Effect of Gender and Muscle Type on Fatty Acid Profile, Sanogenic Indices, and Instrumental and Sensory Analysis of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Meat
2.2. The Fatty Acids Content
2.3. Health Lipid Indices Calculation
2.4. Instrumental and Sensory Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Fatty Acids Content and Sanogenic Indices of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat
3.2. The Instrumental Assessment of Rabbit Meat
3.2.1. The Texture Parameters of Rabbit Meat
3.2.2. The Color Parameters of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat
3.3. The Sensory Parameters of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat
4. Discussion
4.1. The Fatty Acids Content and Sanogenic Indices of FG Rabbit Meat
4.2. The Instrumental Assessment of FG Rabbit Meat
4.2.1. The Texture Parameters of FG Rabbit Meat
4.2.2. The Color Parameters of FG Rabbit Meat
4.3. The Sensory Parameters of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat
4.4. Recommendation of Rabbit Breeding and Meat Consumption
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalle Zotte, A.; Szendro, Z. The role of rabbit meat as functional food. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves dos Santos, J.J.; Fonseca Pascoal, L.A.; Brandão Grisi, C.V.; Costa Santos, V.; Santana Neto, D.C.; Filho, J.J.; Ferreira Herminio, M.P.; Fabricio Dantas, A. Soybean oil and selenium yeast levels in the diet of rabbits on performance, fatty acid profile, enzyme activity and oxidative stability of meat. Livest. Sci. 2022, 263, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzaida, M.D.; Resconi, V.C.; Gimeno, D.; Romero, J.V.; Calanche, J.B.; Barahona, M.; Olleta, J.L.; María, G.A. Effect of Dietary Grape Pomace on Fattening Rabbit Performance, Fatty Acid Composition, and Shelf Life of Meat. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Naeem, H.H.S.; Sallam, K.I.; Zaki, H.M.B.A. Effect of Different Cooking Methods of Rabbit Meat on Topographical Changes, Physicochemical Characteristics, Fatty Acids Profile, Microbial Quality and Sensory Attributes. Meat Sci. 2021, 181, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, C.M.; Almeida, M.; Closson, M.; Garcia-Santos, S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Domínguez, R.; Ferreira, L.; Trindade, H.; Silva, S.; Pinheiro, V. Effect of Total Replacement of Soya Bean Meal by Whole Lupine Seeds and of Gender on the Meat Quality and Fatty Acids Profile of Growing Rabbits. Foods 2022, 11, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, P.; Cesari, V.; Blasco, A. Effect of genetic rabbit lines on lipid content, lipolytic activities and fatty acid composition of hind leg meat and perirenal fat. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutautaitė, M.; Racevičiūtė-Stupelienė, A.; Bliznikas, S.; Vilienė, V. Enhancement of Rabbit Meat Functionality by Replacing Traditional Feed Raw Materials with Alternative and More Sustainable Freshwater Cladophora glomerata Macroalgal Biomass in Their Diets. Foods 2023, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birolo, M.; Xiccato, G.; Bordignon, F.; Dabbou, S.; Zuffellato, A.; Trocino, A. Growth Performance, Digestive Efficiency, and Meat Quality of Two Commercial Crossbred Rabbits Fed Diets Differing in Energy and Protein Levels. Animals 2022, 12, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, M. A comparison of the carcass traits and meat quality of conventionally and organically produced rabbits. Livest. Sci. 2008, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomeño, C.; Blasco, A.; Hernandez, P. Divergent selection for intramuscular fat content in rabbits. II. Correlated responses on carcass and meat quality traits. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4532–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Álvaro, M.; Hernandez, P.; Agha, S.; Blasco, A. Correlated responses to selection for intramuscular fat in several muscles in rabbits. Meat Sci. 2018, 139, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Álvaro, M.; Hernandez, P.; Blasco, A. Divergent selection on intramuscular fat in rabbits: Responses to selection and genetic parameters. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Madrid, B.S.; Varona, L.; Blasco, A.; Hernandez, P.; Casto-Rebollo, C.; Ibáñez-Escriche, N. The effect of divergent selection for intramuscular fat on the domestic rabbit genome. Animal 2020, 14, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle Zotte, A. Rabbit Farming for Meat Purposes. Anim. Front. 2014, 4, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeanu, D.; Creanga, S.; Cristina, S. Research on the meat quality produced by Polyodon Spathula sturgeons’ species related to human nutritional requirements. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 10, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Simeanu, D.; Radu-Rusu, R.-M.; Mintas, O.S.; Simeanu, C. Qualitative and Nutritional Evaluation of Paddlefish (Polyodon spathula) Meat Production. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, E.; Bampidis, V.A.; Păcală, N.; Pentea, M.; Tozer, J.; Prundeanu, H. Nutrient Content of Rabbit Meat as Compared to Chicken, Beef and Pork Meat. J. Anim. Prod. Adv. 2013, 3, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, A.; Nagy, I.; Hernández, P. Genetics of growth, carcass and meat quality in rabbits. Meat Sci. 2018, 145, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bayomi, R.M.; Shata, R.H.M.; Mahmoud, A. Effects of edible chitosan coating containing Salvia rosmarinus essential oil on quality characteristics and shelf life extension of rabbit meat during chilled storage. Food Meas. 2023, 17, 2464–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullere, M.; Zotte, A.D.; Tasoniero, G.; Giaccone, V.; Szendro, Z.; Szín, M.; Odermatt, M.; Gerencsér, Z.; Dal Bosco, A.; Matics, Z. Effect of diet and packaging system on the microbial status, pH, color and sensory traits of rabbit meat evaluated during chilled storage. Meat Sci. 2018, 141, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, A.A.; Osman, A.; Sitohy, M.; Gemiel, D.G.; El-Garhy, O.H.; Azab, I.H.E.; Fahim, N.H.; Abdelmoniem, A.M.; Mehana, A.E.; Imbabi, T.A. Physiological Performance of Rabbits Administered Buffalo Milk Yogurts Enriched with Whey Protein Concentrate, Calcium Caseinate or Spirulina platensis. Foods 2021, 10, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, S.; Machado Duarte, J.M.; Castellinia, C.; D’Amato, R.; Regni, L.; Proietti, P.; Businelli, D.; Cotozzolo, E.; Rodrigues, M.; Dal Bosco, A. Use of olive leaves (whether or not fortified with sodium selenate) in rabbit feeding: Effect on performance, carcass and meat characteristics, and estimated indexes of fatty acid metabolism. Meat Sci. 2018, 143, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrica, M.; Menchetti, L.; Balzaretti, C.M.; Branciari, R.; Ranucci, D.; Cotozzolo, E.; Vigo, D.; Curone, G.; Brecchia, G.; Miraglia, D. Impact of Dietary Supplementation with Goji Berries (Lycium barbarum) on Microbiological Quality, Physico-Chemical, and Sensory Characteristics of Rabbit Meat. Foods 2020, 9, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menchetti, L.; Vecchione, L.; Filipescu, I.; Petrescu, V.F.; Fioretti, B.; Beccari, T.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Codini, M.; Quattrone, A.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M.; et al. Effects of Goji berries supplementation on the productive performance of rabbit. Livest. Sci. 2019, 220, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchetti, L.; Brecchia, G.; Branciari, R.; Barbato, O.; Fioretti, B.; Codini, M.; Bellezza, E.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M.; Miraglia, D. The effect of Goji berries (Lycium barbarum) dietary supplementation on rabbit meat quality. Meat Sci. 2020, 161, 108018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menchetti, L.; Canali, C.; Castellini, C.; Boiti, C.; Brecchia, G. The different effects of linseed and fish oil supplemented diets on insulin sensitivity of rabbit does during pregnancy. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 118, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle Zotte, A.; Cullere, M.; Tasoniero, G.; Gerencsér, Z.; Szendrő, Z.; Novelli, E. Matics Supplementing growing rabbit diets with chestnut hydrolyzable tannins: Effect on meat quality and oxidative status, nutrient digestibilities, and content of tannin metabolites. Meat Sci. 2018, 146, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Petracci, M.; Cavani, C. Effects of dietary inclusion of dehydrated lucerne and whole linseed on rabbit meat quality. World Rabbit Sci. 2006, 14, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dalle Zotte, A.; Singh, Y.; Gerencser, Z.; Matics, Z.; Szendro, Z.; Cappellozza, S.; Cullere, M. Feeding silkworm (Bombyx mori L.) oil to growing rabbits improves the fatty acid composition of meat, liver and perirenal fat. Meat Sci. 2022, 193, 108944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszkiewicz, T.; Gugołek, A. A Comparison of the Quality of Meat from Female and Male Californian and Flemish Giant Gray Rabbits. Animals 2020, 10, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabrout, K.; Khalifah, A.; Ciani, F. Current Applications and Trends in Rabbit Nutraceuticals. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamaratskaia, G.; Havrysh, O.; Korzeniowska, M.; Getya, A. Potential and limitations of rabbit meat in maintaining food security in Ukraine. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Huang, M.; Zhou, G. Differences in physicochemical and nutritional properties of breast and thigh meat from crossbred chickens, commercial broilers and spent hens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmons, J.S.; Weiss, W.P.; Palmquist, D.L.; Harper, W.J. Relationships among dietary roasted soybeans, milk components, and spontaneous oxidized flavor of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, T.L.V.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary heart disease: Seven dietary factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.; Ordóñez, J.A.; Cambero, I.; Santos, C.; Pin, C.; De La Hoz, L. Fatty acid compositions of selected varieties of Spanish dry ham related to their nutritional implications. Food Chem. 2007, 9, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierliță, D.; Pop, I.M.; Lup, F.; Simeanu, D.; Vicas, S.I.; Simeanu, C. The Fatty Acids Composition and Health Lipid Indices in the Sheep Raw Milk Under a Pasture-Based Dairy System. J. Chem. 2018, 69, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struți, D.I.; Mierliță, D.; Simeanu, D.; Pop, I.M.; Socol, C.T.; Papuc, T.; Macri, A.M. The effect of dehulling lupine seeds (Lupinus albus L.) from low-alkaloid varieties on the chemical composition and fatty acids content. J. Chem. 2020, 71, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wereńska, M.; Haraf, G.; Wołoszyn, J.; Goluch, Z.; Okruszek, A.; Teleszko, M. Fatty acid profile and health lipid indicies of goose meat in relation to various types of heat treatment. Poultry Sci. 2021, 100, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariño, B.; Hernández, P.; Pla, M.; Blasco, A. Comparison between rabbit lines for sensory meat quality. Meat Sci. 2007, 75, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, O.C.; Murariu, F.; Frunză, G.; Ciobanu, M.M.; Boișteanu, P.C. Fatty Acid Indices and the Nutritional Properties of Karakul Sheep Meat. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.A.; Kim, H.J.; Jayasena, D.D.; Jo, C. On-Farm and Processing Factors Affecting Rabbit Carcass and Meat Quality Attributes. Food Sci. Anim. Res. 2023, 43, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Bosco, A.; Mugnai, C.; Roscini, V.; Mattioli, S.; Ruggeri, S.; Castellini, C. Effect of Dietary Alfalfa on the Fatty Acid Composition and Indexes of Lipid Metabolism of Rabbit Meat. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbou, S.; Gai, F.; Renna, M.; Rotolo, L.; Dabbou, S.; Lussiana, C.; Kovitvadhi, A.; Brugiapaglia, A.; De Marco, M.; Helal, A.N.; et al. Inclusion of bilberry pomace in rabbit diets: Effects on carcass characteristics and meat quality. Meat Sci. 2017, 124, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agata, M.; Preziuso, G.; Russo, C.; Dalle Zotte, A.; Mourvaki, E.; Paci, G. Effect of an outdoor rearing system on the welfare, growth performance, carcass and meat quality of a slow-growing rabbit population. Meat Sci. 2009, 83, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasinska, E.; Czarniecka-Skubina, E.; Rutkowska, J. Fatty acid and lipid contents differentiation in cuts of rabbit meat. CyTA J. Food 2018, 16, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.C.; van Schalkwyk, D.L.; Muller, M.; Needham, T.; McMillin, K.W. Carcass Yields and Physical-Chemical Meat Quality Characteristics of Namibian Red Hartebeest (Alcelaphus buselaphus) as Influenced by Sex and Muscle. Foods 2021, 10, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, M.M.; Postolache, A.N.; Lipșa, F.D.; Munteanu, M.; Rațu, R.N.; Murariu, O.C.; Boișteanu, P.C. Meat Fatty Acid Composition of Wild Boars Hunted in Romania in Relationship to Gender and Age-Class. Animals 2022, 12, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, P.; Zotte, A.D. Influence of diet on rabbit meat quality. In Nutrition of the Rabbit; de Blas, C., Wiseman, J., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2010; pp. 163–178. [Google Scholar]
- Dalle Zotte, A. Perception of Rabbit Meat Quality and Major Factors Influencing the Rabbit Carcass and Meat Quality. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 75, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Gai, F.; Gasco, L.; Brugiapaglia, A.; Lussiana, C.; Guo, K.J.; Tong, J.M.; Zaccarato, I. Effects of chestnut tannins on carcass characteristics, meat quality, lipid oxidation and fatty acid composition of rabbits. Meat Sci. 2009, 83, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, G.; Martínez, R.; Fradiletti, F.; Cozzano, S.; Repiso, L.; Márquez, R.; Ibáñez, F. Meat quality of rabbits reared with two different feeding strategies: With or without fresh alfalfa ad libitum. World Rabbit Sci. 2013, 21, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bosco, A.; Gerencsér, Z.; Szendrő, Z.; Mugnai, C.; Cullere, M.; Kovàcs, M.; Ruggeri, S.; Mattioli, S.; Castellini, C.; Dalle Zotte, A. Effect of dietary supplementation of Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) and Thyme (Thymus vulgaris) on rabbit meat appearance, oxidative stability and fatty acid profile during retail display. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Bosco, A.; Castellini, C.; Martino, M.; Mattioli, S.; Marconi, O.; Sileoni, V.; Ruggeri, S.; Tei, F.; Benincasa, P. The effect of dietary alfalfa and flax sprouts on rabbit meat antioxidant content, lipid oxidation and fatty acid composition. Meat Sci. 2015, 106, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Vale, M.I.; Cruz, M.; Bolsoni-Lopes, A.; Sa Paula de Andrade, R. Palmitoleic Acid (C16:1n7) Treatment Enhances Fatty Acid Oxidation and Oxygen Consumption in White Adipocytes. Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2015, 29 (Suppl. 1), 884.25. [Google Scholar]
- Betz, I.R.; Qaiyumi, S.J.; Goeritzer, M.; Thiele, A.; Brix, S.; Beyhoff, N.; Grune, J.; Klopfleisch, R.; Greulich, F.; Uhlenhaut, N.H.; et al. Cardioprotective Effects of Palmitoleic Acid (C16:1n7) in a Mouse Model of Catecholamine-Induced Cardiac Damage Are Mediated by PPAR Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.; Pla, M. Changes in collagen, texture and sensory properties of meat when selecting rabbits for growth rate. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Ramírez, J.A.; Pla, M.; Ariño, B.; Hernández, P.; Pascual, M.; Blasco, A.; Guerrero, L.; Hajós, G.; Szerdahelyi, E.N.; et al. Effect of selection for growth rate on the ageing of myofibrils, meat texture properties and the muscle proteolitic potential of m. Longissimus in rabbits. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, T.; Gasperlin, L.; Rajar, A.; Zlender, B. Influence of genotype lines, age at slaughter and sexes on the composition of rabbit meat. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 44, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, A.J.; Oliver, A.M.; Pla, M.; Guerrero, L.; Arino, B.; Blasco, A.; Pascual, M.; Gil, M. Effect of selection for growth rate on biochemical, quality and texture characteristics of meat from rabbits. Meat Sci. 2004, 67, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondret, F.; Combes, S.; Larzul, C.; Rochambeau, H. Effects of divergent selection for body weight at a fixed age on histological, chemical and rheological characteristics of rabbits muscles. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 76, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempa, T.; Bradley, G. Post-Mortem Energy Metabolites, Glycolytic Potential, and Meat Quality Attributes from of Dorper and Merino Lambs. Proceedings 2021, 73, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, J.H.; Choi, M.H.; Rhee, M.S.; Kim, B.C. Estimation of Sensory Pork Loin Tenderness Using Warner-Bratzler Shear Force and Texture Profile Analysis Measurements. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.R.G.; Robledo Torres Filho, A.; Cazedey, H.P.; Fontes, P.R.; Alcinéia-Ramos, L.S.; Ramos, E.M. Comparison of Warner–Bratzler shear force values between round and square cross-section cores from cooked beef and pork Longissimus muscle. Meat Sci. 2015, 103, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodová, D.; Tůmová, E.; Martinec, M.; Bízková, Z.; Skřivanová, V.; Volek, Z.; Zita, L. Effect of housing system and genotype on rabbit meat quality. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 59, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Elzo, M.A.; Jia, X.; Chen, S.; Lai, S. Comparison of Carcass and Meat Quality Traits among Three Rabbit Breeds. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziuso, G.; Dalle Zotte, A.; Paci, G. Meat traits of rabbits housed outdoors: Effect of stocking density. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, R.; López, M. Effect of electrical and mechanical stunning on bleeding, instrumental properties and sensory meat quality in rabbits. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołoszyn, J.; Haraf, G.; Okruszek, A.; Werenska, M.; Goluch, Z.; Teleszko, M. Fatty acid profiles and health lipid indices in the breast muscles of local Polish goose varieties. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bosco, A.D.; Castellini, C.; Bernardini, M. Nutritional quality of rabbit meat as affected by cooking procedure and dietary vitamin. Eur. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerto, M.; Cabrera, M.C.; Saadoun, A. A note of fatty acids profile of meat from broiler chickens supplemented with inorganic or organic selenium. Int. J. Food Sci. 2017, 2017, 7613069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiepko, N.; Chwastowska-Siwecka, I.; Kondratowicz, J.; Mikulski, D. Fatty acid profile, total cholesterol, vitamin content TBARS value of Turkey breast muscle cured with the addition lycopene. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapiye, C.; Chimonyo, M.; Dzama, K.; Hugo, A.; Strydom, P.E.; Muchenje, V. Fatty acid composition of beef from Nguni Steers supplemented with Acacia karroo leaf-meal. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, A.; Tyra, M.; Babicz, M. Fatty acid profile of pork from a local and a commercial breed. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2015, 58, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetín, M.; Apolen, D.; Oravcová, M.; Vavrišínová, K.L.A.; Peškovičová, D.; Luptáková, L.; Krupová, Z.; Bučko, O.; Blaško, J. Fatty acids profile of intramuscular fat in light lambs traditionally and artificially reared. J. Centr. Eur. Agric. 2014, 15, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usturoi, M.G.; Radu-Rusu, R.-M.; Usturoi, A.; Simeanu, C.; Doliș, M.G.; Rațu, R.N.; Simeanu, D. Impact of Different Levels of Crude Protein on Production Performance and Meat Quality in Broiler Selected for Slow Growth. Agriculture 2023, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, D.C.; Petrescu-Mag, R.M. Consumer Behaviour Related to Rabbit Meat as Functional Food. World Rabbit Sci. 2018, 26, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Gerini, F.; Ikram, A.; Saeed, F.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y. Rabbit Meat—Production, Consumption and Consumers’ Attitudes and Behavior. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, F.; Murariu, O.C. Variation of amino acid content in Longissimus dorsi and Triceps brachii muscles in Karakul sheep according to age and muscle region. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2013, 24, S55–S56. [Google Scholar]
- Rațu, R.N.; Veleșcu, I.D.; Stoica, F.; Usturoi, A.; Arsenoaia, V.N.; Crivei, I.C.; Postolache, A.N.; Lipșa, F.D.; Filipov, F.; Florea, A.M.; et al. Application of Agri-Food By-Products in the Food Industry. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovato, S.; Pinto, A.; Di Martino, G.; Mascarello, G.; Rizzoli, V.; Marcolin, S.; Ravarotto, L. Purchasing Habits, Sustainability Perceptions, and Welfare Concerns of Italian Consumers Regarding Rabbit Meat. Foods 2022, 11, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullere, M.; Zotte, A.D. Rabbit meat production and consumption: State of knowledge and future perspectives. Meat Sci. 2018, 143, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujok, J.; Miśta, D.; Wincewicz, E.; Króliczewska, B.; Dzimira, S.; Żuk, M. Atherosclerosis Development and Aortic Contractility in Hypercholesterolemic Rabbits Supplemented with Two Different Flaxseed Varieties. Foods 2021, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sensory Parameters | Granted Scoring (Points) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Color | Extremely Pale | Pale | Pale Pink | Pink | Intense Pink |
| Fibrous appearance | Weakly highlighted | Lightly highlighted | Medium highlighted | Distinctly highlighted | Strongly highlighted |
| Smell/ odor | Imperceptible | Weakly perceptible | Medium perceptible | Distinct perceptible | Very perceptible |
| Taste | Slightly unpleasant | No taste | Tasty enough | Tasty | Very tasty |
| Flavor | Slightly unpleasant | No flavor | Pleasant | Very pleasant | Extremely pleasant |
| Intensity of the flavor | Undetectable | Poor | Sufficiently pleasant | Pleasant and strong | Intense pleasant |
| Juiciness | Dry | Insufficiently juicy | Sufficiently juicy | Juicy | Very juicy |
| Tenderness | Very stiff | Slightly stiff | Sufficiently soft | Soft | Very soft |
| Overall assessment | Unacceptable | Acceptable | Good | Very good | Exceptional |
| Fatty Acids | M/F | LD | p-Value | SM | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SEM | CV% | Mean | SEM | CV% | |||||
| SFA | C14:0 | M | 21.12 | 0.76 | 16.1 | 0.035 n.s | 18.87 | 0.81 | 19.15 | 1.367×10−5 *** |
| F | 38.63 | 1.37 | 15.9 | 56.95 | 1.92 | 15.11 | ||||
| C15:0 | M | 3.97 | 0.13 | 15.1 | 0.046 n.s | 4.97 | 0.15 | 13.16 | 1.525×10−6 *** | |
| F | 7.02 | 0.15 | 9.3 | 11.02 | 0.23 | 9.49 | ||||
| C16:0 | M | 220.11 | 3.91 | 7.95 | 0.057 n.s | 272.32 | 9.16 | 15.04 | 6.317×10−5 *** | |
| F | 409.37 | 5.14 | 5.61 | 614.17 | 23.48 | 17.1 | ||||
| C17:0 | M | 4.91 | 0.22 | 19.8 | 0.021 * | 8.21 | 0.20 | 11.08 | 2.127×10−7 *** | |
| F | 7.96 | 0.14 | 7.67 | 13.04 | 0.12 | 4.12 | ||||
| C18:0 | M | 71.49 | 0.98 | 6.1 | 0.037 * | 82.13 | 1.67 | 9.07 | 2.213×10−6 *** | |
| F | 95.58 | 1.45 | 6.78 | 141.02 | 2.64 | 8.36 | ||||
| MUFA | C16:1n-7 | M | 21.03 | 0.26 | 5.51 | 0.798 n.s. | 28.07 | 1.26 | 20.04 | 1.288×10−5 *** |
| F | 62.11 | 0.81 | 5.82 | 106.04 | 4.30 | 18.15 | ||||
| C18:1n-7 | M | 14.81 | 0.19 | 5.61 | 0.078 n.s. | 15.98 | 0.39 | 11.05 | 1.233×10−6 *** | |
| F | 19.97 | 0.28 | 6.16 | 34.16 | 0.69 | 9.08 | ||||
| C18:1n-9 | M | 208.16 | 5.84 | 12.54 | 0.037 * | 270.99 | 10.34 | 17.07 | 8.462×10−7 *** | |
| F | 358.97 | 4.62 | 5.76 | 593.17 | 12.14 | 9.15 | ||||
| PUFA | C18:2n-6 | M | 180.92 | 6.24 | 15.43 | 0.043 * | 243.19 | 7.00 | 12.87 | 5.235×10−6 *** |
| F | 256.83 | 4.01 | 6.98 | 394.02 | 6.29 | 7.14 | ||||
| C18:3n-3 | M | 14.11 | 0.20 | 6.42 | 0.074 n.s | 21.1 | 0.98 | 20.71 | 6.159×10−6 *** | |
| F | 23.32 | 0.58 | 11.08 | 40.02 | 0.82 | 9.16 | ||||
| C20:2n-6 | M | 2.92 | 0.06 | 9.54 | 0.294 n.s | 3.19 | 0.06 | 7.82 | 1.213×10−4 *** | |
| F | 3.37 | 0.06 | 8.26 | 5.07 | 0.11 | 9.67 | ||||
| C20:3n-6 | M | 3.89 | 0.05 | 5.63 | 0.081 n.s | 5.34 | 0.09 | 7.16 | 0.036 * | |
| F | 3.51 | 0.04 | 5.29 | 5.11 | 0.07 | 6.27 | ||||
| C20:4n-6 | M | 50.97 | 0.82 | 7.19 | 0.018 * | 49.38 | 0.90 | 8.13 | 0.017 * | |
| F | 54.93 | 1.77 | 14.4 | 55.42 | 0.84 | 6.79 | ||||
| C20:5n-3 | M | 11.17 | 0.27 | 10.81 | 0.197 n.s. | 12.33 | 0.25 | 9.17 | 0.272 n.s. | |
| F | 8.98 | 0.25 | 12.22 | 11.57 | 0.35 | 13.38 | ||||
| C22:4n-6 | M | 15.06 | 0.22 | 6.64 | 0.007 ** | 16.14 | 0.27 | 7.42 | 1.707−5 *** | |
| F | 13.95 | 0.21 | 6.81 | 15.2 | 0.21 | 6.18 | ||||
| C22:5n-3 | M | 7.79 | 0.18 | 10.33 | 0.637 n.s | 7.11 | 0.11 | 7.06 | 0.035 * | |
| F | 9.66 | 0.31 | 14.35 | 7.92 | 0.21 | 11.99 | ||||
| C22:6n-3 | M | 24.11 | 0.56 | 10.38 | 0.923 n.s | 22.06 | 0.48 | 9.73 | 0.223 n.s | |
| F | 24.69 | 0.67 | 12.19 | 25.09 | 0.65 | 11.51 | ||||
| Sanogenic Indices | Gender | LD | SM | Mean/Gender | Mean/Breed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total SFA | M | 321.60 | 386.50 | 354.05 | 525.72 |
| F | 558.56 | 836.20 | 697.38 | ||
| Total MUFA | M | 244.01 | 315.04 | 279.53 | 433.37 |
| F | 441.05 | 733.37 | 587.21 | ||
| Total PUFA | M | 310.94 | 379.84 | 345.39 | 412.36 |
| F | 399.24 | 559.42 | 479.33 | ||
| ΣPUFA/ΣSFA | M | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.84 |
| F | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.69 | ||
| ΣPUFA n-6 | M | 253.76 | 317.24 | 285.50 | 344.61 |
| F | 332.59 | 474.82 | 403.71 | ||
| ƩPUFA n-3 | M | 57.18 | 62.60 | 59.89 | 67.76 |
| F | 66.65 | 84.60 | 75.63 | ||
| Σn6/n3 | M | 4.44 | 5.07 | 4.76 | 5.03 |
| F | 4.99 | 5.61 | 5.30 | ||
| EFA | M | 246.00 | 313.67 | 279.84 | 346.06 |
| F | 335.08 | 489.46 | 412.27 | ||
| %EFA | M | 28.06 | 29.01 | 28.54 | 26.01 |
| F | 23.95 | 22.99 | 23.47 | ||
| DFA | M | 626.43 | 777.01 | 701.72 | 943.28 |
| F | 935.87 | 1433.81 | 1184.84 | ||
| %DFA | M | 71.47 | 71.85 | 71.66 | 69.40 |
| F | 66.90 | 67.35 | 67.13 | ||
| NVI | M | 1.34 | 1.36 | 1.35 | 1.28 |
| F | 1.16 | 1.25 | 1.21 | ||
| AI | M | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.42 |
| F | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.48 | ||
| TI | M | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.41 |
| F | 0.40 | 0.54 | 0.47 | ||
| h/H | M | 2.21 | 2.29 | 2.25 | 2.01 |
| F | 1.74 | 1.77 | 1.76 | ||
| PI | M | 2.09 | 2.85 | 2.47 | 3.18 |
| F | 3.03 | 4.74 | 3.89 | ||
| Total fatty acids | M | 876.54 | 1081.38 | 978.96 | 1371.44 |
| F | 1398.85 | 2128.99 | 1763.92 |
| Muscles | Parameters | Gender | Mean ± SEM | CV% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L.D. | Shear force (kg/cm2) | M | 5.62 ± 0.15 | 11.97 | 0.0342 * |
| F | 5.14 ± 0.15 | 12.65 | |||
| Firmness (kg/s × cm2) | M | 2.71 ±0.10 | 17.14 | 0.0011 ** | |
| F | 2.11 ± 0.07 | 14.98 | |||
| Area (kg × s/cm2) | M | 10.89 ± 0.27 | 10.95 | 0.1003 ns | |
| F | 9.49 ± 0.34 | 15.82 | |||
| S.M. | Shear force (kg/cm2) | M | 5.48 ± 0.26 | 20.99 | 0.4017 ns |
| F | 5.16 ± 0.22 | 18.74 | |||
| Firmness (kg/s × cm2) | M | 2.37 ± 0.07 | 12.96 | 0.2030 ns | |
| F | 2.19 ± 0.08 | 16.31 | |||
| Area (kg × s/cm2) | M | 9.31 ± 0.27 | 12.92 | 0.3286 ns | |
| F | 8.57 ± 0.28 | 14.79 |
| Muscles | Parameters | Gender | Mean ± SEM | CV | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L.D. | L* | M | 59.12 ± 0.95 | 7.21 | 0.9912 ns |
| F | 58.32 ± 0.88 | 6.77 | |||
| a* | M | 3.12 ± 0.08 | 6.82 | 0.0138 * | |
| F | 2.87 ± 0.04 | 5.68 | |||
| b* | M | 3.01 ± 0.03 | 4.94 | 0.000002 *** | |
| F | 2.12 ± 0.03 | 5.83 | |||
| S.M. | L* | M | 55.49 ± 0.54 | 4.28 | 0.7384 ns |
| F | 56.16 ± 0.52 | 4.14 | |||
| a* | M | 3.21 ± 0.03 | 4.39 | 0.8296 ns | |
| F | 3.31 ± 0.03 | 4.25 | |||
| b* | M | 2.75 ± 0.03 | 5.02 | 0.1268 ns | |
| F | 2.81 ± 0.02 | 4.41 |
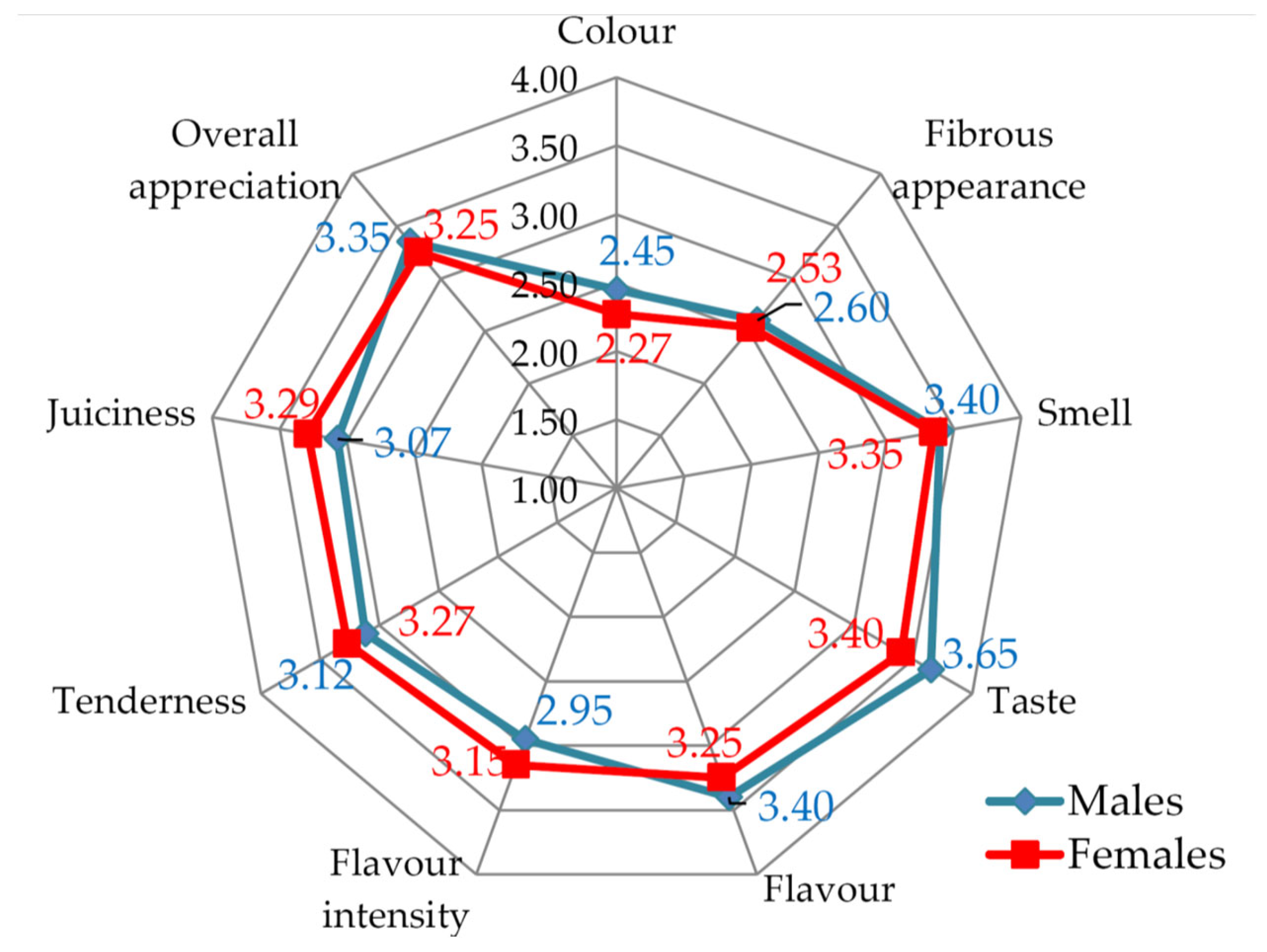
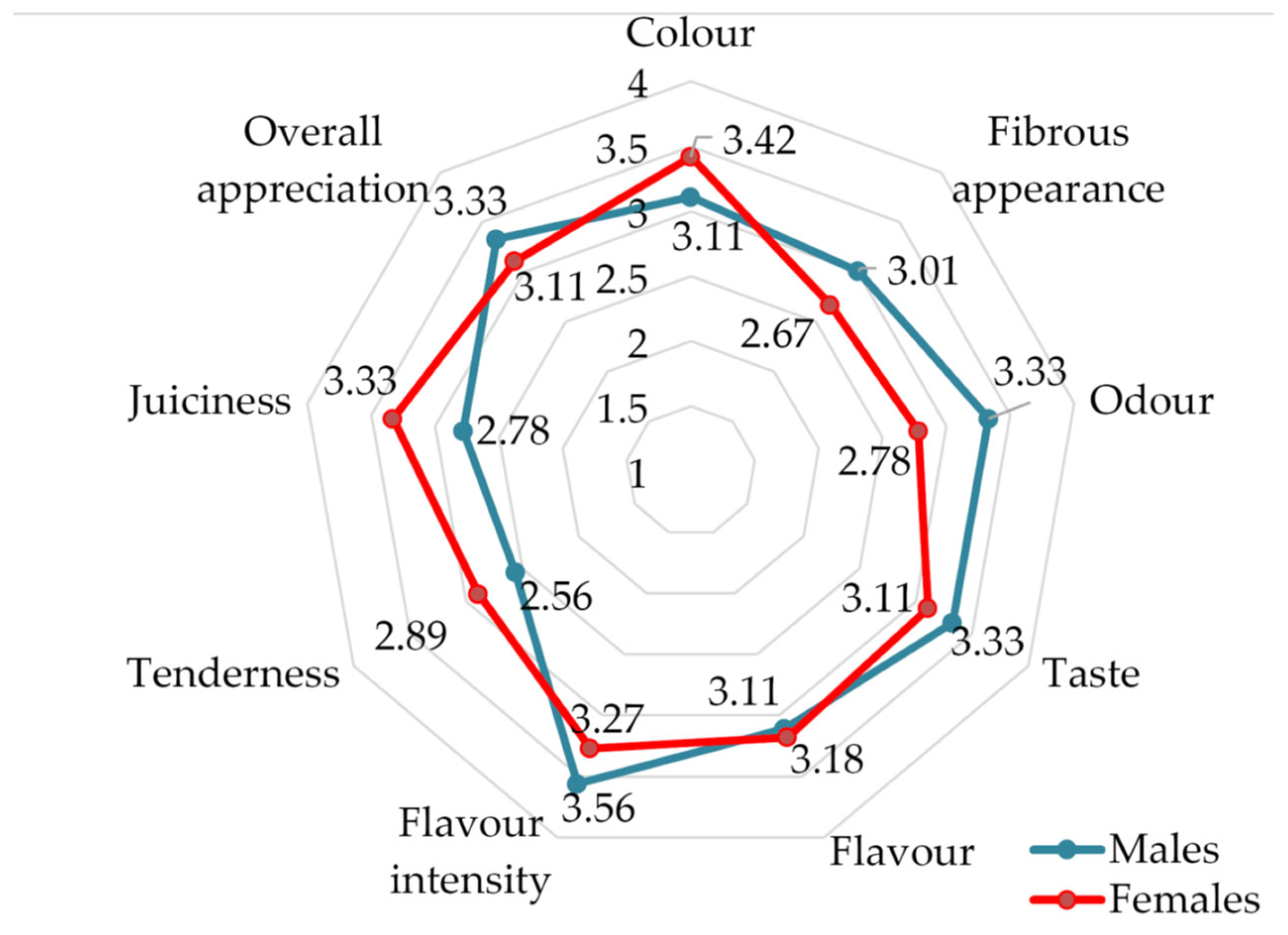
| Sensory Descriptor | Sensory p Values (Males vs. Females) | |
|---|---|---|
| LD | SM | |
| Color | 0.8480/ns | 0.000105/*** |
| Fibrous appearance | 0.000014/*** | 0.000003/*** |
| Smell | 5.9×10−8/*** | 1E×10−9/*** |
| Taste | 0.0028/** | 0.0033/** |
| Flavor | 0.1553/ns | 0.3088/ns |
| Flavor intensity | 6×10−7/*** | 0.0004/*** |
| Tenderness | 3×10−10/*** | 2.93×10−6/*** |
| Juiciness | 1.55×10−6/*** | 1×10−9/*** |
| Overall appreciation | 0.0019/** | 0.0033/** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frunză, G.; Ciobanu, M.-M.; Murariu, O.C.; Rațu, R.N.; Radu-Rusu, R.-M.; Simeanu, C.; Boișteanu, P.-C. Effect of Gender and Muscle Type on Fatty Acid Profile, Sanogenic Indices, and Instrumental and Sensory Analysis of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122265
Frunză G, Ciobanu M-M, Murariu OC, Rațu RN, Radu-Rusu R-M, Simeanu C, Boișteanu P-C. Effect of Gender and Muscle Type on Fatty Acid Profile, Sanogenic Indices, and Instrumental and Sensory Analysis of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat. Agriculture. 2023; 13(12):2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122265
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrunză, Gabriela, Marius-Mihai Ciobanu, Otilia Cristina Murariu, Roxana Nicoleta Rațu, Răzvan-Mihail Radu-Rusu, Cristina Simeanu, and Paul-Corneliu Boișteanu. 2023. "Effect of Gender and Muscle Type on Fatty Acid Profile, Sanogenic Indices, and Instrumental and Sensory Analysis of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat" Agriculture 13, no. 12: 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122265
APA StyleFrunză, G., Ciobanu, M.-M., Murariu, O. C., Rațu, R. N., Radu-Rusu, R.-M., Simeanu, C., & Boișteanu, P.-C. (2023). Effect of Gender and Muscle Type on Fatty Acid Profile, Sanogenic Indices, and Instrumental and Sensory Analysis of Flemish Giant Rabbit Meat. Agriculture, 13(12), 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122265









