Calibration and Experimental Validation of Discrete Element Parameters for Long-Grain Rice with Different Moisture Contents Based on Repose Angle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Material and Particle Size
2.1.1. Moisture Content of Rice Grain
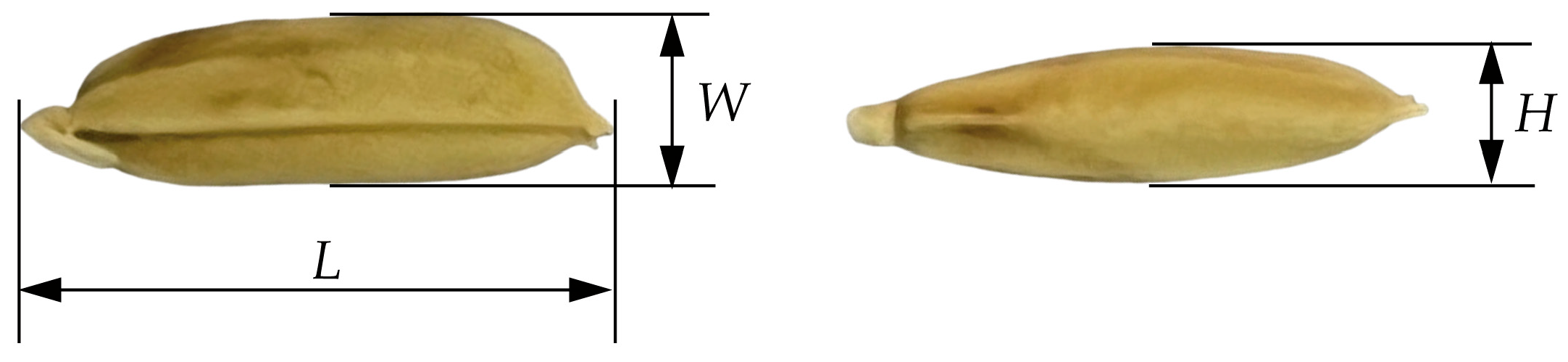
2.1.2. Rice Grain Size
2.2. DEM Modeling and Numerical Methods for Rice Grain Particles
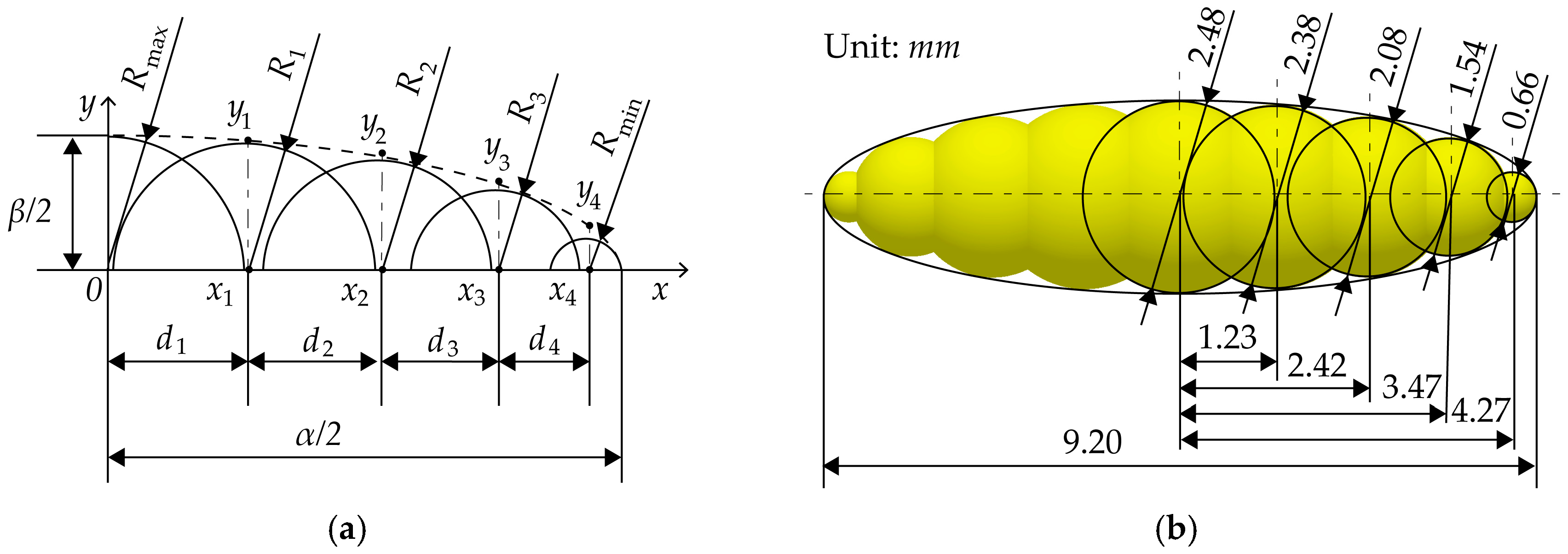
2.2.1. DEM Modeling of Rice Grain Particles
2.2.2. The Numerical Method
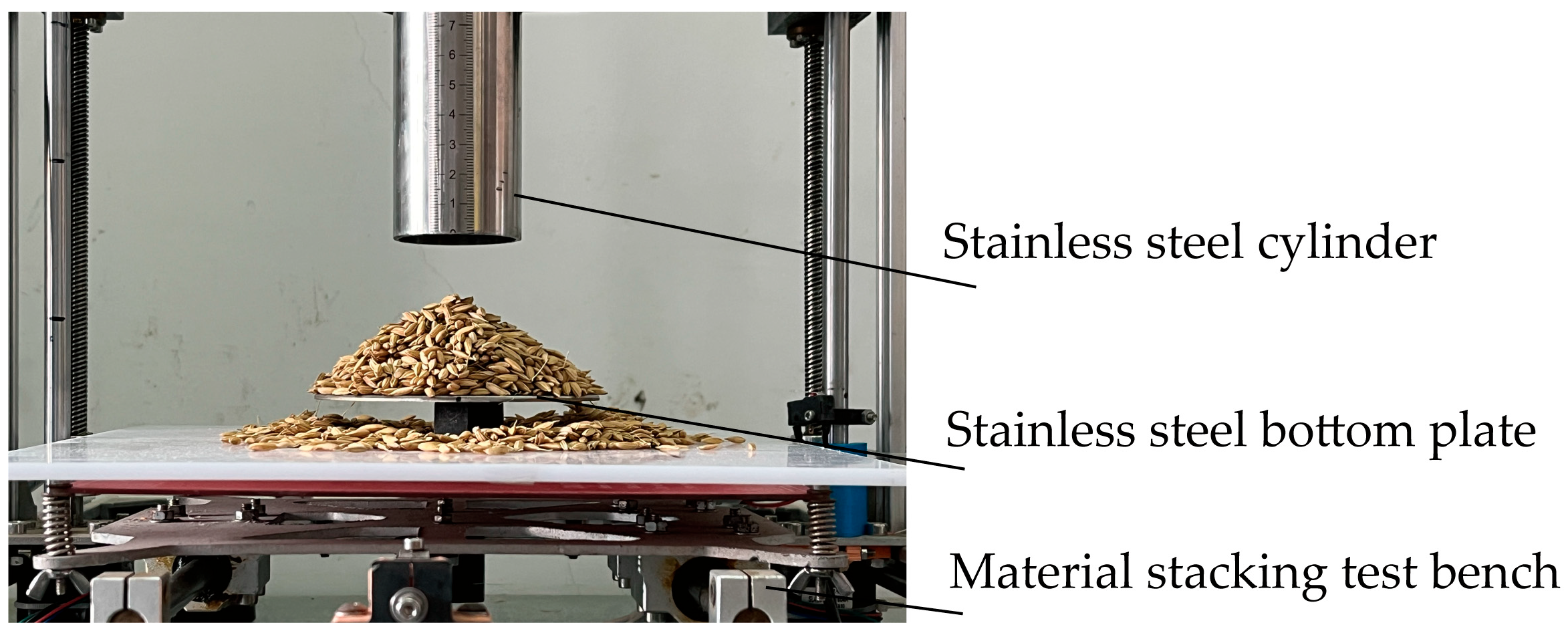
2.3. Repose Angle Test Based on Cylinder Lifting Method
2.4. Calibration Test Method for DEM Simulation Parameters of Rice Grains
2.4.1. PB Test
2.4.2. Steepest Climbing Test
2.4.3. BB Test
2.5. Validation Test
3. Results and Discussion
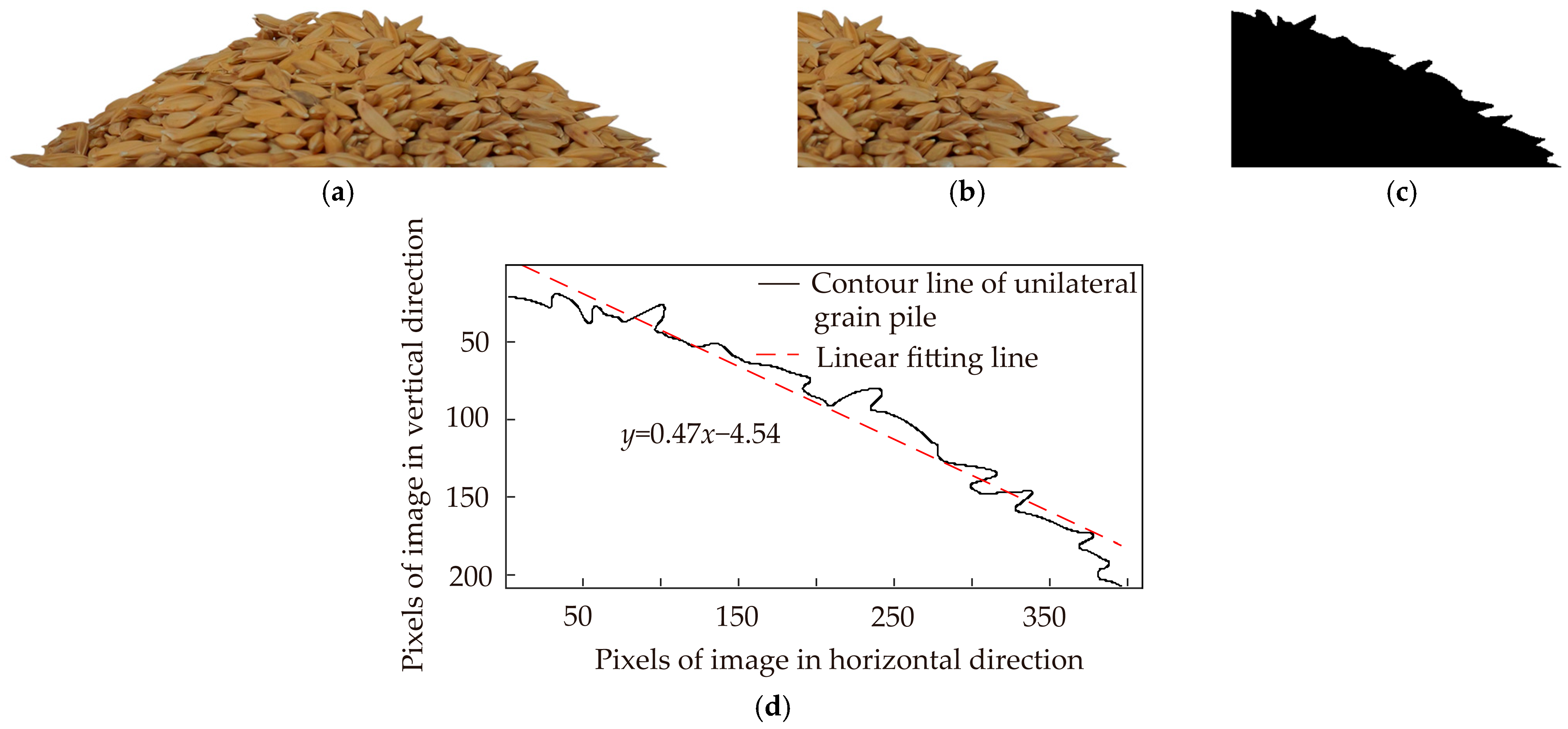
3.1. The Results and Analysis of the Repose Angle Physics Test
3.2. Discrete Element Parameter Calibration Test Results and Analysis
3.2.1. PB Test Results and Analysis
3.2.2. Steepest Climbing Test Results and Analysis
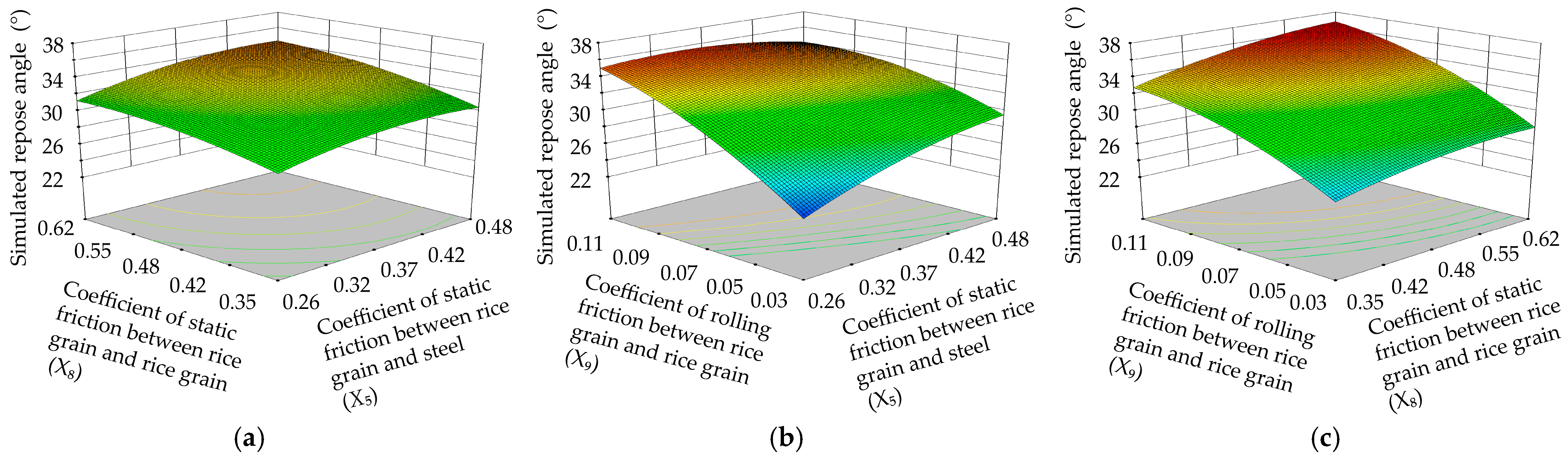
3.2.3. BB Test Results and Analysis
3.2.4. Validation of Repose Angle–Significant Discrete Element Parameter Model
3.3. Moisture Content–Significant Discrete Element Parameter Model
3.4. Validation of Moisture Content–Significant Discrete Element Parameter Model
3.4.1. Validation Test Based on Repose Angle of Rice Grain
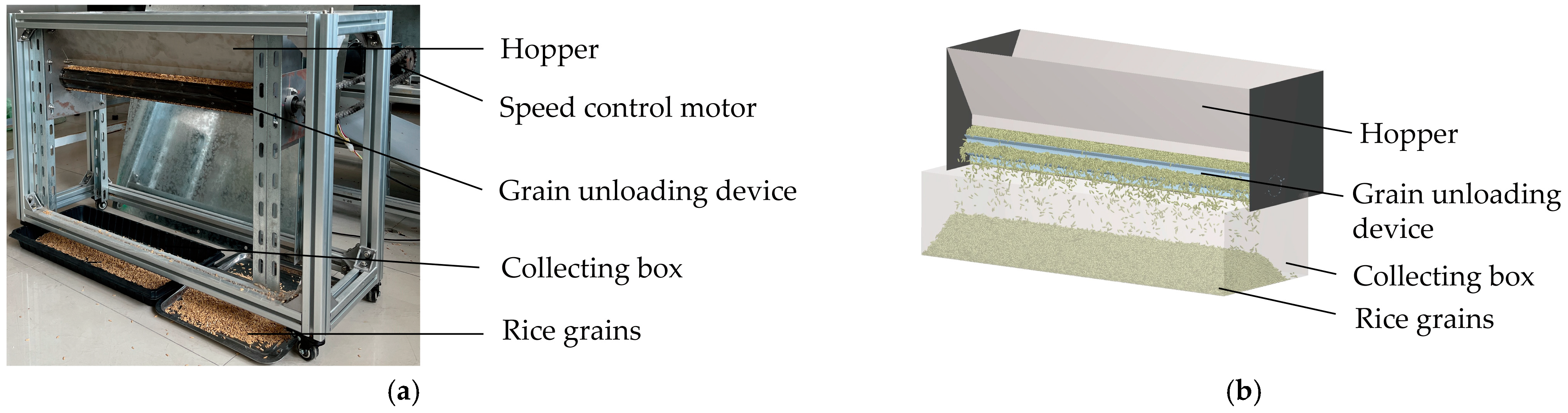
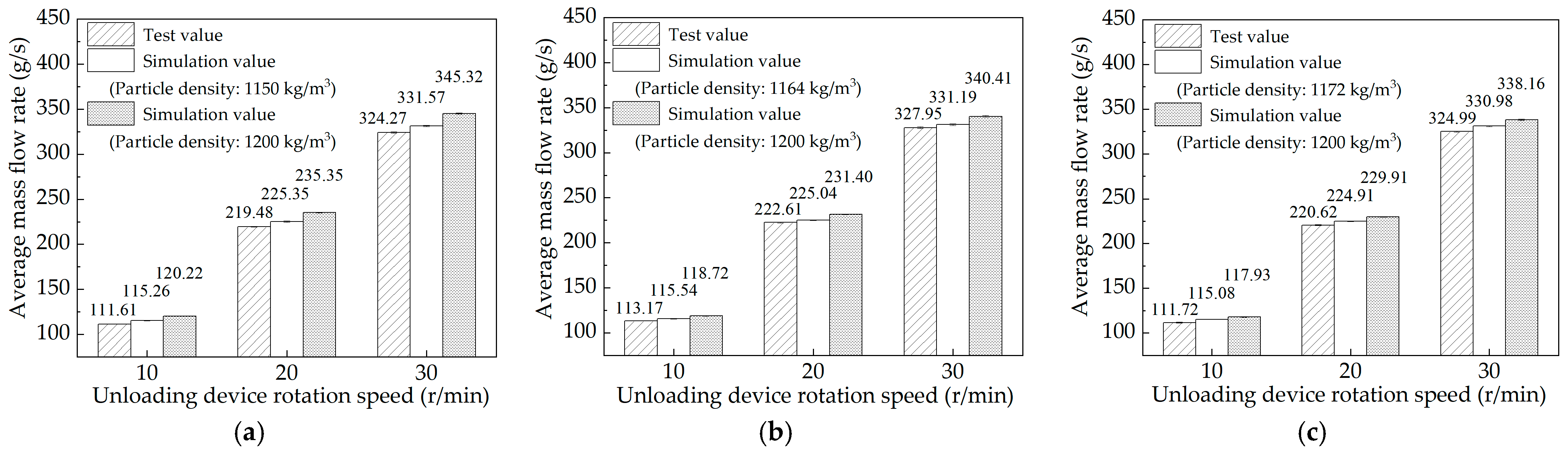
3.4.2. Validation Test for Unloading Mass Flow Rate
4. Conclusions
- (1)
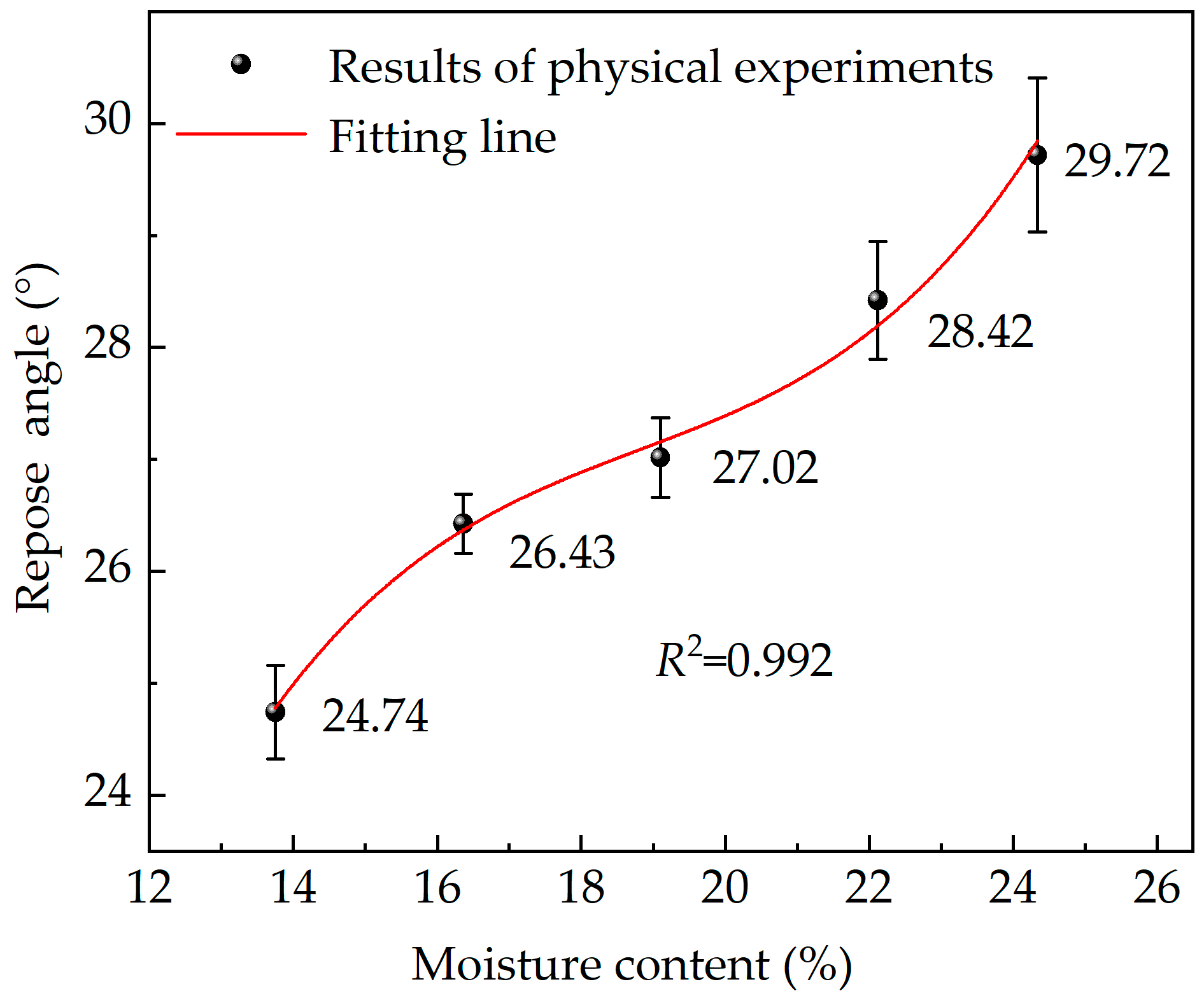
- A moisture content–repose angle model for rice grain, with moisture content ranging from 13.75% to 24.34%, was developed based on physical tests using the cylinder lifting method. The model demonstrated a high correlation with the actual data, with a coefficient of determination of 0.992.
- (2)
- The discrete element parameters of rice grain under different moisture content conditions were determined through the PB test and steepest climbing test: the coefficient of static friction between the rice grains and steel plate was 0.26–0.48, the coefficient of static friction between the rice grains was 0.35–0.62, and the coefficient of rolling friction between the rice grains was 0.03–0.11. The model of the interaction between the repose angle of rice grain and the significant discrete element parameters of the rice was developed by the BB test, and the coefficient of determination of was 0.970. The relative error between the simulated and actual values of the repose angles did not exceed 3.52%, and the average relative error was 1.94%.
- (3)
- A moisture content–significant discrete element parameters model was established based on the relationships between moisture content and repose angle, as well as between the repose angle and significant discrete element parameters. The reliability of the model was verified under calibrated parameters using the cylinder lifting method and the unloading mass flow rate test, which resulted in relative errors less than or equal to 2.09% and 7.72%, respectively. These results showed that the discrete element parameters of rice grains with different moisture contents could be accurately predicted based on this model. Meanwhile, the model still remained applicable despite the slight change in particle size due to the change in moisture content. This study provides a reliable method for the determination of discrete element parameters in the simulation of long-grain rice at different moisture contents.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, W.; Chou, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y. Impacts of extreme climate events on future rice yields in global major rice-producing regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Jia, F.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, B. Effects of rotation speed and outlet opening on particle flow in a vertical rice mill. Powder Technol. 2016, 297, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Han, Y.; Jia, F.; Meng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, S. DEM simulations and experiments investigating the influence of feeding plate angle in a rubber-roll paddy grain huller. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 201, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; Gong, Z. DEM simulation and physical testing of rice seed impact against a grain loss sensor. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 116, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X. Flow pattern and normal pressure distribution in flat bottom silo discharged using wall outlet. Powder Technol. 2016, 295, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.P.; Gan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, A. Discrete particle simulation for mixing of granular materials in ribbon mixers: A scale-up study. Powder Technol. 2022, 400, 117222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahto, L.; De, T.; Chakraborty, J.; Kumar, J.; Tripathi, A.; Sen, M.; Ketterhagen, W. Accelerated DEM simulation of the hopper-screw feeder and tablet-press feeder using the multi-level coarse-graining technique. Powder Technol. 2024, 436, 119466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; You, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Fang, X. Calibration and experimental verification of finite element parameters for alfalfa conditioning model. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bai, J.; Wang, X.; Fang, W.; Hong, T.; Zang, N.; Fang, L.; Wang, G. Calibration and testing of discrete elemental simulation parameters for pod pepper seeds. Agriculture 2024, 14, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, H.; Song, X.; Zhang, F.; Dai, F.; Yang, T.; Li, B. Study on the contact parameter calibration of the maize kernel polyhedral discrete element model. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, D.; Jia, F.; Qiu, H.; Li, A.; Bai, S. Experimental and numerical investigation on the shape approximation of rice particle by multi-sphere particle models. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jia, F.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Influence of granular coefficient of rolling friction onaccumulation characteristics. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Tekeste, M.Z.; Li, Y.; Gaul, A.; Zhu, D.; Liao, J. Scaled-up rice grain modelling for DEM calibration and the validation of hopper flow. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 194, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, K.; Lai, Q. Calibration and experiment of simulation parameters for panax notoginseng seeds based on DEM. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; He, F.; Chen, F.; Zhan, L. Calibration of discrete elemental parameters of wood powder with different moisture content based on angle of repose. J. Agric. Sci. Technol 2025, 27, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Xie, B.; Yan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Q. Moisture content characterization method of wet particles of brown rice based on discrete element simulation. Powder Technol. 2023, 428, 118775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L. An investigation on a comprehensive calibration technique to determine the discrete elemental characteristics of unrotted sheep dung at varying water concentrations. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yan, L.; Jiang, D.; Gou, H.; Fu, X.; Zhang, J. Establishment and research of cotton stalk moisture content–discrete element parameter model based on multiple verification. Processes 2024, 12, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, N. Rapid calibration method for discrete element simulation parameters of columnar granular organic fertilizer with variable moisture content. Powder Technol. 2024, 448, 120354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, P.; He, H.; Ma, Y.; Bu, K.; Xue, J. Calibration of parameters for discrete element simulation model for alfalfa with different moisture contents based on angle of repose test. BioResources 2022, 17, 1467–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, K.; Dong, Y. Measurement and calibration of gluten pellets discrete element parameters at varied moisture content. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 1616–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Xu, F.; Fang, Z. Porosity of flowing rice layer: Experiments and numerical simulation. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 179, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Design and experimental study of 5HP-25 type grain dryer. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Mao, B.; Li, A.; Han, Y.; Jia, F. DEM investigation of particle flow in a vertical rice mill: Influence of particle shape and rotation speed. Powder Technol. 2022, 399, 117105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Che, G.; Wan, L.; Tang, H. Effects of drying approaches combined with variable temperature and tempering on the physicochemical quality of rice. Dry. Technol. 2023, 41, 1199–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y. Critical speed of impact damage on a rice kernel. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2009, 40, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Ding, N.; Jin, C. Effect of Drying Conditions on the Texture and Taste Characteristics of Rough Rice. Dry. Technol. 2011, 29, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, T. Experiment and discrete element model of rice seed based on 3D laser scanning. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Jia, F.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, H. DEM study to determine the relationship between particle velocity fluctuations and contact force disappearance. Powder Technol. 2017, 313, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markauskas, D.; Kacianauskas, R.; Dziugys, A.; Navakas, R. Investigation of adequacy of multi-sphere approximation of elliptical particles for DEM simulations. Granul. Matter 2010, 12, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Jia, F.; Han, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fei, J.; Shen, S.; Hao, X.; Feng, W. Effect of the rotational speeds of the screw conveyor and milling roller on the behaviour of grain flows in the connected chamber of a vertical “conveying-milling” rice mill. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 224, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, I.; Kocsis, L.; Oldal, I.; Farkas, I.; Csatar, A. Grain velocity distribution in a mixed flow dryer. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yao, L.; Wang, H. Simulation prediction method of repose angle for rice particle materials. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 254–260. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.; Wang, X.; Han, D.; Chen, X. Review of material parameter calibration method. Agriculture 2022, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yin, J.; Tang, Z. Monitoring method of rice seeds mass in vibrating tray for vacuum-panel precision seeder. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 114, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Z. Sensor for monitoring rice grain sieve losses in combine harvesters. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 147, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Yang, J.; Wan, X.; Yuan, J.; Liao, Y.; Liao, Q. Calibration and experiment of the discrete element simulation parameters of rape threshing mixture in combine harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, G.; Zhong, W.; Liu, X. DEM study on the mixed feeding process of coal and cylindroid biomass particles in a screw feeder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 2543–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, A.P.; Benjamin, L.S.; Julio, M.O.; Richard, M.L. Surface roughness effects in granular matter: Influence on angle of repose and the absence of segregation. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 031304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rasaq, A.A.; Lateef, O.S.; Hameed, O.O.; Olayinka, R.K. Effect of variety and moisture content on some engineering properties of paddy rice. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadreza, A.; Saeed, M. Effect of de-awing and moisture content on some frictional of paddy. J. Food Process Eng. 2012, 35, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibar, H.; Öztürk, T.; Esen, B. The effect of moisture content on physical and mechanical properties of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Span. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 8, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Yu, J. Experimental verification and simulation analysis of a multi-sphere modelling approach for wheat seed particles based on the discrete element method. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 245, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Siebenmorgen, T.J. Effect of Rice Cultivar, Type, Form, and Moisture Content on the Angle of Repose. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2019, 35, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Types | Parameters | Symbol | Low Level | High Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice grain | Density (kg/m3) | 1050 | 1350 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.2 | 0.3 | ||
| Young’s modulus (MPa) | 20 | 400 | ||
| Rice grain–steel | Coefficient of restitution | 0.10 | 0.76 | |
| Coefficient of static friction | 0.14 | 0.60 | ||
| Coefficient of rolling friction | 0 | 0.1 | ||
| Rice grain–rice grain | Coefficient of restitution | 0.2 | 0.6 | |
| Coefficient of static friction | 0.21 | 0.75 | ||
| Coefficient of rolling friction | 0 | 0.15 | ||
| Virtual parameters | , | - | - |
| No. | Simulated Repose Angle/(°) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1350 | 0.3 | 20 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.21 | 0 | 17.41 |
| 2 | 1050 | 0.3 | 400 | 0.1 | 0.60 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.21 | 0 | 18.36 |
| 3 | 1350 | 0.2 | 400 | 0.76 | 0.14 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.75 | 0 | 8.77 |
| 4 | 1050 | 0.3 | 20 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.75 | 0.15 | 40.32 |
| 5 | 1050 | 0.2 | 400 | 0.1 | 0.60 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.75 | 0.15 | 40.50 |
| 6 | 1050 | 0.2 | 20 | 0.76 | 0.14 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 11.71 |
| 7 | 1350 | 0.2 | 20 | 0.1 | 0.60 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.75 | 0 | 25.80 |
| 8 | 1350 | 0.3 | 20 | 0.1 | 0.14 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.75 | 0.15 | 24.80 |
| 9 | 1350 | 0.3 | 400 | 0.1 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 11.44 |
| 10 | 1050 | 0.3 | 400 | 0.76 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.75 | 0 | 8.28 |
| 11 | 1350 | 0.2 | 400 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 26.88 |
| 12 | 1050 | 0.2 | 20 | 0.1 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.21 | 0 | 5.96 |
| 13 | 1200 | 0.25 | 210 | 0.43 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0.48 | 0.075 | 33.79 |
| 14 | 1200 | 0.25 | 210 | 0.43 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0.48 | 0.075 | 34.46 |
| 15 | 1200 | 0.25 | 210 | 0.43 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0.48 | 0.075 | 34.54 |
| Parameters | Effects | Sum of Squares | Contribution Rate/% | Significance Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.67 | 8.38 | 0.41 | 6 | |
| 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.004 | 9 | |
| −1.96 | 11.54 | 0.57 | 5 | |
| −2.25 | 15.17 | 0.74 | 4 | |
| 16.39 | 805.41 | 39.55 | 1 | |
| 0.48 | 0.69 | 0.03 | 8 | |
| −1.24 | 4.60 | 0.23 | 7 | |
| 9.45 | 268.00 | 13.16 | 3 | |
| 11.85 | 420.91 | 20.67 | 2 |
| No. | Simulated Repose Angle/(°) | Mean Relative Error/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0 | 6.84 | 298.61 |
| 2 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.03 | 19.42 | 40.40 |
| 3 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 33.75 | 19.22 |
| 4 | 0.48 | 0.62 | 0.11 | 36.71 | 25.73 |
| 5 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 0.15 | 40.76 | 33.11 |
| No. | Simulated Repose Angle/(°) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 29.19 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 29.74 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 32.09 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 33.79 |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 22.68 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 29.89 |
| 7 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 34.71 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 35.12 |
| 9 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 25.99 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 28.31 |
| 11 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 32.61 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 36.35 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32.10 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32.62 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32.91 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33.62 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33.22 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F Values | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 188.26 | 9 | 20.92 | 24.87 | 0.0002 ** |
| 12.18 | 1 | 12.18 | 14.48 | 0.0067 ** | |
| 21.16 | 1 | 21.16 | 25.15 | 0.0015 ** | |
| 127.36 | 1 | 127.36 | 151.42 | <0.0001 ** | |
| 0.33 | 1 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.5506 | |
| 11.56 | 1 | 11.56 | 13.74 | 0.0076 ** | |
| 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.4642 | |
| 3.83 | 1 | 3.83 | 4.55 | 0.0704 | |
| 2.29 | 1 | 2.29 | 2.73 | 0.1426 | |
| 7.57 | 1 | 7.57 | 9 | 0.0199 * | |
| Residual | 5.89 | 7 | 0.84 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 4.55 | 3 | 1.52 | 4.53 | 0.0893 |
| Pure Error | 1.34 | 4 | 0.33 |
| Moisture Content/% | Actual Repose Angle/(°) | Simulated Repose Angle/(°) | Relative Error/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.75 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 24.74 | 24.97 | 0.94 |
| 16.36 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 26.43 | 25.89 | 2.04 |
| 19.10 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 27.02 | 27.43 | 1.52 |
| 22.12 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 28.42 | 27.94 | 1.70 |
| 24.34 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.04 | 29.72 | 30.77 | 3.52 |
| Moisture Content/% | Actual Repose Angle/(°) | Simulated Repose Angle/(°) | Relative Error/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.50 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 24.95 | 25.29 | 1.36 |
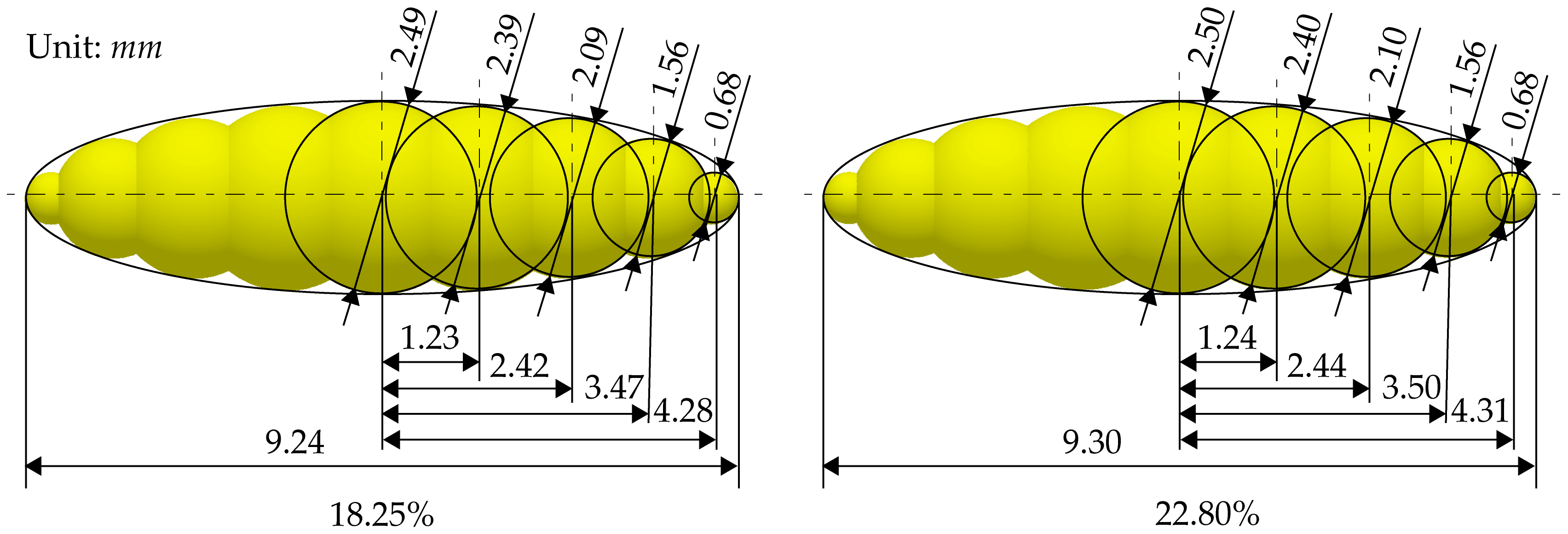
| 18.25 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 27.02 | 26.88 | 0.52 |
| 22.80 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 28.67 | 28.07 | 2.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Che, G.; Wan, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K. Calibration and Experimental Validation of Discrete Element Parameters for Long-Grain Rice with Different Moisture Contents Based on Repose Angle. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101058
Chen Z, Che G, Wan L, Wang H, Zhang K. Calibration and Experimental Validation of Discrete Element Parameters for Long-Grain Rice with Different Moisture Contents Based on Repose Angle. Agriculture. 2025; 15(10):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101058
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhengfa, Gang Che, Lin Wan, Hongchao Wang, and Kun Zhang. 2025. "Calibration and Experimental Validation of Discrete Element Parameters for Long-Grain Rice with Different Moisture Contents Based on Repose Angle" Agriculture 15, no. 10: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101058
APA StyleChen, Z., Che, G., Wan, L., Wang, H., & Zhang, K. (2025). Calibration and Experimental Validation of Discrete Element Parameters for Long-Grain Rice with Different Moisture Contents Based on Repose Angle. Agriculture, 15(10), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101058





