Abstract
The cleaning device is an important part of combine harvesters, as its superior or inferior performance directly affects the performance of the combine harvester greatly. With an increasing rice yield, the current single-duct cleaning performance declines greatly, and causes a large grain sieve loss level and a direct grain loss for the farms. To optimize the existing single-duct cleaning device to meet the large feeding rate requirement, firstly, the terminal velocity of rice grain and MOG (material other than grain) for different varieties was experimentally measured by the custom-made device. The effects of the moisture content of rice grains and the length of short straws on terminal velocity were studied in detail. Then, the gas–solid two-phase flow theory was comprehensively applied by utilizing the discrete element method (DEM) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to study the working mechanism of the existing single-duct cleaning unit, and the cleaning performance was evaluated from the view of the motion law of the threshing output within the cleaning shoe. At last, a multi-duct cleaning device was put forward, and a field experiment was performed to assess the performance of the newly developed cleaning device. The results showed that the grain sieve losses ratio and grain impurity ratio improved dramatically, proving that structure optimization of the cleaning device was feasible.
1. Introduction
According to statistics from the year of 2019, China holds over 2,000,000 combine harvesters, which has increased by 3.36% compared with the year of 2018 [1]. Most rice combine harvesters in China were designed based on rice yields under 9000 kg/ha; a single-duct centrifugal fan plus a reciprocating sieve as the cleaning unit were mostly used as the cleaning device in the current rice combine harvesters. Field experiments indicated that such cleaning devices can achieve a good performance only in cases of feeding rates under 3 kg/s. However, as of now, the tangential flow threshing cylinder and longitudinal axial flow threshing cylinder composite unit is the primary mechanical structure of combine harvesters in the Asian region, and with rice yields increasing continually, exceeding 12,000 kg/ha and always with a high moisture [2], the cleaning unit has to deal with larger output materials up to 3–4 kg/s; thus, the cleaning section capacity has become a limiting factor [3,4].
The agricultural material cleaning process is a typically combined effect of the gas–solid two-phase flow field [5]. It is of great significance to study the air-and-screen cleaning device, to analyze the air flow distribution of the cleaning shoe, and to explore the motion law of agricultural materials on the screen surface, which not only provide the theoretical basis for designing and optimizing the existing typical cleaning unit, but also give theoretical inspiration to look for new cleaning methods. The use of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) for the computation of turbo machinery flows has significantly increased in recent years [6,7]. Flow analysis techniques using a steady Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (N-S) approach has led to remarkable progress in several engineering applications. Furthermore, combined with measurements, CFD provides a complementary tool for simulating, designing, optimizing, and analyzing the flow field inside a turbo machine [8]. The coupling of DEM and CFD provides a means of momentum and energy exchange between solids and fluids, which, in principle, removes the need for some of the semi-empirical approximations employed in CFD solid–fluid models, and is attracting increasing interest from industries. This enables the investigation of fluidized beds, pneumatic conveying, filtration, solid–liquid mixing, and many other systems. Effective modeling of the solid–fluid flow requires methods for adequately characterizing the discrete nature of the solid phase and representing the interaction between solids and fluids. DEM-CFD models reported in the literature have largely been applied to the simulation of fluidized beds and, more recently, to the pneumatic transport of particles [9,10,11,12,13,14]. Many industrial processes involve complex geometry, often with moving parts, and complex flow dynamics. The simulation of such systems requires the use of unstructured fluid meshes, and the ability to handle energy as well as momentum exchange, turbulent flow, and chemical reactions. This capability is now possible in a commercial environment using the co-simulation of EDEM discrete element modeling software with FLUENT. EDEM software is an advanced particle mechanics simulation tool employed for modeling industrial particulate handling and processing operations. It uses a surface mesh to represent boundary surfaces, which enables a one-to-one coupling with the boundary surface elements of the CFD fluid volume mesh. EDEM-FLUENT co-simulation is being used to investigate systems such as particle agglomeration and clumping in fluidized beds, dense-phase conveying, filtration, solid–liquid mixing, pipe erosion, spray coating, and many others.
In this work, the terminal velocity of typical rice varieties was measured by using the developed test-bed, which provides data support for designing the cleaning devices; then, the discrete element method (DEM), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and gas–solid two-phase flow theory were comprehensively applied to study the working mechanism of the existing air-and-screen cleaning unit and to evaluate its performance from the view of the air flow distribution of the cleaning shoe and the motion law of agricultural materials on the sieve. We then put forward a new kind of efficient cleaning device for tangential-longitudinal full-feed combine harvesters. Finally, a field experiment was performed to assess the performance of the newly developed cleaning device.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Terminal Velocity Test-Bed for Each Threshing Output Component
The grain-cleaning process occurs on the cleaning unit of the combine harvesters due to the pneumatic force created by the airflow generated by the fan [15,16]. The role of the airflow is to move the light components of the MOG mixture and evacuate them from the combine. The pneumatic force of the air must be higher than the gravitational force acting on the MOG and lower than the gravitational force acting on the grains. Thus, a certain range of airflow velocity is required to simultaneously satisfy both conditions. Terminal velocities are the most significant properties in aerodynamics, and the terminal velocity at which the particles are suspended stationarily in the vertical air stream can be determined by using different methods: the free-fall, vertical air tunnel, and elutriator methods [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. In this work, the custom-made device illustrated in Figure 1 was used to measure the terminal velocity of the different outputs of the threshing system, and to provide the basic information for designing a cleaning device.
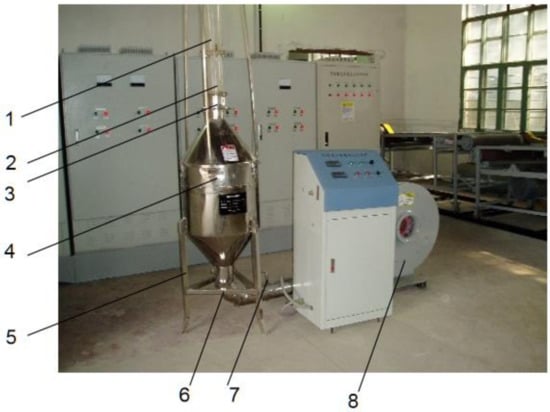

Figure 1.
Setup for terminal velocity measurement of threshing outputs; 1—conical tubes, 2—airflow velocity test port, 3—material inlet, 4—convergence cylinder, 5—regulator tube, 6—stand frame, 7—throttle, 8—fan.
The overall dimensions of the measuring device are 2.2 m × 0.9 m × 3.0 m (long × wide × high). The supporting power of the device is 5.5 kw, the motor revolution speed can be adjusted from around 300 to 1000 rpm, and the terminal velocity measurement range is 0~25 m/s. Before the start of a measurement, the samples were poured through the material inlet (3) onto the perforated plate inside the convergence cylinder (4). Then, the fan (8) speed was increased until the tested material was suspended in the conical tube (1). As most of the tested materials had an irregular shape, it was hard to find an exact suspension height L (m) in the conical tube relative to the perforated plate inside the convergence cylinder. The airflow velocity V1 in the test port (2) was measured with a hot-wire digital anemometer (VT100, KIMO, Paris, France) with a measurement range from 0.15 to 30 m/s and a resolution of 0.01 m/s. Finally, the terminal velocity Vi (m/s) was calculated by substituting the minimum and maximum values of L (m) into the following equation:
where D1 is the diameter of the convergence cylinder (m) and φ = 5.5° is the taper angle of the conical tube (°).
Different samples were selected from the threshing output, which are illustrated in Figure 2. Each component was tested 3 times, and the average terminal velocities were calculated.


Figure 2.
Illustrations of the different components in the threshing outputs for which the terminal velocity was measured.
2.2. Test Materials and Their Basic Physical Characteristics
Three different varieties of the rice threshing output were collected after the rice was threshed by the combine harvesters. Using the 1014B electric heating, constant temperature, vacuum-drying oven (Shanghai Yiti Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), the moisture content of grains and stems was measured by a constant temperature drying method. For this test, the oven temperature was kept at 105° and the drying time was 24 h. One thousand grains were randomly selected and counted, and the 1000-grain mass was scaled by a balance, which was repeated three times to obtain the average value. The three-dimensional size of the full grains, short straws, and leaves was measured by a vernier caliper. A certain quality of the full grains, non-full grains, and short stems were randomly weighed and put into a beaker filled with the proper amount of water. The results showed that the average density of the full grains, blight grains, and short straws was 1.28 g/cm3, 0.19 g/cm3, and 0.16 g/cm3, respectively. The moisture content measurement results and 1000-grain weight of each variety are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Properties of threshing outputs for different rice varieties.
2.3. Analyzing the Motion Law of the Threshing Output in the Existing Cleaning Shoe Based on EDEM-CFD Simulation
2.3.1. EDEM-CFD Coupling Theory
EDEM-FLUENT simulation was used to explore the motion law of the threshing output in the cleaning shoe. There are two models for coupling the particulate flow with fluid flow in the EDEM-CFD coupling interface: Lagrangian and Eulerian. The Lagrangian model allows a momentum exchange between the fluid and the solid phases only. Lagrangian coupling may be considered the equivalent of FLUENT’s discrete phase model (DPM). The Eulerian model allows a momentum exchange between the fluid and solid phases, but also considers the effect of the particle solid fraction on the fluid phase. Lagrangian coupling is less compute-intensive than Eulerian coupling: it should be used in cases where the local solid volume fraction (the solid fraction within a localized area of the simulation domain) remains below 10%. For Lagrangian coupling, the CFD simulation is performed as a single-phase transient calculation. The CFD simulation is iterated until it converges to a time step. A drag force is then calculated on the DEM particles based on the fluid conditions of the mesh cell within which the particle is contained. The DEM solver then takes control of the simulation and performs one (or several) iterations. After the DEM iteration finishes, control is passed back to the CFD solver. A momentum sink is added to each of the mesh cells to represent the effect of energy transfer on the DEM particles. The CFD portion of the coupling model uses the existing Eulerian-Eulerian model in FLUENT [29,30]. In the Eulerian model, an additional volume fraction term ε is added to the conservation equations to take into account the solid phase. In the coupling, although two phases are created in FLUENT, the conservation equations for the solid phase in the original Eulerian-Eulerian model are not solved.
2.3.2. Governing Equations of the Fluid System
The continuous fluid domain is discredited into cells in the CFD method. The CFD solves the following governing equations at each cell for locally averaged state variables such as fluid velocity, pressure, and density [31,32]. The continuity equation for the fluid phase is:
A similar equation exists for the conservation of momentum:
where ρf is the fluid density, t is time, uf is the fluid velocity, p is the air pressure, μf denotes the viscosity, g is the gravity force vector, and S is the momentum sink.
The coupling between the two phases is then achieved through the calculation of the momentum sink of the drag force that arises due to the relative velocity between the phases. Therefore, the momentum sink S is calculated by:
where, ∆V = ∆x∆y∆z, in which ∆x, ∆y, and ∆z are the control volume lengths, and is the fluid viscous resistance. The Di Felice drag model adds a porosity correction term to the free-stream drag model to take into account the effects of neighboring particles on the drag. In this paper, we adopt the Di Felice drag model to calculate FD,i, which can be expressed as:
where:
where dp is the diameter of the considered particle. CD is the particle–fluid drag coefficient that depends on the Reynolds number Re of the particle, and ε−χ denotes a corrective function accounting for the presence of other particles in the system on the drag force of the particle under consideration. A standard k−ε turbulence model and wall function are applied to calculate the airflow.
2.3.3. Governing Equations of DEM Simulation
The DEM as introduced by Cundall and Strack has evolved into an important method for modeling and understanding the behavior of granular materials [33]. EDEM is the leading DE (discrete element) simulation software platform designed for the simulation and analysis of bulk particle handling and processing equipment in a wide variety of industries. In EDEM, the motion of the particle as a rigid body described in the framework of classical mechanics naturally consists of translational and rotational motions. As the particles move, they impact each other and undergo deformations. Contact forces are computed as a function of the particle deformations. A commercial three-dimensional DEM code (EDEM® 2.7, DEM Solutions, Troy, MI, USA) was used in this work. The process is a cycle with a repeated calculation of the equation of motion for all the particles individually using the forces evaluated by using contact models to obtain the acceleration, velocity, and displacement.
The DEM is employed to solve the following equations governing the motion of a particle i in the particle system:
where either the Hooke or Hertzian contact law is employed in conjunction with Coulomb’s friction law to describe the inter particle contact behavior.
The Hertz–Mindlin no-slip contact model uses the spring–dashpot model of interacting particles [33,34]. This model has been successfully applied to the dynamic analysis of agricultural materials. The material and interaction parameters have their effect on the normal and tangential forces, and the moment acting between the interacting particles in the form of the following equations.
The normal force Fn is:
where E* is the equivalent Young’s modulus of the two interacting particles, δn is the normal overlap, R* is the equivalent radius, m* is the equivalent mass, e is the coefficient of restitution, and vnrel is the normal relative velocity.
The tangential force Ft is:
where G* is the equivalent shear modulus of the two interacting particles, δτ is the tangential overlap, and vτrel is the tangential relative velocity. E*, R*, and m* are given by:
The moment from the rolling friction:
where μr is the coefficient of the rolling friction, Ri is the distance of the contact point from the center of the particle i, and ωi is the unit angular velocity of the particle i at the contact point.
2.3.4. Simulation Settings in the EDEM-FLUENT Simulation
As the actual cleaning shoe is too large and complex, the grid mesh and calculation were limited by computer resources; therefore, the cleaning device structure was simplified in this work. The cleaning device width was reduced from 940 mm to 100 mm, whereas the length and height were consistent with the real dimensions, 1900 mm in length and 100 mm in width. The lower sieve mesh was considered to be a square aperture 25 mm × 25 mm formed from steel wires with a diagram of 2 mm. The simulation structure is shown in Figure 3.
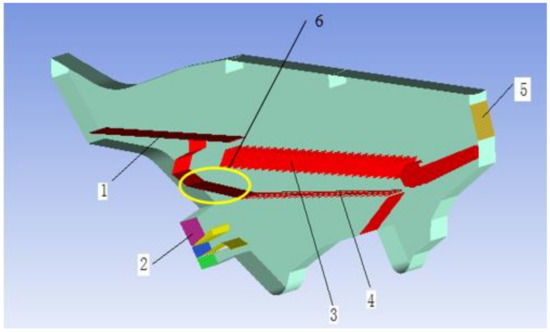
Figure 3.
Three-dimensional model of the existing cleaning shoe: 1. shake plate, 2. airflow inlet, 3. vibrating and cleaning upper sieve, 4. vibrating and cleaning lower sieve, 5. outlet, 6. lower grain pan.
The longitudinal velocity under the longitude threshing cylinder played an important role in the separation of materials; however, this study just focuses on studying the motion of the materials in the cleaning region. Ellipsoid grain particles and short straw particles were created by using composite particles made up of several overlapping spheres to make them feasible to simulate within a reasonable time. The developed grain and short straw particle models are shown in Figure 4. A cross-section of the established short straw model is shown in Figure 4b. Since straw has a hollow structure, 12 sphere particles with a diameter of 1 mm were used to make a circle ring in each layer, where 1 sphere particle was tangential with the other. The distance between the sphere centers in the two layers along the long axis was 0.8 mm.
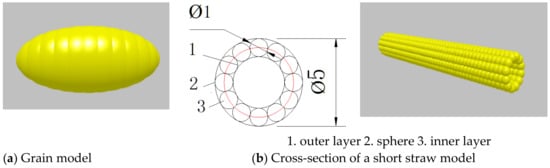
Figure 4.
Developed grain particle model and short straw particle model. (a) Grain model, (b) Cross-section of a short straw model.
The materials were fed onto the front-top section of the vibrating screen by gravity via a particle factory. Materials were loaded from the particle factory at different rates in different regions according to the material actual distribution. Grains were determined to have an initial vertical velocity of 1 m/s and short straws had a velocity of 1.5 m/s at the entering point, according to the material falling velocity in the sieve shoe obtained by a high-speed camera system [32]. The generated time of the materials was 0.5 s; these data are from the pre-test results, which were the mean value of the repeated test results and results from the related literature [19]. The inlet airflow velocity was set to 6 m/s, 7 m/s, and 9 m/s from the upper inlet to lower inlet. The other simulation conditions are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of DEM simulation parameters.
2.3.5. Measurement of Airflow Distribution Inside the Newly Designed Cleaning Shoe
Under the instruction of the EDEM-FLUENT results, a multi-duct cleaning device was developed. To check whether an ideal airflow velocity distribution inside the cleaning shoe can be formed, airflow velocities at certain points inside the cleaning shoe were measured with hot-wire anemometers that had a measurement range of 0.5–50 m/s and a resolution of 0.01 m/s. Each airflow velocity measurement result was obtained by taking the average value for the series of continuous data when the cleaning process with threshing outputs was between 5–20 s. To ensure the accuracy of the measurement results and eliminate the occurrence of accidental errors, a given set of tests was repeated three times. The final measurement results were the average value of them; the location of the airflow measuring sensor is shown in Figure 5.
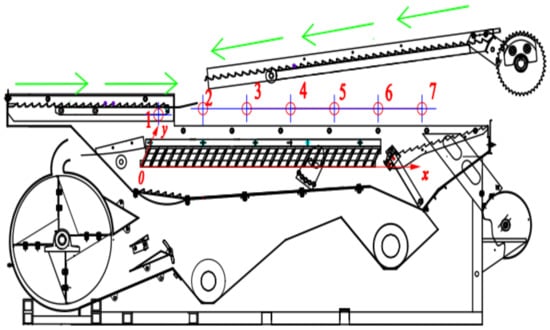
Figure 5.
Distribution diagram of measuring points in the newly designed cleaning shoe. No. 1–7 are the airflow velocity measuring points.
Field experiments were carried out with the combine harvesters. The tested rice had an average height of 85.2 mm and an average spike length of 16.9 mm. The average 1000-kernel weight was 26 g and the average grain output was 10,275 kg ha−1. The average grain to MOG (material other than grain) ratio was 2.9:1 and the average moisture content of the straw and the grains was 66% and 24%, respectively. The header width of the combine harvester was 2.2 m and the forward velocity was 1–1.2 m/s. A tarpaulin was utilized to collect all of the sieve outputs, and then the full grains were filtered out from the material other than grain (MOG) using a stationary re-cleaner (Agriculex ASC-3 Seed Cleaner, Guelph, ON, Canada), weighed, and the grain sieve losses were calculated. Each test length was 50 m.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Physical Characteristics of the Test Samples
From Table 1, it can be seen that there were significant differences in moisture content, three-dimensional size, and 1000-grain weight for different rice varieties, as different rice varieties have different biological mechanical properties and threshing output compositions. With the increase in the moisture content of the full rice grains and blight grains, the corresponding 1000-grain weights were increased accordingly. These differences lead to different requirements for cleaning airflow velocity in the cleaning shoe of rice combine harvesters.
3.2. Terminal Velocity for Each Component’s Analysis
To more intuitively compare the variation in the terminal velocity of full rice grains with different varieties and moisture content, the terminal velocity distribution of the full rice grains was drawn, as shown in Figure 6a–c. It can be seen from Figure 6a–c that the terminal velocity increased with the increasing moisture content, as the 1000-grain weight was increased accordingly. The terminal velocity of the full rice grains and rice grains with short handles is roughly in the range of 6–8 m/s. Therefore, when designing the cleaning device, we should try to avoid having the airflow velocity in the cleaning room be higher than 8 m/s to prevent large grain loss. Short branches with grains have a larger terminal velocity than full grains, as their weight is much larger than single grains. The distribution of the terminal velocity of blight rice grains under different varieties and different moisture content is shown in Figure 6d. The terminal velocity of the blight grains increased with the increase in moisture content accordingly; when the moisture content of the blight grains is the same as full grains, the middle value of the terminal velocity of blight grains is much lower than full grains. The average terminal velocity of the blight rice grains fluctuates in the range of 2.98–4.81 m/s.
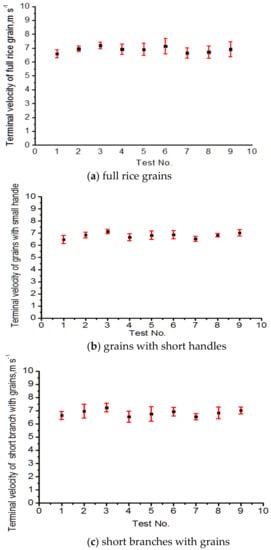
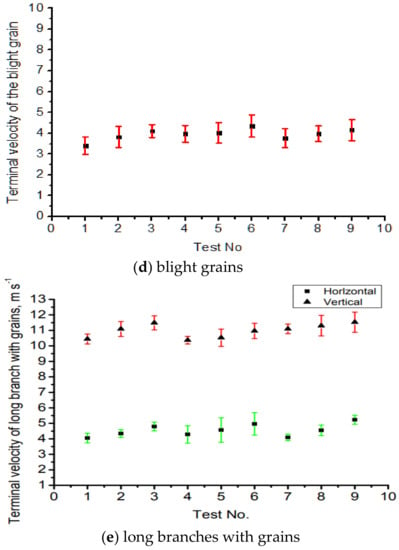
Figure 6.
Terminal velocity distribution for full rice grains, blight grains, grains with short handles, short branches with grains, and long branches with grains, (a) full rice grains, (b) grains with short handles, (c) short branches with grains, (d) blight grains, (e) long branches with grains. No. 1–3: rice variety 1: 24.3%, 25.4%, 26.1%; No. 4–6: rice variety 2: 23.6%, 24.8%, 25.9%; No. 7–9: rice variety 3: 23.2%, 25.3%, 25.9%.
The posture of large branches with grains can be divided into a horizontal state and vertical state. The flight state of the branch in the airflow affects the gravity center and projection area. Due to the non-uniformity of airflow and the influence of the shape of large branches, the large branches with grains move up and down in the conical tube. When the larger branch is in the horizontal state, the gravity center is much lower, the projection area is large, and the terminal velocity is small. When the larger branch is in the vertical state, the gravity center is relatively high, the projection area is small, and the terminal velocity is large. It can be seen from Figure 6e that when the larger branch is in the horizontal position, its terminal velocity was distributed within the range of 6.86–8.52 m s−1, and its terminal velocity was distributed within the range of 9.05–12.15 m/s when the big branch is in the vertical position. The influence of the moisture content on the terminal velocity should be fully considered when designing a cleaning device.
During the threshing process, with the beating of the threshing element, some long stems break and generate more short straws, which are one of the major components in the threshing output mixture. Some short straws pass though the concave grid and enter the cleaning system, and the short straw amount affects the cleaning performance greatly. Straws are neither symmetrical in shape nor uniform in density, and this lack of symmetry causes aerodynamic instability. Therefore, understanding the effect of moisture content variation and short straw length on the terminal velocity of short straws gives more insight into designing a cleaning system. From Figure 7 it can be seen that with the increase in moisture content of the short straws, the maximum terminal velocity increased accordingly, and with the increase in the short straw length, the maximum terminal velocity also increased. The short straws from the bottom of the stem have the largest terminal velocity compared with straws from other parts; this is because straw density from the bottom is larger, and as the mass of the straw with the same length also increased, it needs more energy to lift. The terminal velocity was distributed within the range of 3.12–5.21 m/s.
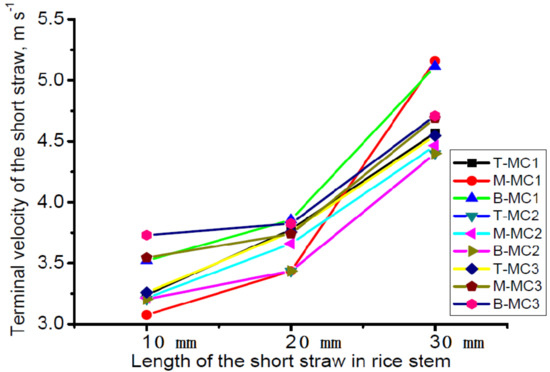
Figure 7.
Terminal velocity of rice straws with different lengths from different parts of the stem. T-MC1—short straw from the top stem with a moisture content of 62.5%; M-MC1—short straw from the middle stem with a moisture content of 62.5%; B-MC1—short straw from the bottom stem with a moisture content of 62.5%; T-MC2—short straw from the top stem with a moisture content of 65.4%; M-MC2—short straw from the middle stem with a moisture content of 65.4%; B-MC2—short straw from the bottom stem with a moisture content of 65.4%; T-MC3—short straw from the top stem with a moisture content of 69.2%; M-MC3—short straw from the middle stem with a moisture content of 69.2%; B-MC3—short straw from the bottom stem with a moisture content of 69.2%.
As can be seen from Figure 8, the terminal velocity of the leaves from different rice varieties was distributed from 2.72 to 3.38 m/s. The effect of the moisture content on the terminal velocity of these leaves is relatively weak and can be ignored. Under the same stem moisture content, the effect of residual length on the terminal velocity can be ignored. When designing the cleaning device, the various physical properties of the residue have little influence on the cleaning quality as the terminal velocity of leaves is lower than that of full grains.
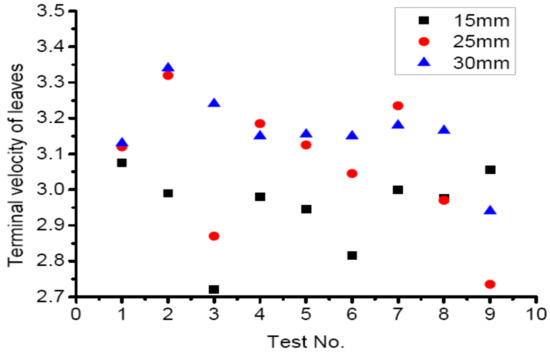
Figure 8.
Terminal velocity of leaves with different varieties and lengths. No. 1–9 are the leave lengths of 15, 25, and 30 mm with a moisture content of 62.5%, 65.4%, and 69.2%, respectively.
As can be seen from Figure 9, there is a clear boundary between grains and the MOG in the terminal velocity. The terminal velocity of full grains and grains with small handles are much higher than that of blight grains, as the grain mass and weight distribution has a great influence on the terminal velocity. The terminal velocity of the big branch in the horizontal state is much lower than that in the vertical state, the reason for which is that the branch projection area in the horizontal state is larger than the branch in the vertical state, and the branches are subjected to a more unstable force in the horizontal state. Therefore, the posture of the large branch is an important factor effecting the cleaning performance. The terminal velocity of branches with grains is similar to that of full grains. There is no significant terminal velocity difference for straws from the top and middle parts of the stem, but the bottom part of the stem has the largest terminal velocity. This is because the straw from the stem bottom always has the highest density, and the weight of the stem from the bottom is higher with the same length; thus, the terminal velocity is also higher. Based on these results it can be concluded that an airflow velocity around 6 m/s would provide good separation in the cleaning shoe, as grains and the MOG can be easily separated; that is to say, large branches (vertical posture) will fall into the tailing auger for re-threshing and re-cleaning, whereas most of the leaves will be blown out of the cleaning shoe instantly. This provides fundamental parameters for further optimizing the cleaning device.
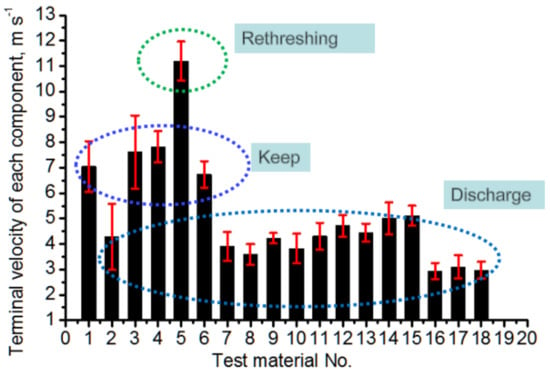
Figure 9.
Terminal velocity contrast between different components. No. 1: full grains, No. 2: blighted grains, No. 3: grains with short handles, No. 4: large branches (horizontal posture), No. 5: large branches (vertical posture), No. 6: small branches with grains, No. 7–9: short straws from the bottom stems, No. 10–12: short straws from the middle stems, No. 13–15: short straws from upper stems, No. 16–18: leaves.
3.3. Analyzing Velocity Variation of Grains and Short Straws in Longitudinal Direction
Figure 10 shows an overview of the vibration screening at various time instances from 0 to 1.351 s with a time step of 10−6 s. Different colors represent different materials. It can be concluded from Figure 11 that the materials generated by the particle factory reach the upper sieve surface when t = 0.172 s. At t = 0.27 s, the materials reach the lower screen surface, and some grains penetrate the sieve directly. At t = 0.313 s, owing to the suspension speed of the short straws distributed from 3.12 to 5.21 m/s, some short straws are blown out of the calculation domain directly. At t = 1.351 s, the total number of grains penetrating the screen has increased. At the same time, some grains are blown out because of the interaction between short straws and grains. The variation in the grain and short straw longitude velocity with time in different regions is shown in Figure 11.
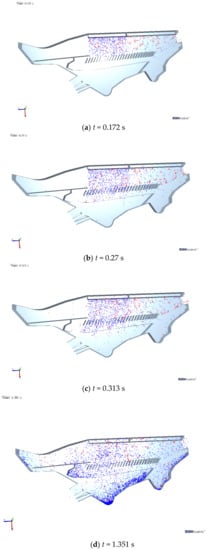
Figure 10.
Simulation of the sieve working process, (a) t = 0.172 s, (b) t = 0.27 s, (c) t = 0.313 s, (d) t = 1.351 s.
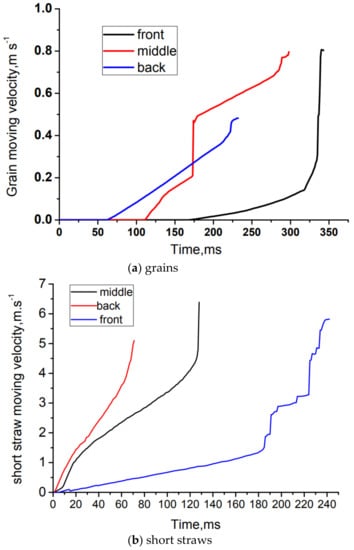
Figure 11.
Variation in grain and short straw longitude velocity with time. (a) grains, (b) short straws.
From Figure 11a we can see that at the front of the sieve, the grains’ longitudinal velocity was increased with a smaller growth acceleration rate. When the grains entered the middle section of the sieve, the grains’ longitudinal velocity increased dramatically, from 0.18 m/s to 0.3 m/s in about 20 ms, then changed to 0.8 m/s owing to the airflow velocity becoming gradually larger in this region. For the grains which collected at the middle of the sieve, the grains’ longitudinal velocity increased with a relative high growth acceleration rate, and when they entered the end section of the sieve, the grains’ longitudinal velocity jumped from 0.2 m/s to about 0.5 m/s. Then, the grains’ longitudinal velocity continued growing, owing to the airflow velocity recovering. For the grains which collected at the end section of the sieve, the grains’ longitudinal velocity increased quickly, from 0 to 0.5 m/s in about 100 ms, and then they were blown out of the calculation domain directly. The longitudinal velocity of short straws was increased with a different growth acceleration rate in a different region of the sieve. Owing to the impediment of the lower grain pan, a mandatory change in airflow direction occurred, leading to a smaller value of airflow velocity in the front of sieve, and resulted in the smallest growth acceleration rate in this area. In the following backward moving process, their longitudinal velocity increased gradually, whereas at the end section of the sieve, some short straws were blown out swiftly.
In summary, the airflow direction changed due to the impediment of the lower grain pan, and the airflow velocity decreased dramatically in this area. Moreover, the threshing outputs which had fallen from the upper grain pan accumulated in the front of the sieve, and the threshing outputs were also difficult to pass through the sieve in this area, making the grain impurity rate increase. There are also some eddy currents at the front part of the sieve, which hinder the material’s backward movement. At the middle section of the upper sieve, the airflow velocity became larger along with the increase in the sieve length; the backward velocity of grains and short straws also increased accordingly. The moving velocity of the short straws was larger than that of the grains, and the total grains penetrating the sieve increased. At the end section of the upper sieve, the airflow velocity was recovering to some extent, and some short straws and grains were blown out swiftly. When the grains reached the lower sieve front, most of the grains penetrated the sieve. However, for the short straws, the chance of penetrating was smaller due to their large volume; therefore, most of them moved with the sieve and had an increasingly backward velocity under the joint action of the sieve vibration and airflow. Finally, the short straws reached the tailings auger for secondary threshing and cleaning.
The above EDEM-CFD simulation indicates that the airflow velocity was smaller at the front of the upper sieve, which was not beneficial for grain stratification and penetration. Since there was an accumulation of a large amount of threshing mixture, most of the short straws cannot be effectively separated. Most of them pass through the sieve with the grains, which leads to a larger grain impurity ratio. On the other hand, at the end of the upper sieve, the airflow velocity was relatively high in places closer to the wall, and some full grains also were blown out and caused a grain loss. To solve this problem, a kind of efficient cleaning device with the major structural improvements as follows was put forward: (1) The length of the lower grain pan was shortened to make it into a streamline arc plate, as the experiment results indicated that there was a slightly mandatory change in the air flow direction, which can help to develop an upward airflow at the end of streamline arc plate and also can prevent vortex generation. (2) A centrifugal fan with double outlets was designed to increase airflow velocity at the front of the sieve. (3) A return conveying plate was adhered under the longitudinal axial flow threshing cylinder to upgrade the processing capacity of the cleaning device. A diagram of the newly developed cleaning device is shown in Figure 12.
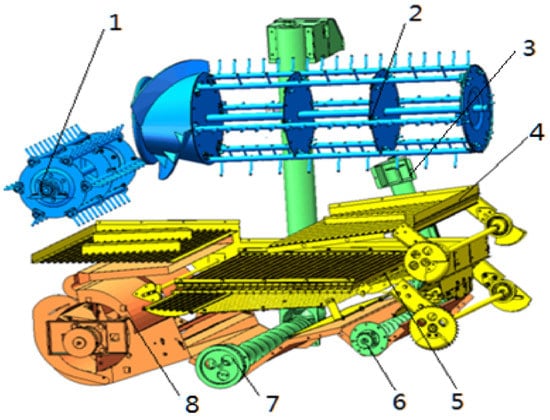
Figure 12.
Diagram of the multi-cleaning system and its main working parts. 1—tangential threshing rotor, 2—longitudinal threshing rotor, 3—tails return duct, 4—return conveying plate, 5—vibrating sieve, 6—tailings auger, 7—grain auger, 8—centrifugal fan.
In working condition, the return conveying plate and sieve perform an intertwined movement with the same amplitude and frequency, the threshing output of the two cylinders falls into the shaking plate and the return conveying plate, respectively, the threshing outputs are mixed evenly in the process of the upper grain pan and sieve moving, and then they are dropped onto the sieve surface like a waterfall. The fallen materials are, firstly, pre-cleaned by the airflow, which is released by the upper outlet of the fan, and light impurities are blown out of the cleaning shoe directly; the total amount of the materials to be cleaned is reduced in this stage. In the continuing role of the vibration sieve, the material continues to jump from the front to the back of the sieve, as the component and thickness of the output materials is changed. The cleaning process is completed after three outlet duct airflows repeatedly act on the outputs. At last, the cleaned grains fall into the grain auger, and then are transported into the grain tank. MOGs fall into the tailing auger, and then are conveyed to the return conveying plate for the secondary cleaning.
The average airflow velocity at different measuring points in the cleaning shoe is shown in Figure 13. From Figure 13 it can be seen that the ideal airflow velocity in different sections is: about 9 m/s in the upper outlet, 4–6 m/s in the middle section, and 3–4 m/s in the tail section. Combined with the terminal velocity of the threshing outputs, it can be understood that there is a good airflow velocity distribution inside the newly designed cleaning shoe, which can be expected to have a better cleaning performance when harvesting rice.
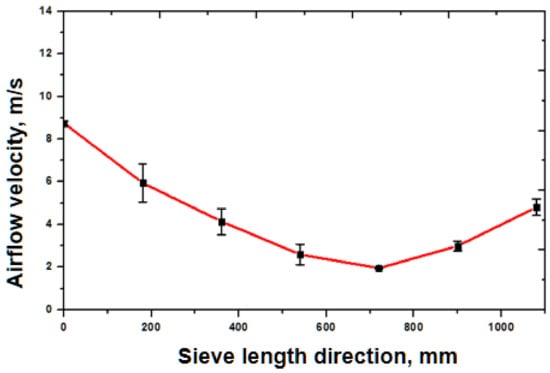
Figure 13.
Average airflow velocity at different measuring points in cleaning shoe.
The field experiment results are shown in Table 3. The data analysis results indicated that the fan speed has a paramount effect on cleaning performance; with the increase in the fan speed, the corresponding grain sieve loss is increased, and the grain impurity ratio declines. From Table 3 it can be seen that the grain sieve loss rate and grain impurity rate declined dramatically compared with the field experiment results reported by the reference [4], which proved that structure optimization of the cleaning device was feasible.

Table 3.
Experimental cleaning performance under different settings.
4. Conclusions
(1) Moisture content has a larger effect on terminal velocity. With the increase in the moisture content, the mass of each component of the threshing outputs increased accordingly, and the terminal velocity increased accordingly. The terminal velocity of grains with stripes and branches with grains was close to that of the full grains, as it is difficult to separate out those with airflow, resulting in a higher grain impurity ratio. The distribution range of the terminal velocity for leaves and short straws has no overlap with that of the full grains; thus, it is convenient to separate them by selecting an appropriate airflow velocity. There is a terminal velocity overlap of short straws from the bottom of the stem, and for a branch in the horizontal state and with full grains, it is difficult to separate the short stems from the bottom of the stem and branch in the horizontal state by airflow. It can be concluded that an airflow velocity around 6 m s−1 would provide good separation of the grains and MOG. Under this condition, a large branch (vertical posture) falls into the tailing auger for re-threshing and re-cleaning, and most of the leaves are blown out of the cleaning shoe instantly.
(2) A new cleaning device including a fan with two outlets, a return pan, and a vibration sieve was developed under the instruction of analyzing the motion law of the threshing output in the cleaning shoe in the single-duct cleaning system, and the cleaning performance improved greatly. However, there is still room for further improvement through optimization of the design of the multi-duct fan with respect to its impact on the airflow distribution in the cleaning section.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L.; methodology, Z.Y.; software, Z.Y.; validation, B.D.; formal analysis, B.D. and J.Z.; investigation, Y.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, B.D.; writing—review and editing, Z.L.; supervision, Z.L.; funding acquisition, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20190859); the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation projects (2019M651746 and 2020T130260); the Key Research and Development Program of Zhenjiang, China (NY2021009); the Postdoctoral Researcher Project in Jiangsu Province, China (2019Z106); the Key Laboratory of Modern Agricultural Equipment and Technology, Jiangsu University (MAET202124), the Jiangsu Association of Science and Technology Young Talent Support Project (2020-21); Young Talents Cultivation Program of Jiangsu University (2022), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, China (No. PAPD-2018-87).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Statistical Situation of Grain Combine Harvester in China from 2016 to 2019. Available online: https://www.chinabaogao.com/data/202201/566288.html (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Ouyang, Y.D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.F. Understanding the genetic and molecular constitutions of heterosis for developing hybrid rice. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Z. Analysis on the eddy current of the air-and-screen cleaning device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2010, 41, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Li, Y.M. Optimization and simulation research of the airway of tangential-axial combine harvester cleaning room. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2015, 2, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, A.B.; Xu, B.H. Particle-scale modelling of gas–solid flow in fluidisation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2003, 78, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggli, F.A.; Holbein, P.; Dupont, P. CFD calculation of a mixed flow pump characteristic from shutoff to maximum flow. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2002, 124, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot, M.G.; de Baerdemaeker, J.; Baelmans, M. Effect of a cross-flow opening on the performance of a centrifugal fan in a combine harvester. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 105, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Nolan, P.F. Modelling reacting localized air pollution using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tsuji, Y. Numerical simulation of two-dimensional fluidized beds using the discrete element method (comparison between the two- and three-dimensional models). Powder Technol. 1998, 96, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, D.G.; Horio, M. Behavior of particles and bubbles around immersed tubes fluidized bed at high temperature and pressure: A DEM simulation. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2001, 27, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibsen, C.H.; Helland, E.; Hjertager, B.H.; Solberg, T.; Tadrist, L.; Occelli, R. Comparison of multi-fluid and discrete particle modelling in numerical predictions of gas particle flow in circulating fluidised beds. Powder Technol. 2004, 149, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.W.; Yu, A.B. Numerical simulation of the gas–solid flow in three-dimensional pneumatic conveying bends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 7058–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.W.; Wang, B.; Vince, A.; Yu, A.B.; Barnett, G.D.; Barnett, P.J. CFD–DEM study of the effect of particle density distribution on the multiphase flow and performance of dense medium cyclone. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.W.; Wang, B.; Yu, A.B.; Vince, A. CFD–DEM modelling of multiphase flow in dense medium cyclones. Powder Technol. 2009, 193, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Xu, L.Z.; De Baerdemaeker, J.; Li, Y.; Saeys, W. Optimisation of a multi-duct cleaning device for rice combine harvesters utilizing CFD and experiments. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 190, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.B.; Jackson, R. A fluid mechanical description of fluidized beds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1967, 6, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharekhani, M.; Kashaninejad, M.; Garmakhany, A.D.; Ranjbari, A. Physical and aerodynamic properties of paddy and white rice as a function of moisture content. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2013, 5, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizollah, S. Evaluation and modeling of aerodynamic properties of mung bean seeds. Int. Agrophysics 2015, 29, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.J.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.D. Simple measurement of restitution coefficient of granular material and its application. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2009, 31, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.; Cui, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Lai, S.; Liu, J. Design and test of air-sweeping suspension velocity testing device for cleaning threshed materials of grain and oil crops. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, L.X.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.S.; Han, R.; Hu, J.P. Experimental study on aerodynamic characteristics of Chinese cabbage seed extraction components. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2020, 42, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, C.H.; Movahhed, S. Assessment of physical and aerodynamic properties of corn kernel (KSC 704). J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 87, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Nahal, A.M.; Arabhosseini, A.; Kianmehr, M.H. Separation of shelled walnut particles using pneumatic method. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2013, 6, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Murilo, D.M.I.; Wellington, S.B.; Maicon, N.O.A.; Reinaldo, P. Pneumatic separation of hulls and meats from cracked soybeans. Food Bioprod. Processing 2009, 87, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Shellard, J.E.; Macmillan, R.H. Aerodynamic properties of threshed wheat materials. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1978, 23, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Gopika, A.; Rajiv, S. Aerodynamic properties of sunflower seed (Helianthus annuus L.). J. Food Eng. 2006, 79, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liao, Q.X.; Zong, W.Y.; Liao, Y.T.; Li, H.T.; Huang, P. Aerodynamic characteristics measurement of extraction components for rape combine harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2012, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Kuang, S.B.; Chu, K.W.; Yu, A.B. Assessments of CFD–DEM models in particle–fluid flow modelling. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 661, 482–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.B.; Wright, B.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhu, H.P.; Zulli, P. Discrete particle simulation of gas–solids flow in a blast-furnace. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2008, 32, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.H.; Yu, A.B.; Chew, S.J.; Zulli, P. Numerical simulation of the gas–solid flow in a bed with lateral gas blasting. Powder Technol. 2000, 109, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.B.; Chu, K.W.; Yu, A.B.; Zou, Z.S.; Feng, Y.Q. Computational investigation of horizontal slug flow in pneumatic conveying. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundall, P.A.; Strack, O.D.L. Discrete numerical-model for granular assemblies. Geotechnique 1979, 29, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzo, A.D.; Maio, F. Homogeneous and bubbling fluidization regimes in DEM–CFD simulations: Hydrodynamic stability of gas and liquid fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzo, A.D.; Maio, F. Comparison of contact-force models for the simulation of collisions in DEM-based granular flow codes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).