Abstract
Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis (S. Enteritidis) is a pathogen that poses a health risk. Blue light (BL), an emerging sanitization technology, was employed for the first time in the present study to inactivate S. Enteritidis on eggshell surfaces and its influence on maintaining eggshell freshness was investigated systematically. The results showed that 415 nm-BL irradiation at a dose of 360 J/cm2 reduced 5.19 log CFU/mL of S. Enteritidis in vitro. The test on eggshells inoculated with S. Enteritidis showed that a BL dose at 54.6 J/cm2 caused a 3.73 log CFU reduction per eggshell surface and the impact of BL inactivation could be sustained in post-5-week storage. The quality of the tested eggs (weight loss, yolk index, Haugh unit (HU) and albumen pH) demonstrated that BL treatments had negligible effects on the albumen pH of eggs. However, compared to the control, BL-treated eggs showed lower weight loss and higher HU after 5 weeks of storage at 25 °C and 65% humidity and yolk index in the control group could not be determined after 5 weeks of storage. Besides, the total amino acid content of the BL-treated egg was higher than the control, exhibiting an advantage of BL irradiation in maintaining the nutrient quality of whole eggs. The current study determined the efficacy of BL against S. Enteritidis on eggshell and suggested that BL could be an effective application in maintaining the freshness and quality of eggs.
1. Introduction
Chicken eggs are popular foodstuff worldwide due to their valuable nutrients, such as complete protein, including all essential amino acids, easily digestible fats, vitamins (A, B2, B6, B9 and B12) and minerals (iron, calcium and potassium) [1]. According to the data provided by FAOSTAT, the production of eggs hen in shell, in 2019, was 83,483,675 tons and, according to a report from the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, global egg production will reach 89 million tons by 2030 [2]. However, poultry-borne pathogens lead to food poisoning in consumers and considerable egg loss and waste. Especially, Salmonella-contaminated eggs and egg-derived products contribute to many salmonellosis cases [3]. Salmonella strains have been frequently isolated from eggshell pieces and different serovars have been linked with egg contamination [4]. Among the Salmonella strains, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis (S. Enteritidis) is frequently recovered from contaminated grade A eggs.
Shell eggs have been reported as one of the principal vehicles for the transmission of bacterial pathogens [5]. The cuticle on eggshells (the organic layer of freshly laid egg) is damaged during extended storage of the egg, leading to the penetration of pathogens attached to the eggshell surface and in the surrounding environment. Therefore, effective disinfection on eggshells is urgently required to maintain good quality egg products by preventing bacterial contaminants from entering eggs.
Nowadays, several antimicrobial approaches have been reported to disinfect S. Enteritidis in eggshells, including ultraviolet C (200–280 nm) [3,6,7], H2O2 [8], ozone [9] and slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) [10], but their applications are limited by disadvantages such as photoreactivation, decolorization in certain products at high doses and harmful effects on human [11]. Blue light (BL), especially in the wavelength range of 405–470 nm, has attracted increasing interest because of its intrinsic antimicrobial property [11]. BL excited the endogenous intracellular porphyrins, leading to the production of highly cytotoxic reactive oxygen species and the following cell damage of bacteria [11,12]. BL is considered to be less detrimental to mammalian cells and human skin cells than ultraviolet irradiation [11]. Moreover, it can penetrate deeper than ultraviolet C [11]. Up to now, BL had been successfully applied in disinfection of some food, including cantaloupe rinds [13], fresh-cut papaya [14], milk [15], cucumbers, processed meat products [16] and packaged sliced cheese [17]. Our previous study demonstrated that methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Cronobacter sakazakii were decreased by 6 log CFU/mL and 8 log CFU/mL under 415-nm BL illumination of 80 and 240.48 J/cm2, respectively and the outer-membrane damage and lipid oxidation were induced by BL irradiation [12,18]. However, up to now, the efficacy of BL on shell egg disinfection has not been studied. Therefore, the purpose of this research was to verify the effectiveness of BL in inactivating S. Enteritidis on eggshells and to explore the effect of BL inactivating S. Enteritidis in maintaining the freshness and quality of eggs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
S. Enteritidis CMCC50041 purchased from National Center for Medical Culture Collections of China was streaked on a Luria–Bertani (LB) agar plate (10 g/L tryptone, 10 g/L NaCl, 5 g/L yeast extract and 20 g/L agar powder) and incubated at 37 °C for 12 h [12]. A single colony was inoculated into 5 mL of LB broth and cultured for 8–10 h, until the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) reached 1.0. The cell density of the S. Enteritidis culture was at approximately 8.0 log CFU/mL.
2.2. In Vitro Bactericidal Test on S. Enteritidis
BL irradiation on S. Enteritidis was carried out according to previous studies [12,18], with minor modifications as follows. Firstly, S. Enteritidis cells were harvested by centrifugation at 25 ± 2 °C for 1 min at 13,600× g and washed three times with a sodium phosphate buffer solution (PBS, 0.2 mol/L, pH 7.4). The washed cell pellet was suspended in PBS at OD600 at 0.1. Secondly, 6 mL of bacterial suspension was transferred to a Petri dish (35 mm bottom outer diameter × 16.5 mm height), which was placed directly below the BL source at a distance of 10 cm. BL was delivered with a central wavelength of 415 nm and the BL panel contained 20 LEDs. With the distance between the BL and the sample, the power density of irradiance was kept at 30.4 mW/cm2 and the irradiance dose per minute was 1.82 J/cm2. During the illumination process, the Petri dish was placed on a magnetic stirring device and the bacterial suspension was gently stirred at a speed of 30 rpm with a micro-magnetic rod (Norcross, Georgia). To calculate the survival rate, 20 μL of the suspension was withdrawn at 0, 5.5, 11, 16.5, 33, 66, 132 and 198 min (at irradiation doses of 0, 10, 20, 30, 60, 120, 240 and 360 J/cm2, respectively). Later, the suspension was diluted and plated on LB agar. The viable cells were enumerated and the bactericidal efficiency was calculated. The experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.3. Preparation and Inoculation of S. Enteritidis onto Eggshells
S. Enteritidis cells were inoculated onto eggshells according to the reported method [8], with minor modifications as follows. The fresh shell eggs were purchased from local supermarkets and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C for less than 2 days. The weight range of each egg was 55–60 g. The eggs were equilibrated to 25 ± 2 °C and each egg was wiped clean with sterile water and allowed to be air dried prior to inoculation. Later, the top surfaces and bottom surfaces, except the equator, were sponged by a sterile cotton ball saturated with an S. Enteritidis suspension at 7.8 × 107 CFU/mL [8]. Based on the method reported by Al-Ajeeli et al. [8], the range of cell density on each eggshell was 106 CFU/egg. Sponged eggs were finally dried in biological safety cabinet at 25 °C for 30 min prior to BL treatment.
2.4. BL Irradiation on Eggshell
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) at 415 nm were applied to illuminate the eggshells in a biosafety cabinet (Figure 1). Before irradiation was started, the egg holder and iron stand were disinfected with 75% alcohol solution and the bacteria-free work bench was sterilized by ultraviolet light for 60 min. The temperature of the aseptic workbench was maintained between 20 and 25 °C, while that of the egg holder was kept at 3–7 °C by placing it close to ice. The top of the egg was about 10 cm under the BL source. The top surface of the eggs was irradiated, at first, for 30 min (irradiation dose at 54.6 J/cm2); then, the egg was turned over and the bottom surface was irradiated later for 30 min. The total irradiation dose was kept at 54.6 J/cm2 and the eggs without BL irradiation were the control group.
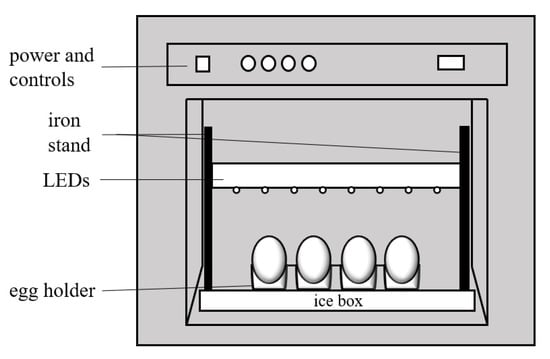
Figure 1.
Schematic of the BL irradiation apparatus for the eggs.
2.5. Enumeration of S. Enteritidis
To determine the viable population of S. Enteritidis, the surface of the inoculated egg was fully swabbed with a sterile cotton swab moistened with 1 mL of 0.9% saline under aseptic conditions. The swab was immersed in 1 mL of 0.9% saline and shaken for 1 min to evenly disperse the bacteria in the saline. The cells suspension was diluted with 0.9% saline. The original cells suspension and its diluents were spread on LB agar plates. The number of viable cells was determined after 48 h of incubation 37 °C. The plates containing 20–200 colonies were chosen for determining cell counts. This method resulted in average S. Enteritidis counts of 6.42 log CFU/eggshell for the 10 replicate trials performed in this study. The S. Enteritidis cells infiltrated from eggshell into the albumen were also counted according to the method reported by Chen et al. [19].
Ten parallel experiments were conducted in each group during the 5-week-storage study and the eggs were stored at 65% RH and 25 °C for 5 weeks. The S. Enteritidis cells were enumerated first; then, the shell eggs were weighed and broken for the Haugh unit (HU), yolk index, albumen pH measurements and amino acid analysis as follows.
2.6. Weight Loss
The eggs were weighed weekly using a digital precision scale (±0.01 g). Weight loss (%) of the irradiated and non-irradiated eggs during storage was calculated with the following formula [20]:
{[initial whole egg weight (g) before inoculation—whole egg weight (g) of each week during storage]/initial whole egg weight (g) before inoculation} × 100%
2.7. Yolk Index, HU and Albumen pH
Broken-out egg measurements were performed using a digital vernier caliper (0.01 mm) (Tsingtao, Shandong, China). The yolk index was calculated as [yolk height (mm)/yolk width (mm)]. The HU was calculated as [100 log (H—1.7 W0.37 + 7.57)], where H = thick albumen height (mm) and W = weight of the egg (g) [21]. The pH of the albumen was measured with a pH meter (Shanghai, China) after both thick and thin albumen were thoroughly mixed.
2.8. Amino Acid Analysis of the Albumen
The protein hydrolysis was evaluated with the previous method [20], with minor modifications as follows. Firstly, 10 eggs with the same parallel treatment were broken; then, the egg albumen was collected, mixed and freeze-dried in a vacuum freeze-dryer (Beckman, Kansas City, MO, USA). Later, 0.1 g freeze-dried albumen was hydrolyzed with 8 mL of 6 M HCl for 22 h at 120 °C in sealed tubes. After hydrolysates were cooled to 25 °C, 4.8 mL of 10 M NaOH and some deionized water were added to obtain the total volume at 25 mL. Finally, the hydrolysates were filtered with double-layer filter paper and 1 mL of filtrate was centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant, at about 400 μL, was collected for amino acid analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography (Agilent 1260, Santa Clara, CA, USA) [22]. The amino acid content was expressed as g/100 g eggs.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Two-way ANOVA (analysis of variance) was employed to compare the statistical significance between the control and the BL-treated eggs. p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. For the bacterial survival study, BL experiments were carried out in triplicate to obtain average and standard deviation (SD). For the egg quality study (weight loss, yolk index, HU and albumen pH), the mean ± SD values were based on ten measurements per treatment.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. In Vitro Bactericidal Test on S. Enteritidis
As shown in Figure 2, the killing curve of BL in the PBS suspension showed in a BL-dose-dependent manner. The significant inactivation was obtained when the BL dose was above 20 J/cm2 (p < 0.05) and a dose up to 360 J/cm2 caused a 5.19 log CFU/mL reduction of S. Enteritidis. Kim et al. [23] reported the antimicrobial effect of a 405 ± 5 nm LED at 4 °C against S. Enteritidis ATCC 13076 (CDC) and S. Saintpaul cells. The cell populations of S. Enteritidis and S. Saintpaul ATCC 9712 were reduced by 2.0 and 1.0 log CFU/mL at 288 J/cm2 and reduced by 5.6 and 1.7 log CFU/mL at 576 J/cm2, respectively. In this study, 415 nm-BL LEDs were employed and the distance to the surface of cell suspension was kept to 10 cm to obtain an irradiance at 30.4 mW/cm2. The bactericidal efficiencies of BL between these experiments were determined by different parameters (e.g., temperature), formats of light application (e.g., treatment distance, time and matrix) and sensitivities of the tested bacteria (e.g., strain or serotypes).
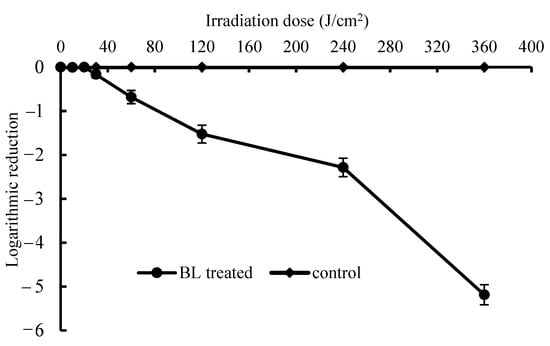
Figure 2.
Light dose-dependent photodynamic inactivation of S. Enteritidis in vitro. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three separate experiments.
3.2. Bactericidal Effect on Eggshells
Figure 3 shows the antimicrobial effect of BL on S. Enteritidis on eggshells during storage for 5 weeks. The initial population of S. Enteritidis on the egg was 6.42 log CFU/eggshell. For the control group, the colonies of S. Enteritidis on the eggshell surface decreased to 4.20 log CFU/eggshell after 1 week and, thereafter, remained stable, at about 4.00 log CFU/eggshell.
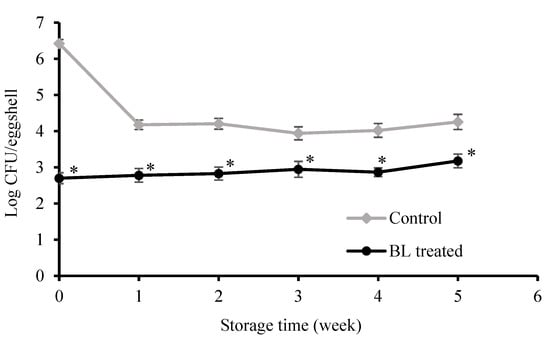
Figure 3.
Inactivation of S. Enteritidis on polluted eggshells and microorganism count on eggshells after storage for 5 weeks. Asterisk (*) indicates significant (p < 0.05) difference between BL-treated and control. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three separate experiments.
Unlike the control, BL treatment achieved a 3.73 log CFU/eggshell decrease after 30 min of irradiation (at the beginning of week 1). For the BL-treated group, the cell density of S. Enteritidis was about 2.70 log CFU/eggshell at the beginning of the storage period and changed slightly from week 1 to week 5. The numbers of survivors per eggshell insignificantly changed (p > 0.05). These data showed that the obvious inactivation efficacy of BL on eggshells could be sustained during the 5-week storage.
The studies of Salmonella inactivation on eggshells are mainly reported in UV and SAEW technologies. The individual ultraviolet showed efficient bactericidal efficiency against Salmonella, such as reductions at 1.6–3.8 log under UVC light at fluences from 0.05 to 3.0 J/cm2 (10 mW/cm2, for 5–300 s) and pulsed UV light at fluences from 1.25 to 18.0 J/cm2 [6] and 5.3 CFU/cm2 was obtained after a 20 s treatment at a total dose of 23.6 ± 0.1 J/cm2 [7]; however, minor sensory changes occurred at the same time [6] and the possible oxidative hazard of ozone generated by ultraviolet had not been investigated. Al-Ajeeli et al. [8] reported that combination of H2O2 (3.5% solution) and UV (254 nm) treatment for 5 s reduced the aerobic plate count in eggshell by 1.87 log CFU/egg. In addition, the research of Gottselig et al. [24] has shown that the H2O2/UV process reduced Salmonella by more than 5 log CFU/egg on the surface of experimentally contaminated eggs. However, its influence on the quality of shell eggs has not been evaluated. Another method is SAEW, while the chemical sanitizer chlorine is known to lead to the formation of toxic chemical by-products harmful to the human health [25]. When the eggs were immersed in SAEW liquid at 26 mg/L for 3 min, S. Enteritidis was decreased by 6.45 log CFU/g [10]; however, the potential toxic by-products were not investigated [10]. Other freshness maintaining methods include individual H2O2 [8] and ozone [9]; their shortcomings were obvious, such as chemical residues [26].
It was notable that, for the control, the population of S. Enteritidis on the eggshell was decreased after 1 week and kept stable thereafter, maybe due to the infiltration of bacteria into the eggs during the first week [27]. In the preliminary tests, different doses of BL, including 27.3, 54.6 and 109.2 J/cm2, were investigated; however, 27.3 J/cm2 led to a low bactericidal rate and almost negligible freshness protection. On the other hand, 109.2 J/cm2 achieved a good sterilization effect, but produced an unpleasant odor. Therefore, the optimal dose was chosen herein at 54.6 J/cm2 in the present study.
Kim et al. [14] disinfected fresh cut papaya contaminated by Salmonella spp. Using 405 ± 5 nm LED illumination at 4 °C for 36–48 h (1.3–1.7 kJ/cm2), they significantly reduced Salmonella on the papaya surface by 0.3–1.3 log CFU/cm2. For other cantaloupe fruit rinds, the number of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp. were decreased by 2.4 log CFU/cm2 and 2.3 log CFU/cm2, respectively [13]. The effects of BL on the physicochemical qualities of egg are further investigated in the following section.
3.3. Weight Loss
As shown in Table 1, it was inevitable that all the eggs lost weight during the 5-week storage. Along the storage time, the weight loss of both BL-treated and non-treated eggs increased. In the present study, the weight reduction for BL-treated eggs at the end of storage (week 5) was 3.09%, whereas that of control was 3.88%. The applied BL caused less weight loss of tested eggs than that in the control group in post-treatment storage (p < 0.05).

Table 1.
Effect of blue light irradiation on weight loss (%), yolk index, Haugh unit and albumen pH of eggs during 5 weeks of storage.
Poultry eggs are prone to lose their weight because of loss of moisture and carbon dioxide through pores in the eggshell [28]. Bhale et al. [29], Caner et al. [30], Kim et al. [20], Zang et al. [10] and Yuceer et al. [31] also reported that the weight of eggs decreased significantly during storage. In general, the weight loss of eggs during storage was mainly resulted from the evaporation of water and the loss of carbon dioxide from the protein through the porous shells [29]. Other evidence showed that weight loss of SAEW-processed eggs increased by 5.52% after 30 days storage at 25 °C [10]. Pires et al. [28] coated eggs with rice protein and stored them at 20 °C for 8 weeks; the uncoated eggs showed the highest weight loss (8.28%) and the weight loss reduction was 5.60%, 5.45% and 5.54% at 5%, 10% and 15% rice protein concentration, respectively. This suggested that the conditions (such as temperature) during storage could influence weight/moisture loss. In the present study, the lesser weight loss of eggs at the 5th week indicated that the BL treatment possibly reduced the generation of carbon dioxide by bacteria, which could be beneficial for keeping the freshness of shell egg at 25 ± 2 °C for a long time.
3.4. Yolk Index
The yolk index, depending on the yolk height and width, is an indirect measure of the strength of the yolk vitelline membrane and the spherical shape of the yolk and is therefore frequently used to indicate freshness [20,31]. The higher the yolk index, the fresher the egg. As shown in Table 1, both control and BL-treated eggs showed similar yolk indexes during the 4 weeks of storage, which were approximately 0.36 (week 0), 0.26 (week 1) and 0.20 (weeks 2–4). However, the control had no morphogenetic yolk at week 5 (Figure 4) and BL-treated eggs showed a yolk index comparable to that at week 4, exhibiting a relatively higher freshness (p < 0.05) after 5-week storage.
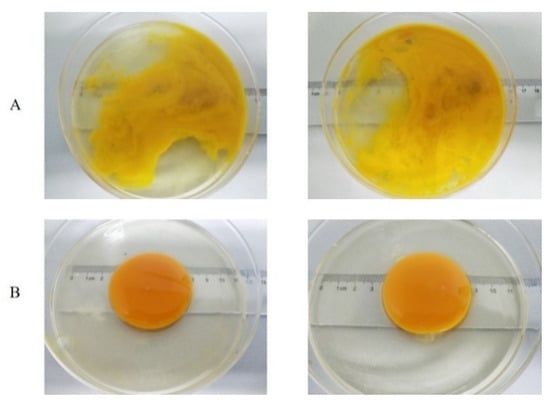
Figure 4.
Comparison of albumen and yolk morphologies between non-irradiated eggs (A) and BL-irradiated eggs (B) after 5 weeks.
The decrease in the yolk index is possibly due to the diffusion of water from the albumen to the yolk and the following weakening of the yolk membrane and liquefaction of the yolk [31]. Zang et al. [10] showed that SAEW could inhibit bacteria from entering the albumen and yolk. Therefore, the yolk index of eggs treated with 30 mg/L SAEW for 3 min was higher than that of the control group. The present results also indicate that BL irradiation effectively preserved yolk quality. The higher the degree of bacterial contamination, the more bacterial infiltration of the egg occurs [27]. S. Enteritidis could penetrate the vitelline membrane into the yolk and proliferate rapidly in the yolk [32], leading to the rupture of the vitelline membrane and the mixing of yolk and albumen. In the current study, after storage for 4 weeks, S. Enteritidis cells that infiltrated into the albumen in BL-irradiated eggs kept at about 12 CFU/mL, while those of untreated eggs was detected at the 220-fold greater level of 2640 CFU/mL, supporting the disappearance of yolk after 5 weeks.
3.5. HU
HU, another key indicator reflecting albumen quality of the egg [29,31], was measured according to the height of the albumen and the weight of the eggs. As shown in Table 1, the HU decreased in both BL-irradiated and non-irradiated eggs. The result was in agreement with those of previous reports [10,26,29]. After 4 weeks, the HU of BL-irradiated egg decreased from the initial 86.27 ± 5.89 to 49.28 ± 3.28; however, the HU of the control group dropped faster, from 86.27 ± 5.89 to 33.54 ± 2.82. At the end of storage (5 weeks), the yolk of the control was disrupted and dispersed into the albumen (HU value at zero), while the BL-treated egg displayed a complete yolk with a HU value of 45.66 ± 2.64. It demonstrated that the bacterial inactivation with BL significantly maintained the stability of egg yolk and albumen (p < 0.05). In addition, we observed that the albumen of the control sample became thinner and the yolk collapsed because of more contamination with S. Enteritidis. In comparison, BL-irradiated eggs maintained good integrity of both albumen and yolk. Yuceer et al. [31] reported similar results, showing that ozone treatment of eggs slowed the decrease in HU (p < 0.05). Another study showed that S. Enteritidis could penetrate the egg in 4–5 days [27] and grow in the egg, causing deterioration of the gel structure of thick albumen [33]. In the control, more S. Enteritidis from the shell likely infiltrated albumen and yolk, resulting in proteolysis and lipolysis. Consequently, the albumen and yolk were broken down and mixed together. The results indicated that BL treatment could preserve albumen quality by inactivating S. Enteritidis.
3.6. Albumen pH
The albumen pH is mainly defined by the dissolved CO2, bicarbonate ions, carbonate ions and proteins [34]. As shown in Table 1, a similar trend of albumen pH change during storage period was observed in both control and BL-treated eggs (p < 0.05). The albumen pH of BL-treated eggs was increased from an initial 8.92 ± 0.04 to 9.48 ± 0.05 after 1 week of storage, then stayed between 9.04 ± 0.16 and 9.32 ± 0.22. Similar changes occurred in eggs of the control group. After 1 week of storage, the albumen pH reached 9.54 ± 0.02, then stayed between 8.95 ± 0.17 and 9.34 ± 0.02, which was also higher than the value at the beginning of storage (8.92 ± 0.04). The current work showed that BL irradiation or application did not have a significant impact on albumen pH change (p > 0.05).
In our experiment, one-third of the non-irradiated eggs were rotten and smelly after 3 weeks of storage. The odor most likely came from H2S [35], which did not result in significant difference between BL-treated eggs and the controls.
3.7. Amino Acid Profiles
As far as we know, the amino acid profiles of egg albumen were rarely reported and were therefore evaluated in the present study. As shown in Table 2, with the extension of storage time, all groups showed reduction in amino acid contents, which is a normal phenomenon for egg storage. However, the total contents of amino acid in BL illuminated eggs were higher than those in the control group, similar to the trend of weight loss and HU values. The amino acid content of untreated eggs was 84.58 ± 0.35 g/100 g at week 0 and gradually decreased to 72.9 ± 0.27 g/100 g after 5 weeks. However, the amino acid level of BL-treated eggs was maintained at a 4.80% higher level, at 76.4 ± 0.32 g/100 g. Especially, the content of essential amino acids (threonine, lysine, phenylalanine, methionine, isoleucine, leucine and valine) of BL-treated eggs after 5 weeks was 4.62% greater than the control, showing a higher protein nutrient value. BL slowed down the loss of amino acid content in eggs probably because of the disinfection of bacteria consuming amino acids. The current data demonstrated herein, for the first time, that BL could have a role to maintain the amino acid content of eggs.

Table 2.
Effects of BL-treated eggs on amino acid composition (g/100 g) of freeze-dried albumen during 5 weeks of storage.
Based on the results mentioned above, it is showed, for the first time, that 415-nm BL could efficiently inactivate S. Enteritidis on eggshell and maintain the freshness of shell eggs. As far as we know, 415-nm BL is a freshness-maintaining approach for shell eggs, since it showed high bactericidal efficiency and less adverse effects. Therefore, BL displayed good potential for field application in keeping the freshness of the egg and its feasibility was preliminarily confirmed by the tests on several batches of eggs purchased from local supermarkets (data not shown). Future work will be carried out on a broader scale and it is worth noting that the irradiation dose should be adjusted dependent on the type and contamination density of pathogenic bacteria on eggshell.
4. Conclusions
The current study evaluated the efficiency of 415-nm BL in egg disinfection and systematically evaluated its influence on egg freshness during 5-week storage. It showed that a BL dose of 360 J/cm2 led to a 5.19 log CFU/mL reduction in S. Enteritidis in vitro and 54.6 J/cm2 of BL illumination led to a reduction of 3.73 log CFU/eggshell on shell eggs. The remaining S. Enteritidis population on eggshells after BL treatment had no significant growth during the 5-week storage. The investigation also showed that 54.6 J/cm2 of BL illumination with applied dose did not have significant detrimental impact on the quality of whole eggs. The dynamic changes of albumen pH were similar in BL-treated and control group. The decreases in egg weight, yolk index, HU and total amino acid contents were slowed down by BL illumination. The current findings suggested that the 415 nm BL could be an effective application of S. Enteritidis decontamination on eggshell with potential of maintaining the quality of egg albumen.
Author Contributions
Funding acquisition, experiment design and supervision, writing—review and editing, X.H.; experiment design and management, data analysis and paper writing, X.S.; experiment management, data analysis, writing—review and editing, S.L.; review and editing, S.W.; experiment management, Z.C.; experiment management, X.Z.; experiment management, Z.L.; experiment management, J.W.; funding acquisition, review and editing, X.W.(Xiaohong Wang); review and editing, C.L.; experiment suggestion, X.W. (Xiaoyuan Wang). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1600100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31201290), the National First-Class Discipline, Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (C2017407035) and the Science and Technology Research Projects of University in Hebei Province (QN2016022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adeyeye, E.I. Nutritional values of the lipid composition of the free-range chicken eggs. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. 2012, 3, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdelaine, P.; Braine, A.; Gonnier, V.; Spiess, M.P. Science et Technologie de L’oeuf et des Ovoproduits; Nau, F., Guérin-Dubiard, C., Baron, F., Eds.; Editions Tec et Doc Lavoisier: Paris, France, 2010; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, S.; Zang, Y.T.; Li, Y.J.; Shu, D.Q. The synergistic effects of slightly acidic electrolyzed water and UV-C light on the inactivation of Salmonella enteritidis on contaminated eggshells. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6914–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Musgrove, M.T.; Murata, M.; Tominaga, N.; Kawamoto, S. Comparative study of shell swab and shell crush methods for the recovery of Salmonella from shell eggs. J. Food Saf. 2008, 28, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, J.A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Ayers, T.; Tauxe, R.V.; Braden, C.R.; Angulo, F.J.; Griffin, P.M. Attribution of foodborne illnesses, hospitalizations, and deaths to food commodities by using outbreak data, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holck, A.L.; Liland, K.H.; Dromtorp, S.M.; Carlehog, M.; Mc, L.A. Comparison of UV-C and pulsed UV light treatments for reduction of Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli on eggs. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keklik, N.M.; Demirci, A.; Patterson, P.H.; Puri, V.M. Pulsed UV light inactivation of Salmonella Enteritidis on eggshells and its effects on egg quality. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajeeli, M.N.; Taylor, T.M.; Alvarado, C.Z.; Coufal, C.D. Comparison of eggshell surface sanitization technologies and impacts on consumer acceptability. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Romo, L.A.; Yousef, A.E. Inactivation of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis on shell eggs by ozone and UV radiation. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.T.; Bing, S.; Li, Y.J.; Shu, D.Q.; Huang, A.M.; Wu, H.X.; Lan, L.T.; Wu, H.D. Efficacy of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on the microbial safety and shelf life of shelled eggs. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5932–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Gupta, A.; Murray, C.K.; Vrahas, M.S.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R. Blue light for infectious diseases: Propionibacterium acnes, Helicobacter pylori, and beyond? Drug Resist. Updates 2012, 15, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Dai, T.; Wang, X. Inactivation of Cronobacter sakazakii by blue light illumination and the resulting oxidative damage to fatty acids. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josewin, S.W.; Kim, M.J.; Yuk, H.G. Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp. on cantaloupe rinds by blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Bang, W.S.; Yuk, H.G. 405 ± 5 nm light emitting diode illumination causes photodynamic inactivation of Salmonella spp. on fresh-cut papaya without deterioration. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos, C.; Sellera, F.P.; de Freitas, L.M.; Gargano, R.G.; Telles, E.O.; Freitas, R.O.; Baptista, M.S.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Lincopan, N.; Pogliani, F.C.; et al. Inactivation of milk-borne pathogens by blue light exposure. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 103, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guffey, J.S.; Payne, W.C.; Motts, S.D.; Towery, P.; Hobson, T.; Harrell, G.; Meurer, L.; Lancaster, K. Inactivation of Salmonella on tainted foods: Using blue light to disinfect cucumbers and processed meat products. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 4, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, J.E.; Lee, S.Y. Antibacterial effect and mechanisms of action of 460–470nm light-emitting diode against Listeria monocytogenes and Pseudomonas fluorescens on the surface of packaged sliced cheese. Food Microbiol. 2020, 86, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chu, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, T.; Hu, X. Changes of intracellular porphyrin, reactive oxygen species, and fatty acids profiles during inactivation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by antimicrobial blue light. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Thesmar, H.S.; Kerr, W.L. Outgrowth of Salmonellae and the physical property of albumen and vitelline membrane as influenced by egg storage conditions. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Youn, D.K.; No, H.K.; Choi, S.W.; Prinyawiwatkul, W. Effects of chitosan coating and storage position on quality and shelf life of eggs. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2009, 44, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugh, R.R. The Haugh unit for measuring egg quality. US. Egg Poult. Mag. 1937, 43, 552–555. [Google Scholar]
- Koros, A.; Varga, Z.; Molnar-Perl, I. Simultaneous analysis of amino acids and amines as their o-phthalaldehyde-ethanethiol-9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate derivatives in cheese by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1203, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Yuk, H.G. Antibacterial mechanism of 405-nanometer light-emitting diode against Salmonella at refrigeration temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottselig, S.M.; Dunn-Horrocks, S.L.; Woodring, K.S.; Coufal, C.D.; Duong, T. Advanced oxidation process sanitization of eggshell surfaces. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende, A.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Gil, M.I. Minimal processing for healthy traditional foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinetta, V.; Vaidya, N.; Linton, R.; Morgan, M. Evaluation of chlorine dioxide gas residues on selected food produce. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, T11–T15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reu, K.; Grijspeerdt, K.; Messens, W.; Heyndrickx, M.; Uyttendaele, M.; Debevere, J.; Herman, L. Eggshell factors influencing eggshell penetration and whole egg contamination by different bacteria, including Salmonella enteritidis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 112, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, P.G.S.; Machado, G.S.; Franceschi, C.H.; Kindlein, L.; Andretta, I. Rice protein coating in extending the shelf-life of conventional eggs. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhale, S.D.; No, H.K.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Farr, A.J.; Nadarajah, K.; Meyers, S.P. Chitosan coating improves shelf life of eggs. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 2378–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caner, C.; Yuceer, M. Efficacy of various protein-based coating on enhancing the shelf life of fresh eggs during storage. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuceer, M.; Aday, M.S.; Caner, C. Ozone treatment of shell eggs to preserve functional quality and enhance shelf life during storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2755–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gast, R.K.; Holt, P.S.; Murase, T. Penetration of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella heidelberg into egg yolks in an in vitro contamination model. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nongtaodum, S.; Jangchud, A.; Jangchud, K.; Dhamvithee, P.; No, H.K.; Prinyawiwatkul, W. Oil coating affects internal quality and sensory acceptance of selected attributes of raw eggs during storage. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, S329–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechevalier, V.; Jeantet, R.; Arhaliass, A.; Legrand, J.; Nau, F. Egg white drying: Influence of industrial processing steps on protein structure and functionalities. J. Food Eng. 2007, 83, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishanina, T.V.; Libiad, M.; Banerjee, R. Biogenesis of reactive sulfur species for signaling by hydrogen sulfide oxidation pathways. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 457–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).