Interactive Effects of Salinity Stress and Irrigation Intervals on Plant Growth, Nutritional Value, and Phytochemical Content in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Location
2.2. Plant Preparation, Irrigation, and Treatments
2.3. Determination of Plant Growth
2.3.1. Leaf Length and Number of Leaves
2.3.2. Plant Weight
2.4. Chlorophyll Content
2.5. Nutritional Analysis
2.5.1. Sample Preparation
2.5.2. Mineral Analysis
2.5.3. Proximate Analysis
Moisture Content
Crude Fat Content
Ash Content
Crude Protein
Neutral Detergent Fibre (NDF)
2.6. Phytochemical and Antioxidant Assays
2.6.1. Sample Preparation
2.6.2. Total Polyphenols
2.6.3. Estimation of Flavonol Content
2.6.4. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
2.6.5. Ferric Reducing/Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Salinity and Irrigation Interval on Plant Growth Parameters
3.1.1. Leaf Length and Number of Leaves
3.1.2. Total Fresh Weight and Dry Weight
3.2. Effect of Salinity and Irrigation Intervals on Leaf Chlorophyll Content
3.3. Effect of Salinity and Irrigation Intervals on the Mineral Content of Dried Leaves of M. crystallinum
3.3.1. Macronutrients
3.3.2. Micronutrients
3.4. Effect of Salinity and Irrigation Intervals on Proximate Composition of Dried Leaves of M. crystallinum
3.5. Effect of Salinity and Irrigation Intervals on Phytochemicals and Antioxidant Activity of Dried Leaves of M. crystallinum
3.5.1. Total Polyphenols
3.5.2. Total Flavonols
3.5.3. FRAP Capacity
3.5.4. DPPH Capacity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atzori, G.; Nissim, W.; Macchiavelli, T.; Vita, F.; Azzarello, E.; Pandolfi, C.; Masi, E.; Mancuso, S. Tetragonia tetragonioides (Pallas) Kuntz. as Promising Salt-Tolerant Crop in a Saline Agricultural Context. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, G.; de Vos, A.C.; van Rijsselberghe, M.; Vignolini, P.; Rozema, J.; Mancuso, S.; van Bodegom, P.M. Effects of Increased Seawater Salinity Irrigation on Growth and Quality of the Edible Halophyte Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. under Field Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 187, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Razzaq, A.; Mehmood, S.S.; Zou, X.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Xu, J. Impact of Climate Change on Crops Adaptation and Strategies to Tackle Its Outcome: A Review. Plants 2019, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaloul, S.; Abdellaoui, R.; Mahmoudi, M.; Bouhamda, T.; Bakhshandeh, E.; Boughalleb, F. Seasonal Environmental Changes Affect Differently the Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Two Limonium Species in Sabkha Biotope. Physiol. Plant 2021, 172, 2112–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.; Irulappan, V.; Bagavathiannan, M.V.; Senthil-Kumar, M. Impact of Combined Abiotic and Biotic Stresses on Plant Growth and Avenues for Crop Improvement by Exploiting Physio-Morphological Traits. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavridou, E.; Webster, R.J.; Robson, P.R.H. Novel Miscanthus Genotypes Selected for Different Drought Tolerance Phenotypes Show Enhanced Tolerance across Combinations of Salinity and Drought Treatments. Ann. Bot. 2019, 124, 653–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, L.; Zeng, F.; Li, X. Negative Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Salinity, Drought, and Combined Stresses on Halophyte Halogeton Glomeratus. Physiol. Plant 2021, 173, 2307–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, S.; Sánchez-Blanco, M.J. Comparison of Individual and Combined Effects of Salinity and Deficit Irrigation on Physiological, Nutritional and Ornamental Aspects of Tolerance in Callistemon Laevis Plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 185, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, H.; Khattak, J.Z.K.; Ksiksi, T.S.; Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Sohail, H.; Ali, Q.; Zamin, M.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Saud, S.; et al. Negative Impact of Long-Term Exposure of Salinity and Drought Stress on Native Tetraena mandavillei L. Physiol. Plant 2021, 172, 1336–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Koyro, H.W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Gul, B.; Liu, X. Low Salinity Improves Photosynthetic Performance in Panicum Antidotale Under Drought Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, H.; Zamin, M.; Adnan, M.; Shah, A.N.; Alharby, H.F.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Alabdallah, N.M.; Alzahrani, S.S.; Alharbi, B.M.; Saud, S.; et al. Exploring Suitability of Salsola imbricata (Fetid Saltwort) for Salinity and Drought Conditions: A Step Toward Sustainable Landscaping Under Changing Climate. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 900210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Mattson, N. Response of Common Ice Plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L.) to Photoperiod/Daily Light Integral in Vertical Hydroponic Production. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, M.D.C.; Garmendia, I. Optimum Growth and Quality of the Edible Ice Plant under Saline Conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, M.M.; Martín-diana, A.B.; Rico, D.; López-caballero, M.E.; Martínez-álvarez, O. Antioxidant, Antihypertensive, Hypoglycaemic and Nootropic Activity of a Polyphenolic Extract from the Halophyte Ice Plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum). Foods 2022, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śliwa-Cebula, M.; Koniarz, T.; Szara-Bąk, M.; Baran, A.; Miszalski, Z.; Kaszycki, P. Phytoremediation of Metal-Contaminated Bottom Sediments by the Common Ice Plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L.) in Poland. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 23, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Mattson, N.; Stelick, A.; Dando, R. Sensory Evaluation of Common Ice Plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L.) in Response to Sodium Chloride Concentration in Hydroponic Nutrient Solution. Foods 2022, 11, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loconsole, D.; Murillo-Amador, B.; Cristiano, G.; de Lucia, B. Halophyte Common Ice Plants: A Future Solution to Arable Land Salinization. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.H.; Barkla, B.J.; Vera-Estrella, R.; Pantoja, O.; Lee, S.Y.; Bohnert, H.J.; Dassanayake, M. Cell Type-Specific Responses to Salinity—The Epidermal Bladder Cell Transcriptome of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, C.; Fischer-Schliebs, E.; Bertl, A.; Thiel, G.; Homann, U. Na+/H+ Antiporters Are Differentially Regulated in Response to NaCl Stress in Leaves and Roots of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarie, S.; Shimoda, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Baumann, K.; Sunagawa, H.; Kondo, A.; Ueno, O.; Nakahara, T.; Nose, A.; Cushman, J.C. Salt Tolerance, Salt Accumulation, and Ionic Homeostasis in an Epidermal Bladder-Cell-Less Mutant of the Common Ice Plant Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulawa, B.; Sogoni, A.; Jimoh, M.O.; Laubscher, C.P. Potassium Application Enhanced Plant Growth, Mineral Composition, Proximate and Phytochemical Content in Trachyandra divaricata Kunth (Sandkool). Plants 2022, 11, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimoh, M.O.; Afolayan, A.J.; Lewu, F.B. Nutrients and Antinutrient Constituents of Amaranthus caudatus L. Cultivated on Different Soils. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3570–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC, (Association of Official Analytical Chemist). Official Methods of Analysis; Latimer, G.W., Jr., Ed.; AOAC International: Washinton, DC, USA, 2016; ISBN 0935584870. [Google Scholar]
- Sogoni, A.; Jimoh, M.; Kambizi, L.; Laubscher, C. The Impact of Salt Stress on Plant Growth, Mineral Composition, and Antioxidant Activity in Tetragonia Decumbens Mill.: An Underutilized Edible Halophyte in South Africa. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, J.A.; Hyung, N.I.; Youn, Y.; Lee, J.Y. Silencing of Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase in Chrysanthemum Ray Florets Enhances Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Antioxidant Capacity. Plants 2022, 11, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohikhena, F.U.; Wintola, O.A.; Afolayan, A.J. Evaluation of the Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Phragmanthera capitata (Sprengel) Balle (Loranthaceae), a Mistletoe Growing on Rubber Tree, Using the Dilution Techniques. Sci. World J. 2017, 2017, 9658598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. [2] Ferric Reducing/Antioxidant Power Assay: Direct Measure of Total Antioxidant Activity of Biological Fluids and Modified Version for Simultaneous Measurement of Total Antioxidant Power and Ascorbic Acid Concentration. Methods Enzym. 1999, 299, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimoh, M.A.; Idris, O.A.; Jimoh, M.O. Cytotoxicity, Phytochemical, Antiparasitic Screening, and Antioxidant Activities of Mucuna pruriens (Fabaceae). Plants 2020, 9, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ors, S.; Ekinci, M.; Yildirim, E.; Sahin, U.; Turan, M.; Dursun, A. Interactive Effects of Salinity and Drought Stress on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Physiology of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) Seedlings. South Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 137, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ors, S.; Suarez, D.L. Spinach Biomass Yield and Physiological Response to Interactive Salinity and Water Stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 190, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Ekinci, M.; Ors, S.; Turan, M.; Yildiz, S.; Yildirim, E. Effects of Individual and Combined Effects of Salinity and Drought on Physiological, Nutritional and Biochemical Properties of Cabbage (Brassica Oleracea var. Capitata). Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarie, S.; Tada, M.; Kimura, M.; Suzuki, H.; Morokuma, M.; Toyota, M.; Nakamura, I. Growth and Salt Accumulation Capacity of the Common Ice Plant in the Tsunami-Affected Soil. Plant Prod. Sci. 2022, 25, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calone, R.; Mircea, D.-M.; González-Orenga, S.; Boscaiu, M.; Zuzunaga-Rosas, J.; Barbanti, L.; Vicente, O. Effect of Recurrent Salt and Drought Stress Treatments on the Endangered Halophyte Limonium angustebracteatum Erben. Plants 2023, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petretto, G.L.; Urgeghe, P.P.; Massa, D.; Melito, S. Effect of Salinity (NaCl) on Plant Growth, Nutrient Content, and Glucosinolate Hydrolysis Products Trends in Rocket Genotypes. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilaie, M.N.; Arani, A.M.; Etessami, H.; Dinarvand, M.; Dolati, A. Halotolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria-Mediated Alleviation of Salinity and Dust Stress and Improvement of Forage Yield in the Desert Halophyte Seidlitzia rosmarinus. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 201, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Parveen, A.; Malik, Z.; Kamran, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Abbasi, G.H.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, S.; Sathish, M.; Okla, M.K.; et al. Zn Alleviated Salt Toxicity in Solanum lycopersicum L. Seedlings by Reducing Na+ Transfer, Improving Gas Exchange, Defense System and Zn Contents. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 186, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, A.A.; Assimakopoulou, A.; Panagopoulos, P.; Bakea, M.; Vidalis, N.; Karapanos, I.C.; Rouphael, Y.; Petropoulos, S.A. Hedypnois cretica, L. and Urospermum picroides, L. Plant Growth, Nutrient Status and Quality Characteristics under Salinity Stress. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, L.; Resek, E.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Rocha, M.I.; Pereira, H.; Bandarra, N.; da Silva, M.M.; Varela, J.; Custódio, L. Halophytes: Gourmet Food with Nutritional Health Benefits? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 59, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Feijão, E.; Pinto, M.V.; Matos, A.R.; Silva, A.; Figueiredo, A.; Fonseca, V.F.; Reis-Santos, P.; Caçador, I. Nutritional Valuation and Food Safety of Endemic Mediterranean Halophytes Species Cultivated in Abandoned Salt Pans under a Natural Irrigation Scheme. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2022, 265, 107733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, Y.; Eshel, A.; Pasternak, D.; Sagi, M. The Development of Halophyte-Based Agriculture: Past and Present. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, Y.; Wuddineh, W.A.; Myrzabayeva, M.; Alikulov, Z.; Khozin-Goldberg, I.; Shpigel, M.; Samocha, T.M.; Sagi, M. Effect of Seawater Concentration on the Productivity and Nutritional Value of Annual Salicornia and Perennial Sarcocornia Halophytes as Leafy Vegetable Crops. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 128, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekmirzaev, G.; Ouddane, B.; Beltrao, J.; Fujii, Y. The Impact of Salt Concentration on the Mineral Nutrition of Tetragonia tetragonioides. Agriculture 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzecí, E.; Kowalczyk, M.; Araujo, A.; Zbieta Gałęska, E.; Wrzecí Nska, M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Araujo, J.P. Reproductive Consequences of Electrolyte Disturbances in Domestic Animals. Biology 2022, 11, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricia, O.; Zoue, L.; Megnanou, R.-M.; Doue, R.; Niamke, S. Proximate composition and nutritive value of leafy vegetables consumed in northern côte d’ivoire. Eur. Sci. J. 2014, 10, 1857–7881. [Google Scholar]
- Mih, A.M.; Ngone, A.M.; Ndam, L.M.; Mih, A.M.; Ngone, A.M.; Ndam, L.M. Assessment of Nutritional Composition of Wild Vegetables Consumed by the People of Lebialem Highlands, South Western Cameroon. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 8, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in Prevention and Therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.S.; Khan, U.; Sadiq, A.; Khalid, W.; Hussain, M.; Yasmeen, A.; Asghar, Z.; Rehana, H. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and Immunity Booster Green Foods: A Mini Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3971–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, R.; Gill, B.S. Mineral and Amino Acid Contents of Different Flaxseed Cultivars in Relation to Its Selected Functional Properties. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diviš, P.; Pořízka, J.; Vespalcov, M.; Matějíček, A.; Kaplan, J. Elemental Composition of Fruits from Different Black Elder (Sambucus nigra L.) Cultivars Grown in the Czech Republic. J. Elem. 2015, 20, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Parida, A.K.; Rangani, J.; Panda, A. Antioxidant Activities, Metabolic Profiling, Proximate Analysis, Mineral Nutrient Composition of Salvadora Persica Fruit Unravel a Potential Functional Food and a Natural Source of Pharmaceuticals. Front. Pharm. 2017, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afuape, A.O.; Afolayan, A.J.; Buwa-Komoreng, L.V. Proximate, Vitamins, Minerals and Anti-Nutritive Constituents of the Leaf and Stem of Helichrysum odoratissimum (L.) Sweet: A Folk Medicinal Plant in South Africa. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2022, 13, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparrotta, S.; Masi, E.; Atzori, G.; Diamanti, I.; Azzarello, E.; Mancuso, S.; Pandolfi, C. Growing Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) with Different Seawater Concentrations: Effects on Fresh, Boiled and Steamed Leaves. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntuli, N.R. Nutrient Content of Scarcely Known Wild Leafy Vegetables from Northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 127, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundola, A.F.; Bvenura, C.; Afolayan, A.J. Nutrient and Antinutrient Compositions and Heavy Metal Uptake and Accumulation in S. Nigrum Cultivated on Different Soil Types. Sci. World J. 2018, 2018, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegbaju, O.D.; Otunola, G.A.; Afolayan, A.J. Proximate, Mineral, Vitamin and Anti-Nutrient Content of Celosia Argentea at Three Stages of Maturity. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Jafari, S.M. The Importance of Minerals in Human Nutrition: Bioavailability, Food Fortification, Processing Effects and Nanoencapsulation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.X.; Chen, D.; Xu, J. Physiochemical Properties of Jet-Cooked Amaranth and Improved Rheological Properties by Processed Oat Bran. Future Foods 2022, 5, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, O.; Bamidele, T.; Malachi, O.; Oladejo, A. Comparative Proximate, Minerals and Antinutrient Analysis of Selected Nigerian Leafy Vegetables. J. Appl. Life Sci. Int. 2018, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, D.J.; Iqbal, S.; Ismail, M. Proximate Composition, Nutritional Attributes and Mineral Composition of Peperomia pellucida L. (Ketumpangan Air) Grown in Malaysia. Molecules 2012, 17, 11139–11145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Orenga, S.; Grigore, M.-N.; Boscaiu, M.; Vicente, O. Constitutive and Induced Salt Tolerance Mechanisms and Potential Uses of Limonium Mill. Species. Agronomy 2021, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Phan, A.D.T.; Srivarathan, S.; Akter, S.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Cozzolino, D. Proximate Composition, Functional and Antimicrobial Properties of Wild Harvest Terminalia Carpentariae Fruit. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi Goharrizi, K.; Amirmahani, F.; Salehi, F. Assessment of Changes in Physiological and Biochemical Traits in Four Pistachio Rootstocks under Drought, Salinity and Drought + Salinity Stresses. Physiol. Plant 2020, 168, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alla, M.M.N.; Khedr, A.H.A.; Serag, M.M.; Abu-Alnaga, A.Z.; Nada, R.M. Regulation of Metabolomics in Atriplex Halimus Growth under Salt and Drought Stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 67, 281–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.Q.; Feng, R.J.; Liang, N.; Yuan, H.J.; Sun, W. bin Sodium Chloride Stimulates Growth and Alleviates Sorbitol-Induced Osmotic Stress in Sugar Beet Seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 75, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkhi, I.; Charfi, S.; el Hachlafi, N.; Mechchate, H.; Guaouguaou, F.E.; el Omari, N.; Bakrim, S.; Balahbib, A.; Zengin, G.; Bouyahya, A. Genetic Diversity, Antimicrobial, Nutritional, and Phytochemical Properties of Chenopodium Album: A Comprehensive Review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 110979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tshayingwe, A.; Jimoh, M.O.; Sogoni, A.; Wilmot, C.M.; Laubscher, C.P. Light Intensity and Growth Media Influence Growth, Nutrition, and Phytochemical Content in Trachyandra divaricata Kunth. Agronomy 2023, 13, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngxabi, S.; Jimoh, M.O.; Kambizi, L.; Laubscher, C.P. Growth Characteristics, Phytochemical Contents, and Antioxidant Capacity of Trachyandra ciliata (L.f) Kunth Grown in Hydroponics under Varying Degrees of Salinity. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkcukankcuka, M.; Jimoh, M.O.; Griesel, G.; Laubscher, C.P. Growth Characteristics, Chlorophyll Content and Nutrients Uptake in Tetragonia Decumbens Mill. Cultivated under Different Fertigation Regimes in Hydroponics. Crop Pasture Sci. 2022, 73, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
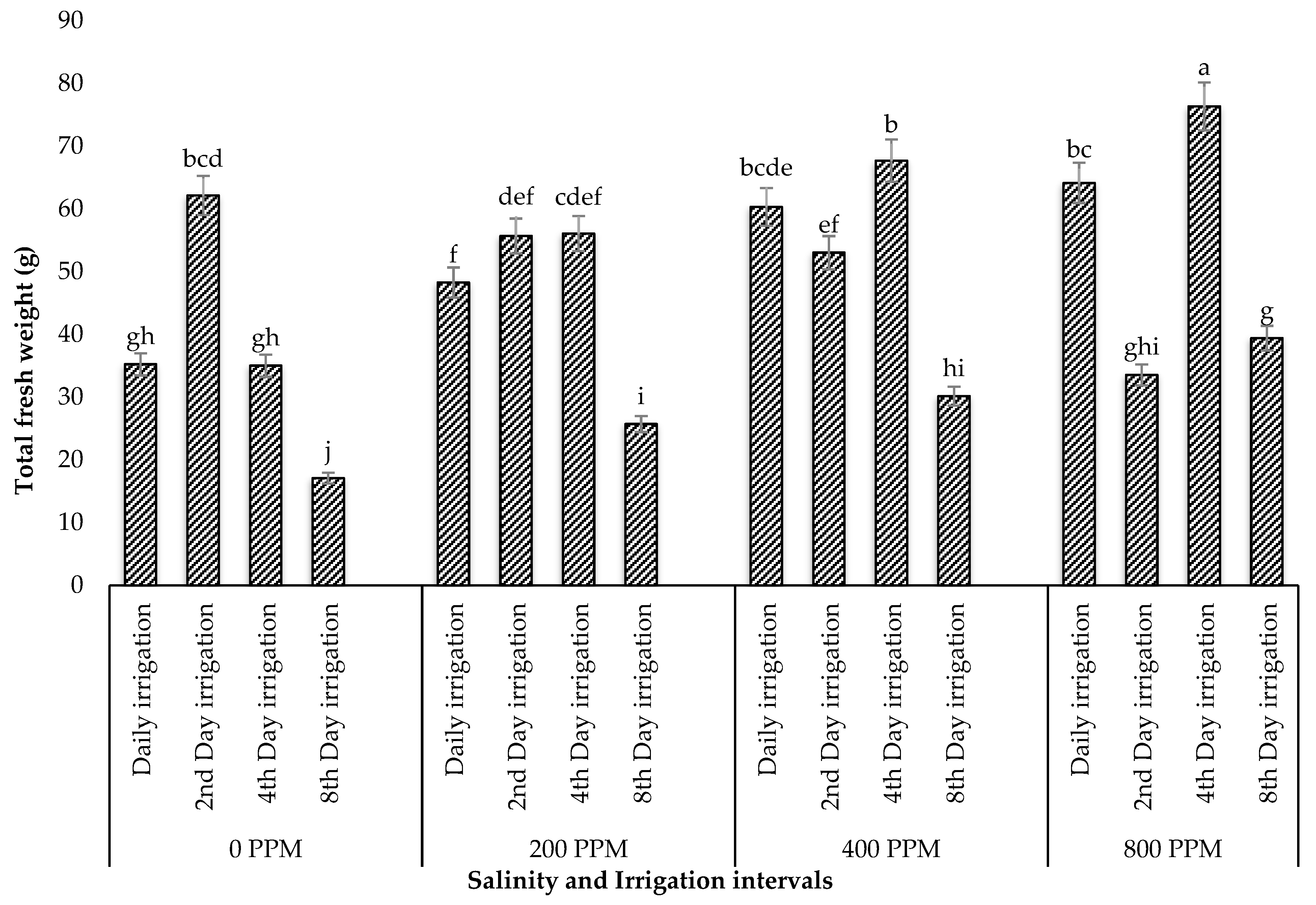
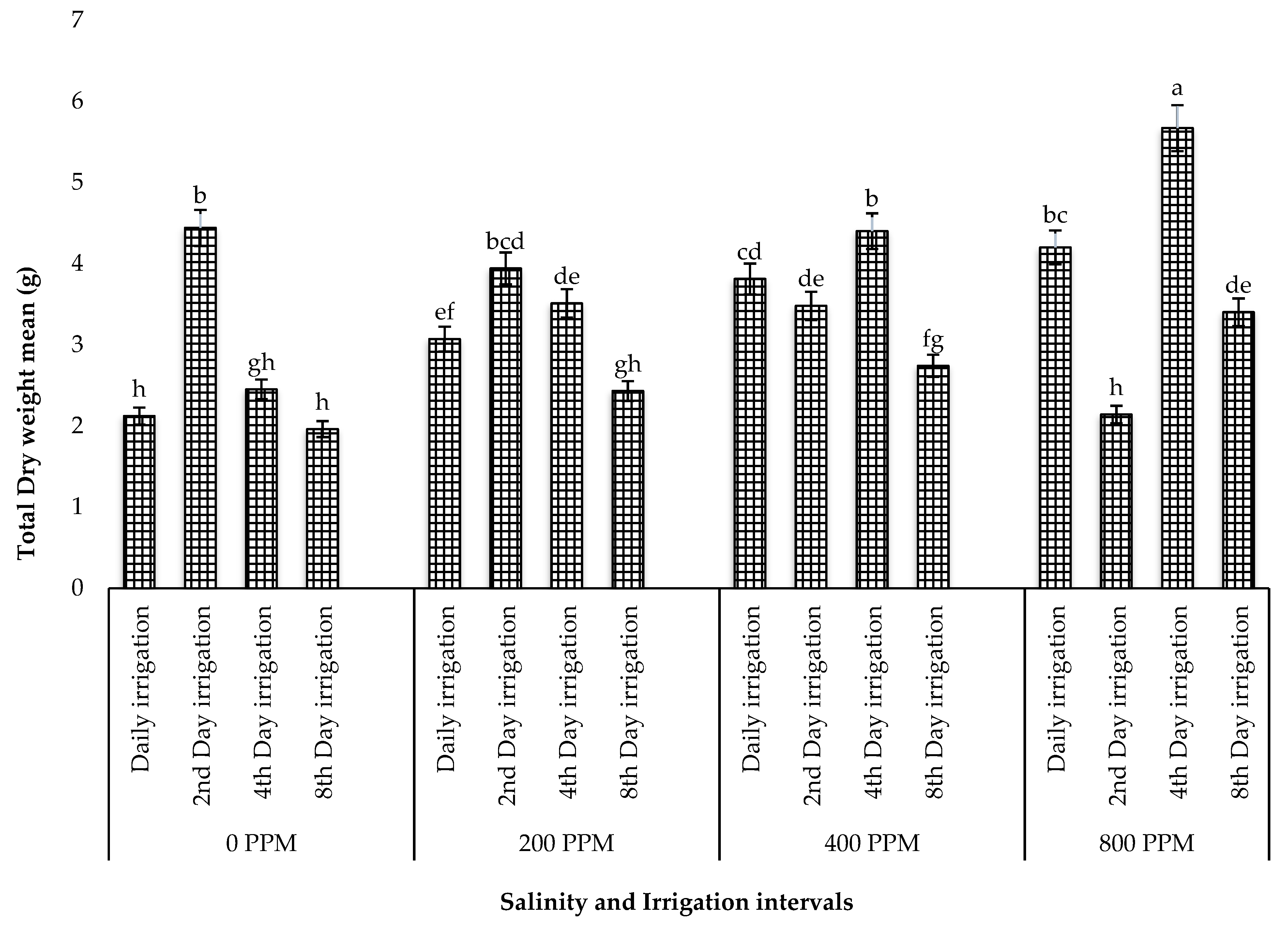
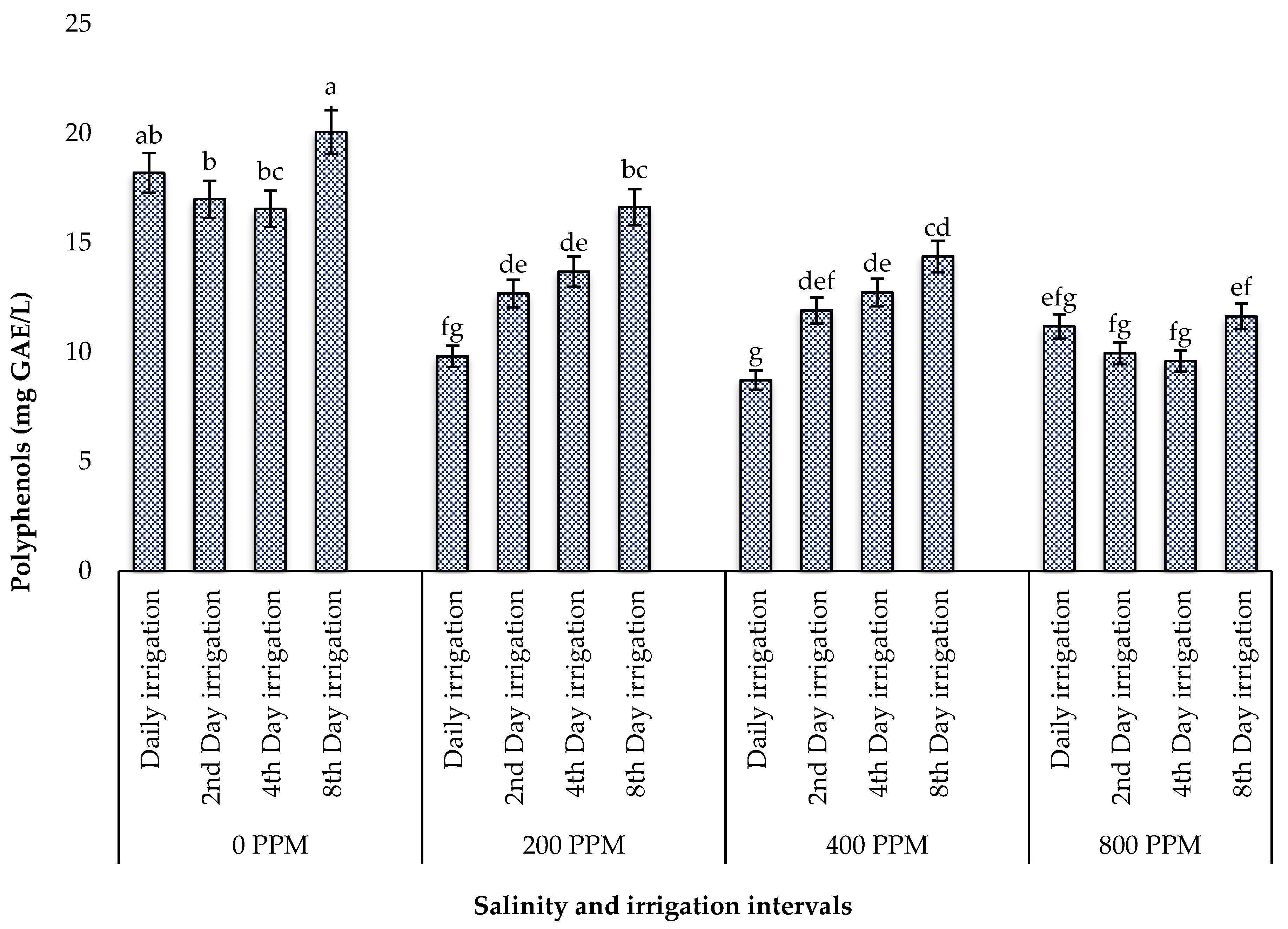
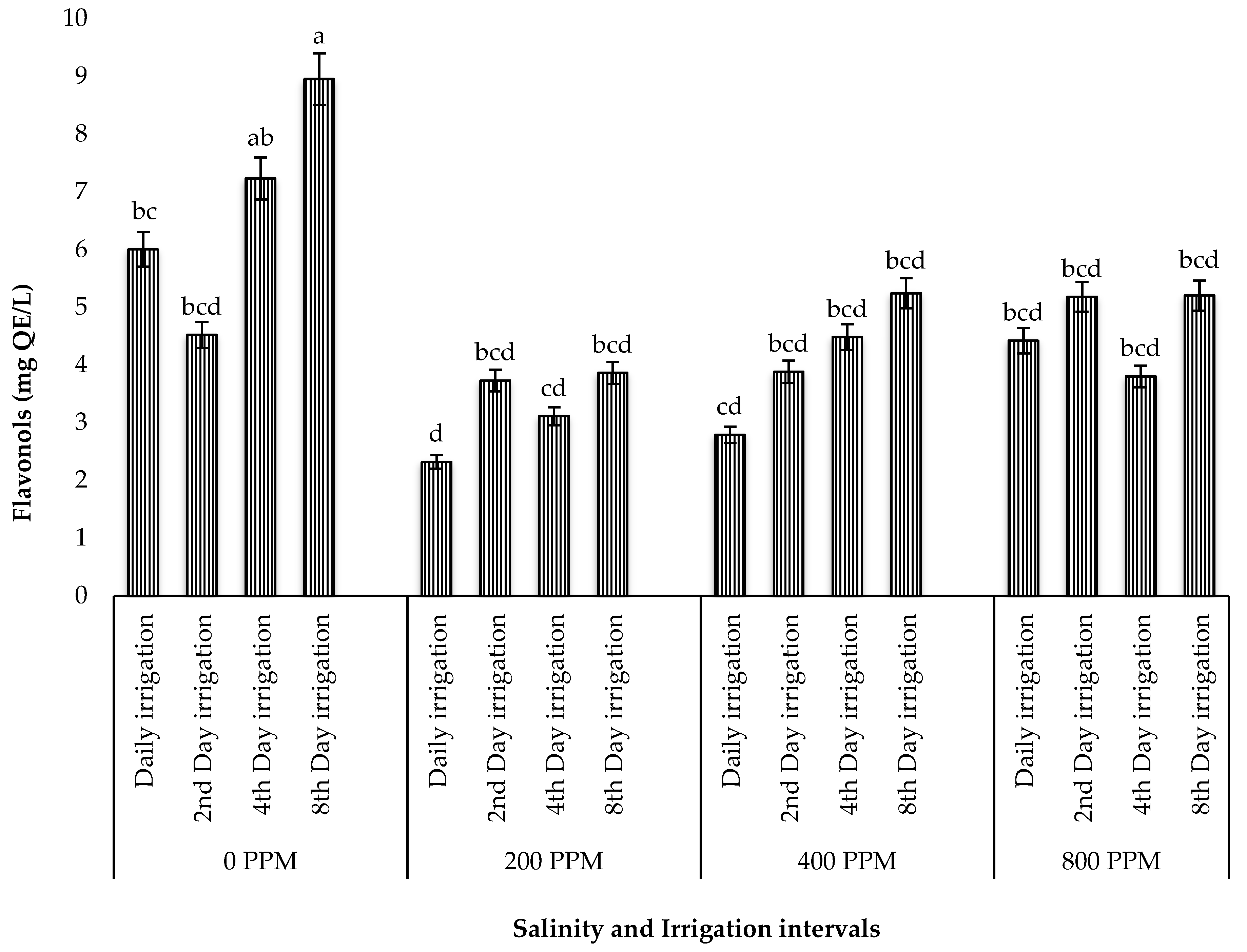
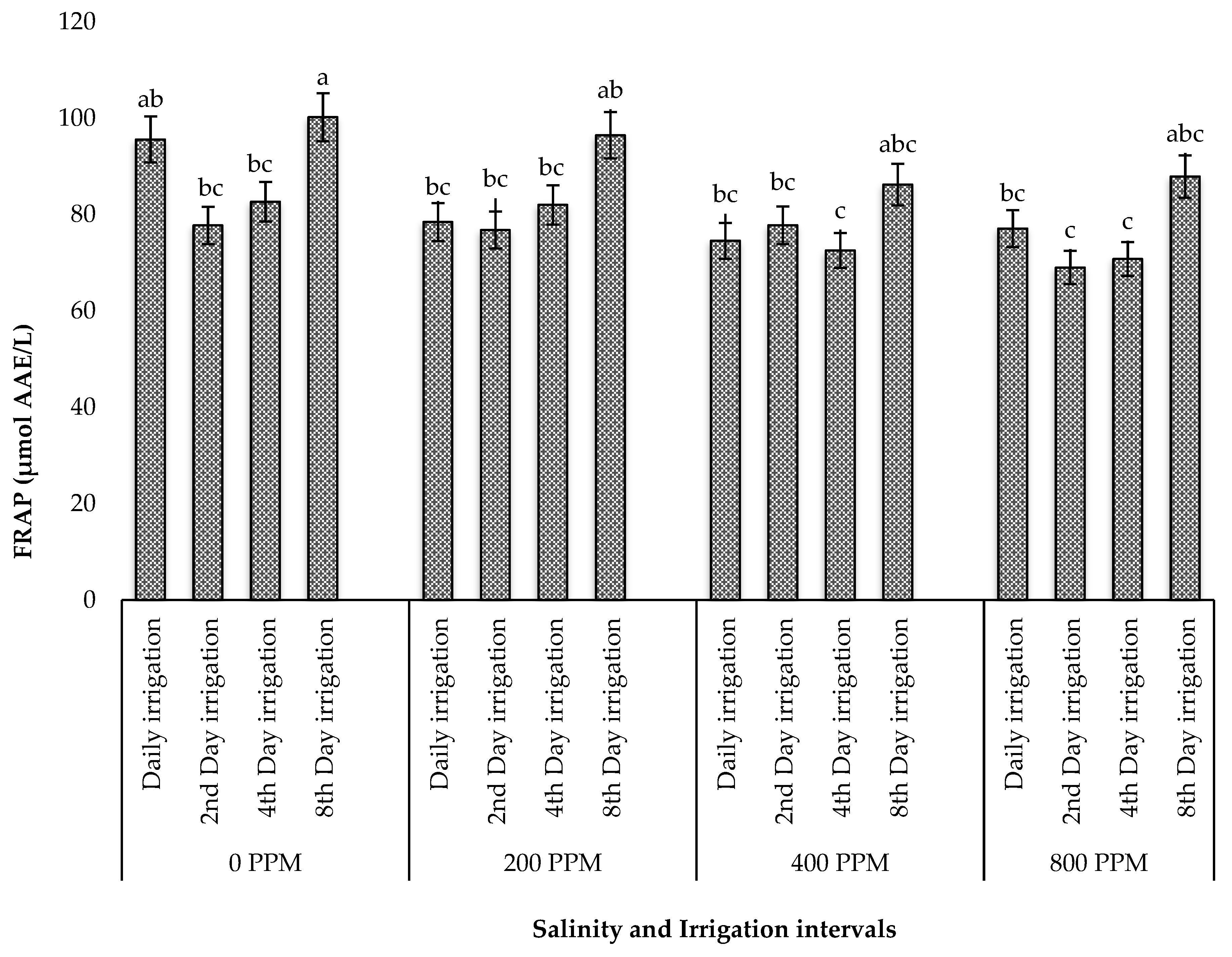
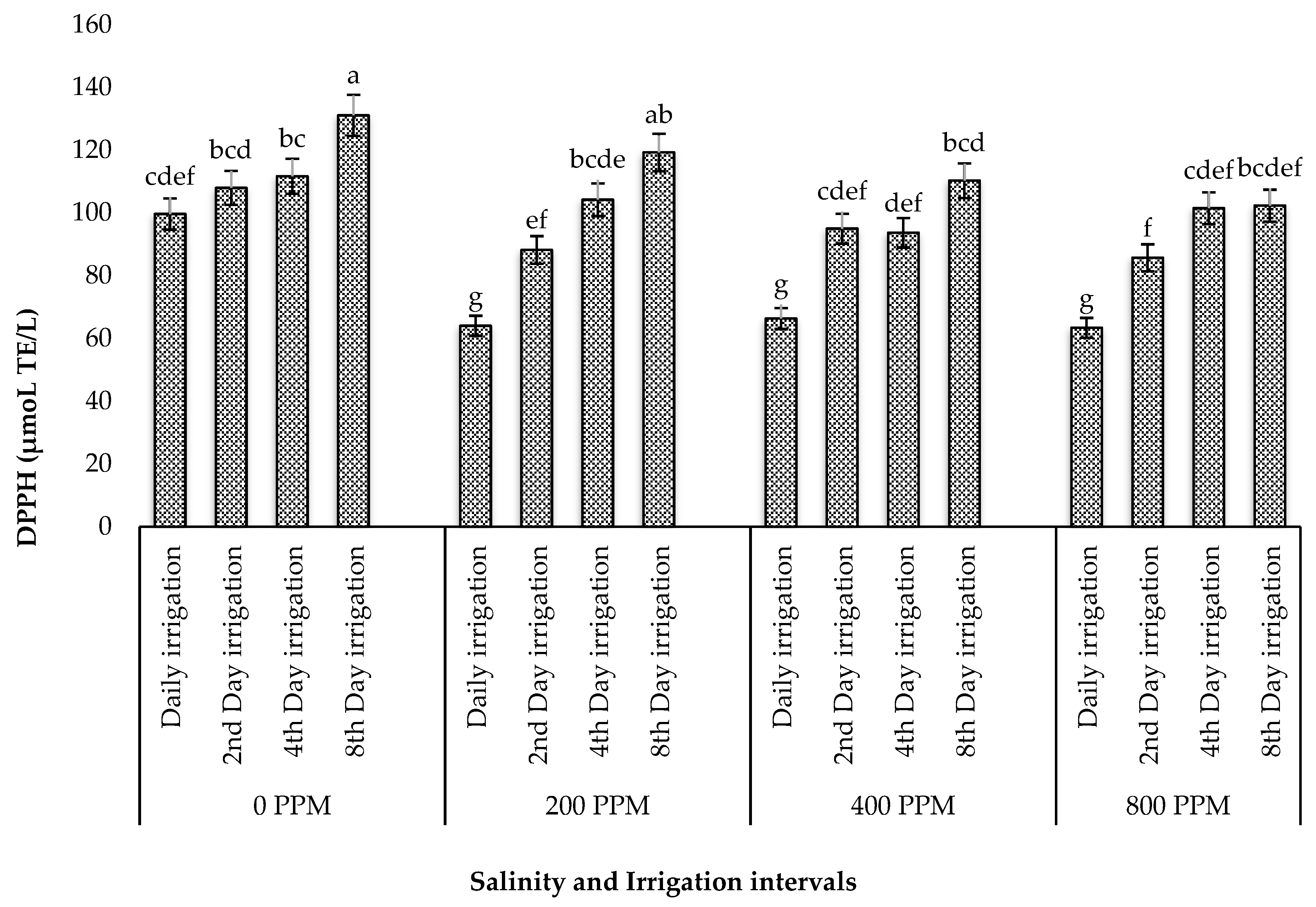
| Salt Concentration | Irrigation Interval | Leaf Length | Leaf Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ppm | Daily | 10.05 ± 0.97 | 12.00 ± 0.35 bcd |
| 2nd Day | 15.75 ± 0.93 | 12.42 ± 0.43 bc | |
| 4th Day | 12.58 ± 0.78 | 11.67 ± 0.48 bcd | |
| 8th Day | 10.75 ± 0.94 | 10.67 ± 0.28 cd | |
| 200 ppm | Daily | 11.83 ± 0.98 | 10.00 ± 0.01 d |
| 2nd Day | 13.50 ± 0.75 | 10.33 ± 0.23 cd | |
| 4th Day | 13.25 ± 1.05 | 10.67 ± 0.28 cd | |
| 8th Day | 12.33 ± 0.98 | 10.50 ± 0.26 cd | |
| 400 ppm | Daily | 10.92 ± 0.61 | 11.33 ± 0.62 bcd |
| 2nd Day | 11.75 ± 0.96 | 10.83 ± 0.52 cd | |
| 4th Day | 12.08 ± 1.33 | 13.17 ± 0.76 ab | |
| 8th Day | 11.33 ± 0.91 | 10.00 ±0.01 d | |
| 800 ppm | Daily | 12.33 ± 0.76 | 11.50 ± 0.44 bcd |
| 2nd Day | 12.92 ± 0.80 | 10.67 ± 0.57 cd | |
| 4th Day | 13.00 ± 1.03 | 14.75 ± 0.79 a | |
| 8th Day | 10.50 ± 1.06 | 11.50 ± 0.50 bcd | |
| Two-way ANOVA F-Statistic | |||
| Irrigation | 5.5 * | 12.6 * | |
| Salinity | 1.1 ns | 10.1 * | |
| Salinity × Irrigation | 1.4 ns | 4.6 * | |
| Salt Concentration | Irrigation Intervals | Week 2 | Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ppm | Daily | 0.97 ± 0.01 c | 1.01 ± 0.01 bcd | 1.03 ± 0.01 | 1.14 ± 0.01 cd |
| 2nd Day | 0.97 ± 0.04 c | 1.01 ± 0.01 bcd | 1.05 ± 0.01 | 1.16 ± 0.01 bc | |
| 4th Day | 1.13 ± 0.01 a | 1.14 ± 0.02 a | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 1.24 ± 0.01 a | |
| 8th Day | 1.03 ± 0.01 abc | 1.03 ± 0.02 abcd | 1.05 ± 0.01 | 1.22 ± 0.01 ab | |
| 200 ppm | Daily | 0.97 ± 0.01 c | 1.02 ± 0.04 abcd | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 1.05 ± 0.02 e |
| 2nd Day | 1.00 ± 0.01 c | 1.00 ± 0.01 cd | 1.01 ± 0.00 | 1.09 ± 0.01 de | |
| 4th Day | 1.12 ± 0.01 ab | 1.12 ± 0.01 ab | 1.01 ± 0.02 | 1.08 ± 0.01 de | |
| 8th Day | 1.04 ± 1.01 abc | 1.04 ± 0.01 abcd | 1.03 ± 0.01 | 1.10 ± 0.01 cd | |
| 400 ppm | Daily | 0.98 ± 0.01 c | 0.98 ± 0.01 d | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 1.08 ± 0.01 de |
| 2nd Day | 1.05 ± 0.01 abc | 1.05 ± 0.01 abcd | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 1.05 ± 0.01 e | |
| 4th Day | 1.00 ± 0.01 bc | 1.10 ± 0.07 abc | 1.01 ± 0.01 | 1.05 ± 0.01 e | |
| 8th Day | 1.03 ± 0.01 abc | 1.03 ± 0.01 abcd | 1.04 ± 0.01 | 1.14 ± 0.01 cd | |
| 800 ppm | Daily | 1.05 ± 0.07 abc | 0.98 ± 0.01 d | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 1.09 ± 0.01 de |
| 2nd Day | 1.07 ± 0.01 abc | 1.08 ± 0.01 abcd | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 1.09 ± 0.01 de | |
| 4th Day | 1.01 ± 0.01 bc | 1.03 ± 0.01 abcd | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 1.06 ± 0.01 de | |
| 8th Day | 1.01 ± 0.01 bc | 1.03 ± 0.01 abcd | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 1.01 ± 0.01 e | |
| Two-way ANOVA F-Statistic | |||||
| Irrigation | 6.12 * | 12.01 * | 2.26 * | 23.8 * | |
| Salinity | 0.59 ns | 0.48 ns | 7.8 ns | 58.8 * | |
| Salinity × Irrigation | 4.80 * | 2.46 * | 1.70 ns | 6.8 * | |
| Salt Concentrations | Irrigation Intervals | Nitrogen (mg/100 g) | Phosphorus (mg/100 g) | Potassium (mg/100 g) | Calcium (mg/100 g) | Magnesium (mg/100 g) | K/Ca + Mg (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ppm | Daily | 1978 ± 8.30 | 330 ± 2.61 | 7090 ± 12.11 | 2115 ± 0.12 ab | 640 ± 2.11 | 1150 ± 0.05 cd |
| 2nd day | 2049 ± 9.61 | 330 ± 2.89 | 8525 ± 14.14 | 2095 ± 0.11 abc | 740 ± 2.76 | 1315 ± 1.10 a–d | |
| 4th day | 2129 ± 12.61 | 310 ± 1.88 | 7880 ± 11.35 | 1800 ± 0.27 a–d | 745 ± 1.89 | 1330 ± 0.02 a–d | |
| 8th day | 2440 ± 11.77 | 230 ± 2.59 | 9855 ± 9.22 | 1620 ± 0.05 a–d | 1135 ± 2.03 | 1450 ± 0.06 abc | |
| 200 ppm | Daily | 1784 ± 7.22 | 230 ± 2.84 | 3565 ± 8.25 | 930 ± 2.22 d | 370 ± 1.88 | 1190 ± 0.66 bcd |
| 2nd day | 1831 ± 5.72 | 200 ± 5.71 | 4910 ± 6.65 | 1215 ± 1.88 bcd | 450 ± 1.37 | 1285 ± 0.98 bcd | |
| 4th day | 1868 ± 11.5 | 270 ± 3.22 | 6330 ± 1.22 | 1300 ± 2.44 a–d | 630 ± 0.88 | 1390 ± 1.89 a–d | |
| 8th day | 2294 ± 6.33 | 165 ± 1.98 | 8790 ± 3.72 | 1305 ± 2.88 a–d | 980 ± 3.11 | 1540 ± 2.65 ab | |
| 400 ppm | Daily | 1648 ± 8.22 | 180 ± 2.88 | 3310 ± 1.58 | 905 ± 2.55 d | 340 ± 1.75 | 1155 ± 1.87 cd |
| 2nd day | 1698 ± 6.21 | 130 ± 2.11 | 4095 ± 1.93 | 1010 ± 3.78 bcd | 395 ± 1.22 | 1265 ± 2.65 bcd | |
| 4th day | 1676 ± 11.3 | 335 ± 1.88 | 6995 ± 2.08 | 2350 ± 4.11a | 675 ± 1.99 | 1060 ± 2.88 d | |
| 8th day | 2025 ± 8.66 | 120 ± 1.74 | 7500 ± 0.97 | 750 ± 2.58 d | 870 ± 1.55 | 1435 ± 3.11 abc | |
| 800 ppm | Daily | 1567 ± 7.55 | 165 ± 1.88 | 3170 ± 4.33 | 950 ± 3.88 d | 340 ± 2.76 | 1080 ± 1.98 cd |
| 2nd day | 1612 ± 12.25 | 130 ± 2.30 | 3870 ± 8.14 | 860 ± 4.01 d | 345 ± 2.31 | 1395 ± 1.66 a–d | |
| 4th day | 1581 ± 11.21 | 210 ± 2.91 | 4540 ± 3.98 | 1340 ± 2.94 a–d | 520 ± 1.89 | 1055 ± 2.89 d | |
| 8th day | 1888 ± 9.22 | 115 ± 1.82 | 7070 ± 2.38 | 985 ± 1.96 cd | 725 ± 2.11 | 1660 ± 2.11 a | |
| Two-way ANOVA F-Statistic | |||||||
| Irrigation | 73.9 * | 11.1 * | 27.2 * | 5.9 * | 95.3 * | 25.5 * | |
| Salinity | 93.4 * | 15.8 * | 23.1 * | 15.4 * | 37.1 * | 2.4 ns | |
| Salinity × Irrigation | 0.1 ns | 1.8 ns | 1.4 ns | 3.8 * | 1.9 ns | 2.8 * | |
| Salt Concentrations | Irrigation Intervals | Mn (mg/100 g) | Fe (mg/100 g) | Zn (mg/100 g) | Cu (mg/100 g) | Na (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ppm | Daily | 5.35 ± 0.02 | 43.35 ± 1.05 bc | 11.7 ± 0.01 | 1.05 ± 0.001 | 3135 ± 1.10 |
| 2nd day | 9.65 ± 0.31 | 57.55 ± 2.08 b | 14.25 ± 0.02 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 2290 ± 1.98 | |
| 4th day | 11.07 ± 0.06 | 44 ± 0.85 bc | 14.55 ± 0.011 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 5510 ± 1.11 | |
| 8th day | 15.70 ± 0.01 | 59.10 ± 0.140 b | 16.45 ± 0.11 | 0.1 ± 0.08 | 2235 ± 1.20 | |
| 200 ppm | Daily | 6.40 ± 0.09 | 37.15 ± 0.18 bc | 9.45 ± 0.05 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 10,099 ± 0.11 |
| 2nd day | 9.35 ± 0.066 | 37.15 ± 0.12 bc | 13.45 ± 0.52 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 9190 ± 0.21 | |
| 4th day | 9.25 ± 0.09 | 32.40 ± 0.17 bc | 11.80 ± 0.02 | 0 ± 0.00 | 11,100 ± 0.22 | |
| 8th day | 14.30 ± 0.08 | 80.4 ± 0.21 a | 16.45 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 9975 ± 0.18 | |
| 400 ppm | Daily | 6.30 ± 0.05 | 40.35 ± 0.14 bc | 9.65 ± 0.09 | 0.1 ± 0.02 | 11,115 ± 0.52 |
| 2nd day | 11.05 ± 0.05 | 55.15 ± 0.09 b | 11.95 ± 0.21 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 10,535 ± 0.91 | |
| 4th day | 8.75 ± 0.02 | 60.65 ± 0.10 b | 13 ± 0.05 | 0 ± 0.00 | 7120 ± 0.87 | |
| 8th day | 15.20 ± 0.25 | 57.75 ± 0.09 b | 19.15 ± 0.15 | 0.1 ± 0.001 | 9875 ± 0.66 | |
| 800 ppm | Daily | 6.65 ± 0.02 | 40.70 ± 0.11 bc | 8.60 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.001 | 11,605 ± 0.47 |
| 2nd day | 8.40 ± 0.12 | 37.50 ± 0.08 bc | 10.15 ± 0.22 | 0.15 ± 0.001 | 11,350 ± 0.57 | |
| 4th day | 9.60 ± 0.28 | 37.10 ± 0.11 bc | 9.20 ± 0.11 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 14,530 ± 0.66 | |
| 8th day | 15.35 ± 0.03 | 57.75 ± 0.13 b | 17.55 ± 0.12 | 0 ± 0.00 | 13,980 ± 1.52 | |
| Two-way ANOVA F-Statistic | ||||||
| Irrigation | 40.8 * | 12 * | 36.3 * | 4.1 * | 1.01 ns | |
| Salinity | 0.2 ns | 3.2 ns | 5.3 * | 5.3 * | 1 ns | |
| Salinity × Irrigation | 0.8 ns | 6.2 * | 0.2 ns | 2.1 ns | 1 ns | |
| Salt Concentrations | Irrigation Intervals | ADF (%) | Ash (%) | Crude Fat (%) | Moisture (%) | NDF (%) | Protein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ppm | Daily | 20.26 ± 0.99 ab | 37.22 ± 2.01 | 2.03 ± 0.02 a | 8.36 ± 0.22 | 27.48 ± 0.96 | 12.37 ± 0.02 |
| 2nd day | 23.42 ± 0.90 a | 37.61 ± 1.66 | 1.73 ± 0.021 abc | 7.98 ± 0.05 | 29.63 ± 1.03 | 12.81 ± 0.80 | |
| 4th day | 19.86 ± 0.94 ab | 35.67 ± 1.55 | 1.76 ± 0.06 ab | 8.39 ± 0.20 | 26.09 ± 1.09 | 13.31 ± 0.06 | |
| 8th day | 24.21 ± 0.38 a | 40.29 ± 1.91 | 1.86 ± 0.01 ab | 7.7 ± 0.09 | 29.83 ± 1.22 | 15.26 ± 0.90 | |
| 200 ppm | Daily | 16.72 ± 1.35 bc | 43.26 ± 0.02 | 1.50 ± 0.012 bcd | 10.09 ± 0.63 | 21.84 ± 0.09 | 11.15 ± 0.61 |
| 2nd day | 18.36 ± 0.99 bc | 44.94 ± 0.25 | 1.38 ± 0.03 cd | 8.64 ± 0.111 | 24.46 ± 0.22 | 11.44 ± 0.67 | |
| 4th day | 17.61 ± 1.49 bc | 42.38 ± 2.11 | 1.49 ± 0.61 bcd | 9.42 ± 1.00 | 23.94 ± 0.00 | 11.67 ± 0.08 | |
| 8th day | 19.89 ± 1.65 ab | 41.83 ± 2.03 | 1.7 ± 0.066 abc | 8.85 ± 0.28 | 26.57 ± 0.11 | 14.34 ± 1.61 | |
| 400 ppm | Daily | 17.03 ± 1.01 bc | 45.41 ± 2.27 | 1.17 ± 0.02 d | 10.77 ± 0.08 | 22.15 ± 1.011 | 10.30 ± 0.91 |
| 2nd day | 16.12 ± 1.09 bc | 46.35 ± 1.83 | 1.21 ± 0.023 d | 9.44 ± 0.22 | 21.83 ± 0.88 | 10.62 ± 0.08 | |
| 4th day | 16.47 ± 2.09 bc | 46.81 ± 1.67 | 1.42 ± 0.071 bcd | 8.86 ± 0.023 | 21.87 ± 0.08 | 10.48 ± 0.06 | |
| 8th day | 16.89 ± 1.00 bc | 46.77 ± 2.32 | 1.64 ± 0.25 abc | 8.61 ± 0.09 | 23.65 ± 0.13 | 12.66 ± 0.21 | |
| 800 ppm | Daily | 15.98 ± 2.331 bc | 48.11 ± 1.20 | 1.22 ± 0.01 d | 9.24 ± 0.22 | 20.73 ± 0.32 | 9.78 ± 1.22 |
| 2nd day | 16.34 ± 1.22 bc | 48.18 ± 2.99 | 1.15 ± 0.031 d | 9.31 ± 0.61 | 21.95 ± 1.22 | 10.07 ± 0.33 | |
| 4th day | 17.8 ± 1.49 bc | 52.51 ± 1.85 | 1.32 ± 0.02 cd | 8.63 ± 0.08 | 22.42 ± 2.11 | 9.88 ± 0.51 | |
| 8th day | 14.54 ± 0.89 c | 45.71 ± 1.367 | 1.16 ± 0.111 d | 8.62 ± 1.00 | 20.48 ± 1.33 | 11.81 ± 0.15 | |
| Two-way ANOVA F-Statistic | |||||||
| Irrigation | 2.1 ns | 1.3 ns | 7.9 * | 9.6 * | 5 * | 73.9 * | |
| Salinity | 38.2 * | 42.8 * | 48.2 * | 4.8 * | 53.8 * | 93.4 * | |
| Salinity × Irrigation | 3.3 * | 2.4 ns | 4.1 * | 1.5 ns | 2.5 ns | 0.9 ns | |
| Treatments | Two-Way ANOVA F-Statistic | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Fresh Weight | Total Dry Weight | Total Polyphenols | Total Flavonols | FRAP Capacity | DPPH Capacity | |
| Irrigation | 79.03 * | 70.52 * | 166.90 * | 17.26 * | 7.30 * | 43.98 * |
| Salinity | 255.72 * | 98.50 * | 40.89 * | 5.47 * | 13.10 * | 115.76 * |
| Salinity × Irrigation | 60.37 * | 78.61 * | 9.36 * | 1.97 * | 1.01 * | 4.10 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mndi, O.; Sogoni, A.; Jimoh, M.O.; Wilmot, C.M.; Rautenbach, F.; Laubscher, C.P. Interactive Effects of Salinity Stress and Irrigation Intervals on Plant Growth, Nutritional Value, and Phytochemical Content in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051026
Mndi O, Sogoni A, Jimoh MO, Wilmot CM, Rautenbach F, Laubscher CP. Interactive Effects of Salinity Stress and Irrigation Intervals on Plant Growth, Nutritional Value, and Phytochemical Content in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. Agriculture. 2023; 13(5):1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051026
Chicago/Turabian StyleMndi, Okuhle, Avela Sogoni, Muhali Olaide Jimoh, Carolyn Margaret Wilmot, Fanie Rautenbach, and Charles Petrus Laubscher. 2023. "Interactive Effects of Salinity Stress and Irrigation Intervals on Plant Growth, Nutritional Value, and Phytochemical Content in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L." Agriculture 13, no. 5: 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051026
APA StyleMndi, O., Sogoni, A., Jimoh, M. O., Wilmot, C. M., Rautenbach, F., & Laubscher, C. P. (2023). Interactive Effects of Salinity Stress and Irrigation Intervals on Plant Growth, Nutritional Value, and Phytochemical Content in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. Agriculture, 13(5), 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051026








