Suppressive Role of Androgen/Androgen Receptor Signaling via Chemokines on Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
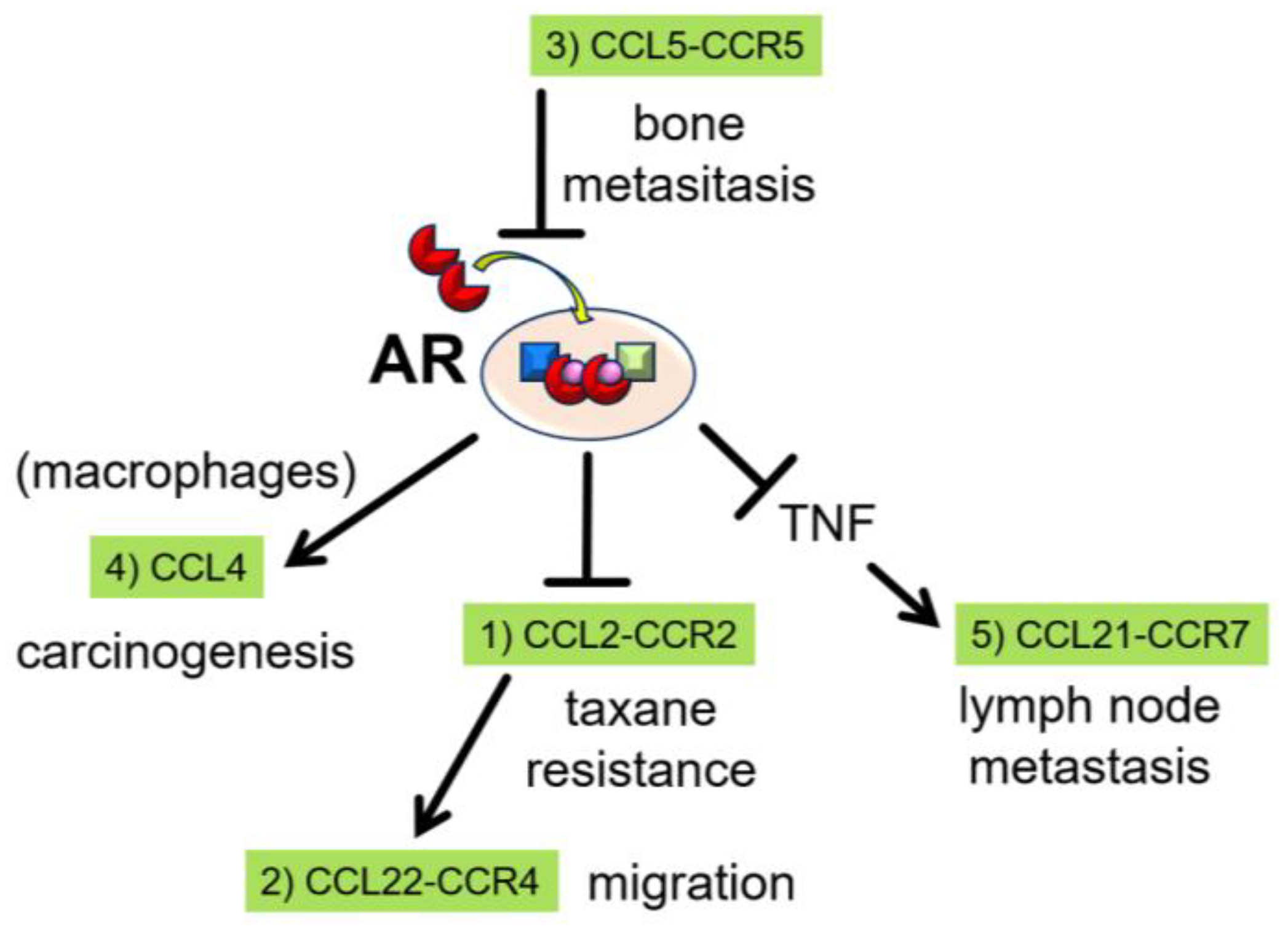
1. Introduction
2. The Role of CCL2 as a Downstream Mediator of Androgen/AR Signaling
3. The Role of CCL22 as a Further Downstream Mediator of CCL2
4. The Role of CCL5 as an Upstream Mediator of Androgen/AR Signaling
5. Treatment Strategies Targeting CCL-CCR Axes and Androgen/AR Signaling
5.1. CCL2-CCR2 Axis
5.2. CCL22-CCR4 Axis
5.3. CCL5-CCR5 Axis and Others
6. CCL Involvement Various Pathways of Prostate Cancer Progression
6.1. Carcinogenesis
6.2. Lymph Node Metastasis
6.3. Resistance to Taxanes
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | androgen receptor |
| ADT | androgen-deprivation therapy |
| CRPC | castration-resistant prostate cancer |
| CCL | C-C motif ligand |
| CCR | CCL-receptor |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| siAR | AR-siRNA |
| scr | scramble RNA |
| TAMs | tumor-associated macrophages |
| Tregs | regulatory T cells |
| TGF β1 | transforming growth factor-β1 |
| Thr308 | threonine 308 |
| Ser473 | serine 473 |
| ATL | adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma |
| TNF | tumor necrotic factor |
| PARP | poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Parkin, D.M.; Steliarova-Foucher, E. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximum androgen blockade in advanced prostate cancer: An overview of the randomised trials. Prostate Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet 2000, 355, 1491–1498.
- Samson, D.J.; Seidenfeld, J.; Schmitt, B.; Hasselblad, V.; Albertsen, P.C.; Bennett, C.L.; Wilt, T.J.; Aronson, N. Systematic review and meta-analysis of monotherapy compared with combined androgen blockade for patients with advanced prostate carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 95, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, H.I.; Sawyers, C.L. Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: Directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8253–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, T.; Yang, J.C.; Gao, A.C.; Evans, C.P. Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Altuwaijri, S.; Lai, K.P.; Wu, C.T.; Ricke, W.A.; Messing, E.M.; Yao, J.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Androgen receptor is a tumor suppressor and proliferator in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12182–12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, K.; Fang, L.Y.; Mizokami, A.; Namiki, M.; Li, L.; Lin, W.J.; Chang, C. Targeting the androgen receptor with siRNA promotes prostate cancer metastasis through enhanced macrophage recruitment via CCL2/CCR2-induced STAT3 activation. EMBO. Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.H.; Izumi, K.; Lee, S.O.; Lin, W.J.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Anti-androgen receptor ASC-J9 versus anti-androgens MDV3100 (Enzalutamide) or Casodex (Bicalutamide) leads to opposite effects on prostate cancer metastasis via differential modulation of macrophage infiltration and STAT3-CCL2 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A.; Lin, H.P.; Ho, H.M.; Iwamoto, H.; Maolake, A.; Natsagdorj, A.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kadono, Y.; Miyamoto, H.; et al. Serum chemokine (CC motif) ligand 2 level as a diagnostic, predictive, and prognostic biomarker for prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8389–8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maolake, A.; Izumi, K.; Shigehara, K.; Natsagdorj, A.; Iwamoto, H.; Kadomoto, S.; Takezawa, Y.; Machioka, K.; Narimoto, K.; Namiki, M.; et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote prostate cancer migration through activation of the CCL22-CCR4 axis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9739–9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urata, S.; Izumi, K.; Hiratsuka, K.; Maolake, A.; Natsagdorj, A.; Shigehara, K.; Iwamoto, H.; Kadomoto, S.; Makino, T.; Naito, R.; et al. C-C motif ligand 5 promotes migration of prostate cancer cells in the prostate cancer bone metastasis microenvironment. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.P.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Nelson, P.S.; Montgomery, B. Androgen deprivation therapy: Progress in understanding mechanisms of resistance and optimizing androgen depletion. Nat. Clin. Pract. Urol. 2009, 6, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, S.; Cookson, M.S. Mechanisms leading to the development of hormone-resistant prostate cancer. Urol. Clin. North. Am. 2006, 33, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, M.; Hara, T.; Kusaka, M. Overcoming persistent dependency on androgen signaling after progression to castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4319–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalla, A.K.; Estes, N.; Patel, J.; Rao, J.S. N-cadherin mediates angiogenesis by regulating monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression via PI3K/Akt signaling in prostate cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junicho, A.; Matsuda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kishi, H.; Korkmaz, K.; Saatcioglu, F.; Fuse, H.; Muraguchi, A. Protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 regulates androgen receptor signaling in prostate carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 278, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl, P.; Alexander, S. Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: Plasticity and reciprocity. Cell 2011, 147, 992–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulghani, J.; Gu, L.; Dagvadorj, A.; Lutz, J.; Leiby, B.; Bonuccelli, G.; Lisanti, M.P.; Zellweger, T.; Alanen, K.; Mirtti, T.; et al. Stat3 promotes metastatic progression of prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azare, J.; Leslie, K.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Gerald, W.; Weinreb, P.H.; Violette, S.M.; Bromberg, J. Constitutively activated Stat3 induces tumorigenesis and enhances cell motility of prostate epithelial cells through integrin beta 6. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 4444–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, B.E.; Leong, K.G.; Yue, P.; Li, L.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Chen, D.; Seo, K.; Modrusan, Z.; Gao, W.Q.; Settleman, J.; et al. Androgen deprivation causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the prostate: Implications for androgen-deprivation therapy. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, K.; Larsen, C.G.; DuBois, G.C.; Oppenheim, J.J. Purification and characterization of a novel monocyte chemotactic and activating factor produced by a human myelomonocytic cell line. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 169, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loberg, R.D.; Ying, C.; Craig, M.; Yan, L.; Snyder, L.A.; Pienta, K.J. CCL2 as an important mediator of prostate cancer growth in vivo through the regulation of macrophage infiltration. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefetz-Sela, S.; Stein, I.; Klieger, Y.; Porat, R.; Sade-Feldman, M.; Zreik, F.; Nagler, A.; Pappo, O.; Quagliata, L.; Dazert, E.; et al. Acquisition of an immunosuppressive protumorigenic macrophage phenotype depending on c-Jun phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17582–17587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkhanud, P.B.; Baatar, D.; Bodogai, M.; Hakim, F.; Gress, R.; Anderson, R.L.; Deng, J.; Xu, M.; Briest, S.; Biragyn, A. Breast cancer lung metastasis requires expression of chemokine receptor CCR4 and regulatory T cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5996–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sozzani, S.; Locati, M.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A. Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends. Immunol. 2002, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.A.; Putzi, M.; Mucci, N.; Smith, D.C.; Wojno, K.; Korenchuk, S.; Pienta, K.J. Rapid (“warm”) autopsy study for procurement of metastatic prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A.; Li, Y.Q.; Narimoto, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Kadono, Y.; Kitagawa, Y.; Konaka, H.; Koh, E.; Keller, E.T.; et al. Tranilast inhibits hormone refractory prostate cancer cell proliferation and suppresses transforming growth factor beta1-associated osteoblastic changes. Prostate 2009, 69, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Pang, Y.; Moses, H.L. TGF-beta and immune cells: An important regulatory axis in the tumor microenvironment and progression. Trends. Immunol. 2010, 31, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, K.; Sud, S.; McGregor, N.A.; Martinovski, G.; Rice, B.T.; Craig, M.J.; Varsos, Z.S.; Roca, H.; Pienta, K.J. The chemokine CCL2 increases prostate tumor growth and bone metastasis through macrophage and osteoclast recruitment. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Loberg, R.; Liao, J.; Ying, C.; Snyder, L.A.; Pienta, K.J.; McCauley, L.K. A destructive cascade mediated by CCL2 facilitates prostate cancer growth in bone. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, R.; Irie, T.; Suzuki, K.; Sawada, T.; Miwa, N.; Sasaki, A.; Tsunoda, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Mishima, K. The beta-catenin signaling pathway induces aggressive potential in breast cancer by up-regulating the chemokine CCL5. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 338, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaday, G.G.; Peehl, D.M.; Kadam, P.A.; Lawrence, D.M. Expression of CCL5 (RANTES) and CCR5 in prostate cancer. Prostate 2006, 66, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Fujita, Y.; Nakane, K.; Mizutani, K.; Terazawa, R.; Ehara, H.; Kanimoto, Y.; Kojima, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Deguchi, T.; et al. CCR1/CCL5 interaction promotes invasion of taxane-resistant PC3 prostate cancer cells by increasing secretion of MMPs 2/9 and by activating ERK and Rac signaling. Cytokine 2013, 64, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ok Lee, S.; Liang, L.; Huang, C.K.; Li, L.; Wen, S.; Chang, C. Infiltrating bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells increase prostate cancer stem cell population and metastatic ability via secreting cytokines to suppress androgen receptor signaling. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Lee, S.O.; Cui, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, L.; Chang, C. Infiltrating bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) increase prostate cancer cell invasion via altering the CCL5/HIF2alpha/androgen receptor signals. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27555–27565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.R.; Slavin, S.; Da, J.; Hsu, I.; Luo, J.; Xiao, G.Q.; Ding, J.; Chou, F.J.; Yeh, S. Estrogen receptor α in cancer associated fibroblasts suppresses prostate cancer invasion via reducing CCL5, IL6 and macrophage infiltration in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pienta, K.J.; Machiels, J.P.; Schrijvers, D.; Alekseev, B.; Shkolnik, M.; Crabb, S.J.; Li, S.; Seetharam, S.; Puchalski, T.A.; Takimoto, C.; et al. Phase 2 study of carlumab (CNTO 888), a human monoclonal antibody against CC-chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Investig. New. Drugs. 2013, 31, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilums, M.; Zweemer, A.J.; Dekkers, S.; Askar, Y.; de Vries, H.; Saunders, J.; Stamos, D.; Brussee, J.; Heitman, L.H.; IJzerman, A.P. Design and synthesis of novel small molecule CCR2 antagonists: Evaluation of 4-aminopiperidine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5377–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junker, A.; Kokornaczyk, A.K.; Zweemer, A.J.; Frehland, B.; Schepmann, D.; Yamaguchi, J.; Itami, K.; Faust, A.; Hermann, S.; Wagner, S.; et al. Synthesis, binding affinity and structure-activity relationships of novel, selective and dual targeting CCR2 and CCR5 receptor antagonists. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 2407–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. AKT/PKB signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell 2007, 129, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assinder, S.J.; Dong, Q.; Kovacevic, Z.; Richardson, D.R. The TGF-beta, PI3K/Akt and PTEN pathways: Established and proposed biochemical integration in prostate cancer. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, P.K.; Sellers, W.R. Akt-regulated pathways in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7465–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, D.C.; Wu, K.; Kwok, A.W.; Wong, Y.H. G protein-coupled receptor-induced Akt activity in cellular proliferation and apoptosis. FEBS. J. 2007, 274, 6025–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loberg, R.D.; Day, L.L.; Harwood, J.; Ying, C.; St John, L.N.; Giles, R.; Neeley, C.K.; Pienta, K.J. CCL2 is a potent regulator of prostate cancer cell migration and proliferation. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loberg, R.D.; Ying, C.; Craig, M.; Day, L.L.; Sargent, E.; Neeley, C.; Wojno, K.; Snyder, L.A.; Yan, L.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting CCL2 with systemic delivery of neutralizing antibodies induces prostate cancer tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9417–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, H.; Varsos, Z.; Pienta, K.J. CCL2 protects prostate cancer PC3 cells from autophagic death via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-dependent survivin up-regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25057–25073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Utsunomiya, A.; Jo, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kato, K.; Yoshida, S.; Takemoto, S.; Suzushima, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Imaizumi, Y.; et al. Mogamulizumab for relapsed adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Updated follow-up analysis of phase I and II studies. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 2022–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Tobinai, K.; Tsukasaki, K.; Uike, N.; Uozumi, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Hanada, S.; Tamura, K.; et al. Phase I study of KW-0761, a defucosylated humanized anti-CCR4 antibody, in relapsed patients with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, C.; Roda, D.; Rosello, S.; Oliveira, M.; Macarulla, T.; Pérez-Fidalgo, J.A.; Morales-Barrera, R.; Sanchis-García, J.M.; Musib, L.; Budha, N.; et al. A First-in-Human Phase I Study of the ATP-Competitive AKT Inhibitor Ipatasertib Demonstrates Robust and Safe Targeting of AKT in Patients with Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Dent, R.; Im, S.A.; Espié, M.; Blau, S.; Tan, A.R.; Isakoff, S.J.; Oliveira, M.; Saura, C.; Wongchenko, M.J.; et al. Ipatasertib plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel as first-line therapy for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (LOTUS): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, H.; Izumi, K.; Natsagdorj, A.; Naito, R.; Makino, T.; Kadomoto, S.; Hiratsuka, K.; Shigehara, K.; Kadono, Y.; Narimoto, K.; et al. Coffee diterpenes kahweol acetate and cafestol synergistically inhibit the proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2019, 79, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.Y.; Izumi, K.; Lai, K.P.; Liang, L.; Li, L.; Miyamoto, H.; Lin, W.J.; Chang, C. Infiltrating macrophages promote prostate tumorigenesis via modulating androgen receptor-mediated CCL4-STAT3 signaling. Cancer. Res. 2013, 73, 5633–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, K.; Li, L.; Chang, C. Androgen receptor and immune inflammation in benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Clin. Investig. 2014, 4, 935–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.S.; Nastiuk, K.L.; Krolewski, J.J. TNF is necessary for castration-induced prostate regression, whereas TRAIL and FasL are dispensable. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maolake, A.; Izumi, K.; Natsagdorj, A.; Iwamoto, H.; Kadomoto, S.; Makino, T.; Naito, R.; Shigehara, K.; Kadono, Y.; Hiratsuka, K.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces prostate cancer cell migration in lymphatic metastasis through CCR7 upregulation. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, F.; Gardner, D.H.; Nayar, S.; Steinthal, N.; Buckley, C.D.; Luther, S.A. Stromal Fibroblasts in Tertiary Lymphoid Structures: A Novel Target in Chronic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bono, J.S.; Oudard, S.; Ozguroglu, M.; Hansen, S.; Machiels, J.P.; Kocak, I.; Gravis, G.; Bodrogi, I.; Mackenzie, M.J.; Shen, L.; et al. Prednisone plus cabazitaxel or mitoxantrone for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing after docetaxel treatment: A randomised open-label trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machioka, K.; Izumi, K.; Kadono, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Naito, R.; Makino, T.; Kadomoto, S.; Natsagdorj, A.; Keller, E.T.; Zhang, J.; et al. Establishment and characterization of two cabazitaxel-resistant prostate cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16185–16196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsagdorj, A.; Izumi, K.; Hiratsuka, K.; Machioka, K.; Iwamoto, H.; Naito, R.; Makino, T.; Kadomoto, S.; Shigehara, K.; Kadono, Y.; et al. CCL2 induces resistance to the antiproliferative effect of cabazitaxel in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. Suppressive Role of Androgen/Androgen Receptor Signaling via Chemokines on Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030354
Izumi K, Mizokami A. Suppressive Role of Androgen/Androgen Receptor Signaling via Chemokines on Prostate Cancer Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(3):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030354
Chicago/Turabian StyleIzumi, Kouji, and Atsushi Mizokami. 2019. "Suppressive Role of Androgen/Androgen Receptor Signaling via Chemokines on Prostate Cancer Cells" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 3: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030354
APA StyleIzumi, K., & Mizokami, A. (2019). Suppressive Role of Androgen/Androgen Receptor Signaling via Chemokines on Prostate Cancer Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(3), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030354




