Nutrient Characterization in Soil Aggregate Fractions with Different Fertilizer Treatments in Greenhouse Vegetable Cultivation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Soil Aggregate Fractions
2.5. Determination of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.6. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fraction and Stability of Soil Aggregate
3.2. Nutrient Content in Soil Aggregate
3.3. Aggregate Associated Nutrient Stock
3.4. Nutrient Stoichiometry of Soil Aggregate
3.5. The Relationship between Nutrients and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil Aggregate
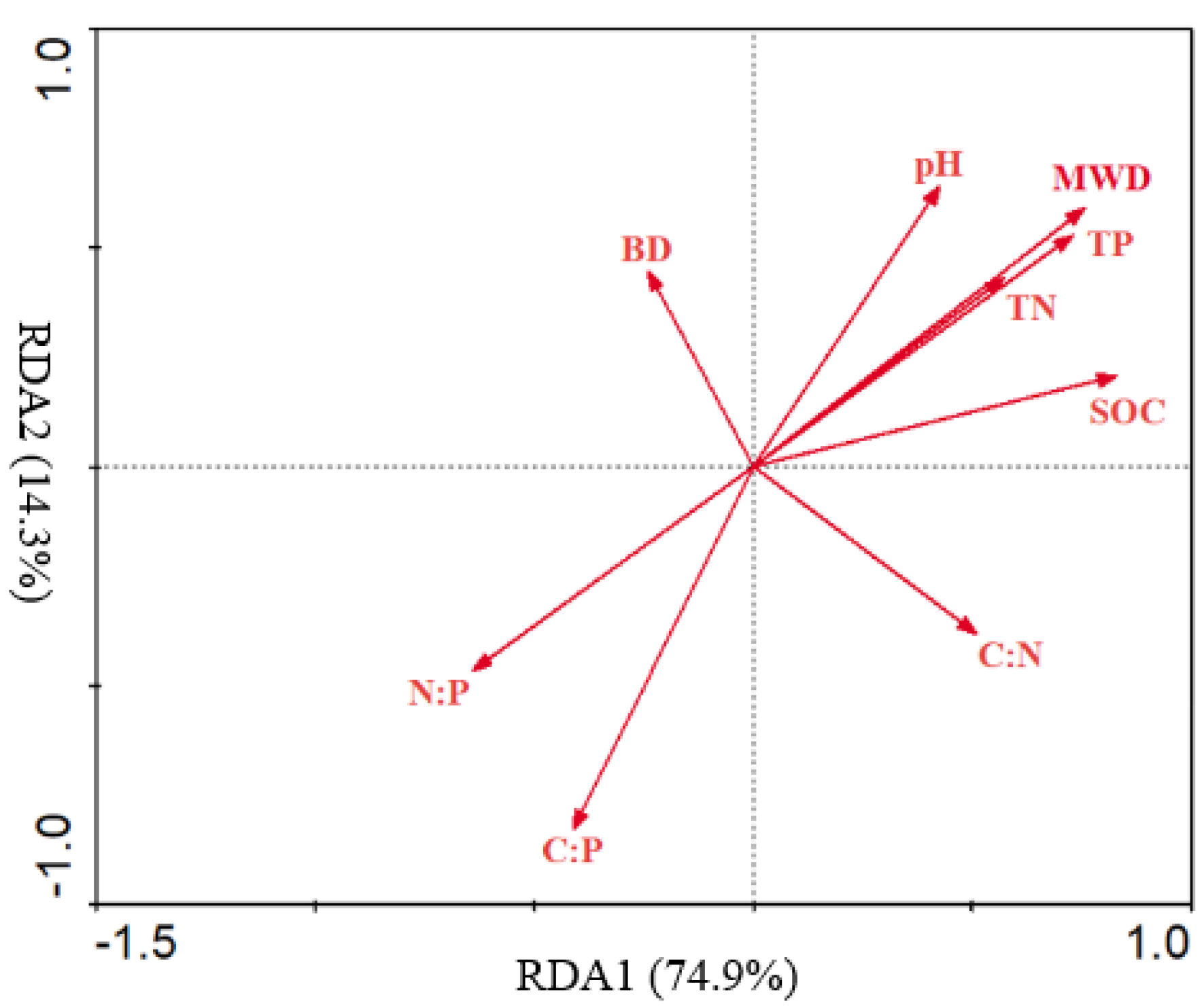
3.6. Soil Physicochemical Factors’ Effects on Aggregate Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.Y.; Wu, G.X.; Chen, J.W.; Cui, P.; Chen, Z.X.; Yan, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.C.; Niu, D.X.; Li, B.G.; et al. Integration of solar technology to modern greenhouse in China: Current status, challenges and prospect. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Liang, L.; Li, H.L.; Zhao, G. Status, deficiency and development suggestions of protected agriculture in China. North. Hortic. 2019, 5, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.J.; Cui, H.Y.; Jia, L.M.; Xie, X.Y.; Li, J.M.; Wei, Z.M. Assessing the use of composts from multiple sources based on the characteristics of carbon mineralization in soil. Waste Manag. 2017, 70, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.L.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, S.G.; Yu, H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Tan, W.B.; Cui, D.Y.; Xi, B.D. Untangling the response of fungal community structure, composition and function in soil aggregate fractions to food waste compost addition. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Kang, K.; Jia, L. Modified montmorillonite and illite adjusted the pref-erence of biotic and abiotic pathways of humus formation during chicken manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, S.; Porras, J.C.R.; Herencia, J.F.; Madejon, E. Chemical and biochemical properties in a silty loam soil under conventional and organic management. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 90, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X. Effects of long-term fertilization on corn productivity and its sustainability in an Ultisol of southern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wei, Y.X.; Liu, J.Z.; Yuan, J.C.; Liang, Y.; Ren, J.; Cai, H.G. Effects of maize straw and its biochar application on organic and humic carbon in water-stable aggregates of a Mollisol in Northeast China: A five-year field experiment. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, Z.; Shi, W.C.; Li, L.C.; Tian, R.M.; Huang, J.; Lin, R.S.; Wang, B.; Zhou, B. Material conversion, microbial community composition and metabolic functional succession during green soybean hull composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.P.; Banerjee, S.; He, J.Z.; Fan, J.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Wei, X.Y.; Hu, H.W.; Zheng, Y.; Duan, C.J.; Wan, S.; et al. Manure application increases microbiome complexity in soil aggregate fractions: Results of an 18-year field experiment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 307, 107249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guber, A.K.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Levkovsky, E.V. Fractal mass-size scaling of wetting soil aggregates. Ecol. Model. 2005, 182, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, J.R.; Singh, B.P.; Cowie, A.L.; Fang, Y.Y.; Collins, D.; Dougherty, W.J.; Singh, B.K. Carbon and nutrient mineralisation dynamics in aggregate-size classes from different tillage systems after input of canola and wheat residues. Soil Biol. Bio-Chem. 2018, 116, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Paustian, K. Aggregate-associated soil organic matter as an ecosystem property and a measurement tool. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.J.; Zeng, X.B.; Huang, T.; Che, Z.X.; Su, S.M.; Bai, L.Y. Response of soil organic carbon and its aggregate fractions to long-term fertilization in irrigated desert soil of China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 2758–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Jia, Z.K.; Liang, L.Y.; Yang, B.P.; Ding, R.X.; Nie, J.F.; Wang, J.P. Maize straw effects on soil aggregation and other properties in arid land. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 153, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Q.H.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yu, X.C.; Peng, X. Carbon sequestration efficiency in paddy soil and upland soil under long-term fertilization in southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 130, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.W.; Friman, V.P.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.Q.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.W.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.R. Long-term fertilization regimes drive the abundance and composition of N-cycling-related prokaryotic groups via soil particle-size differentiation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Giani, L. Water-stable aggregates, glomalin-related soil protein, and carbohydrates in a chronosequence of sandy hydromorphic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wu, S.; Lu, X.; Ren, Z.; Wu, Q.; Xu, M.; Ren, C.; Yang, G.; Han, X. Organic carbon, nitrogen accumulation, and soil aggregate dynamics as affected by vegetation restoration patterns in the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2021, 196, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Tayasu, I.; Komatsuzaki, M.; Uchida, M.; Shibata, Y.; Kaneko, N. Changes in soil aggregate carbon dynamics under no-tillage with respect to earthworm biomass revealed by radiocarbon analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.F.; Ge, N.N.; Yu, S.; Wei, X.R.; Wang, X.; Jin, J.W.; Liu, X.T.; Shao, M.G.; Wei, Y.C.; Kang, L. Response of aggregate associated organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous to re-vegetation in agropastoral ecotone of northern China. Geoderma 2019, 341, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schluter, S.; Vogel, H.J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmi, B.; Nath, A.J.; Lal, R.; Das, A.K. Water stable aggregates and the associated active and recalcitrant carbon in soil under rubber plantation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbie, S.E. Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: Revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, X.J.; Xiao, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, B.H. Effects of farmland conversion on the stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil aggregates on the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2019, 351, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Liang, S.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, W.B.; Wang, Y.J. Machine learning for the prediction of L-chinensis carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents and understanding of mechanisms underlying grassland degradation. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, Y.F. Spatial characteristics of ecological stoichiometry and their driving factors in farmland soils in Poyang Lake Plain, Southeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Ren, L.; Song, L.; Duan, Y.; Hao, W. Plant stoichiometry characteristics and relationships with soil nutrients in robin-ia pseudoacacia communities of different planting ages. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, C.A.; Richardson, A.E.; Wade, L.J.; Batten, G.D.; Kirkegaard, J.A. Carbon-nutrient stoichiometry to increase soil carbon sequestration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 60, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Ju, W.L.; Jin, X.L.; Li, M.D.; Shen, G.T.; Duan, C.J.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhao, W.; Fang, L.C. Associated soil aggregate nutrients and controlling factors on aggregate stability in semiarid grassland under different grazing prohibition timeframes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Xiang, W.H.; Gou, M.M.; Chen, L.; Lei, P.F.; Fang, X.; Deng, X.W.; Ouyang, S. Effects of forest restoration on soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and their stoichiometry in Hunan, Southern China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hui, D.F.; Yang, X.T.; Deng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Ren, H. Soil C:N:P stoichiometry in tropical forests on Hainan Island of China: Spatial and vertical variations. Catena 2021, 201, 105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Kerkhoff, A.J.; Swenson, N.G.; Enquist, B.J. Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.R.; An, S.S. Ecological stoichiometry in leaves, roots, litters and soil among different plant communities in a desertified region of Northern China. Catena 2018, 166, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Xie, Z.H.; Yu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, C.K.; Wang, G.H.; Wu, J.J.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.B. Impact of surface soil manuring on particulate carbon fractions in relevant to nutrient stoichiometry in a Mollisol profile. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 207, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.T. Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.L.; Ding, W.X.; Xiang, J.; Qin, S.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Ziadi, N. Carbon sequestration in an intensively cultivated sandy loam soil in the North China Plain as affected by compost and inorganic fertilizer application. Geoderma 2014, 230, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Peng, B.; Wang, R.; Batbayar, J.; Hoogmoed, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Sun, B. Responses of crop productivity and physical protection of organic carbon by macroaggregates to long-term fertilization of an Anthrosol. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, S.S.; Nyborg, M.; Goddard, T.; Puurveen, D. Long-term tillage, straw management, and nitrogen fertilization effects on organic matter and mineralizable carbon and nitrogen in a black chernozem soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2012, 43, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Xiang, Y.; Xue, Z.J.; An, S.S.; Darboux, F. Soil aggregation and intra-aggregate carbon fractions in relation to vegetation succession on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2015, 124, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Aggregate and soil organic matter dynamics under conventional and no-tillage systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: A mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.S.; Chen, S.; Hu, R.G.; Li, Y.Y. Aggregate stability and size distribution of red soils under different land uses integrally regulated by soil organic matter, and iron and aluminum oxides. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.Y.; Ding, W.X.; Luo, J.F.; Geng, R.L.; Cai, Z.C. Long-term application of organic manure and mineral fertilizers on aggregation and aggregate-associated carbon in a sandy loam soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.F.; Zhou, L.K.; Chen, L.J.; Li, R.H. Compositional proportion of soil characteristic microaggregates and soil fertility evaluation. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2001, 38, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.F.; Xin, X.L.; Zhu, A.N.; Zhang, J.B.; Yang, W.H. Effects of tillage and residue managements on organic C accumulation and soil aggregation in a sandy loam soil of the North China Plain. Catena 2017, 156, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Xu, H.W.; Wu, X. Soil aggregate stability and its stoichiometric characteristics in robinia pseudoacacia forest within different vegetation zones on the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 2904–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Gao, P.; Bai, T.J.; Cao, W.; Xie, J.Y.; Liu, C.M.; Yuan, X.Y. Distribution and stoichiometry of water-stable aggregates of different vegetation restoration patterns in degraded red soil regions. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.Y.; Hou, M.M.; Zhou, Y.T.; Wang, R.J.; Zhang, S.L.; Yang, X.Y.; Sun, B.H. Carbon sequestration and mineralization of aggregate-associated carbon in an intensively cultivated Anthrosol in north China as affected by long term fertilization. Ge-oderma 2017, 296, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Wang, J.; Fang, K.; Cao, L.; Sha, Z.; Cao, L. Wheat straw incorporation affecting soil carbon and nitrogen fractions in Chinese paddy soil. Agriculture 2021, 11, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craswell, E.T.; Saffigna, P.G.; Waring, S.A. The mineralization of organic nitrogen in dry soil aggregates of different sizes. Plant Soil 1970, 33, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Mulvaney, R.L.; Ellsworth, T.R.; Boast, C.W. The myth of nitrogen fertilization for soil carbon sequestration. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.Q.; Yu, G.R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 8, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar]
- Manjaiah, K.M.; Voroney, R.P.; Sen, U. Soil organic carbon stocks, storage profile and microbial biomass under different crop management systems in a tropical agricultural ecosystem. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. Nutrient and stoichiometric characteristics of aggregates in a sloping farmland area under different tillage practices. Sustainability 2021, 13, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.T.; Hu, F.N.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Liu, G.; Zhao, S.W. Shifts in soil nutrient concentrations and C:N:P stoichiometry during long-term natural vegetation restoration. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.C.; Xin, L.I.; Dong, Y.H.; Ya-Yun, L.I.; Cheng, M.; Shao-Shan, A.N. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics and physical-chemical properties of soils at different latitudes on the loess plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 870–879. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Sheng, M.; Tian, J. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, southwest China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.T.; Wei, Z.J.; Dai, J.; Dai, J.Z.; Yan, R.R.; Liu, W.T.; Wang, T.L. Responses of plant and soil C:N:P stoichiometry to ferti-lization in Leymus chinensis mowing meadow. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 26, 620–627. [Google Scholar]
- Peltre, C.; Bruun, S.; Du, C.; Thomsen, I.K.; Jensen, L.S. Assessing soil constituents and labile soil organic carbon by mid-infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, K.; Taguchi, S.; Sato, S. Soil aggregate formation and stability induced by starch and cellulose. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 87, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S.; Gessner, M.O. N:P ratios influence litter decomposition and colonization by fungi and bacteria in microcosms. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Treatments | Chemical Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Organic Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CF | 450 | 180 | 180 | 0 |
| OF | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19,500 |
| CO | 225 | 180 | 180 | 9750 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Dai, W.; Fang, K.; Gao, H.; Sha, Z.; Cao, L. Nutrient Characterization in Soil Aggregate Fractions with Different Fertilizer Treatments in Greenhouse Vegetable Cultivation. Agriculture 2022, 12, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040440
Wang J, Dai W, Fang K, Gao H, Sha Z, Cao L. Nutrient Characterization in Soil Aggregate Fractions with Different Fertilizer Treatments in Greenhouse Vegetable Cultivation. Agriculture. 2022; 12(4):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040440
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jun, Wei Dai, Kaikai Fang, Hui Gao, Zhimin Sha, and Linkui Cao. 2022. "Nutrient Characterization in Soil Aggregate Fractions with Different Fertilizer Treatments in Greenhouse Vegetable Cultivation" Agriculture 12, no. 4: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040440
APA StyleWang, J., Dai, W., Fang, K., Gao, H., Sha, Z., & Cao, L. (2022). Nutrient Characterization in Soil Aggregate Fractions with Different Fertilizer Treatments in Greenhouse Vegetable Cultivation. Agriculture, 12(4), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040440






