Pilot Study on the Use of a Laser-Structured Double Diamond Electrode (DDE) for Biofilm Removal from Dental Implant Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Intraoral Formation of Wild-Type Biofilm
2.2. Electrochemical Disinfection
2.2.1. Boron-Doped Double Diamond Electrode
2.2.2. Treatment of Discs
2.3. Biofilm Measurement
2.4. Identification of Biofilm Microorganisms
3. Results
3.1. Multipecies Biofilm Formation
Composition of Natural Biofilms
3.2. Elimination of Microorganisms
3.2.1. Inactivation of Bacterial Colonization by Mechanical Debridement and Electrochemical Disinfection
3.2.2. Surviving Microorganisms
3.2.3. Removal of Biofilm
3.2.4. BDD Treatment of Implants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derks, J.; Schaller, D.; Håkansson, J.; Wennström, J.L.; Tomasi, C.; Berglundh, T. Effectiveness of implant therapy analyzed in a Swedish population: Prevalence of peri-implantitis. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, T.-H.; Wang, C.-W.; Salem, D.M.; Levin, L. Nonsurgical and surgical management of biologic complications around dental implants: Peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Quintessence Int. 2020, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Canullo, L.; Cochran, D.; De Bruyn, H. “Peri-implantitis”: A complication of a foreign body or a man-made “disease”. Facts and fiction. Clin. Impl. Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepsen, S.; Berglundh, T.; Genco, R.; Aass, A.M.; Demirel, K.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; Giovannoli, J.L.; Goldstein, M.; Lambert, F.; et al. Primary prevention of peri-implantitis: Managing peri-implant mucositis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42 (Suppl. 16), S152–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakic, M.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Monje, A.; Radovanovic, S.; Wang, H.L.; Cochran, D.; Sculean, A.; Canullo, L. How frequent does peri-implantitis occur? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Chrcanovic, B.; Östman, P.O.; Sennerby, L. Initial and long-term crestal bone responses to modern dental implants. Periodontology 2000, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Buser, D.; Sennerby, L. Crestal bone loss and oral implants. Clin. Implants Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máximo, M.B.; Cutrim de Mendonça, A.; Santos, V.R.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Feres, M.; Mendes Duarte, P. Short-term clinical and microbiological evaluations of peri-implant diseases before and after mechanical anti-infective therapies. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Eberhard, J.; Glage, S.; Held, N.; Voigt, H.; Schwabe, K.; Winkel, A.; Stiesch, M. Development of a peri-implantitis model in the rat. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2020, 31, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuero, E.; Graziani, F.; Sanz, I.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M. Management of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Periodontology 2014, 66, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Tapia, B.; Valles, C.; Ribeiro-Amaral, T.; Mor, C.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M.; Nart, J. The adjunctive effect of a titanium brush in implant surface decontamination at peri-implantitis surgical regenerative interventions: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Waal, Y.C.M.; Raghoebar, G.M.; Huddleston Slater, J.J.R.; Meijer, H.J.A.; Winkel, E.G.; van Winkelhoff, A.J. Implant decontamination during surgical peri-implantitis treatment: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Waal, Y.C.M.; Raghoebar, G.M.; Meijer, H.J.A.; Winkel, E.G.; van Winkelhoff, A.J. Implant decontamination with 2% chlorhexidine during surgical peri-implantitis treatment: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentenaar, D.F.M.; De Waal, Y.C.M.; Strooker, H.; Meijer, H.J.A.; van Winkelhoff, A.-J.; Raghoebar, G.R. Implant decontamination with phosphoric acid during surgical peri-implantitis treatment: A RCT. Int. J. Implants Dent. 2017, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes Duarte, P.; Cutrim de Mendonça, A.; Máximo, M.B.; Santos, V.R.; Ferreira Bastos, M.; Nociti, F.H. Effect of anti-infective mechanical therapy on clinical parameters and cytokine levels in human peri-implant diseases. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conserva, E.; Pisciotta, A.; Bertoni, L.; Bertani, G.; Meto, A.; Colombari, B.; Blasi, E.; Bellini, P.; de Pol, A.; Consolo, U.; et al. Evaluation of biological response of STRO-1/c-Kit enriched human dental pulp stem cells to titanium surfaces treated with two different cleaning systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meto, A.; Conserva, E.; Liccardi, F.; Colombari, B.; Consolo, U.; Blasi, E. Differential efficacy of two dental implant decontamination techniques in reducing microbial biofilm and re-growth onto titanium disks in vitro. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagri Isler, C.; Unsal, B.; Soysal, F.; Ozcan, G.; Peker, E.; Karaca, I.R. The effects of ozone therapy as an adjunct to the surgical treatment of peri-implantitis. J. Periodontal Implants Sci. 2018, 48, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I.; Persson, G.R. Treatment modalities for peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Am. J. Dent. 2013, 26, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, F.; Sahm, N.; Iglhaut, G.; Becker, J. Impact of the method of surface debridement and decontamination on the clinical outcome following combined surgical therapy of peri-implantitis: A randomized controlled clinical study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Hegewald, A.; John, G.; Sahm, N.; Becker, J. Four-year follow-up of combined surgical therapy of advanced peri-implantitis evaluating two methods of surface decontamination. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupf, S.; Idlibi, A.N.; Marrawi, F.A.; Hannig, M.; Schubert, A.; von Mueller, L.; Spitzer, W.; Holtmann, H.; Lehmann, A.; Rueppell, A.; et al. Removing biofilms from microstructured titanium ex vivo: A novel approach using atmospheric plasma technology. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estefanía-Fresco, R.; García-de-la-Fuente, A.M.; Egaña-Fernández-Valderrama, A.; Bravo, M.; Aguirre-Zorzano, L.A. One-year results of a nonsurgical treatment protocol for peri-implantitis. A retrospective case series. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchenbecker Rösing, C.; Fiorini, T.; Haas, A.N.; Muniz, F.W.M.G.; Oppermann, R.V.; Susin, C. The impact of maintenance on peri-implant health. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33 (Suppl. 1), e074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.K.; Paeng, K.; Jung, U.W.; Choi, S.H.; Sanz, M.; Sanz-Martín, I. The effect of five mechanical instrumentation protocols on implant surface topography and roughness: A scanning electron microscope and confocal laser scanning microscope analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keim, D.; Nickles, K.; Dannewitz, B.; Ratka, C.; Eickholz, P.; Petsos, H. In vitro efficacy of three different implant surface decontamination methods in three different defect configurations. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuna, T.; Kuhlmann, L.; Bishti, S.; Sirazitdinova, E.; Deserno, T.; Wolfart, S. Removal of simulated biofilm at different implant crown designs with interproximal oral hygiene aids: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Rudolph, M.; Bause, V.; Terfort, A. Electrochemical removal of biofilms from titanium dental implant surfaces. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 121, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal-Gutelmacher, E.; Eliezer, D. Hydrogen assisted degradation of titanium based alloys. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal-Gutelmacher, E.; Eliezer, D. The hydrogen embrittlement of titanium-based alloys. JOM 2005, 57, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorr, B.; Ghanem, H.; Rosiwal, S.; Geißdörfer, W.; Burkovski, A. Elimination of bacterial contaminations by treatment of water with boron-doped diamond electrodes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, A.-L.; Koch, M.; Rosiwal, S.; Burkovski, A.; Karl, M. Grobecker-Karl, T. Electrochemical disinfection of experimentally infected teeth by boron-doped diamond electrode treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göltz, M.; Koch, M.; Detsch, R.; Karl, M.; Burkovski, A.; Rosiwal, S. Influence of in-situ electrochemical oxidation on implant surface and colonizing microorganisms evaluated by scatter electron microscopy. Materials 2019, 12, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Göltz, M.; Xiangjun, M.; Karl, M.; Rosiwal, S.; Burkovski, A. Electrochemical disinfection of dental implants experimentally contaminated with microorganisms as a model for periimplantitis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jum’h, I.; Abdelhay, A.; Al-Ta’ani, H.; Telfah, A.; Alnaief, M.; Rosiwal, S. Fabrication and application of boron doped diamond BDD electrode in olive mill wastewater treatment in Jordan. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2017, 7, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Huang, W. Recent developments and advances in boron-doped diamond electrodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conserva, E.; Generali, L.; Bandieri, A.; Cavani, F.; Borghi, F.; Consolo, U. Plaque accumulation on titanium disks with different surface treatments: An in vivo investigation. Odontology 2018, 106, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Kolter, R. Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signaling pathways: A genetic analysis. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teughels, W.; Van Assche, N.; Sliepen, I.; Quirynen, M. Effect of material characteristics and/or surface topography on biofilm development. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2006, 17 (Suppl. 2), 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memar, M.Y.; Ghotaslou, R.; Samiei, M.; Adibkia, K. Antimicrobial use of reactive oxygen therapy: Current insights. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, F. Chemical basis of reactive oxygen species Reactivity and involvement in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobbs, A.H.; Lamont, R.J.; Jenkinson, H.F. Streptococcus adherence and colonization. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 407–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuer, W.; Stiesch, M.; Abraham, W.R. Microbial diversity of supra- and subgingival biofilms on freshly colonized titanium implant abutments in the human mouth. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol.Infect. Dis. 2010, 30, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhl, S.; Eidt, A.; Melzl, H.; Reischl, U.; Cisar, J.O. Probing of microbial biofilm communities for coadhesion partners. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6583–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Martin, I.; Doolittle-Hall, J.; Teles, R.P.; Patel, M.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E.; Teles, F.R.F. Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.; Nibali, L.; Spratt, D.; Dopico, J.; Mardas, N.; Petrie, A.; Donos, N. Peri–implant and periodontal microbiome diversity in aggressive periodontitis patients: A pilot study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzukibashi, O.; Uchibori, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Umezawa, K.; Mashimo, C.; Nambu, T.; Saito, M.; Hashizume-Takizawa, T.; Ochiai, T. Isolation and identification methods of Rothia species in oral cavities. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 134, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibali, L.; Sousa, V.; Davrandi, M.; Spratt, D.; Alyahya, Q.; Dopico, J.; Donos, N. Differences in the periodontal microbiome of successfully treated and persistent aggressive periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, A.; Freifrau von Maltzahn, N.; Stumpp, N.; Dalton, M.; Yang, I.; Stiesch, M. Biofilm formation on zirconia and titanium over time—An in vivo model study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2020, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenbrander, P.; Palmer, R.; Periasamy, S.; Jakubovics, N.S. Oral multispecies biofilm development and the key role of cell–cell distance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenbrander, P.E.; Jakubovics, N.S.; Chalmers, N.I.; Palmer R.J., Jr. Human oral multi-species biofilms: Bacterial Communities in health and disease. In The Biofilm Mode of Life: Mechanisms and Adaptations; Kjelleberg, S., Givskov, M., Eds.; Horizon Bioscience: Norfolk, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]

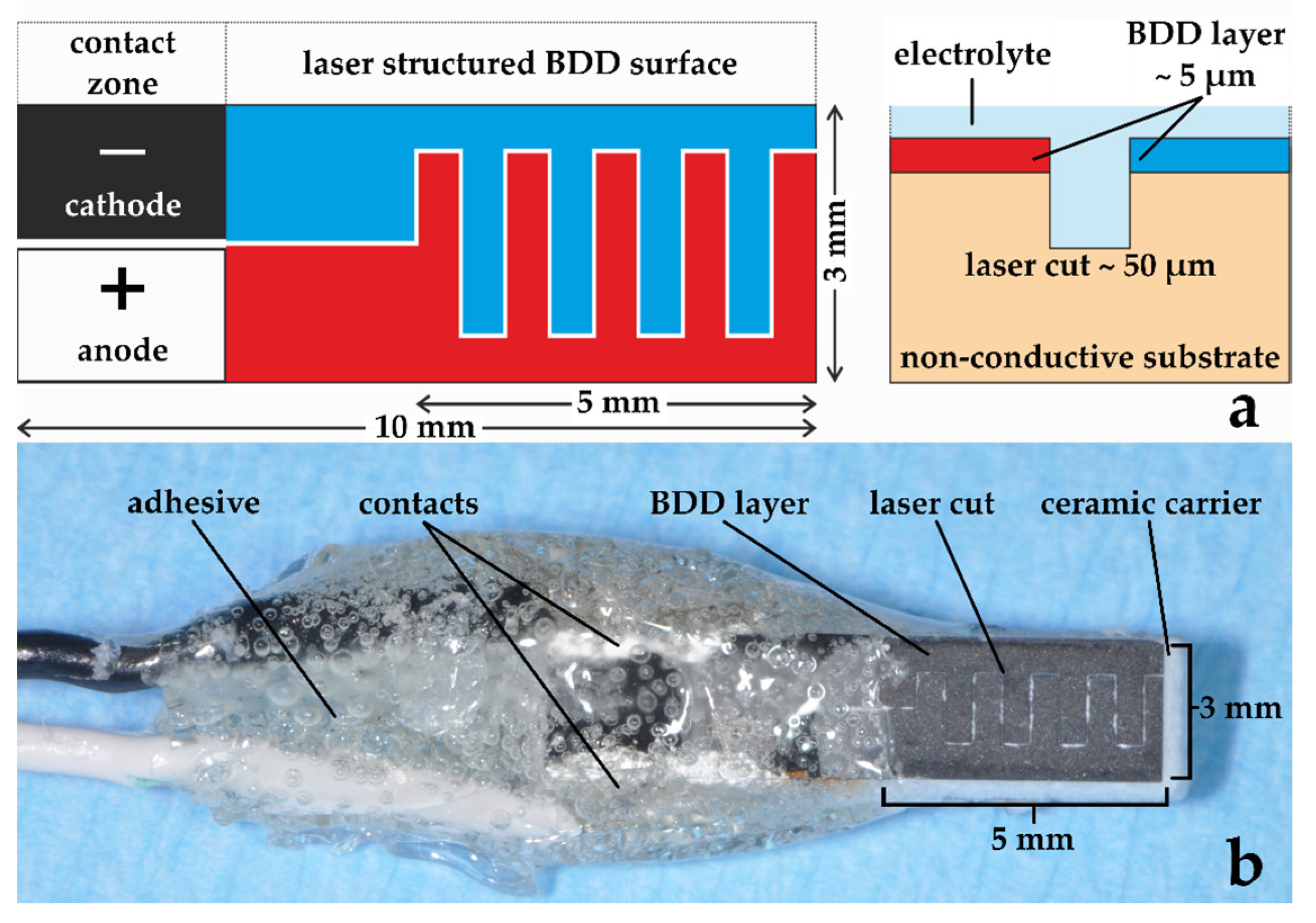
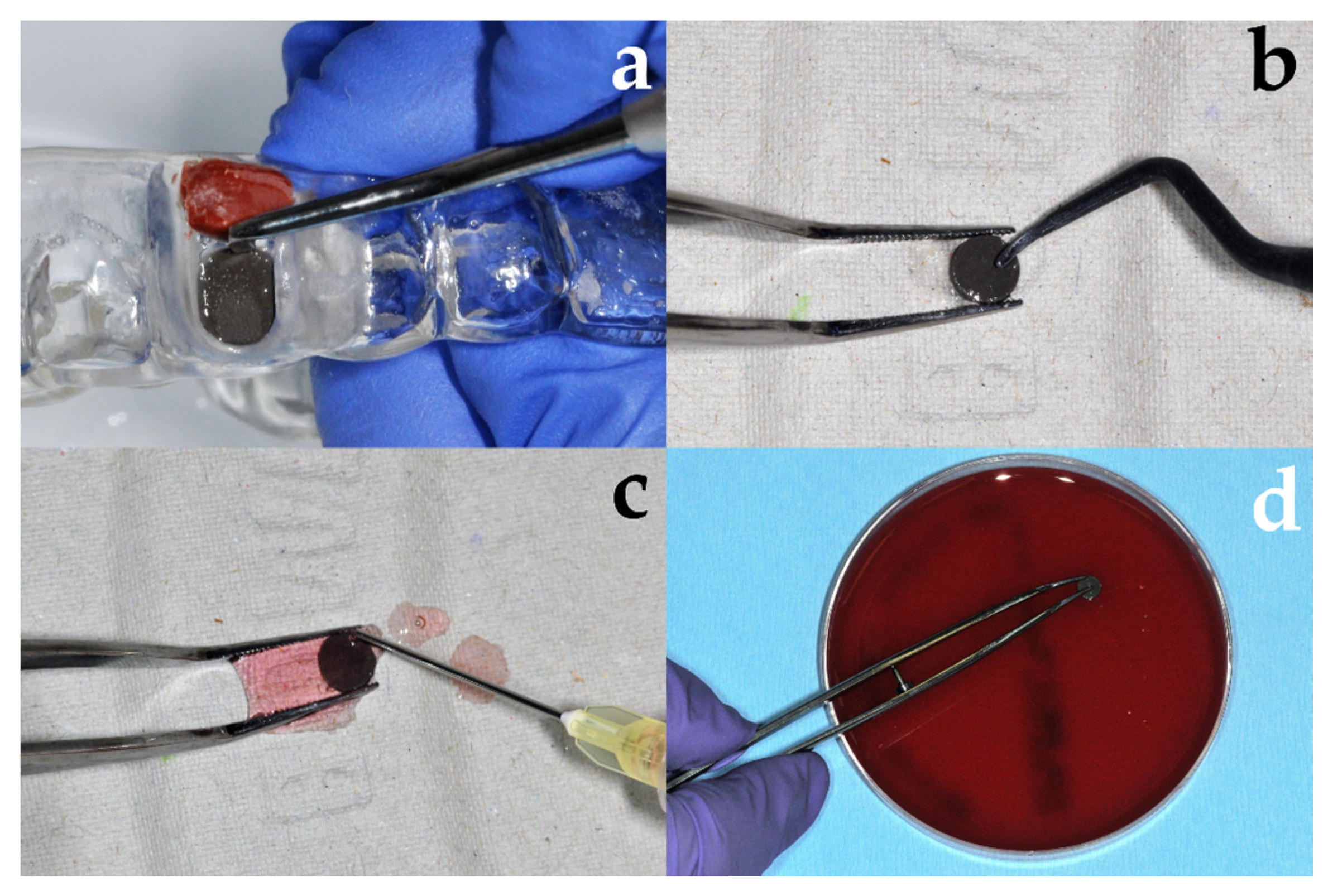
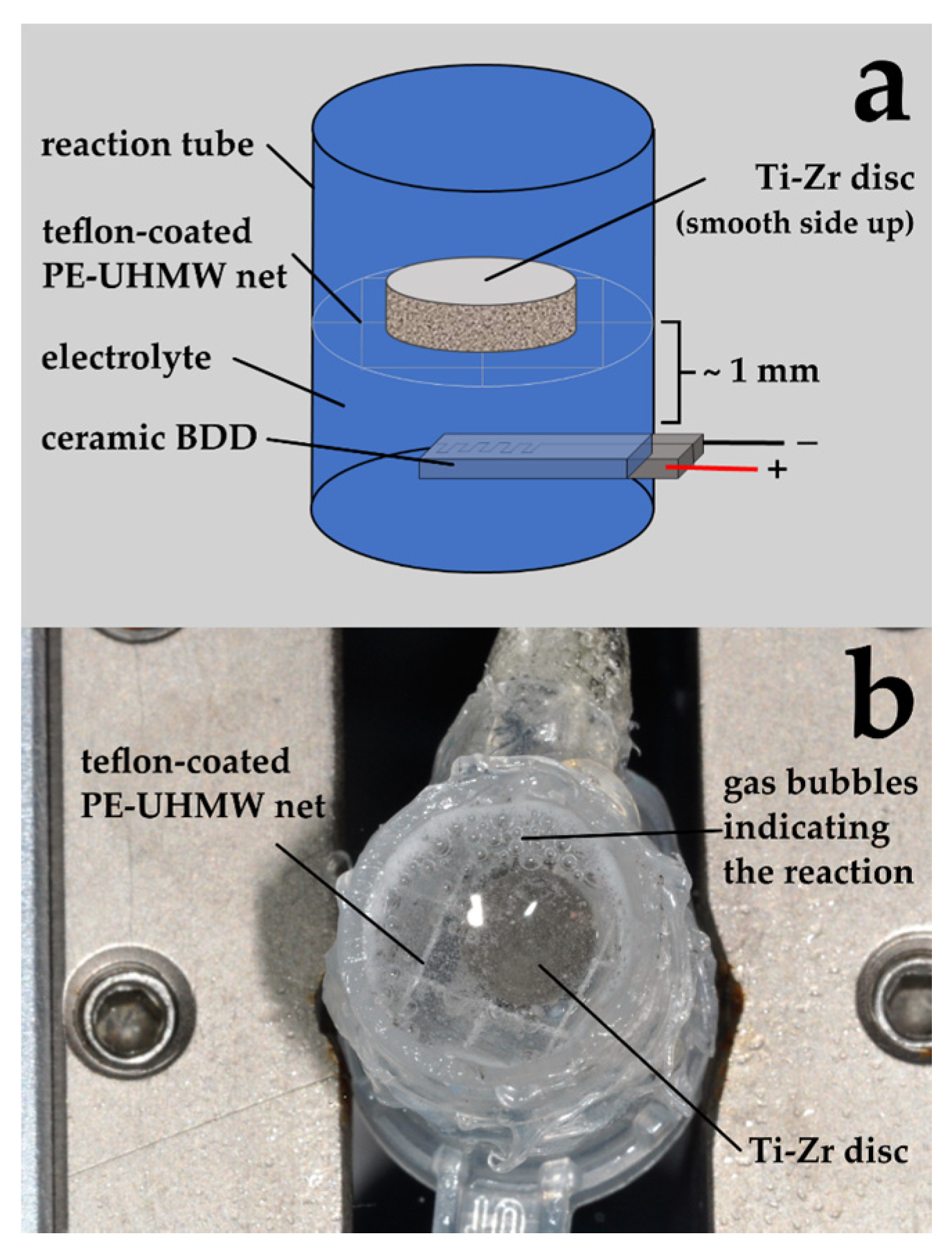
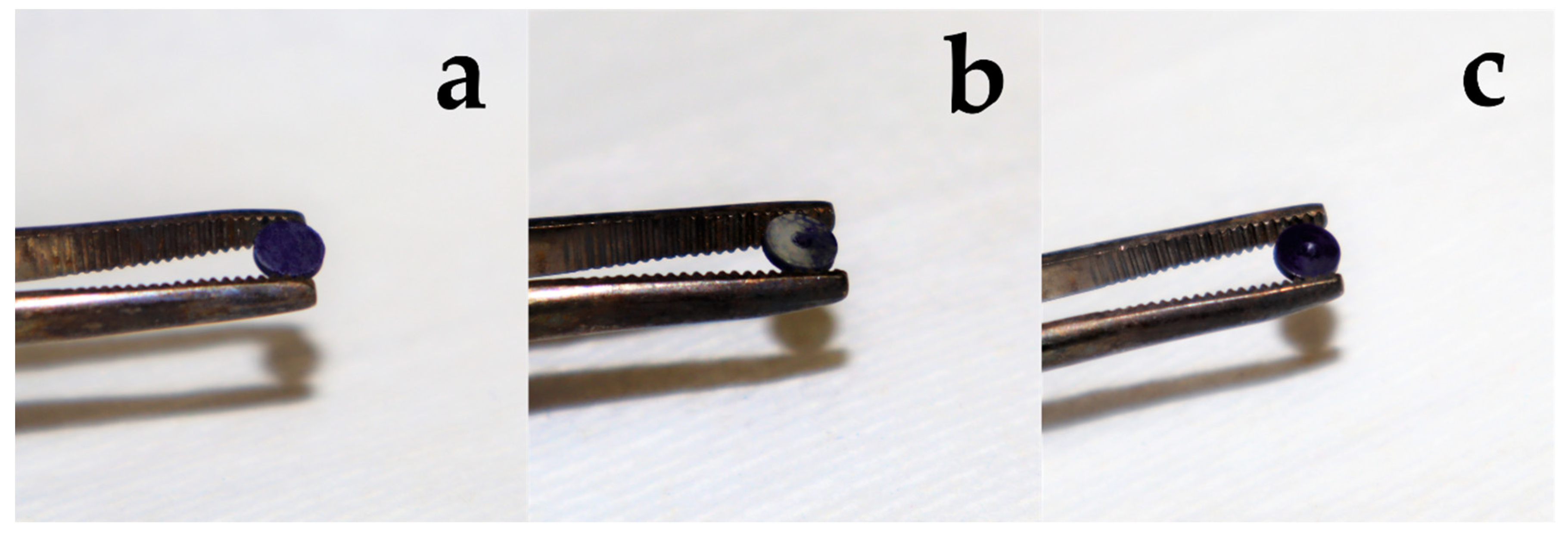

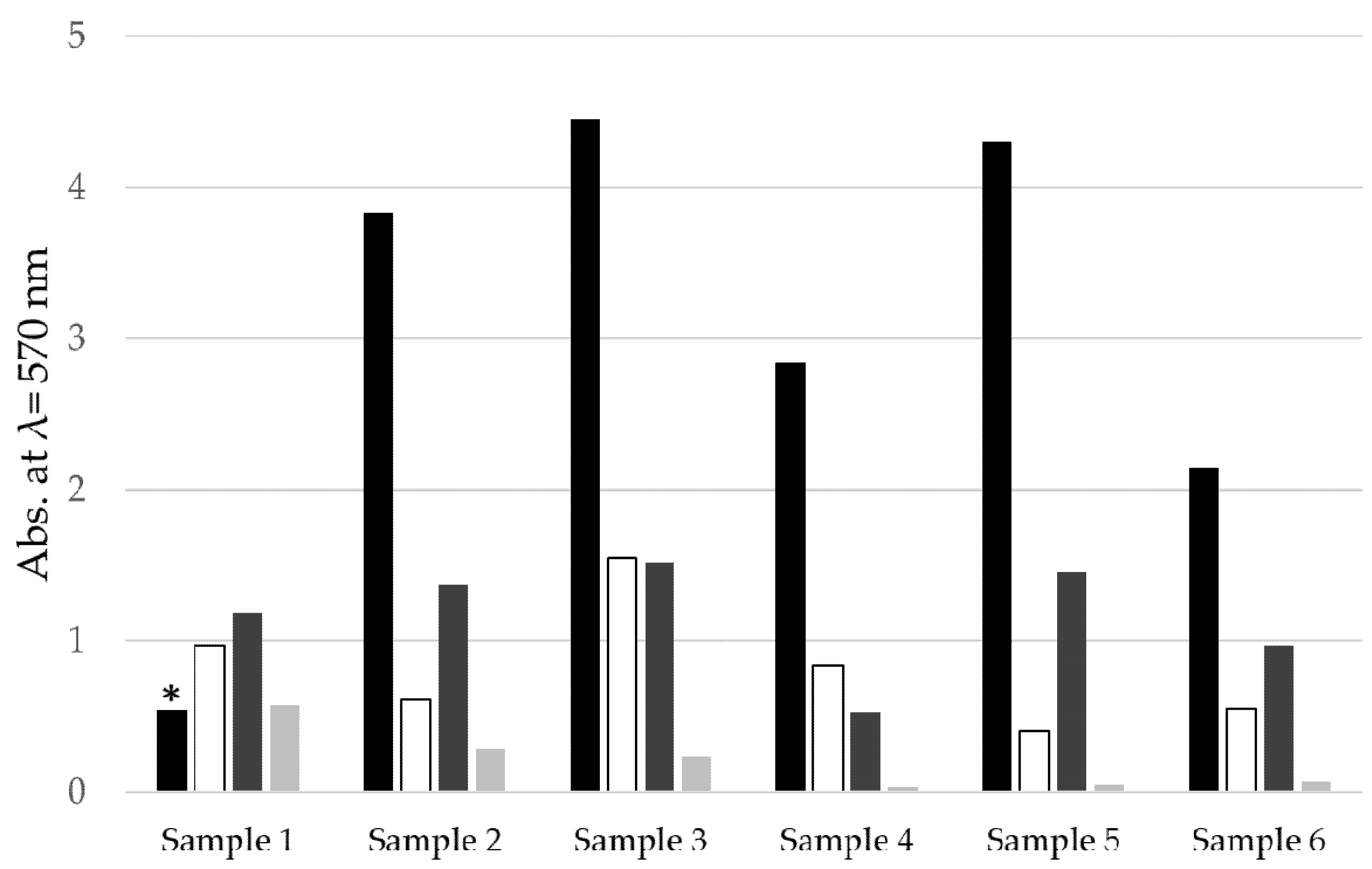
| Group | Abbreviation | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Positive | No treatment |
| Chemo-mechanical debridement (Figure 3) | Curette | Mechanical debridement using plastic curettes and irrigation with chlorhexidine for 30 sec |
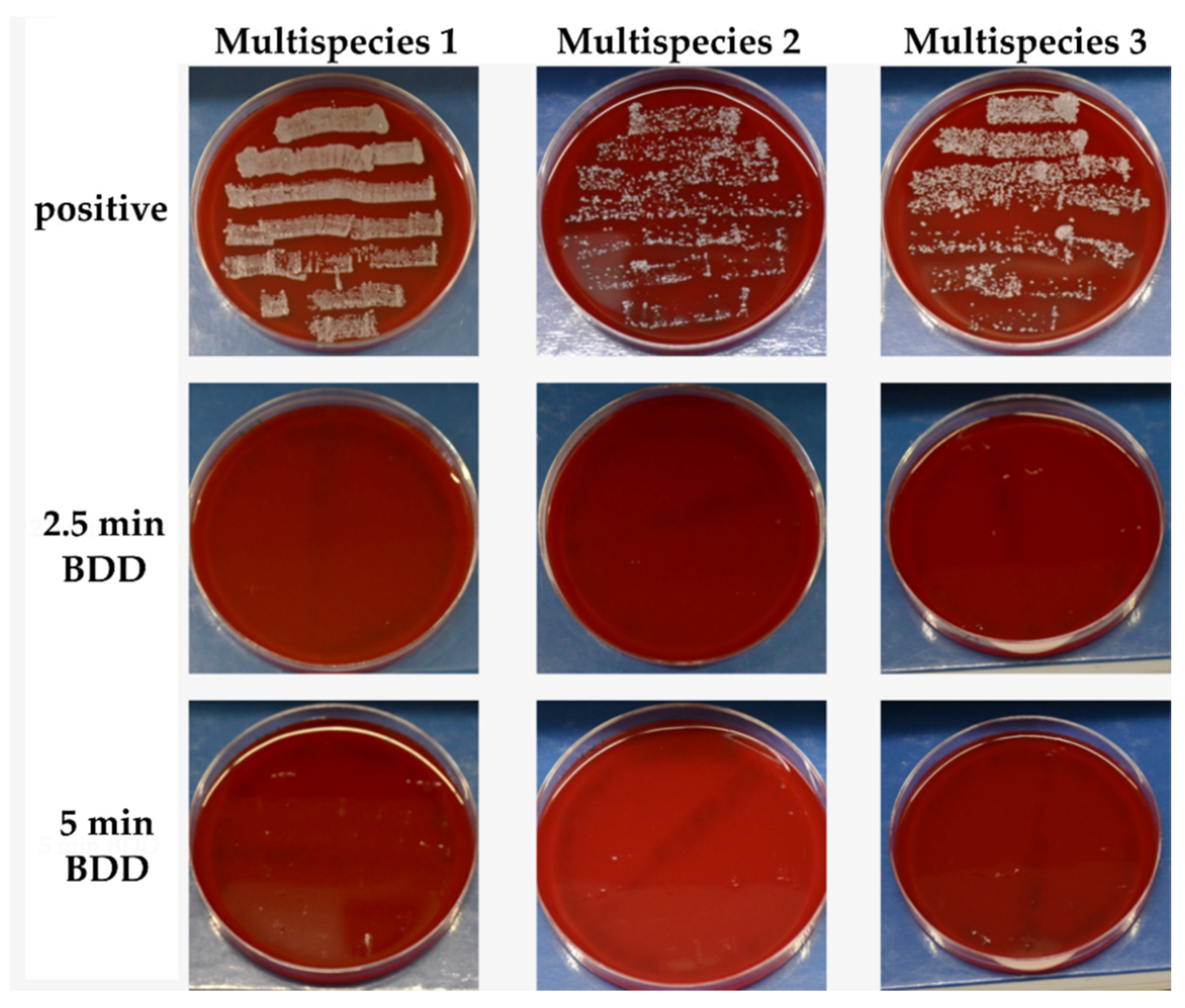
| Electrochemical disinfection (Figure 4) [32,34] | 2.5 min BDD | Immersion in physiological NaCl solution and electrochemical disinfection for 2.5 min at 6 V (Sample 1–3) or 9 V (Sample 4–6) |
| 5 min BDD | Immersion in physiological NaCl solution and electrochemical disinfection for 5 min at 6 V (Sample 1–3) or 9 V (Sample 4–6) |
| Organisms | Score |
|---|---|
| Sample 1 | |
| Bacillus subtilis | 2.251 |
| Micrococcus luteus | 2.086 |
| Neisseria flavescens | 2.187 |
| Neisseria sp. | 2.171 |
| Rothia mucilaginosa | 2.267 |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | 2.326 |
| Streptococcus cristatus | 2.142 |
| Streptococcus oralis | 2.11 |
| Streptococcus mitis | 2.37 |
| Streptococcus sanguinis | 2.151 |
| Sample 2 | |
| Micrococcus luteus | 2.173 |
| Neisseria mucosa | 2.111 |
| Neisseria sp. | 2.231 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 2.082 |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | 2.382 |
| Staphylococcus succinus | 2.047 |
| Streptococcus oralis | 2.062 |
| Streptococcus parasanguinis | 2.082 |
| Streptococcus salivarius ssp salivarius | 2.171 |
| Streptococcus vestibularis | 2.224 |
| Sample 3 | |
| Neisseria sp. | 2.145 |
| Rothia dentocariosa | 2.277 |
| Streptococcus mitis | 2.257 |
| Streptococcus oralis | 2.118 |
| Sample 4 | |
| Candida albicans | 2.21 |
| Lactobacillus paracasei | 2.432 |
| Mirococcus luteus | 2.212 |
| Neisseria subflava | 2.196 |
| Rothia mucilaginosa | 2.281 |
| Streptococcus mitis | 2.258 |
| Streptococcus oralis | 2.328 |
| Streptococcus salivarius | 2.281 |
| Streptococcus salivarius ssp. salivarius | 2.318 |
| Streptococcus vestibularis | 2.365 |
| Sample 5 | |
| Gemella haemolysans | 2.323 |
| Lactobacillus paracasei | 2.376 |
| Micrococcus luteus | 2.284 |
| Neisseria mucosa | 2.247 |
| Streptococcus gordonii | 2.188 |
| Streptococcus mitis | 2.308 |
| Streptococcus oralis | 2.321 |
| Sample 6 | |
| Micrococcus luteus | 2.287 |
| Neisseria flavescens | 2.247 |
| Rothia mucilaginosa | 2.27 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 2.102 |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | 1.95 |
| Streptococcus oralis | 2.292 |
| Streptococcus peroris | 2.091 |
| Streptococcus salivarius | 2.333 |
| Sensitive at 6 V | Survival of 2.5 min of DDE Treatment | Survival of 5 min of DDE Treatment |
| Neisseria flavescens Neisseria mucosa Rothia dentocariosa Staphylococcus epidermidis Staphylococcus succinus Streptococcus christatus Streptococcus oralis Streptococcus parasanguinis Streptococcus salivarius ssp. salivarius Streptococcus sanguinis Streptococcus vestibularis | Not tested | Bacillus subtilis Neisseria sp. Rothia mucilaginosa Staphylococcus haemolyticus Streptococcus mitis |
| Sensitive at 9 V | Survival of 2.5 min of DDE Treatment | Survival of 5 min of DDE Treatment |
| Candida albicans Gemella haemolysans Lactobacillus paracasei Neisseria flavescens Neisseria mucosa Neisseria subflava Staphylococcus epidermidis Staphylococcus haemolyticus Streptococcus gordonii Streptococcus mitis Streptococcus peroris Streptococcus salivarius ssp. salivarius Streptococcus vestibularis | Streptococcus oralis Streptococcus salivarius Rothia mucilaginosa | No surviving microorganisms. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koch, M.; Burkovski, A.; Zulla, M.; Rosiwal, S.; Geißdörfer, W.; Dittmar, R.; Grobecker-Karl, T. Pilot Study on the Use of a Laser-Structured Double Diamond Electrode (DDE) for Biofilm Removal from Dental Implant Surfaces. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9093036
Koch M, Burkovski A, Zulla M, Rosiwal S, Geißdörfer W, Dittmar R, Grobecker-Karl T. Pilot Study on the Use of a Laser-Structured Double Diamond Electrode (DDE) for Biofilm Removal from Dental Implant Surfaces. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9093036
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoch, Maximilian, Andreas Burkovski, Manuel Zulla, Stefan Rosiwal, Walter Geißdörfer, Roman Dittmar, and Tanja Grobecker-Karl. 2020. "Pilot Study on the Use of a Laser-Structured Double Diamond Electrode (DDE) for Biofilm Removal from Dental Implant Surfaces" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9093036
APA StyleKoch, M., Burkovski, A., Zulla, M., Rosiwal, S., Geißdörfer, W., Dittmar, R., & Grobecker-Karl, T. (2020). Pilot Study on the Use of a Laser-Structured Double Diamond Electrode (DDE) for Biofilm Removal from Dental Implant Surfaces. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9093036






