Clinical Relevance of Serum Galactose Deficient IgA1 in Patients with IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Clinical and Pathological Parameters
2.3. Measurement of Serum Gd-IgA1
2.4. Treatment and Clinical Outcome
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Study Population
3.2. Association of Serum Gd-IgA1 Level with Clinical and Pathological Parameters in IgAN Patients
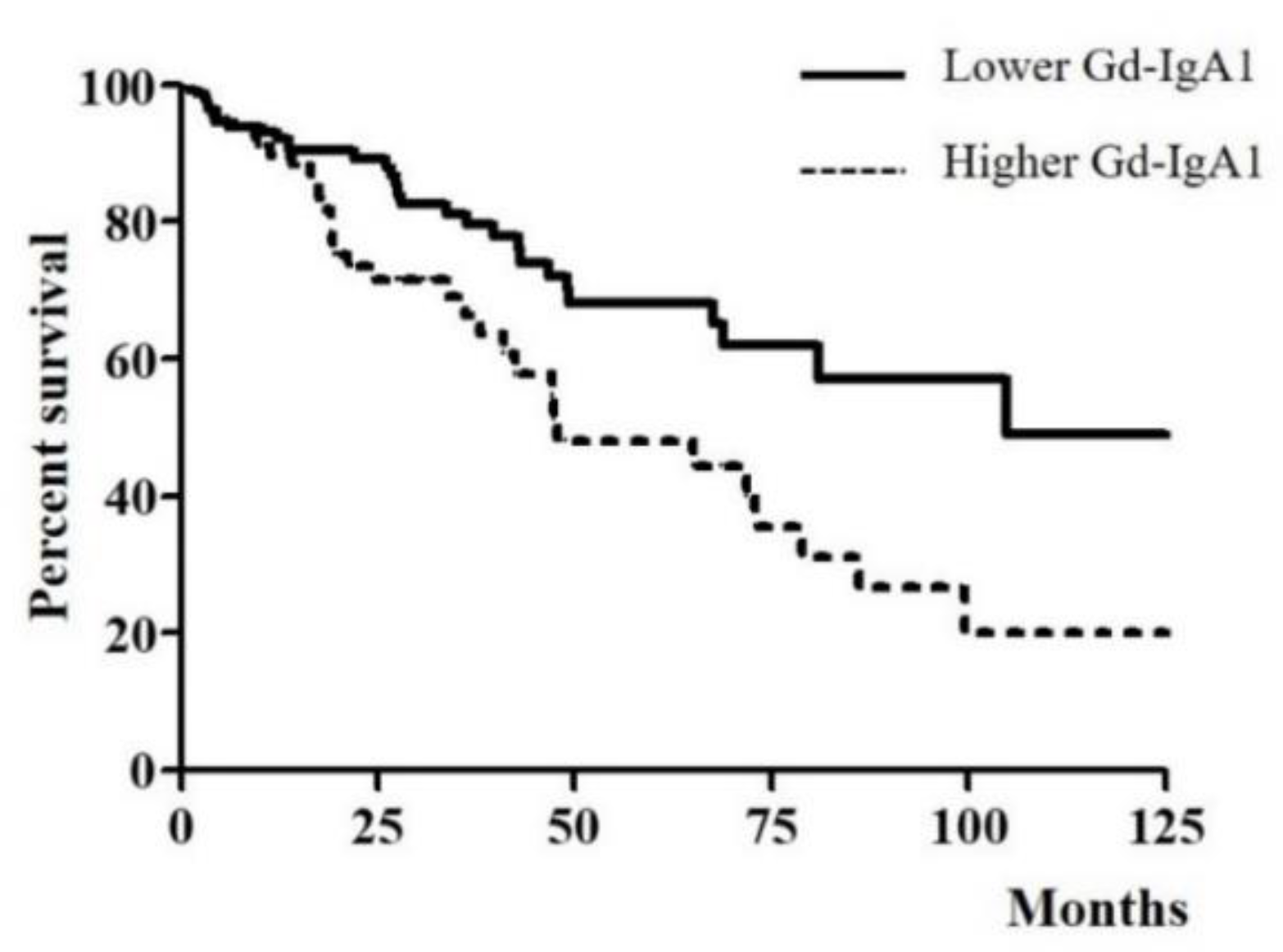
3.3. Association of Serum Gd-IgA1 Level and CKD Progression in IgAN Patients
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyatt, R.J.; Julian, B.A. IgA nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2402–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoux, F.C.; Mohey, H.; Afiani, A. Natural history of primary IgA nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, J.; Feehally, J. IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H. Biomarkers for IgA nephropathy on the basis of multi-hit pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schena, F.P.; Cox, S.N. Biomarkers and Precision Medicine in IgA Nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, A.C.; Harper, S.J.; Feehally, J. Galactosylation of N- and O-linked carbohydrate moieties of IgA1 and IgG in IgA nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1995, 100, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppo, R.; Amore, A. Aberrant glycosylation in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1544–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, Z.; Wyatt, R.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Tomana, M.; Julian, B.A.; Mestecky, J.; Huang, W.Q.; Anreddy, S.R.; Hall, S.; Hastings, M.C.; et al. Patients with IgA nephropathy have increased serum galactose-deficient IgA1 levels. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Herr, A.B.; Renfrow, M.B.; Wyatt, R.J.; Scolari, F.; Mestecky, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; et al. The pathophysiology of IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, W.; Wei, L.; Li, H.; Gao, S.; Yan, T.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Clinical Significance of Galactose-Deficient IgA1 by KM55 in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Suzuki, T.; Saito, T.; Kanazawa, N.; Tachibana, S.; Iseri, K.; Sugiyama, M.; Iyoda, M.; Shibata, T. Clinical significance of serum and mesangial galactose-deficient IgA1 in patients with IgA nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Lingaiah, R.; Mani, K.; Barwad, A.; Singh, G.; Balooni, V.; Bhowmik, D.; Agarwal, S.K. Significance of serum galactose deficient IgA1 as a potential biomarker for IgA nephropathy: A case control study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimarchi, H.; Barratt, J.; Cattran, D.C.; Cook, H.T.; Coppo, R.; Haas, M.; Liu, Z.H.; Roberts, I.S.; Yuzawa, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Oxford Classification of IgA nephropathy 2016: An update from the IgA Nephropathy Classification Working Group. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inker, L.A.; Astor, B.C.; Fox, C.H.; Isakova, T.; Lash, J.P.; Peralta, C.A.; Kurella Tamura, M.; Feldman, H.I. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Hinglais, N. Intercapillary deposits of IgA-IgG. J. Urol. Nephrol. 1968, 74, 694–695. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, M.C.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Suzuki, H.; Berthoux, F.; Julian, B.A.; Sanders, J.T.; Renfrow, M.B.; Novak, J.; Wyatt, R.J. Biomarkers in IgA nephropathy: Relationship to pathogenetic hits. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2013, 7, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, T. Clinical and histological features and therapeutic strategies for IgA nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.A.; Kelepouris, E. Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy: Advances in Understanding of Pathogenesis and Treatment. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 47 (Suppl. S1), 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Hou, P.; Lv, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Li, Y.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.G.; Novak, J.; Zhang, H. The level of galactose-deficient IgA1 in the sera of patients with IgA nephropathy is associated with disease progression. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.X.; Zhao, M.H. Aberrantly glycosylated serum IgA1 are closely associated with pathologic phenotypes of IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lai, K.N.; Chan, L.Y.; Leung, J.C. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial injury in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, S110–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.C.K.; Lai, K.N.; Tang, S.C.W. Role of Mesangial-Podocytic-Tubular Cross-Talk in IgA Nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutake, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Hiura, N.; Yanagawa, H.; Makita, Y.; Kaneko, E.; Tomino, Y. Novel lectin-independent approach to detect galactose-deficient IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Yasutake, J.; Makita, Y.; Tanbo, Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Sofue, T.; Kano, T.; Suzuki, Y. IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis with nephritis have a shared feature involving galactose-deficient IgA1-oriented pathogenesis. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

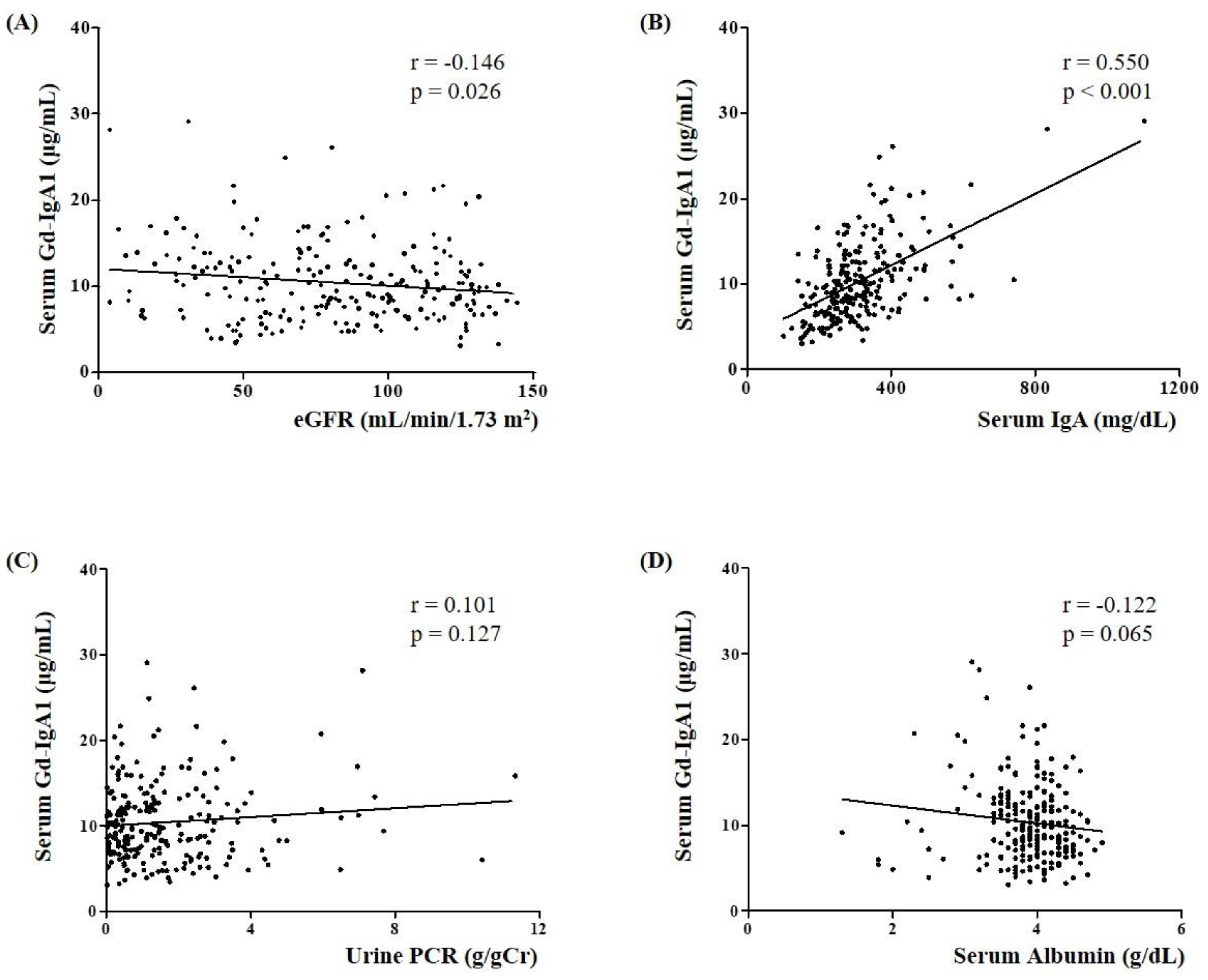
| IgAN (n = 230) | MN (n = 35) | MCD (n = 21) | LN (n = 8) | TBMD (n = 10) | Heathy Controls (n = 15) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 41.00 (31.00–52.00) b | 53.00 (41.25–63.75) a | 48.00 (21.00–62.00) | 44.00 (22.00–53.00) | 40.00 (20.50–46.50) b | 25.00 (21.75–50.50) b |
| Male (n, %) | 115 (50.0%) | 23 (65.7%) | 13 (61.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (50.0%) | 12 (80.0%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.50 (21.28–25.68) | 23.19 (22.12–24.28) | 25.20 (21.79–28.25) | 21.75 (19.90–22.47) | 23.29 (21.75–24.77) | 22.32 (20.95–24.23) |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.90 (3.60–4.20) b,c,d,f | 3.35 (2.57–4.10) a,c,e,f | 2.20 (1.90–2.40) a,b,e,f | 2.90(2.22–3.60) a,e,f | 4.50(4.15–4.65) b,c,d | 4.60 (4.33–4.73) a,b,c,d |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.94 (0.74–1.38) | 0.80 (0.60–1.03) | 0.90 (0.70–1.45) | 0.60 (0.56–1.87) | 0.73 (0.55–0.85) | 0.76 (0.67–0.99) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 84.18 (52.50–113.91) e | 90.90 (77.91–115.59) | 85.32 (53.20–112.16) | 110.89 (31.06–132.90) | 121.75 (110.69–130.39) a | 125.29 (87.29–137.78) |
| C3 (mg/dL) | 107.00 (92.00–121.00) d | 112.00 (95.52–125.25) d | 114.00 (105.50–129.00) d | 45.95 (32.83–56.75) a,b,c,e,f | 97.40 (89.45–105.00) d | 102.00 (84.07–111.25) d |
| IgA (mg/dL) | 287.0 (240.00–361.50) e,f | 214.00 (175.50–283.75) | 264.00 (220.00–353.00) | 264.00 (220.00–353.00) | 177.00 (151.00–199.50) a | 171.00 (124.00–204.50) a |
| Urine PCR (g/gCr) | 1.24 (0.46–2.34) b,c | 3.89 (1.64–6.22) a,c,e,f | 8.63 (4.81–13.95) a,b,d,e,f | 2.28 (0.62–4.09) c | 0.60 (0.03–0.63) b,c | 0.04 (0.19–0.07) b,c |
| Urine RBC grade | ||||||
| <5/HPF | 45 (19.6%) | 17 (48.6%) | 12 (57.1%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1 (10.0%) | – |
| 5–9/HPF | 30 (13.0%) | 6 (17.1%) | 6 (28.6%) | 2 (25.0%) | 3 (30.0%) | – |
| 10–29/HPF | 59 (25.7%) | 6 (17.1%) | 1 (4.8%) | 2 (25.0%) | 5 (50.0%) | – |
| ≥30/HPF | 96 (41.7%) | 6 (17.1%) | 2 (9.5%) | 3 (37.5%) | 1 (10.0%) | – |
| Serum Gd–IgA1 (μg/mL) | 9.66 (7.14–12.60)b,c,d,e,f | 6.65 (4.21–9.51) a | 5.60 (4.86–7.38) a | 4.95 (2.40–7.71) a | 5.19 (4.71–6.16) a | 4.43 (3.44–5.15) a |
| Oxford Classification | n (%) | Serum Gd-IgA1 (μg/mL) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 0 | 135 (58.7%) | 8.77 (6.64–12.17) | 0.414 |
| 1 | 95 (41.3%) | 10.57 (7.94–13.46) | ||
| E | 0 | 174 (76.5%) | 9.41 (7.12–13.29) | 0.898 |
| 1 | 56 (23.5%) | 9.91 (7.61–12.17) | ||
| S | 0 | 167 (72.6%) | 9.73 (7.19–12.47) | 0.672 |
| 1 | 63 (27.4%) | 9.42 (7.12–12.95) | ||
| T | 0 | 193 (83.9%) | 9.15 (6.93–12.18) | 0.024 |
| 1,2 | 37 (16.1%) | 10.93 (8.45–16.69) | ||
| C | 0 | 170 (73.9%) | 9.89 (7.19–13.00) | 0.268 |
| 1,2 | 60 (26.1%) | 8.69 (6.22–12.16) |
| Lower Gd-IgA1 (<11.31 μg/mL) n = 148 | Higher Gd-IgA1 (≥11.31 μg/mL) n = 82 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 40.00 (26.50–52.00) | 42.00 (34.00–49.00) | 0.238 |
| Male (n, %) | 74 (50%) | 41 (50%) | 0.999 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.50 (21.16–25.71) | 23.44 (21.48–25.65) | 0.794 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.00 (3.70–4.30) | 3.80 (3.50–4.10) | 0.012 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.90 (0.74–1.19) | 1.10 (0.80–1.70) | 0.001 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 92.96 (59.44–118.15) | 72.59 (41.83–108.38) | 0.001 |
| C3 (mg/dL) | 107.00 (95.05–120.50) | 107.0 (92.00–423.00) | 0.478 |
| Serum IgA (mg/dL) | 269.00 (228.50–324.00) | 354.0 (278.00–423.00) | <0.001 |
| Urine PCR (g/gCr) | 1.11 (0.36–2.33) | 1.22 (0.51–2.44) | 0.337 |
| Prior medications (n, %) | |||
| ARB or ACEi | 33 (22.3%) | 22 (26.8%) | 0.440 |
| CCB | 23 (15.5%) | 9 (11.0%) | 0.226 |
| Beta blocker | 6 (4.1%) | 3 (3.7%) | 0.593 |
| Statin | 10 (6.8%) | 5 (6.1%) | 0.543 |
| Urine RBC grade (n, %) | 0.867 | ||
| <5/HPF | 28 (18.9%) | 17 (20.7%) | |
| 5–9/HPF | 21 (14.2%) | 9 (11.0%) | |
| 10–29/HPF | 39 (26.4%) | 20 (24.4%) | |
| ≥30/HPF | 60; (40.5%) | 36 (43.9%) | |
| Serum Gd–IgA1 (μg/mL) | 7.95 (6.23–9.36) | 13.84 (12.44–16.73) | <0.001 |
| Therapeutic strategies (n, %) | |||
| ARB or ACEi | 103 (69.6%) | 57 (69.5%) | 0.990 |
| Immunosuppressant | 28 (55.4%) | 46 (56.1%) | 0.515 |
| Follow–up duration (months) | 22.55 (11.68–45.83) | 22.41 (13.05–42.32) | 0.998 |
| CKD progression | 31 (20.9%) | 33 (40.2%) | 0.002 |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age (years) | 1.029 (1.012–1.046) | 0.001 | 1.016 (0.996–1.035) | 0.111 |
| Male (vs. Female) | 1.076 (0.659–1.759) | 0.769 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.997 (0.921–1.079) | 0.939 | ||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 0.985 (0.978–0.991) | <0.001 | 0.991 (0.982–0.999) | 0.048 |
| Urine PCR(g/g) | 1.191 (1.081–1.313) | <0.001 | 1.116 (0.991–1.256) | 0.070 |
| Prior medications | ||||
| ARB or ACEi | 1.587 (00.903–2.789) | 0.109 | ||
| CCB | 1.420 (0.698–2.888) | 0.333 | ||
| Beta blocker | 2.540 (0.783–8.268) | 0.120 | ||
| Statin | 1.070 (0.333–3.438) | 0.909 | ||
| Oxford classification | ||||
| M | 1.226 (0.747–2.012) | 0.420 | ||
| S | 1.502 (0.885–2.550) | 0.132 | ||
| E | 1.340 (0.733–2.451) | 0.341 | ||
| T | 1.698 (0.955–3.018) | 0.071 | 1.151 (0.614–2.158) | 0.661 |
| C | 1.532 (0.870–2.699) | 0.140 | ||
| Therapeutic strategies | ||||
| ARB or ACEi | 1.523 (0.857–2.706) | 0.151 | ||
| Immunosuppressant | 1.344 (0.796–2.269) | 0.268 | ||
| Lower serum Gd–IgA1 level | 1 | |||
| Higher serum Gd–IgA1 level | 2.283 (1.388–3.756) | 0.001 | 1.933 (1.164–3.208) | 0.011 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.S.; Hwang, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Moon, J.-Y.; Kong, J.Y.; Jeong, K.H. Clinical Relevance of Serum Galactose Deficient IgA1 in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113549
Kim JS, Hwang HS, Lee SH, Kim YG, Moon J-Y, Kong JY, Jeong KH. Clinical Relevance of Serum Galactose Deficient IgA1 in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(11):3549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113549
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jin Sug, Hyeon Seok Hwang, Sang Ho Lee, Yang Gyun Kim, Ju-Young Moon, Ji Yoon Kong, and Kyung Hwan Jeong. 2020. "Clinical Relevance of Serum Galactose Deficient IgA1 in Patients with IgA Nephropathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 11: 3549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113549
APA StyleKim, J. S., Hwang, H. S., Lee, S. H., Kim, Y. G., Moon, J.-Y., Kong, J. Y., & Jeong, K. H. (2020). Clinical Relevance of Serum Galactose Deficient IgA1 in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113549





