Musculoskeletal Pain and Non-Classroom Teaching in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Analysis of the Impact on Students from Two Spanish Universities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Design of the Study and Sample
2.2. Variables in the Study
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garrett, L. COVID-19: The medium is the message. Lancet 2020, 395, 942–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Spain. Royal Decree 463/2020, of March 14th, declaring the state of alarm. Span. State Bull. 2020, 87, 27629–27636. [Google Scholar]
- Rapanta, C.; Botturi, L.; Goodyear, P.; Guàrdia, L.; Koole, M. Online university teaching during and after the Covid-19 crisis: Refocusing teacher presence and learning activity. Postdigit. Sci. Educ. 2020, 2, 923–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, A.; Acharya, J. Distant virtual medical education during COVID-19: Half a loaf of bread. Clin. Teach. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdig, R.E.; Baumgartner, E.; Hartshorne, R.; Kaplan-Rakowski, R.; Mouza, C. Teaching, Technology, and Teacher Education During the Covid-19 pandemic: Stories From the Field; Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE): Waynesville, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kapasia, N.; Paul, P.; Roy, A.; Saha, J.; Zaveri, A.; Mallick, R.; Barman, B.; Das, P.; Chouhan, P. Impact of lockdown on learning status of undergraduate and postgraduate students during COVID-19 pandemic in West Bengal, India. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 116, 105194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.; Sperling, P.; Poulsen, M.S.; Emmersen, J.; Andersen, S. Medical students for health-care staff shortages during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, e79–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Román-Mata, S.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Puertas-Molero, P.; Badicu, G.; González-Valero, G. A predictive study of resilience and its relationship with academic and work dimensions during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirni, P.; Lavanco, G.; Smirni, D. Anxiety in older adolescents at the time of COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, A.L.; Mathias, J.L.; Denson, L.A. Psychological functioning of people living with chronic pain: A meta-analytic review. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2015, 54, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Sullivan, M.D.; Turk, D.C.; Wasan, A.D. The role of psychosocial processes in the development and maintenance of chronic pain. J. Pain 2016, 17, T70–T92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, H. Self-efficacy and chronic pain outcomes: A meta-analytic review. J. Pain 2014, 15, 800–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, A.M.; Laimi, K.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Kunttu, K. Trends of weekly musculoskeletal pain from 2000 to 2012: National study of Finnish university students. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Barbosa, R.E.; Ávila-Assunção, A.; Maria-Araújo, T. Musculoskeletal pain among healthcare workers: An exploratory study on gender differences. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2013, 56, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbin, A.J.I.; Garbin, C.A.S.; Arcieri, R.M.; Rovida, T.A.S.; Freire, A.C.G.F. Musculoskeletal pain and ergonomic aspects of dentistry. Rev. Dor. 2015, 16, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, B.; de Lima, G.; Andolhe, R.; dos Santos, A.I.; Pereira, L. Musculoskeletal pain in undergraduate health students: Prevalence and associated factors. Rev. Esc. Enferm. USP 2019, 53, e03444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caromano, F.A.; Amorim, C.A.P.; Rebelo, C.F.; Contesini, A.M.; Fávero, F.M.; Costa, J.R.; Kawai, M.; Voos, M.C. Prolonged sitting and physical discomfort in university students. Acta Fisiatr. 2015, 22, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kazemi, S.S.; Javanmardi, E.; Ghazanfari, E. Relationship between general health and musculoskeletal disorders among tarbiat modares university students. Int. J. Musculosk. Pain Prev. 2017, 2, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Gotfryd, A.O.; Valesin-Filho, E.S.; Viola, D.C.M.; Lenza, M.; Silva, J.A.; Emi, A.S.; Tomiosso, R.; de Azevedo, C.; Antonioli, E.; Ferretti, M. Analysis of epidemiology, lifestyle, and psychosocial factors in patients with back pain admitted to an orthopedic emergency unit. Einstein 2015, 13, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, J.; Dunlop, D.D.; Semanik, P.A.; Chang, A.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Gilbert, A.L.; Jackson, R.D.; Chang, R.W.; Lee, J. Reallocating time spent in sleep, sedentary behavior and physical activity and its association with pain: A pilot sleep study from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuorinka, I.; Jonsson, B.; Kilbom, A.; Vinterberg, H.; Biering-Sørensen, F.; Andersson, G.; Jørgensen, K. Standardised Nordic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Appl. Ergon. 1987, 18, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Rodríguez, R.; Díaz-Pulido, B.; Gutiérrez-Ortega, C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, B.; Torres-Lacomba, M. Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the standardised Nordic Questionnaire Spanish Version in musicians. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, C.; Campion, K.; Foster, A.; Newman, S.; O’rourke, A.; Thomas, P. Questionnaire development: An examination of the Nordic Musculoskeletal questionnaire. Appl. Ergon. 1992, 23, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remor, E. Psychometric properties of a European Spanish version of the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS). Span. J. Psychol. 2006, 9, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A Global measure of Perceived Stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, H.M.; González-Cabrera, J. Psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the Perceived Stress Scales (PSS). Psicol. Conduct 2007, 15, 457–477. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Fumero, A.; Delclos, G.L.; Douphrate, D.I.; Felknor, S.A.; Vargas-Prada, S.; Serra, C.; Coggon, D.; Ruiz, D.G. Low back pain among office workers in three Spanish-speaking countries: Findings from the CUPID study. Inj. Prev. 2017, 23, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Jing, Q.; Wei, C.; Lu, J. Risk factors of non-specific neck pain and low back pain in computer-using office workers in China: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontrup, C.; Taylor, W.R.; Fliesser, M.; Visscher, R.; Green, T.; Wippert, P.M.; Zemp, R. Low back pain and its relationship with sitting behaviour among sedentary office workers. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 81, 102894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, M.; Dudel, C.; Vogt, T.; Oksuzyan, A. Trends in gender differences in health at working ages among west and east germans. SSM Popul. Health 2019, 7, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.E.; Anisimowicz, Y.; Miedema, B.; Hogg, W.; Wodchis, W.P.; Aubrey-Bassler, K. The influence of gender and other patient characteristics on health care-seeking behaviour: A QUALICOPC study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2016, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundell, C.; Bergström, E.; Larsén, K. Low back pain and associated disability in Swedish adolescents. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, R.; Hirano, T.; Watanabe, K.; Sano, A.; Sato, T.; Ito, T.; Endo, N.; Tanabe, N. Gender differences in the prevalence of low back pain associated with sports activities in children and adolescents: A six-year annual survey of a birth cohort in Niigata City, Japan. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C. Development of neck and hand-wrist symptoms in relation to duration of computer use at work. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2003, 29, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, V. Musculoskeletal disorders and visual strain in intensive data processing workers. Occup. Med. 2005, 55, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoe, V.C.; Urquhart, D.M.; Kelsall, H.L.; Zamri, E.N.; Sim, M.R. Ergonomic interventions for preventing work-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limb and neck among office workers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 10, CD008570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggon, D.; Ntani, G.; Palmer, K.T.; Felli, V.E.; Harari, R.; Barrero, L.H.; Felkor, A.S.; Gimeno, D.; Cattrell, A.; Vargas-Prada, S.; et al. Patterns of multisite pain and associations with risk factors. Pain 2013, 154, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerr, F.; Marcus, M.; Monteilh, C. Epidemiology of musculoskeletal disorders among computer users: Lesson learned from the role of posture and keyboard use. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2004, 14, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.S.; Leite, R.D.V.; Lelis, C.M.; Chaves, T.C. Differences in ergonomic and workstation factors between computer office workers with and without reported musculoskeletal pain. Work 2017, 57, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gelius, P.; Tcymbal, A.; Abu-Omar, K.; Mendes, R.; Morais, S.T.; Whiting, S.; Breda, J. Status and contents of physical activity recommendations in European Union countries: A systematic comparative analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamri, E.; Moy, F.; Hoe, V. Association of psychological distress and work psychosocial factors with self-reported musculoskeletal pain among secondary school teachers in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestroni, L.; Read, P.; Bishop, C.; Papadopoulos, K.; Suchomel, T.J.; Comfort, P.; Turner, A. The benefits of strength training on musculoskeletal system health: Practical applications for interdisciplinary care. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1431–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mohannadi, A.S.; Albuflasa, A.M.; Sayegh, S.; Salman, A.; Farooq, A. A cross-sectional study exploring motivators and barriers to physical activity participation among hospital workers. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2020, 12, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebeke, R. Low-income women’s perceived barriers to physical activity: Focus group results. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2008, 21, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, S.J.; Atkin, A.J.; Cavill, N.; Foster, C. Correlates of physical activity in youth: A review of quantitative systematic reviews. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2011, 4, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deforche, B.; van Dyck, D.; Verloigne, M.; de Bourdeaudhuij, I. Perceived social and physical environmental correlates of physical activity in older adolescents and the moderating effect of self-efficacy. Prev. Med. 2010, 50, S24–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvy, S.; Roemmich, J.N.; Bowker, J.C.; Romero, N.D.; Stadler, P.J.; Epstein, L.H. Effect of peers and friends on youth physical activity and motivation to be physically active. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2009, 34, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawman, H.G.; Wilson, D.K.; van Horn, M.L.; Zarrett, N. The role of motivation in understanding social contextual influences on physical activity in underserved adolescents in the ACT Trial: A cross-sectional study. Child. Obes. 2012, 8, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebar, A.L.; Dimmock, J.A.; Jackson, B.; Rhodes, R.E.; Kates, A.; Starling, J.; Vandelanotte, C. A systematic review of the effects of non-conscious regulatory processes in physical activity. Health Psychol. Rev. 2016, 10, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, M.P.; de León, J.M.; Ruiz-Sánchez, J.P.; González, M.G.; González, A.M.; Pérez, E.P. Chronic pain: Relationship with prefrontal symptoms and perceived stress. Rev. Soc. Esp. Dolor 2017, 24, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinstrup, J.; Jakobsen, M.D.; Calatayud, J.; Jay, K.; Andersen, L.L. Association of stress and musculoskeletal pain with poor sleep: Cross-sectional study among 3,600 hospital workers. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
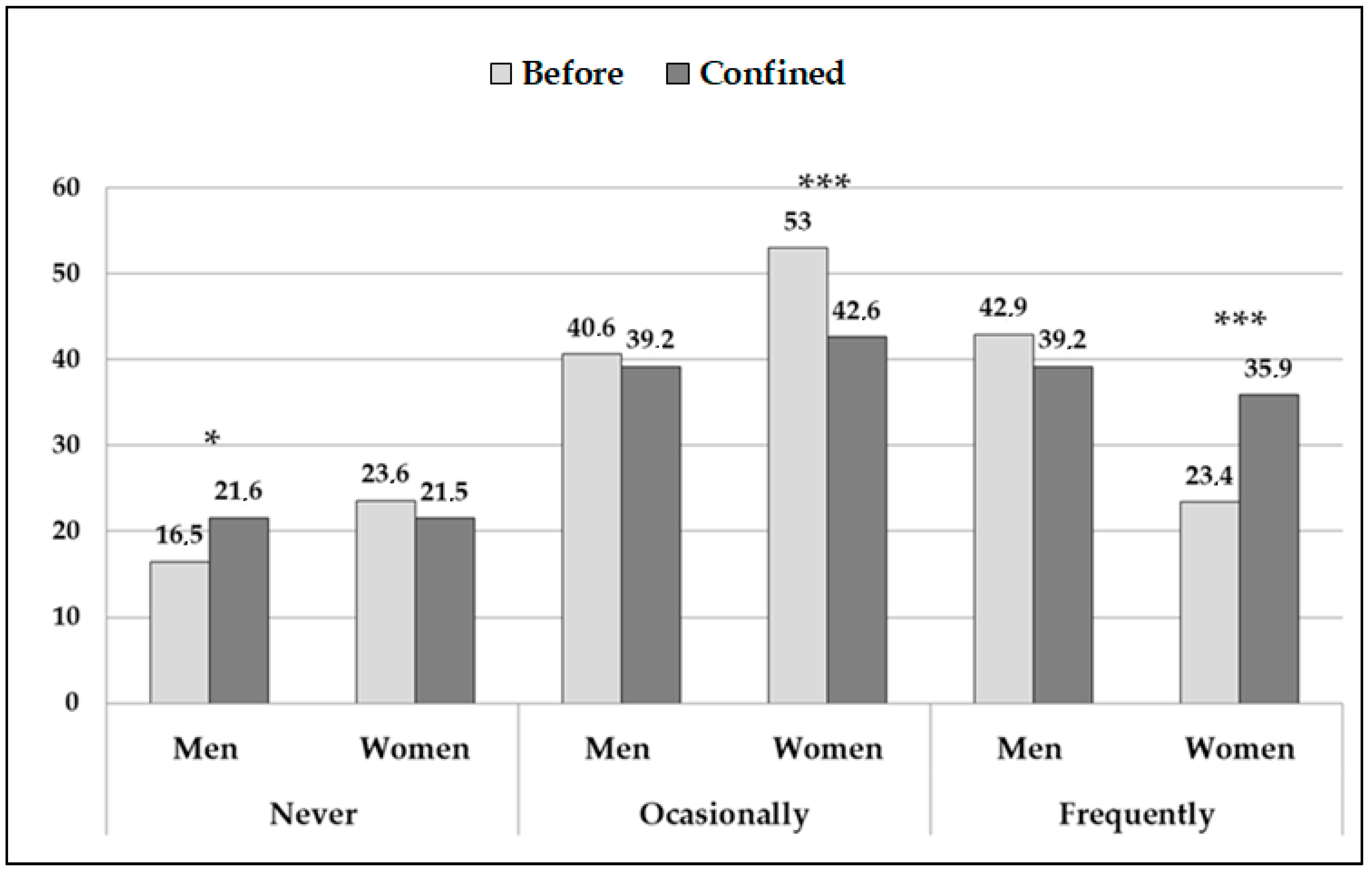
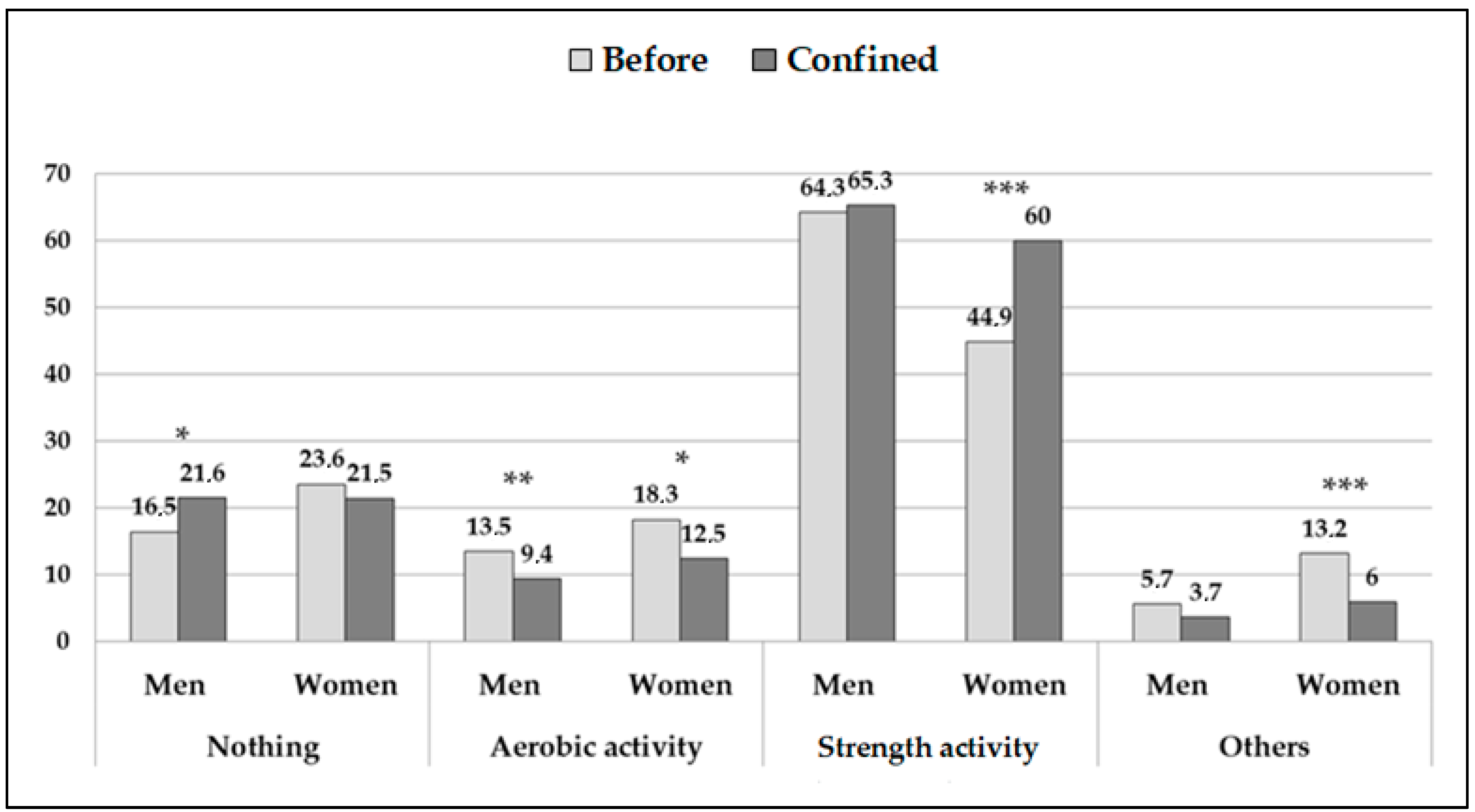
| All (n = 1198) | Men (n = 352) | Women (n = 846) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 22.8 ± 5.9 | 23.5 ± 7.1 ** | 22.5 ± 5.3 ** |
| Hours sitting daily (n) | 7 ± 2.6 | 6.7 ± 2.7 * | 7.1 ± 2.6 * |
| People with whom lived (n) | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 2.4 ± 1 | 2.5 ± 1.2 |
| PA12 (n) | 3.7 ± 2.2 | 3.1 ± 2.2 *** | 3.9 ± 2.2 *** |
| AL12 (n) | 0.9 ± 1.4 | 0.6 ± 1 *** | 1 ± 1.5 *** |
| PAC (n) | 3.2 ± 2 | 2.7 ± 1.9 *** | 3.4 ± 2 *** |
| PSS (score) | 21.9 ± 4.8 | 20.8 ± 5 *** | 22.4 ± 4.6 *** |
| Workspace (frequency (percentage)) | |||
| Specific | 885 (73.9%) | 254 (72.2%) | 631 (74.6%) |
| Improvised common area | 313 (26.1%) | 98 (27.8%) | 215 (25.4%) |
| All (n = 1198) | Men (n = 352) | Women (n = 846) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Painful Areas During the Previous 12 Months | ||||
| Neck | 824 (68.8%) | 200 (56.8%) | 624 (73.8%) | |
| Dorsal | 468 ** (39.1%) | 113 (32.1%) | 355 ** (42%) | |
| Lumbar | 742 (61.9%) | 176 (50%) | 566 (66.9%) | |
| Shoulders: | ||||
| In one | 189 *** (15.8%) | 62 (17.6%) | 127 *** (15%) | |
| In both | 386 (32.2%) | 76 * (21.6%) | 310 * (36.6%) | |
| Elbows | ||||
| In one | 65 * (5.4%) | 20 (5.7%) | 45 (5.3%) | |
| In both | 40 * (3.3%) | 12 (3.4%) | 28 (3.3%) | |
| Hands | ||||
| In one | 200 ** (16.7%) | 60 (17%) | 140 ** (16.5%) | |
| In both | 104 *** (8.7%) | 35 *** (9.9%) | 69 * (8.2%) | |
| Hips | 218 ** (18.2%) | 51 (14.5%) | 167 *** (19.7%) | |
| Knees | 414 ** (34.6%) | 110 * (31.3%) | 304 * (35.9%) | |
| Ankles | 200 *** (16.7%) | 63 *** (17.9%) | 137 (16.2%) | |
| Painful Areas During Lockdown | ||||
| Neck | 837 (69.9%) | 213 (60.5%) | 624 (73.8%) | |
| Dorsal | 493 ** (41.2%) | 122 (34.7%) | 371 ** (43.9%) | |
| Lumbar | 759 (63.4%) | 182 (51.7%) | 577 (68.2%) | |
| Shoulders: | ||||
| In one | 162 *** (13.5%) | 60 (17%) | 102 *** (12.1%) | |
| In both | 385 (32.1%) | 64 * (18.2%) | 321 * (37.9%) | |
| Elbows | ||||
| In one | 57 * (4.8%) | 18 (5.1%) | 39 (4.6%) | |
| In both | 34 * (2.8%) | 11 (3.1%) | 23 (2.7%) | |
| Hands | ||||
| In one | 185 ** (15.4%) | 57 (16.2%) | 128 ** (15.1%) | |
| In both | 71 *** (5.9%) | 17 *** (4.8%) | 54 * (6.4%) | |
| Hips | 177 ** (14.8%) | 49 (13.9%) | 128 *** (15.1%) | |
| Knees | 377 ** (31.5%) | 94 * (26.7%) | 283 * (33.5%) | |
| Ankles | 159 *** (13.3%) | 38 *** (10.8%) | 121 (14.3%) | |
| Variable | OR | SE | p | IC 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 1.852 | 0.506 | 0.02 | 1.084–3.164 |
| Age | 1.141 | 0.057 | 0.008 | 1.035–1.258 |
| Frequency of PA during the lockdown | 0.632 | 0.091 | 0.001 | 0.476–0.839 |
| Time spent sitting down daily | 1.045 | 0.048 | 0.34 | 0.954–1.143 |
| Self-perceived stress | 1.031 | 0.024 | 0.19 | 0.985–1.079 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leirós-Rodríguez, R.; Rodríguez-Nogueira, Ó.; Pinto-Carral, A.; Álvarez-Álvarez, M.J.; Galán-Martín, M.Á.; Montero-Cuadrado, F.; Benítez-Andrades, J.A. Musculoskeletal Pain and Non-Classroom Teaching in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Analysis of the Impact on Students from Two Spanish Universities. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4053. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124053
Leirós-Rodríguez R, Rodríguez-Nogueira Ó, Pinto-Carral A, Álvarez-Álvarez MJ, Galán-Martín MÁ, Montero-Cuadrado F, Benítez-Andrades JA. Musculoskeletal Pain and Non-Classroom Teaching in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Analysis of the Impact on Students from Two Spanish Universities. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):4053. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124053
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeirós-Rodríguez, Raquel, Óscar Rodríguez-Nogueira, Arrate Pinto-Carral, Mª José Álvarez-Álvarez, Miguel Á. Galán-Martín, Federico Montero-Cuadrado, and José Alberto Benítez-Andrades. 2020. "Musculoskeletal Pain and Non-Classroom Teaching in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Analysis of the Impact on Students from Two Spanish Universities" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 4053. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124053
APA StyleLeirós-Rodríguez, R., Rodríguez-Nogueira, Ó., Pinto-Carral, A., Álvarez-Álvarez, M. J., Galán-Martín, M. Á., Montero-Cuadrado, F., & Benítez-Andrades, J. A. (2020). Musculoskeletal Pain and Non-Classroom Teaching in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Analysis of the Impact on Students from Two Spanish Universities. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 4053. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124053







