Design of a Leaf-Bottom Pest Control Robot with Adaptive Chassis and Adjustable Selective Nozzle
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A leaf-bottom pest control robot is designed for multiple types of ridges and different ground clearances. It achieves its goals through an adaptive chassis and adjustable selective nozzle;
- (2)
- A multi-CBAM-YOLOv5s network is developed. It improves the accuracy of identifying tiny leaf-bottom spotted bad point defects on the leaf underside by up to 85%.
- (3)
- A new complex multi-type agricultural scene precision selective pesticide automation scheme is provided.
2. Design of a Leaf-Bottom Pest Control Robot
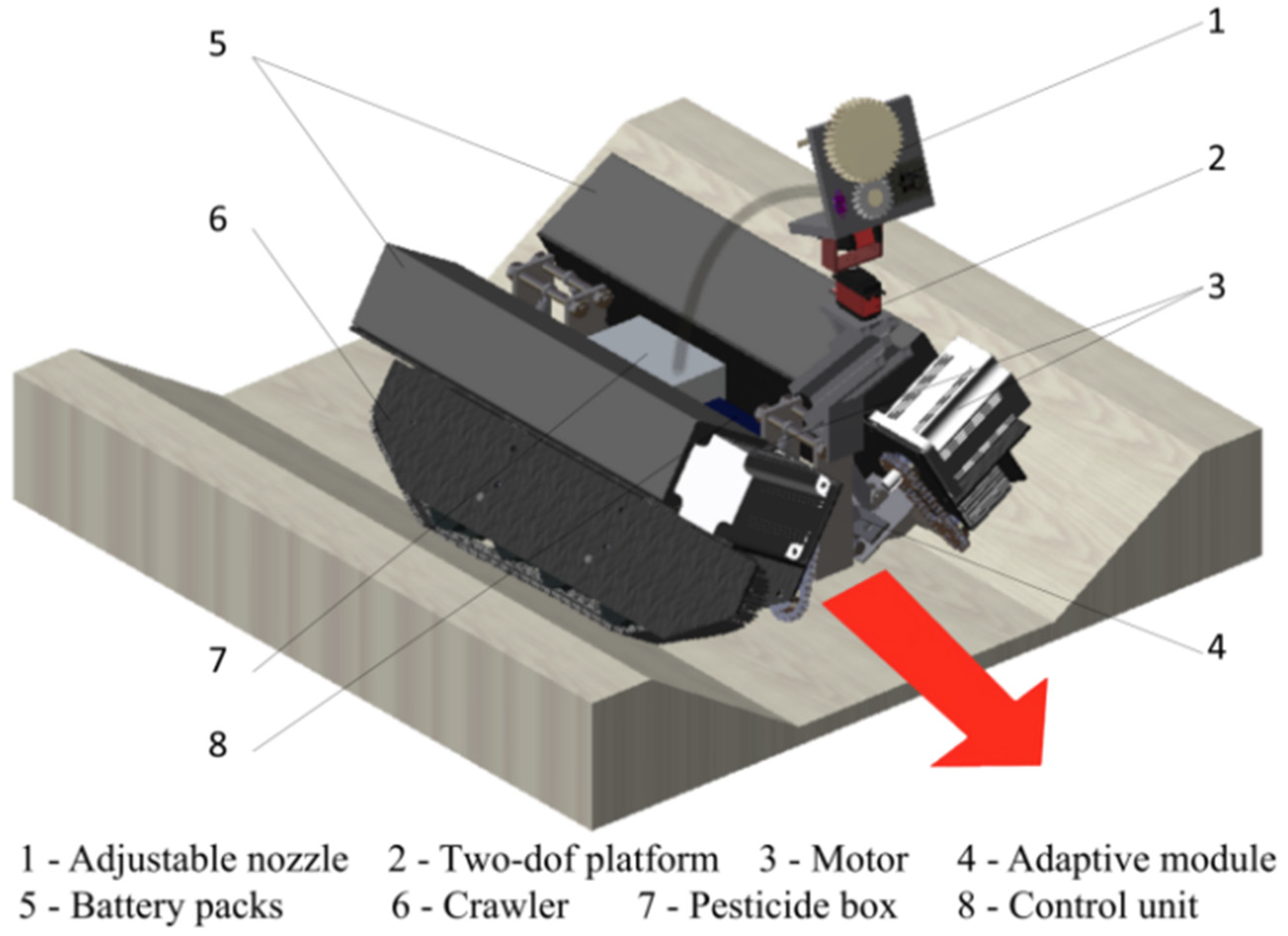
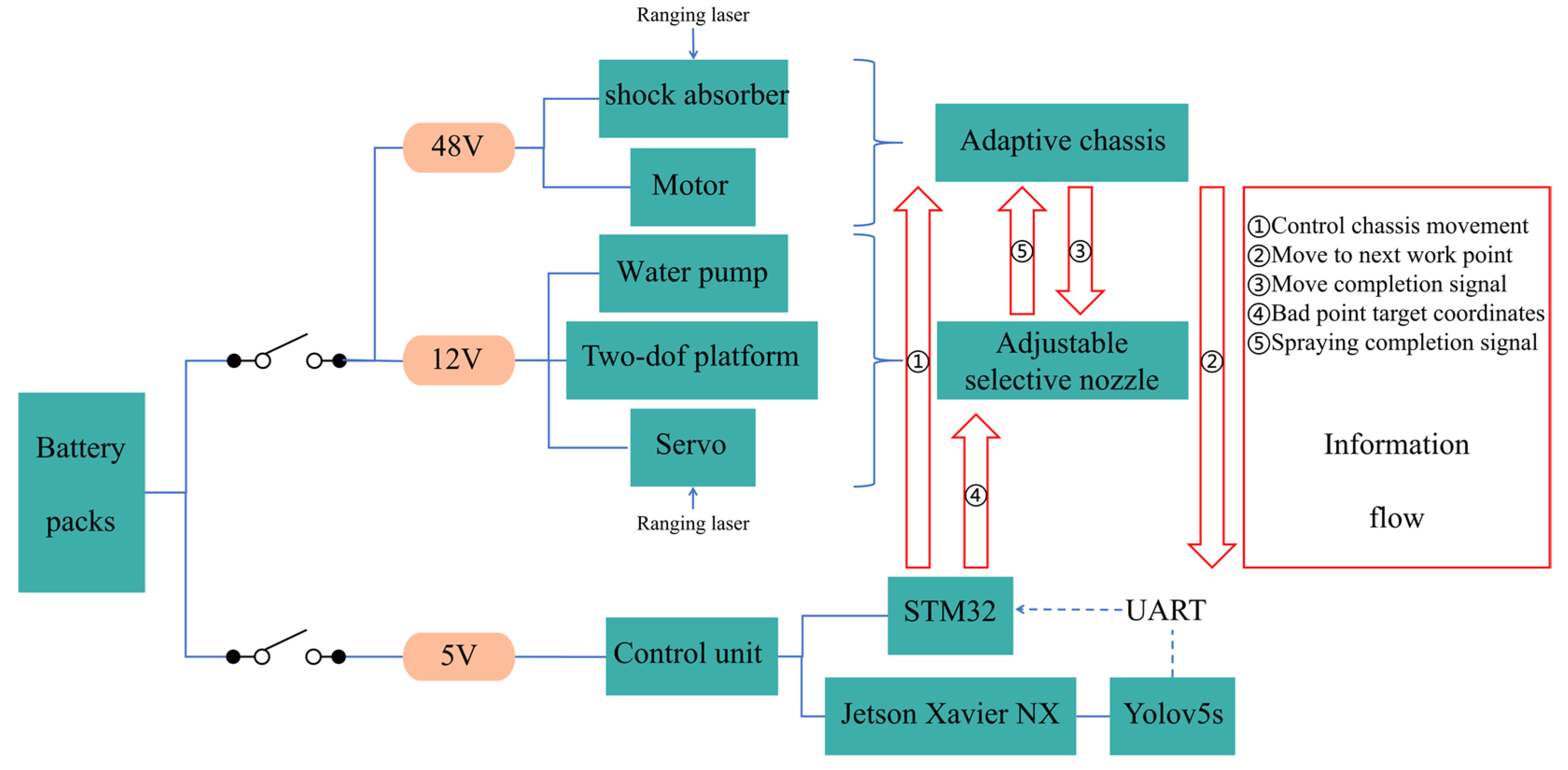
2.1. General Introduction
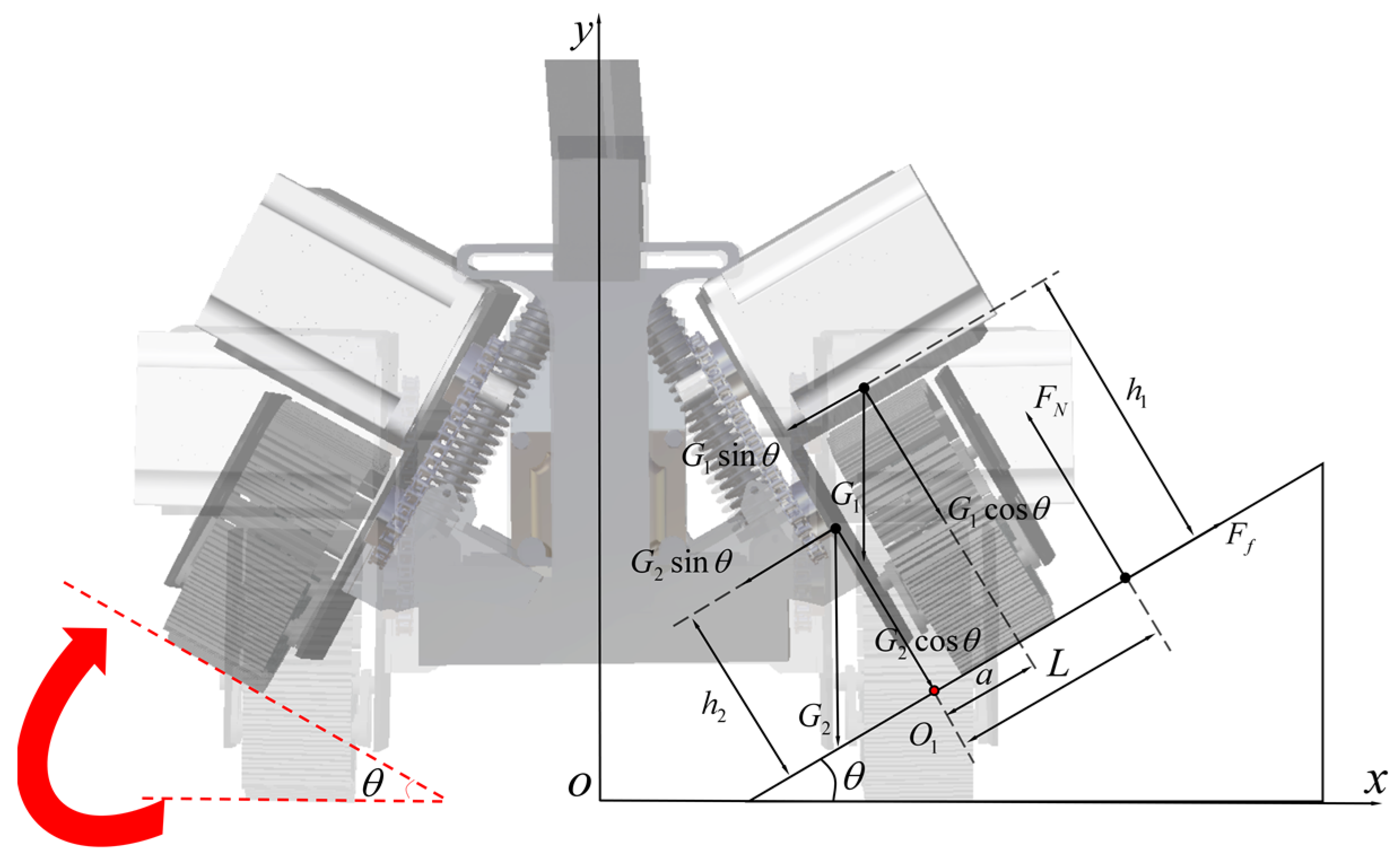
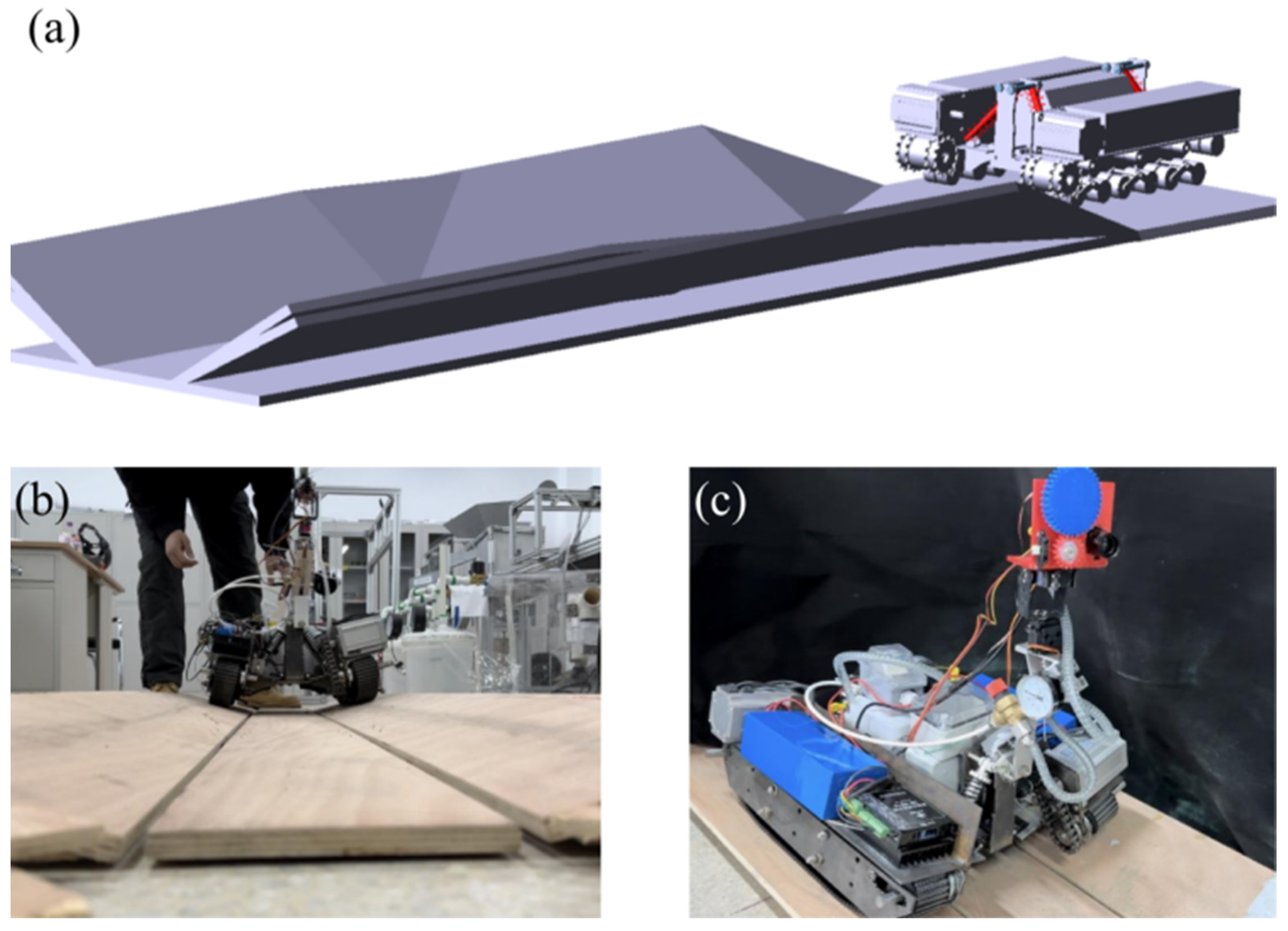
2.2. Adaptive Chassis
- (1)
- and are the lower and upper fulcrums of shock absorption, respectively.
- (2)
- AB is the rotation axis.
- (3)
- The angle of rotation of plane CAB around the Y-axis is swing angle.
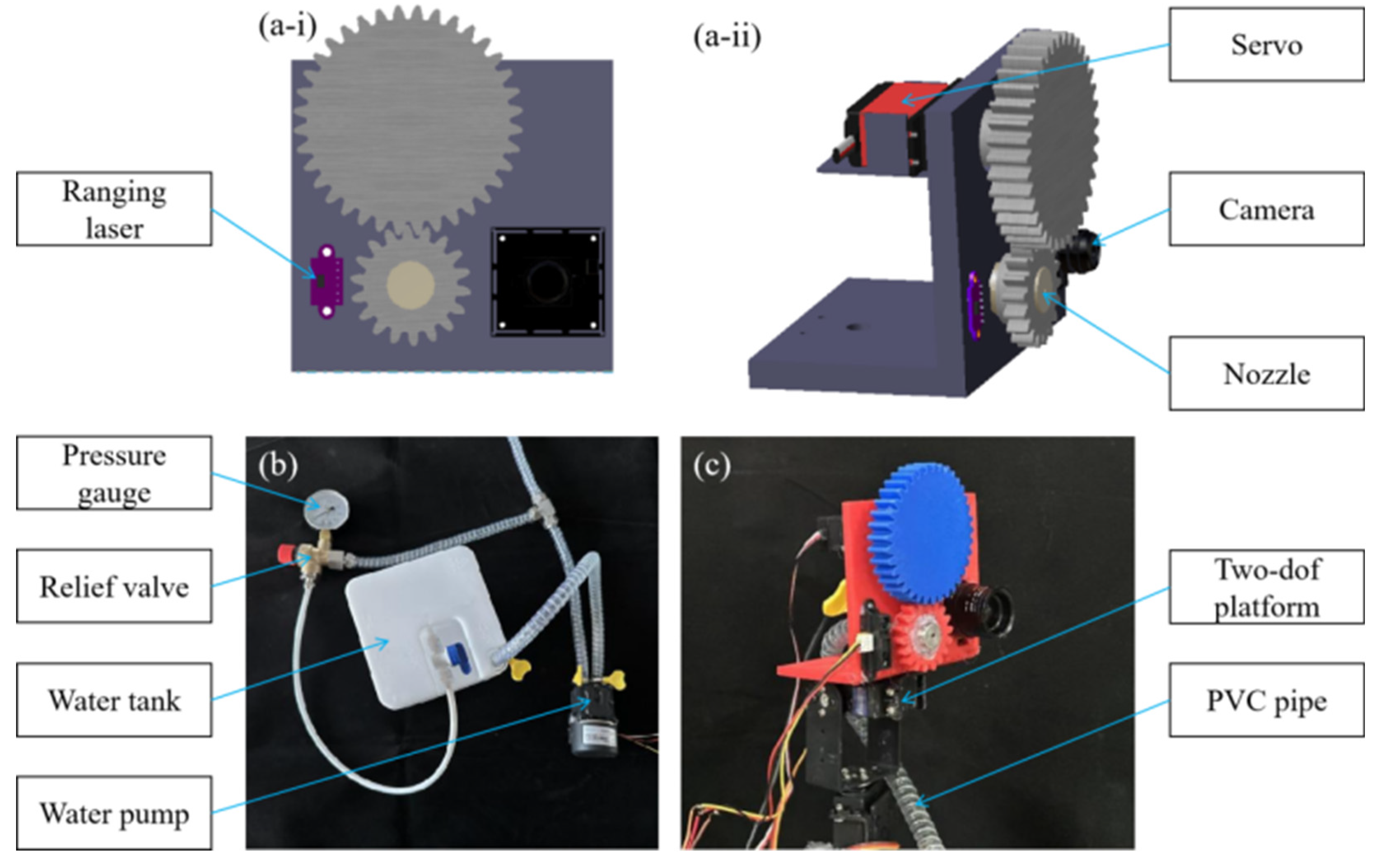
2.3. Adjustable Selective Nozzle
- (1)
- Automatic spray cone angle adjustment module (changes the angle of the spray);
- (2)
- Feedback diaphragm liquid pump with adjustable pressure (changes the height of the water column);
- (3)
- Two-dof tracking gimbal carrying the nozzle (for selective spraying).
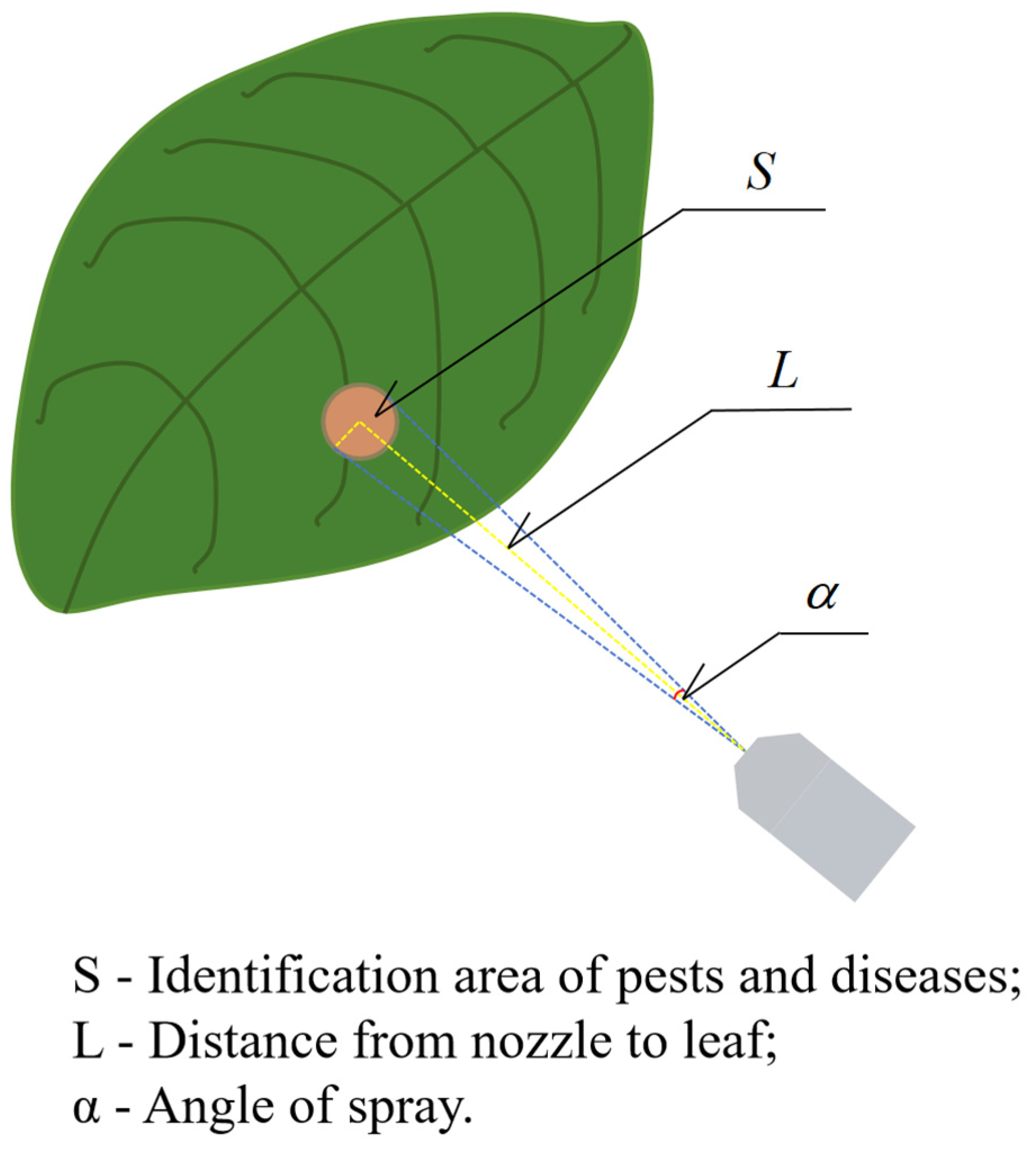
- (1)
- Considering the anticipated operating scenarios and preliminary experimental results, the plan sets the spray cone angle variation to 10°~60°, corresponding to a controllable servo angle of 270°.
- (2)
- Considering the precision of edge angle control of the servo, the servo angle control is set within a middle range, hence the gear ratio design is 3:1.
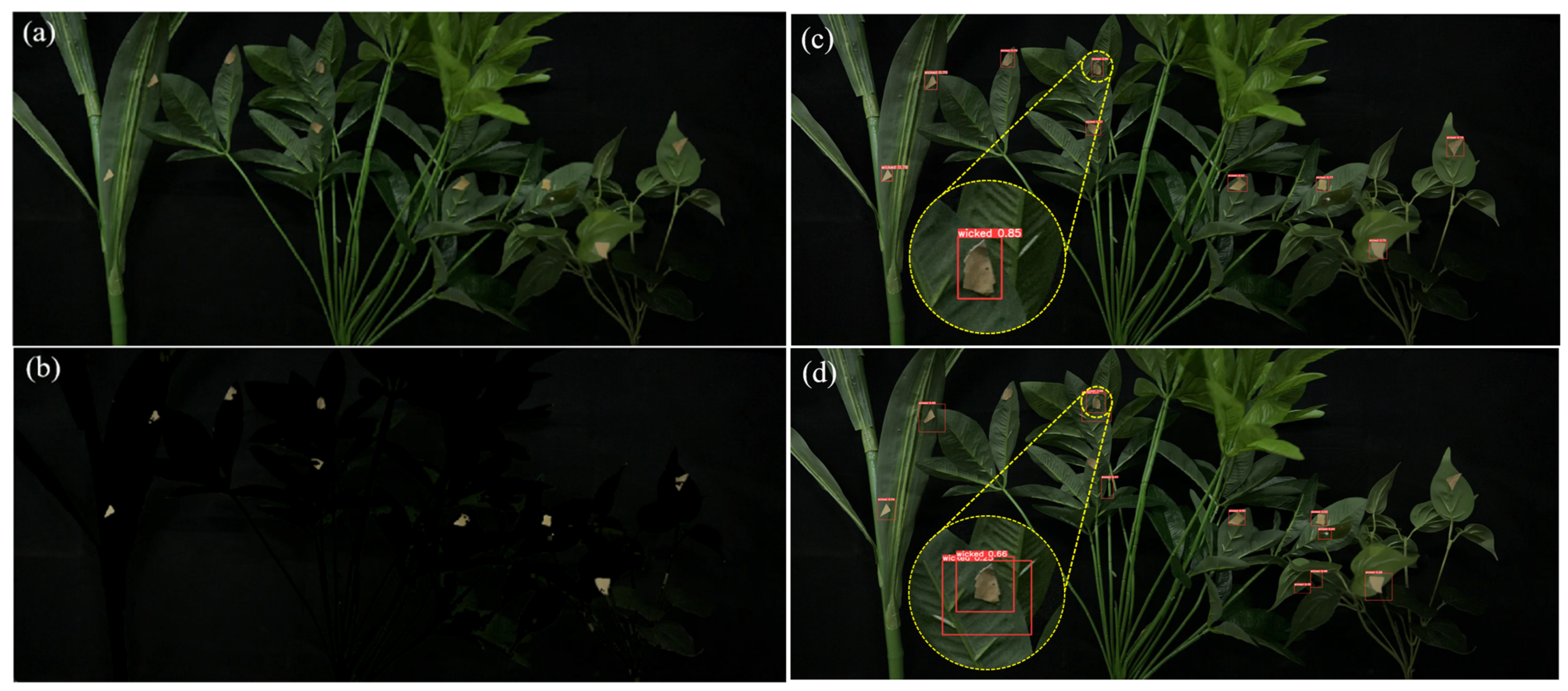
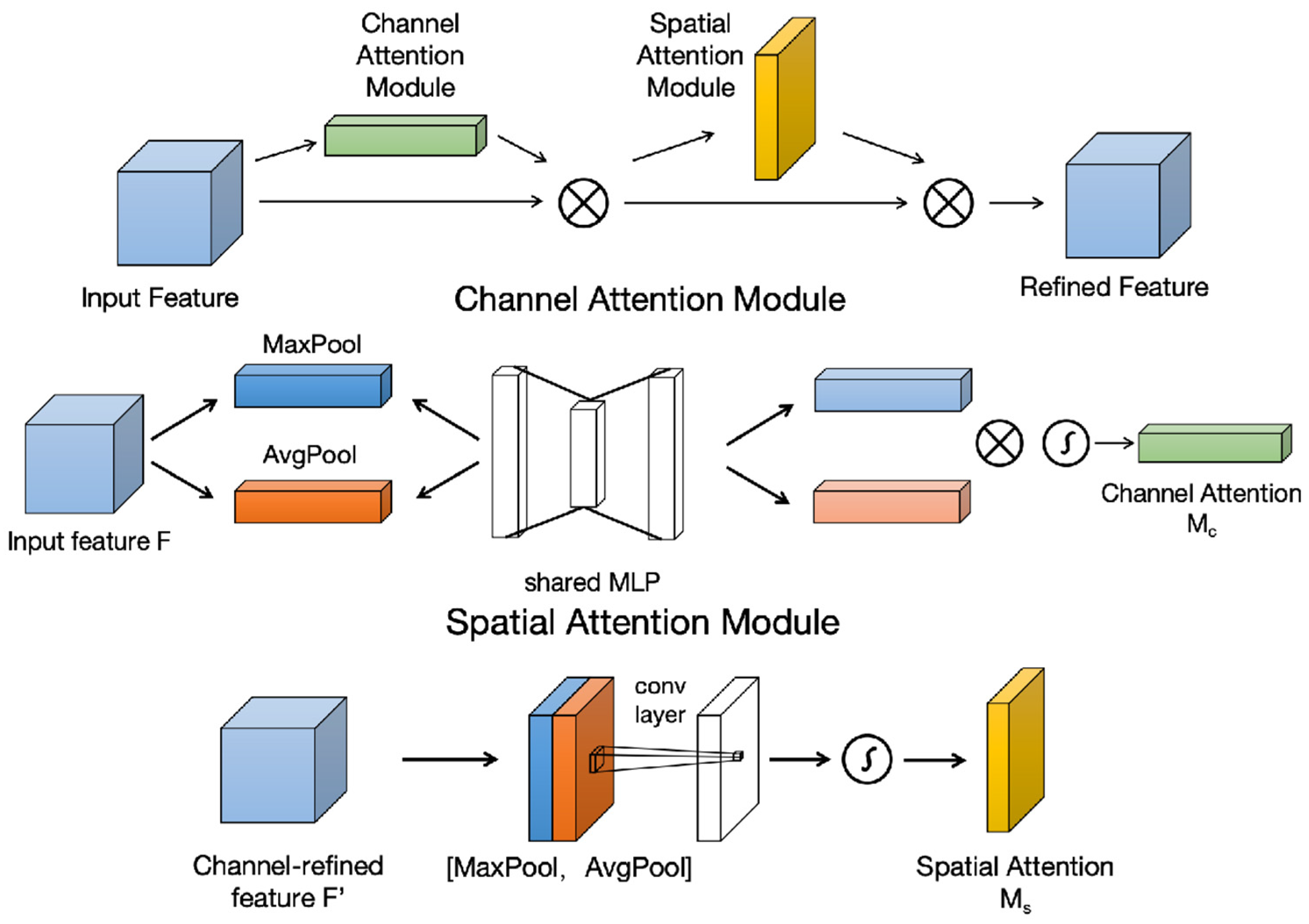
2.4. Multi-CBAM-YOLOv5s
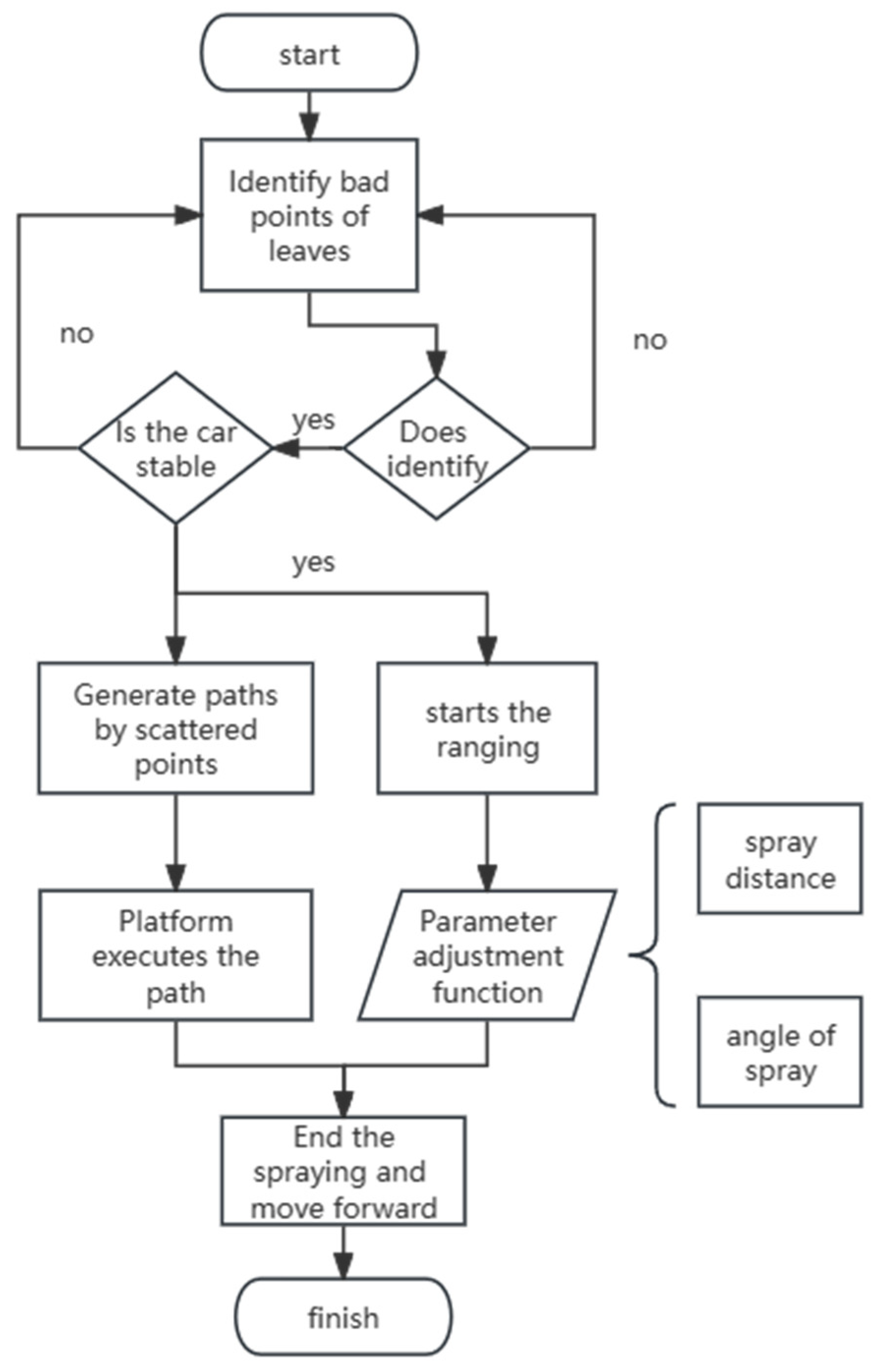
3. Experimental Verification
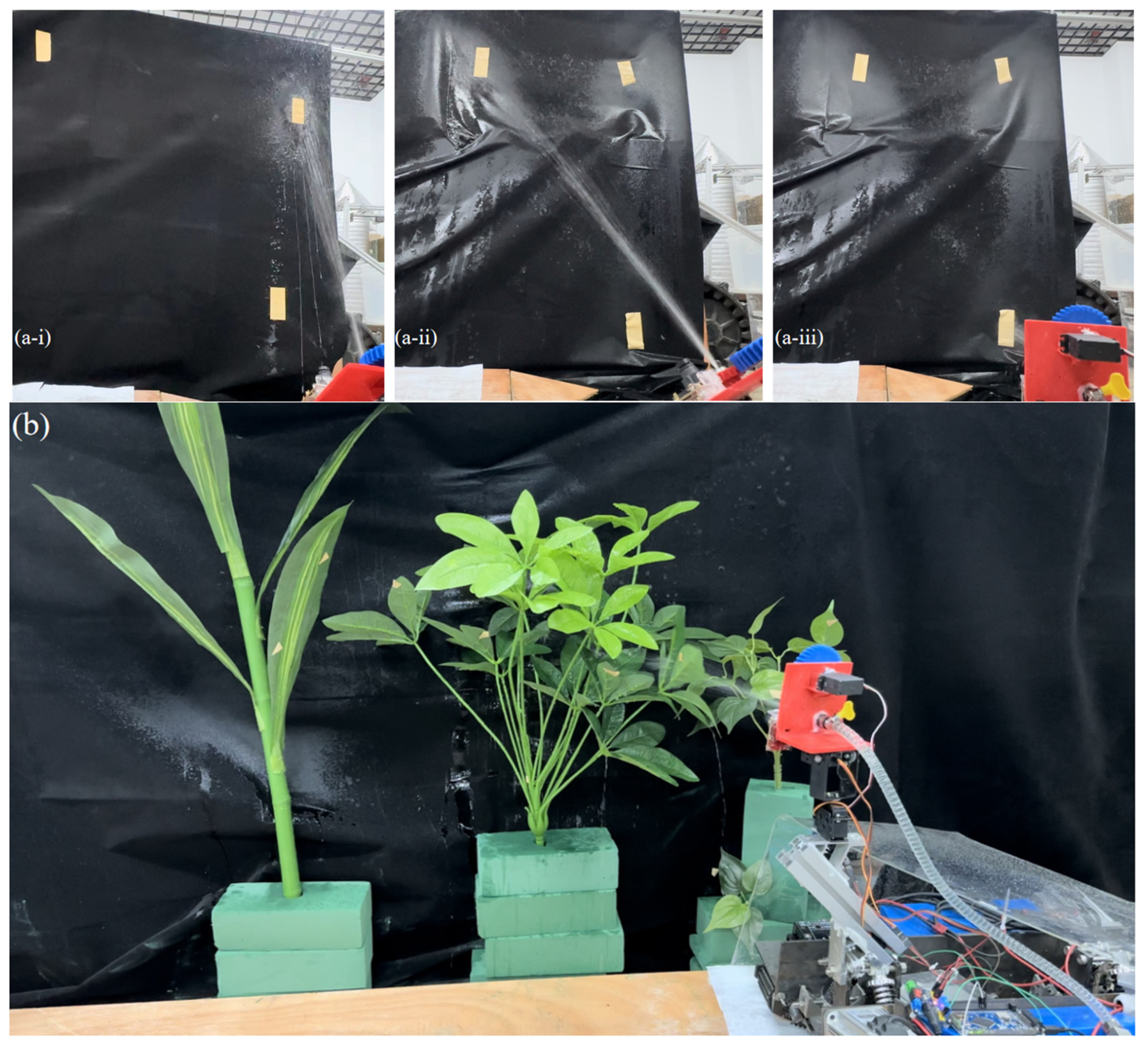
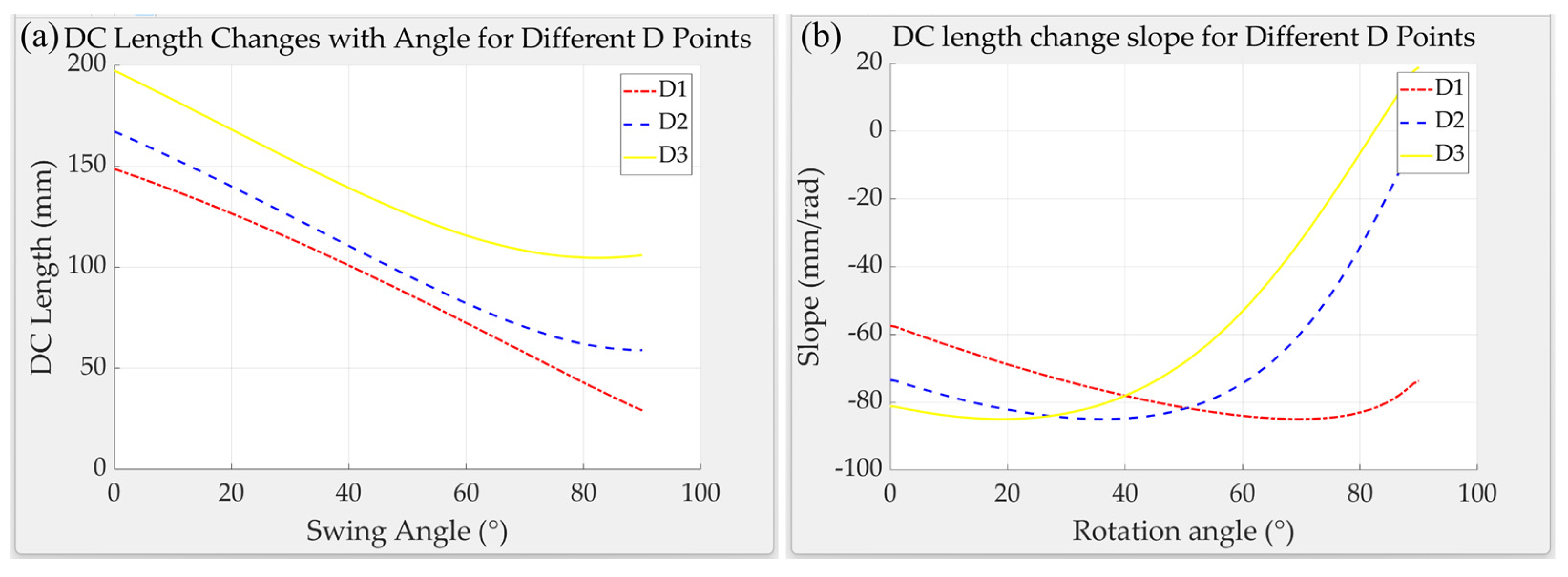
3.1. Adaptive Chassis Movement Function Test
3.2. Leaf-Bottom Spotted Bad Point Recognition and Spraying System Test
4. Discussion
- (1)
- Spraying the leaf surface, while pests and diseases are usually located at the bottom of the leaf.
- (2)
- The size is too large for leaf-bottom spraying.
- (3)
- Different crops require customized machines.
- (4)
- Non-intelligent operations.
- (1)
- Without damaging the ridge slope, it is possible to enter ridges of different sizes to carry out insect removal operations at the bottom of leaves.
- (2)
- A variety of pests and diseases can be identified in a complex field environment.
- (3)
- Automatically adjust parameters to accurately control insect pests on the bottom of leaves.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.J.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullino, M.L.; Albales, R.; Al-Jboory, I.J.; Angelotti, F.; Chakraborty, S.; Garrett, K.A.; Hurley, B.P.; Juroszek, P.; Makkouk, K.M.; Stephenson, T. Scientific Review of the Impact of Climate Change on Plant Pests; FAO on Behalf of the IPPC Secretariat: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Oerke, E.-C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agric. Sci. 2005, 144, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovgaard, M.; Renjel Encinas, S.; Jensen, O.C.; Andersen, J.H.; Condarco, G.; Jørs, E. Pesticide Residues in Commercial Lettuce, Onion, and Potato Samples From Bolivia—A Threat to Public Health? Environ. Health Insights 2017, 11, 1178630217704194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; JieHua, Z.; YanLi, Y.; Hao, T.; HePing, L.; MingShou, F.; Ying, S.; DaoFeng, D.; GuiJiang, W.; WanXing, W.; et al. Status of Major Diseases and Insect Pests of Potato and Pesticide Usage in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2019, 52, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Agricultural Yearbook. Chinese Agriculture Yearbook 2017; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Vitousek, P. An experiment for the world. Nature 2013, 497, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lan, Y.; Fritz, B.K.; Hoffmann, W.C.; Liu, S. Review of agricultural spraying technologies for plant protection using unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changhai, C.; Chunhui, B.; Mingjun, W.; Mo, Y. The Design of Potato Combined Machine of Traction Type is Including Rotary Tillage Fertilizer Sow and Spray. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2018, 40, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, E.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Song, Z.; Yang, S.; Chen, J. Design and experiment of a high-clearance self-propelled sprayer chassis. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, B.S.; Kumar, A.; Modi, R.U.; Namdev, S.K. Design and performance evaluation of self-propelled intra-canopy boom spraying system. J. Agric. Eng. 2020, 57, 195–209. [Google Scholar]
- Wongsuk, S.; Qi, P.; Wang, C.; Zeng, A.; Sun, F.; Yu, F.; Zhao, X.; Xiongkui, H. Spray performance and control efficacy against pests in paddy rice by UAV-based pesticide application: Effects of atomization, UAV configuration and flight velocity. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 2072–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.-C.; Qiu, B.-J.; Xue, X.-Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z.-F.; Zhou, Q.-Q. Droplet deposition and control effect of insecticides sprayed with an unmanned aerial vehicle against plant hoppers. Crop Prot. 2016, 85, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Z. Research progress of electrostatic spray technology over the last two decades. J. Energy Eng. 2021, 147, 03121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Jin, L.; Jia, Z.; Bao, R.; Qian, X. Design and experiment on electrostatic spraying system for unmanned aerial vehicle. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Law, S.E. Agricultural electrostatic spray application: A review of significant research and development during the 20th century. J. Electrost. 2001, 51, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jat, D.; Dubey, K.; Potdar, R.R.; Chakraborty, S.K.; Kumar, S.P.; Chandel, N.S.; Rajwade, Y.A.; Subeesh, A. Development of an automated mobile robotic sprayer to prevent workers’ exposure of agro-chemicals inside polyhouse. J. Field Robot. 2023, 40, 1388–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, A.T.; Vanalkar, A.V.; Kalambe, K.B.; Badar, A.M. Pesticide spraying robot for precision agriculture: A categorical literature review and future trends. J. Field Robot. 2022, 39, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Luo, Q.; Ma, G.; Wan, F.; He, C.; Yue, Y.; Yue, Y.; Huang, X. Simulation Analysis and Testing of Tracked Universal Chassis Passability in Hilly Mountainous Orchards. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantelli, L.; Bonaccorso, F.; Longo, D.; Melita, C.D.; Schillaci, G.; Muscato, G. A Small Versatile Electrical Robot for Autonomous Spraying in Agriculture. Agriengineering 2019, 1, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Xi, D.; Zhang, T.; Sun, W. Design and test of stem diameter inspection spherical robot. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberti, R.; Marchi, M.; Tirelli, P.; Calcante, A.; Iriti, M.; Tona, E.; Hocevar, M.; Baur, J.; Pfaff, J.; Schuetz, C.; et al. Selective spraying of grapevines for disease control using a modular agricultural robot. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 146, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, J.; Kim, J.; Son, H.I. Field evaluations of a deep learning-based intelligent spraying robot with flow control for pear orchards. Precis. Agric. 2022, 23, 712–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2015; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2016; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, E.; Yang, G.; Liang, Z.; Tan, M. MD-YOLO: Multi-scale Dense YOLO for small target pest detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 213, 108233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.-f.; Cao, H.-x. Rice Blast Disease Recognition Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; He, D. Channel pruned YOLO V5s-based deep learning approach for rapid and accurate apple fruitlet detection before fruit thinning. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 210, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Xu, F.; Guo, H.; Tian, X.; Li, M.; Bao, Z.; Li, Y. An improved YOLOv5 model based on visual attention mechanism: Application to recognition of tomato virus disease. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 194, 106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M. An improved YOLOv5-based vegetable disease detection method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Wang, J.; Duan, Y.; Fu, B.; Kang, J.-R.; Shi, Y. MobileNet based apple leaf diseases identification. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2022, 27, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, C. TinySegformer: A lightweight visual segmentation model for real-time agricultural pest detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.D. Resistance of plants to insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1965, 10, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.S.; Palandri, J.; Lakehal-Ayat, M.; Chakravarty, P.; Wolf-Monheim, F.; Blaschko, M.B. Kinematics design of a MacPherson suspension architecture based on bayesian optimization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 53, 2261–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]


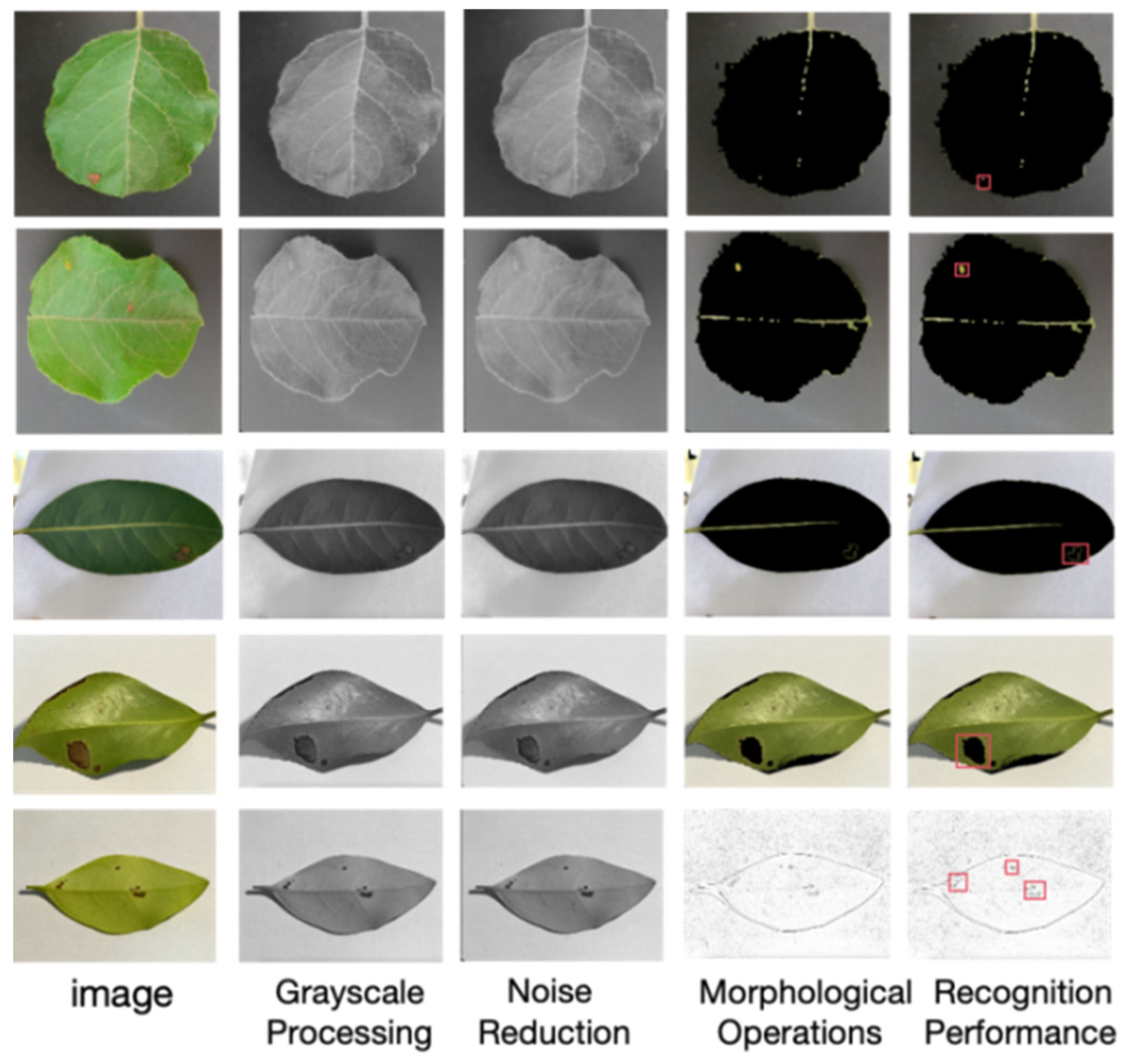
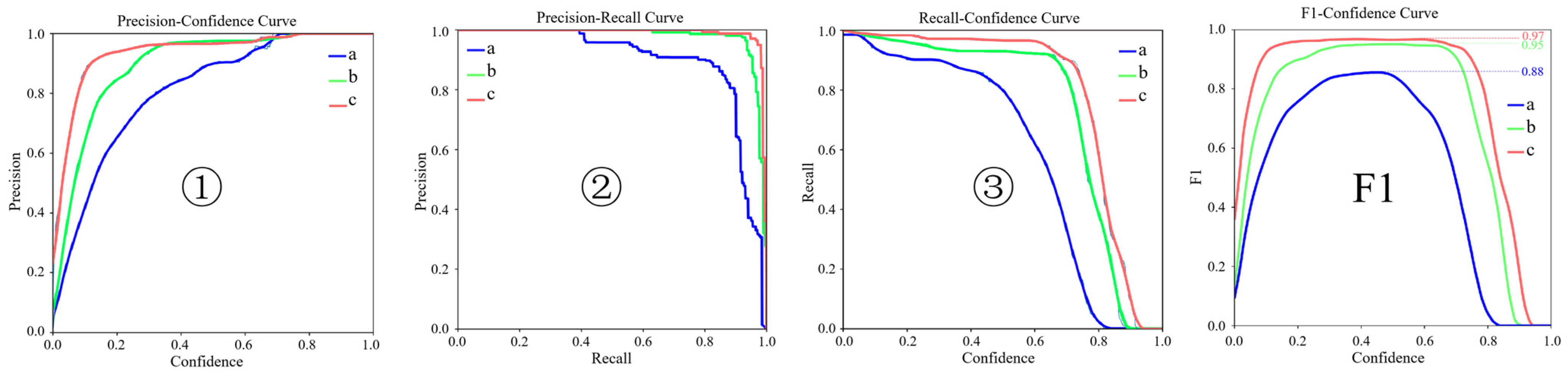







| Deep Learning Models | Precision | Recall | mAP_0.5 | mAP_0.5:0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yolov5s-SE | 0.959 | 0.942 | 0.958 | 0.47 |
| Yolov5s-SimAM | 0.973 | 0.919 | 0.954 | 0.52 |
| Yolov5s-cbam | 0.988 | 0.956 | 0.990 | 0.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Gao, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, H. Design of a Leaf-Bottom Pest Control Robot with Adaptive Chassis and Adjustable Selective Nozzle. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14081341
Li D, Gao F, Li Z, Zhang Y, Gao C, Li H. Design of a Leaf-Bottom Pest Control Robot with Adaptive Chassis and Adjustable Selective Nozzle. Agriculture. 2024; 14(8):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14081341
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongshen, Fei Gao, Zemin Li, Yutong Zhang, Chuang Gao, and Hongbo Li. 2024. "Design of a Leaf-Bottom Pest Control Robot with Adaptive Chassis and Adjustable Selective Nozzle" Agriculture 14, no. 8: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14081341
APA StyleLi, D., Gao, F., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Gao, C., & Li, H. (2024). Design of a Leaf-Bottom Pest Control Robot with Adaptive Chassis and Adjustable Selective Nozzle. Agriculture, 14(8), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14081341






