Immunomodulation of Murine Chronic DSS-Induced Colitis by Tuftsin–Phosphorylcholine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tuftsin–Phosphorylcholine (TPC) Synthesis
2.2. Mice
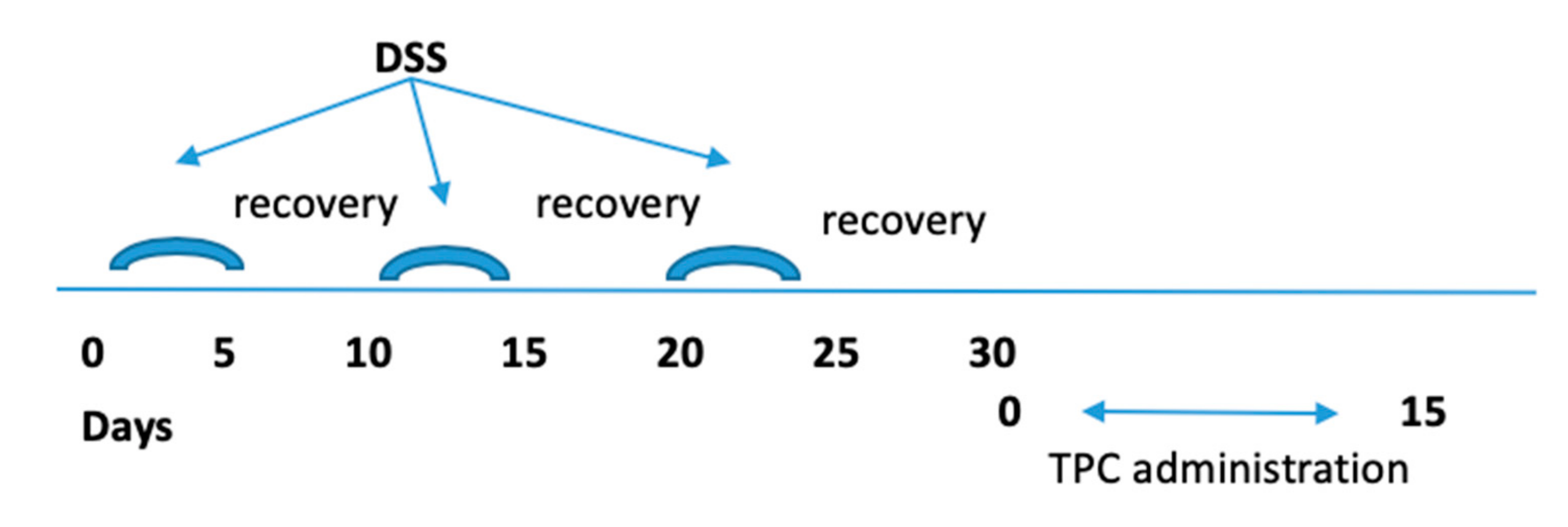
2.3. Induction of Chronic Colitis and Protocol of Treatment
2.4. Monitoring of DSS Chronic Colitis
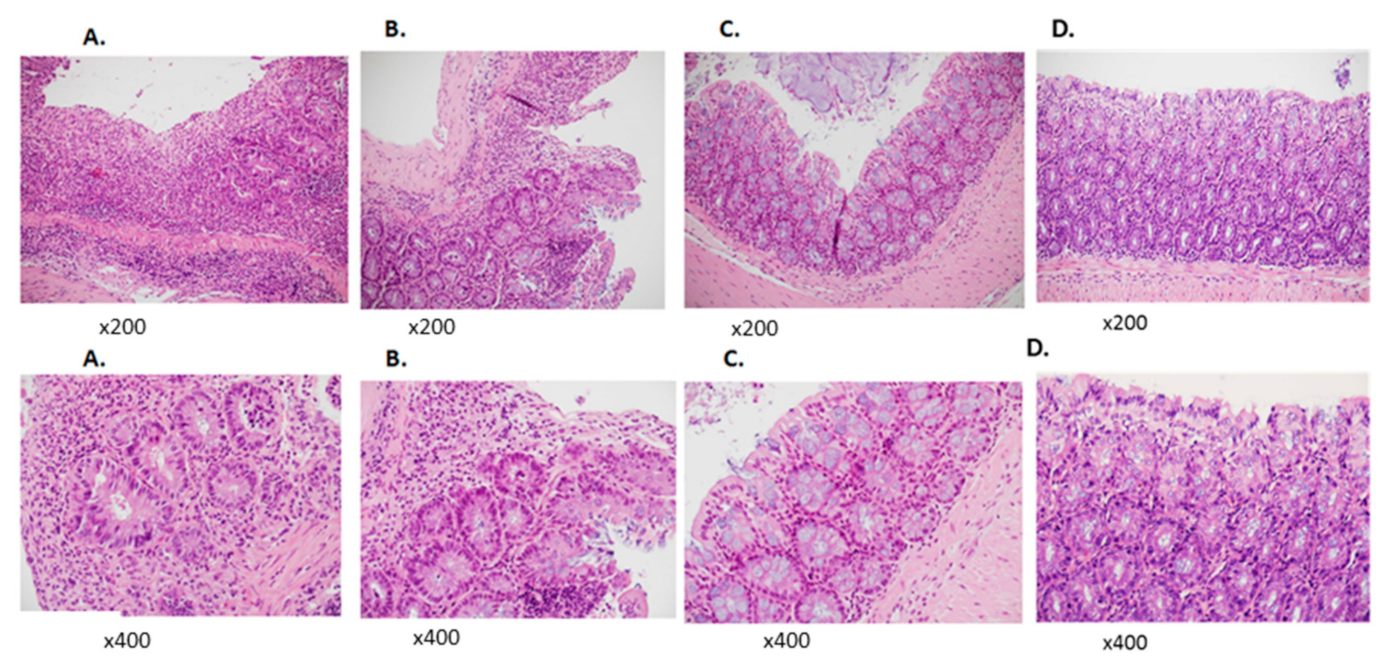
2.5. Histopathological Analysis
2.6. T Regulatory Analysis by Flow Cytometry
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
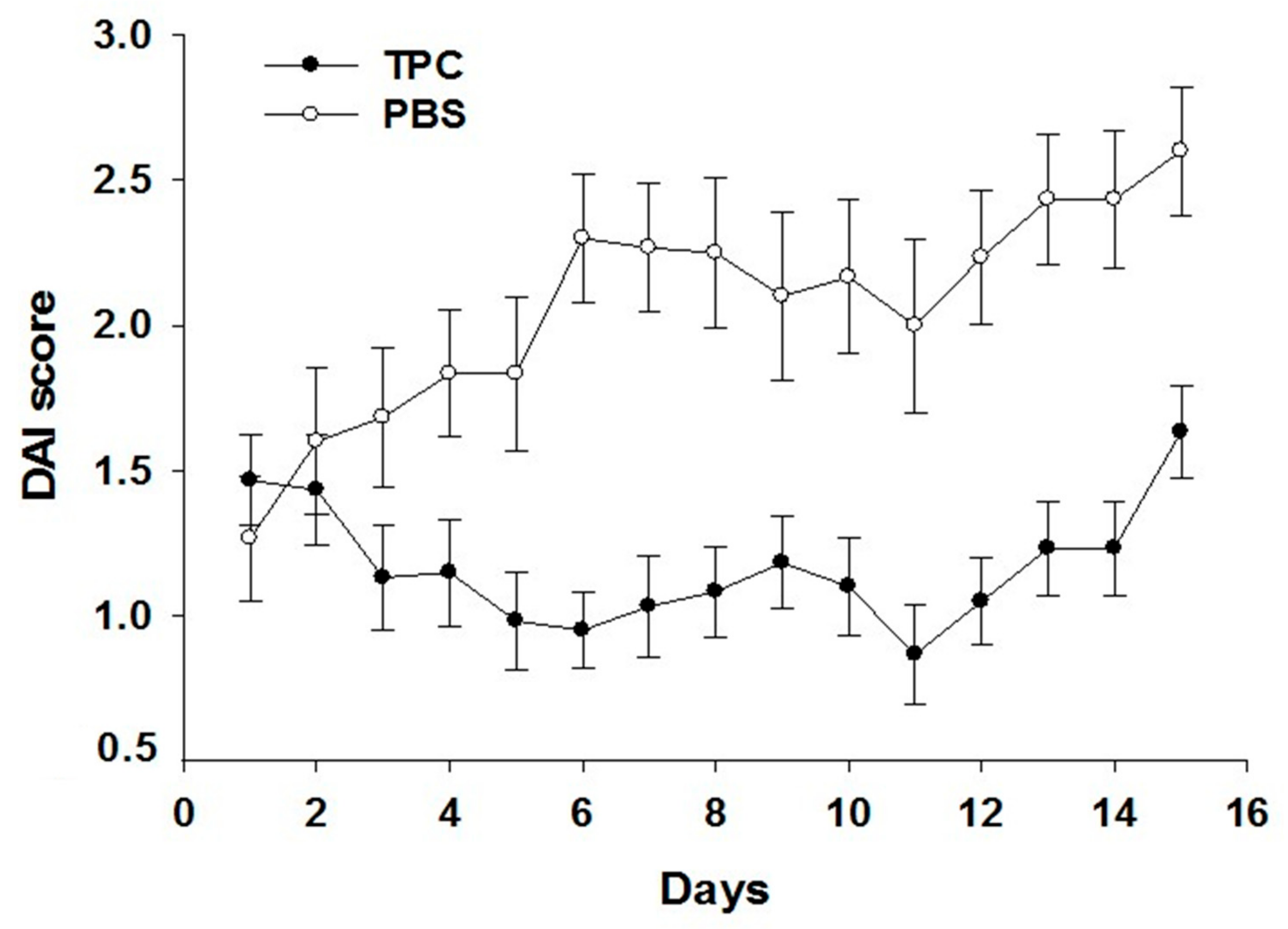
3.1. TPC Significantly Attenuated Disease Activity in a Murine Chronic Colitis Model
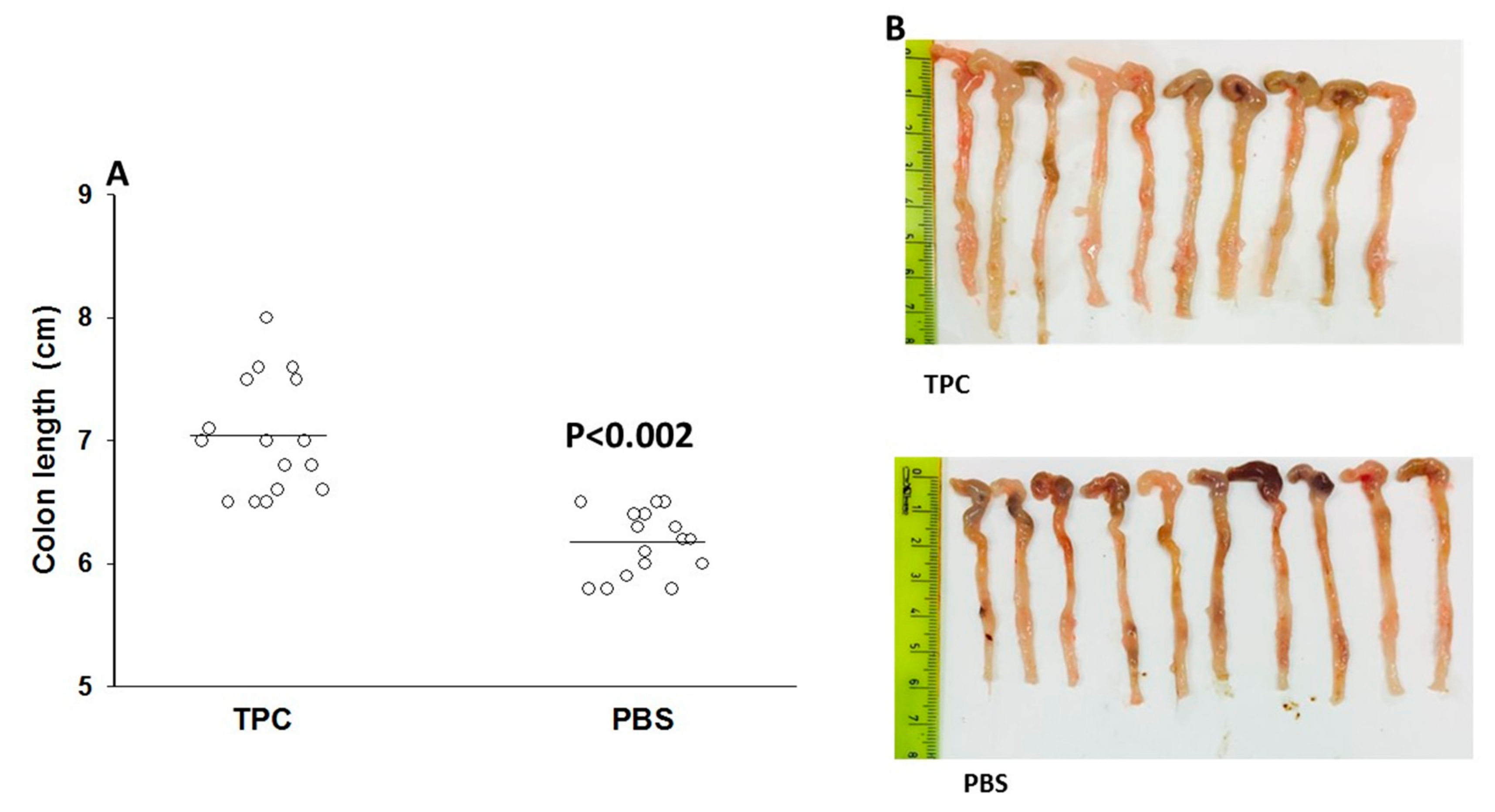
3.2. TPC Reduced Inflammation in Murine Chronic Colitis Model
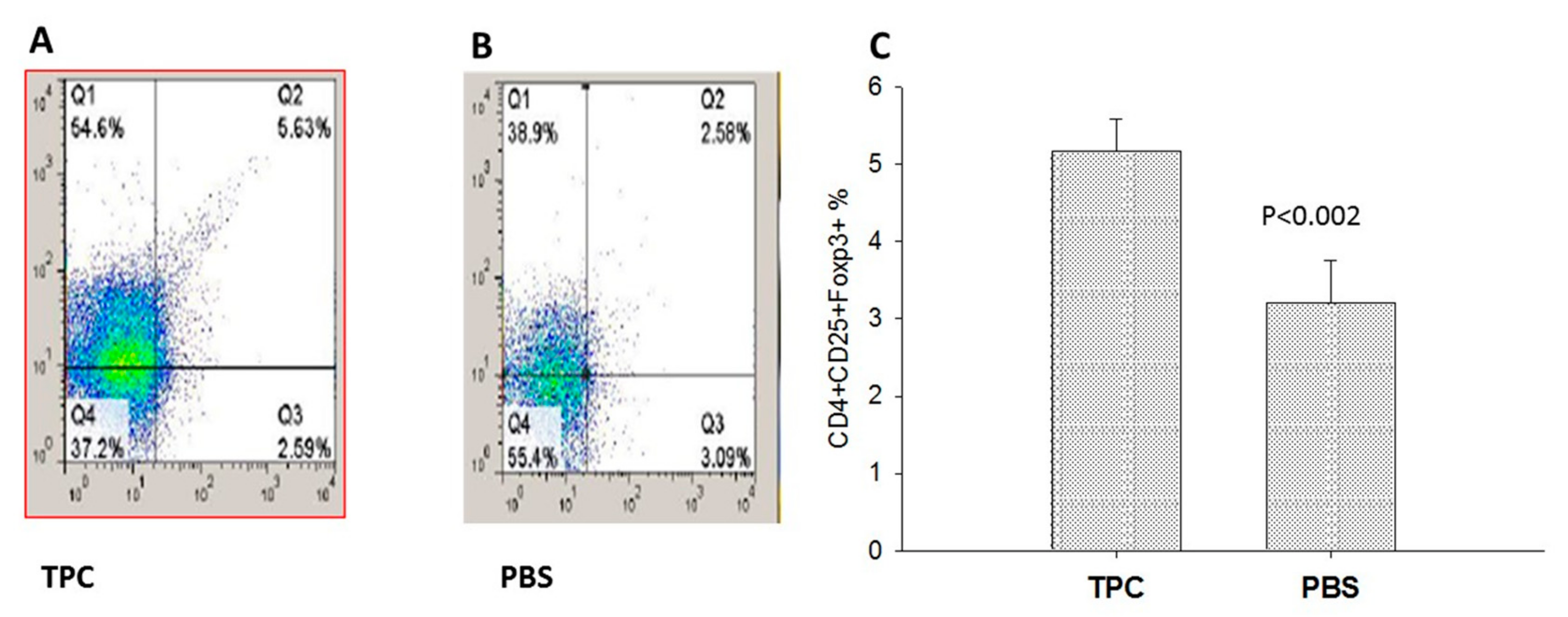
3.3. MLN T Regulatory Cell Expansion upon TPC Treatment in the Murine Chronic Colitis Model
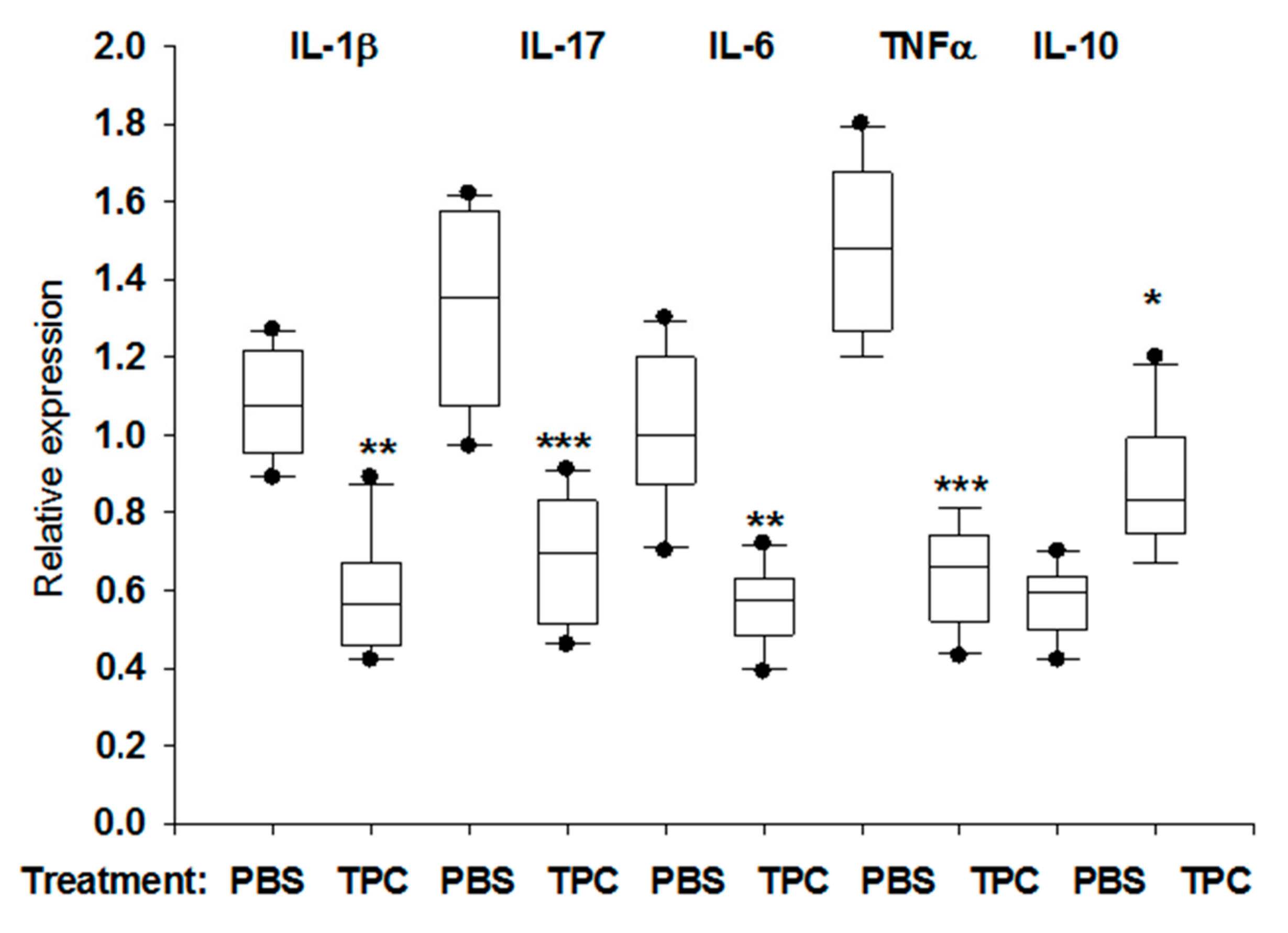
3.4. TPC Immunomodulated MLN Cytokine mRNA Levels in Murine Chronic Colitis Model
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cosnes, J.; Gower-Rousseau, C.; Seksik, P.; Cortot, A. Epidemiology and natural history of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, E.V., Jr. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1504–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, J.F. The hygiene hypothesis in autoimmunity: The role of pathogens and commensals. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstock, J.V.; Elliott, D.E. Helminths and the IBD hygiene hypothesis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.S.; Maizels, R.M. Regulation of allergy and autoimmunity in helminth infection. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 26, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijk, L.M.; van Die, I. Worms to the rescue: Can worm glycans protect from autoimmune diseases? IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.A.; Friberg, I.M.; Little, S.; Bradley, J.E. Review series on helminths, immune modulation and the hygiene hypothesis: Immunity against helminths and immunological phenomena in modern human populations: Coevolutionary legacies? Immunology 2009, 126, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; Rutitzky, L.I.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Stadecker, M.J.; Gause, W.C. Protective immune mechanisms in helminth infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, H.S.; van Oijen, M.G.; de Jong, D.J. Serious events with infliximab in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A 9-year cohort study in the Netherlands. Drug Saf. 2008, 31, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidder, H.; Schnitzler, F.; Ferrante, M.; Noman, M.; Katsanos, K.; Segaert, S.; Henckaerts, L.; Van Assche, G.; Vermeire, S.; Rutgeerts, P. Long-term safety of infliximab for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: A single-centre cohort study. Gut 2009, 58, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibolet, O.; Regushevskaya, E.; Brezis, M.; Soares-Weiser, K. Cyclosporine A for induction of remission in severe ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shor, D.B.; Shoenfeld, Y. Autoimmunity: Will worms cure rheumatoid arthritis? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, L.; Setiawan, T.; Blum, A.M.; Urban, J.; Stoyanoff, K.; Arihiro, S.; Reinecker, H.C.; Weinstock, J.V. Heligmosomoides polygyrus infection can inhibit colitis through direct interaction with innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3184–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correale, J.; Farez, M.F. The impact of parasite infections on the course of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 233, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, A.; Tonks, P.; Jones, F.M.; O’Shea, H.; Hutchings, P.; Fulford, A.J.; Dunne, D.W. Infection with Schistosoma mansoni prevents insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in non-obese diabetic mice. Parasite Immunol. 1999, 21, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Leung, B.P.; Harnett, M.; Gracie, J.A.; Liew, F.Y.; Harnett, W. A novel therapeutic approach targeting articular inflammation using the filarial nematode-derived phosphorylcholine-containing glycoprotein ES-62. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnett, W.; Harnett, M.M. Phosphorylcholine: Friend or foe of the immune system? Immunol. Today 1999, 20, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, A.; Gensicka-Kowalewska, M.; Cholewinski, G.; Dzierzbicka, K. Tuftsin—Properties and Analogs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3711–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, V.A.; Nishioka, K. “Tuftsin”: A natural phagocytosis stimulating peptide. Nature 1970, 228, 672–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemion, I.Z.; Kluczyk, A. Tuftsin: On the 30-year anniversary of Victor Najjar’s discovery. Peptides 1999, 20, 645–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridkin, M.; Najjar, V.A. Tuftsin: Its chemistry, biology, and clinical potential. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1989, 24, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Han, S.; Yao, L.; Chen, A.; Yang, Q.; Bo, H.; Xu, P.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced immune response induced by a potential influenza A vaccine based on branched M2e polypeptides linked to tuftsin. Vaccine 2012, 30, 6527–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashi, T.; Blank, M.; Ben-Ami Shor, D.; Fridkin, M.; Versini, M.; Gendelman, O.; Volkov, A.; Barshak, I.; Shoenfeld, Y. Successful modulation of murine lupus nephritis with tuftsin-phosphorylcholine. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashi, T.; Shovman, O.; Fridkin, M.; Volkov, A.; Barshack, I.; Blank, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Novel therapeutic compound tuftsin-phosphorylcholine attenuates collagen-induced arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 184, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, M.; Bashi, T.; Lachnish, J.; Ben-Ami-Shor, D.; Shovman, O.; Fridkin, M.; Eisenstein, M.; Volkov, A.; Barshack, I.; Shoenfeld, Y. Helminths-based bi-functional molecule, tuftsin-phosphorylcholine (TPC), ameliorates an established murine arthritis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ami Shor, D.; Bashi, T.; Lachnish, J.; Fridkin, M.; Bizzaro, G.; Barshak, I.; Blank, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Phosphorylcholine-tuftsin compound prevents development of dextransulfate-sodium-salt induced murine colitis: Implications for the treatment of human inflammatory bowel disease. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 56, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergeevna Novikova, N.; Zurabovna Derevtsova, K.; Andreevna Korneva, E.; Tamara Viktorovna, F.; Ostrinki, Y.; Abraham, L.; Quinn, S.; Segal, Y.; Churilov, L.; Blank, M.; et al. Tuftsin-phosphorylcholine attenuate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Croci, S.; Bonacini, M.; Muratore, F.; Caruso, A.; Fontana, A.; Boiardi, L.; Soriano, A.; Cavazza, A.; Cimino, L.; Belloni, L.; et al. The therapeutic potential of tuftsin-phosphorylcholine in giant cell arteritis. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 98, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Sang, L.; Zhai, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Lu, C.; Sun, X. IL-33 alleviates DSS-induced chronic colitis in C57BL/6 mice colon lamina propria by suppressing Th17 cell response as well as Th1 cell response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, C.; Uhlig, H.H.; Powrie, F. Cutting edge: Cure of colitis by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3939–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, H.H.; Coombes, J.; Mottet, C.; Izcue, A.; Thompson, C.; Fanger, A.; Tannapfel, A.; Fontenot, J.D.; Ramsdell, F.; Powrie, F. Characterization of Foxp3+ CD4+ CD25+ and IL-10-secreting CD4+CD25+ T cells during cure of colitis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5852–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.T.; Saruta, M.; Avanesyan, A.; Fleshner, P.R.; Banham, A.H.; Papadakis, K.A. Expression and functional characterization of FOXP3+ CD4+ regulatory T cells in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correale, J.; Farez, M. Association between parasite infection and immune responses in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccone, P.; Burton, O.T.; Gibbs, S.; Miller, N.; Jones, F.M.; Dunne, D.W.; Cooke, A. Immune modulation by Schistosoma mansoni antigens in NOD mice: Effects on both innate and adaptive immune systems. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 795210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.E.; Weinstock, J.V. Helminth-host immunological interactions: Prevention and control of immune-mediated diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1247, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, P.; Fehervari, Z.; Jones, F.M.; Sidobre, S.; Kronenberg, M.; Dunne, D.W.; Cooke, A. Schistosoma mansoni antigens modulate the activity of the innate immune response and prevent onset of type 1 diabetes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Niwa, M.; McLachlan, S.M.; Rapoport, B. Schistosoma mansoni and alpha-galactosylceramide: Prophylactic effect of Th1 Immune suppression in a mouse model of Graves’ hyperthyroidism. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanarek, N.; Grivennikov, S.I.; Leshets, M.; Lasry, A.; Alkalay, I.; Horwitz, E.; Shaul, Y.D.; Stachler, M.; Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N.; et al. Critical role for IL-1beta in DNA damage-induced mucositis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E702–E711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.M.; Ma, T.Y. IL-1beta causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4641–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.K.; Croft, A.M.; Bager, P. Helminth therapy (worms) for induction of remission in inflammatory bowel disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ami Shor, D.; Harel, M.; Eliakim, R.; Shoenfeld, Y. The hygiene theory harnessing helminths and their ova to treat autoimmunity. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bager, P.; Arnved, J.; Ronborg, S.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Poulsen, L.K.; Westergaard, T.; Petersen, H.W.; Kristensen, B.; Thamsborg, S.; Roepstorff, A.; et al. Trichuris suis ova therapy for allergic rhinitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, R.W.; Elliott, D.E.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Thompson, R.A.; Weinstock, J.V. Trichuris suis therapy for active ulcerative colitis: A randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Elliott, D.E.; Weinstock, J.; Summers, R.W.; Landry-Wheeler, A.; Silver, N.; Harnett, M.D.; Hanauer, S.B. Randomised clinical trial: The safety and tolerability of Trichuris suis ova in patients with Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, D.; Hooi, D.; Feary, J.; Venn, A.; Telford, G.; Brown, A.; Britton, J.; Pritchard, D. Immunologic profiles of persons recruited for a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of hookworm infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feary, J.; Venn, A.; Brown, A.; Hooi, D.; Falcone, F.H.; Mortimer, K.; Pritchard, D.I.; Britton, J. Safety of hookworm infection in individuals with measurable airway responsiveness: A randomized placebo-controlled feasibility study. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feary, J.R.; Venn, A.J.; Mortimer, K.; Brown, A.P.; Hooi, D.; Falcone, F.H.; Pritchard, D.I.; Britton, J.R. Experimental hookworm infection: A randomized placebo-controlled trial in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 40, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daveson, A.J.; Jones, D.M.; Gaze, S.; McSorley, H.; Clouston, A.; Pascoe, A.; Cooke, S.; Speare, R.; Macdonald, G.A.; Anderson, R.; et al. Effect of hookworm infection on wheat challenge in celiac disease--a randomised double-blinded placebo controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, R.W.; Elliott, D.E.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Thompson, R.; Weinstock, J.V. Trichuris suis therapy in Crohn’s disease. Gut 2005, 54, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben-Ami Shor, D.; Lachnish, J.; Bashi, T.; Dahan, S.; Shemer, A.; Segal, Y.; Shovman, O.; Halpert, G.; Volkov, A.; Barshack, I.; et al. Immunomodulation of Murine Chronic DSS-Induced Colitis by Tuftsin–Phosphorylcholine. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010065
Ben-Ami Shor D, Lachnish J, Bashi T, Dahan S, Shemer A, Segal Y, Shovman O, Halpert G, Volkov A, Barshack I, et al. Immunomodulation of Murine Chronic DSS-Induced Colitis by Tuftsin–Phosphorylcholine. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen-Ami Shor, Dana, Jordan Lachnish, Tomer Bashi, Shani Dahan, Asaf Shemer, Yahel Segal, Ora Shovman, Gilad Halpert, Alexander Volkov, Iris Barshack, and et al. 2020. "Immunomodulation of Murine Chronic DSS-Induced Colitis by Tuftsin–Phosphorylcholine" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010065
APA StyleBen-Ami Shor, D., Lachnish, J., Bashi, T., Dahan, S., Shemer, A., Segal, Y., Shovman, O., Halpert, G., Volkov, A., Barshack, I., Amital, H., Blank, M., & Shoenfeld, Y. (2020). Immunomodulation of Murine Chronic DSS-Induced Colitis by Tuftsin–Phosphorylcholine. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010065






