Serum Interleukin-6 and -8 as Predictors of Response to Vedolizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Cohort
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Souza, H.S.P.; Fiocchi, C.; Iliopoulos, D. The IBD interactome: An integrated view of aetiology, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Actis, G.C.; Pellicano, R.; Fagoonee, S.; Ribaldone, D.G. History of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, P.; Neurath, M.F.; Ng, S.C.; El-Omar, E.M.; Sharara, A.I.; Kobayashi, T.; Hisamatsu, T.; Hibi, T.; Rogler, G. Mechanism-Based Treatment Strategies for IBD: Cytokines, Cell Adhesion Molecules, JAK Inhibitors, Gut Flora, and More. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2019, 4, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Sandborn, W.J.; Colombel, J.F.; Vermeire, S.; Glover, S.C.; Rimola, J.; Siegelman, J.; Jones, S.; Bornstein, J.D.; Feagan, B.G. Endoscopic, Radiologic, and Histologic Healing With Vedolizumab in Patients With Active Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, B.E.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Loftus, E.V.; Danese, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Törüner, M.; Jonaitis, L.; Abhyankar, B.; Chen, J.; Rogers, R.; et al. Vedolizumab versus Adalimumab for moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, D.; Chapman, T.; Yang, L.L.; Wyant, T.; Egan, R.; Fedyk, E.R. The binding specificity and selective antagonism of vedolizumab, an anti-α4β7 integrin therapeutic antibody in development for inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoni, G.; Bagnoli, S.; Le Grazie, M.; Campani, C.; Rogai, F.; Manetti, N.; Bensi, C.; Macrì, G.; Galli, A.; Milla, M. Long-term efficacy and safety of vedolizumab in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: A real-life experience from a tertiary referral center. J. Dig. Dis. 2019, 20, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumolo, M.G.; Bertani, L.; Ceccarelli, L.; Laino, G.; Di Fluri, G.; Albano, E.; Tapete, G.; Costa, F. From bench to bedside: Fecal calprotectin in inflammatory bowel diseases clinical setting. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3681–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Rosso, C.; Saracco, G.M.; Astegiano, M.; Pellicano, R. Fecal calprotectin: Beyond intestinal organic diseases. Panminerva Med. 2018, 60, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.L.; Sundrud, M.S. Cytokine networks and T-cell subsets in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Muñoz, F.; Dominguez-Lopez, A.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K. Role of cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 4280–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.; Pohin, M.; Powrie, F. Cytokine Networks in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 992–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, Y.; Hosomi, S.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, K.; Yukawa, T.; Otani, K.; Nagami, Y.; Tanaka, F.; Taira, K.; Kamata, N.; et al. Serum interleukin-6 level is associated with response to infliximab in ulcerative colitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Chiba, T.; Nakamura, S.; Matsumoto, T. Changes in cytokine profile may predict therapeutic efficacy of infliximab in patients with ulcerative colitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soendergaard, C.; Seidelin, J.B.; Steenholdt, C.; Nielsen, O.H. Putative biomarkers of vedolizumab resistance and underlying inflammatory pathways involved in IBD. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2018, 5, e000208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, L.; Baglietto, L.; Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Tapete, G.; Albano, E.; Ceccarelli, L.; Mumolo, M.G.; Pellegrini, C.; Lucenteforte, E.; et al. Assessment of serum cytokines predicts clinical and endoscopic outcomes to vedolizumab in ulcerative colitis patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Rosso, C.; Stalla, F.; Rizzo, M.; Massano, A.; Abate, M.L.; Olivero, A.; Armandi, A.; Vanni, E.; Younes, R.; et al. On-Treatment Decrease of Serum Interleukin-6 as a Predictor of Clinical Response to Biologic Therapy in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Eliakim, R.; Ardizzone, S.; Armuzzi, A.; Barreiro-de Acosta, M.; Burisch, J.; Gecse, K.B.; Hart, A.L.; Hindryckx, P.; et al. Third European Evidence-based Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Part 1: Definitions, Diagnosis, Extra-intestinal Manifestations, Pregnancy, Cancer Surveillance, Surgery, and Ileo-anal Pouch Disorders. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomollón, F.; Dignass, A.; Annese, V.; Tilg, H.; Van Assche, G.; Lindsay, J.O.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Cullen, G.J.; Daperno, M.; Kucharzik, T.; et al. 3rd European Evidence-based Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Crohn’s Disease 2016: Part 1: Diagnosis and Medical Management. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, B. Bio-Rad’s Bio-Plex® suspension array system, xMAP technology overview. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 118, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Sandborn, W.; Sands, B.E.; Reinisch, W.; Bemelman, W.; Bryant, R.V.; D’Haens, G.; Dotan, I.; Dubinsky, M.; Feagan, B.; et al. Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE): Determining Therapeutic Goals for Treat-to-Target. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiot, A.; Serrero, M.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Filippi, J.; Pariente, B.; Roblin, X.; Buisson, A.; Stefanescu, C.; Trang-Poisson, C.; Altwegg, R.; et al. One-year effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: A prospective multicentre cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, C.; Marsal, J.; Bergemalm, D.; Vigren, L.; Björk, J.; Eberhardson, M.; Karling, P.; Söderman, C.; SWIBREG Vedolizumab Study Group; Myrelid, P.; et al. Long-term effectiveness of vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease: A national study based on the Swedish National Quality Registry for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (SWIBREG). Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallmach, A.; Langbein, C.; Atreya, R.; Bruns, T.; Dignass, A.; Ende, K.; Hampe, J.; Hartmann, F.; Neurath, M.F.; Maul, J.; et al. Vedolizumab provides clinical benefit over 1 year in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease—A prospective multicenter observational study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 1199–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barré, A.; Colombel, J.-F.; Ungaro, R. Review article: Predictors of response to vedolizumab and ustekinumab in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribano, M.L. Vedolizumab for inflammatory bowel disease: From randomized controlled trials to real-life evidence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, W.; Bressler, B.; Curtis, R.; Parikh, A.; Yang, H.; Rosario, M.; Røseth, A.; Danese, S.; Feagan, B.; Sands, B.E.; et al. Fecal Calprotectin Responses Following Induction Therapy With Vedolizumab in Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Post Hoc Analysis of GEMINI 1. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haens, G.; Ferrante, M.; Vermeire, S.; Baert, F.; Noman, M.; Moortgat, L.; Geens, P.; Iwens, D.; Aerden, I.; Van Assche, G.; et al. Fecal calprotectin is a surrogate marker for endoscopic lesions in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ma, J.; Geng, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, X. Fecal calprotectin concentrations in healthy children aged 1-18 months. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Penna, F.G.C.; Rosa, R.M.; da Cunha, P.F.S.; de Souza, S.C.S.; de Abreu Ferrari, M.D.L. Faecal calprotectin is the biomarker that best distinguishes remission from different degrees of endoscopic activity in Crohn’s disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, T.; Ungar, B.; Yung, D.E.; Ben-Horin, S.; Eliakim, R.; Kopylov, U. Vedolizumab in IBD-Lessons from real-world experience; A systematic review and pooled analysis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2018, 12, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buer, L.C.T.; Moum, B.A.; Cvancarova, M.; Warren, D.J.; Bolstad, N.; Medhus, A.W.; Høivik, M.L. Real world data on effectiveness, safety and therapeutic drug monitoring of vedolizumab in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. A single center cohort. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreesen, E.; Verstockt, B.; Bian, S.; de Bruyn, M.; Compernolle, G.; Tops, S.; Noman, M.; Van Assche, G.; Ferrante, M.; Gils, A.; et al. Evidence to Support Monitoring of Vedolizumab Trough Concentrations in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefferinckx, C.; Minsart, C.; Cremer, A.; Amininejad, L.; Tafciu, V.; Quertinmont, E.; Tops, S.; Devière, J.; Gils, A.; van Gossum, A.; et al. Early vedolizumab trough levels at induction in inflammatory bowel disease patients with treatment failure during maintenance. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoub, W.; Williet, N.; Pouillon, L.; Di-Bernado, T.; De Carvalho Bittencourt, M.; Nancey, S.; Lopez, A.; Paul, S.; Zallot, C.; Roblin, X.; et al. Early vedolizumab trough levels predict mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease: A multicentre prospective observational study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, L.; Pugliese, D.; Tonucci, T.P.; Bertani, L.; Costa, F.; Privitera, G.; Tolusso, B.; Di Mario, C.; Albano, E.; Tapete, G.; et al. Early vedolizumab trough levels predict treatment persistence over the first year in inflammatory bowel disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, E.K.; Shows, D.M.; Chiorean, M.V.; Lord, J.D. Identification of Candidate Biomarkers Associated with Response to Vedolizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battat, R.; Dulai, P.S.; Vande Casteele, N.; Evans, E.; Hester, K.D.; Webster, E.; Jain, A.; Proudfoot, J.A.; Mairalles, A.; Neill, J.; et al. Biomarkers Are Associated With Clinical and Endoscopic Outcomes With Vedolizumab Treatment in Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, L.; Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Tapete, G.; Baiano Svizzero, G.; Marchi, S.; Blandizzi, C.; Costa, F. Evaluation of cytokine levels as putative biomarkers to predict the pharmacological response to biologic therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2019, 65, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombel, J.-F.; Panaccione, R.; Bossuyt, P.; Lukas, M.; Baert, F.; Vaňásek, T.; Danalioglu, A.; Novacek, G.; Armuzzi, A.; Hébuterne, X.; et al. Effect of tight control management on Crohn’s disease (CALM): A multicentre, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Fon, J.; Uylaki, W.; Cummins, A.G.; Barry, S. Cells, cytokines and inflammatory bowel disease: A clinical perspective. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 5, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahida, Y.R.; Ceska, M.; Effenberger, F.; Kurlak, L.; Lindley, I.; Hawkey, C.J. Enhanced synthesis of neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin-8 in active ulcerative colitis. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 1992, 82, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, A.W. The role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48 (Suppl. 2), e12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Perálvarez, M.L.; García-Sánchez, V.; Villar-Pastor, C.M.; González, R.; Iglesias-Flores, E.; Muntane, J.; Gómez-Camacho, F. Role of serum cytokine profile in ulcerative colitis assessment. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, D.S.; Shah, K.; Whittaker, M.A.; Nitch-Smith, H.; Brown, J.F.; Shute, J.K.; Trebble, T.M. Cytokine mucosal expression in ulcerative colitis, the relationship between cytokine release and disease activity. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeissig, S.; Rosati, E.; Dowds, C.M.; Aden, K.; Bethge, J.; Schulte, B.; Pan, W.H.; Mishra, N.; Zuhayra, M.; Marx, M.; et al. Vedolizumab is associated with changes in innate rather than adaptive immunity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2019, 68, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarur, A.J.; Jain, A.; Quintero, M.A.; Czul, F.; Deshpande, A.R.; Kerman, D.H.; Abreu, M.T. Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Crohn’s Disease Nonresponders to Optimal Antitumor Necrosis Factor Therapy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricanek, P.; Brackmann, S.; Perminow, G.; Lyckander, L.G.; Sponheim, J.; Holme, O.; Høie, O.; Rydning, A.; Vatn, M.H.; IBSEN II Study Group. Evaluation of disease activity in IBD at the time of diagnosis by the use of clinical, biochemical, and fecal markers. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Malter, L.; Hudesman, D. Disease monitoring in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11246–11259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, S.L.; Abbatista, M.; Brade, J.; Singer, M.V.; Böcker, U. Interleukin-18 serum levels in inflammatory bowel diseases: Correlation with disease activity and inflammatory markers. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2009, 139, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Il-6 in inflammation, Immunity, And disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, 16295–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, V.; Andus, T.; Caesar, I.; Roth, M.; Schölmerich, J. Evidence for continuous stimulation of interleukin-6 production in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billiet, T.; Cleynen, I.; Ballet, V.; Claes, K.; Princen, F.; Singh, S.; Ferrante, M.; Van Assche, G.; Gils, A.; Vermeire, S. Evolution of cytokines and inflammatory biomarkers during infliximab induction therapy and the impact of inflammatory burden on primary response in patients with Crohn’s disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriconi, F.; Raddatz, D.; Ho, N.A.H.; Yeruva, S.; Dudas, J.; Ramadori, G. Quantitative gene expression of cytokines in peripheral blood leukocytes stimulated in vitro: Modulation by the anti-tumor nerosis factor-alpha antibody infliximab and comparison with the mucosal cytokine expression in patients with ulcerative colitis. Transl. Res. 2007, 150, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | IBD | CD | UC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 54 | 14 | 40 |
| Age (years), median (range) | 48 (18–80) | 46 (18–80) | 56 (20–76) |
| Sex (M/F) | 14/40 | 10/4 | 10/30 |
| Smoke (current/never/ex) | 8/25/21 | 3/8/3 | 5/17/18 |
| Years of illness, median (range) | 14 (2–33) | 18 (3–33) | 11 (2–27) |
| Montreal classification | - | - | - |
| (CD: L1/L2/L3/L4; UC: E1/E2/E3) | 1/1/12/1 | 3/16/21 | |
| Clinical activity (mean, 95% CI) (CD: HBI; UC: pMAYO) | 7.1 (5.2–9) | 5.3 (4.6–5.9) | |
| Biochemical activity | - | - | - |
| Faecal calprotectin (mg/kg), | 559 (382–816) | 1620 (519–5064) | 463 (314–683) |
| (geometric mean, 95% CI) | - | - | - |
| CRP (mg/L), | 9.3 (6.9–12.8) | 8.4 (1.5–46.39 | 9.8 (6.9–13.7) |
| (geometric mean, 95% CI) | - | - | - |
| ESR (positive/negative) | 33/21 | 6/8 | 27/13 |
| Concomitant medications | - | - | - |
| Mesalazine (yes/no, %) | 48/6 (88.9%) | 9/5 (64.3%) | 39/1 (97.5%) |
| Systemic corticosteroids (yes/no, %) | 33/21 (61.1%) | 9/5 (64.3%) | 24/16 (60.0%) |
| Azathioprine (yes/no, %) | 8/46 (14.8%) | 2/12 (14.3%) | 6/34 (15.0%) |
| Parameters | Patients with CD (n = 14) | Patients with UC (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 (pg/mL), (geometric mean, range) | 2.1 (0.6–7.1) | 2.5 (0.2–29.8) | 0.770 |
| IL-8 (pg/mL), (geometric mean, range) | 3.4 (OOR–29.7) | 6.7 (OOR–61.4) | 0.380 |
| Parameters | T0 | T1 | p-Value (T1 vs. T0) | T2 | p-Value (T2 vs. T0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cohort (n = 54) | |||||
| Calprotectin (mg/kg), (geometric mean, 95% CI) | 559 (382–816) | 205 (129–325) | < 0.001 | 151 (83–275) | < 0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L), (geometric mean, 95% CI) | 9.3 (6.9–12.8) | 5.1 (3.4–7.6) | 0.007 | 4.4 (2.9–6.8) | 0.006 |
| ESR (positive/negative) | 33/21 | 29/25 | 0.050 | 26/28 | 0.020 |
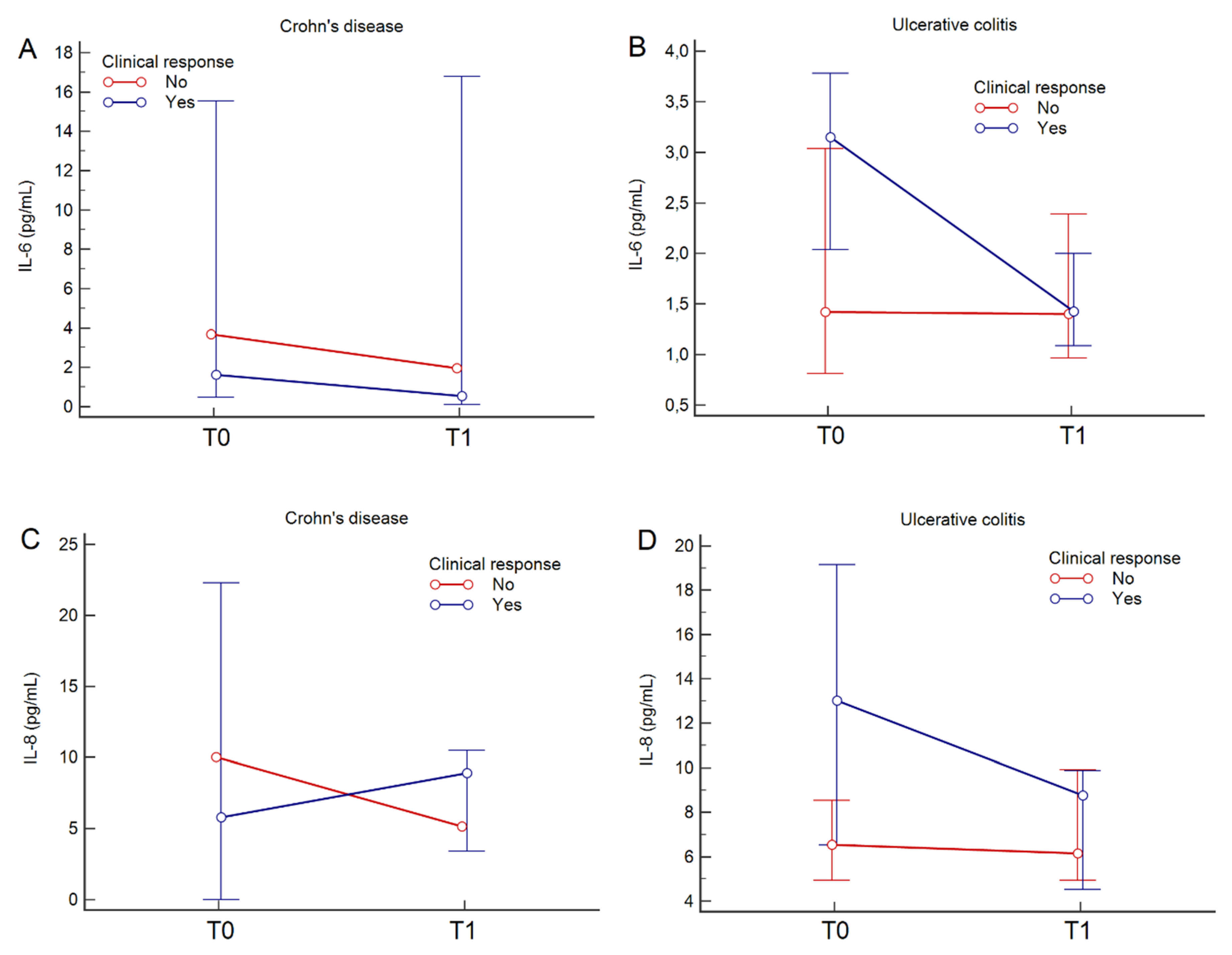
| IL-6 (pg/mL), (median, 95% CI) | 2.5 (1.5–3.5) | 1.4 (1.1–1.9) | 0.007 | N/P | N/A |
| IL-8 (pg/mL), (median, 95% CI) | 8.2 (5.2–12.2) | 8.0 (5.1–9.6) | 0.060 | N/P | N/A |
| CD (n = 14) | |||||
| Calprotectin (mg/kg), (geometric mean, 95% CI) | 1620 (519–5064) | 608 (173–2129) | 0.039 | 414 (45–3799) | 0.017 |
| CRP (mg/L), (geometric mean, 95% CI) | 8.4 (1.5–46.3) | 6.4 (2.0–20.3) | 0.619 | 4.4 (1.0–18.8) | 0.039 |
| ESR (positive/negative) | 6/8 | 5/9 | 1.000 | 4/10 | 0.500 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL), (median, 95% CI) | 1.6 (0.9–6.0) | 2.0 (0.2–16.5) | 0.414 | N/P | N/A |
| IL-8 (pg/mL), (median, 95% CI) | 5.8 (1.9–14.6) | 8.9 (3.5–14.4) | 0.970 | N/P | N/A |
| UC (n = 40) | |||||
| FC (mg/kg), (geometric mean, 95% CI) | 463 (314–683) | 169 (103–277) | 0.001 | 134 (70–255) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L), (geometric mean, 95% CI) | 9.8 (6.9–13.7) | 4.8 (3.1–7.5) | 0.007 | 4.4 (2.8–7.0) | 0.013 |
| ESR (positive/negative) | 27/13 | 24/16 | 0.250 | 22/18 | 0.063 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL), (median, 95% CI) | 2.5 (1.4–3.4) | 1.4 (1.2–1.9) | 0.009 | N/P | N/A |
| IL-8 (pg/mL), (median, 95% CI) | 8.3 (6.2–14.0) | 8.0 (5.0–9.6) | 0.032 | N/P | N/A |
| Variables | OR, 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
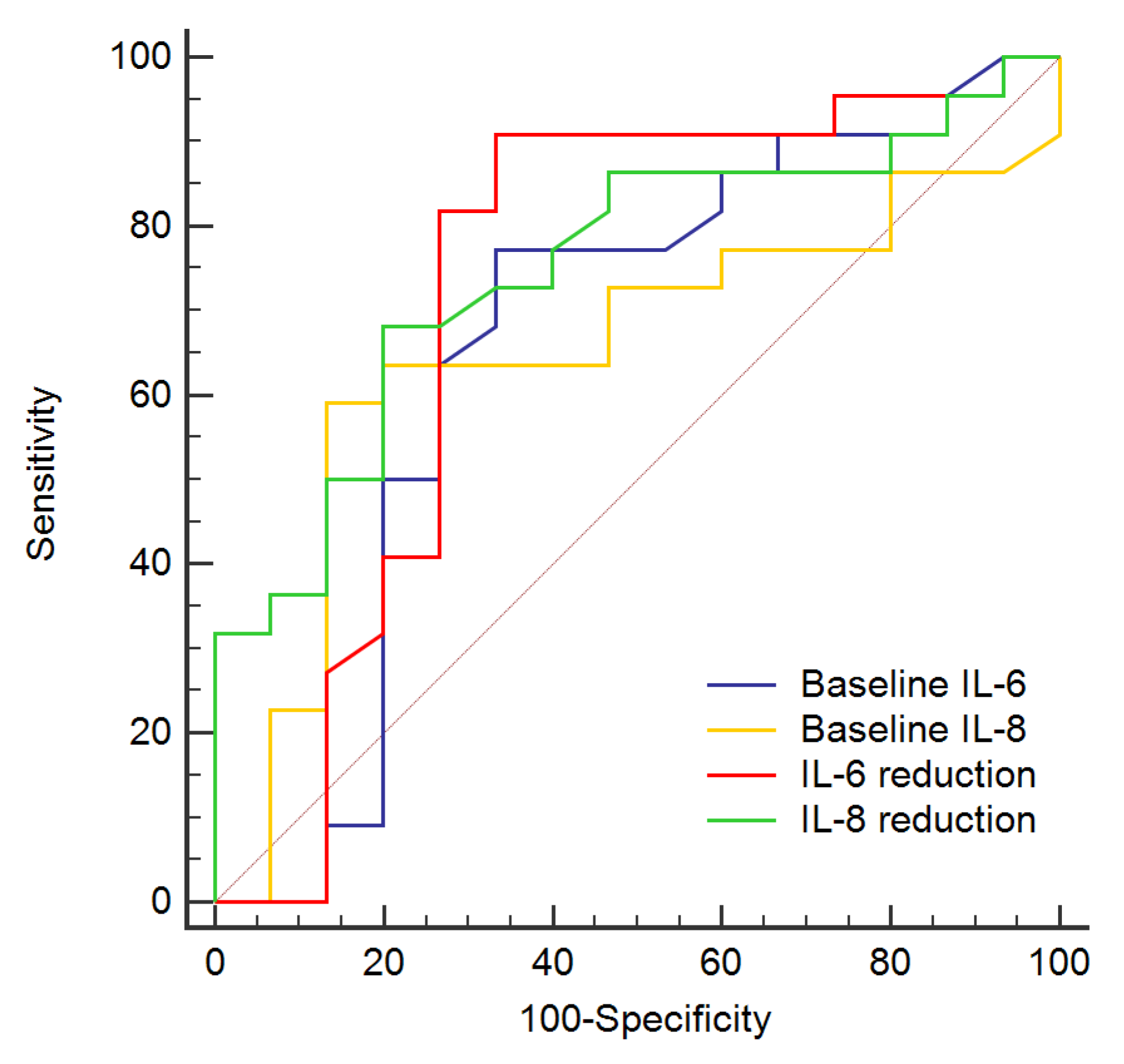
| Baseline IL-8 > 8.6 pg/mL | 14.74, 1.78–122.14 | 0.013 |
| IL-6 reduction > 0.4 pg/mL | 10.81, 1.58–73.68 | 0.015 |
| Disease activity | 0.70, 0.21–2.28 | 0.550 |
| Disease extent (E3) | 0.18, 0.02–1.35 | 0.097 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertani, L.; Caviglia, G.P.; Antonioli, L.; Pellicano, R.; Fagoonee, S.; Astegiano, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Blandizzi, C.; Costa, F.; et al. Serum Interleukin-6 and -8 as Predictors of Response to Vedolizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051323
Bertani L, Caviglia GP, Antonioli L, Pellicano R, Fagoonee S, Astegiano M, Saracco GM, Bugianesi E, Blandizzi C, Costa F, et al. Serum Interleukin-6 and -8 as Predictors of Response to Vedolizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051323
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertani, Lorenzo, Gian Paolo Caviglia, Luca Antonioli, Rinaldo Pellicano, Sharmila Fagoonee, Marco Astegiano, Giorgio Maria Saracco, Elisabetta Bugianesi, Corrado Blandizzi, Francesco Costa, and et al. 2020. "Serum Interleukin-6 and -8 as Predictors of Response to Vedolizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051323
APA StyleBertani, L., Caviglia, G. P., Antonioli, L., Pellicano, R., Fagoonee, S., Astegiano, M., Saracco, G. M., Bugianesi, E., Blandizzi, C., Costa, F., & Ribaldone, D. G. (2020). Serum Interleukin-6 and -8 as Predictors of Response to Vedolizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051323









