Bacterial Burden in the Air of Indoor Riding Arenas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Riding Arenas and Riding Programs
2.2. Sampling Methods
2.3. Identification of Bacteria
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
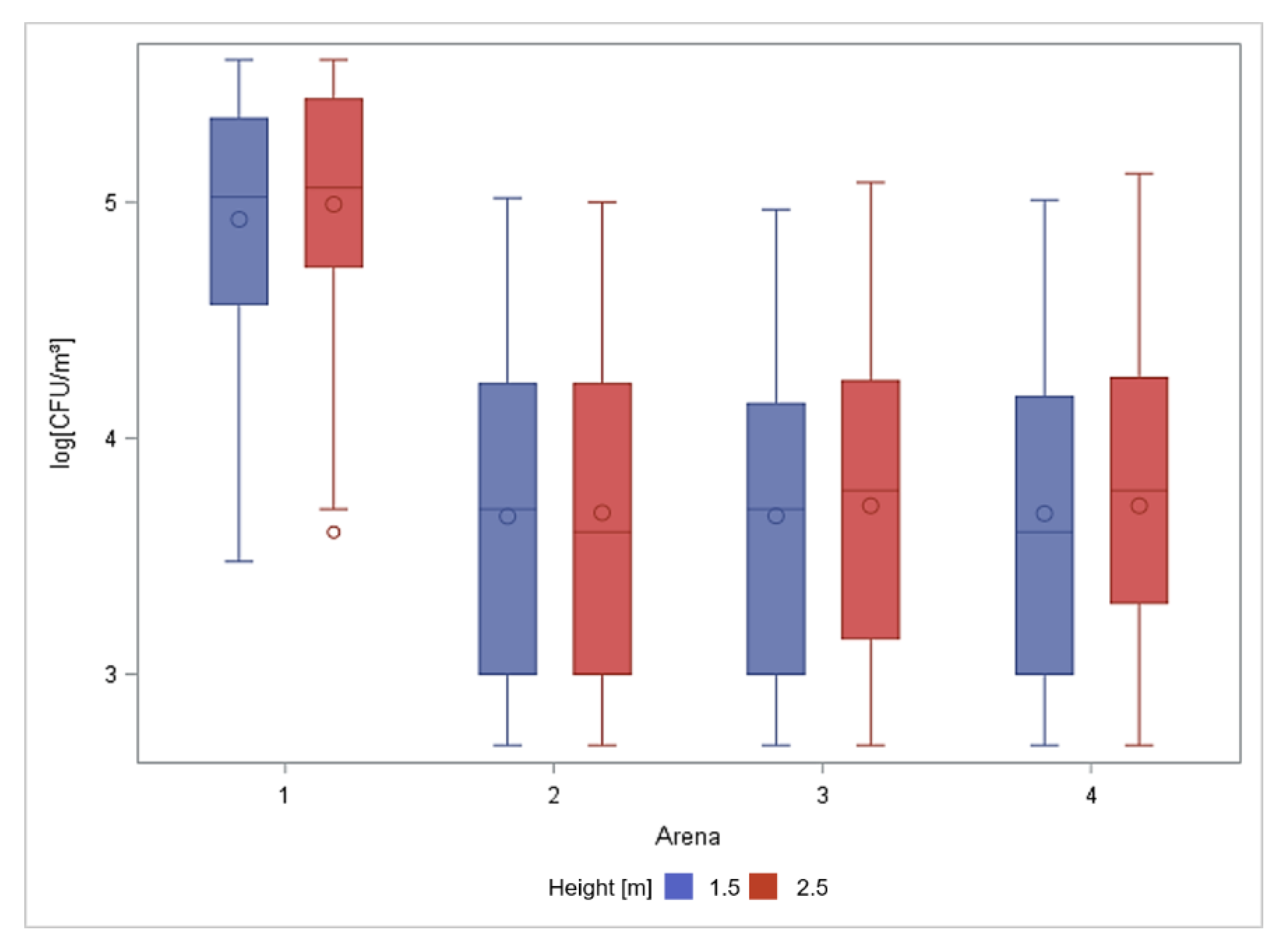
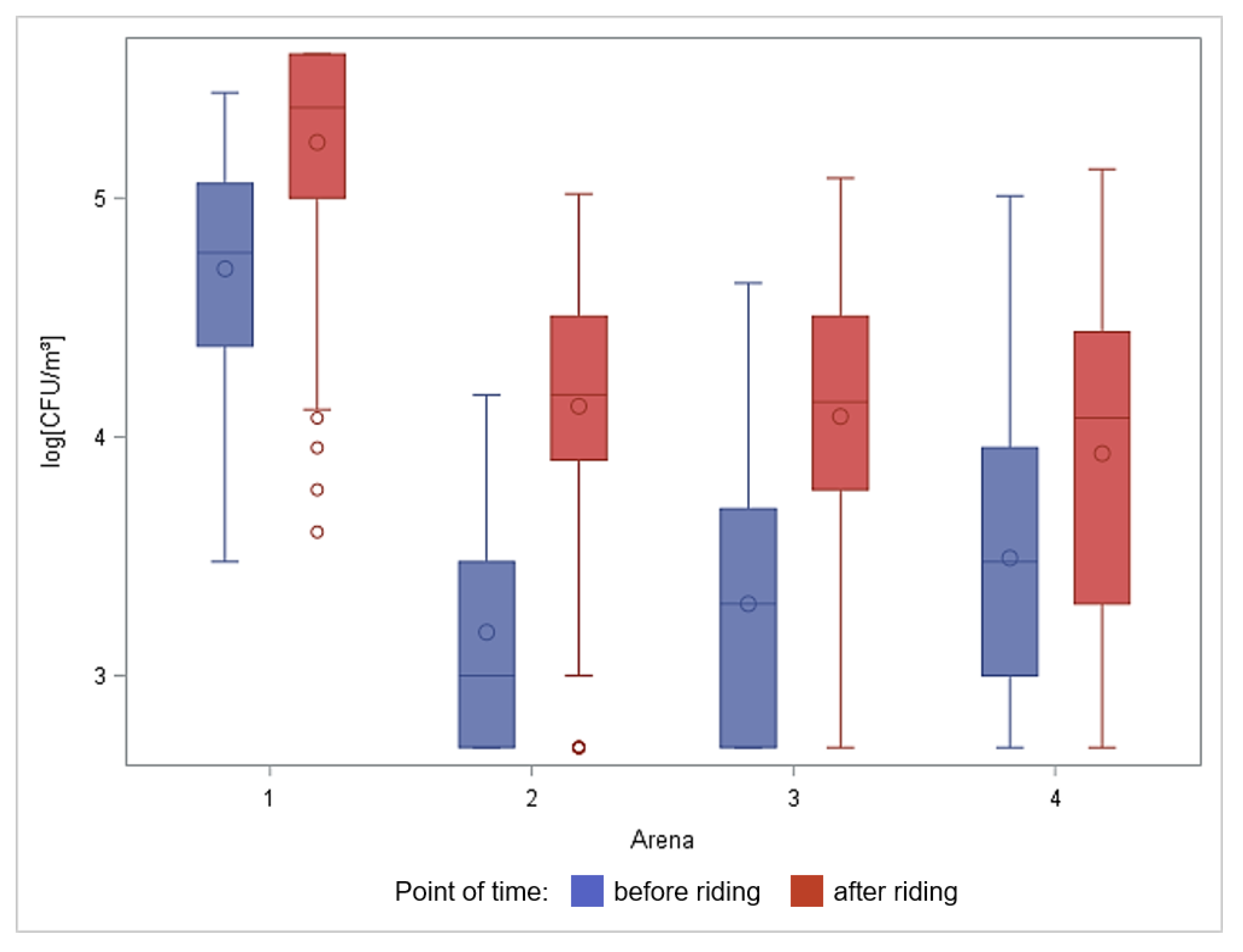
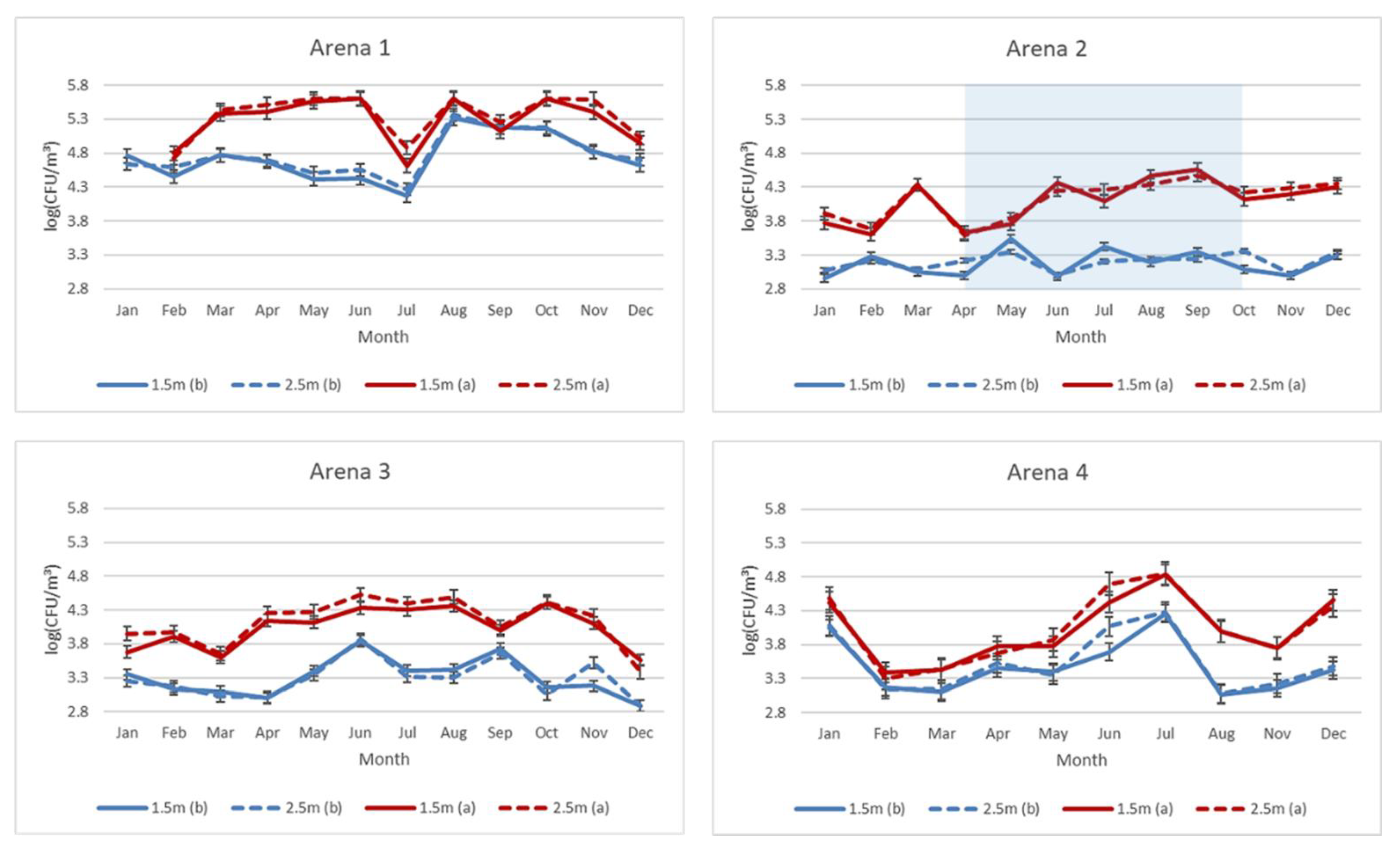
3.1. Total Number of Culturable Aerobic Bacteria in Air Samples
3.2. Total Number of Culturable Aerobic Bacteria in Ground Samples
3.3. Bacteria Species in Air and Ground Samples
4. Discussion
4.1. Aerobe Bacteria in Air Samples
4.2. Aerobe Bacteria in Ground Samples
4.3. Bacteria Species
4.4. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grzyb, J.; Podstawski, Z.; Bulski, K. Bacterial aerosol, particulate matter, and microclimatic parameters in the horse stables in Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 26992–27006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzińska, K.; Szejniuk, B.; Jurek, A.; Michalska, M.; Traczykowski, A.; Berleć, K. Evaluation Of Selected Physical And Microbiological Parameters Of Air In A Box-Stall Stable. Acta Sci. Pol. Zootech. 2016, 15, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, K.; Gaebel, G. Anatomie und Physiologie der Haustiere; UTB: Stuttgart, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mazan, M. Equine exercise physiology-challenges to the respiratory system. Anim. Front. 2022, 12, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapp, H.J.; Weiß, R.; Bockfisch, F.J.; Becker, M.; Stechele, M. Untersuchungen in Reithallen und an verschiedenen Reitbahnbelägen unter dem Aspekt der Atemwegsbelastung beim Pferd (Lufthygienische Untersuchungen in Reithallen). Tierärztliche Prax 1991, 19, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Krzywanek, H. Leistungsphysiologie. In Handbuch: Pferdepraxis; Dietz, O., Huskamp, B., Eds.; Enke Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2005; pp. 34–59. [Google Scholar]
- Pirie, R.S. Recurrent airway obstruction: A review. Equine. Vet. J. 2014, 46, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, J.W.; Reid, S.W.J.; Christley, R.M. A survey of horse owners in Great Britain regarding horses in their care. Part 2: Risk factors for recurrent airway obstruction. Equine Vet. J. 2007, 39, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullone, M.; Lavoie, J.P. Asthma “of horses and men”—How can equine heaves help us better understand human asthma immunopathology and its functional consequences? Mol. Immunol. 2015, 66, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasko, A.J.; Barkema, H.W.; Nicol, J.; Fernandez, N.; Logie, N.; Léguillette, R. Evaluation of a risk-screening questionnaire to detect equine lung inflammation: Results of a large field study. Equine. Vet. J. 2011, 43, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, V.; Swinburne, J.E.; Blott, S.C.; Nussbaumer, P.; Ramseyer, A.; Klukowska-Rötzler, J.; Dolf, G.; Marti, E.; Burger, D.; Leeb, T. Genetics of recurrent airway obstruction (RAO). Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr 2008, 115, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Ivester, K.M.; Couëtil, L.L.; Zimmerman, N.J. Investigating the link between particulate exposure and airway inflammation in the horse. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, P.H.; Parkin, T.D.; Shepherd, M.C. Lower respiratory tract disease in Thoroughbred racehorses: Analysis of endoscopic data from a UK training yard. Equine. Vet. J. 2008, 40, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivester, K.M.; Couëtil, L.L.; Moore, G.E. An observational study of environmental exposures, airway cytology, and performance in racing thoroughbreds. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couetil, L.; Cardwell, J.M.; Leguillette, R.; Mazan, M.; Richard, E.; Bienzle, D.; Bullone, M.; Gerber, V.; Ivester, K.; Lavoie, J.P.; et al. Equine Asthma: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couëtil, L.L.; Cardwell, J.M.; Gerber, V.; Lavoie, J.-P.; Léguillette, R.; Richard, E.A. Inflammatory Airway Disease of Horses—Revised Consensus Statement. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christley, R.M.; Hodgson, D.R.; Rose, R.J.; Hodgson, J.L.; Wood, J.L.; Reid, S.W. Coughing in thoroughbred racehorses: Risk factors and tracheal endoscopic and cytological findings. Vet. Rec. 2001, 148, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couëtil, L.L.; Ward, M.P. Analysis of risk factors for recurrent airway obstruction in North American horses: 1,444 cases (1990-1999). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesarowski, D.B.; Viel, L.; Mcdonell, W.N. Repeated environmental challenge of control horses and horses with recurrent airway obstruction heaves. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 145, A55. [Google Scholar]
- Ramseyer, A.; Gaillard, C.; Burger, D.; Straub, R.; Jost, U.; Boog, C.; Marti, E.; Gerber, V. Effects of genetic and environmental factors on chronic lower airway disease in horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.L.; Newton, J.R.; Chanter, N.; Mumford, J.A. Association between respiratory disease and bacterial and viral infections in British racehorses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Couëtil, L.L.; Ward, M.P.; Clark, S.P. Effect of airway disease on blood gas exchange in racehorses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2005, 19, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcombe, S.J.; Robinson, N.E.; Derksen, F.J.; Bertold, B.; Genovese, R.; Miller, R.; de Feiter Rupp, H.; Carr, E.A.; Eberhart, S.W.; Boruta, D.; et al. Effect of tracheal mucus and tracheal cytology on racing performance in Thoroughbred racehorses. Equine. Vet. J. 2006, 38, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirie, R.S.; Collie, D.D.; Dixon, P.M.; McGorum, B.C. Inhaled endotoxin and organic dust particulates have synergistic proinflammatory effects in equine heaves (organic dust-induced asthma). Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, S.; Wouters, I.M.; Houben, R.; Jamshidifard, A.R.; Van Eerdenburg, F.; Heederik, D.J. Exposure to inhalable dust, endotoxins, beta(1->3)-glucans, and airborne microorganisms in horse stables. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2009, 53, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquenne, P.; Marchand, G.; Duchaine, C. Measurement of endotoxins in bioaerosols at workplace: A critical review of literature and a standardization issue. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2013, 57, 137–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayaram, A.; Seeber, P.A.; Greenwood, A.D. Environmental Detection and Potential Transmission of Equine Herpesviruses. Pathogens 2021, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.S.; Green, C.; Main, J.P.; Taylor, P.M.; Cunningham, F.M.; Cook, A.J.; Marr, C.M. Retrospective study of the relationships between age, inflammation and the isolation of bacteria from the lower respiratory tract of thoroughbred horses. Vet. Rec. 2000, 146, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, M.H.; Wood, J.L.; Whitwell, K.E.; Chanter, N.; Mackintosh, M.E.; Mumford, J.A. Respiratory disease in thoroughbred horses in training: The relationships between disease and viruses, bacteria and environment. Vet. Rec. 1996, 139, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leuken, J.P.G.; Swart, A.N.; Havelaar, A.H.; Van Pul, A.; Van der Hoek, W.; Heederik, D. Atmospheric dispersion modelling of bioaerosols that are pathogenic to humans and livestock - A review to inform risk assessment studies. Microb. Risk. Anal. 2016, 1, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, M. Particle size distribution of airborne micro-organisms in the environment-A review. Landbauforsch. Volkenrode 2015, 65, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Art, T.; Lekeux, P. Exercise-induced physiological adjustments to stressful conditions in sports horses. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2005, 92, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lühe, T.; Mielenz, N.; Schulz, J.; Dreyer-Rendelsmann, C.; Kemper, N. Factors associated with dust dispersed in the air of indoor riding arenas. Equine. Vet. J. 2017, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banhazi, T.; Woodward, R. Reducing the concentration of airborne particles in horse stables. In Proceedings of the XIII. International Congress on Animal Hygiene, Tartu, Estonia, 17–21 June 2007; pp. 438–487. [Google Scholar]
- Deaton, C.M.; Deaton, L.; Jose-Cunilleras, E.; Vincent, T.L.; Baird, A.W.; Dacre, K.; Marlin, D.J. Early onset airway obstruction in response to organic dust in the horse. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2007, 102, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, R. Ventilation and Air Hygine Parameters in Horse Stables; Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University Utrecht: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Elfman, L.; Wlinder, R.; Riihimäki, M.; Pringle, J. Air Quality in Horse Stables. In Chemistry, Emission Control, Radioactive Pollution and Indoor Air Quality; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, K.; Hessel, E.F.; Van den Weghe, H.F.A. Generation of Airborne Particles from Different Bedding Materials Used for Horse Keeping. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2008, 28, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, E.F.; Garlipp, F.; Van den Weghe, H.F.A. Generation of Airborne Particles from Horse Feeds Depending on Type and Processing. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2009, 29, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenput, S.; Istasse, L.; Nicks, B.; Lekeux, P. Airborne dust and aeroallergen concentrations in different sources of feed and bedding for horses. Vet. Q 1997, 19, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, E.; Ferrucci, F.; Salimei, E.; Antonin, M.; Codazza, D.; Caniatti, M. Relationship between the conditions of lower airways in healthy horses, environmental factors and air quality in stables. Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2000, 16, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wheeler, E.; Diehl, N.; Zajaczkowski, J.; Brown, D. Horse riding arena dust measurements. Livest. Environ. VII-Proc. Seventh Int. Symp. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venable, E.; Kraemer, J.; Sparks, S.; Goyer, C. Effect of Crumb Rubber Made From Recycled Tires on Air Quality in an Indoor Riding Arena: A Pilot Study. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2016, 36, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulfin, K.; Cowie, H.; Galea, K.S.; Connolly, A.; Coggins, M.A. Occupational Exposures in an Equestrian Centre to Respirable Dust and Respirable Crystalline Silica. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, M. Untersuchungen über die quantitative Zusammensetzung der aeroben Bakterienflora von Stallstaub unterschiedlicher Herkunft. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover, Foundation, Hanover, Germany, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Zeitler-Feicht, M.; Beissert, S.; Groth, W. Zur bakteriellen Kontamination von Absetzstaub in Pferdeställen. Tierärztliche Umsch. 1998, 43, 728–733. [Google Scholar]
- Choudat, D.; Goehen, M.; Korobaeff, M.; Boulet, A.; Dewitte, J.D.; Martin, M.H. Respiratory symptoms and bronchial reactivity among pig and dairy farmers. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1994, 20, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danuser, B.; Weber, C.; Künzli, N.; Schindler, C.; Nowak, D. Respiratory symptoms in Swiss farmers: An epidemiological study of risk factors. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2001, 39, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Donnell, P.E.; Coggins, M.A.; Hogan, V.J.; Fleming, G.T. Exposure assessment of airborne contaminants in the indoor environment of Irish swine farms. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2008, 15, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daly, S.W.; Harris, A.R. Modeling Exposure to Fecal Contamination in Drinking Water due to Multiple Water Source Use. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3419–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, H.; Salthammer, T.; Morawska, L. Human exposure to air contaminants in sports environments. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 1109–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, J.; Formosa, L.; Seedorf, J.; Hartung, J. Measurement of culturable airborne staphylococci downwind from a naturally ventilated broiler house. Aerobiologia 2011, 27, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Kampf, C.J.; Weber, B.; Huffman, J.A.; Pöhlker, C.; Andreae, M.O.; Lang-Yona, N.; Burrows, S.M.; Gunthe, S.S.; Elbert, W.; et al. Bioaerosols in the Earth system: Climate, health, and ecosystem interactions. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 346–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny-Koladka, K. Microbiological quality of air in free-range and box-stall stable horse keeping systems. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millerick-May, M.L.; Karmaus, W.; Derksen, F.J.; Berthold, B.; Robinson, N.E. Airborne particulates (PM10) and tracheal mucus: A case-control study at an American Thoroughbred racetrack. Equine. Vet. J. 2015, 47, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, N.; Corallo, C.; Miracco, C.; Papakostas, P.; Montella, A.; Figura, N.; Nuti, R. Erythema nodosum associated with Staphylococcus xylosus septicemia. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloos, W.E.; Zimmerman, R.J.; Smith, R.F. Preliminary studies on the characterization and distribution of Staphylococcus and Micrococcus species on animal skin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 31, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimozawa, K.; Anzai, T.; Kamada, M.; Takatori, K. Fungal and Bacterial Isolation from Racehorses with Infectious Dermatosis. J. Equine Sci. 1997, 8, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Othman, A.A.; Hiblu, M.A.; Abbassi, M.S.; Abouzeed, Y.M.; Ahmed, M.O. Nasal colonization and antibiotic resistance patterns of Staphylococcus species isolated from healthy horses in Tripoli, Libya. J. Equine Sci. 2021, 32, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bino, E.; Laukova, A.; Scerbova, J.; Kubasova, I.; Kandricakova, A.; Strompfova, V.; Miltko, R.; Belzecki, G. Fecal coagulase-negative staphylococci from horses, their species variability, and biofilm formation. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2019, 64, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, J.R.; Wood, J.L.; Chanter, N. A case control study of factors and infections associated with clinically apparent respiratory disease in UK Thoroughbred racehorses. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 60, 107–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raidal, S.L. Equine pleuropneumonia. Br. Vet. J. 1995, 151, 233–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.H.; Castillo, A.; Kinney, K.A.; Zuniga, A.; Mohammad, Z.; Lacey, R.E.; King, M.D. Monitoring of Pathogenic Bioaerosols in Beef Slaughter Facilities Based on Air Sampling and Airflow Modeling. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2019, 35, 1015–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Arena 1 | Arena 2 | Arena 3 | Arena 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Riding horses in stable | 32 | 24 | 50 | 56 |
| Size (m2) | 20 × 40 | 20 × 40 | 20 × 40 | 25 × 50 |
| Direct proximity to stable 1 | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Footing material | Sand | Sand/Wood shavings | Sand | Sand |
| Age of footing material | 4 years | 2 years | 0.5 years | 2 years |
| Underground | Natural ground | Natural ground | Natural ground | Natural ground |
| Arena | No. | Mean | Std | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 49 | 5.44 a | 0.25 | 4.70 | 5.90 |
| 2 | 56 | 5.19 b | 0.32 | 4.62 | 5.90 |
| 3 | 56 | 4.99 b | 0.33 | 4.08 | 5.58 |
| 4 | 49 | 4.91 b | 0.35 | 4.15 | 5.72 |
| Bacteria Species | Air Samples | Ground Samples |
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus xylosus | 528 (59%) | 154 (71%) |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 65 (7%) | 8 (4%) |
| Staphylococcus equorum | 52 (6%) | 12 (5%) |
| Others 1 | 255 (28%) | 44 (20%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lühe, T.; Volkmann, N.; Probst, J.; Dreyer-Rendelsmann, C.; Schulz, J.; Kemper, N. Bacterial Burden in the Air of Indoor Riding Arenas. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122111
Lühe T, Volkmann N, Probst J, Dreyer-Rendelsmann C, Schulz J, Kemper N. Bacterial Burden in the Air of Indoor Riding Arenas. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122111
Chicago/Turabian StyleLühe, Torsten, Nina Volkmann, Jeanette Probst, Cornelia Dreyer-Rendelsmann, Jochen Schulz, and Nicole Kemper. 2022. "Bacterial Burden in the Air of Indoor Riding Arenas" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122111
APA StyleLühe, T., Volkmann, N., Probst, J., Dreyer-Rendelsmann, C., Schulz, J., & Kemper, N. (2022). Bacterial Burden in the Air of Indoor Riding Arenas. Agriculture, 12(12), 2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122111








