Intraocular Inflammation Control and Changes in Retinal and Choroidal Architecture in Refractory Non-Infectious Uveitis Patients after Adalimumab Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Adalimumab Administration
2.4. Ophthalmic Examination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Efficacy Objectives
3. Results
3.1. Inflammation Control
3.2. Changes in Macular Thickness and Visual Acuity
3.3. Changes in Choroidal Thickness
3.4. Changes in Systemic and Local Therapies
3.5. Side Effects and Safety of the Anti-TNF-α Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massa, H.; Pipis, S.Y.; Adewoyin, T.; Vergados, A.; Patra, S.; Panos, G.D. Macular Edema Associated with Non-Infectious Uveitis: Pathophysiology, Etiology, Prevalence, Impact and Management Challenges. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 13, 1761–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, J.E.; Suhler, E.; Skup, M.; Tari, S.; Macaulay, D.; Chao, J.; Ganguli, A. Prevalence of Noninfectious Uveitis in the United States: A Claims-Based Analysis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, A.E.; Ribeiro, E.; Korobelnik, J.F.; Delyfer, M.N.; Rougier, M.B. Efficacy of Anti-TNF-α Therapy for the Treatment of Non-Infectious Uveitis: A Retrospective Study of 21 Patients. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2018, 26, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardeau, C.; Champion, E.; Massamba, N.; Lehoang, P. Uveitic Macular Edema. Eye 2016, 30, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritz, D.C.; Wong, I.G. Incidence and Prevalence of Uveitis in Northern California: The Northern California Epidemiology of Uveitis Study. Ophthalmology 2004, 111, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhler, E.B.; Lloyd, M.J.; Choi, D.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Austin, D.F. Incidence and Prevalence of Uveitis in Veterans Affairs Medical Centers of the Pacific Northwest. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 146, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallouzi, M.O.; Moore, D.J.; Calvert, M.; Murray, P.I.; Bucknall, N.; Denniston, A.K. The Effectiveness of Pharmacological Agents for the Treatment of Uveitic Macular Oedema (UMO): A Systematic Review Protocol. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaal, M.R.; Abiad, B.H.; Hamam, R.N. Uveitis in the Aging Eye: Incidence, Patterns, and Differential Diagnosis. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 509456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N. Uveitis in Developing Countries. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 61, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardenoye, C.W.T.A.; van Kooij, B.; Rothova, A. Impact of Macular Edema on Visual Acuity in Uveitis. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 1446–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, O.M.; Meads, C.A.; Murray, P.I. Uveitis: A Potentially Blinding Disease. Ophthalmologica 2004, 218, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, P.K. Prospective Evaluation of Visual Acuity Assessment: A Comparison of Snellen versus ETDRS Charts in Clinical Practice (an Aos Thesis). Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2009, 107, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rothova, A.; Suttorp-van Schulten, M.S.A.; Frits Treffers, W.; Kijlstra, A. Causes and Frequency of Blindness in Patients with Intraocular Inflammatory Disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 80, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koronis, S.; Stavrakas, P.; Balidis, M.; Kozeis, N.; Tranos, P.G. Update in Treatment of Uveitic Macular Edema. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentincic, N.V.; de Groot-Mijnes, J.D.F.; Kraut, A.; Korosec, P.; Hawlina, M.; Rothova, A. Intraocular and Serum Cytokine Profiles in Patients with Intermediate Uveitis. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Omri, S.; Behar-Cohen, F.; De Kozak, Y.; Sennlaub, F.; Mafra Verissimo, L.; Jonet, L.; Savoldelli, M.; Omri, B.; Crisanti, P. Microglia/Macrophages Migrate through Retinal Epithelium Barrier by a Transcellular Route in Diabetic Retinopathy: Role of PKCζ in the Goto Kakizaki Rat Model. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlmann, D.; Macedo, S.; Stübiger, N.; Pleyer, U.; Joussen, A.M.; Winterhalter, S. Multimodal Imaging in Birdshot Retinochoroiditis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2017, 25, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbort, C.P.; LeHoang, P.; Guex-Crosier, Y. Schematic Interpretation of Indocyanine Green Angiography in Posterior Uveitis Using a Standard Angiographic Protocol. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliari, G.; Hinkle, D.M.; Foster, C.S. The Spectrum of Fundus Autofluorescence Findings in Birdshot Chorioretinopathy. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 2009, 567693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J. Current Concepts in the Management of Uveitic Macular Edema. Johns Hopkins Adv. Stud. Ophthalmol. 2010, 30, 138–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jabs, D.A.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Foster, C.S.; Holland, G.N.; Jaffe, G.J.; Louie, J.S.; Nussenblatt, R.B.; Stiehm, E.R.; Tessler, H.; Van Gelder, R.N.; et al. Guidelines for the Use of Immunosuppressive Drugs in Patients with Ocular Inflammatory Disorders: Recommendations of an Expert Panel. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 130, 492–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, H.; Lau, C.; Maycock, N.; McCluskey, P.; Lightman, S. Outcome of Intravitreal Triamcinolone in Uveitis. Ophthalmology 2005, 112, 1916.e1–1916.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, P.; Kumar, C.S.; Abbas, Z.; Garg, S. Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Different Methods of Posterior Subtenon Injection. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2008, 16, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCluskey, P.J.; Towler, H.M.A.; Lightman, S. Regular Review: Management of Chronic Uveitis. Br. Med. J. 2000, 102, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezo, V.; Lau, C.; Comer, M.; Lightman, S. Clinical Outcome of Chronic Immunosuppression in Patients with Non-Infectious Uveitis. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2005, 33, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuter, C.M.E.; Kötter, I.; Günaydin, I.; Stübiger, N.; Doycheva, D.G.; Zierhut, M. Efficacy and Tolerability of Interferon Alpha Treatment in Patients with Chronic Cystoid Macular Oedema Due to Non-Infectious Uveitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, P.; Mariotti, C.; Cimino, L.; Mercanti, L.; Giovannini, A. Long-Term Control of Cystoid Macular Oedema in Noninfectious Uveitis with Mycophenolate Mofetil. Int. Ophthalmol. 2009, 29, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artornsombudh, P.; Gevorgyan, O.; Payal, A.; Siddique, S.S.; Foster, C.S. Infliximab Treatment of Patients with Birdshot Retinochoroidopathy. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeHoang, P.; Cassoux, N.; George, F.; Kullmann, N.; Kazatchkine, M.D. Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIg) for the Treatment of Birdshot Retinochoroidopathy. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2000, 8, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeples, L.R.; Spry, P.; Lee, R.W.J.; Carreño, E. Adalimumab in Refractory Cystoid Macular Edema Associated with Birdshot Chorioretinopathy. Int. Ophthalmol. 2018, 38, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balevic, S.J.; Rabinovich, C.E. Profile of Adalimumab and Its Potential in the Treatment of Uveitis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 2997–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Merrill, P.T.; Jaffe, G.J.; Dick, A.D.; Kurup, S.K.; Sheppard, J.; Schlaen, A.; Pavesio, C.; Cimino, L.; Van Calster, J.; et al. Adalimumab for Prevention of Uveitic Flare in Patients with Inactive Non-Infectious Uveitis Controlled by Corticosteroids (VISUAL II): A Multicentre, Double-Masked, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, J.; Joshi, A.; Betts, K.A.; Hudgens, S.; Tari, S.; Chen, N.; Skup, M.; Dick, A.D. Effect of Adalimumab on Visual Functioning in Patients with Noninfectious Intermediate Uveitis, Posterior Uveitis, and Panuveitis in the VISUAL-1 and VISUAL-2 Trials. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhler, E.B.; Adán, A.; Brézin, A.P.; Fortin, E.; Goto, H.; Jaffe, G.J.; Kaburaki, T.; Kramer, M.; Lim, L.L.; Muccioli, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Adalimumab in Patients with Noninfectious Uveitis in an Ongoing Open-Label Study: VISUAL III. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, G.J.; Dick, A.D.; Brézin, A.P.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Thorne, J.E.; Kestelyn, P.; Barisani-Asenbauer, T.; Franco, P.; Heiligenhaus, A.; Scales, D.; et al. Adalimumab in Patients with Active Noninfectious Uveitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabs, D.A.; Nussenblatt, R.B.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Atmaca, L.S.; Becker, M.D.; Brezin, A.P.; Chee, S.P.; Davis, J.L.; Deschenes, J.; de Smet, M.; et al. Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature for Reporting Clinical Data. Results of the First International Workshop. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 140, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirani, V.; Pelliccioni, P.; De Turris, S.; Rosati, A.; Franceschi, A.; Cesari, C.; Nicolai, M.; Mariotti, C. The Eye as a Window to Systemic Infectious Diseases: Old Enemies, New Imaging. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Kwon, H.J.; Kim, S.S.; Koh, H.J.; Lee, S.C. Choroidal Thickness in Behcet’s Uveitis: An Enhanced Depth Imaging-Optical Coherence Tomography and Its Association with Angiographic Changes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 6033–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Berton, M.; Bini, S.; Casciano, M.; Cavarzeran, F.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective Retinal Spots and Visual Function after Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment in Center-Involving Diabetic Macular Edema. Retina 2016, 36, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Torresin, T.; Bini, S.; Convento, E.; Pilotto, E.; Parrozzani, R.; Midena, E. Imaging Retinal Inflammatory Biomarkers after Intravitreal Steroid and Anti-VEGF Treatment in Diabetic Macular Oedema. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, B.; Yildirim, H. The Causes of Hyperreflective Dots in Optical Coherence Tomography Excluding Diabetic Macular Edema and Retinal Venous Occlusion§§. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2015, 9, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baert, F.; Kondragunta, V.; Lockton, S.; Casteele, N.V.; Hauenstein, S.; Singh, S.; Karmiris, K.; Ferrante, M.; Gils, A.; Vermeire, S. Antibodies to Adalimumab Are Associated with Future Inflammation in Crohnis Patients Receivingmaintenance Adalimumab Therapy: A Post Hoc Analysis of the Karmiris Trial. Gut 2016, 65, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strik, A.S.; van den Brink, G.R.; Ponsioen, C.; Mathot, R.; Löwenberg, M.; D’Haens, G.R. Suppression of Anti-Drug Antibodies to Infliximab or Adalimumab with the Addition of an Immunomodulator in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungar, B.; Kopylov, U.; Engel, T.; Yavzori, M.; Fudim, E.; Picard, O.; Lang, A.; Williet, N.; Paul, S.; Chowers, Y.; et al. Addition of an Immunomodulator Can Reverse Antibody Formation and Loss of Response in Patients Treated with Adalimumab. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmar-Demir, G.; Ayranci, O.; Kurtuncu, M.; Vanli, E.N.; Mutlu, M.; Tugal-Tutkun, I. Cyclosporine for Behçet’s Uveitis: Is It Associated with an Increased Risk of Neurological Involvement? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26 (Suppl. 50), S84–S90. [Google Scholar]
- Kruh, J.N.; Yang, P.; Suelves, A.M.; Foster, C.S. Infliximab for the Treatment of Refractory Noninfectious Uveitis: A Study of 88 Patients with Long-Term Follow-Up. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhler, E.B.; Smith, J.R.; Giles, T.R.; Lauer, A.K.; Wertheim, M.S.; Kurz, D.E.; Kurz, P.A.; Lim, L.; Mackensen, F.; Pickard, T.D.; et al. Infliximab Therapy for Refractory Uveitis: 2-Year Results of a Prospective Trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
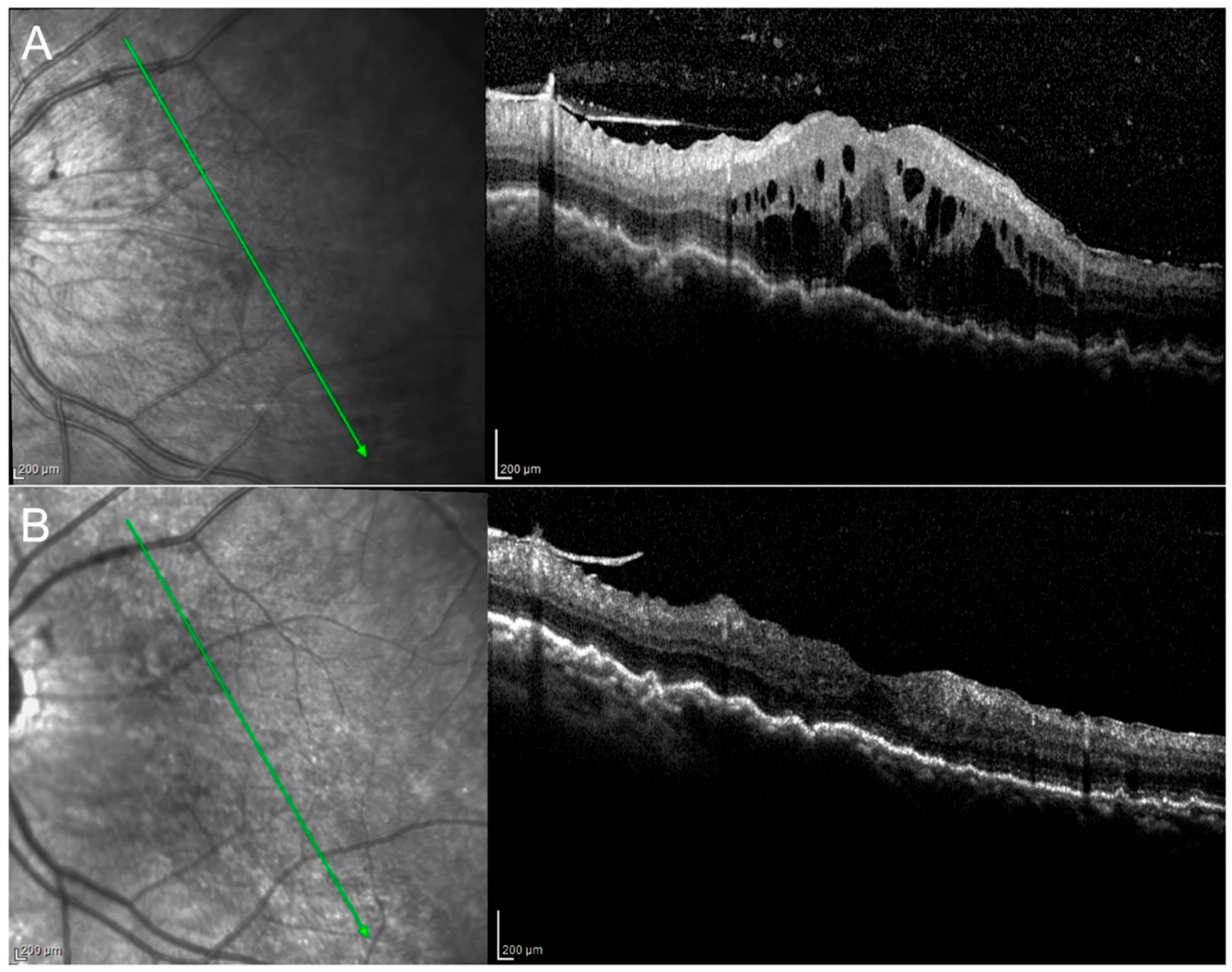

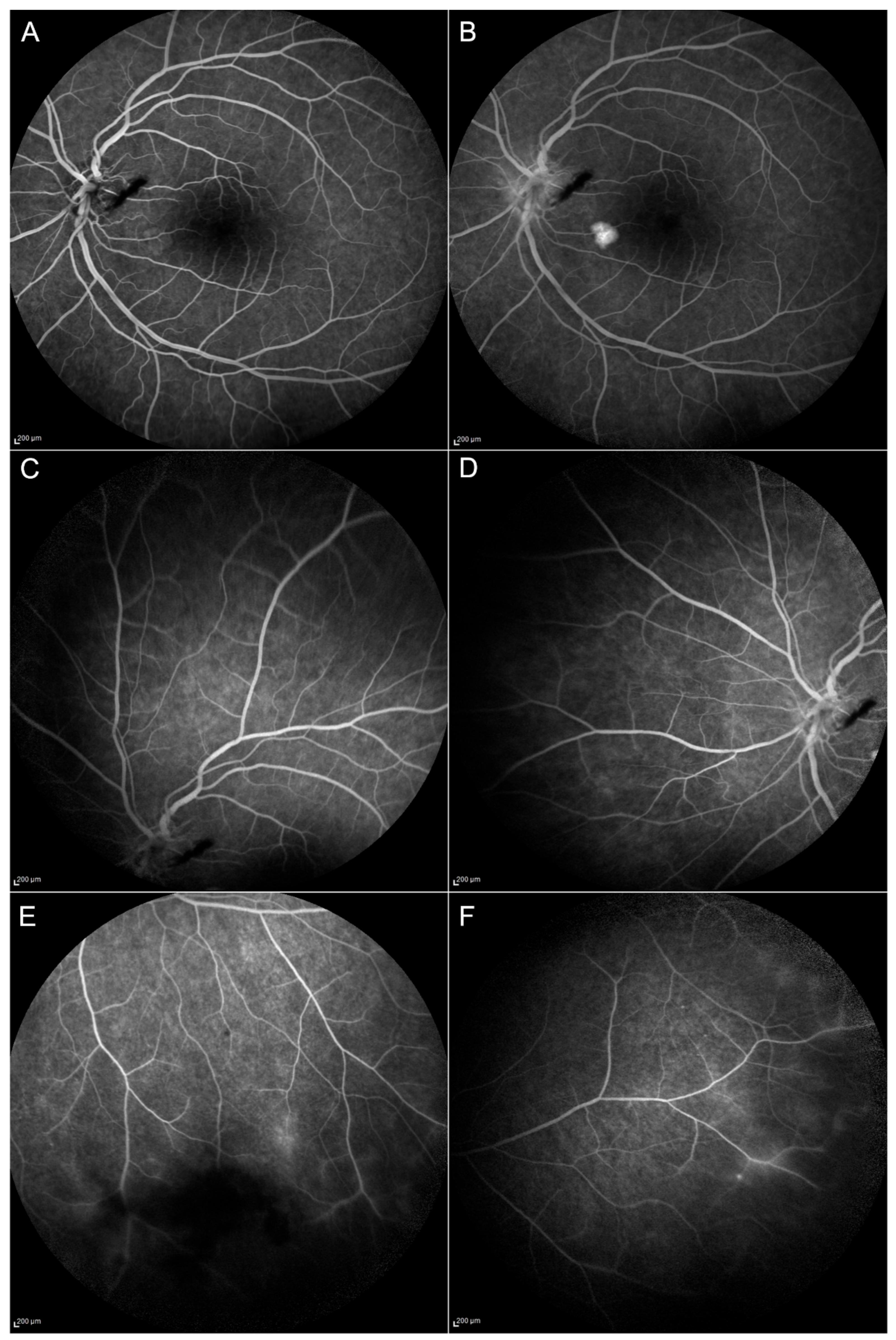

| Patient No. | Etiology | Classification | Uni/Bilateral | Previous Treatment | Current Treatments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drugs in Addition to Anti-TNF | Daily Steroid Dose > 10 mg | |||||
| 1 | Psoriatic arthritis | Posterior | Bilateral | Etanercept | No | no |
| 2 | Psoriatic arthritis | Panuveitis | Bilateral | Prednisone, MTX | MTX | no |
| 3 | Behçet | Posterior | Unilateral | Prednisone, AZA | Prednisone | no |
| 4 | Behçet | Posterior | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | Prednisone | yes |
| 5 | Behçet | Posterior | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | Prednisone | yes |
| 6 | Behçet | Posterior | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | Prednisone | yes |
| 7 | Behçet | Panuveitis | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | AZA | no |
| 8 | Behçet | Panuveitis | Bilateral | Prednisone, MTX | Prednisone, MTX | yes |
| 9 | Behçet | Panuveitis | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | Prednisone | no |
| 10 | Behçet + Rheumatoid arthritis | Panuveitis | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | AZA | no |
| 11 | Behçet + Multifocal choroiditis | Posterior | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | AZA | no |
| 12 | Behçet, SLE | Posterior | Bilateral | AZA, Hydroxychloroquine | AZA | no |
| 13 | Birdshot Choroiditis | Panuveitis | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | AZA | no |
| 14 | Panuveitis | Panuveitis | Bilateral | Prednisone | Prednisone | no |
| 15 | Pars Planitis | Intermediate | Bilateral | Prednisone, CSA | CSA | no |
| 16 | Pars Planitis | Intermediate | Bilateral | Prednisone, CSA | Prednisone | no |
| 17 | Pars Planitis | Intermediate | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA, CSA | CSA | no |
| 18 | Sarcoidosis | Panuveitis | Bilateral | Prednisone, AZA | Prednisone | no |
| Anterior Chamber Flare | 1+ | 2+ | 3+ | 4+ | ||
| M0 | Patients (n = 8) | 7 | 1 | - | - | |
| M12 | Patients (n = 1) | 1 | - | - | - | |
| Anterior Chamber Cells | 0.5+ | 1+ | 2+ | 3+ | 4+ | |
| M0 | Patients (n = 8) | 3 | 4 | 1 | - | - |
| M12 | Patients (n = 1) | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| Vitreous Haze | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| M0 | Patients (n = 9) | 1 | 4 | 4 | - | - |
| M12 | Patients (n = 4) | 3 | - | 1 | - | - |
| M0 | M3 | M6 | M9 | M12 | M > 12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choroidal Thickness (micron)—Median | 236.0 | 223.5 | 208.75 | 223.5 | 208.75 | 208.75 |
| IQR | 260 302 | 263.0 338.75 | 257.5 305.75 | 251.5 296 | 236.5 286.25 | 238.5 288.5 |
| Friedman Test | 0.07 | |||||
| p-value between baseline and last follow-up visit (Wilcoxon signed-rank test) | 0.01 | |||||
| Macular Thickness (micron)—Median | 229.75 | 212.75 | 209.5 | 218.75 | 213 | 197.25 |
| IQR | 247 389 | 234.5 279 | 236 284.75 | 238 286.75 | 239.5 279.5 | 239.5 279.5 |
| Friedman Test | 0.35 | |||||
| p-value between baseline and last follow-up visit (Wilcoxon signed-rank test) | 0.07 | |||||
| Vasculitis (Number of Quadrants)—Median | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| IQR | 0 4 | 0 1.75 | 0 1 | 0 1 | 0 0.75 | 0 0 |
| Friedman Test | <0.001 | |||||
| p-value between baseline and other evaluations (Wilcoxon signed-rank test with Bonferroni adjustment) | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| M0 | M > 12 | |
|---|---|---|
| BCVA (LogMAR) | ||
| Mean | 0.51 | 0.24 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| ERM | ||
| Number | 4 | 5 |
| Percentage | 22.22 | 27.78 |
| Spots | ||
| Number | 4 | 2 |
| Percentage | 22.22 | 11.11 |
| Papillitis | ||
| Number | 4 | 2 |
| Percentage | 22.22 | 11.11 |
| Vitritis | ||
| Number | 9 | 4 |
| Percentage | 50.00 | 22.22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirani, V.; Pelliccioni, P.; De Turris, S.; Rosati, A.; Franceschi, A.; Pasanisi, P.; Gesuita, R.; Nicolai, M.; Mariotti, C. Intraocular Inflammation Control and Changes in Retinal and Choroidal Architecture in Refractory Non-Infectious Uveitis Patients after Adalimumab Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020510
Pirani V, Pelliccioni P, De Turris S, Rosati A, Franceschi A, Pasanisi P, Gesuita R, Nicolai M, Mariotti C. Intraocular Inflammation Control and Changes in Retinal and Choroidal Architecture in Refractory Non-Infectious Uveitis Patients after Adalimumab Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(2):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020510
Chicago/Turabian StylePirani, Vittorio, Paolo Pelliccioni, Serena De Turris, Alessandro Rosati, Alessandro Franceschi, Pierangelo Pasanisi, Rosaria Gesuita, Michele Nicolai, and Cesare Mariotti. 2020. "Intraocular Inflammation Control and Changes in Retinal and Choroidal Architecture in Refractory Non-Infectious Uveitis Patients after Adalimumab Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 2: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020510
APA StylePirani, V., Pelliccioni, P., De Turris, S., Rosati, A., Franceschi, A., Pasanisi, P., Gesuita, R., Nicolai, M., & Mariotti, C. (2020). Intraocular Inflammation Control and Changes in Retinal and Choroidal Architecture in Refractory Non-Infectious Uveitis Patients after Adalimumab Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(2), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020510





