Abstract
This study was conducted to determine the effect of pre-harvest glyphosate application on spring wheat quality characteristics, ranging from kernel quality to baking quality. Two wheat cultivars were grown in three locations, and glyphosate was applied at the recommended rate at the soft dough stage (early application) and the ripe stage (recommended application time). When glyphosate was applied at the soft dough stage, kernel weight, wheat protein and wet gluten decreased significantly (p ≤ 0.05), however, gluten index significantly increased (p ≤ 0.05). Dough quality, farinograph stability, and quality number were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher when glyphosate was applied at the soft dough stage, and absorption and the mixing tolerance index were lower. As for baking quality, loaf volume and mix time were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher in the treated samples in comparison to the untreated control, and other baking quality characteristics did not show any significant difference. Overall, the results indicate that spring wheat quality characteristics are impacted to the greatest degree when glyphosate is applied earlier than recommended at the soft dough stage, as opposed to the recommended application at the ripe stage of physiological development.
1. Introduction
Glyphosate is the most widely used herbicide in crop production. Glyphosate inhibits the 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) enzyme found in the shikimic acid pathway [1]. The inhibition of EPSPS leads to reduced feedback in the inhibition pathway, which results in the accumulation of shikimate-3-phosphate, which is converted to shikimate or shikimic acid. Glyphosate is considered as a non-selective, broad spectrum herbicide, because the EPSPS enzyme in higher plants is inhibited by glyphosate. Many researchers assume that the deficiency of aromatic amino acid production in glyphosate treated plants leads to plant destruction [2]. However, there are indications that the deregulation of the shikimic acid pathway is the cause for plant mortality, where increased carbon flow to shikimate-3-phosphate causes shortages in the carbon required for other essential pathways [3]. For example, studies conducted on sugar beet demonstrate that the deregulation of the shikimic acid pathway results in a reduced rate of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase regeneration, photosynthesis and starch synthesis [4].
Glyphosate is sometimes used as a harvest aid during wheat cultivation and is sprayed prior to harvest to facilitate grain drying. It is also used as a harvest aid for other crops, such as dry beans, lentils and soybean. Reasons such as untimely rainfall or unfavorable damp conditions makes wheat more susceptible to pre-harvest sprouting and mildew development, which makes it important to decrease the moisture content of wheat kernels close to harvest [5], thus herbicides such as glyphosate are used as harvest aids to facilitate the timely harvest of crops [6]. When glyphosate is used as a harvest aid, it should be applied at a kernel moisture content of 30% or less [7]. Glyphosate causes a sudden stop in the physiological maturation process of wheat and leads to increases in the shikimic acid content in the grain, as reported by Bresnahan et al. [8]. Additionally, there are indications that glyphosate application could cause the accumulation of water-soluble fiber components such as fructans in wheat kernels, as opposed to their movement towards other parts of the plant (soluble carbohydrates such as fructans accumulate in leaves, stems and apices prior to anthesis) [9].
If applied early, glyphosate could terminate the physiological maturation process of wheat disrupting the grain filling process, which results in negative effects on grain yield [7]. Such effects have been observed, especially when glyphosate is applied at high grain moisture levels (50% moisture content). Decreases in grain yield, test weight, kernel weight and kernel size were observed in such instances. Yenish and Young [10] studied the effect of applying glyphosate at the milk stage, soft dough, hard dough, seven days after the hard dough stage and a day before harvest and determined that application at the milk stage causes detrimental effects on yield. Thus, there are clear indications that application timing of glyphosate-based herbicides is critical in preserving grain yield as well as other quality parameters. Glyphosate rates of 1 kg ha−1 caused decreases in germination energy and at 2 kg ha−1 thousand kernel weight was decreased, according to a study by Jaskulski and Jaskulska [11]. Additionally, Krenchinski et al. [12] studied the effects of several herbicides used for desiccation and found that glyphosate, paraquat, glufosinate-ammonium, diquat and clethodium caused decreases in grain yield, while herbicides such as paraquat and clethodium caused reductions in seedling length and vigor in seeds from treated plants, respectively. McNeal et al. [13] studied eight harvest aids and found that harvest aid application did not have a profound effect on the end-product quality of hard red spring wheat. However, applying harvest aids at higher moisture levels showed negative effects on wheat protein content, loaf volume and bread texture scores. Additionally, glyphosate application caused wheat dough to become tougher, requiring comparatively more energy for optimal dough development [14]. However, as in the previous study, quality parameters such as protein content and mixograph peak height, peak width and total energy of the curve were not affected by glyphosate application.
Baker’s yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, could be impacted to different degrees according to the herbicide that is used, as demonstrated by Sharma et al. [15], who studied different agrochemicals, such as endosulfan, hexaconazole, propiconazole, malathion, chlorpyriphos and deltamethrin. The presence of such chemicals suppressed yeast growth, at times up to approximately 45%, which could lead to negative effects on the end-product quality of fermented goods. Low et al. [16] investigated the role of yeast in degrading glyphosate and reported that yeast plays an important role in metabolizing glyphosate during fermentation, where approximately 21% of glyphosate is degraded within the first hour of fermentation. Similarly, Hack et al. [17] reported that baker’s yeast metabolizes the herbicide atrazine. Braconi et al. [18] also observed that glyphosate could impact wine fermentation due to interactions with yeast. However, Roisch and Lingens [19] indicated that glyphosate does not affect the synthesis of aromatic amino acids in baker’s yeast at levels of 2 mmol l−1. Given this evidence, it is possible that glyphosate could impact the fermentation that occurs during bread production, leading to decreases in baking quality of wheat flour.
To our knowledge, the effect of pre-harvest glyphosate application on spring wheat quality has not been studied extensively and it is important to understand such effects, so that negative outcomes can be avoided. To that end, the objective of this study was to determine the effect of pre-harvest glyphosate applied at different stages of maturity, namely at the soft dough stage (45% moisture content) and the ripe stage (physiological maturity/30% moisture content and recommended application stage), on different spring wheat quality characteristics, ranging from kernel quality to end-product baking performance. For this purpose, a field study was conducted where glyphosate was applied at the recommended rate, and upon harvest, quality characteristics were determined according to standard AACC-I methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
In this study, a randomized complete block design with a split-plot arrangement was used with location as the main plot, and a factorial combination of treatment and cultivar as the sub-plot. Two wheat cultivars, Glenn and Prosper (Pros), were grown at three locations, namely, Minot (Min), Carrington (Car) and Prosper (Pro) in North Dakota. Glyphosate was sprayed at the recommended rate (1.1 kg active ingredient/ha) at the soft dough stage (SD) and the ripe stage (RP) (grain is physiologically mature at this point) and harvested upon reaching an appropriate moisture for harvest. The ripe stage was chosen because glyphosate is registered to be applied at least seven days prior to harvest, when using as a harvest aid during wheat cultivation. The soft dough stage was chosen as an extreme point, where the moisture content is higher than that at the ripe stage, to evaluate its effect when applied earlier in the maturation process. A control (Con), where glyphosate was not sprayed was also included. Each treatment was repeated three times, bringing the total number of samples to 54.
2.2. Quality Analyses of Harvested Samples
To determine the nitrogen content of wheat kernels, the American Association of Cereal Chemists—International (AACC-I) method 46-30.01 was used [20]. A Dumas nitrogen analyzer was used for this purpose. The protein content was determined at 12% moisture basis (m.b) and a conversion factor of 5.7 was used. The test weight was determined using the AACC-I method 55-10.01. A sample of 10 g of cleaned wheat was used to determine 1000-kernel weight using an electronic seed counter (Seedburo Equipment Count-A-Pak Model 77 Totalizer, Seedburo Equipment Company, Des Plaines, IL, USA). Kernel vitreousness was determined by way of visual observations and the approximate percentage of kernels having vitreous endosperm was determined. Falling number was determined according to the AACC-I method 56-81.01, and the results were reported in seconds at 14% moisture basis (m.b.).
The samples were cleaned and milled in the Wheat Quality Laboratory facilities. A Bühler ML-202 laboratory scale mill (Bühler Group, Switzerland) was used for milling, and straight grade flour was blended and reported as flour extraction. The standard AACC-I method mentioned above for protein analysis was used to determine flour protein content, and AACC-I method 08-01.01 was used to measure flour ash content. To determine gluten index and wet gluten, the AACC-I approved method 38-12.02 was used.
Flour mixing characteristics were evaluated using farinograph analysis (Farinograph-E, C. W. Brabender, Brabender GmbH, Duisburg, Germany), according to the AACC-I approved method 54-21.02, and the Brabender software was used to determine farinograph characteristics, such as peak time, stability, mixing tolerance, quality number and absorption. Baking tests were used to assess the breadmaking quality of the samples, for which 100 g pup loaves were used. The baking tests were performed according to the AACC-I approved method 10-09.01, with some modifications. The fermentation time was shortened to 2 hours, fungal amylase was used instead of malt power, instant dry yeast was used in place of compressed yeast and 1 mL of 10% ammonium phosphate was used in each loaf. Baking quality parameters, such as loaf volume, were assessed according to the AACC-I method 10-05.01 and other parameters such as, crust color, crumb color, crumb grain and texture and loaf symmetry, which were determined using the AACC-I method 10-12.01.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The SAS software (Version 9.4, SAS Institute, Cary, NC) was used to perform an Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and a mean separation (Fisher’s protected LSD).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Glyphosate on Kernel, Milling and Flour Quality
Compared to the control, 1000-kernel weight (TKW) was significantly (p ≤ 0.05) lower when treated at the soft dough stage, compared to the control and the ripe stage treatment, indicating that applying too early can impact seed weight (Table 1). During the physiological maturation of wheat, the grain filling process takes place from anthesis to harvest [21]. Therefore, when glyphosate is applied at the soft dough stage, it is possible that the grain filling process was interrupted, leading to lower kernel weight. Additionally, previous work has shown that glyphosate application, which leads to the inhibition of the shikimic acid pathway, could affect the carbon flow, which could also impact grain filling by limited starch synthesis [22]. As for the cultivar x treatment interaction data, the lowest TKW occurred in the soft dough stage treatment for both cultivars, indicating that an early application could have negative effects on kernel weight, as previously found for treatment effects. As for differences between locations, TKW was lower in the samples treated at the soft dough stage only in the Prosper location, indicating different response to glyphosate according to growing locations.

Table 1.
Average values for kernel, milling and flour quality characteristics for different glyphosate treatments a.
Manthey et al. [6] studied the effect of pre-harvest application of herbicide, including glyphosate, paraquat and 2,4-D and observed a decrease in TKW when glyphosate was applied at the soft dough stage. Zollinger et al. [23] and Darwent, Kirkland, Baig and Lefkovitch [14] also reported that an application of glyphosate prior to the hard dough stage or physiological maturity caused decreases in kernel weight and kernel size. Similar observations, where harvest aids caused negative effects on grain quality, were found in other crops such as dry bean [24], sorghum seed [25], soybean [26], peas [27] and rice [28]. However, contrary to the findings of the current study, He et al. [29], who studied the impact of the harvest aids, such as diquat, paraquat and ethephan on rice quality, reported that pre-harvest application of these herbicides did not affect the TKW of rice. Similar observations were made by Boudreaux and Griffin [30], who studied soybean. Esfahani et al. [31] found that harvest aids like paraquat can cause minor reductions in the oil content of rapeseed, without causing significant effects on yield and quality. Bellé et al. [32] reported that a glyphosate application at the soft dough or the ripe stage did not affect seed weight, however, they found that seed germination was negatively impacted by an early glyphosate application.
Wheat kernel vitreousness is a measure of the compactness of starch granules in the protein matrix, and vitreous kernels have been found to be harder than non-vitreous kernels [33]. Vitreousness has been identified as a factor impacting the extent of coarse particle size reduction during wheat milling [34]. In this experiment, kernel vitreousness was not significantly different between the different glyphosate treated samples (Table 1).
Significant differences were found for kernel vitreousness between mean values of the cultivar x treatment interaction. However, the values obtained for cultivar Glenn were generally higher in comparison to the cultivar Prosper, although, within each cultivar, the effect of treatment did not show a clear trend. For example, the value for the control was highest in both cultivars, however, the lowest was observed in the samples treated at the ripe stage (physiological maturity) in cultivar Glenn, and the soft dough stage in cultivar Prosper. There was location x treatment interaction for vitreousness, indicating that the environment can play an important role in how glyphosate application may affect kernel vitreousness. Further supporting the findings for environmental effects on kernel vitreousness, previous studies have shown that vitreousness is mainly impacted by environmental conditions, such as the availability of water and nitrogen, as well as temperature during grain maturation [35].
Wheat protein content and composition (glutenin to gliadin ratio) are important parameters affecting end-use quality [36]. Wheat protein content (determined as a percentage), which is a measure of the amount of protein in the whole kernel, was significantly different between treatments, where samples treated at the soft dough stage showed significantly lower values compared to samples treated at physiological maturity and the control (Table 1). This could be because protein deposition is interrupted by glyphosate when applied relative early during grain filling, leading to decreases in protein production [37]. As for the cultivar x treatment interaction, cultivar Prosper showed significantly lower values for wheat protein content, in comparison to cultivar Glenn. However, for both cultivars, the lowest wheat protein content was observed in the samples treated at the soft dough stage. With reference to each location, Carrington and Minot did not show significant differences between the treatments, nevertheless, in Prosper, the wheat protein content was lower in the samples treated at the soft dough stage, compared to the ripe stage application and the control. Previous work on wheat proteins have shown that genotype, environment and the interaction can affect protein content, as observed in the present study [38,39].
Falling number is used to determine the effect of alpha-amylase activity in wheat [40]. Increased alpha-amylase activity can be caused by pre-harvest sprouting, triggered by rainfall before harvest. In this study, falling number was higher in the treated samples in comparison to the control. However, the average falling number values for the different treatments are higher than 350 seconds (benchmark for sound wheat kernels), which indicates that the treatment did not cause functional differences. The cultivar x treatment interaction was also significant for falling number, and in both cultivars the lowest value was found in the control (Table 1). At locations Carrington and Minot, significant differences were not observed for falling number; however, in Prosper, the control showed significantly lower values than the treated samples. Although the results suggest that glyphosate may cause increased falling number, which is indicative of low alpha-amylase activity, it is unclear how glyphosate could cause such an impact. However, previous work has shown that in addition to pre-harvest sprouting, late maturity alpha-amylase and retained pericarp alpha-amylase could cause low falling numbers [41]. Genes corresponding to late maturity alpha-amylase appear to be genetic defects and are found in particular genotypes. These genes are subjected to complex modulation by environmental factors, which further complicates its activity. Additionally, genotype and environment also affect the alpha-amylase activity in wheat [42].
Grain texture affects wheat milling and end-use quality characteristics, which include milling yield, flour particle size and starch damage [43]. Wheat grain texture is determined by two genes, puroindoline a and puroindoline b, which are found at the Hardness (Ha) locus. Variations in the abundance and activity of these puroindolines have been shown to affect milling quality. Milling yield is important economically as higher flour yield is beneficial for the industry. Milling quality was determined by percentage extraction in this study. This parameter was lower in the glyphosate-treated samples compared to the control (Table 1). For the cultivar x treatment interaction, percentage extraction was somewhat lower in cultivar Glenn compared to cultivar Prosper; however, the cultivars showed different trends for the different glyphosate treatments. At the different locations, percentage extraction did not show a similar trend for the different treatments, although differences were observed between locations. That is, percentage extraction was not lowest in the control in all locations. Therefore, the data suggests that the effect of glyphosate on milling quality is also impacted by factors such as growing environment. In this context, it is somewhat difficult to elucidate why pre-harvest glyphosate application could lower percentage extraction in some locations, however it is possible that changes in the carbon flow caused by shikimic acid accumulation could affect grain weight, leading to lower extraction. The TKW showed a significant simple linear correlation with flour extraction rate (r = 0.740, p < 0.001), as represented in Figure 1, supporting that the inhibition of carbon accumulation in grain might result in low grain TKW and consequently, low flour extraction. Effects of glyphosate on starch-protein interactions could also be a contributing factor. However, further studies are needed to firmly establish this association.
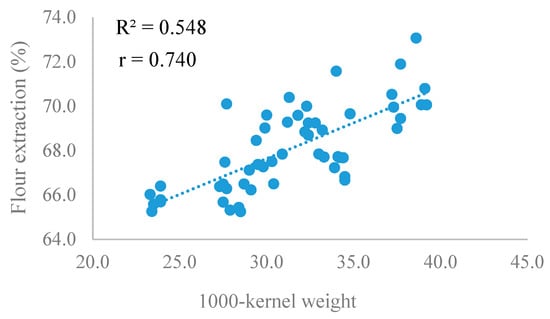
Figure 1.
Correlation between 1000 kernel weight and flour milling extraction.
Several flour quality characteristics were also impacted by pre-harvest glyphosate applications, as shown in Table 1. Flour protein content, which is the protein content of refined flour, did not show significant differences between treatments, although flour protein content in the samples treated at the soft dough stage showed slightly lower values than samples treated at the ripe stage and the control, similar to the observations made for wheat protein content. As mentioned earlier, wheat protein content and composition are important determinants of end-use quality, and it is interesting that a pre-harvest glyphosate application does not affect protein content. As for the cultivar x treatment interaction, flour protein content was significantly lower in cultivar Prosper compared to cultivar Glenn, which highlights the influence of genotype on flour protein content, as found in previous studies [44]. Additionally, flour protein content was significantly different at the different locations, highlighting the effect of environmental conditions. At two locations (Carrington and Prosper), grain from wheat treated at the soft dough stage showed the lowest flour protein content but at Minot, no significant difference was shown. This indicates a possibility that glyphosate could cause significant differences in protein content depending on environmental conditions, possibly reducing protein content when applied too early in some environments.
Gluten is composed of gliadin and glutenin proteins, which together impact the visco-elastic properties of wheat dough [45]. Early studies on wheat quality identified gluten content estimation as an important test for determining wheat quality [46]. In this study, wet gluten, which is representative of gluten content, was significantly lower in samples treated at the soft dough stage, compared to the samples treated at the ripe stage and the control (Table 1). In the analysis of cultivar x treatment interactions, wet gluten was significantly lower in cultivar Prosper compared to Glenn, and in both cultivars the lowest value was observed in the samples treated at the soft dough stage. Wet gluten was also significantly different between locations; however, the treatments did not show the same trend at all three locations. For example, in Carrington, significant differences were not observed between the different treatments, however the control showed the lowest value in Minot, whereas samples treated at the soft dough stage showed the lowest value in Prosper. The differences in wet gluten caused by pre-harvest application of glyphosate could be due to the impact of glyphosate on gluten protein chemistry. Although protein content is not affected by glyphosate, the inhibition of the shikimic acid pathway and the accumulation of shikimic acid could impact the chemical properties of gliadin and glutenin proteins, which are deposited late in the grain filling process, compared to proteins such as albumins and globulins, which are deposited early [21].
In contrast to the observations for wet gluten, gluten index, which is indicative of protein quality, was highest in the samples treated at the soft dough stage, and lowest in the samples treated at the ripe stage (Table 1). Manthey et al. [6] also reported that gluten index was increased two to eight units when glyphosate was applied at the soft dough and the ripe stages/ physiological maturity. Thus, the findings for protein content are in agreement with those of Manthey et al. [6]. Gluten index was significantly lower in cultivar Prosper compared to Glenn, and in both cultivars the highest gluten index was found when treated at the soft dough stage. As for the location x treatment interaction, the gluten index was highest when applied at the soft dough stage at locations Carrington and Prosper. Previous work on factors affecting gluten index have reported that genotype is the most important factor determining gluten index, while environmental factors and agricultural practices have a substantial effect on gluten index [47]. Glyphosate may cause significant differences in gluten index by affecting the deposition of glutenin and gliadin proteins, as mentioned earlier. The ratio of glutenin to gliadin is critical in determining dough and baking quality, thus changes in this ratio may translate into effects on end-use quality characteristics.
Flour ash content measures the mineral content of wheat flour, and traditionally, it has been a measure of flour purity and low ash content is preferred [48]. In this study, flour ash did not differ between treatments (Table 1). The ash content was somewhat lower in the cultivar Glenn compared to Prosper; however, the values were within a very narrow range (0.53–0.56). The location x treatment interaction was not significant for this characteristic.
In this study, all kernel, milling and flour quality characteristics were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) affected by cultivar and location. Many studies have discussed the effect of genotype, environment and the genotype x environment interaction on kernel quality traits. For example, Bhatta et al. [49] and Mladenov et al. [50] determined that end-use quality traits are influenced by genotype, environment and their interaction. Similar observations were made by Fowler and Roche [51], who reported that a large environmental effect can be observed for wheat yield, protein and protein related parameters. Moreover, Horvat et al. [52], who studied the distribution of protein components in different genotypes and environments, determined that growing year had a significant effect on crude protein content, total gliadin and total high molecular weight and low molecular weight glutenin protein. Additionally, they found that the gliadins to glutenins ratio was affected by genotype and year to the same extent. In this context, the results of the current study align with previous findings where genotype and location are determining factors for kernel and flour quality traits.
3.2. Effect of Glyphosate on Dough Quality
Farinograph measurements are indicative of dough properties and are also useful in predicting how flour will behave in bread and other baked goods. In this study, farinograph analysis was used to determine the effect of pre-harvest glyphosate application on dough quality characteristics. These results are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Farinograph dough quality parameters, as affected by treatments and their interactions a.
Farinograph absorption, which indicates the optimum amount of water needed for processing wheat flour, was significantly lower when glyphosate was applied at the soft dough stage, compared to the control and application at the ripe stage, and absorption was somewhat higher in the cultivar Glenn compared to Prosper (Table 2). In each cultivar, the lowest absorption was found in the samples treated at the soft dough stage. As for the location x treatment interaction, Carrington did not show significant differences between treatments, whereas the lowest values were observed in samples treated at the soft dough stage at Minot and Prosper. Previous studies on factors affecting farinograph absorption have shown that increasing particle size, protein content, starch damage and pentosan content increase absorption [53]. Decreased wheat hardness, protein content and pentosan content have been shown to have the opposite effect. In the analysis of kernel quality characteristics, minor differences were observed in protein content. Although not significant, these differences may have caused the differences in absorption. However, as previously stated, shikimic acid accumulation as a result of a glyphosate application affects the carbon flow, thus the production of pentosans may be affected. Therefore, it is possible that this could also lead to decreases in water absorption.
In general, farinograph peak time, stability, mixing tolerance index (MTI) and quality number are indicators of dough behavior and dough strength. Farinograph peak time, which is an indicator for optimum mixing time, did not show significant differences between treatments (Table 2). In the cultivar x treatment interaction data, the cultivar Glenn generally showed higher values compared to Prosper, and in the location x treatment interaction, differences in treatments was only observed in Carrington, which showed the lowest value for the samples treated at the soft dough stage. Farinograph stability indicates how stable the dough is to over-mixing and dough strength, and higher values are favorable. In this experiment, the highest stability was reported in the samples treated at the soft dough stage. Similar to peak time, for the cultivar x treatment interaction, Glenn showed higher stability compared to Prosper, and variations in stability was most prominent at Carrington. Mixing tolerance index (MTI), which indicates the degree of softening during mixing, was lowest in the samples treated at the soft dough stage. As for the cultivar x treatment interaction, Glenn showed lower values than Prosper, and as for the location x treatment interaction, the lowest MTI was observed in samples treated at the soft dough stage in all three locations. Higher farinograph quality number is favorable, as it indicates strong dough. In this study, the highest quality number was found in the samples treated at the soft dough stage, which is in agreement with the observations made for stability and MTI. Additionally, the observations for the cultivar x treatment and location x treatment were in line with the findings for stability and MTI.
Manthey et al. [6] reported dough mixing stability was increased, when glyphosate was applied at the soft dough or ripe stages. This could be due to changes in protein composition and chemistry that is caused by glyphosate through the inhibition of the shikimic acid pathway and the effects of glyphosate on carbon flow. This might be supported by a significant correlation between gluten index and farinograph stability (r = 0.737, p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 2.
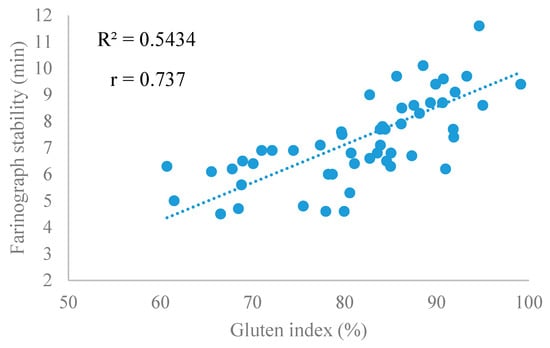
Figure 2.
Correlation between gluten index and farinograph stability.
Gliadin and glutenin proteins, which together make gluten proteins, have different effects on dough behavior. Uthayakumaran et al. [54] and Khatkar et al. [55] showed that gliadins generally have a negative effect on dough properties. However, Huebner and Bietz [56] and Park et al. [57] found evidence supporting that gliadins have a favorable effect. The role of individual gliadin types (α/β-, γ and ω) is not yet clear. As for glutenin proteins, Khatkar et al. [58] and Uthayakumaran, Gras, Stoddard and Bekes [36] reported that these proteins are favorable for dough strength and that the ratio between glutenins and gliadins is a critical factor determining dough quality. In this context, glyphosate may cause changes to the deposition of gliadin and glutenin proteins, which may alter the chemistry and/or the ratio of these proteins, leading to favorable dough properties.
All farinograph parameters were significantly affected by cultivar and location, and the interaction between cultivar x location was significant for farinograph absorption and stability (Table 2). In this study, dough quality parameters were affected by genotype, environment and their interaction. Baker and Kosmolak [59] determined that genotype-environment interactions are important in determining dough quality traits determined by mixograph analysis and falling number, less important in determining farinograph traits such as absorption, and least important in determining flour protein. As mentioned earlier, according to Horvat et al. (2015) genotype and growing year and location (environment) have significant effects on protein composition. Therefore, the differences in gliadin and glutenin protein compositions caused by genotype and environmental conditions could be the reason why cultivar and location were significant for all farinograph dough quality parameters. Moreover, Mladenov et al. [50] found that farinograph absorption, peak time and quality number are significantly affected by the genotype, environments and the interaction of these factors.
3.3. Effect of Glyphosate on Baking Quality
In this study, baking quality was also evaluated, to determine how breadmaking is affected by the pre-harvest application of glyphosate. The results of this analysis are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Baking quality parameters as affected by treatment and the interaction between treatment and other factors a.
In the analysis of baking quality, glyphosate treatment affected bake absorption, mix time, loaf volume and crumb color. Bake absorption was significantly lower in the control and samples treated at the soft dough stage compared to the treatment at the ripe stage. In the farinograph analysis, the lowest absorption was found in the samples treated at the soft dough stage, therefore the reason for this is not clear. Additionally, mix time was highest when samples were treated at soft dough stage, which can be explained with the observations made for dough quality. In the farinograph analysis, where the samples treated at the soft dough showed highest values for stability and quality number indicating good dough quality, which may have resulted in increasing the bake mix time. Loaf volume was significantly higher in the treated samples (both ripe and soft dough) compared to the untreated control. Specifically, the cultivar, Prosper, showed higher volume for the treatment at ripe stage (Table 3) together with flour protein and wet gluten (Table 1). In the previous section, dough quality was significantly affected when glyphosate was applied at the soft dough stage, therefore it is reasonable that loaf volume was higher when treated at the soft dough stage. However, dough quality was not significantly affected when applied at the ripe stage, therefore it is unclear why loaf volume was significantly higher when treated at the ripe stage compared to the control.
In contrast to the observations made for loaf volume in the present study, Manthey et al. [6] and Darwent, Kirkland, Baig and Lefkovitch [14] reported that pre-harvest herbicide treatments did not affect loaf volume. McNeal et al. [13] also reported that harvest aids do not affect the milling and baking quality of hard red spring wheat. Significant differences that were observed in loaf volume can also be attributed to the differences observed in gluten index, (where gluten index was highest when applied at the soft dough stage), since loaf volume is directly related to the quality and composition of wheat gluten proteins [60]. On the other hand, other breadmaking quality characteristics may not have been significantly affected by glyphosate treatment, because the gluten index for all samples were within the range of 75–90%, which as Curic et al. [61] described, was within the range needed for obtaining good quality bread. In addition to treatments, baking quality traits were also impacted by cultivar and location, and as previously explained this could be due to changes in protein quality that is caused by genotypic and environmental effects. As Roisch and Lingens [19] and Gélinas et al. [62] reported, glyphosate does not have a significant impact on yeast activity, and this may be the reason why most baking quality traits were not significantly affected by glyphosate.
Interactions between cultivar x treatment also showed significant differences on baking quality (Table 3). In general, some quality traits showed significantly higher or lower values in specific cultivars, highlighting the effect of genotype. For example, cultivar Glenn showed higher loaf volume compared to cultivar Prosper. For the different cultivars, bake absorption did not show a specific trend. Mix time, as previously mentioned, was highest when treated at the soft dough stage in both cultivars. Dough optimization score did not show a clear trend. Loaf volume was highest when treated at the soft dough stage for cultivar Glenn and highest at the ripe stage in cultivar Prosper. Therefore, there could be a genotype specific response in the case of this parameter. Symmetry, crust color, grain and texture, crumb color, crumb texture, fermentation height, oven-rise and specific volume were for the most part not significantly different for the cultivar x treatment interaction. As for the location x treatment interaction, most of the baking quality parameters identified did not show significant differences. However, for loaf volume, the highest value was observed in samples treated at the soft dough stage in all three locations. Crumb texture was also affected by location as Carrington generally showed higher scores compared to the other two locations.
Kernel, dough quality and baking quality traits were also influenced by genotype and environment, as previous studies have found. For example, Hristov et al. [63] reported that protein content, sedimentation value and loaf volume are affected by location. Similarly, Mladenov, Przulj, Hristov, Djuric and Milovanovic [50] determined that loaf volume and bake score are impacted by genotype, environments, and the interaction in winter wheat cultivars. Peterson et al. [64] studied the effect of environment on baking quality of hard red spring wheat and found that variations attributed to environmental effects was greater than those caused by genotype for dough and baking quality traits.
Overall, this study indicates that certain wheat quality characteristics, such as, TKW, wheat protein content, percentage extraction, wet gluten, gluten index, farinograph parameters, bake mix time and loaf volume are impacted by pre-harvest glyphosate treatment. In general, the effects were more pronounced when glyphosate was applied at the soft dough stage compared to the ripe stage. The soft dough stage comes before the ripe stage in the grain filling process, and application at this stage may interfere in the deposition of starch and proteins. Early application can also impact the chemical composition and other physicochemical properties of wheat starch and proteins, which could result in more prominent effects on wheat quality, when glyphosate is applied at the soft dough stage. Additionally, when the shikimic acid pathway is inhibited as a result of glyphosate application, the carbon flow is disrupted, which could lead to changes in the physicochemical and functional properties of wheat starch and proteins. The results of the quality analyses were also impacted by cultivar, location and the interaction between these two factors. Therefore, the effects of pre-harvest glyphosate application can be affected by the interaction of multiple factors. Overall, this study highlights the importance of timely application of herbicides to avoid any negative effects on wheat quality characteristics.
4. Conclusions
Although glyphosate and other such herbicides are sometimes used prior to harvest, the effect of such practices have not been investigated extensively in the context of spring wheat. In this study, two hard red spring wheat cultivars were grown in three locations across North Dakota and sprayed with a glyphosate-based harvest aid at the soft dough and ripe stages of development, to determine the effect of pre-harvest glyphosate application on wheat quality traits. Quality analyses were performed according to AACC-I approved methods, and the results were analyzed using statistical tools. In line with previous findings regarding the effect of genotype and location/environment on wheat quality, the results of the current study also showed that cultivar, location and their interaction have significant effects on wheat quality traits, ranging from kernel quality to baking quality. The glyphosate application stage significantly affected kernel quality traits such as TKW, falling number, wheat protein content, percentage extraction, wet gluten and gluten index. Thousand kernel weight and protein related characteristics were profoundly affected when glyphosate was applied at the soft dough stage, indicating that early application could lead to decreases in kernel weight, however, gluten index was improved by early application, possibly due to the effects of glyphosate on the disruption of protein deposition and interference in the carbon flow. There was a general improvement in dough quality parameters, with an application of glyphosate, as indicated by farinograph stability, MTI and quality number. These observations can also be linked to changes in protein composition caused by glyphosate, as a result of the disruption of protein deposition pathways and the effects of shikimic acid accumulation. Loaf volume was found to be higher in the treated samples (both soft dough and ripe), in comparison to the control. However, most of the other baking quality traits were not significantly affected by glyphosate treatment. Thus, the results of this study indicate that the biochemical and compositional properties of wheat starch and proteins may be impacted by pre-harvest glyphosate application, possibly by the disruption of biochemical pathways responsible for starch and protein deposition, which results in changes in wheat quality characteristics, as observed in this study. Additionally, application at the soft dough stage caused more prominent effects on quality characteristics compared to an application at the ripe stage, which highlights the importance of proper timing of application of harvest aids like glyphosate.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S.; Methodology, J.K.R. and S.S.; Software, J.-B.O.; Validation, M.M., J.-B.O. and S.S.; Formal Analysis, M.M. and J.-B.O.; Investigation, M.M. and J.K.R.; Resources, J.K.R. and S.S.; Data Curation, M.M.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.M.; Writing—Review and Editing, M.M., J.-B.O., K.H., J.K.R. and S.S.; Visualization, M.M. and J.-B.O.; Supervision, S.S.; Project Administration, S.S.; Funding Acquisition, S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded through North Dakota Wheat Commission check off funds.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by growers through check off funds through the North Dakota Wheat Commission.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Duke, S.O.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate: A once-in-a-century herbicide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.M.; Kroes, R.; Munro, I.C. Safety evaluation and risk assessment of the herbicide Roundup and its active ingredient, glyphosate, for humans. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2000, 31, 117–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siehl, D.L. Herbicide Activity: Toxicology, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; Roe, R.M., Burton, J.D., Kuhr, R.J., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 37–67. [Google Scholar]
- Servaites, J.C.; Tucci, M.A.; Geiger, D.R. Glyphosate effects on carbon assimilation, ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity, and metabolite levels in sugar-beet leaves. Plant Physiol. 1987, 85, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.E.; Edwards, N.M. The Implications of Frequently Encountered Grading Factors on the Processing Quality of Durum Wheat; Association of Operative Millers: Lenexa, KS, USA, 1998; pp. 7165–7171. [Google Scholar]
- Manthey, F.A.; Chakraborty, M.; Peel, M.D.; Pederson, J.D. Effect of preharvest applied herbicides on breadmaking quality of hard red spring wheat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwent, A.L.; Kirkland, K.J.; Townleysmith, L.; Harker, K.N.; Cessna, A.J.; Lukow, O.M.; Lefkovitch, L.P. Effect of preharvest applications of glyphosate on the drying, yield and quality of wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1994, 74, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresnahan, G.A.; Manthey, F.A.; Howatt, K.A.; Chakraborty, M. Glyphosate applied preharvest induces shikimic acid accumulation in hard red spring wheat (Triticum aestivum). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4004–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, C.J.; Cairns, A.J. Fructan metabolism in grasses and cereals. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1991, 42, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenish, J.P.; Young, F.L. Effect of preharvest glyphosate application on seed and seedling quality of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum). Weed Technol. 2000, 14, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskulski, D.; Jaskulska, I. The effect of pre-harvest glyphosate application on grain quality and volunteer winter wheat. Rom. Agric. Res. 2014, 31, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Krenchinski, F.H.; Cesco, V.J.S.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Pereira, V.G.C.; Albrecht, A.P.; Albrecht, L.P. Yield and physiological quality of wheat seeds after desiccation with different herbicides. J. Seed Sci. 2017, 39, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, F.H.; Hodgson, J.M.; McGuire, C.F.; Berg, M.A. Chemical desiccation experiments with hard red spring wheat, Triticum aestivum L. Agron. J. 1973, 65, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwent, A.L.; Kirkland, K.J.; Baig, M.N.; Lefkovitch, L.P. Preharvest applications of glyphosate for Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense) control. Weed Technol. 1994, 8, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Satya, S.; Kumar, V.; Tewary, D.K. Dissipation of pesticides during bread-making. Chem. Health Saf. 2005, 12, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, F.L.; Shaw, I.C.; Gerrard, J.A. The effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the stability of the herbicide glyphosate during bread leavening. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 40, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hack, M.; Nitz, S.; Parlar, H. Behavior of [14C]atrazine, [14C]terbutylazine, and their major metabolites in the brewing process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braconi, D.; Sotgiu, M.; Millucci, L.; Paffetti, A.; Tasso, F.; Alisi, C.; Martini, S.; Rappijoli, R.; Lusini, P.; Sprocati, A.R.; et al. Comparative analysis of the effects of locally used herbicides and their active ingredients on a wild-type wine Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3163–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roisch, U.; Lingens, F. The mechanism of action of the herbicide N-(phosphonomethyl) glycine: Its effect on the growth and the enzymes of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli Hoppe Seylers, Z. Physiol. Chem. 1980, 361, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACCI. Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists. Available online: http://methods.aaccnet.org/ (accessed on 31 May 2017).
- Stone, P.J.; Savin, R. Grain quality and its physiological determinants. In Wheat: Ecology and Physiology of Yield Determination; Sattore, E.H., Slafer, G.A., Eds.; The Haworth Press: Binghamton, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zobiole, L.H.S.; Kremer, R.J.; Oliveira, R.S.; Constantin, J. Glyphosate affects chlorophyll, nodulation and nutrient accumulation of “second generation” glyphosate-resistant soybean (Glycine max L.). Pest Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 99, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollinger, R.K.; Manthey, F.A.; Fitterer, S.A. Effect of preharvest herbicides on durum wheat quality. In Proceedings of the 52nd Western Society of Weed Science, Colorado Spring, CO, USA, 8–11 March 1999; p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.G.; Smith, J.A. Influence of harvest-aid herbicides on dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) desiccation, seed yield, and quality. Weed Technol. 2002, 16, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.R.; Bovey, R.W.; Veech, J.A. Growth responses in sorghum and wheat induced by glyphosate. Weed Sci. 1977, 25, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.C.; Shaw, D.R. Effect of preharvest desiccants on group IV glycine max seed viability. Weed Sci. 2000, 48, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.N.; Darwent, A.L.; Harker, K.N.; O’Donovan, J.T. Preharvest applications of glyphosate affect emergence and seedling growth of field pea (Pisum sativum). Weed Technol. 2003, 17, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.A.; Bollich, P.K. Effects of pre-harvest desiccants on rice yield and quality. Crop Prot. 2007, 26, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-Q.; Cheng, J.-P.; Liu, L.-F.; Li, X.-D.; Yang, B.; Zhang, H.-S.; Wang, Z.-F. Effects of pre-harvest chemical application on rice desiccation and seed quality. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreaux, J.M.; Griffin, J.L. Application timing of harvest aid herbicides affects soybean harvest and yield. Weed Technol. 2011, 25, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, M.; Fardi, M.; Asghari, J.; Rabiei, M.; Samizadeh, H. Effects of pre-harvest application of parquat on grain moisture reduction, grain yield and quality of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) cultivars. Casp. J. Env. Sci. 2012, 10, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bellé, C.; Kulczynski, S.M.; Basso, C.J.; Edu Kaspary, T.; Lamego, F.P.; Pinto, M.A.B. Yield and quality of wheat seeds as a function of desiccation stages and herbicides. J. Seed Sci. 2014, 36, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, S.J.; van Schepdael, L.; Dexter, J.E. Measurement of hard vitreous kernels in durum wheat by machine vision. Cereal Chem. 2003, 80, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greffeuille, V.; Abecassis, J.; Barouh, N.; Villeneuve, P.; Mabille, F.; Bar L’Helgouac’h, C.; Lullien-Pellerin, V. Analysis of the milling reduction of bread wheat farina: Physical and biochemical characterisation. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 45, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, A.; Cacak-Pietrzak, G.; Gondek, E.W.A. Mechanical and acoustic properties of spring wheat versus its technological quality factors. J. Texture Stud. 2011, 42, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthayakumaran, S.; Gras, P.W.; Stoddard, F.L.; Bekes, F. Effect of varying protein content and glutenin-to-gliadin ratio on the functional properties of wheat dough. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, K.R.; Kilborn, R.H.; Morgan, B.C.; Babb, J.C. Effects of frost and immaturity on the quality of a Canadian hard red spring wheat. Cereal Chem. 1991, 68, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlen, A.K.; Hafskjold, R.; Kalhovd, A.H.; Sahlström, S.; Longva, Å.; Magnus, E.M. Effects of cultivar and temperature during grain filling on wheat protein content, composition, and dough mixing properties. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triboï, E.; Martre, P.; Triboï-Blondel, A.M. Environmentally-induced changes in protein composition in developing grains of wheat are related to changes in total protein content. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perten, H. Application of falling number method for evaluating α-amylase activity. Cereal Chem. 1964, 41, 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Mares, D.; Mrva, K. Late-maturity α-amylase: Low falling number in wheat in the absence of preharvest sprouting. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, E. Effect of two wheat genotypes and Swedish environment on falling number, amylase activities, and protein concentration and composition. Euphytica 2002, 126, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, A.C.; Beecher, B.; Martin, J.M.; Meyer, F.; Talbert, L.; Lanning, S.; Giroux, M.J. Hard wheat milling and bread baking traits affected by the seed-specific overexpression of puroindolines. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.J.; Graybosch, R.A.; Baenziger, P.S.; Grombacher, A.W. Genotype and environment effects on quality characteristics of hard red winter wheat. Crop Sci. 1992, 32, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, F.; Iametti, S.; Mamone, G.; Ferranti, P. The performing protein: Beyond wheat proteomics? Cereal Chem. 2013, 90, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.G.; Ponte, J.G., Jr.; Kulp, K. Significance of gluten content as an index of flour quality. Cereal Chem. 1987, 64, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, D.H.; Bonfil, D.J.; Svoray, T. Multi scale analysis of the factors influencing wheat quality as determined by gluten index. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 123, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, J.J.C. The distribution of ash in the wheat kernel. Cereal Chem. 1959, 36, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatta, M.; Regassa, T.; Rose, D.J.; Baenziger, P.S.; Eskridge, K.M.; Santra, D.K.; Poudel, R. Genotype, environment, seeding rate, and top-dressed nitrogen effects on end-use quality of modern Nebraska winter wheat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 5311–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenov, N.; Przulj, N.; Hristov, N.; Djuric, V.; Milovanovic, M. Cultivar-by-environment interactions for wheat quality traits in semiarid conditions. Cereal Chem. 2001, 78, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.B.; Roche, I.A.D.L. Wheat quality evaluation. 3. Influence of genotype and environment. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1975, 55, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, D.; Drezner, G.; Sudar, R.; Simic, G.; Dvojkovic, K.; Spanic, V.; Magdic, D. Distribution of wheat protein components under different genetic backgrounds and environments. Turk. J. Field Crop. 2015, 20, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, Y. Factors Influencing Farinograph Absorption of Canada Western Red Winter Wheat Genotypes; University of Manitoba: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Uthayakumaran, S.; Tomoskozi, S.; Tatham, A.S.; Savage, A.W.J.; Gianibelli, M.C.; Stoddard, F.L.; Bekes, F. Effects of gliadin fractions on functional properties of wheat dough depending on molecular size and hydrophobicity. Cereal Chem. 2001, 78, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, B.S.; Fido, R.J.; Tatham, A.S.; Schofield, J.D. Functional properties of wheat gliadins. I. Effects on mixing characteristics and bread making quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 35, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, F.R.; Bietz, J.A. Assessment of the potential breadmaking quality of hard wheats by reversed-phase high-performance liquid-chromatography of gliadins. J. Cereal Sci. 1986, 4, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Bean, S.R.; Chung, O.K.; Seib, P.A. Levels of protein and protein composition in hard winter wheat flours and the relationship to breadmaking. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, B.S.; Bell, A.E.; Schofield, J.D. The dynamic rheological properties of glutens and gluten subfractions from wheats of good and poor bread-making quality. J. Cereal Sci. 1995, 22, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.J.; Kosmolak, F.G. Effects of genotype-environment interaction on bread wheat quality in Western Canada. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1977, 57, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malalgoda, M.; Ohm, J.B.; Meinhardt, S.; Simsek, S. Association between gluten protein composition and breadmaking quality characteristics in historical and modern spring wheat. Cereal Chem. 2018, 95, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curic, D.; Karlovic, D.; Tusak, D.; Petrovic, B.; Dugum, J. Gluten as a standard of wheat flour quality. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2001, 39, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas, P.; Gagnon, F.; McKinnon, C. Wheat preharvest herbicide application, whole-grain flour properties, yeast activity and the degradation of glyphosate in bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, N.; Mladenov, N.; Djuric, V.; Kondic-Spika, A.; Marjanovic-Jeromela, A.; Simic, D. Genotype by environment interactions in wheat quality breeding programs in southeast Europe. Euphytica 2010, 174, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.J.; Graybosch, R.A.; Shelton, D.R.; Baenziger, P.S. Baking quality of hard winter wheat: Response of cultivars to environment in the great plains. Euphytica 1998, 100, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).