, A., Bai, L., Hu, J., & Liu, H. (2025). Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Reveals Candidate Genes and Regulatory Pathways Shaping Duck Meat Color. Agriculture, 15(10), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101059





