A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Accuracy of in Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Objective and Definition of Reference Standard
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction and Quality Evaluation of the Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Meta-Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search Results
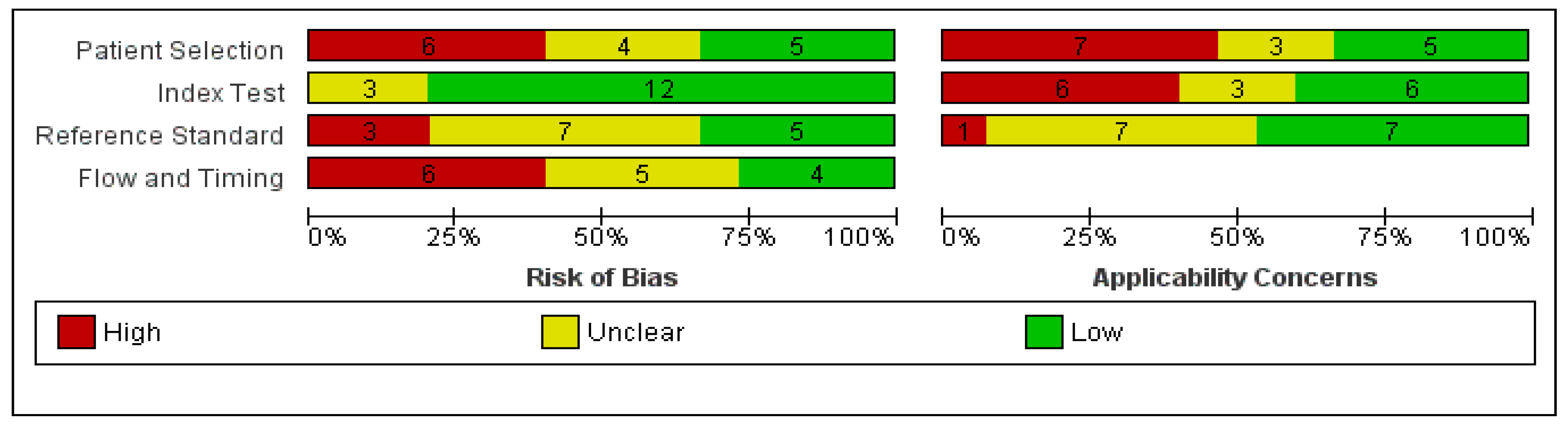
3.2. Quality Assessment of Study Reports
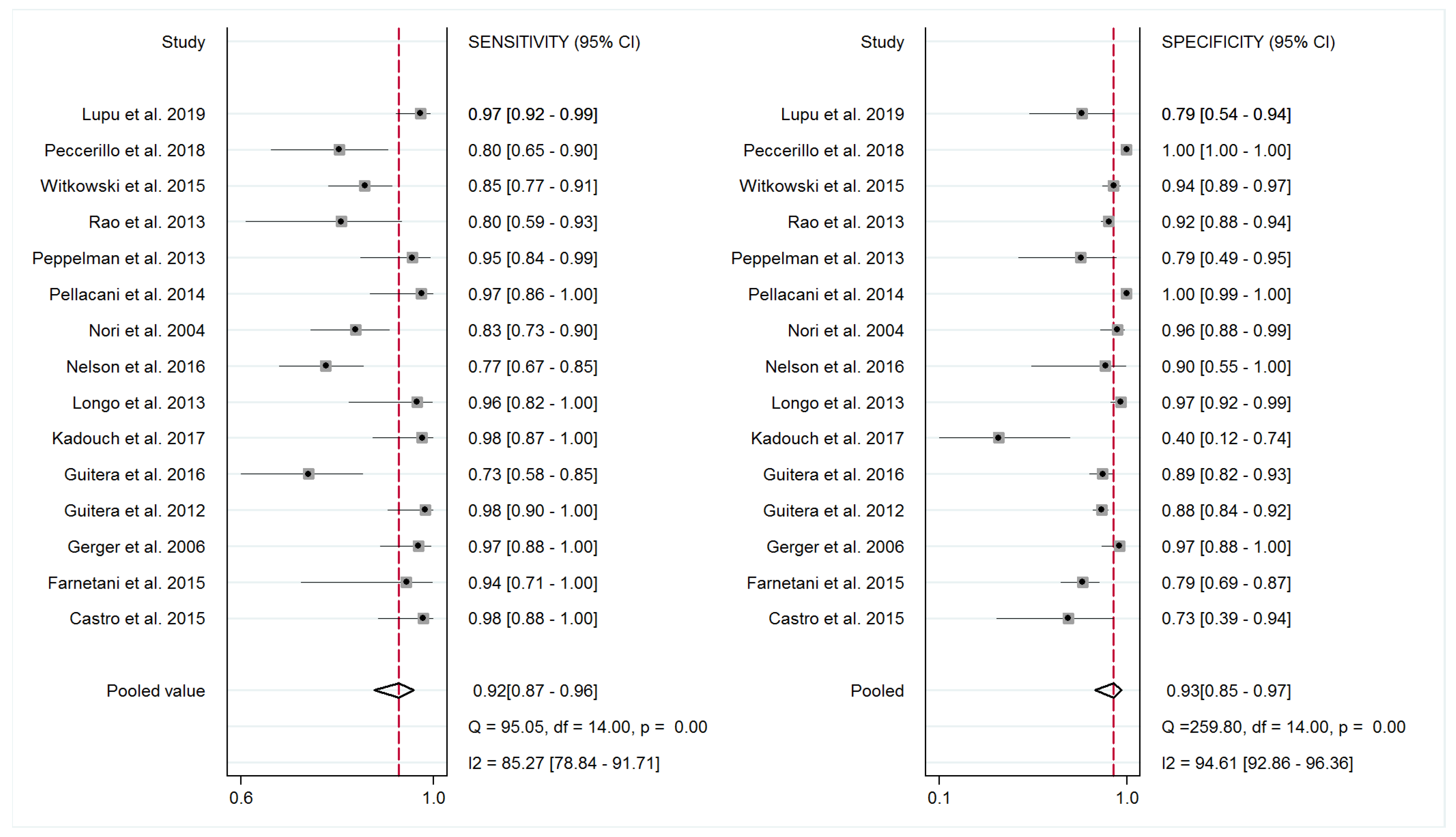
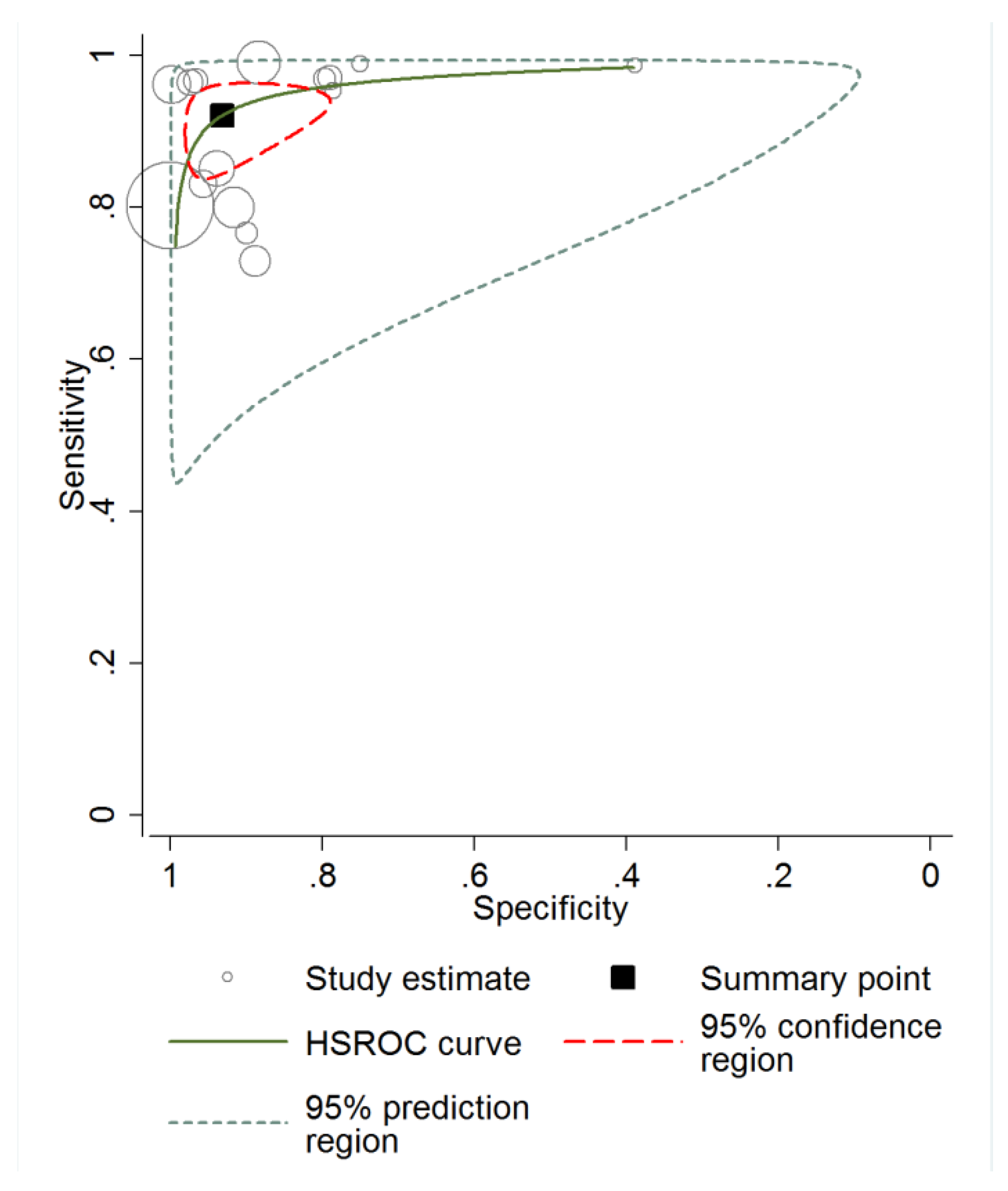
3.3. Diagnostic Accuracy of RCM and Meta-Analysis
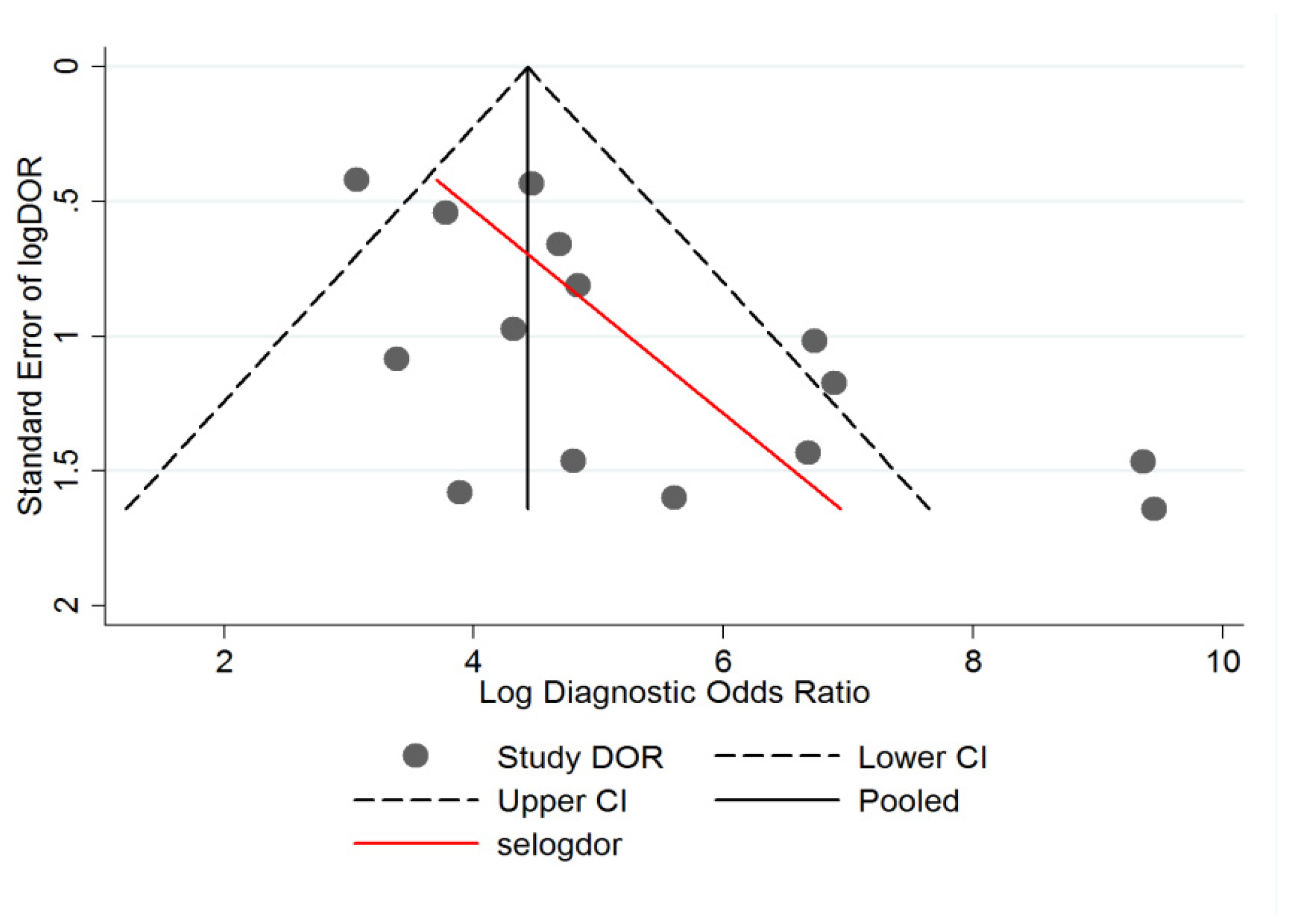
3.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
4. Discussion
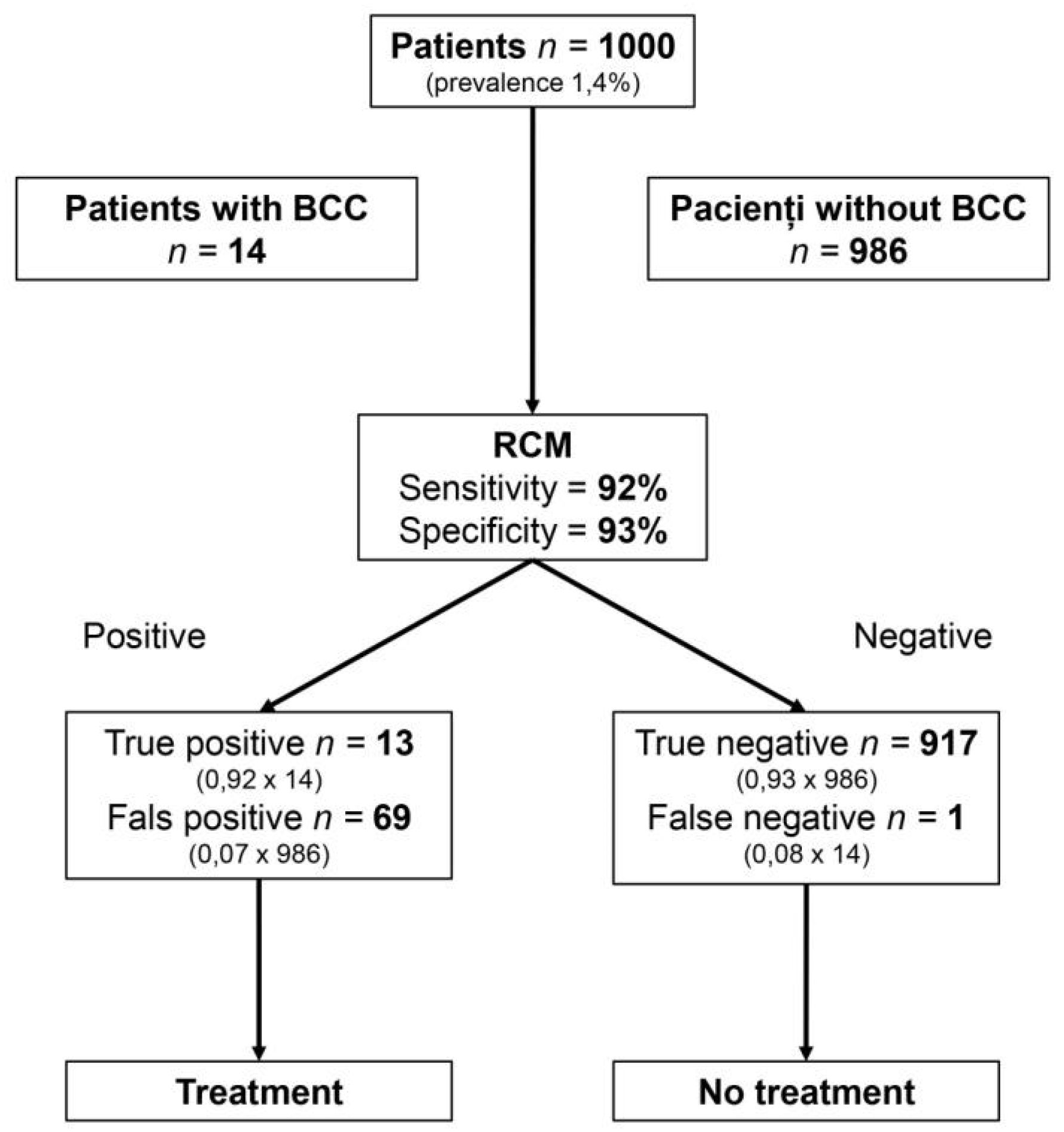
5. Clinical Relevance
6. Strengths and Limitations
7. Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birch-Johansen, F.; Jensen, A.; Mortensen, L.; Olesen, A.B.; Kjaer, S.K. Trends in the incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer in denmark 1978–2007: Rapid incidence increase among young danish women. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.L.; Weinstock, M.A. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in the united states: Incidence. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1994, 30, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakatelli, M.; Ulrich, C.; del Marmol, V.; Euvrard, S.; Stockfleth, E.; Abeni, D. Epidemiology of nonmelanoma skin cancer (nmsc) in europe: Accurate and comparable data are needed for effective public health monitoring and interventions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156 (Suppl. 3), 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagheorghe, L.M.L.; Lupu, M.; Pehoiu, A.G.; Voiculescu, V.M.; Giurcaneanu, C. Basal cell carcinoma—Increasing incidence leads to global health burden. RoJCED 2015, 2, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kadouch, D.J.; Leeflang, M.M.; Elshot, Y.S.; Longo, C.; Ulrich, M.; van der Wal, A.C.; Wolkerstorfer, A.; Bekkenk, M.W.; de Rie, M.A. Diagnostic accuracy of confocal microscopy imaging vs. Punch biopsy for diagnosing and subtyping basal cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučinskienė, V.; Samulėnienė, D.; Gineikienė, A.; Raišutis, R.; Kažys, R.; Valiukevičienė, S. Preoperative assessment of skin tumor thickness and structure using 14-mhz ultrasound. Medicina 2014, 50, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuke, S.; Vogler, N.; Meyer, T.; Akimov, D.; Kluschke, F.; Röwert-Huber, H.-J.; Lademann, J.; Dietzek, B.; Popp, J. Detection and discrimination of non-melanoma skin cancer by multimodal imaging. Healthcare 2013, 1, 64–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahradyan, A.; Howell, A.C.; Wolfswinkel, E.M.; Tsuha, M.; Sheth, P.; Wong, A.K. Updates on the management of non-melanoma skin cancer (nmsc). Healthcare 2017, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconeasa, A.; Boda, D.; Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Căruntu, C.; Vlădău, L.; Guţu, D. The role of confocal microscopy in the dermato–oncology practice. J. Med. Life 2011, 4, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Ilie, M.A.; Caruntu, C.; Lupu, M.; Lixandru, D.; Georgescu, S.-R.; Bastian, A.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M.; Zurac, S.A.; Boda, D. Current and future applications of confocal laser scanning microscopy imaging in skin oncology. Oncol. Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajadhyaksha, M.; Grossman, M.; Esterowitz, D.; Webb, R.H.; Anderson, R.R. In vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy of human skin: Melanin provides strong contrast. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruntu, C.; Boda, D.; Gutu, D.E.; Caruntu, A. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of basal cell carcinoma with cystic degeneration. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghita, M.A.; Caruntu, C.; Rosca, A.E.; Kaleshi, H.; Caruntu, A.; Moraru, L.; Docea, A.O.; Zurac, S.; Boda, D.; Neagu, M.; et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy and dermoscopy for in vivo, non-invasive skin imaging of superficial basal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaišnorienė, I.; Rotomskis, R.; Kulvietis, V.; Eidukevičius, R.; Žalgevičienė, V.; Laurinavičienė, A.; Venius, J.; Didžiapetrienė, J. Nevomelanocytic atypia detection by in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy. Medicina 2014, 50, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupu, M.; Caruntu, C.; Solomon, I.; Popa, A.; Lisievici, C.; Draghici, C.; Papagheorghe, L.; Voiculescu, V.M.; Giurcaneanu, C. The use of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy and dermoscopy in the preoperative determination of basal cell carcinoma histopathological subtypes. DermatoVenerol. 2017, 62, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lupu, M.; Caruntu, A.; Caruntu, C.; Boda, D.; Moraru, L.; Voiculescu, V.; Bastian, A. Non-invasive imaging of actinic cheilitis and squamous cell carcinoma of the lip. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 8, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupu, M.; Căruntu, A.; Moraru, L.; Voiculescu, V.M.; Boda, D.; Tănase, C.; Căruntu, C. Non-invasive imaging techniques for early diagnosis of radiation-induced squamous cell carcinoma of the lip. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Lupu, M.; Cãruntu, C.; Vâjâitu, C.; Solomon, I.; Voiculescu, V.M.; Popa, M.I.; Drãghici, C.; Giurcãneanu, C. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of spoke-wheel structures in a pigmented basal cell carcinoma. Case report. DermatoVenerol 2019, 64, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lupu, M.; Popa, I.M.; Voiculescu, V.M.; Boda, D.; Caruntu, C.; Zurac, S.; Giurcaneanu, C. A retrospective study of the diagnostic accuracy of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy for basal cell carcinoma diagnosis and subtyping. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S. Clinical applications of reflectance confocal microscopy in the management of cutaneous tumors. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2008, 99, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Niemeyer, A.; Berkes, B.; Marra, D.; Schanbacher, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Owens, M.; Morgan, B. 5% imiquimod cream and reflectance-mode confocal microscopy as adjunct modalities to mohs micrographic surgery for treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol. Surg. 2004, 30, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marra, D.E.; Torres, A.; Schanbacher, C.F.; Gonzalez, S. Detection of residual basal cell carcinoma by in vivo confocal microscopy. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlgrimm-Siess, V.; Horn, M.; Koller, S.; Ludwig, R.; Gerger, A.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R. Monitoring efficacy of cryotherapy for superficial basal cell carcinomas with in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy: A preliminary study. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 53, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, M.; Zanca, A.; Calzavara-Pinton, P. In vivo non-invasive evaluation of actinic keratoses response to methyl-aminolevulinate-photodynamic therapy (mal-pdt) by reflectance confocal microscopy. Cosmetics 2014, 1, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, R.G.; Jensen, D.; Suarez, A.L.; Hanson, A.H.; McLaughlin, L.; Duke, J.; Dellavalle, R.P. Outpatient follow-up and secondary prevention for melanoma patients. Cancers 2010, 2, 1178–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianoși, S.L.; Forsea, A.M.; Lupu, M.; Ilie, M.A.; Zurac, S.; Boda, D.; Ianosi, G.; Neagoe, D.; Tutunaru, C.; Popa, C.M. Role of modern imaging techniques for the in vivo diagnosis of lichen planus. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruntu, C.; Boda, D. Evaluation through in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of the cutaneous neurogenic inflammatory reaction induced by capsaicin in human subjects. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 085003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Căruntu, C.; Boda, D.; Căruntu, A.; Rotaru, M.; Baderca, F.; Zurac, S. In vivo imaging techniques for psoriatic lesions. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lacarrubba, F.; Verzi, A.E.; Errichetti, E.; Stinco, G.; Micali, G. Darier disease: Dermoscopy, confocal microscopy, and histologic correlations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, e97–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, A.-M.; Ilie, M.-A.; Chitu, V.; Razvan, A.; Lixandru, D.; Tanase, C.; Boda, D.; Caruntu, C.; Zurac, S. In vivo diagnosis of primary cutaneous amyloidosis—The role of reflectance confocal microscopy. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazzaro, G.; Farnetani, F.; Moltrasio, C.; Passoni, E.; Pellacani, G.; Berti, E. Image gallery: Demodex folliculorum longitudinal appearance with reflectance confocal microscopy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacarrubba, F.; Verzì, A.E.; Micali, G. Detailed analysis of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy for sarcoptes scabiei hominis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 350, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinotti, E.; Perrot, J.; Labeille, B.; Cambazard, F. Reflectance confocal microscopy for cutaneous infections and infestations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The prisma statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, T.A.; Alabousi, M.; Skidmore, B.; Korevaar, D.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; Moher, D.; Thombs, B.; McInnes, M.D.F. Recommendations for reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M. Quadas-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeflang, M.M.G. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, J.J.; Macaskill, P.; Irwig, L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2005, 58, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nori, S.; Rius-Díaz, F.; Cuevas, J.; Goldgeier, M.; Jaen, P.; Torres, A.; González, S. Sensitivity and specificity of reflectance-mode confocal microscopy for in vivo diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma: A multicenter study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerger, A.; Koller, S.; Weger, W.; Richtig, E.; Kerl, H.; Samonigg, H.; Krippl, P.; Smolle, J. Sensitivity and specificity of confocal laser-scanning microscopy for in vivo diagnosis of malignant skin tumors. Cancer 2006, 107, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitera, P.; Menzies, S.W.; Longo, C.; Cesinaro, A.M.; Scolyer, R.A.; Pellacani, G. In vivo confocal microscopy for diagnosis of melanoma and basal cell carcinoma using a two-step method: Analysis of 710 consecutive clinically equivocal cases. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, C.; Farnetani, F.; Ciardo, S.; Cesinaro, A.M.; Moscarella, E.; Ponti, G.; Zalaudek, I.; Argenziano, G.; Pellacani, G. Is confocal microscopy a valuable tool in diagnosing nodular lesions? A study of 140 cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppelman, M.; Wolberink, E.A.; Blokx, W.A.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.; van Erp, P.E.; Gerritsen, M.J. In vivo diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma subtype by reflectance confocal microscopy. Dermatology 2013, 227, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, B.K.; Mateus, R.; Wassef, C.; Pellacani, G. In vivo confocal microscopy in clinical practice: Comparison of bedside diagnostic accuracy of a trained physician and distant diagnosis of an expert reader. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, e295–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellacani, G.; Pepe, P.; Casari, A.; Longo, C. Reflectance confocal microscopy as a second-level examination in skin oncology improves diagnostic accuracy and saves unnecessary excisions: A longitudinal prospective study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.P.; Stephens, A.; Fraga-Braghiroli, N.A.; Oliviero, M.C.; Rezze, G.G.; Rabinovitz, H.; Scope, A. Accuracy of in vivo confocal microscopy for diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma: A comparative study between handheld and wide-probe confocal imaging. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnetani, F.; Scope, A.; Braun, R.P.; Gonzalez, S.; Guitera, P.; Malvehy, J.; Manfredini, M.; Marghoob, A.A.; Moscarella, E.; Oliviero, M. Skin cancer diagnosis with reflectance confocal microscopy: Reproducibility of feature recognition and accuracy of diagnosis. JAMA Dermatol 2015, 151, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitera, P.; Menzies, S.W.; Argenziano, G.; Longo, C.; Losi, A.; Drummond, M.; Scolyer, R.A.; Pellacani, G. Dermoscopy and in vivo confocal microscopy are complementary techniques for diagnosis of difficult amelanotic and light-coloured skin lesions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.A.; Scope, A.; Rishpon, A.; Rabinovitz, H.S.; Oliviero, M.C.; Laman, S.D.; Cole, C.M.; Chang, Y.H.H.; Swanson, D.L. Accuracy and confidence in the clinical diagnosis of basal cell cancer using dermoscopy and reflex confocal microscopy. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, A.; Łudzik, J.; DeCarvalho, N.; Ciardo, S.; Longo, C.; DiNardo, A.; Pellacani, G. Non-invasive diagnosis of pink basal cell carcinoma: How much can we rely on dermoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy? Skin Res. Technol. 2016, 22, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, F.; Mandel, V.D.; Di Tullio, F.; Ciardo, S.; Chester, J.; Kaleci, S.; de Carvalho, N.; Del Duca, E.; Giannetti, L.; Mazzoni, L.; et al. Lesions mimicking melanoma at dermoscopy confirmed basal cell carcinoma: Evaluation with reflectance confocal microscopy. Dermatology 2018, 235, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbord, R.M.; Whiting, P. Metandi: Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy using hierarchical logistic regression. Stata J. 2009, 9, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellacani, G.; Vinceti, M.; Bassoli, S.; Braun, R.; Gonzalez, S.; Guitera, P.; Longo, C.; Marghoob, A.A.; Menzies, S.W.; Puig, S.; et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy and features of melanocytic lesions: An internet-based study of the reproducibility of terminologyfeatures of melanocytic lesions. Arch. Dermatol. 2009, 145, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van Dijk, A.; den Outer, P.N.; Slaper, H. Climate and Ozone Change Effects on Ultraviolet Radiation and Risks (Coeur) Using and Validating Earth Observation. Available online: http://www.rivm.nl/dsresource?objectid=rivmp:9586&type=org&disposition=inline&ns_nc=1 (accessed on 6 July 2019).
- Leiter, U.; Eigentler, T.; Garbe, C. Epidemiology of skin cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 810, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, C.A.; Chen, A.C.; Choy, B.; Fernandez-Penas, P.; Damian, D.L.; Scolyer, R.A. Classification of high risk basal cell carcinoma subtypes: Experience of the ontrac study with proposed definitions and guidelines for pathological reporting. Pathology 2016, 48, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trakatelli, M.; Morton, C.; Nagore, E.; Ulrich, C.; Del Marmol, V.; Peris, K.; Basset-Seguin, N. Update of the european guidelines for basal cell carcinoma management. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2014, 24, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.F.; Korevaar, D.A.; Altman, D.G.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Hooft, L.; Irwig, L.; Levine, D.; Reitsma, J.B.; de Vet, H.C.W.; et al. Stard 2015 guidelines for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


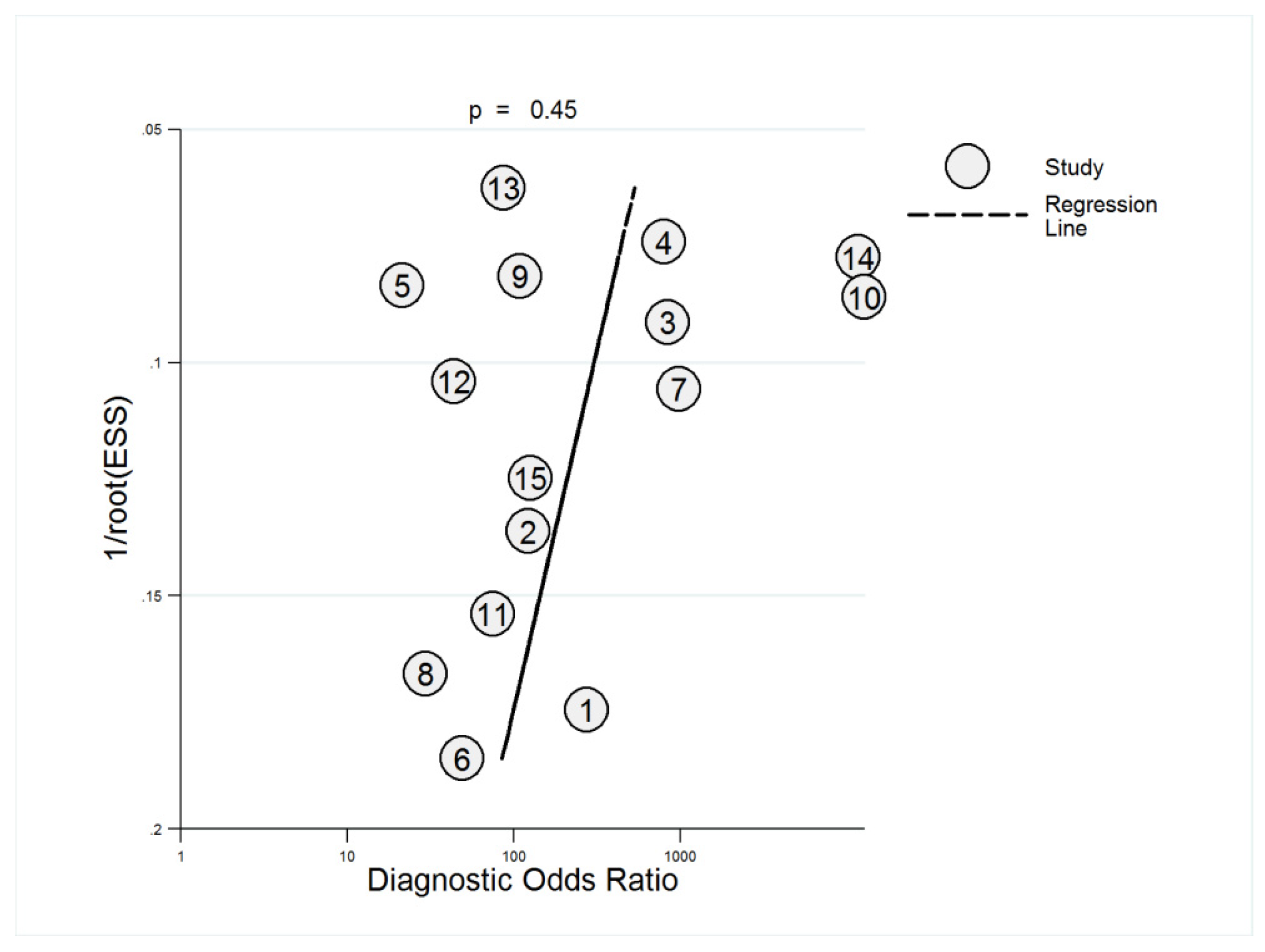
| Author, Year, [Reference] | Country | No. of Centers | Study Design | Types of Lesion | No. of Investigators | Experience Level | Reference Standard | RCM device | No.of Patients (M/F) | Age (Mean/ Median) | No. of Lesions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Castro et al. 2015 [46] | Brazil&USA | 2 | prospective | BCC | 2 | low | histopathology (incisional) | VivaScope 1500 | 32 (20/12) | 65 | 54 |
| Gerger et al. 2006 [40] | Austria | 1 | prospective | melanoma, BCC, nevi, SebK | 4 | low | clinic & histopathology (excisional) | VivaScope 1500 | 119 (62/57) | n/a | 120 |
| Guitera et al. 2012 [41] | Australia&Italy | 2 | prospective | melanoma, BCC, SCC, nevi | 2 | high | histopathology (excisional) | VivaScope 1000&1500 | 663 (354/309) | 53 | 710 |
| Longo et al. 2013 [42] | Italy | 2 | retrospective | melanoma, BCC, SCC, nevi, SebK, DF | 1 | high | histopathology (n/a) | VivaScope 1000&1500 | 140 (64/76) | 50 | 140 |
| Nori et al. 2004 [39] | USA&Spain | 4 | retrospective | BCC, various others | 1 | low | clinical & histopathology (incisional) | VivaScope 1000 & Wellman Laboratories prototype | 145 (n/a) | n/a | 152 |
| Peppelman et al. 2013 [43] | Netherlands | 1 | prospective | BCC | n/a | n/a | histopathology (incisional) | VivaScope 1500 | 27 (16/11) | 66 | 57 |
| Rao et al. 2013 [44] | USA | 1 | retrospective | melanoma, BCC, various benign | 2 | low | histopathology (incisional) | VivaScope 1500 | n/a | n/a | 334 |
| Pellacani et al. 2014 [45] | Italy | 1 | prospective | melanoma, BCC, various benign | 1 | n/a | histopathology (excisional) | VivaScope 1500 | 408 | 41 | 292 |
| Farnetani et al. 2015 [47] | Italy | 1 | retrospective | melanoma, BCC, AKs, various benign | 9 | high & low | histopathology (n/a) | VivaScope 1500 | n/a | n/a | 100 |
| Guitera et al. 2016 [48] | Australia&Italy | 3 | retrospective | melanoma, BCC, AKs, various benign | 1 | high | histopathology (excisional) | VivaScope 1500 | n/a | 54.8 | 191 |
| Kadouch et al. 2017 [5] | Netherlands | 2 | prospective | BCC | 2 | low | histopathology (excisional) | VivaScope 1500 | 46 | 64 | 46 |
| Nelson et al. 2016 [49] | USA | 1 | prospective | BCC | 8 | low | histopathology (biopsy) | VivaScope 1500 | 87 (65/22) | 73 | 100 |
| Witkowski et al. 2015 [50] | Italy | 1 | retrospective | BCC, melanoma, SCC, various benign | 1 | n/a | histopathology (n/a) | VivaScope 1500 | n/a | n/a | 260 |
| Peccerillo et al. 2018 [51] | Italy | 1 | retrospective | BCC, melanoma, SCC, SebK, DF | 2 | high | histopathology (n/a) | VivaScope 1500 | n/a | n/a | 1484 |
| Lupu et al. 2019 [19] | Romania | 2 | retrospective | BCC, SCC, AKs, Bowen’s disease, various benign | 2 | high | histopathology (excisional) | VivaScope 1500 | 87 (36/51) | 68.1 | 123 |
| Author, Year, [Reference] | Reflectance Confocal Microscopic Criteria |
|---|---|
| Castro et al. 2015 [46] | hyporefractile silhouettes, tumor islands, epidermal streaming, peripheral palisading, peri-tumoral clefting, peri-tumoral collagen bundles, increased vascularization, dendritic structures |
| Gerger et al. 2006 [40] | increased vascularization, epidermal streaming, peri-tumoral collagen bundles |
| Guitera et al. 2012 [41] | epidermal streaming, dilated horizontal blood vessels, basaloid cord or nodule, epidermal shadow, glomerular vessels, non-visible dermal papillae, epidermal disarray, dendritic structures, peri-tumoral clefting, cells with visible nuclei inside tumor islands |
| Longo et al. 2013 [42] | epidermal disarray, ulceration or erosion, cauliflower architecture, hyporefractile silhouettes, bright filaments inside tumor islands, increased vascularization, inflammatory infiltrate |
| Nori et al. 2004 [39] | elongated monomorphic nuclei, inflammatory infiltrate, increased vascularization, epidermal pleomorphism |
| Peppelman et al. 2013 [43] | tumor islands, peri-tumoral clefting, peripheral palisading, elongated and polarized nuclei, keratinocyte atypia and spongiosis, solar elastosis, increased vascularization, inflammatory infiltrate, leukocyte rolling |
| Rao et al. 2013 [44] | diagnostic criteria not specified |
| Pellacani et al. 2014 [45] | diagnostic criteria not specified |
| Farnetani et al. 2015 [47] | basaloid cords, ulceration, disarray at the dermal-epidermal junction |
| Guitera et al. 2016 [48] | epidermal streaming, basaloid cord or nodule, peri-tumoral fibrilar polarized pattern, peri-tumoral clefting, epidermal shadow, dark nodules, dilated horizontal blood vessels, glomerular vessels |
| Kadouch et al. 2017 [5] | diagnostic criteria not specified |
| Nelson et al. 2016 [49] | tumor islands, peri-tumoral clefting, hyporefractile silhouettes, canalicular vessels, dendritic cells |
| Witkowski et al. 2015 | diagnostic criteria not specified |
| Peccerillo et al. 2018 [51] | mild keratinocyte atypia, streaming epidermis, cords connected to the epidermis, dark silhouettes, peri-tumoral clefts, ulceration/erosion, tumor island size and location (epidermal or dermal), branch-like structures in tumor island, peripheral palisading, vascular morphology (linear or coiled vessels) and diameter, collagen surrounding tumor islands, solar elastosis and inflammatory infiltrates |
| Lupu et al. 2019 [19] | keratinocyte atypia, epidermal streaming, ulceration, cords connected to the epidermis, small tumor islands (diameter <300 m), large tumor islands (diameter >300 m), hyporefractile silhouettes, peripheral palisading, clefting, increased vascularization, “onion-like” structures, peri-tumoral collagen bundles, inflammation represented by bright dots and plump bright cells, and dendritic cells inside tumor islands |
| Covariate | Coefficient | Standard Error | p | RDOR | (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | 2.236 | 0.9 | 0.037 | 9.35 | (1.17; 74.56) |
| RCM device | −0.838 | 1.09 | 0.46 | 0.43 | (0,03; 5.38) |
| Reference standard | 1.184 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 3.27 | (0.93; 11.47) |
| Investigator experience | 0.067 | 0.59 | 0.91 | 1.07 | (0.27; 4.2) |
| Number of centers | 0.561 | 0.79 | 0.5 | 1.75 | (0.28; 10.98) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lupu, M.; Popa, I.M.; Voiculescu, V.M.; Caruntu, A.; Caruntu, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Accuracy of in Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091462
Lupu M, Popa IM, Voiculescu VM, Caruntu A, Caruntu C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Accuracy of in Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(9):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091462
Chicago/Turabian StyleLupu, Mihai, Iris Maria Popa, Vlad Mihai Voiculescu, Ana Caruntu, and Constantin Caruntu. 2019. "A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Accuracy of in Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 9: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091462
APA StyleLupu, M., Popa, I. M., Voiculescu, V. M., Caruntu, A., & Caruntu, C. (2019). A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Accuracy of in Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(9), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091462








