Tacrolimus Modulates TGF-β Signaling to Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells
Abstract
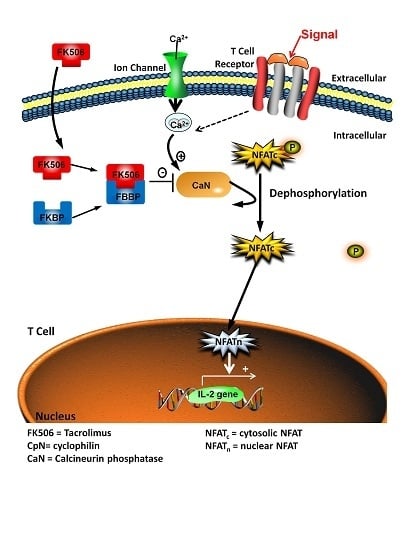
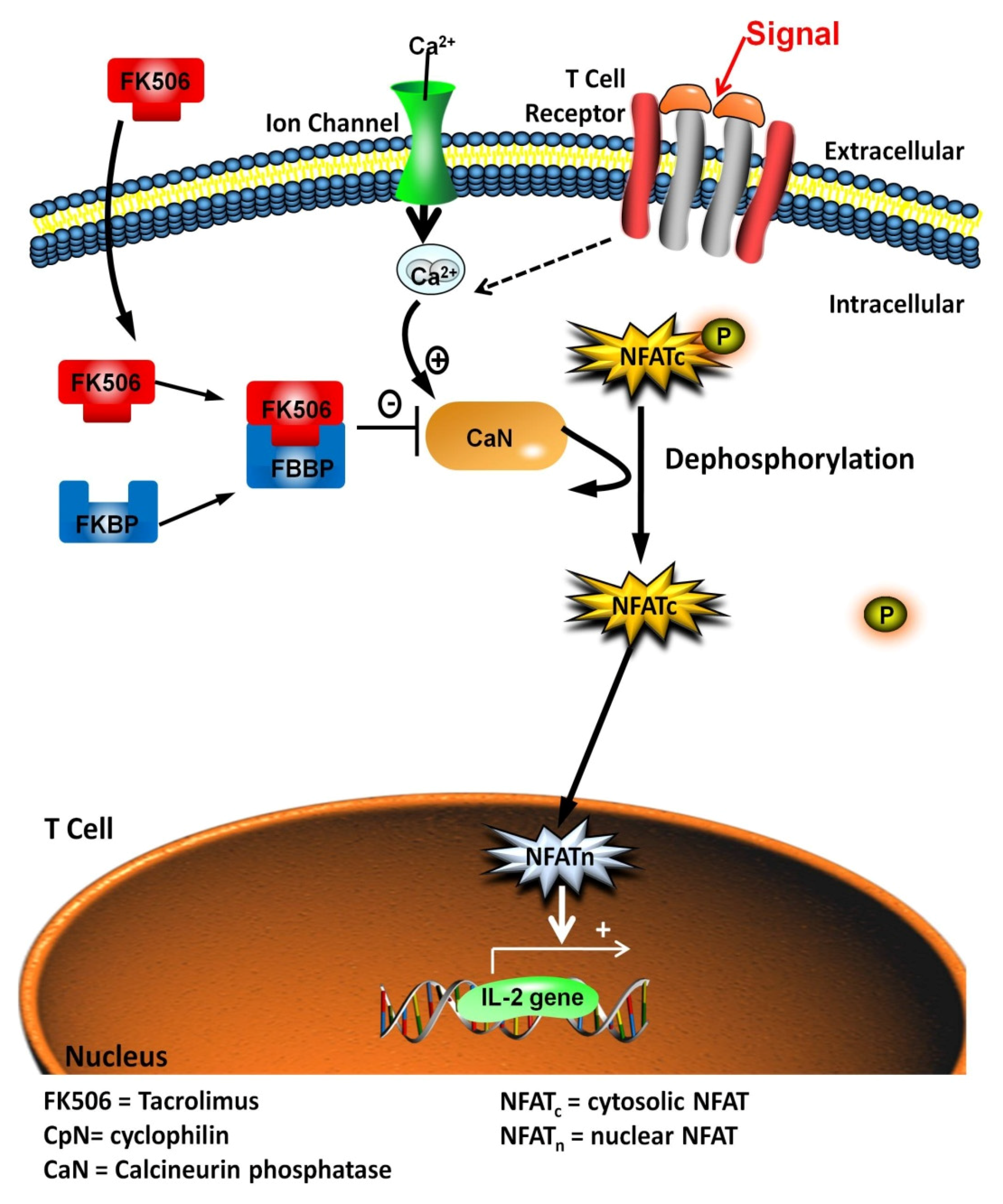
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
3. Results and Discussion
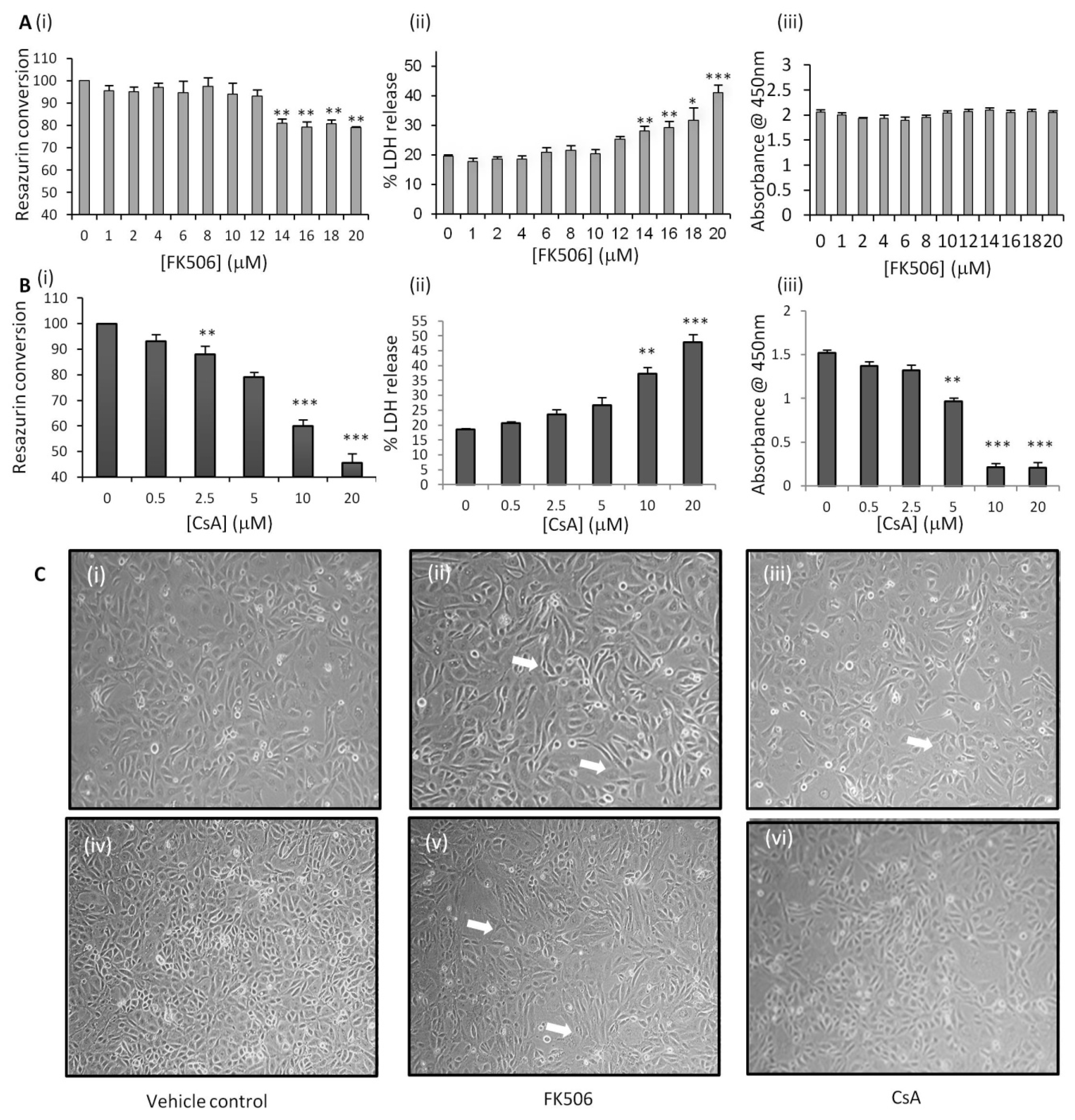
3.1. FK506 Treatment Resulted in Significant Increases in Both LDH Release and Resazurin Conversion Without Affecting RPTEC Proliferation
3.2. FK506 Treatment Induced Morphological Alterations in the RPTECs
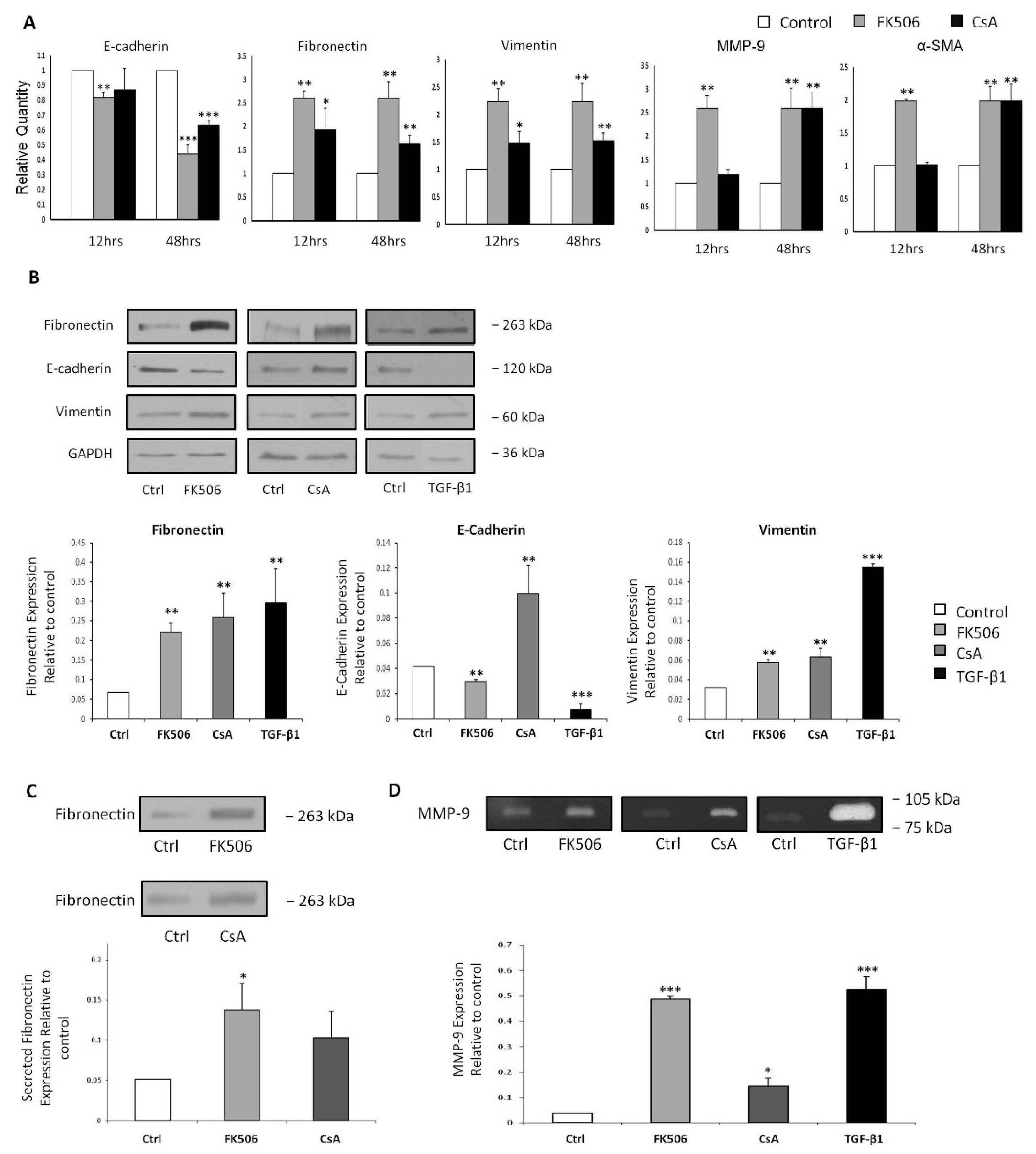
3.3. FK506 Induced Myofibroblast Transition in the RPTEC Cells
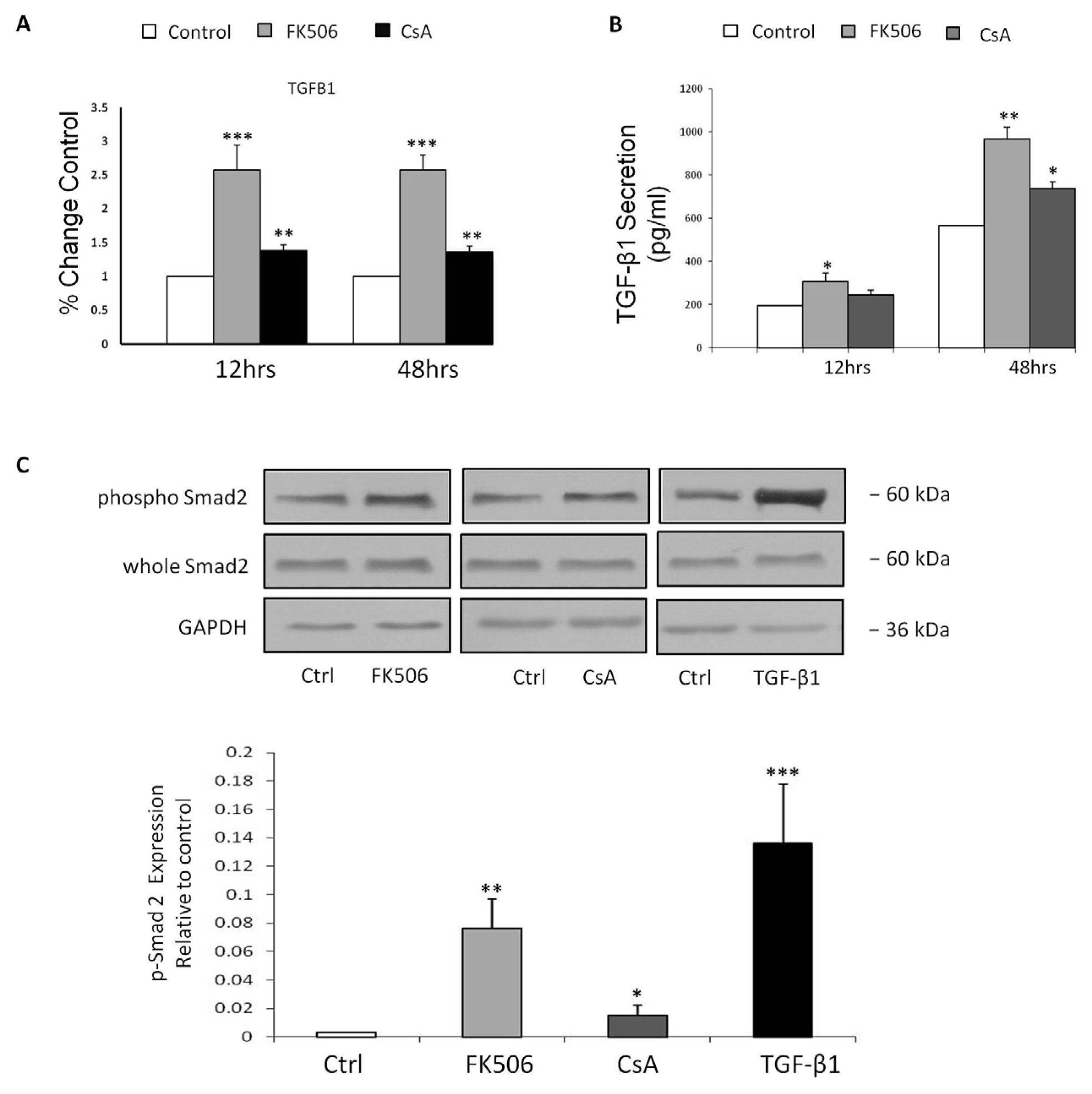
3.4. FK506 Increased TGF-β1 mRNA Levels and TGF-β1 Peptide Release from RPTEC Cells, with Concomitant Increases in Phospho-Smad2 Whole Cell Protein Levels
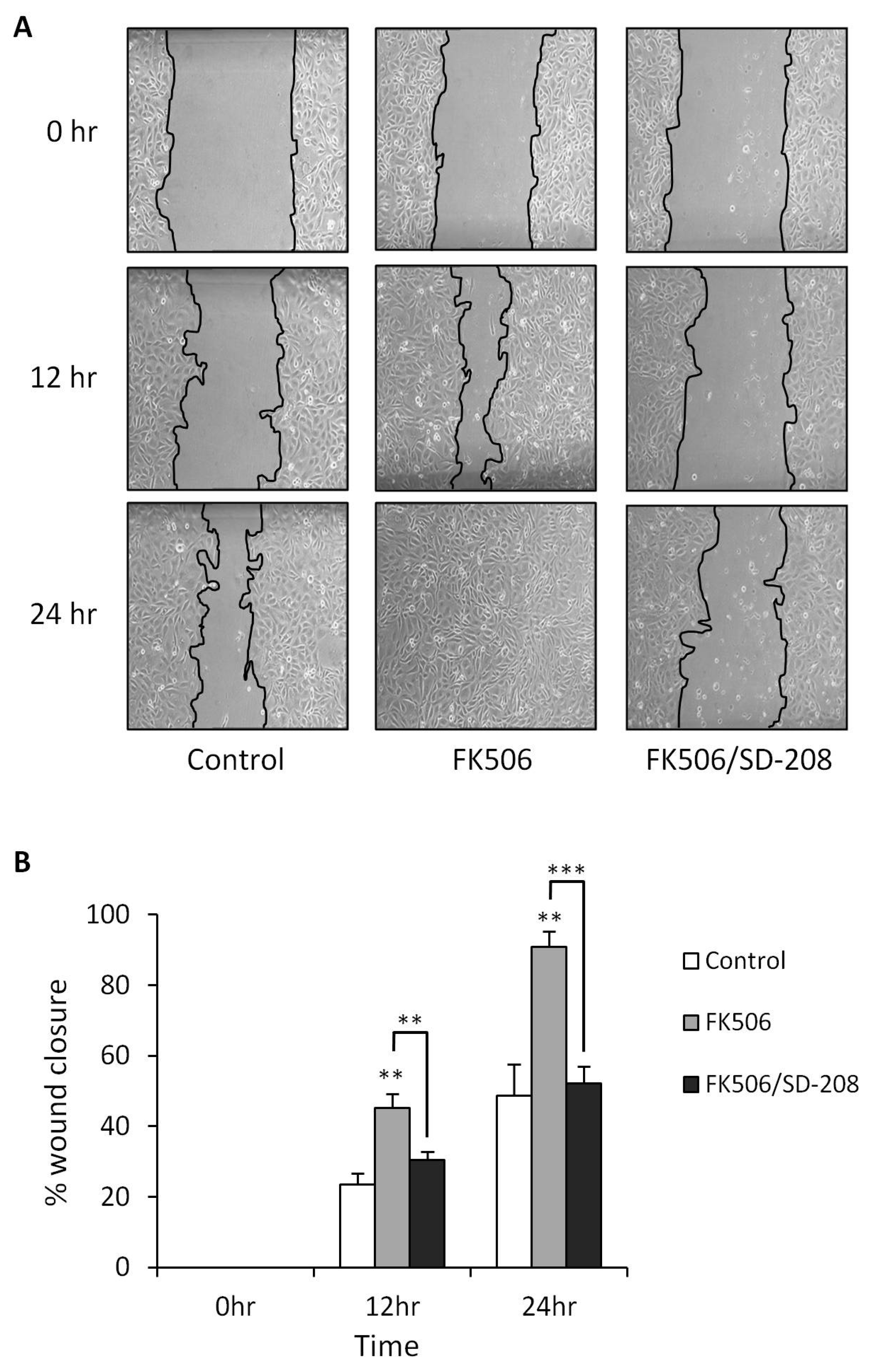
3.5. Treatment of RPTEC cells with FK506 Induced Increased Cell Migration Which Was Alleviated Following Co-Treatment with a TGF-β RI Kinase Inhibitor
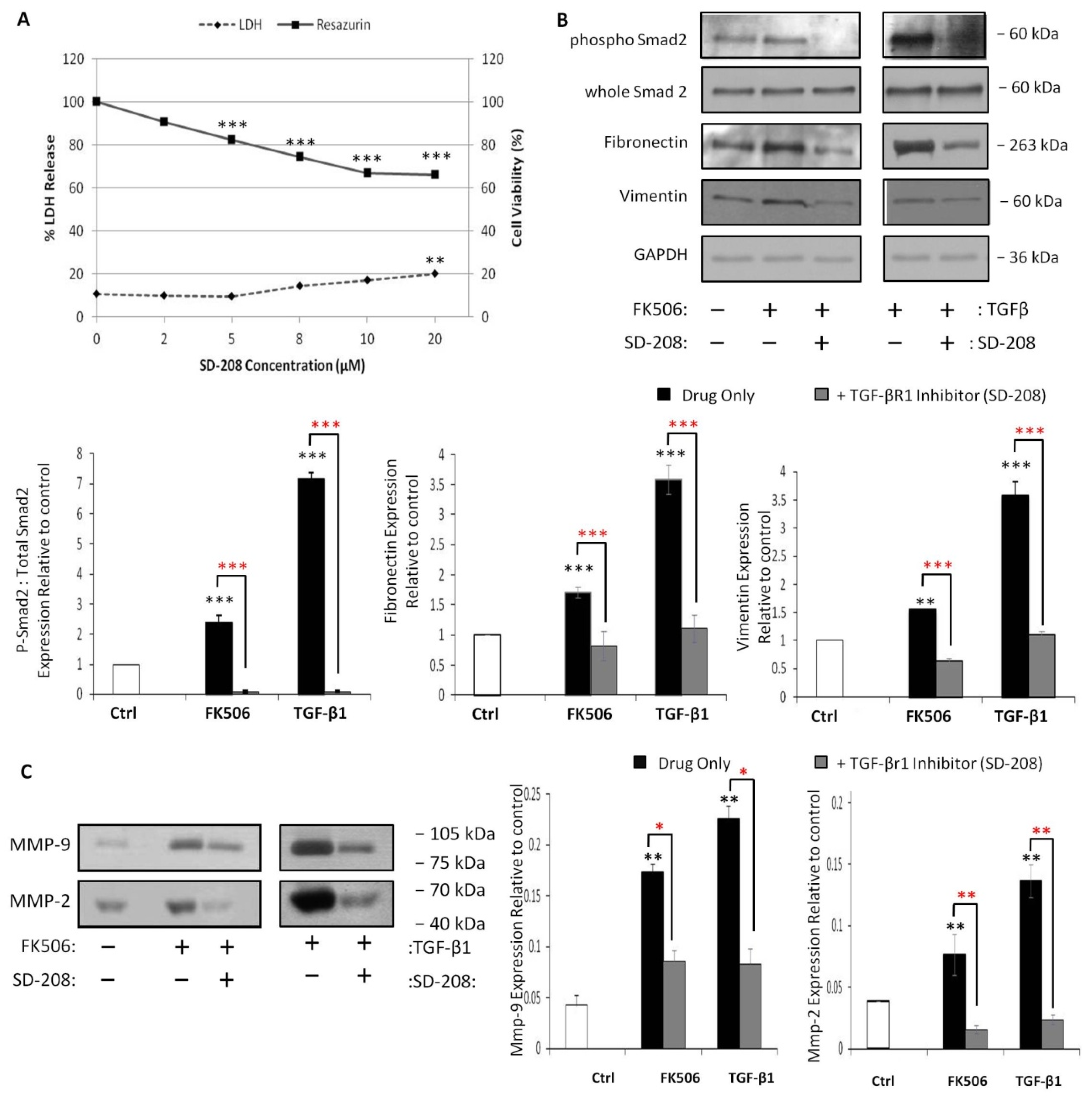
3.6. Pre-Incubation with a TGF-β Receptor 1 Kinase Inhibitor Completely Blocks Smad 2 Activation and Prevents Induction of EMT Markers by FK506
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-SMA | Alpha smooth muscle actin |
| ANOVA | One way Analysis of Variance |
| BrdU | Bromodeoxyuridine |
| CaCl2 | Calcium Chloride |
| CaN | Calcineurin Phosphatase |
| cDNA | Complimentary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CNI(s) | Calcineurin inhibitor(s) |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| CpN | Cyclophilin |
| CsA | Cyclosporine A |
| Ctrl | Control |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| DMEM/F-12 | DMEM/Nutrient mix F-12 |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ELISA | Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| EMT | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition |
| ESRD | End Stage Renal Disease |
| FK506 | FK506, Tacrolimus |
| FKBP12 | FK506 Binding Protein 12 |
| HK-2 | Human Kidney-2 |
| kDA | Kilodaltons |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| Mg | Milligrams |
| mM | Millimolar |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| NaCl | Sodium Chloride |
| NFAT | Nuclear Factor of Activated T-cells |
| NFATC | Cytosolic Nuclear Factor of Activated T-Cells |
| NFATN | Nuclear Nuclear Factor of Activated T-Cells |
| Ng | Nanograms |
| nM | Nanomolar |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| Pg | Picograms |
| PTECs | Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| rRNA | Ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| RT-PCR | Real Time-polymerase chain reaction |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulphate |
| SDS-PAGE | SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| S.E.M | Standard error of the mean |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 |
| TIF | Tubulointerstitial fibrosis |
| U | Units |
| µg | Micrograms |
| µL | Microlitres |
| μM | Micromolar |
| v/v | Volume per Volume |
References
- Hallan, S.I.; Coresh, J.; Astor, B.C.; Asberg, A.; Powe, N.R.; Romundstad, H.A.; Hallan, S.; Lydersen, S.; Holmen, J. International comparison of the relationship of chronic kidney disease prevalence and ESRD risk. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coresh, J.; Selvin, E.; Stevens, L.A.; Manzi, J.W.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Levey, A.S. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2007, 298, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, D.C.; Plantinga, L.C.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Saran, R.; Hedgeman, E.; Saydah, S.H.; Williams, D.E.; Powe, N.E. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in persons with undiagnosed or prehypertension in the United States. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P. Chronic kidney disease: A public health priority and harbinger of premature cardiovascular disease. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 268, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, S.; O’Hare, A.M. Interaction of aging and chronic kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2009, 29, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedla, F.M.; Brar, A.; Browne, R.; Brown, C. Hypertension in chronic kidney disease: Navigating the evidence. Int. J. Hypertens. 2011, 2011, 132405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdi, U.; Toto, R.D. Anemia, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, S.M.; Nair, H.; Ching, I.; Taheri, S.; Dasgupta, I. Overweight, obesity and chronic kidney disease. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2009, 112, c121–c127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.E.; di Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Juncos, L.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, J.E. Obesity, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christians, U.; Schmitz, V.; Schoning, W.; Bendrick-Peart, J.; Klawitter, J.; Haschke, M. Toxicodynamic therapeutic drug monitoring of immunosuppressants: Promises, reality, and challenges. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Borrows, R.J.; Fung, C.L.; O’Connell, P.J.; Allen, R.D.; Chapman, J.R. The natural history of chronic allograft nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, D.; Perico, N.; Gaspari, F.; Remuzzi, G. Nephrotoxic aspects of cyclosporine. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 234S–239S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, A.; Francois, H.; Frangie, C.; Ahmad, L.; Charpentier, B.; Durrbach, A. Prevention of calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity in renal transplantation. Transpl. Immunol. 2008, 20, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillebout, E.; Nochy, D.; Hill, G.; Conti, F.; Antoine, C.; Calmus, Y.; Glotz, D. Renal histopathological lesions after orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT). Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girlanda, R. Complications of Post-Transplant Immunosuppression. In Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering; Andrades, P.J.A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Crotia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ojo, A.O.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K.; Wolfe, R.A.; Leichtman, A.B.; Young, J.; Christensen, L.; Merion, R.M. Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayegh, M.H.; Remuzzi, G. Current and Future Immunosuppressive Therapies Following Transplantation; Springer: Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, F.J. FK506, an immunosuppressant targeting calcineurin function. Curr. Med. Chem. 2000, 7, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katari, S.R.; Magnone, M.; Shapiro, R.; Jordan, M.; Scantlebury, V.; Vivas, A.; Gritsch, J.; McCauley, J.; Starzl, T.; Demetris, A.J.; et al. Clinical features of acute reversible tacrolimus (FK 506) nephrotoxicity in kidney transplant recipients. Clin. Transplant. 1997, 11, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Mattos, A.M.; Olyaei, A.J.; Bennett, W.M. Nephrotoxicity of immunosuppressive drugs: Long-term consequences and challenges for the future. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, B.K.; Montagnino, G.; del Castillo, D.; Margreiter, R.; Sperschneider, H.; Olbricht, C.J.; Krüger, B.; Ortuño, J.; Köhler, H.; Kunzendorf, U.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus compared with cyclosporin A microemulsion in renal transplantation: 2 year follow-up results. Nephrol. Dial Transplant. 2005, 20, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Margreiter, R. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus compared with ciclosporin microemulsion in renal transplantation: A randomised multicentre study. Lancet 2002, 359, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, A.C.; Woodroffe, R.C.; Taylor, R.S.; Chapman, J.R.; Craig, J.C. Tacrolimus versus ciclosporin as primary immunosuppression for kidney transplant recipients: Meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomised trial data. BMJ 2005, 331, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Prasad, G.V.; Huang, M.; Nash, M.M.; Famure, O.; Park, J.; Thenganatt, M.A.; Chowdhury, N.; Cole, E.H.; Fenton, S.S.; et al. A comparison of the effects of C2-cyclosporine and C0-tacrolimus on renal function and cardiovascular risk factors in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 2006, 82, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OPTN & SRTR Annual Data Report 2011. Available online: http://srtr.transplant.hrsa.gov/annual_reports/2011/ (accessed on 15 March 2013).
- Ekberg, H.; Tedesco-Silva, H.; Demirbas, A.; Vitko, S.; Nashan, B.; Gürkan, A.; Margreiter, R.; Hugo, C.; Grinyó, J.M.; Frei, U.; et al. Reduced exposure to calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2562–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, F.; Manresa, A.A.; Leeming, D.J.; Karsdal, M.A.; Boor, P. The extracellular matrix in the kidney: A source of novel non-invasive biomarkers of kidney fibrosis? Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2014, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastaldi, M.P.; Ferrario, F.; Giardino, L.; Dell’Antonio, G.; Grillo, C.; Grillo, P.; Strutz, F.; Muller, G.A.; Colasanti, G.; D’Amico, G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tubular epithelial cells in human renal biopsies. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, G.J.; Hewitson, T.D. The role of tubulointerstitial injury in chronic renal failure. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2000, 9, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstic, J.; Santibanez, J.F. Transforming growth factor-beta and matrix metalloproteinases: Functional interactions in tumor stroma-infiltrating myeloid cells. Sci. World J. 2013, 2014, 521754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.D.; Bai, Y.; Gunst, S.J. Silencing of p21-activated kinase attenuates vimentin phosphorylation on Ser-56 and reorientation of the vimentin network during stimulation of smooth muscle cells by 5-hydroxytryptamine. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, I.; Skalli, O.; Gabbiani, G. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed by myofibroblasts during experimental wound healing. Lab. Investig. 1990, 63, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.P.; Hinz, B.; Swartz, M.A. Interstitial fluid flow induces myofibroblast differentiation and collagen alignment in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4731–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, T.L.; Warner, S.M.; Stefanowicz, D.; Shaheen, F.; Pechkovsky, D.V.; Murray, L.A.; Argentieri, R.; Kicic, A.; Stick, S.M.; Bai, T.R.; et al. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in primary airway epithelial cells from patients with asthma by transforming growth factor-beta1. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, H.Y.; Wang, D.X.; Deng, Z.T.; Ye, X.L. TGF-beta1 induces human bronchial epithelial cell-to-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Lung 2009, 187, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMorrow, T.; Gaffney, M.M.; Slattery, C.; Campbell, E.; Ryan, M.P. Cyclosporine A induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, P.; Koppelstaetter, C.; Aydin, S.; Abberger, T.; Wolf, A.M.; Mayer, G.; Pfaller, W. Cyclosporine A induces senescence in renal tubular epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2007, 293, F831–F838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, W.; Gstraunthaler, G. Nephrotoxicity testing in vitro-what we know and what we need to know. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppelstaetter, C.; Jennings, P.; Ryan, M.P.; Morin, J.P.; Hartung, T.; Pfaller, W. Assessment of a new cell culture perfusion apparatus for in vitro chronic toxicity testing. Part 1: Technical description. ALTEX 2004, 21, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kino, T.; Hatanaka, H.; Miyata, S.; Inamura, N.; Nishiyama, M.; Yajima, T.; Goto, T.; Okuhara, M.; Kohsaka, M.; Aoki, H.; et al. FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. II. Immunosuppressive effect of FK-506 in vitro. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1987, 40, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, G.P.; Lee, X.; Basile, G.; Acosta, M.; Scott, G.; Roskelley, C.; Medrano, E.E.; Linskens, M.; Rubeli, I.; Pereira-Smith, O.; et al. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9363–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyapalan, J.C.; Ferreira, M.; Sedivy, J.M.; Herbig, U. Accumulation of senescent cells in mitotic tissue of aging primates. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2007, 128, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasile, E.; Tomita, Y.; Brown, L.F.; Kocher, O.; Dvorak, H.F. Differential expression of thymosin beta-10 by early passage and senescent vascular endothelium is modulated by VPF/VEGF: Evidence for senescent endothelial cells in vivo at sites of atherosclerosis. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahama, H.; Obata, K.; Sugita, M.; Horio, M.; Oka, K.; Moriyama, T. Effect of FK 506 in the treatment of autoimmune glomerulonephritis in Brown Norway rats. Nephron 1999, 81, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slattery, C.; Campbell, E.; McMorrow, T.; Ryan, M.P. Cyclosporine A-induced renal fibrosis: A role for epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galichon, P.; Vittoz, N.; Xu-Dubois, Y.C.; Xu-Dubois, Y.C.; Cornaire, E.; Vandermeersch, S.; Mesnard, L.; Hertig, A.; Rondeau, E. Epithelial phenotypic changes detect cyclosporine in vivo nephrotoxicity at a reversible stage. Transplantation 2011, 92, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet, A.; Baelde, H.J.; Vleming, L.J.; de Heer, E.; Bruijn, J.A. Distribution of fibronectin isoforms in human renal disease. J. Pathol. 2001, 193, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihab, F.S.; Bennett, W.M.; Tanner, A.M.; Andoh, T.F. Mechanism of fibrosis in experimental tacrolimus nephrotoxicity. Transplantation 1997, 64, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, A.; Plummer, M.; Bromberek, C.; Bresnahan, B.; Hariharan, S. Expression of TGF-beta and fibrogenic genes in transplant recipients with tacrolimus and cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiling, D.; Clark, R.A. Fibronectin provides a conduit for fibroblast transmigration from collagenous stroma into fibrin clot provisional matrix. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eckes, B.; Dogic, D.; Colucci-Guyon, E.; Wang, N.; Maniotis, A.; Ingber, D.; Merckling, A.; Langa, F.; Aumailley, M.; Delouvee, A.; et al. Impaired mechanical stability, migration and contractile capacity in vimentin-deficient fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goffin, J.M.; Pittet, P.; Csucs, G.; Lussi, J.W.; Meister, J.J.; Hinz, B. Focal adhesion size controls tension-dependent recruitment of alpha-smooth muscle actin to stress fibers. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal fibrogenesis: Pathologic significance, molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninova, D.; Covarrubias, M.; Rea, D.J.; Park, W.D.; Grande, J.P.; Stegall, M.D. Acute nephrotoxicity of tacrolimus and sirolimus in renal isografts: Differential intragraft expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 and alpha-smooth muscle actin. Transplantation 2004, 78, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.M.; Wu, Y.G.; Liang, C.; Zhang, P.; Dong, J.; Ren, K.J.; Zhang, W.; Fang, F.; Shen, J.J. FK506 ameliorates renal injury in early experimental diabetic rats induced by streptozotocin. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos-van Groningen, M.C.; Scholten, E.M.; Lelieveld, P.M.; Rowshani, A.T.; Baelde, H.J.; Bajema, I.M.; Florquin, S.; Bemelman, F.J.; de Heer, E.; de Fijter, J.W.; et al. Molecular comparison of calcineurin inhibitor-induced fibrogenic responses in protocol renal transplant biopsies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition and its implications in renal interstitial fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinade, L.; Goncalves, C.A.; Wofchuk, S.; Gottfried, C.; Rodnight, R. Evidence for a role for calcium ions in the dephosphorylation of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in immature hippocampal slices and in astrocyte cultures from the rat. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1997, 104, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaska, J.; Vuoriluoto, K.; Huovinen, T.; Izawa, I.; Inagaki, M.; Parker, P.J. PKCε-mediated phosphorylation of vimentin controls integrin recycling and motility. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3834–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, C.C.; Chen, G.S.; Chiou, M.H.; Wu, C.S.; Chang, C.H.; Yu, H.S. FK506 promotes melanocyte and melanoblast growth and creates a favourable milieu for cell migration via keratinocytes: Possible mechanisms of how tacrolimus ointment induces repigmentation in patients with vitiligo. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, M.; Bonner, G.; Maeshima, Y.; Colorado, P.; Muller, G.A.; Strutz, F.; Kalluri, R. Renal fibrosis: Collagen composition and assembly regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molitoris, B.A.; Falk, S.A.; Dahl, R.H. Ischemia-induced loss of epithelial polarity. Role of the tight junction. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuazza, G.; Becker, A.; Williams, S.S.; Chakravarty, S.; Troung, H.T.; Lin, F.; Baum, M. Claudins 6, 9, and 13 are developmentally expressed renal tight junction proteins. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 291, F1132–F1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, T.; Takeichi, M. Cadherin superfamily genes: Functions, genomic organization, and neurologic diversity. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pallet, N.; Bouvier, N.; Bendjallabah, A.; Rabant, M.; Flinois, J.P.; Hertig, A.; Legendre, C.; Beaune, P.; Thervet, E.; Anlicheau, D. Cyclosporine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress triggers tubular phenotypic changes and death. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Cytoplasmic O-glycosylation prevents cell surface transport of E-cadherin during apoptosis. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5999–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Kubo, A.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. A peculiar internalization of claudins, tight junction-specific adhesion molecules, during the intercellular movement of epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Weber, C.R.; Turner, J.R. The tight junction protein complex undergoes rapid and continuous molecular remodeling at steady state. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 181, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, J.B.; Factor, V.M.; Mozes, M.; Nagy, P.; Sanderson, N.; Bottinger, E.P.; Klotman, P.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Transgenic mice with increased plasma levels of TGF-beta 1 develop progressive renal disease. Lab. Investig. 1996, 74, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mengel, M.; Bock, O.; Priess, M.; Haller, H.; Kreipe, H.; Gwinner, W. Expression of pro- and antifibrotic genes in protocol biopsies from renal allografts with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy. Clin. Nephrol. 2008, 69, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottinger, E.P.; Bitzer, M. TGF-beta signaling in renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remuzzi, G.; Ruggenenti, P.; Benigni, A. Understanding the nature of renal disease progression. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.W.; Saunders, H.J.; Johnson, F.J.; Huq, S.O.; Field, M.J.; Pollock, C.A. Cyclosporin exerts a direct fibrogenic effect on human tubulointerstitial cells: Roles of insulin-like growth factor I, transforming growth factor beta1, and platelet-derived growth factor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forino, M.; Torregrossa, R.; Ceol, M.; Murer, L.; Della Vella, M.; Del Prete, D.; D’Angelo, A.; Anglani, F. TGFbeta1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition, but not myofibroblast transdifferentiation of human kidney tubular epithelial cells in primary culture. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2006, 87, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Park, S.Y.; Joo, C.K. Transforming growth factor-beta1 represses E-cadherin production via slug expression in lens epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 2708–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, P.; Maode, L.; Li, F.; Sheng, H. Comparison of expression of TGF-beta1, its receptors TGFbeta1R-I and TGFbeta1R-II in rat kidneys during chronic nephropathy induced by cyclosporine and tacrolimus. Transplant. Proc. 2006, 38, 2180–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.H.; Derynck, R. Specificity and versatility in TGF-beta signaling through Smads. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 659–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, M.; Chen, Y.G.; Massague, J.; Kuriyan, J. Crystal structure of the cytoplasmic domain of the type I TGF beta receptor in complex with FKBP12. Cell 1999, 96, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Romano, S.; Mallardo, M.; D’Angelillo, A.; Cali, G.; Corcione, N.; Ferraro, P.; Romano, M.F. FK506 can activate transforming growth factor-beta signalling in vascular smooth muscle cells and promote proliferation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. Cell size and invasion in TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition is regulated by activation of the mTOR pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eger, A.; Stockinger, A.; Park, J.; Langkopf, M.; Mikula, M.; Gotzmann, J.; Mikulitis, W.; Beug, H.; Foisner, R. beta-Catenin and TGFbeta signalling cooperate to maintain a mesenchymal phenotype after FosER-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y.A.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.S.; Seo, J.H. Sustained co-cultivation with human placenta-derived MSCs enhances ALK5/Smad3 signaling in human breast epithelial cells, leading to EMT and differentiation. Differentiation 2009, 77, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safina, A.; Vandette, E.; Bakin, A.V. ALK5 promotes tumor angiogenesis by upregulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 in tumor cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2407–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bennett, J.; Cassidy, H.; Slattery, C.; Ryan, M.P.; McMorrow, T. Tacrolimus Modulates TGF-β Signaling to Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050050
Bennett J, Cassidy H, Slattery C, Ryan MP, McMorrow T. Tacrolimus Modulates TGF-β Signaling to Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2016; 5(5):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050050
Chicago/Turabian StyleBennett, Jason, Hilary Cassidy, Craig Slattery, Michael P. Ryan, and Tara McMorrow. 2016. "Tacrolimus Modulates TGF-β Signaling to Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells" Journal of Clinical Medicine 5, no. 5: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050050
APA StyleBennett, J., Cassidy, H., Slattery, C., Ryan, M. P., & McMorrow, T. (2016). Tacrolimus Modulates TGF-β Signaling to Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 5(5), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050050