Validation of Molecular Markers of Barley Net Blotch Resistance Loci on Chromosome 3H for Marker-Assisted Selection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Pathogen Isolates and Culture Conditions
2.3. Fungal Preparation, Inoculation of Seedlings, and Disease Assessment
2.4. Development of KASP Markers
2.5. Testing the Diagnostic Value of SNP-Markers
2.6. Development of PCR Markers
3. Results
3.1. Resistance of Barley Cultivars and Accessions to Ptt Isolates
3.2. Segregation Analysis
3.3. KASP Genotyping Results
3.4. Allele-Specific PCR Markers Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathre, D.E. (Ed.) Compendium of Barley Diseases, 2nd ed.; American Phytopathological Society Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1997; ISBN 089054218X. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.P.; Steffenson, B.J.; Webster, R.K. Host range of Pyrenophora teres f. teres isolates from California. Plant Dis. 1993, 77, 942–947. [Google Scholar]
- Garozi, R.; Angelotti, P.; Feksa, H.R.; Tessmann, D.J. First Report of Pyrenophora teres f. teres Causing Leaf Spot on Wheat in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelló, A.E.; Couretot, L.; Curti, A.; Uranga, J.P.; Consolo, V.F. First report of spot lesion of wheat caused by Pyrenophora teres f. sp maculata observed in Argentina. Crop Prot. 2019, 122, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, L.A.; Ternyuk, I.G.; Mironenko, N.V. Pyrenophora teres, an agent causing wheat leaf spot. Microbiology 2010, 79, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, B.; Csősz, M.; Kopahnke, D.; Varga, J. First report on Pyrenophora teres causing lesions of wheat leaves in Hungary. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedegård-Petersen, V. Pyrenophora teres f. maculata f. nov. and Pyrenophora teres f. teres on barley in Denmark. In Yearbook of the Royal Veterinary and Agricultural University; Royal Veterinary and Agricultural University: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1971; pp. 124–144. [Google Scholar]
- Smedegård-Petersen, V. Pathogenesis and Genetics of Net-Spot Blotch and Leaf Stripe of Barley Caused by Pyrenophora teres and Pyrenophora graminea, DSR Forlgag; Royal Veterinary and Agricultural University: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1976; 176p. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimova, A.V.; Mironenko, N.V.; Levshtanov, S.A. The first finding of the fungus Pyrenophora teres f. maculata in the Krasnodar region. Plant Prot. News 2011, 3, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lashina, N.M.; Afanasenko, O.S. Susceptibility to leaf blights of commercial barley cultivars in North-Western region of Russia. Plant Prot. News 2019, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afanasenko, O.S.; Koziakov, A.V.; Hedlay, P.E.; Lashina, N.M.; Anisimova, A.V.; Manninen, O.; Jalli, M.; Potokina, E.K. Mapping of the loci controlling the resistance to Pyrenophora teres f. teres and Cochliobolus sativus in two double haploid barley populations. Russ. J. Genet. Appl. Res. 2015, 5, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasenko, O.S.; Jalli, M.; Pinnschmidt, H.O.; Filatova, O.; Platz, G.J. Development of an international standard set of barley differential genotypes for Pyrenophora teres f. teres. Plant Pathol. 2009, 58, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekauz, A. Characterization and distribution of pathogenic variation in Pyrenophora teres f. teres and P. teres f. maculata from western Canada. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1990, 12, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Zhong, S.; Stasko, A.K.; Edwards, M.C.; Friesen, T.L. Virulence Profile and Genetic Structure of a North Dakota Population of Pyrenophora teres f. teres, the Causal Agent of Net Form Net Blotch of Barley. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffenson, B.J.; Webster, R. Pathotype diversity of Pyrenophora teres f. teres on Barley. Phytopathololy 1992, 82, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oğuz, A.Ç.; Karakaya, A. Pathotypes of Pyrenophora teres on barley in Turkey. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2017, 56, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouajila, A.; Zoghlami, N.; Al Ahmed, M.; Baum, M.; Ghorbel, A.; Nazari, K. Comparative virulence of Pyrenophora teres f. teres from Syria and Tunisia and screening for resistance sources in barley: Implications for breeding. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 53, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boungab, K.; Belabid, L.; Fortas, Z.; Bayaa, B. Pathotype diversity among Algerian isolates of Pyrenophora teres f. teres. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2012, 51, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, R.; Bryngelsson, T.; Gustafsson, M. Viulence studies of Swedish net blotch isolates (Drechslera teres) and identification of resistant barley lines. Euphytica 1997, 94, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakazi, F.; Göransson, M.; Stefánsson, T.S.; Hokka, M.; Jalli, M.; Hallson, J.H. Virulence of Icelandic Pyrenophora teres f. teres populations and resistance of Icelandic spring barley lines. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 104, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffenson, B.J.; Hayes, P.M.; Kleinhofs, A. Genetics of seedling and adult plant resistance to net blotch (Pyrenophora teres f. teres) and spot blotch (Cochliobolus sativus) in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1996, 92, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, H.; Platz, G.J.; Chalmers, K.; Raman, R.; Read, B.J.; Barr, A.R.; Moody, D.B. Mapping of genetic regions associated with net form of net blotch resistance in barley. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2003, 54, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Lapitan, N.L.; Steffenson, B. QTL mapping of net blotch resistance genes in a doubled-haploid population of six-rowed barley. Euphytica 2004, 137, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, M.; Gupta, S.; Platz, G.J.; Ablett, G.A.; Loughman, R.; Embiri, L.C.; Poulsen, D.; Li, C.D.; Lance, R.C.M.; Galwey, N.W.; et al. Mapping and validation of the genes for resistance to Pyrenophora teres f. teres in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2003, 54, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cakir, M.; Gupta, S.; Li, C.; Hayden, M.; Mather, D.E.; Ablett, G.A.; Platz, G.J.; Broughton, S.; Chalmers, K.J.; Loughman, R.; et al. Genetic mapping and QTL analysis of disease resistance traits in the barley population Baudin × AC Metcalfe. Crop Pasture Sci. 2011, 62, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, T.L.; Faris, J.D.; Lai, Z.; Steffenson, B.J. Identification and chromosomal location of major genes for resistance to Pyrenophora teres in a doubled-haploid barley population. Genome 2006, 49, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, T.S.; Rossnagel, B.G.; Pozniak, C.J.; Scoles, G.J. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with barley net blotch resistance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 116, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, T.S.; Rossnagel, B.G.; Scoles, G.J. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with spot blotch and net blotch resistance in a doubled-haploid barley population. Mol. Breed. 2012, 30, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmensiek, A.; Platz, G.J.; Mace, E.; Poulsen, D.; Sutherland, M.W. Mapping of adult plant resistance to net form of net blotch in three Australian barley populations. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 58, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierre, S.S.; Gustus, C.; Steffenson, B.J.; Dill-Macky, R.; Smith, K.P. Mapping net form net blotch and Septoria speckled leaf blotch resistance loci in barley. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manninen, O.M.; Jalli, M.; Kalendar, R.; Schulman, A.; Afanasenko, O.; Robinson, J. Mapping of major spot-type and net-type net blotch resistance genes in the Ethiopian barley (Hordeum vulgare) line CI 9819. Genome 2006, 49, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- König, J.; Perovic, D.; Kopahnke, D.; Ordon, F. Mapping seedling resistance to net form of net blotch (Pyrenophora teres f. teres) in barley using detached leaf assay. Plant Breed. 2014, 133, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koladia, V.M.; Faris, J.D.; Brueggeman, J.K.; Richards, R.S.; Chao, S.; Friesen, T.L. Genetic analysis of net form net blotch resistance in barley lines CIho 5791 and Tifang against a global collection of P. teres f. teres isolates. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Platz, G.J.; de Klerk, D.; Fowler, R.A.; Smit, F.; Potgieter, F.G.; Prins, R. Identification and mapping of net form of net blotch resistance in south African barley. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinglasan, E.; Hickey, L.; Ziems, L.; Fowler, R.; Anisimova, A.; Baranova, O.; Lashina, N.; Afanasenko, O. Genetic characterization of resistance to Pyrenophora teres f. teres in the International Barley Differential Canadian Lake Shore. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonneberger, R.; Ficke, A.; Lillemo, M. Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to net form net blotch in a collection of Nordic barley germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 2025–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatter, T.; Maurer, A.; Kopahnke, D.; Perovic, D.; Ordon, F.; Pillen, K. A nested association mapping population identifies multiple small effect QTL conferring resistance against net blotch (Pyrenophora teres f. teres) in wild barley. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.K.; Friesen, T.L.; Brueggeman, R.S. Association mapping utilizing diverse barley lines reveals net form net blotch seedling resistance/susceptibility loci. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezrou, R.; Verma, R.P.S.; Chao, S.; Brueggeman, R.S.; Belgadi, L.; Arbaoui, M.; Rehman, S.; Gyawali, S. Genome-wide association studies of net form of net blotch resistance at seedling and adult plant stages in spring barley collection. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanova, I.V.; Lashina, N.M.; Mustafin, Z.S.; Gorobets, S.A.; Efimov, V.M.; Afanasenko, O.S.; Khlestkina, E.K. SNPs associated with barley resistance to isolates of Pyrenophora teres f. teres. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakazi, F.; Afanasenko, O.; Anisimova, A.; Platz, J.; ·Snowdon, R.; Kovaleva, O.; Zubkovich, A.; Ordon, F. Genetic analysis of a worldwide barley collection for resistance to net form of net blotch disease (Pyrenophora teres f. teres). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2633–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Stefenson, B.J.; Smith, K.P.; Smith, M.; Dill-Macky, R. Identification of quantitative trait loci for net form net blotch resistance in contemporary barley breeding germplasm from the USA using genome-wide association mapping. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daba, S.D.; Horsley, R.D.; Brueggeman, R.; Chao, S.; Mohammadi, M. Genome-623 wide association studies and candidate gene identification for leaf scald and net blotch in 624 barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, S.J.; Wyatt, N.A.; Brueggeman, R.S.; Friesen, T.L. Research advances in the Pyrenophora teres—Barley interaction. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mode, C.J.; Schaller, C.W. Two additional factors for host resistance to net blotch in barley. Agron. J. 1958, 50, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bockelman, H.E.; Sharp, E.L.; Eslick, R.F. Trisomic analysis of genes for resistance to scald and net blotch in several barley cultivars. Can. J. Bot. 1977, 55, 2142–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, R.A.; Platz, G.J.; Bell, K.L.; Fletcher, S.E.H.; Franckowiak, J.D.; Hickey, L.T. Pathogenic variation of Pyrenophora teres f. teres in Australia. Austral. Plant Pathol. 2017, 46, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascher, M.; Wicker, T.; Jenkins, J.; Plott, C.; Lux, T.; Koh, C.S.; Ens, J.; Gundlach, H.; Boston, L.B.; Tulpová, Z.; et al. Long-read sequence assembly: A technical evaluation in barley. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1888–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vida, G.; Gál, M.; Uhrin, A.; Veisz, O.; Syed, N.H.; Flavell, A.J.; Wang, Z.; Bedő, Z. Molecular markers for the identification of resistance genes and marker-assisted selection in breeding wheat for leaf rust resistance. Euphytica 2009, 170, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Li, C.D.; Loughman, R.; Cakir, M.; Platz, G.; Westcott, S.; Bradley, J.; Broughton, S.; Lance, R. Quantitative trait loci and epistatic interactions in barley conferring resistance to net type net blotch (Pyrenophora teres f. teres) isolates. Plant Breed. 2010, 129, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bespalova, L.A.; Vasilyev, A.V.; Karlov, G.I.; Soloviev, A.A.; Afanasenko, O.S.; Davoyan, R.O.; Davoyan, E.R.; Divashuk, M.G.; Koshkin, V.A.; Potokina, E.K.; et al. Application of molecular markers in winter wheat and triticale breeding in Krasnodar Lukyanenko Research Institute of Agriculture. In Proceedings of the International Conferece of Wheat Genetic Resources and Genomics (WGRG), Novosibirsk, Russia, 28 August–1 September 2011; p. 48. Available online: http://www.bionet.nsc.ru/wgrg/tezis.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Lüders, T.; Ahlemeyer, J.; Förster, J.; Weyen, J.; Roßa, E.; Korzun, V.; Lex, J.; Friedt, W.; Ordon, F. Verification of marker-trait associations in bi-parental winter barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) DH populations. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semagn, K.; Babu, R.; Hearne, S.; Olsen, M. Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive allele specific PCR (KASP): Overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol. Bred. 2014, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Holme, J.; Anthony, J. SNP genotyping: The KASP assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1145, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertiro, B.T.; Ogugo, V.; Worku, M.; Das, B.; Olsen, M.; Labuschagne, M.; Semagn, K. Comparison of Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) and genotyping by sequencing (GBS) for quality control analysis in maize. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasheed, A.; Wen, W.; Gao, F.; Zhai, S.; Jin, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dreisigacker, S.; Xia, X.; et al. Development and validation of KASP assays for genes underpinning key economic traits in bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1843–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-T.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, M.; Rudd, J.C.; Xue, Q.; Ibrahim, A.M.H.; Garza, L.; Wang, S.; et al. Development and validation of KASP markers for the greenbug resistance gene Gb7 and the Hessian fly resistance gene H32 in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekauz, A. A numerical scale to classify reactions of barley to Pyrenophora teres. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1985, 7, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Boudiar, R.; Casas, A.M.; Igartua, E.; Contreras-Moreira, B. BARLEYMAP: Physical and genetic mapping of nucleotide sequences and annotation of surrounding loci in barley. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascher, M.; Gundlach, H.; Himmelbach, A.; Stein, N. A chromosome conformation capture ordered sequence of the barley genome. Nature 2017, 544, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mascher, M.; Muehlbauer, G.J.; Rokhsar, D.S.; Chapman, J.; Schmutz, J.; Barry, K.; Muñoz-Amatriaín, M.; Close, T.J.; Wise, R.P.; Schulman, A.H.; et al. Anchoring and ordering NGS contig assemblies by population sequencing (POPSEQ). Plant J. 2013, 76, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M.; Ugene Team. Unipro UGENE: A unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, S.J.; Gyenis, L.; Bossolini, E.; Hayes, P.M.; Matus, I.; Smith, K.P.; Steffenson, B.J.; Tuberosa, R.; Muehlbauer, G.J. Validation of Quantitative Trait Loci for Multiple Disease Resistance in Barley Using Advanced Backcross Lines Developed with a Wild Barley. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- König, J.; Perovic, D.; Kopahnke, D.; Ordon, F. Development of an efficient method for assessing resistance to the net type of net blotch (Pyrenophora teres f. teres) in winter barley and mapping of quantitative trait loci for resistance. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Zhu, C. The role of receptor-like protein kinases (RLKs) in abiotic stress response in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashisht, A.A.; Tuteja, N. Stress responsive DEAD-box helicases: A new pathway to engineer plant stress tolerance. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2006, 84, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Huang, L.; Yin, X.; Zhao, G.; Lin, F.; Xia, X.; Xu, G. OsSGL, a novel DUF1645 domain-containing protein, confers enhanced drought tolerance in transgenic rice and Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Li, M.; Zhang, B.; Cui, Y.; Yin, X.; Xia, X. Poaceae Orthologs of Rice OsSGL, DUF1645 Domain-Containing Genes, Positively Regulate Drought Tolerance, Grain Length and Weight in Rice. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; Du, M.; Li, J. The Sm Gene Conferring Resistance to Gray Leaf Spot Disease Encodes a NBS-LRR Plant Resistance Protein in Tomato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, N.; Delbono, S.; Çelik Oğuz, A.; Cattivelli, L.; Valè, G.; Tondelli, A. Resistance of European Spring 2-Row Barley Cultivars to Pyrenophora graminea and Detection of Associated Loci. Agronomy 2021, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Mahmood, T. Functional role of DREB and ERF transcription factors: Regulating stress-responsive network in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, G.K. Role of plant U-BOX (PUB) protein in stress and development. Plant Stress 2013, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liebrand, T.W.; van den Berg, G.C.; Zhang, Z.; Smit, P.; Cordewener, J.H.; America, A.H.; Sklenar, J.; Jones, A.M.; Tameling, W.I.; Robatzek, S.; et al. Receptor-like kinase SOBIR1/EVR interacts with receptor-like proteins in plant immunity against fungal infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10010–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todorovska, E. Retrotransposons and their role in plant—genome evolution. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2007, 21, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barkan, A.; Small, I. Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 415–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Fu, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, K.; Yan, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; Min, D.-H. Genome-wide analysis of the serine carboxypeptidase-like protein family in Triticum aestivum reveals TaSCPL184-6D is involved in abiotic stress response. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmi, A. DUF581 is plant specific FCS-like zinc finger involved in protein-protein interaction. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoth, C.; Salus, M.S.; Girke, T.; Eulgem, T. The synthetic elicitor 3,5-dichloroanthranilic acid induces NPR1-dependent and npr1-independent mechanisms of disease resistance in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Venegas, R.; Avramova, Z. Evolution of the PWWP-domain encoding genes in the plant and animal lineages. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goff, K.E.; Ramonell, K.M. The role and regulation of receptor-like kinases in plant defense. Gene Regul. Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.T.; Liu, J.X.; Han, J.J. Chromatin remodeling factors regulate environmental stress responses in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewicz, D.; Archacki, R.; Palusiński, A.; Kotliński, M.; Fogtman, A.; Iwanicka-Nowicka, R.; Sosnowska, K.; Kuciński, J.; Pupel, P.; Olędzki, J.; et al. HD2C histone deacetylase and a SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex interact and both are involved in mediating the heat stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2108–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


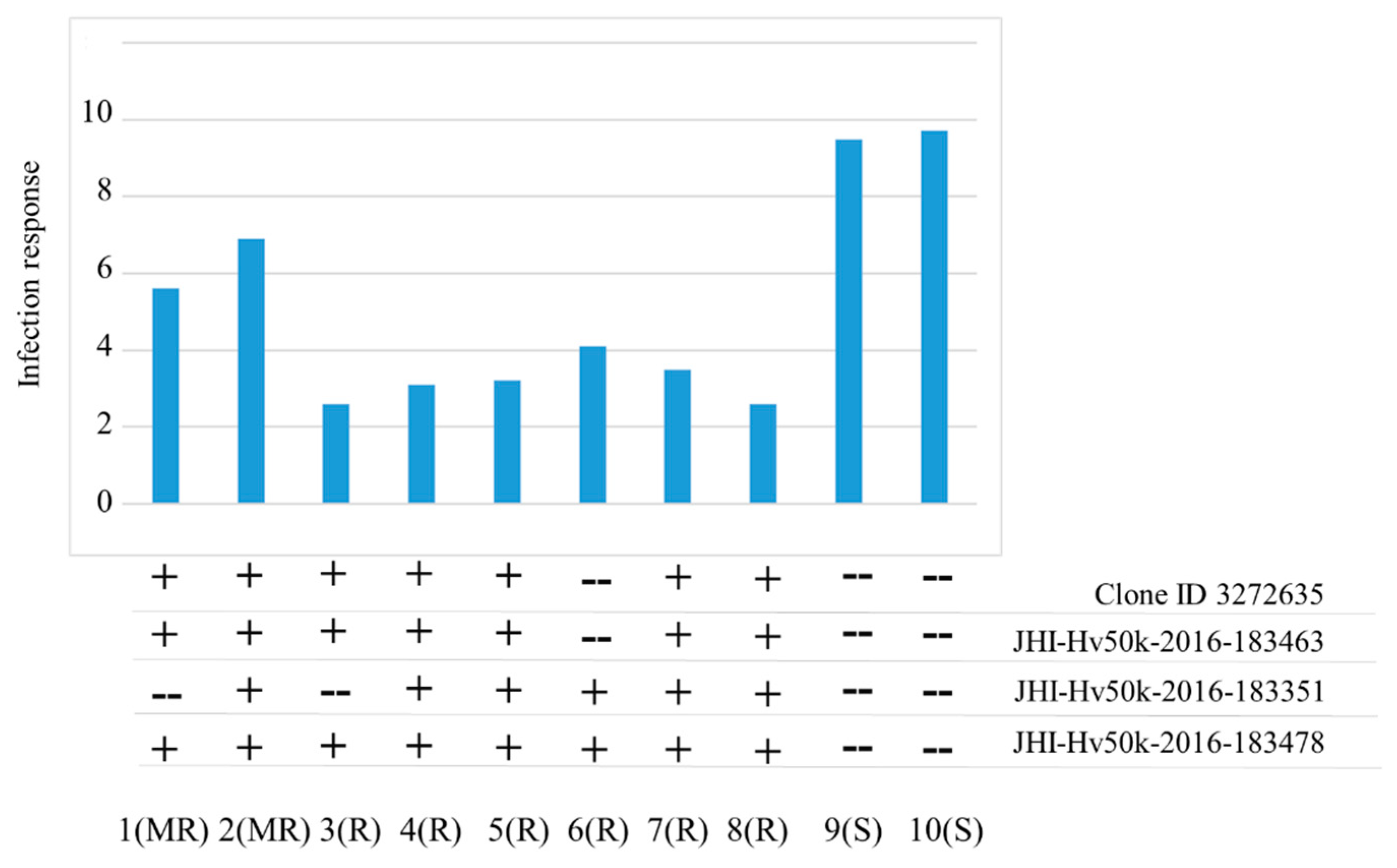
| Isolate | Origin | Barley Cultivar | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| F18 | Belarus, Zhodino | Fest | 2017 |
| S18 | Russia, Krasnodar | Sprinter | 2017 |
| B18 | Russia, Leningrad region | Tausen’ | 2016 |
| V13 | Russia, Leningrad region | Suzdalets | 2015 |
| Pr2 | Russia, Far East region | Primorskij 207 | 2015 |
| Germ7 | Germany, Quedlinburg | unknown | 2011 |
| Czech11.1 | Czech Republic, Lysice | unknown | 2011 |
| Can11 | Canada, Alberta | Harrington | 2010 |
| SA7 | South Africa, Bredasdorp | unknown | 2017 |
| Mor1 | Morocco, Brachoua of Zaer region | Amalou | 2017 |
| N | Barley Genotypes | Infection Responses (IRs) to Isolates | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F 18 | S 18 | B 18 | V 13 | Pr2 | Germ 7 | Cz 11.1 | Can11 | SA 7 | Mor 1 | Mean | ||
| 1. | Gesine (susceptible) Germany | 9 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9.6 |
| 2. | Harrington, TR 306 (susceptible) Canada | 10 | 9.8 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 9.3 | 9.7 | 8.8 | 7.8 | 8.9 |
| 3. | Local Turkey k-7689 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 5.8 | 3.7 | 4 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 4.5 | 6.2 | 5.8 |
| 4. | S-328 Mexico k-28671 | 9 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6.5 | 3.8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6.8 |
| 5. | Morex (C.I.15773) k-26959 | 1.7 | 3.8 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2.6 |
| 6. | Fox (C.I.9190, NFC 883) k-19182 | 1.7 | 2 | 1 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 6 | 5.5 | 3 | 2.9 |
| 7. | Zolo k-18552 | 1.5 | 3 | 1 | 1.4 | 3.7 | 6 | 1.7 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 3.1 |
| 8. | Local Ecuador k-21578 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 7 | 3.5 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 3.9 |
| 9. | Harbin (C.I. 4929) k-19282 | 4 | 5.3 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 4.3 | 7 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| 10. | Canadian Lake Shore, (C.I. 2750) k-25282 | 1 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 5.5 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.7 |
| DH or F2 Population | IRs of Parents | Number of Resistant (R) and Susceptible (S) Plants | Genetic Ratio | Chi Square | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | R | S | |||
| DH CLS/Harrington | 1.0 | 10 | 20 | 21 | 1:1 | 0.02 |
| F2 Morex/Gesine | 1.7 | 10 | 71 | 24 | 3:1 | 0.003 |
| F2 Fox/Gesine | 1.7 | 9.0 | 46 | 36 | 3:1 9:7 | 15.62 0.000 |
| F2 Zolo/Gesine | 1.5 | 9.0 | 58 | 26 | 3:1 | 1.59 |
| F2 k-21578/Gesine | 1 | 9.0 | 66 | 33 | 3:1 | 3.67 |
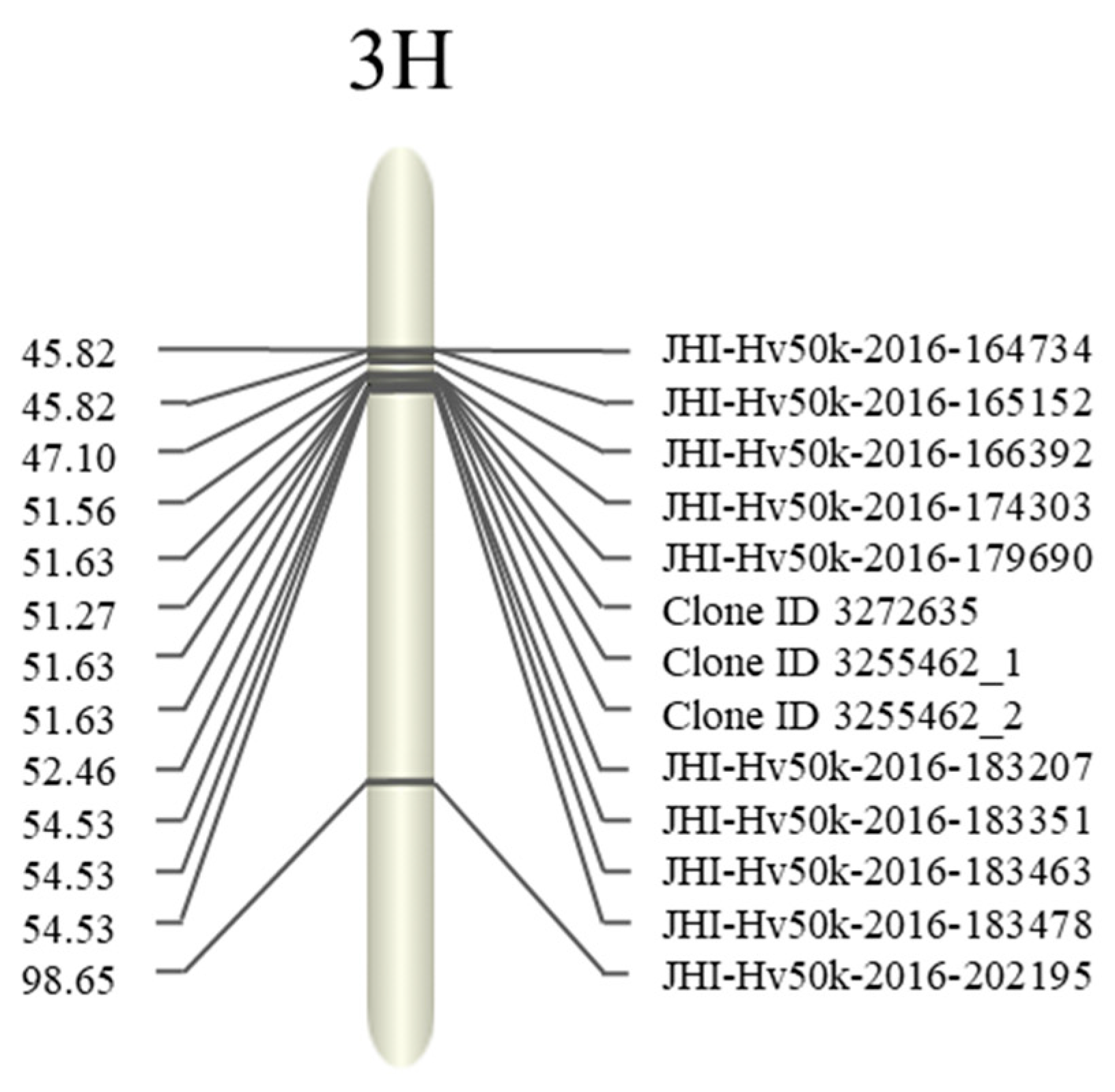
| SNP | Position | Sequence Containing SNP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| cM | bp | ||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-164734 | 45.82 | 48,713,634 | CTTTATGAGATCAACTGCTTCCTGCAGAAGTTTAGCCTTTCCCATAAGAT[C/T]CACCATACAGCCATAATGCTCGTGCTTGGGTTCAATCCTGTATTCCTGGA |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-165152 | 45.82 | 61,409,056 | TGACATTGAGCTGCTTTGCTTTGGTTCATCTCCGTTCTTCTTTTCTTTTA[C/G]TTTGAGCGGCAGCAGCACTGATGATGATGACGACGACGATGATGGACGGG |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-166356 | 47.31 | 102,070,302 | CCTCTTTACCAAGGATTCGTGTCTTTTTTGTTTAACCTTGTGAGTTCTGA[T/C]TGACTACTAAAAAGATCCGTGCCTGGTATCTTTCATGAAATAGCCCCATT |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-166392 | 47.1 | 112,536,071 | AAGACGGTTGGGTCTCCGGCTCTCCGACGCACACACGCCGCGCCGTCCAG[T/C]TGGTGGTTTCGTTGCTTTTTCTTTGAACTGCCCACCTTGTATAATCAATC |
| SCRI_RS_160464 | 51.56 | 255,019,281 | CTTGTAGTCGGTCGGTGTGTGGGAAGTTGGGATGAGAATGAACAAAAAGG[T/A]AAAAAGAAGAAATGAAAAGGATGAAAAAAGTTGGTGAAAAAGCTTGCACT |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-173670 | 51.56 | 285,191,294 | TTGCACTTGTGAAACTATTTGAATGTCTAAATGGGCTAACGAATGTTGCC[T/C]TTGCGAACCATGGTAGCAGAAGTCCATGACAAGGATACCTAAAATTTCAG |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-174303 | 51.56 | 301,082,623 | AGACTGTTCTTTGCCAGATGTTGATTATCTCTACTCTCCACATGACAACT[G/A]TCATCCAAAACAACAACAGGTACAGGGAACCCCATAACAGGTTTACGGTT |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-179690 | 51.63 | 389,686,103 | GCGTGACCTCGGTAAAAAAACTTAGCCCGTCTGAAATTTTGCTTGAATCA[G/A]TACTTTCGCACTGAGTTAGATCTTCATTATACTTTCGACAATAGATTGTG |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-183207 | 52.46 | 442,203,921 | TTGCCACCAAAAGTGCTCTTGAGTTGACATGTTTATATATTGTTCTCGCC[A/T]ACTTGCTCCAGCATTTGCATAATAATCTGTAAACAGCTCGGACACTTCTT |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-183351 | 54.53 | 442,550,473 | TCTTGACGCCGGGAACCAGCATGAGAAGATATTTGAATGATGACATTTGC[T/C]TCTGGGATATCAATGGAATTATCACCCACCTATGCATTAATAGCAGAGAT |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-202195 | 98.65 | 553,150,117 | GGAAAGAAGATTGCTGCTTTCGTTCCCAATGATGGTTGCCTGAACTTCAT[C/T]GAGGAAAATGTATGTTCCCCATCTTGTACTTCTCAAATGTATGTTCTACA |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-183463 | 54.53 | 443,119,491 | TATCCATGGACCTGAAAGTGCCAAATTGTATAAGCCATATCATGTTTTTT[T/C]AGTACAAGCCAGATCATGCTTACAATGCTCACTTTATTCTTTCAAACATA |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-183478 | 54.53 | 44,311,006 | GCTAACTTTGTCACCAGCTGTGGTTCTTCTGATGTGTTTGTTTCTACCA[C/A]ATTTGTGTCTGTTAGTACTGGAACTTCAGAACTTTGAGGTTCGTTAGTTG |
| Clone ID 3272635 | 51.27 | 391,906,604 | CATCAAGAAGGCTGAGTCAAAGCCACGGGAGCCTAAGAAGAGGGTATAAC[C/G]TGCAGCTGGTGTTATATTGAGGTCCTTATAACCTTCACCTTGCATGCTCT |
| Clone ID 3255462_1 | 51.63 | 363,531,898 | GAAATTGGACATGTCAATCCGACCAAGAGATTCAGGAGAAATCCTCTCTA[G/A]GAAACCAAAATCAGATATAAGGATCTTTGCAGCGCGTTCATCCCATGCAT |
| Clone ID 3255462_2 | 51.63 | 363,531,871 | AGATTCAGGAGAAATCCTCTCTAGGAAACCAAAATCAGATATAAGGATCT[T/C]TGCAGCGCGTTCATCCCATGCATGGGCAGGAATGCCGGATAATTCCAGGC |
| Position | Number of Plants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | SNP | Genetic Position (cM) | Physical Position (bp) | Allele | Resistant | Susceptible |
| DH population Canadian Lake Shore/Harrington | ||||||
| 1 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-179690 | 51.63 | 389,686,103 | GG | 20 | 0 |
| AG | 0 | 0 | ||||
| AA | 0 | 21 | ||||
| 2 | Clone ID 3272635 | 51.27 | 391,906,604 | GG | 19 | 0 |
| CG | 0 | 0 | ||||
| CC | 1 | 20 | ||||
| 3 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183463 | 54.53 | 443,119,491 | CC | 1 | 21 |
| CT | 0 | 0 | ||||
| TT | 19 | 0 | ||||
| 4 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183478 | 54.53 | 443,111,006 | CC | 19 | 0 |
| CA | 0 | 0 | ||||
| AA | 1 | 21 | ||||
| 5 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183207 | 52.46 | 442,203,921 | TT | 19 | 0 |
| TA | 0 | 0 | ||||
| AA | 1 | 21 | ||||
| 6 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-164734 | 45.82 | 48,713,634 | CC | 20 | 0 |
| CT | 0 | 0 | ||||
| TT | 0 | 21 | ||||
| 7 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-165152 | 45.82 | 61,409,056 | CC | 20 | 0 |
| CG | 0 | 0 | ||||
| GG | 0 | 21 | ||||
| 8 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-166392 | 47.1 | 112,536,071 | CC | 0 | 21 |
| TC | 0 | 0 | ||||
| TT | 20 | 0 | ||||
| 9 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183351 | 54.53 | 442,550,473 | CC | 1 | 21 |
| CT | 0 | 0 | ||||
| TT | 19 | 0 | ||||
| 10 | Clone ID 3255462_1 | 51.63 | 363,531,898 | GG | 19 | 0 |
| AG | 0 | 0 | ||||
| AA | 1 | 21 | ||||
| 11 | Clone ID 3255462_2 | 51.63 | 363,531,871 | CC | 1 | 21 |
| CT | 0 | 0 | ||||
| TT | 19 | 0 | ||||
| Population F2 Fox/Gesine | ||||||
| 12 | Clone ID 3272635 | 51.27 | 391,906,604 | GG | 9 | 2 |
| CG | 10 | 4 | ||||
| CC | 0 | 11 | ||||
| 13 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183463 | 54.53 | 443,119,491 | CC | 0 | 12 |
| CT | 7 | 4 | ||||
| TT | 9 | 2 | ||||
| 14 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183478 | 54.53 | 443,111,006 | CC | 10 | 2 |
| CA | 9 | 4 | ||||
| AA | 0 | 12 | ||||
| 15 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183207 | 52.46 | 442,203,921 | TT | 10 | 1 |
| TA | 8 | 4 | ||||
| AA | 0 | 12 | ||||
| 16 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183351 | 54.53 | 442,550,473 | CC | 0 | 12 |
| CT | 9 | 4 | ||||
| TT | 10 | 2 | ||||
| Population F2 Morex/Gesine | ||||||
| 17 | Clone ID 3272635 | 51.27 | 391,906,604 | GG | 6 | 1 |
| CG | 11 | 4 | ||||
| CC | 2 | 19 | ||||
| 18 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183463 | 54.53 | 443,119,491 | CC | 2 | 18 |
| CT | 11 | 6 | ||||
| TT | 6 | 0 | ||||
| 19 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183478 | 54.53 | 443,111,006 | CC | 6 | 0 |
| CA | 11 | 6 | ||||
| AA | 2 | 19 | ||||
| 20 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183207 | 52.46 | 442,203,921 | TT | 6 | 0 |
| TA | 11 | 5 | ||||
| AA | 2 | 20 | ||||
| Population F2 Zolo/Gesine | ||||||
| 21 | Clone ID 3272635 | 51.27 | 391,906,604 | GG | 9 | 2 |
| CG | 10 | 4 | ||||
| CC | 0 | 11 | ||||
| 22 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183463 | 54.53 | 443,119,491 | CC | 0 | 12 |
| CT | 7 | 4 | ||||
| TT | 9 | 2 | ||||
| 23 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183478 | 54.53 | 443,111,006 | CC | 10 | 2 |
| CA | 9 | 4 | ||||
| AA | 0 | 12 | ||||
| 24 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183207 | 52.46 | 442,203,921 | TT | 10 | 1 |
| TA | 8 | 4 | ||||
| AA | 0 | 12 | ||||
| 25 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183351 | 54.53 | 442,550,473 | CC | 0 | 12 |
| CT | 9 | 4 | ||||
| TT | 10 | 2 | ||||
| Population F2 Local k-21578/Gesine | ||||||
| 26 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-179690 | 51.63 | 389,686,103 | GG | 18 | 0 |
| AG | 1 | 8 | ||||
| AA | 1 | 9 | ||||
| 27 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183463 | 54.53 | 443,119,491 | CC | 1 | 11 |
| CT | 10 | 7 | ||||
| TT | 9 | 0 | ||||
| 28 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183478 | 54.53 | 443,111,006 | CC | 9 | 0 |
| CA | 10 | 7 | ||||
| AA | 1 | 11 | ||||
| 29 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183207 | 52.46 | 442,203,921 | TT | 9 | 0 |
| TA | 10 | 7 | ||||
| AA | 1 | 11 | ||||
| 30 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-166392 | 47.1 | 112,536,071 | CC | 1 | 10 |
| TC | 1 | 8 | ||||
| TT | 18 | 0 | ||||
| 31 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-183351 | 54.53 | 442,550,473 | CC | 1 | 11 |
| CT | 10 | 7 | ||||
| TT | 9 | 0 | ||||
| QTL | Genetic Position (cM) * | Physical Position (bp) ** | Markers | Literature | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rpt-3H-4 | 46.0 | NA | Bmag0828-Bmac0067 | [63] | OUH602/Harrington RIL |
| 45.82 | NA | 11_20356 | [38] | GWAS Isolate LDN | |
| 45.82 | 48,713,634 | JHI-Hv50 k-2016-164734 | [41] | GWAS | |
| 47.1–47.31 | 102,070,302 112,536,071 | JHI-Hv50 k-2016-166356 JHI-Hv50 k-2016-166392 | [41] | GWAS | |
| QTLUH-3H | 45–51 | NA | HVM33 | [64] | DH Uschi/HHOR3073 Adult |
| QRptts-3HL | 47.61 | NA | 12_30721 | [38] | GWAS Isolate 15A |
| 54.53 | 442,550,473 | JHI-Hv50 k-2016-183351 | [41] | GWAS | |
| qPttCLS | 51.27–51.63 | 398,203,862–435,526,243 | 3255462, 3257991, 3272635, 4190028 | [35] | DH CLS/Harrington DArTseq markers |
| NBP_QRPtt3-2 | 52.01–54.53 | NA 443,115,672 443,551,729 | 11_10728 SCRI_RS_152172 SCRI_RS_186102 | [36] | GWAS |
| 51.2–52.46 | 189,518,077 184,635,059 442,203,921 | JHI-Hv50k-2016-169338, SCRI_RS_186341, JHI-Hv50k-2016-183207 | [40] | GWAS A2.6.0 | |
| QPt.3H-3 | 51.63 | NA | i_11_10966 | [37] | Wild barley NAM population HEB-25 |
| 52.01 | 442,185,927 | SCRI_RS_221644 | [33] | RIL CIho 5791/Tifang F6 | |
| 51.56 | 255,019,281 285,191,294 301,082,623 | SCRI_RS_160464 JHI-Hv50 k-2016-173670 JHI-Hv50 k-2016-174303 | [41] | GWAS |
| SNP | Physical Map (bp) | Gene | Type of Mutation | Amino Acid Submission | Polymorphism | Protein Product * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant | Susceptible | ||||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-164734 | 48,713,634 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0236970 | E | C/T | CC | TT | Pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-165152 | 61,409,056 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0238960 | D | G/C | CC | GG | DUF581 family protein |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-166392 | 112,536,071 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0246080 | U | C/T | TT | CC | plant/protein (protein of unknown function, DUF538) |
| 301,082,623 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0265210 | E | G/A | AA | GG | Tudor/PWWP/MBT superfamily protein | |
| Clone ID 3255462_2 | 363,531,871 | BART1_0-u20880 | T/C | TT | CC | Nontranslating CDS | |
| Clone ID 3255462_1 | 363,531,898 | BART1_0-u20880 | A/G | GG | AA | Nontranslating CDS | |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-179690 | 389,686,103 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0274650 | I | A/G | GG | AA | DUF1645 family protein |
| Clone ID 3272635 | 391,906,604 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0275090 | I | G/C | GG | CC | SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A-like protein 1 |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-183207 | 442,203,921 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0281340 | D | A/T | TT | AA | Receptor-like protein kinase |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-183351 | 442,550,473 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0281430 | E | C/T | TT | CC | DNA repair helicase |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-183478 | 443,111,006 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0281530 | E | C/A | CC | AA | DUF1645 family protein |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-183463 | 443,119,491 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0281540 | I | T/C | TT | CC | RING/U-box superfamily protein |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afanasenko, O.; Rozanova, I.; Gofman, A.; Lashina, N.; Novakazi, F.; Mironenko, N.; Baranova, O.; Zubkovich, A. Validation of Molecular Markers of Barley Net Blotch Resistance Loci on Chromosome 3H for Marker-Assisted Selection. Agriculture 2022, 12, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040439
Afanasenko O, Rozanova I, Gofman A, Lashina N, Novakazi F, Mironenko N, Baranova O, Zubkovich A. Validation of Molecular Markers of Barley Net Blotch Resistance Loci on Chromosome 3H for Marker-Assisted Selection. Agriculture. 2022; 12(4):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040439
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfanasenko, Olga, Irina Rozanova, Anastasiia Gofman, Nina Lashina, Fluturë Novakazi, Nina Mironenko, Olga Baranova, and Alexandr Zubkovich. 2022. "Validation of Molecular Markers of Barley Net Blotch Resistance Loci on Chromosome 3H for Marker-Assisted Selection" Agriculture 12, no. 4: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040439
APA StyleAfanasenko, O., Rozanova, I., Gofman, A., Lashina, N., Novakazi, F., Mironenko, N., Baranova, O., & Zubkovich, A. (2022). Validation of Molecular Markers of Barley Net Blotch Resistance Loci on Chromosome 3H for Marker-Assisted Selection. Agriculture, 12(4), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040439







